Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Fabrication and Characterization
2.2. Module Fabrication
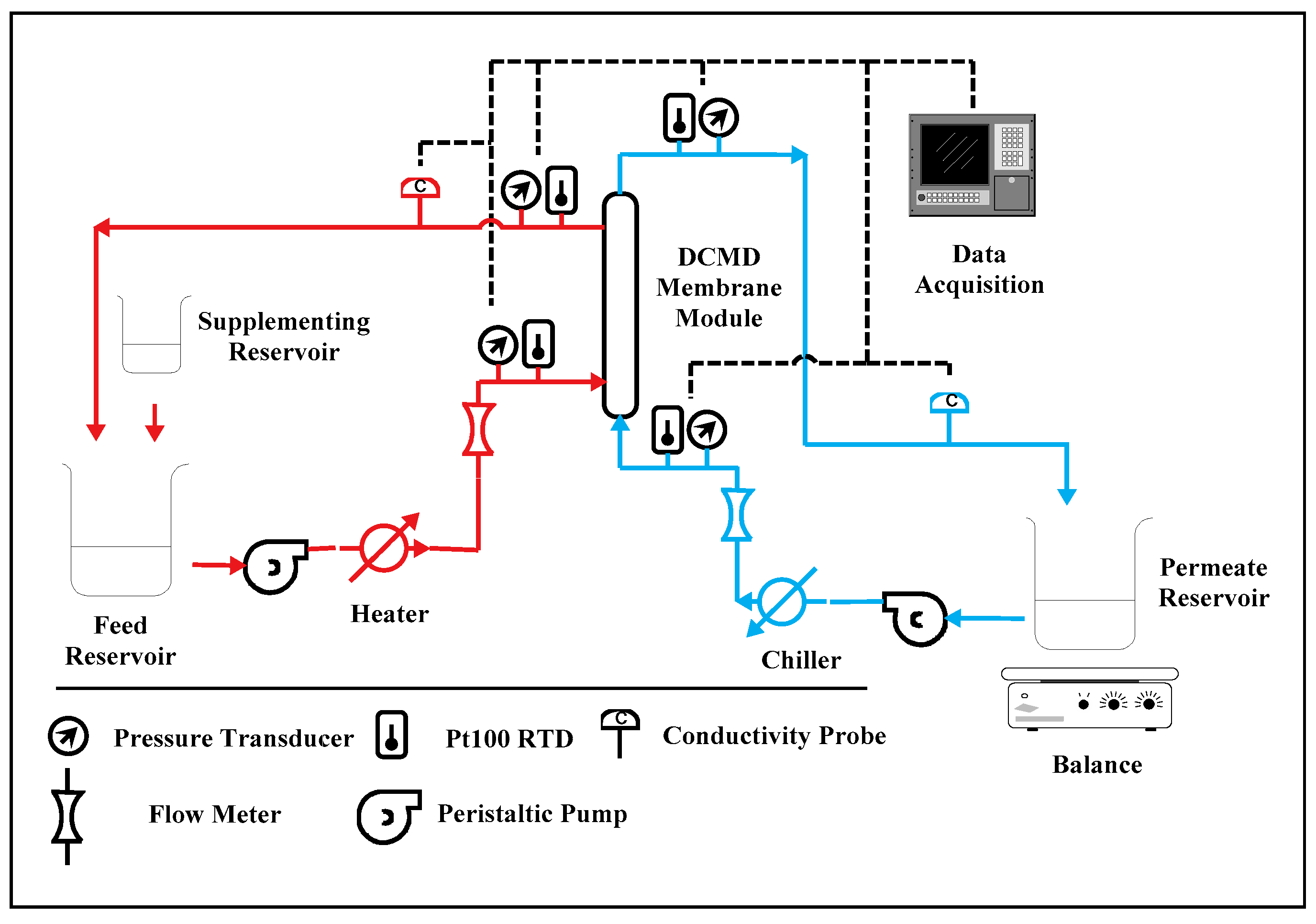
2.3. Experimental Setup for Lab-Scale Testing
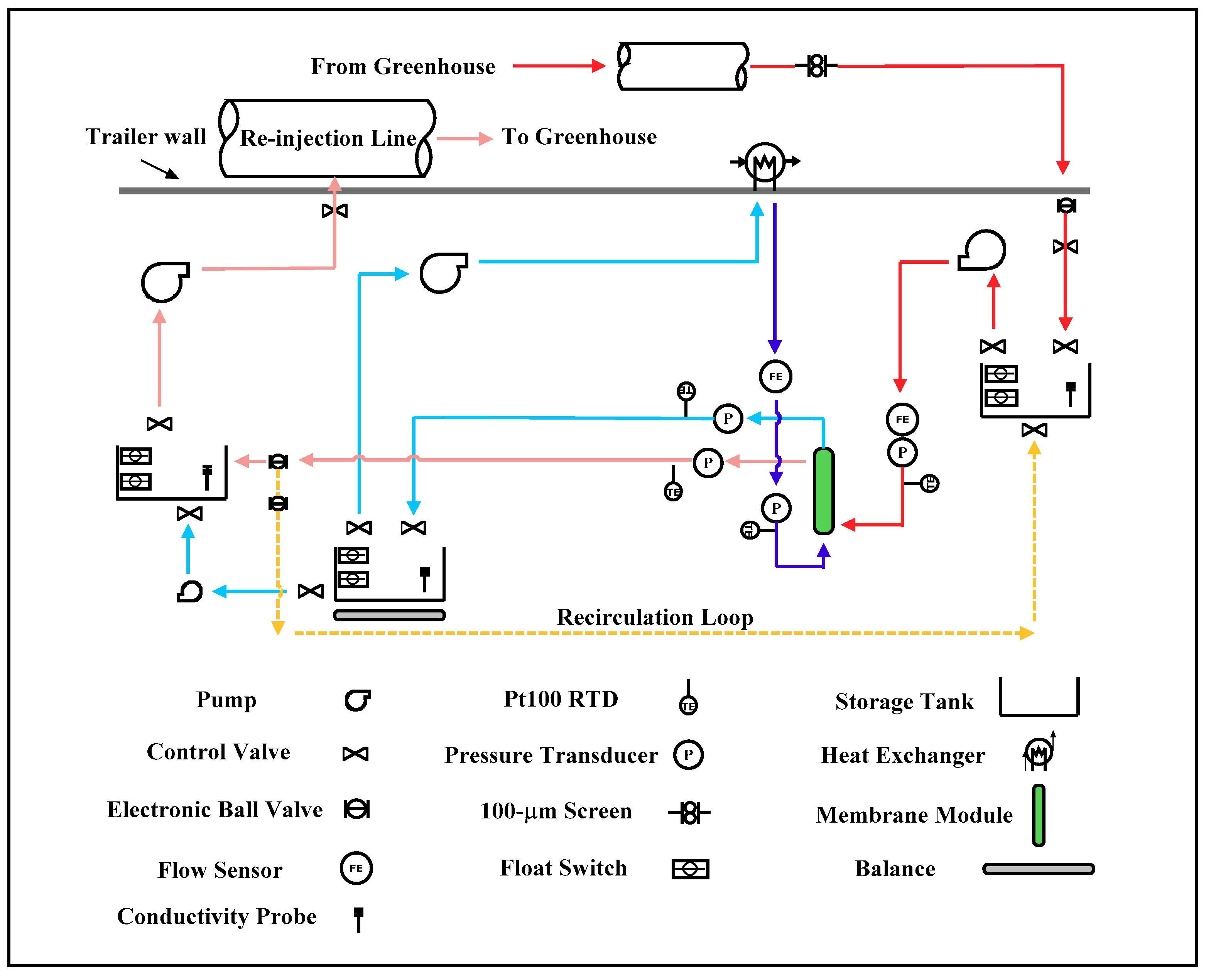
2.4. Field Testing
Field DCMD System
3. Results and Discussion
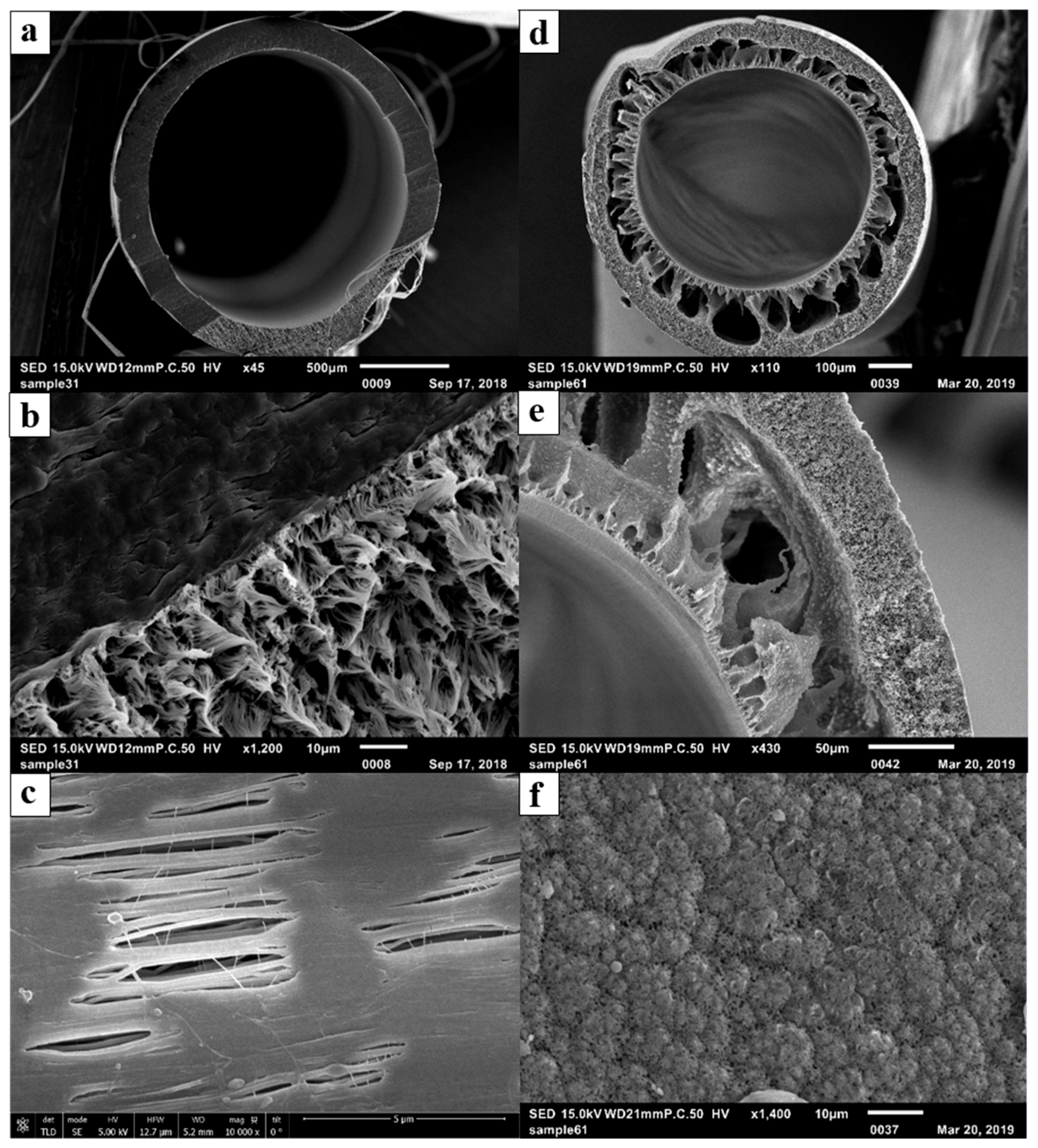
3.1. Membrane Characteristics
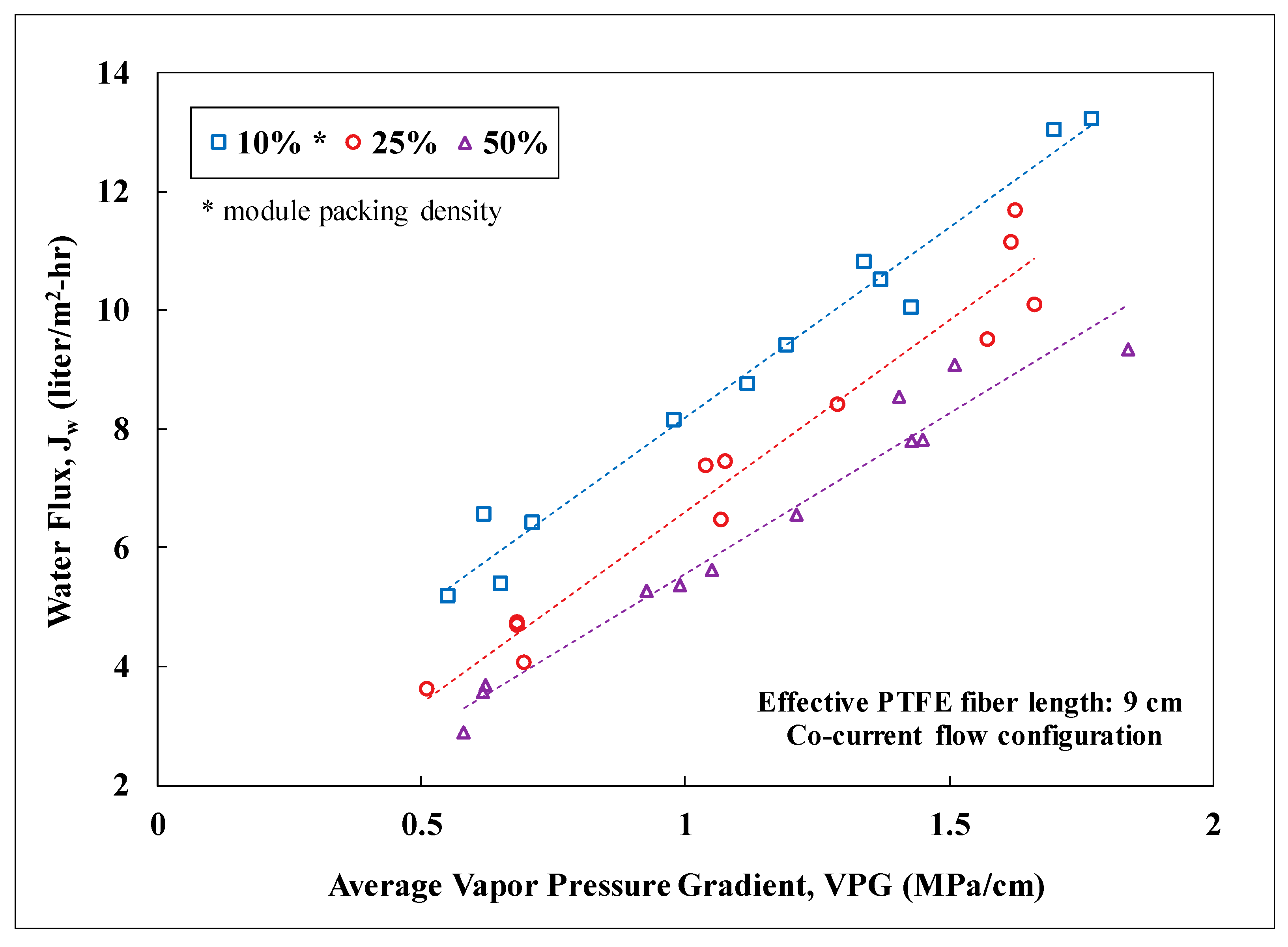
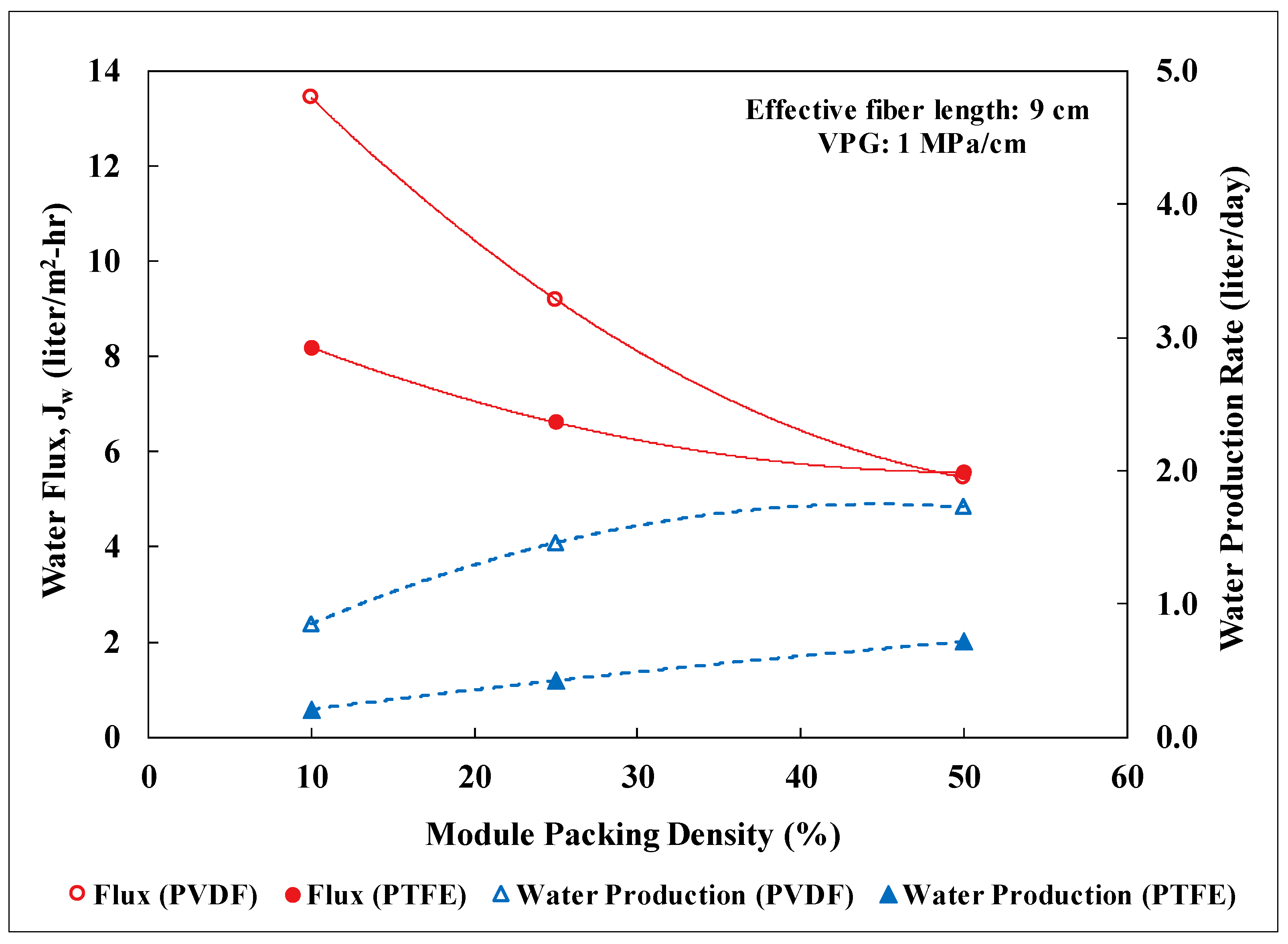
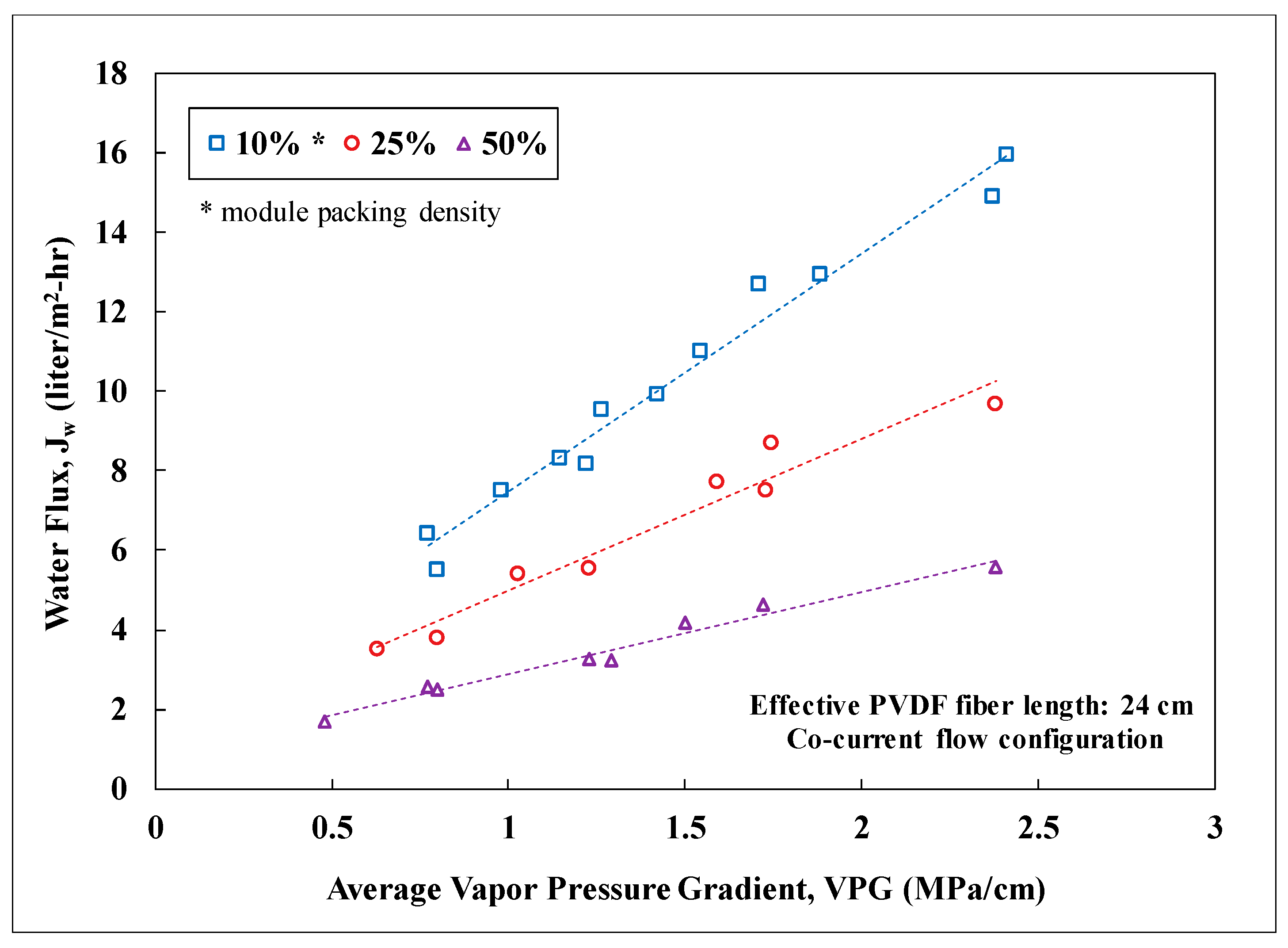
3.2. Lab-Scale Membrane Performance
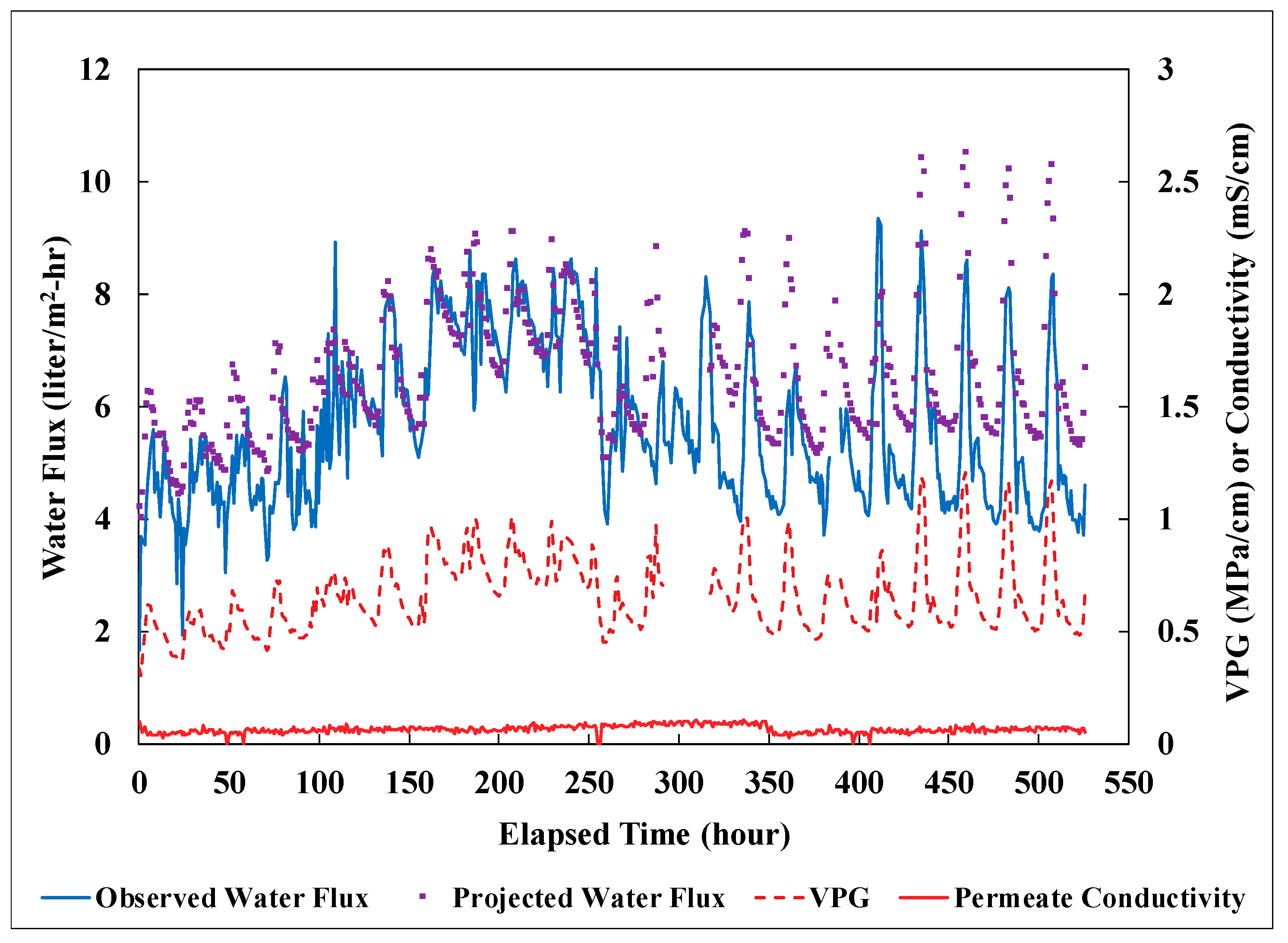
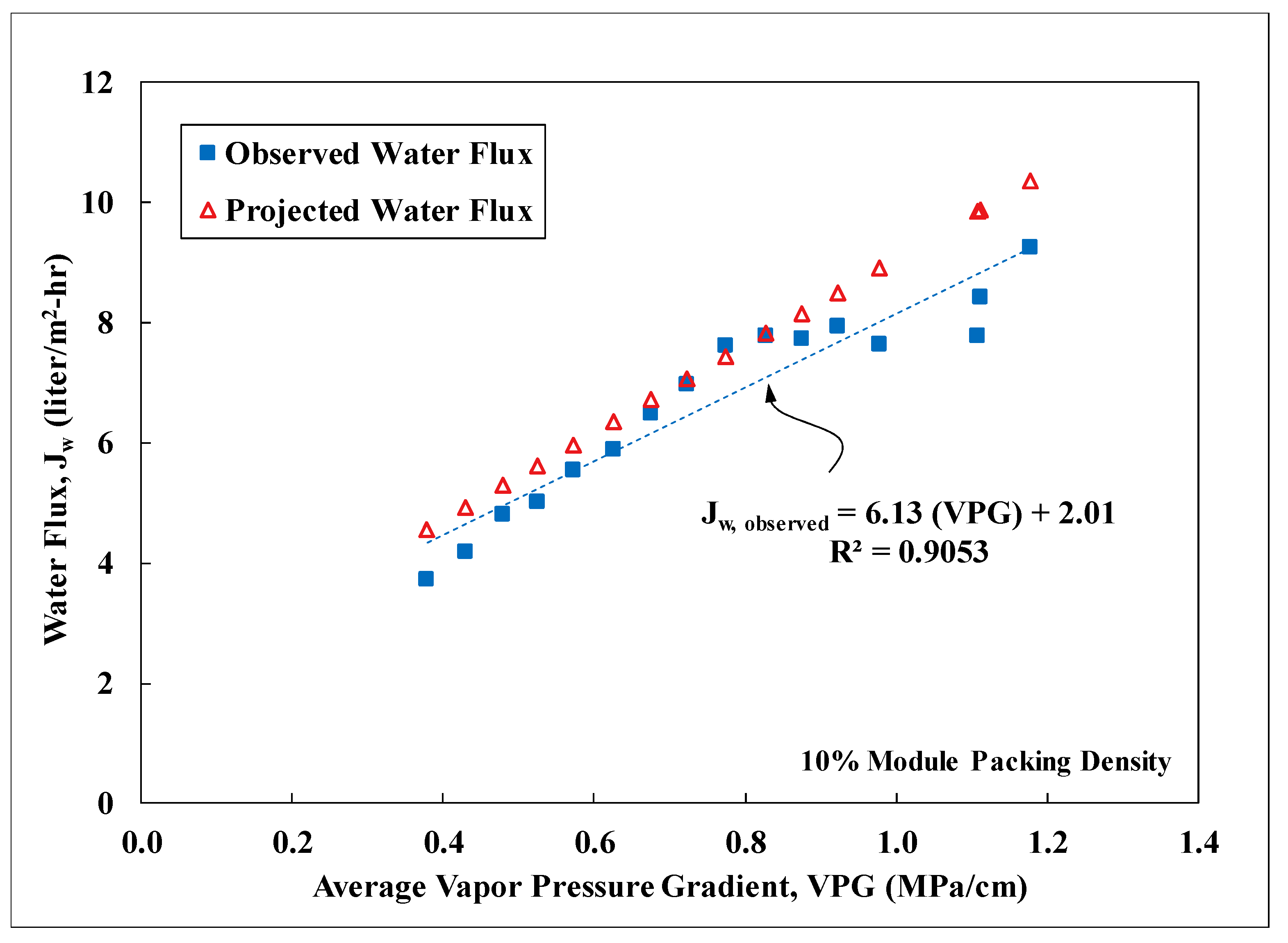
3.3. Field Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tidwell, V.C.; Moreland, B.D.; Zemlick, K.M.; Roberts, B.L.; Passell, H.D.; Jensen, D.; Forsgren, C.; Sehlke, G.; Cook, M.A.; King, C.W.; et al. Mapping water availability, projected use and cost in the western United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanton, J.S.; Anning, D.W.; Brown, C.J.; Moore, R.B.; McGuire, V.L.; Qi, S.L.; Harris, A.C.; Dennehy, K.F.; McMahon, P.B.; Degnan, J.R.; et al. Brackish Groundwater in the United States; USGS Professional Paper 1833; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2017.
- Gleick, P.H. Roadmap for sustainable water resources in southwestern North America. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 107, 21300–21305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, S.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Carnevale, M.C.; Rosselli, A.; Drioli, E. Preparation of hollow fibre membranes from PVDF/PVP blends and their application in VMD. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Chung, T. Recent advances in membrane distillation processes: Membrane development, configuration design and application exploring. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.S.; Gryta, M. Hydrophobic PVDF hollow fiber membranes with narrow pore size distribution and ultra-thin skin for fresh water production through membrane distillation. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2008, 63, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, M.M.; Chung, T.S. Membrane distillation with hydrophobic macrovoid-free PVDF-PTFE hollow fiber membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 66, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.D.; Duke, M.; Xie, Z.; Gray, S. Performance of asymmetric hollow fibre membranes in membrane distillation under various configurations and vacuum enhancement. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Teoh, M.M.; Chung, T. Morphological architecture of dual-layer hollow fiber for membrane distillation with higher desalination performance. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5489–5500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, T.; Wang, P.; Yang, X.; Cai, X.; Lu, J. Fabrication and characterization of novel asymmetric polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes by the nonsolvent thermally induced phase separation (NTIPS) method for membrane distillation applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 489, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, S.; Boo, C.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Engineering flat sheet microporous PVDF films for membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 492, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Sirkar, K.K. Influence of microporous membrane properties on the desalination performance in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 513, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.C.; Laumbach, A.; Reprogle, R.; Medin, C. Geothermal Membrane Distillation in Industrial Greenhouse Applications: Membrane Fabrication and Characterization. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018, 35, 815–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryta, M.; Barancewicz, M. Influence of morphology of PVDF capillary membranes on the performance of direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 358, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.H.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Electrospun Superhydrophobic Membranes with Unique Structures for Membrane Distillation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 16035–16048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; An, A.K.; Hadi, P.; Lee, S.; Woo, Y.C.; Shon, H.K. Advanced multi-nozzle electrospun functionalized titanium dioxide/polyvinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (TiO2/PVDF-HFP) composite membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Shim, W.G.; He, T.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Superhydrophobic nanofiber membrane containing carbon nanotubes for high-performance direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Jeong, J.; Kim, W.; Choi, D.; Lee, S.; Hwang, W. Conformable superoleophobic surfaces with multi-scale structures on polymer substrates. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 8272–8282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boo, C.; Lee, J.; Elimelech, M. Omniphobic Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Membrane for Desalination of Shale Gas Produced Water by Membrane Distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12275–12282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Huang, S.; Pan, Y.; Zhao, X. Flexible, Durable, and Unconditioned Superoleophobic/Superhydrophilic Surfaces for Controllable Transport and Oil-Water Separation. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1706867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Qiu, F.; Yang, D.; Xue, M. In situ one-step fabrication of durable Superhydrophobic-superoleophilic cellulose/LDH membrane with hierarchical structure for efficiency oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 328, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.J.; Deka, B.J.; Guo, J.; Woo, Y.C.; Shon, H.K.; An, A.K. Engineering the re-Entrant Hierarchy and Surface Energy of PDMS-PVDF Membrane for Membrane Distillation Using a Facile and Benign Microsphere Coating. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 10117–10126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Chen, G.; Zhang, K.Q.; Al-Deyab, S.S. Robust translucent Superhydrophobic PDMS/PMMA film by facile one-step spray for self-cleaning and efficient emulsion separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 330, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Tijing, L.D.; Phuntsho, S.; He, T.; Choi, J.S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. CF4 plasma-modified omniphobic electrospun nanofiber membrane for produced water brine treatment by membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 234–242. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, S.S.; Gandhi, M.; Chen, S.S.; Chang, H.M.; Dan, C.T.N.; Le, H.Q. Anti-wetting behaviour of a superhydrophobic octadecyltrimethoxysilane blended PVDF/recycled carbon black composite membrane for enhanced desalination. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2018, 4, 1612–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, S.S.; Chen, S.S.; Sangeetha, D.; Chang, H.M.; Thanh, C.N.D.; Le, Q.H.; Ku, H.M. Developments in forward osmosis and membrane distillation for desalination of waters. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2018, 16, 1247–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Dong, J.; Zhang, J. Roles of silanes and silicones in forming Superhydrophobic and superoleophobic materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 13677–13725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Dong, X.; Huang, J.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Z. Rational construction of highly transparent Superhydrophobic coatings based on a non-particle, fluorine-free and water-rich system for versatile oil-water separation. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinetti, C.R.; Childress, A.E.; Cath, T.Y. High recovery of concentrated RO brines using forward osmosis and membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 331, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.J.; He, K.; Gray, S.; Zhang, J.; Moon, S. Direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD): Experimental study on the commercial PTFE membrane and modeling. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Gray, S.; Li, J.D. Modeling heat and mass transfers in DCMD using compressible membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 387, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adnan, S.; Hoang, M.; Wang, H.; Xie, Z. Commercial PTFE membranes for membrane distillation application: Effect of microstructure and support material. Desalination 2012, 284, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francis, L.; Ghaffour, N.; Alsaadi, A.S.; Nunes, S.P.; Amy, G.L. Performance evaluation of the DCMD desalination process under bench scale and large scale module operating conditions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 455, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Nejati, S.; Boo, C.; Hu, Y.; Osuji, C.O.; Elimelech, M. Omniphobic Membrane for Robust Membrane Distillation. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 1, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, W.S.; Francis, L.; Amy, G.; Ghaffour, N. Performance modeling of direct contact membrane distillation (DCMD) seawater desalination process using a commercial composite membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 478, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, M.G.; Zhu, B.; Cran, M.; Dow, N.; Milne, N.; Desai, D.; Duke, M. Membrane Distillation of Meat Industry Effluent with Hydrophilic Polyurethane Coated Polytetrafluoroethylene Membranes. Membranes 2017, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.V.; Dow, N.; Milne, N.; Zhang, J.; Naidoo, L.; Gray, S.; Duke, M. Membrane Distillation Trial on Textile Wastewater Containing Surfectants Using Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic-Coated Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) Membranes. Membranes 2018, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, J.D.; Gray, S. Effect of applied pressure on performance of PTFE membrane in DCMD. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 514–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaleni, M.M.; Bavarian, M.; Nejati, S. Model-guided design of high-performance membrane distillation modules for water desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.Y.; Chung, T.S. Polybenzimidazole Nanofiltration Hollow Fiber for Cephalexin Separation. AIChE J. 2006, 52, 1363–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.C.; Reprogle, R. Thermal Conductivity of Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakomania. Available online: http://www.packomania.com (accessed on 11 March 2019).
- Reid, R.C.; Prausnitz, J.M.; Poling, B.E. The Properties of Gases and Liquids, 4th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, C. Computational Fluid Dynamic Modeling of Geothermal Membrane Distillation. Master’s Thesis, New Mexico Institute of Mining and Technology, Socorro, NM, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, F.Y.C.; Medin, C.; Arning, A. Mechanical Vibration for the Control of Membrane Fouling in Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Symmetry 2019, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qtaishat, M.; Rana, D.; Khayet, M.; Matsuura, T. Preparation and characterization of novel hydrophobic/hydrophilic polyetherimide composite membranes for desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 327, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Dow, N.; Ostarcevic, E.; Li, J.D.; Gray, S. Identification of material and physical features of membrane distillation membranes for high performance desalination. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Masson Farms |
|---|---|
| Ca+ | 104 |
| Mg2+ | 11.4 |
| K+ | 191 |
| Na+ | 1221 |
| Li+ | 1.1 |
| Fe2+ | 0.2 |
| Sr2+ | 2.3 |
| F− | 5.5 |
| Cl− | 2022 |
| 27.6 | |
| 11.6 | |
| B | 0.9 |
| Si (as SiO2) | 58.2 |
| pH | 7.5 |
| TDS | 3800 |
| Temperature (°C) | 92 |
| Membrane Characteristic | PVDF | PTFE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Outer diameter (µm) a | 841 ± 5 | 1799 ± 50 | |
| Wall thickness (µm) a | 122 ± 22 | 178 ± 12 | |
| Macrovoid to sponge ratio b | 1.08 | N/A | |
| Pore size | 0.319/0.333/0.422 c | 0.385/0.495/0.831 d | |
| Porosity | 0.79 ± 0.05 | 0.50 ± 0.04 | |
| Failure stress | 1.32 | >21.5 | |
| Young’s modulus | 15.66 | 348 | |
| Liquid entry pressure, LEPw (bar) | at 22 °C | 1.32 | 1.37 |
| at 81 °C | 0.53 | - | |
| Membrane Characteristic | This Study | This Study | Zhang et al. a | Millipore b | Membrane Solutions c | GE Osmonics c | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Hollow fiber | Hollow fiber | Hollow fiber | Flat sheet | Flat sheet | Flat sheet | |||
| Material | PTFE | PVDF | PTFE | PTFE | PTFE | PTFE | |||
| Membrane configuration | Symmetric | Sponge/macrovoid | Symmetric | N/A | Active layer/fabric | Active layer/scrim | |||
| Thickness | Active | 178 | 122 | 365 | N/A | 30 | 67 | ||
| Support | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 185 | 97 | |||
| Nominal pore size of active layer (µm) | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.25 | 1 | 0.45 | |||
| Porosity (active layer) | 0.5 | 0.79 | 0.85 | 0.7 | 0.92 | 0.88 | |||
| Feed TDS (mg/L) | 5000 | 5000 | 10,000 | 29,250 | 10,000 | 10,000 | |||
| Flow configuration | Co-current | Co-current | Counter-current | Counter-current | Counter-current | Counter-current | |||
| Module packing density (%) | 10 | 50 | 10 | 50 | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |
| Feed inlet (°C) | 65 | 64 | 62 | 64 | 60 | 65 | 60 | 60 | |
| Permeate inlet (°C) | 22 | 31 | 28 | 36 | 20 | 15 | 20 | 20 | |
| Water flux (LMH) d | 9.4 | 5.3 | 17.3 | 5.7 | 4 | 12.6 | 11 | 16.5 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, F.Y.C.; Arning, A. Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Membranes 2019, 9, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040052
Huang FYC, Arning A. Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Membranes. 2019; 9(4):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040052
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Frank Y. C., and Allie Arning. 2019. "Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation" Membranes 9, no. 4: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040052
APA StyleHuang, F. Y. C., & Arning, A. (2019). Performance Comparison between Polyvinylidene Fluoride and Polytetrafluoroethylene Hollow Fiber Membranes for Direct Contact Membrane Distillation. Membranes, 9(4), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes9040052




