Recent Advances in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Separators
Abstract
1. Introduction
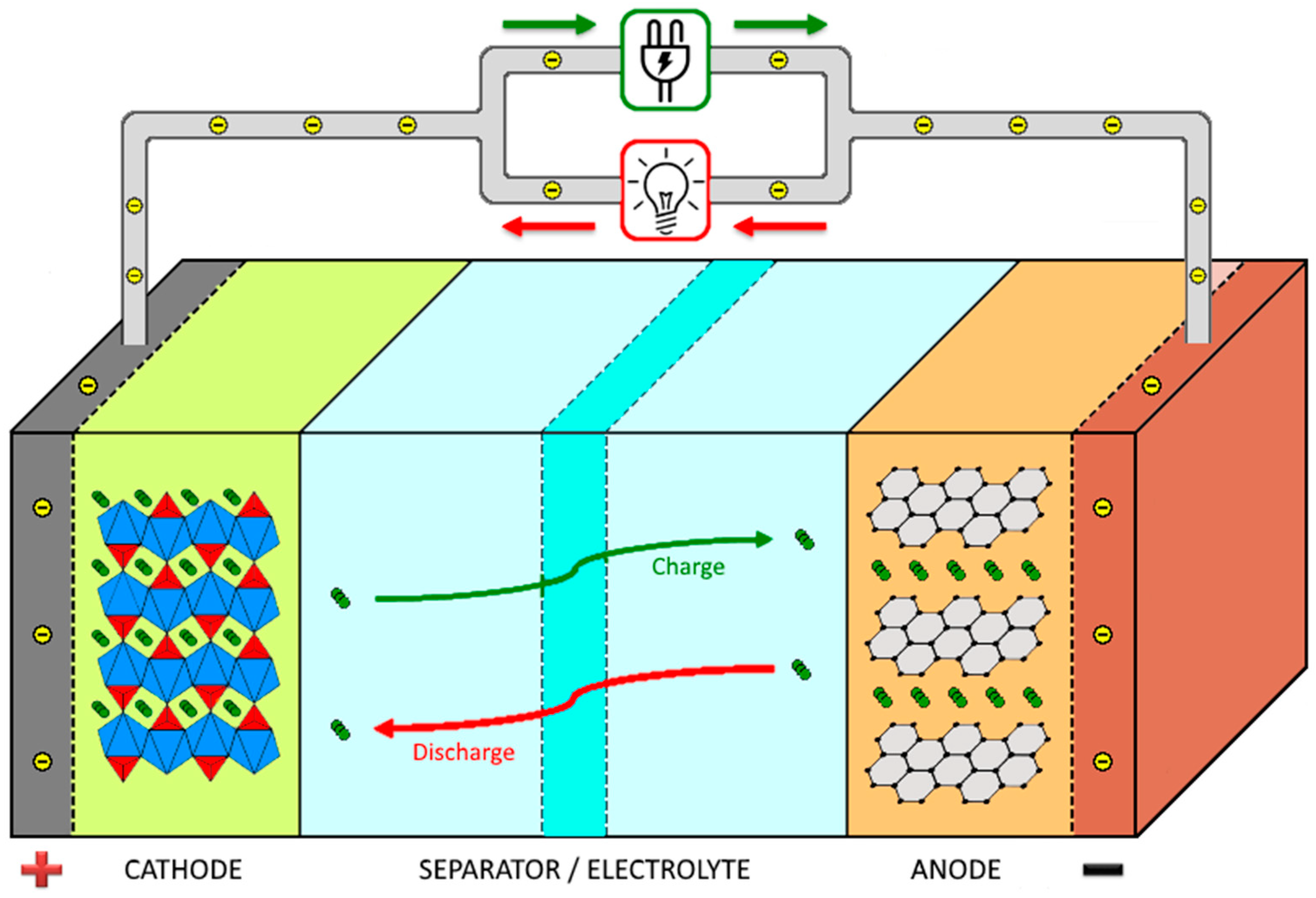
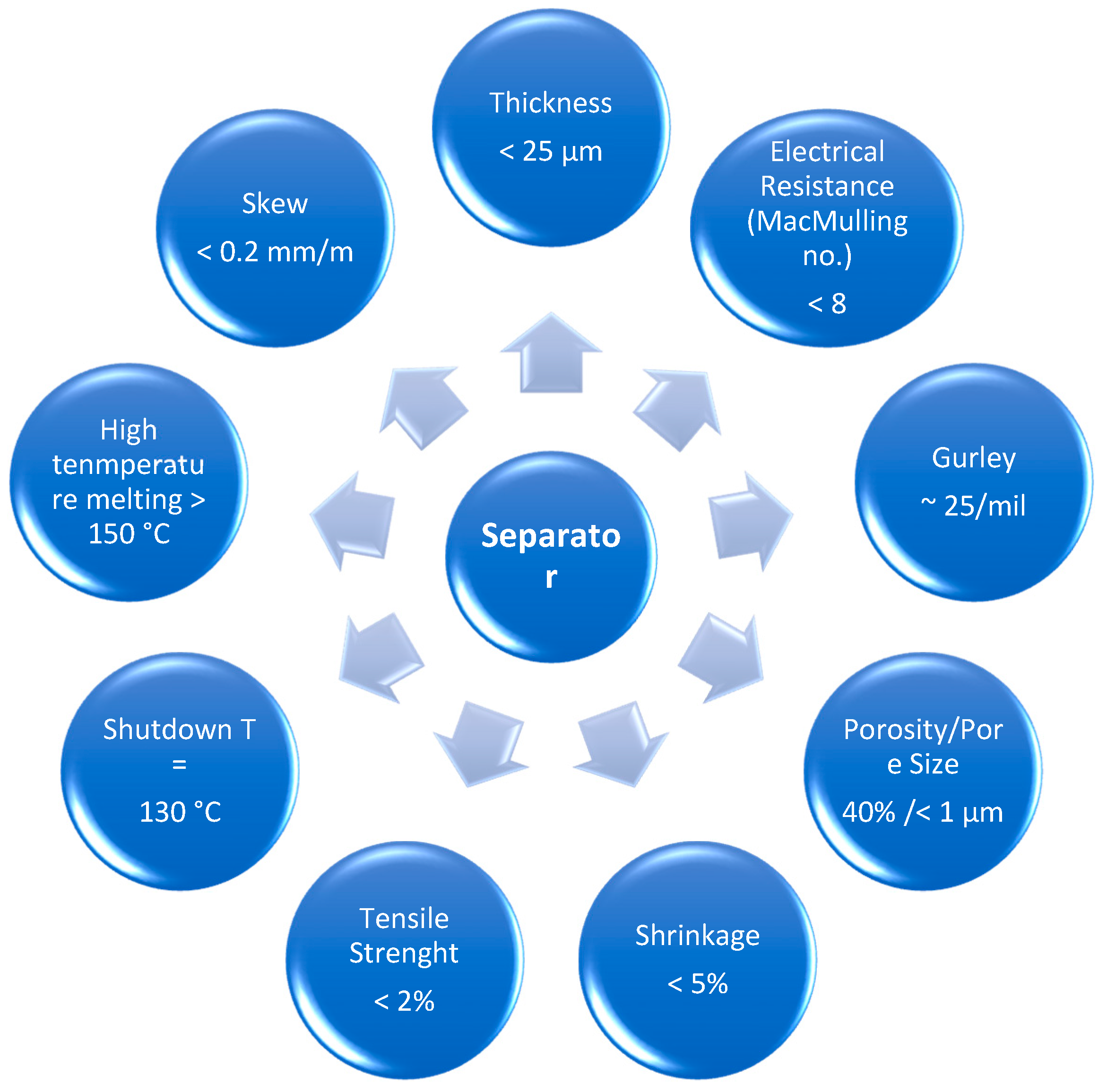
2. Battery Separator: Function, Characteristics, and Types
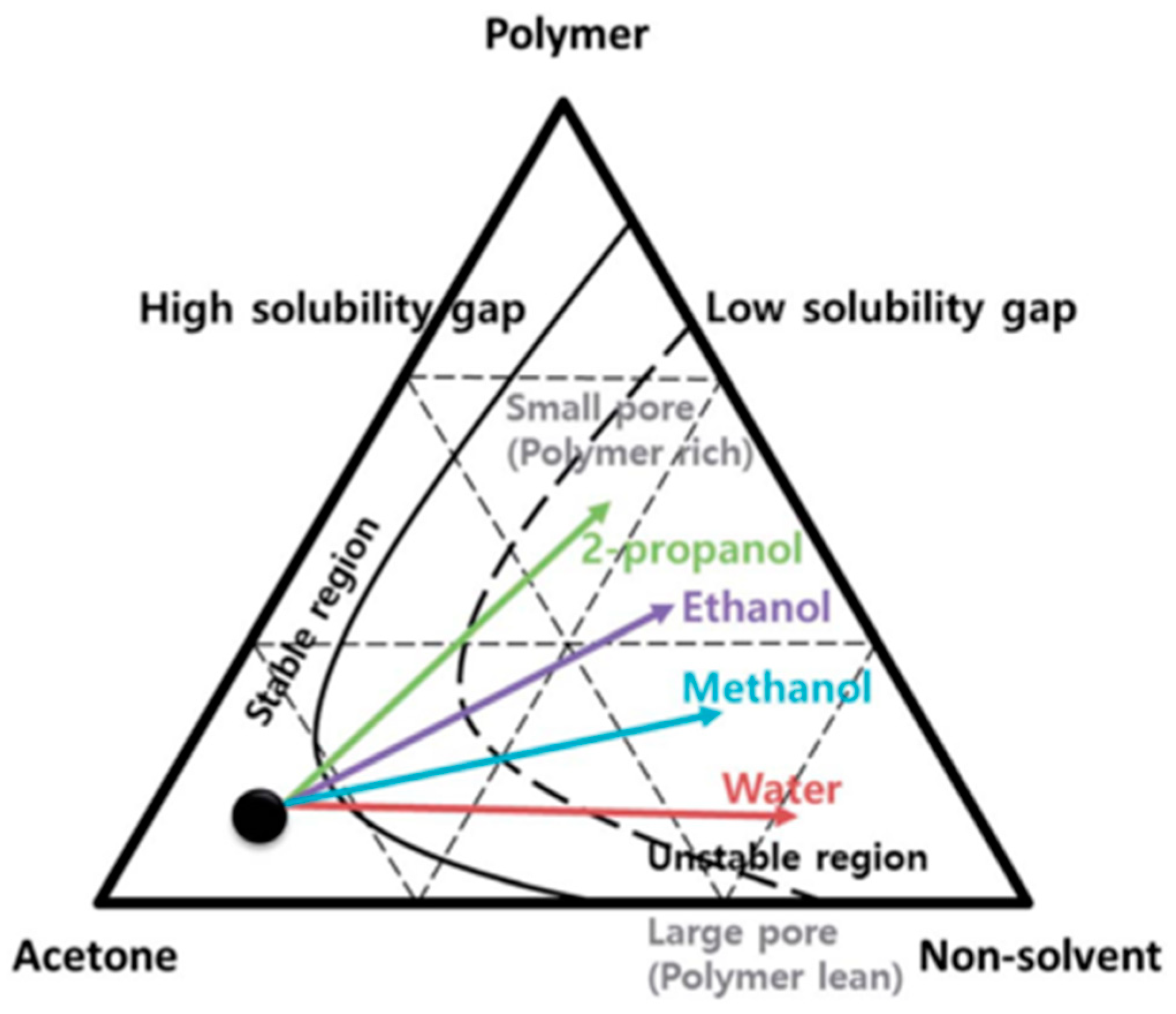
3. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers
3.1. Single Polymer and Co-Polymers
3.2. Surface Modification of the Separator Membranes
3.3. Composite Membranes
3.4. Polymer Blend Separator Membranes
4. Conclusions and Future Trends
List of Symbols and Abbreviations
| (C2H5)3CH3NBF4 | Triethylmethylammonium tetrafluoroborate |
| [C2mim][NTf2] | 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide |
| Al(OH)3 | Aluminum hydroxide |
| Al2O3 | Aluminum oxide |
| AlO(OH) | Bohemite |
| AN | Acetonitrile |
| BC | Boron-containing cross-linker |
| CA | Cellulose acetate |
| CMC | carboxymethyl cellulose |
| CNF | Carbon nanofiber |
| DEC | Diethyl carbonate |
| DEM | Diethoxymethane |
| DMAc | Dimethyl acetamide |
| DMC | Dimethyl carbonate |
| DME | 1,2-dimethoxyethane |
| DMF | Dimethyl formamide |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DNA-CTMA | Deoxyribonucleic acid-cetyltrimethylammonium |
| DOL | 1,3-dioxolane |
| EC | Ethylene carbonate |
| EMC | Ethyl methyl carbonate |
| EMImNfO-LiNfO | 1-ethyl-3- methylimidazolium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate/lithium nonafluoro-1-butanesulfonate |
| EMITf | 1-ethyl 3-methyl imidazolium trifluoromethane sulfonate |
| EMITFSI | 1-ethyl-3-methyl-imidazolium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| EP | Ethyl propionate |
| Et4N-BF4 | Tetraethylammonium tetrafluoroboratein |
| GF | Glass fiber |
| GO | Graphene oxides |
| GPE | Gel polymer electrolyte |
| H2SO4 | Sulfuric acid |
| HDPE | High density polyethylene |
| HEC | Hydroxyethyl cellulose |
| HMSS | Hollow mesoporous silica spheres |
| HTPB-g-MPEG | Hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene-grafted-methoxyl polyethylene glycol |
| KOH | Potassium hydroxide |
| LiClO4 | Lithium percholorate |
| LiCoO2 | Lithium cobalt oxide |
| LiFAP | Lithium Tris(pentafluoroethane)-trifluorophosphate |
| LiNfO/BMImNfO | Lithium nonafluorobutanesulfonate/1-butyl-3-me-thylimidazolium nonafluorobutanesulfonate |
| LiNO3 | Lithium nitrate |
| LiPF6 | Lithium hexafluorophosphate |
| LiPVAOB | Lithium polyvinyl alcohol oxalate borate |
| Li-S | Lithium-sulfur |
| LiTFSI | lithium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide |
| LLTO | Li0.33La0.557TiO3 |
| MA | Meldrum’s acid |
| MC | Methyl cellulose |
| MEP | Ethylene oxide-propylene oxide |
| Mg(OH)2 | Magnesium hydroxide |
| MgAl2O4 | Magnesium aluminate |
| MMT | Montmorillonite |
| MOF-808 | Zirconium (IV) metal-organic framework |
| m-SBA 15 | Mesoporous silica |
| NaA | NaA zeolite |
| NaClO4 | Sodium perchlorate |
| NaTf | Sodium trifluoromethane sulfonate |
| NCC | Nanocrystalline cellulose |
| NIPS | Non-solvent induced phase separation |
| NMP | N-methyl-2-pyrrolidone |
| OIL | Oligomeric ionic liquid (bromide bis(tri-fluoromethane)sulfonimide) |
| P(MMA-co-PEGMA) | Poly(methyl methacrylate-co-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate) |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| PBA | Poly(butyl acrylate) |
| PC | Propylene carbonate |
| PDA | Polydopamine |
| PDMS-g-(PPO-PEO) | Poly(dimethylsiloxane)-graft-poly(propylene oxide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide) |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PEG | Polyethylene glycol |
| PEGDA | Poly(ethylene glicol)diacrylate |
| PEGDMA | Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate |
| PEGMEA | Poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether acrylate |
| PEI | Polyetherimide |
| PEO | Polyethilene oxide |
| PET | Polyethylene terephthalate |
| PFSA | Perflourosulfonic acid |
| PI | Polyimide |
| PLTB | Polimeric lithium tartaric acid borate |
| PMIA | Poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) |
| PMMA | Polymethyl methacrylate |
| POSS | Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| P-PAEK | Phenolphthaleyne-poly(aryl ether ketone) |
| PSx-PEO3 | Polysiloxane-comb-propyl(triethylene oxide) |
| PSU | Poly(sulfone) |
| PTFE | Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) |
| PVA | Polyvinyl alcohol |
| PVC | Poly(vinyl chloride) |
| PVDF | Poly(vinylidene fluoride) |
| PVDF-co-CTFE | Polyvinylidene fluoride-co-chlorotrifluoroethylene |
| PVDF-co-HFP | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) |
| PVDF-HFP | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropene)Poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) |
| PVDF-PE | Polyvinylidene difluoride-coated polyethylene |
| PVDF-TrFE | Poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene) |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PVSK | Polyvinylsulfate potassium salt |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| SCPC | Self-charging power cell |
| SiO2 | Silicon dioxide |
| SN | Succinonitrile |
| SnO2 | Tin oxide |
| TAIC | Triallyl isocyanurate |
| TEABF4 | Tetraethyl ammonium tetrafluoroborate |
| TiO2 | Titanium dioxide |
| TIPS | Thermal-induced phase separation |
| TTT | 1,3,5-trially-1,3,5-triazine-2,4,6(1 H,3 H,5 H)-trione |
| VC | Vinylene carbonate |
| x-PEGDA | x-polyethylene glycol diacrylate |
| ZnO | Zinc oxide |
| ZrO2 | Zirconium dioxide |
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Megahed, S.; Ebner, W. Lithium-ion battery for electronic applications. J. Power Sources 1995, 54, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, J.; Correia, V.; Castro, H.; Martins, P.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Polymer-based smart materials by printing technologies: Improving application and integration. Add. Manuf. 2018, 21, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodenough, J.B.; Park, K.S. The li-ion rechargeable battery: A perspective. JACS 2013, 135, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Costa, C.M. Printed Batteries: Materials, Technologies and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Manthiram, A. An outlook on lithium ion battery technology. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 1063–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Research, A.M. Lithium-Ion Battery Market—Global Opportunity Analysis and Industry Forecast; Allied Market Research: London, UK, 2016; pp. 2015–2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshio, M.; Brodd, R.J.; Kozawa, A. Lithium-Ion Batteries Science and Technologies; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.P. Lithium-Ion Batteries Fundamentals and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.M.; Rodrigues, H.M.; Gören, A.; Machado, A.V.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) lithium-ion battery separators and their compatibilization with ionic liquid—A green solvent approach. Chem. Select 2017, 2, 5394–5402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, P.; Zhang, Z.J. Battery separators. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 4419–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.M.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Battery separators based on vinylidene fluoride (vdf) polymers and copolymers for lithium ion battery applications. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 11404–11417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Dai, J.; Huang, S.; Li, C.; Shen, X.; Zhang, P.; Wu, D.; Sun, D.; Zhao, J. A simple method to prepare a polydopamine modified core-shell structure composite separator for application in high-safety lithium-ion batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 518, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nho, Y.C.; Sohn, J.Y.; Shin, J.; Park, J.S.; Lim, Y.M.; Kang, P.H. Preparation of nanocomposite γ-al2o3/polyethylene separator crosslinked by electron beam irradiation for lithium secondary battery. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2017, 132, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashmi, S.A.; Bhat, M.Y.; Singh, M.K.; Sundaram, N.T.K.; Raghupathy, B.P.C.; Tanaka, H. Ionic liquid-based sodium ion-conducting composite gel polymer electrolytes: Effect of active and passive fillers. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 2817–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Deng, L.; Sun, Y.; Teh, K.S.; Shi, C.; Tan, Q.; Zhao, J.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. A high-safety pvdf/Al2O3 composite separator for Li-ion batteries via tip-induced electrospinning and dip-coating. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24410–24416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, S.; Sun, D.; Jin, Y. Preparation and evaluation of a separator with an asymmetric structure for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 105461–105468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, H.; Jin, X.; Xie, X. Composite melt-blown nonwoven fabrics with large pore size as li-ion battery separator. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wu, X.; He, J.; Li, J.; Lai, Y. Preparation and performance of a novel gel polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinylidene fluoride)/graphene separator for lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 235, 500–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbarnia, A.; Khan, W.S.; Ghazinezami, A.; Asmatulu, R. Investigating the thermal, mechanical, and electrochemical properties of pvdf/pvp nanofibrous membranes for supercapacitor applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X.; Hao, X.; Sun, W.; Rooney, D.; Sun, K. Flexible carbon nanofiber/polyvinylidene fluoride composite membranes as interlayers in high-performance lithium[sbnd]sulfur batteries. J. Power Sources 2016, 329, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.-S.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.-J. Ionic liquid polymer electrolytes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 2719–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.F.; Jung, J.T.; Wang, H.H.; Lee, S.Y.; Moore, T.; Sanguineti, A.; Drioli, E.; Lee, Y.M. Microporous pvdf membranes via thermally induced phase separation (tips) and stretching methods. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 509, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, C.; Costa, C.M.; Correia, D.M.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Oliveira, J.; Martins, P.; Gonçalves, R.; Cardoso, V.F.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based structures for advanced applications. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalwa, H.S. Ferroelectric Polymers: Chemistry: Physics, and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, R.E.; Ferreira, J.C.C.; Costa, C.M.; Machado, A.V.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Tailoring poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-chlorotrifluoroethylene) microstructure and physicochemical properties by exploring its binary phase diagram with dimethylformamide. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2015, 53, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.E.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Ferreira, J.C.C.; Costa, C.M.; Machado, A.V.; Silva, M.M.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Microstructural variations of poly(vinylidene fluoride co-hexafluoropropylene) and their influence on the thermal, dielectric and piezoelectric properties. Polym. Test. 2014, 40, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.M.; Rodrigues, L.C.; Sencadas, V.; Silva, M.M.; Rocha, J.G.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Effect of degree of porosity on the properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride–trifluorethylene) for li-ion battery separators. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407–408, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idris, N.H.; Rahman, M.M.; Wang, J.-Z.; Liu, H.-K. Microporous gel polymer electrolytes for lithium rechargeable battery application. J. Power Sources 2012, 201, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tõnurist, K.; Vaas, I.; Thomberg, T.; Jänes, A.; Kurig, H.; Romann, T.; Lust, E. Application of multistep electrospinning method for preparation of electrical double-layer capacitor half-cells. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 119, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Tan, L.; Liu, W.; Ma, J.; Li, L. Polydopamine coated electrospun poly(vinyldiene fluoride) nanofibrous membrane as separator for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 248, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Morimura, W.; Kuratani, R.; Nishikawa, S. Ion transport in separator membranes of lithium secondary batteries. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 4702–4708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiao, S.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wu, Y. A composite gel polymer electrolyte with high performance based on poly(vinylidene fluoride) and polyborate for lithium ion batteries. Adv. Energy Mater. 2014, 4, 1300647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabelli, D.; Leprêtre, J.C.; Dumas, L.; Rouif, S.; Portinha, D.; Fleury, E.; Sanchez, J.Y. Crosslinking of poly(vinylene fluoride) separators by gamma-irradiation for electrochemical high power charge applications. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 169, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, M.; Pléha, D. Nonwoven separators fabrication and analysis methods. ECS Trans. 2015, 70, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.Q.; Wan, L.S.; Xu, Z.K. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) separators with dual-asymmetric structure for high-performance lithium ion batteries. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. (Engl. Ed.) 2016, 34, 1423–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Fu, Y.; Zhao, T.; Gao, X.; Xing, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, X. All-solid-state flexible self-charging power cell basing on piezo-electrolyte for harvesting/storing body-motion energy and powering wearable electronics. Nano Energy 2017, 39, 590–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liu, L.; Yang, Q.; Liu, J.; Yu, T.; Yang, F.; Crittenden, J. Pvdf layer as a separator on the solution-side of air-cathodes: The electricity generation, fouling and regeneration. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 52361–52368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, R.; Jin, H.; Li, X.; Fei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Huang, H.; Lai-Wa Chan, H.; Wang, Y.; Chai, Y. A rectification-free piezo-supercapacitor with a polyvinylidene fluoride separator and functionalized carbon cloth electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 14963–14970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janakiraman, S.; Surendran, A.; Ghosh, S.; Anandhan, S.; Venimadhav, A. Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) fluoride separator for sodium ion battery with high coulombic efficiency. Solid State Ionics 2016, 292, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, M.; Costa, C.M.; Dias, J.; Maceiras, A.; Vilas, J.L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. On the relevance of the polar β-phase of poly(vinylidene fluoride) for high performance lithium-ion battery separators. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 26216–26225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeschke, S.; Mutke, M.; Jiang, Z.; Alt, B.; Wiemhofer, H.D. Study of carbamate-modified disiloxane in porous pvdf-hfp membranes: New electrolytes/separators for lithium-ion batteries. Chemphyschem 2014, 15, 1761–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karuppasamy, K.; Reddy, P.A.; Srinivas, G.; Tewari, A.; Sharma, R.; Shajan, X.S.; Gupta, D. Electrochemical and cycling performances of novel nonafluorobutanesulfonate (nonaflate) ionic liquid based ternary gel polymer electrolyte membranes for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulakshmi, N.; Stephan, A.M. Electrospun trilayer polymeric membranes as separator for lithium–ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 127, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, B.; Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, G. Honeycomb-like porous gel polymer electrolyte membrane for lithium ion batteries with enhanced safety. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, J.; Choi, Y.; Chung, K.Y.; Park, J.H. Controlled pore evolution during phase inversion from the combinatorial non-solvent approach: Application to battery separators. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 9496–9501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Alcoutlabi, M.; Toprakci, O.; Xu, G.; Watson, J.V.; Zhang, X. Preparation and characterization of electrospun nanofiber-coated membrane separators for lithium-ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 2451–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurita, R.; Zaccaria, M.; Gherardi, M.; Fabiani, D.; Merlettini, A.; Pollicino, A.; Focarete, M.L.; Colombo, V. Plasma processing of electrospun li-ion battery separators to improve electrolyte uptake. Plasma Process. Polym. 2016, 13, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, L.-F.; Shi, J.; Li, H.; Zhu, B.K.; Zhu, L.P. Construction of porous pvdf coating layer and electrochemical performances of the corresponding modified polyethylene separators for lithium ion batteries. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.-S.; Jeong, K.M.; Kim, K.; Yi, C.-W. Effects of capacity ratios between anode and cathode on electrochemical properties for lithium polymer batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 155, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Huang, X.; Lin, X.; Cao, J.; Yang, J.; Lei, C. The functional aqueous slurry coated separator using polyvinylidene fluoride powder particles for lithium-ion batteries. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 786, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Huang, S.; Xu, Z.; Xiao, Z.; Shi, C.; Zhao, J.; Zhu, R.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. Polyethylene terephthalate/poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite separator for li-ion battery. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2015, 48, 245304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Li, M.X.; Chang, Z.; Wang, Y.F.; Gao, J.; Zhu, Y.S.; Wu, Y.P.; Huang, W. A sandwich pvdf/hec/pvdf gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 245, 752–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, W.; Feng, J.; Ma, Z.; Shao, G. High capacity and cycle stability rechargeable lithium-sulfur batteries by sandwiched gel polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 210, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.-Y.; Kim, H.-T.; Chang, D.-R. Multilayered separator based on porous polyethylene layer, Al2O3 layer, and electro-spun pvdf nanofiber layer for lithium batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2014, 18, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Shi, C.; Huang, S.; Qiu, X.; Wang, H.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhao, J.; Sun, D.; Lin, L. Electrospun nanofibers for sandwiched polyimide/poly (vinylidene fluoride)/polyimide separators with the thermal shutdown function. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 176, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.I.; Choi, Y.; Chung, K.Y.; Park, J.H. A structurable gel-polymer electrolyte for sodium ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Xie, X.; Yuan, A.; Xia, B. Effect of drying temperature on a thin pvdf-hfp/pet composite nonwoven separator for lithium-ion batteries. Ionics 2017, 23, 929–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dai, Z.; Xu, J.; Guo, B.; He, X. Effect of silica nanoparticles/poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) coated layers on the performance of polypropylene separator for lithium-ion batteries. J. Energy Chem. 2014, 23, 582–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Xie, X.; Kretschmer, K.; Huang, X.; Sun, B.; Wang, G. Porous poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) polymer membrane with sandwich-like architecture for highly safe lithium ion batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.S.; Yang, C.C.; Luo, S.P.; Chen, Y.L.; Wei, C.N.; Lue, S.J. Pvdf-hfp/pet/pvdf-hfp composite membrane for lithium-ion power batteries. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 6862–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, H.; Lee, T.; Ryou, M.-H.; Lee, Y.M. Synergistic thermal stabilization of ceramic/co-polyimide coated polypropylene separators for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2015, 294, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcoutlabi, M.; Lee, H.; Zhang, X. Nanofiber-based membrane separators for lithium-ion batteries. MRS Proc. 2015, 1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.J.; Kwon, H.K.; Park, M.S.; Yim, T.; Yu, J.S.; Kim, Y.J. Ceramic composite separators coated with moisturized zro2 nanoparticles for improving the electrochemical performance and thermal stability of lithium ion batteries. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 9337–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Li, C.; Shi, C.; Yang, C.; Deng, L.; Zhang, W.; Peng, L.; Dai, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, P.; et al. Core-shell structured ceramic nonwoven separators by atomic layer deposition for safe lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Zhao, L.; Gong, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Preparation of high performance lithium-ion batteries with a separator–cathode assembly. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 34184–34190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtmann, J.; Schäfer, M.; Niemöller, A.; Winter, M.; Lex-Balducci, A.; Obeidi, S. Boehmite-based ceramic separator for lithium-ion batteries. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2016, 46, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.; Lee, J.S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.-C. Gel polymer electrolytes containing anion-trapping boron moieties for lithium-ion battery applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 27740–27752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Ma, J.; Li, B.; Zuo, Y.; Xia, D. Enhanced cycle performance of lithium-sulfur batteries using a separator modified with a pvdf-c layer. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 20276–20281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Liu, J.; He, C.; Li, J.; Wu, X. Composite of polyvinylidene fluoride–cellulose acetate with Al(OH)3 as a separator for high-performance lithium ion battery. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 541, 661–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, N.; Ouchen, F.; Rau, I.; Kumar, J.; Ouchen, F.; Smarra, D.A.; Subramanyam, G.; Grote, J.G. DNA based electrolyte/separator for lithium battery application. In Nanobiosystems: Processing, Characterization, and Applications VIII; Society of Photo-optical Instrumentation Engineers: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9557, p. 95570A. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmawati, S.A.; Sulistyaningsih; Putro, A.Z.A.; Widyanto, N.F.; Jumari, A.; Purwanto, A.; Dyartanti, E.R. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite polymer electrolytes poly(vinylidone fluoride)/nanoclay. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 1710, p. 030053. [Google Scholar]
- Bolloli, M.; Antonelli, C.; Molméret, Y.; Alloin, F.; Iojoiu, C.; Sanchez, J.Y. Nanocomposite poly(vynilidene fluoride)/nanocrystalline cellulose porous membranes as separators for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 214, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.L. Crosslinked electrospun poly(vinylidene difluoride) fiber mat as a matrix of gel polymer electrolyte for fast-charging lithium-ion battery. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 258, 1329–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Yang, S.; Zhao, X.; Du, P.; Xiong, J. Electrospun montmorillonite modified poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanocomposite separators for lithium-ion batteries. Mater. Res. Bull. 2016, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.B.; Wang, M.; Liu, S.X.; Xue, C.; Tian, Z.F.; Zou, Y.; Ren, X.M. Proton conductance of a superior water-stable metal-organic framework and its composite membrane with poly(vinylidene fluoride). Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 4169–4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.L.; Jiao, X.N. Preparation and characterization of polyvinylidene fluoride/octaphenyl-polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane hybrid lithium-ion battery separators by electrospinning. Solid State Ionics 2017, 310, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chao, C.Y.; Han, P.L.; Yan, X.R.; Zhang, H.H. Preparation and properties of gel-filled pvdf separators for lithium ion cells. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Wang, N.; Mao, X.; Si, Y.; Yu, J.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; El-Newehy, M.; Ding, B. Sandwich-structured pvdf/pmia/pvdf nanofibrous separators with robust mechanical strength and thermal stability for lithium ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 14511–14518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Yin, M.; Nie, G.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Chao, D.; Liu, X. Poly(aryl ether ketone) composite membrane as a high-performance lithium-ion batteries separator. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 2714–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng-Nan, H.; Jiang, Z.-Q.; Li, F.-B.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.-L. Preparation and characterization of pfsa-pvdf blend nanofiber membrane and its preliminary application investigation. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 7544–7552. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Zhu, J.; Zang, J.; Chen, C.; Lu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Yan, C.; Dirican, M.; Kalai Selvan, R.; Zhang, X. A novel bi-functional double-layer rgo–pvdf/pvdf composite nanofiber membrane separator with enhanced thermal stability and effective polysulfide inhibition for high-performance lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 15096–15104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanilmaz, M.; Lu, Y.; Dirican, M.; Fu, K.; Zhang, X. Nanoparticle-on-nanofiber hybrid membrane separators for lithium-ion batteries via combining electrospraying and electrospinning techniques. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 456, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ma, X.; Cao, C.; Li, J.; Zhu, Y. Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/SiO2 composite membranes prepared by electrospinning and their excellent properties for nonwoven separators for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 251, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, J.; Shang, Y.; Wang, L.; He, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y. Nanocomposite polymer membrane derived from nano tio2-pmma and glass fiber nonwoven: High thermal endurance and cycle stability in lithium ion battery applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 17697–17703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.-S.; Xie, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, S.; Kim, S.J.; Song, H.-K.; Wang, Z.L. Highly porous piezoelectric pvdf membrane as effective lithium ion transfer channels for enhanced self-charging power cell. Nano Energy 2015, 14, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Nie, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, Y. Pvdf mesoporous nanostructures as the piezo-separator for a self-charging power cell. Nano Energy 2014, 10, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wang, K.; Wang, R.; Jiang, M.; Han, J.; Gu, T.; Cheng, S.; Jiang, K. Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based hybrid gel polymer electrolytes for additive-free lithium sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 17889–17895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamshad, A.; Chao, T.; Muhammad, W.; Weiqiang, L.; Zhaohuan, W.; Songhao, W.; Bismark, B.; Jingna, L.; Junaid, A.; Jie, X.; et al. Highly efficient pvdf-hfp/colloidal alumina composite separator for high-temperature lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 5, 1701147. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Han, J.; Zhang, K.; Cui, X.; Xu, Z. Pore-forming technology development of polymer separators for power lithium-ion battery. In Proceedings of Sae-China Congress 2014: Selected Papers; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2014; pp. 89–95. [Google Scholar]
- Yeon, D.; Lee, Y.; Ryou, M.-H.; Lee, Y.M. New flame-retardant composite separators based on metal hydroxides for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 157, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Song, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, X.; Shu, D.; Nan, J. Al2O3/pvdf-hfp-cmc/pe separator prepared using aqueous slurry and post-hot-pressing method for polymer lithium-ion batteries with enhanced safety. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 212, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Gao, T.; Kirsch, D.; Liu, B.; Song, J.; Yang, B.; Hu, L. 3d printed separator for the thermal management of high-performance li metal anodes. Energy Storage Mater. 2018, 12, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.R.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, A.; Yan, X.; Shen, S.; Ke, C.; Zhang, J. Preparation of microporous cellulose/poly(vinylidene fluoride-hexafluoropropylene) membrane for lithium ion batteries by phase inversion method. J. Power Sources 2018, 379, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, J.K.; Park, J.H. Clay nanosheets in skeletons of controlled phase inversion separators for thermally stable li-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 3399–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuppasamy, K.; Reddy, P.A.; Srinivas, G.; Sharma, R.; Tewari, A.; Kumar, G.H.; Gupta, D. An efficient way to achieve high ionic conductivity and electrochemical stability of safer nonaflate anion-based ionic liquid gel polymer electrolytes (ilgpes) for rechargeable lithium ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 1145–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Zhang, K.; Chung, K.Y.; Wang, D.H.; Park, J.H. Pvdf-hfp/exfoliated graphene oxide nanosheet hybrid separators for thermally stable li-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80706–80711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Gong, Y.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Hollow mesoporous silica sphere-embedded composite separator for high-performance lithium-ion battery. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 2847–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitag, A.; Langklotz, U.; Rost, A.; Stamm, M.; Ionov, L. Ionically conductive polymer/ceramic separator for lithium-sulfur batteries. Energy Storage Mater. 2017, 9, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleman, M.; Kumar, Y.; Hashmi, S.A. High-rate supercapacitive performance of go/r-go electrodes interfaced with plastic-crystal-based flexible gel polymer electrolyte. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 182, 995–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Liu, W.; Li, P.; Ning, J.; Wei, Q. Electrochemical properties of llto/fluoropolymer-shell cellulose-core fibrous membrane for separator of high performance lithium-ion battery. Materials 2016, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Improved performance of pvdf-hfp/pi nanofiber membrane for lithium ion battery separator prepared by a bicomponent cross-electrospinning method. Mater. Lett. 2014, 133, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-H.; Kim, J.-H.; Choi, E.-S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.-Y. Nanoporous polymer scaffold-embedded nonwoven composite separator membranes for high-rate lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 54312–54321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmaraj, O.; Rao, B.N.; Jena, P.; Venkateswarlu, M.; Satyanarayana, N. Electrospun nanocomposite fibrous polymer electrolyte for secondary lithium battery applications. In AIP Conference Proceedings; American Institute of Physics: College Park, MD, USA, 2014; Volume 1591, pp. 1723–1725. [Google Scholar]
- Raja, M.; Angulakshmi, N.; Thomas, S.; Kumar, T.P.; Stephan, A.M. Thin, flexible and thermally stable ceramic membranes as separator for lithium-ion batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, M.; Fabiani, D.; Cannucciari, G.; Gualandi, C.; Focarete, M.L.; Arbizzani, C.; De Giorgio, F.; Mastragostino, M. Effect of silica and tin oxide nanoparticles on properties of nanofibrous electrospun separators. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A915–A920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, M.; Kumar, T.P.; Sanjeev, G.; Zolin, L.; Gerbaldi, C.; Stephan, A.M. Montmorillonite-based ceramic membranes as novel lithium-ion battery separators. Ionics 2014, 20, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. A novel naa-type zeolite-embedded composite separator for lithium-ion battery. Mater. Lett. 2015, 145, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-C.; Lian, Z.-Y. Electrochemical performance of lini1/3co1/3mn1/302 lithium polymer battery based on pvdf-hfp/m-sba15 composite polymer membranes. Ceram. Trans. 2014, 246, 18–202. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.-C.; Lian, Z.-Y.; Lin, S.J.; Shih, J.-Y.; Chen, W.-H. Preparation and application of pvdf-hfp composite polymer electrolytes in lini0.5co0.2mn0.3o2 lithium-polymer batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 134, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, P.L.; Tsao, C.H.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, S.T.; Hsu, H.M. A new strategy for preparing oligomeric ionic liquid gel polymer electrolytes for high-performance and nonflammable lithium ion batteries. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Gao, H. A sandwich-like composite nonwoven separator for li-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 215, 525–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Gong, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yan, C. Organic–inorganic binary nanoparticle-based composite separators for high performance lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 8778–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Zhao, X.M.; Jiao, X.N.; Qi, D.Y. Composite nanofiber membrane for lithium-ion batteries prepared by electrostatic spun/spray deposition. J. Electrochem. Energy Convers. Storage 2016, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, H.; Jin, X.; Huang, C. Improved performances of lithium-ion batteries with a separator based on inorganic fibers. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suriyakumar, S.; Raja, M.; Angulakshmi, N.; Nahm, K.S.; Stephan, A.M. A flexible zirconium oxide based-ceramic membrane as a separator for lithium-ion batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92020–92027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solarajan, A.K.; Murugadoss, V.; Angaiah, S. Dimensional stability and electrochemical behaviour of zro2 incorporated electrospun pvdf-hfp based nanocomposite polymer membrane electrolyte for li-ion capacitors. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, M.; Meng, J.; Ni, P. Development of plasma-treated polypropylene nonwoven-based composites for high-performance lithium-ion battery separators. Electrochim. Acta 2015, 167, 396–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yang, W. Improved performance of lithium ion battery separator enabled by co-electrospinnig polyimide/poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) and the incorporation of tio2-(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate). J. Power Sources 2015, 273, 1127–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Shen, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, G. A novel separator material consisting of zeoliticimidazolate framework-4 (zif-4) and its electrochemical performance for lithium-ions battery. J. Power Sources 2017, 369, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, C.; He, J.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Wu, X. An enhanced poly(vinylidene fluoride) matrix separator with high density polyethylene for good performance lithium ion batteries. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2017, 21, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Niu, D.-H.; Zhou, H.; Chao, C.-Y.; Wu, L.-J.; Han, P.-L. Preparation and characterization of pvdf separators for lithium ion cells using hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene grafted methoxyl polyethylene glycol (htpb-g-mpeg) as additive. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.Y.; Yang, Y.Q.; Li, M.X.; Wang, F.X.; Chang, Z.; Wu, Y.P.; Liu, X. A composite membrane based on a biocompatible cellulose as a host of gel polymer electrolyte for lithium ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2014, 270, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizzani, C.; Colò, F.; De Giorgio, F.; Guidotti, M.; Mastragostino, M.; Alloin, F.; Bolloli, M.; Molméret, Y.; Sanchez, J.Y. A non-conventional fluorinated separator in high-voltage graphite/lini0.4mn1.6o4 cells. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbizzani, C.; De Giorgio, F.; Mastragostino, M. Characterization tests for plug-in hybrid electric vehicle application of graphite/lini0.4mn1.6o4 cells with two different separators and electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2014, 266, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.Y.; Liang, H.Q.; Gu, L.; Yu, Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Xu, Z.K. Pvdf/pan blend separators via thermally induced phase separation for lithium ion batteries. Polymer 2016, 107, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Yin, M.; Liu, H.; Na, B.; Lv, R.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y. Modification and characterization of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride)/poly (acrylonitrile) blend separator membranes. Composites Part B 2017, 112, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, G.; Xiong, C. Properties of gel polymer electrolytes based on poly(butyl acrylate) semi-interpenetrating polymeric networks toward li-ion batteries. Ionics 2017, 23, 2319–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Z.-Y.; Chen, Y.-M.; Zhu, B.-K.; Zhu, L.-P. Preparation and properties of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/poly(dimethylsiloxane) graft (poly(propylene oxide)-block-poly(ethylene oxide)) blend porous separators and corresponding electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 116, 413–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.M.; Poliquit, B.Z.; Lee, Y.-G.; Won, J.; Ko, J.M.; Cho, W.I. Enhanced separator properties by thermal curing of poly(ethylene glycol)diacrylate-based gel polymer electrolytes for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 120, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Monaca, A.; Arbizzani, C.; De Giorgio, F.; Focarete, M.L.; Fabiani, D.; Zaccaria, M. Electrospun membranes based on pvdf-peo blends for lithium batteries. ECS Trans. 2016, 73, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monaca, A.L.; Giorgio, F.D.; Focarete, M.L.; Fabiani, D.; Zaccaria, M.; Arbizzani, C. Polyvinylidene difluoride–polyethyleneoxide blends for electrospun separators in li-ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, A6431–A6439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Nagaishi, T.; Shi, J.; Lee, H.; Wong, P.Y.; Sui, J.; Hyodo, K.; Kim, I.S. Enhanced wettability and thermal stability of a novel polyethylene terephthalate-based poly(vinylidene fluoride) nanofiber hybrid membrane for the separator of lithium-ion batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 26400–26406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Son, C.W.; Lee, S.; Kim, D.Y.; Park, C.; Eom, K.S.; Fuller, T.F.; Joh, H.I.; Jo, S.M. Multicore-shell nanofiber architecture of polyimide/polyvinylidene fluoride blend for thermal and long-term stability of lithium ion battery separator. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yvonne, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Omollo, E.; Ncube, S. Properties of electrospun pvdf/pmma/ca membrane as lithium based battery separator. Cellulose 2014, 21, 2811–2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lin, C.-E.; Shi, J.-L.; Ma, X.-T.; Zhu, B.-K.; Zhu, L.-P. Preparation and characterization of safety pvdf/p(mma-co-pegma) active separators by studying the liquid electrolyte distribution in this kind of membrane. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 115, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.L.; Lin, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Guo, H. Electrospun pvdf/pmma/sio2 membrane separators for rechargeable lithium-ion batteries. Key Eng. Mater. 2015, 645-646, 1201–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, T.; Jia, R.; Lang, X.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y. Preparation and electrochemical performance of pvdf ultrafine porous fiber separator-cum-electrolyte for supercapacitor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gören, A.; Costa, C.M.; Tamaño Machiavello, M.N.; Cíntora-Juárez, D.; Nunes-Pereira, J.; Tirado, J.L.; Silva, M.M.; Gomez Ribelles, J.L.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Effect of the degree of porosity on the performance of poly(vinylidene fluoride-trifluoroethylene)/poly(ethylene oxide) blend membranes for lithium-ion battery separators. Solid State Ionics 2015, 280, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
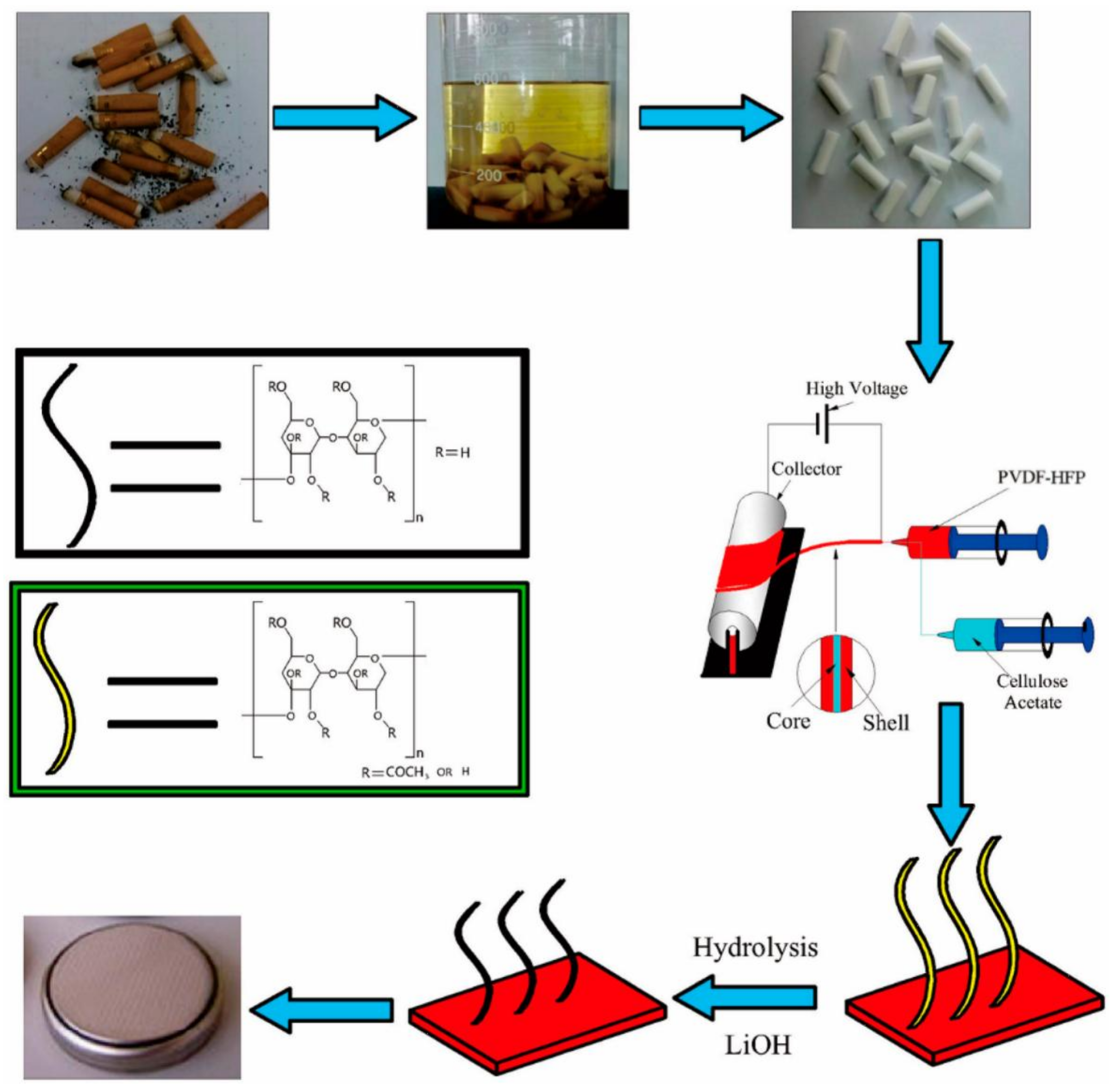
- Huang, F.; Xu, Y.; Peng, B.; Su, Y.; Jiang, F.; Hsieh, Y.-L.; Wei, Q. Coaxial electrospun cellulose-core fluoropolymer-shell fibrous membrane from recycled cigarette filter as separator for high performance lithium-ion battery. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Liu, J.; Li, J.; Lai, Y.; Wu, X. Enhanced ionic conductivity and electrochemical capacity of lithium ion battery based on pvdf-hfp/hdpe membrane. Mater. Lett. 2016, 170, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqui, U.R.; Ahmad, A.L.; Hamid, N.A. Effect of polyaniline (pani) on poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouro propylene) (pvdf-co-hfp) polymer electrolyte membrane prepared by breath figure method. Polym. Test. 2017, 60, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Sakumoto, T.; Mori, Y.; Wei, K.; Kim, B.-S.; Song, K.-H.; Kim, I.-S. Fabrication and characterization of reinforced electrospun poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene) nanofiber membranes. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 92, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, G.; Qin, B.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, B.; Hu, P.; Zhang, C.; Xu, G.; Yao, J.; Cui, G. A polyborate coated cellulose composite separator for high performance lithium ion batteries. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, A834–A838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidel, S.M.; Jeschke, S.; Vettikuzha, P.; Wiemhofer, H.D. Pvdf-hfp/ether-modified polysiloxane membranes obtained via airbrush spraying as active separators for application in lithium ion batteries. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 12048–12051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitag, A.; Stamm, M.; Ionov, L. Separator for lithium-sulfur battery based on polymer blend membrane. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Xiao, K.; Yu, J.; Ding, B. Closely packed x-poly(ethylene glycol diacrylate) coated polyetherimide/poly(vinylidene fluoride) fiber separators for lithium ion batteries with enhanced thermostability and improved electrolyte wettability. J. Power Sources 2016, 325, 292–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Separator | Characteristics | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Microporous | Operates at low temperatures (<100 °C); pore size = 50–100 Å | Nonwoven fibers (cotton, nylon, polyester, glass), polymers (PP, PE, PVC, PTFE), rubber, asbestos, wood |
| Nonwoven | Resistance to degradation by electrolytes; thickness > 25 µm; pore size = 1–100 µm | Polyolefins (PE, PP, PA, PTFE; PVDF; PVC) |
| Ion exchange membrane | High chemical resistance; impervious to electrolytes; pore size < 20 Å | PE, PP, Teflon-based films |
| Supported liquid membrane | Solid matrix with a liquid phase; insolubility in electrolyte; high chemical stability | PP, PSU, PTFE, CA |
| Polymer electrolyte | Simultaneously separator and electrolyte; high chemical and mechanical integrity | Polyethers, PEO, PPO, lithium salts |
| Solid ion conductor | simultaneously separator and electrolyte | - |
| Polymer | Melting Temp./°C | Degree of Crystallinity/% | Young Modulus/MPa | Dielectric Constant |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | ~170 | 40–60 | 1500–3000 | 6–12 |
| PVDF-TrFE | ~120 | 20–30 | 1600–2200 | 18 |
| PVDF-HFP | 130–140 | 15–35 | 500–1000 | 11 |
| PVDF-CTFE | ~165 | 15–25 | 155–200 | 13 |
| Materials | Electrolyte Solution | Porosity and Uptake (%) | Conductivity (S·cm−1) and Capacity (mAh·g−1) | Main Goal/Achievement | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | 1 M (C2H5)3CH3NBF4 + AN | -/- | -/- | Study of multistep electrospinning technique on the fabrication of PVDF composite membranes; High specific power. | [30] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DEC (1:1, w/w) | -/816 | 6.83 × 10−4/101.1 (0.5C) | Performance comparison with a PVDF-PDA separator; Enhanced cycling performance. | [31] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DEC (1:1, v/v) | 7/- | -/- | Analysis of the migration mechanism of cation and anions through the separator; The separator allows the control of structural stability and ion mobility. | [32] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMCC (1:1:1, w/w/w) | -/- | -/95 (0.2C) | Production of a PVDF membrane; Good capacity retention. | [33] |
| PVDF | 1 M TEABF4 in AN/PC and 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC | 80/- | 1.8 × 10−2 (25 °C)/- | Manufacturing of a PVDF separator; Favorable mechanical properties. | [34] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiBF4 in EC/DMC (50:50 wt. %) | -/- | 4.17 × 10−3 (20 °C)/- | Comparison of PVDF membrane performance with Nafigate separators. | [35] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC (1:1:1) | 78.9/427 | 1.72 × 10−3/164.3 (C/5) | Synthesis of dual asymmetric structure separators; Improved electrolyte uptake and ionic conductivity. | [36] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC (1:1:1) | -/- | -/447.36 (0.3C) | Production of a solid state SCPC with a PVDF separator; High storage capacity and stability. | [37] |
| PVDF | - | -/- | -/- | Assembly of a PVDF separator for air-cathode as application in microbial fuel cells; Improved electricity generation. | [38] |
| PVDF | PVA/H2SO4 | -/- | -/- | Production of a PVDF separator for piezoelectric supercapacitors; High mechanical strength and elevated capacitance. | [39] |
| PVDF | 1 M NaClO4 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 81/34 | 7.38 × 10−4 (29 °C)/153 | Production of an electroactive electrospun PVDF separator for sodium ion batteries. | [40] |
| PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 70/66 | 1.5 × 10−3/102 (2C) | Study of the effect of different PVDF copolymers as lithium ion battery separators. Demonstration of the relevance of β-phase content. | [41] |
| PVDF-TrFE | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 72/84 | 1.1 × 10−3/118 (2C) | ||
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 56/79 | 1.3 × 10−1/107 (2C) | ||
| PVDF-CTFE | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 59/80 | 1.5 × 10−3/85 (2C) | ||
| PVDF | [C2mim][NTf2] | 20/98 | 2.3 × 10−4 (25 °C)/74.6 (C/5) | Preparation of PVDF separators using a green solvent and ionic liquid as the electrolyte. | [9] |
| PVDF-HFP | LiTFSI | 48/248 | 5.2 × 10−5 (20 °C)/- | Application of disiloxane-based electrolytes on PVDF-HFP for the production of gel electrolyte separators; Good thermal and mechanical stability. | [42] |
| PVDF-HFP | LiNfO/BMImNfO | -/- | 2.61 × 10−2/(100 °C) 138.1 (C/4) | Production of ionic liquid gel polymer electrolytes; High ionic conductivity. | [43] |
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:2) | 70/247 | 3.2 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Evaluation of the performance of PVDF-HFP, as a single polymer membrane. Understanding of the method of avoiding the formation of beads in the nanofibers of PVDF-HFP; Good electrolyte uptake. | [44] |
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DMC (1:1) | 78/86.2 | 1.03 × 10−3/145 (0.2C) | Development of a PVDF-HFP gel polymer electrolyte membrane with honeycomb type porous structure; Excellent electrochemical performance. | [45] |
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/- | -/- | Production of separators with controlled pore structure; Improved rates and cycling performances. | [46] |
| PVDF-CTFE | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DMC:EMC (1:1:1, v:v) | 74/- | 7.51 × 10−4 (25 °C)/147 (0.2C) | Preparation of a nanofiber-coated composite separator by electrospinning;High discharge capacity and good cycling stability. | [47] |
| Materials | Electrolyte Solution | Porosity and Uptake (%) | Conductivity (S·cm−1) and Capacity (mAh·g−1) | Main Goal/Achievement | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF (plasma-treated) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/1200 | -/- | Study of the effect of plasma treatment in PVDF separators; Improved electrolyte uptake and mechanical properties. | [48] |
| PE/PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:EMC:DEC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | -/- | 0.89 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Investigation into the pore formation process in a coating layer for separators; Enhanced ionic conductivity. | [49] |
| PE/PVDF | 1.10 M LiPF6 in EC/PC/EP (3:1:6, v:v:v) | -/- | -/1436 (0.2C) | Study of the electrochemical performance of PE/PVDF separators; Enhanced cycling performance. | [50] |
| PVDF/PP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 58/140 | 5.9 × 10−4/145 (0.5C) | Coating of PVDF particles in the surface of a PP membrane; Increased electrolyte uptake. | [51] |
| PET/PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1, w/w/w) | -/- | 8.36 × 10−3/- | Investigation of the performance of a hot-pressed PET/PVDF separator; Excellent mechanical behavior. | [52] |
| PVDF/HEC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/135.4 | 8.8 × 10−4 (25 °C)/140 | Preparation of a PVDF/HEC/PVDF membrane with a sandwich structure; High electrolyte uptake and ionic conductivity. | [53] |
| PVDF/PMMA | 1 M LiTFSI in DME/DOL (1:1) | -/294 | 1.95 × 10−3 (25 °C)/1711.8 | Preparation of a sandwiched GPE based on PVDF and PMMA for lithium-sulfur batteries; High discharge capacity and cycle stability. | [54] |
| PDA/PVDF | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DEC (1:1, wt:wt) | -/1160 | 9.62 × 10−4/104.5 (0.5C) | Prove that the PDA coating can be promising for manufacturing electrospun nanofiber separators; Better cycling performance and elevated power capability. | [31] |
| PE/(PVDF/Al2O3) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 60.3/125, 314 | 1.14-1.23 × 10−3/- | Development of a multilayer coating for separators; Improvement of thermal stability and electrolyte wetting. | [55] |
| PI/PVDF/PI | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | 83/476 | 3.46 × 10−3/114.8 (0.5C) | Production of an electrospun sandwich-type separator; Superior porosity, electrolyte uptake, and ionic conductivity. | [56] |
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M NaClO4 in EC/PC (1:1) | -/- | 3.8 × 10−3/291.1 (0.2C) | Development of a PVDF-HFP-coated GF separator for sodium ion batteries; Good cycling performance. | [57] |
| PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in DMC/EMC/EC (1:1:1) | 53.5/106.9 | 8.34 × 10−4/131.33 (5C) | Study of the effect of the drying temperature on the performance of the separator. | [58] |
| PP/(PVDF-HFP/SiO2) | 1 M LiPF6 in DEC/EC (1:1, v/v) | -/- | 7.2 × 10−4/- | Analysis on the effect of a PVDF-HFP/SiO2 coating layer for PP separators; Better electrolyte uptake and ionic conductivity. | [59] |
| PMMA/PVDF-HFP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DMC (1:1) | -/342 | 1.31 × 10−3/143 (0.2C) | Investigation and analysis of a produced PMMA/PVDF-HFP electrolyte membrane; Exceptional thermal and electrochemical stability. | [60] |
| PVDF-HFP/PDA | LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | 72.8/254 | 1.40 × 10−3 (20 °C)/- | Production of a PVDF-HFP/PDA separator by a dip-coating method. | [12] |
| PVDF-HFP/PET | 1 M LiClO4 in DMSO | -/282 | 6.39 × 10−3 (25 °C)/158 (0.1C) | Combination of PVDF-HFP with a SiO2 nanoparticle-modified PET matrix; Improved thermal stability, electrolyte uptake, and ionic conductivity. | [61] |
| PP/(AlO2/PVDF-HFP) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v/v) | -/- | 7.95 × 10−4/98.6 (0.2C) | Inspection of the performance of a separator for PP membrane coating; Improved thermal stability. | [62] |
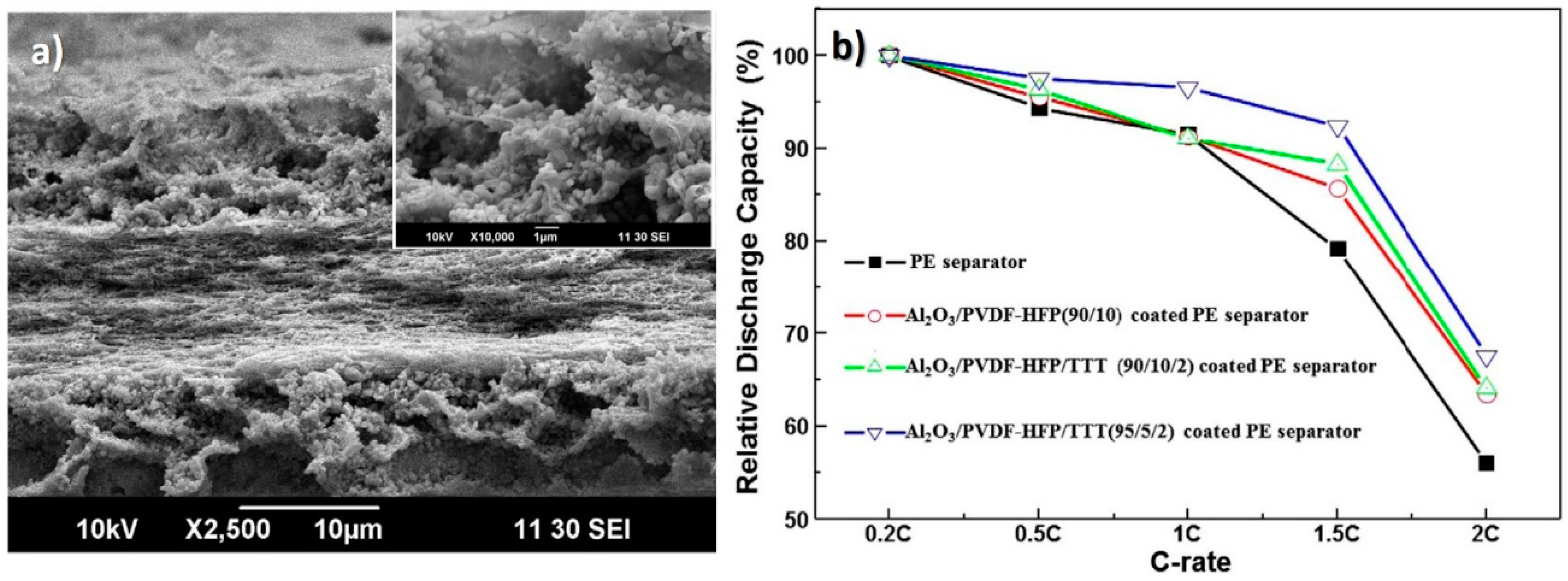
| γ-Al2O3/PVDF-HFP/TTT | 1 M LiClO4 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/157 | 1.3 × 10−3/~100 (0.5C) | Dip coating of a PE separator with γ-Al2O3/PVDF-HFP/TTT; Increased electrolyte uptake and ionic conductivity. | [13] |
| PP/PE/PP/PVDF-co-CTFE | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC (1:1:1, v:v:v) | -/- | -/- | Fabrication of PVDF-co-CTFE nanofiber coatings for improving the performance of polyolefin separators; High electrolyte uptake and good wettability. | [63] |
| Materials | Fillers | Electrolyte Solution | Porosity and Uptake (%) | Conductivity (S·cm−1) and Capacity (mAh·g−1) | Main Goal/Achievement | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | Al2O3 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | 55.8/153.5 | 2.23 × 10−3 (25 °C)/114.2 | Production of a composite PVDF/Al2O3; High thermal stability and ionic conductivity, low discharge capacity decay. | [15] |
| PVDF | Al2O3 | EC/DMC (1:1) | -/230 | 1.24 × 10−3/151.97 (C) | Core-shell composite nonwoven separator of PVDF-HFP@Al2O3; high heat resistance up to 200 °C without any shrinkage, | [65] |
| PVDF | Al2O3 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | 67/230 | 1.49 × 10−3/146.3 (0.2C) | Separator-cathode assembly with PVDF/Al2O3; Good electrochemical performance. | [66] |
| PVDF | AlO(OH) nanoparticles | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (3:7) | -/65 | -/- | Ceramic separator based on boehmite nanoparticles; Improved safety and wettability. | [67] |
| PVDF | BC | 1 M LiTFSI in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/- | 4.2×10−3 (30 °C)/- | Preparation of GPEs based on cross-linkers; High ionic conductivity and thermal stability. | [68] |
| PVDF | Carbon | 1 M LiTFSI and 0.1 M LiNO3 in DOL/DME (1:1) | -/- | -/827 (0.5C) | PVDF-C separator by phase inversion technique; Superior rate performance and stability. | [69] |
| PVDF | CNF | 1 M LiTFSI in DOL/DME (1:1) | -/119 | -/1739.2 (C) | Production of CNF/PVDF separators for Li-S batteries Great battery discharge capacity and cycling stability. | [20] |
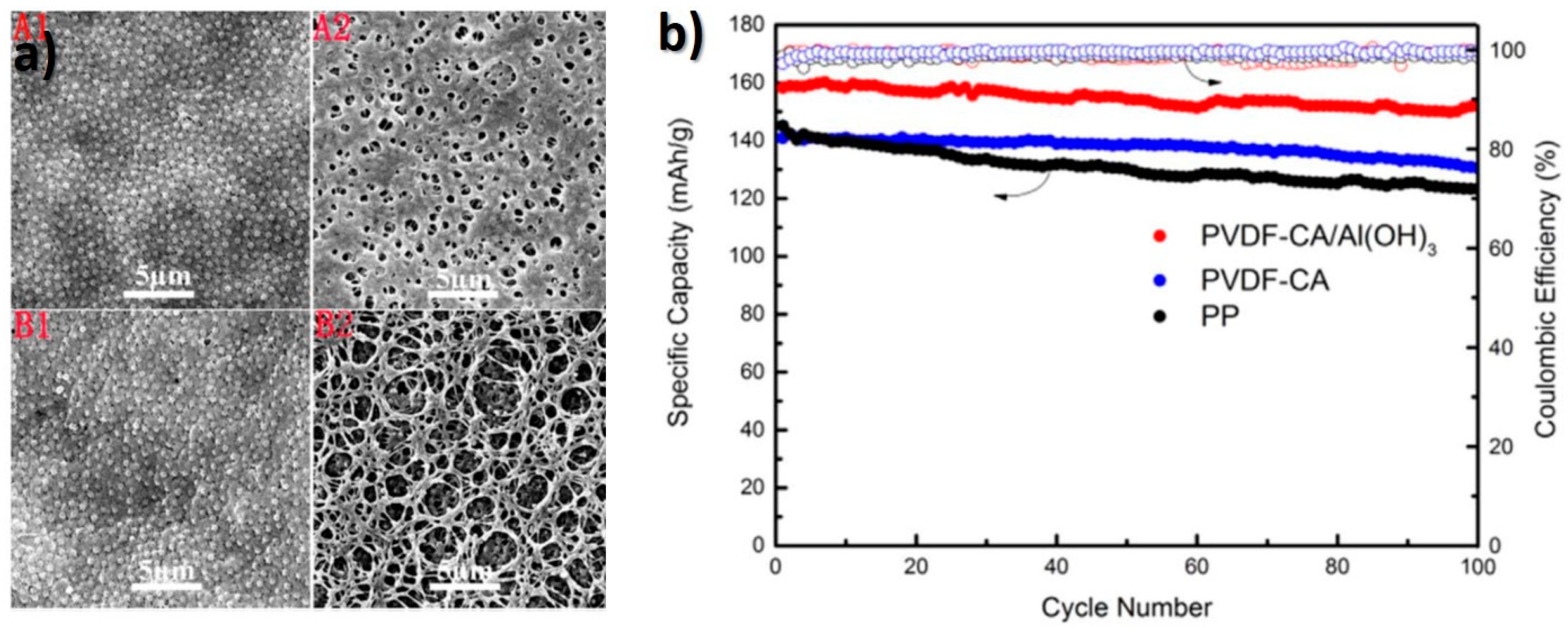
| PVDF | Cellulose acetate/Al(OH)3 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 68.6/403.9 | 2.85 × 10−3/151.97 (C) | Environmental friendly materials in a separator; High electrolyte uptake, ionic conductivity and cycling performance. | [70] |
| PVDF | DNA-CTMA | LiAsF6 in EC/EMC/DMC | -/- | -/- | PVDF/DNA-CTMA membrane as a solid polymer/gel electrolyte separator; Improved thermal and mechanical properties. | [71] |
| PVDF | LiPVAOB | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMCC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | -/88.5 | 2.6 × 10−4/120 (0.2C) | Composite gel polymer electrolyte PVDF/LiPVAOB membrane; Good ionic conductivity. | [33] |
| PVDF | Nanoclays/PVP | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 87.4/553.3 | -/- | Study of the influence of solvents in the separator High porosity and uptake. | [72] |
| PVDF | NCC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/- | 3.73 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Preparation of NCC-PVDF separators by phase inversion; Improved wettability and mechanical properties. | [73] |
| PVDF | MA groups | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 67.4/- | 1.48 × 10−3/136 (0.2C) | Study of the addition of MA groups to the PVDF structure; High ionic conductivity. | [74] |
| PVDF | MMT | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DEC (1:1:1) | 84.08/333 | 4.20 × 10−3 (25 °C)/144 | Effect of different contents of MMT filler in PVDF separators; High ionic conductivity and porosity. | [75] |
| PVDF | MOF-808 | - | -/- | 1.56 × 10−4 (65 °C)/- | Production of a MOF/polymer membrane; Good mechanical properties and durability. | [76] |
| PVDF | Octaphenyl-POSS | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 66.1/912 | 4.2 × 10−3/145.8 (0.5C) | Electrospun membrane with octaphenyl-POSS particles; Increased uptake and porosity, high ionic conductivity. | [77] |
| PVDF | Polyether (PEGDA+PEGMEA) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/230 | ~1.4 × 10−3 (25 °C)/93 (0.5C) | Preparation of GPEs with PVDF and polyethers. | [78] |
| PVDF | PMIA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | -/- | 8.1 × 10−4/135.29 (0.2C) | Composite sandwich type separator, by electrospinning; High capacity retention and good rate performance. | [79] |
| PVDF | P-PAEK | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 71.7/123.7 | /141.6 (C/2) | Development of a P-PAEK/PVDF separator High wettability and electrolyte uptake. | [80] |
| PVDF | PFSA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/- | 1.53 × 10−3/137.9 (C) | PVDF/PFSA blend membrane; High stability and discharge capacity. | [81] |
| PVDF | rGO | 1 M LiTFSI + 0.1 M LiNO3 in DME/DOL (1:1) | 71/380 | /646 | Double-layer PVDF/rGO membrane by electrospinning; High safety and cycling stability. | [82] |
| PVDF | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 54.1/279.5 | -/175.7 | Synthesis of a composite separator with SiO2; High wettability, uptake and thermal/mechanical stability. | [17] |
| PVDF | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (1:1 in volume) | 70/370 | 2.6 × 10−3/132 (C) | Addition of SiO2 nanoparticles on PVDF membranes; Improvement of wettability and ionic conductivity. | [83] |
| PVDF | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | 85/646 | 7.47 × 10−3/159 (0.2C) | Electrospun PVDF/SiO2 composite separator; Excellent thermal stability and high ionic conductivity. | [84] |
| PVDF | SnO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1 w:w) | -/- | -/- | Use of SnO2 nanoparticles in a PVDF electrospun separator; Good cycling performance. | [85] |
| PVDF | ZnO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (1:2) | -/- | -/- | Piezo-separator for integration on a self-charging power cell; Enhanced electrochemical performance. | [86] |
| PVDF | ZnO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/- | -/- | Piezo-separator for self-charging power cells; Stable and efficient performance. | [87] |
| PVDF | ZrO2/PEO | 1 M LiTFSI in DOL/DME (1:1) | -/147.3 | 3.2 × 10−4 (25 °C)/1429 (0.2C) | GPE for lithium-sulfur batteries; High discharge capacity and rate performance. | [88] |
| PVDF-HFP | Al2O3 | 0.5 M NaTf/EMITf | -/- | 6.3–6.8 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Introduction of Al2O3 in a gel polymer electrolyte; Improved mechanical properties. | [14] |
| PVDF-HFP | Al2O3 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC +2% VC | -/372 | 1.3 × 10−3/155 (0.5C) | Colloidal Al2O3 composite separator; enhancement of the mechanical strength of the PVDF-HFP separator. | [89] |
| PVDF-HFP | Al2O3 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (v:v:v = 1:1:1) | -/420 | 4.7 × 10−4/109 (4C) | Production of a low cost membrane, with a simple and easy scalable manufacturing process; High electrolyte uptake and good electrochemical stability and performance. | [90] |
| PVDF-HFP | Al(OH)3 | 1.15 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (3:7, v:v) | 84/127 | 10−3/81 (C/2) | Upgrading the battery safety operation by the addition of metal hydroxides in composite separators; Suitable electrolyte uptake. | [91] |
| PVDF-HFP | Al2O3/CMC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/PC/EMC (2:3:1:3) | 42.7/- | 9.3 × 10−4 (25 °C)/- | Composite separator with Al2O3/CMC; Safer and more stable separators. | [92] |
| PVDF-HFP | BN | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/- | -/150 (0.2C) | 3D separator; improved cycling stability with lower voltage polarization | [93] |
| PVDF-HFP | CA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC | 85/310 | 1.89 × 10−3/136 (8C) | Porous and honeycomb-structured membrane; higher lithium-ion transference number and improved rate performance | [94] |
| PVDF-HFP | Clay | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1, v:v:v) | -/- | 1.49 × 10−3/- | New technique to incorporate clay sheets in a PVDF-HFP matrix, as separator; Thermal stability and higher ionic conductivity. | [95] |
| PVDF-HFP | EMImNfO-LiNfO | - | -/- | 3.92 × 10−4/(20 °C) 57 (C) | Introduction of anion-based IL and lithium salt in a GPE; High thermal stability, good electrochemical properties. | [96] |
| PVDF-HFP | GO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/71 | 1.115 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Addition of GO in separators to increase thermal properties; improved electrochemical and mechanical properties. | [97] |
| PVDF-HFP | Graphene | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 88/470 | 3.61 × 10−3/149 (C) | PVDF-HFP/graphene GPE by NIPS; Increased porosity, uptake and ionic conductivity. | [18] |
| PVDF-HFP | HMSS | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | ~70/285 | 2.57 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Development of PVDF-HFP with HMSS separators; Increased wettability and porosity. | [98] |
| PVDF-HFP | Li1,3Al0,3Ti1,7(PO4)3 | 1 M LiTFSI + 0.25 M LiNO3 in DME/DOL (1:1) | 34/143.9 | 8.8 × 10−4 (25 °C)/1614 | Ceramic/polymer membrane for lithium-sulfur cells; High ionic conductivity and discharge capacity. | [99] |
| PVDF-HFP | LiTSFI/SN | - | -/- | 1.97 × 10−3 (20 °C)/- | Production of supercapacitors with GO electrodes and GPE; High ionic conductivity. | [100] |
| PVDF-HFP | LLTO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 69.8/497 | 13.897 × 10−3 (25 °C)/155.56 | Incorporation of LLTO in a PVDF-HFP separator; Improved ionic conductivity. | [101] |
| PVDF-HFP | PI | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 73/350 | 1.46 × 10−3/- | Evaluation of a bicomponent electrospinning method to produce the separator, Good physical properties and improved electrochemical stability. | [102] |
| PVDF-HFP | PET/SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 60/- | 9.3 × 10−4/- | Separator with an organized porous structure, with benefits for cell operation at high C-rates; Excellent cell performance. | [103] |
| PVDF-HFP | MgAl2O4 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC:DEC (1:1, v:v) | -/- | 2.80 × 10−3/140 (0.1C) | Influence of different quantities of the MgAl2O4 filler in the membrane; Good ionic conductivity. | [104] |
| PVDF-HFP | MgAl2O4 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, w:w) | 60/81 | 10−3 (30 °C)/140 (C/10) | MgAl2O4 as filler of thin and flexible separator; Good thermal stability and stable cycling performance. | [105] |
| PVDF-HFP | Mg(OH)2 | 1.15 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (3:7, v:v) | 64/115 | 8.08 × 10−4/105 (C/2) | Upgrading the battery safety operation by the addition of metal hydroxides in composite separators; High thermal stability and good capacity retention. | [106] |
| PVDF-HFP | MMT | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | 40/251 | 9.01 × 10−4/105 (0.1C) | Use of montmorillonite as filler; High thermal stability and stable cycling performance. | [107] |
| PVDF-HFP | NaA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | 65/194 | 2.1 × 10−3/- | Separator with incorporation of NaA zeolite; Excellent thermal stability and wettability. | [108] |
| PVDF-HFP | NaAlO2 | 0.5 M NaTf/EMITf | -/- | 5.5–6.5 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Introduction of NaAlO2 in a gel polymer electrolyte; Improved ionic conductivity. | [14] |
| PVDF-HFP | m-SBA15 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/82.83 | 3.23 × 10−3/156 (0.1C) | A PVDF-HFP composite membrane with m-SBA15 as filler; High coulomb efficiency. | [109] |
| PVDF-HFP | m-SBA15 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/85.36 | 3.78 × 10−3/198.6 (0.1C) | Effect of the addition of a silica filler on a PVDF-HFP composite matrix separator; High coulomb efficiency. | [110] |
| PVDF-HFP | OIL | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | -/13 | 2 × 10−3 (25 °C)/141 (C) | Synthesis of OIL from a phenolic epoxy resin; Non-flammability, good cell performance. | [111] |
| PVDF-HFP | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:2) | 65.41/217 | -/124.5 (C) | Synthesis of dual asymmetric structure separators with SiO2 particles; High thermal stability and electrolyte uptake. | [16] |
| PVDF-HFP | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in DMC/EMC/DC/VC (46.08:22.91:27.22:3.79) | 26.7/202 | 8.47 × 10−4 (25 °C)/154.4 | Composite separator with SiO2; Improved thermal stability and cycling performance. | [112] |
| PVDF-HFP | TiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1, v:v:v) | 58/330 | 3.45 × 10−3/122 (10C) | Evaluation of the performance of a nanocomposite polymer membrane with addition of TiO2; Excellent electrochemical performance. | [85] |
| PVDF-HFP | ZrO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1) | 71/182 | 1.48 × 10−3 S·cm−1 (25 °C)/126.8 mAhg−1 (0.5C) | Preparation of ZrO2/PVDF-HFP by the dip-coating method High wettability, ionic conductivity, and thermal resistance. | [113] |
| PVDF-HFP | ZrO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC (1:3) | -/- | 2.06 × 10−3 (25 °C)/149.7 | Improvement of the electrochemical properties of a electrospun membrane High uptake and ionic conductivity. | [114] |
| PVDF-HFP | ZrO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | 87.53/351.2 | 3.2 × 10−4/646 (0.2C) | Inorganic fibers as substrates to separators; High thermal stability and good mechanical properties. | [115] |
| PVDF-HFP | ZrO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 60/160 | 10−3 (25 °C)/75 (C) | Development of thin and flexible ZrO2 separators High porosity and thermal stability. | [116] |
| PVDF-HFP | ZrO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 95.7/481 | 2.695 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Incorporation of ZrO2 in PVDF-HFP electrospun membranes; High ionic conductivity and cycling stability. | [117] |
| PVP/PVDF | Black carbon nanoparticles | 6 M KOH | -/- | -/- | Production of separators for supercapacitor applications Improved thermal and mechanical properties. | [19] |
| PP/PVDF-HFP | PMMA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1, v:v) | 77.9/212 | 1.57 × 10−3/138 (0.2C) | Physical and electrochemical performances of a PP/PVDF-HFP/PMMA composite separator; Enhanced thermal stability and electrolyte uptake. | [52] |
| PP/PVDF-HFP | SiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | -/290 | 1.76 × 10−3/150 (0.2C) | PP/PVDF-HFP separator, with the inclusion of SiO2 nanoparticles; Favorable chemical stability and discharge capacity. | [118] |
| PI/PVDF-HFP | TiO2 | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | -/- | 1.88 × 10−3/161 (0.5C) | Electrospun PI/PVDF-HFP membrane, with addition of TiO2 nanoparticles; Excellent electrochemical properties. | [119] |
| Materials | Blends | Electrolyte Solution | Porosity and Uptake (%) | Conductivity (S·cm−1) and Capacity (mAh·g−1) | Main Goal/Achievement | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF | HDPE | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | 58/260 | 2.54 × 10−3 S·cm−1 (25 °C)/156.1 mAhg−1 (0.1C) | Production of a sponge-like PVDF/HDPE film; High ionic conductivity and cycling performance. | [121] |
| PVDF | HTPB-g-MPEG | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 56/350 | 3.1 × 10−3/116 (C) | Enhancement of the stability of entrapped liquid electrolyte and corresponding ion conductivity. | [122] |
| PVDF | MC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEM/EMC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | -/138.6 | 1.5 × 10−3/110 (C) | PVDF composite separator with cellulose material; Excellent electrochemical performance. | [123] |
| PVDF | MEP | 1 M TEABF4 in AN/PC and 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC | 77/- | 1.3 × 10−2/- | Manufacturing by phase inversion, with MEP as a cross-linking agent; Good mechanical strength. | [34] |
| PVDF | NCC | 1 M LiFAP in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/- | -/- | Separators with applications in hybrid electric vehicles; Favorable performance at high-voltage cells. | [124] |
| PVDF | NCC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/- | -/108 (1C) | Separators with applications in hybrid electric vehicles; Influence on high-rate cell operation. | [125] |
| PVDF | PAN | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/DEC (1:1:1) | 77.7/414.5 | 2.9 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Improved thermal and mechanical properties; High cycling stability. | [126] |
| PVDF | PAN | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | -/320 | 1.45 × 10−3/145.71 (0.2C) | Production of an electrospun blended membrane; High thermal and mechanical stability. | [127] |
| PVDF | PBA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC/DMC (1:1:1) | -/120 | 8.1 × 10−4 (25 °C)/95 (0.1C) | Preparation of cross-linked PBA/PVDF GPE; Good cycling stability. | [128] |
| PVDF | PDMS-g-(PPO-PEO) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | 80.1/512 | 4.5 × 10−3/120 (1C) | Porous separator; Good electrochemical stability. | [129] |
| PVDF | PEGDA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/- | 3.3 × 10−3/117 (0.1C) | Separator produced by thermal polymerization; High capacity retention. | [130] |
| PVDF | PEO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | /530 | -/- | Production of blended membranes by electrospinning; improved conductivity and uptake. | [131] |
| PVDF | PEO | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | -/527 | -/- | Development of electrospun membranes; High electrolyte uptake, low shutdown temperature. | [132] |
| PVDF | PET | - | 80/270 | -/- | Synthesis of a hybrid separator; High wettability and electrolyte uptake. | [133] |
| PVDF | PI | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/PC/DEC/VC (35.4:17.2:45.1:2.3) | -/- | 1.3 × 10−3/141 | Preparation of the separator by electrospinning; Improved thermal stability and mechanical properties. | [134] |
| PVDF | PMMA/CA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1, w:w) | 99.1/323 | -/- | Elevated porosity and electrolyte uptake. | [135] |
| PVDF | P(MMA-co-PEGMA) | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/EMC/DMC (1:1:1, w:w:w) | -/372 | 3.01 × 10−3/- | Porous separator; Improved capacity retention. | [136] |
| PVDF | PMMA/SiO2 | - | 80.1/293.2 | 1.97 × 10−3/- | Evaluation of the effect of a PMMA and SiO2 blend on a PVDF electrospun membrane as a separator; High electrolyte uptake and improved ionic conductivity. | [137] |
| PVDF | PVP | 1 M Et4N-BF4/PC | -/360 | 1.8 × 10−3 (25 °C)/- | Separators for supercapacitors; High uptake and power density. | [138] |
| PVDF | TAIC | 1 M TEABF4 in AN/PC and 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DEC | 75/- | 1.4 × 10−2/- | Manufacturing of separator by phase inversion, with TAIC as cross-linking agent. High ionic conductivity. | [34] |
| PVDF-TrFE | PEO | 1 M LiTFSI in PC | 44.5/107 | 5.4 × 10−4/124 (C/5) | Research on the physical and chemical properties of a PVDF-TrFE/PEO blend Favorable cycling performance. | [139] |
| PVDF-HFP | CA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1, v:v:v) | 66.36/355 | 6.16 × 10−3/138 (0.2C) | Investigation of the use of CA from waste cigarette filters, in PVDF-HFP membranes; Good electrochemical performance and excellent thermal stability. | [140] |
| PVDF-HFP | HDPE | - | 71/300 | 2.97 × 10−3 (25 °C)/140.5 (C) | Preparation of the separator by non-solvent-induced phase separation; High ionic conductivity. | [141] |
| PVDF-HFP | PANI | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1) | 83/270 | 1.96 × 10−3/- | High thermal stability, electrolyte uptake, and ionic conductivity | [142] |
| PVDF-HFP | PEG/PEGDMA | 1 M LiClO4 in EC/DEC (1:1, v:v) | 71/212 | 1.70 × 10−3/- | Investigation into a strengthened electrospun nanofiber membrane separator; High porosity and electrolyte uptake. | [143] |
| PVDF-HFP | PLTB | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:1, v:v) | 70/260 | 1.78 × 10−3/138 (0.5C) | Excellent electrochemical performance. | [144] |
| PVDF-HFP | PSx-PEO3 | 1 M LiTFSI in EC/DMC (1:1, w:w) | -/520 | 4.2 × 10−4 (20 °C)/123 (C) | Production of a safe PVDF-HFP blended membrane, which can be sprayed; Elevated electrolyte uptake. | [145] |
| PVDF-HFP | PVSK | 1 M LiTFSI + 0.25 M LiNO3 in DME/DOL (1:1) | 27/- | -/1220 | Improved cycling performance. | [146] |
| PVDF-HFP | PVC | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC (1:2) | 62/230 | 1.58 × 10−3/125 (0.1 C) | Tri-layer polymer membrane; Good mechanical and thermal stability. | [44] |
| PEI/PVDF | x-PEGDA | 1 M LiPF6 in EC/DMC/EMC (1:1:1) | 64.6/235.6 | 1.38 × 10−3 (25 °C)/160.3 (0.2C) | Production of x-PEGDA-coated PEI/PVDF membranes; high wettability, porosity, and ionic conductivity. | [147] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbosa, J.C.; Dias, J.P.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Costa, C.M. Recent Advances in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Separators. Membranes 2018, 8, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030045
Barbosa JC, Dias JP, Lanceros-Méndez S, Costa CM. Recent Advances in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Separators. Membranes. 2018; 8(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbosa, João C., José P. Dias, Senentxu Lanceros-Méndez, and Carlos M. Costa. 2018. "Recent Advances in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Separators" Membranes 8, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030045
APA StyleBarbosa, J. C., Dias, J. P., Lanceros-Méndez, S., & Costa, C. M. (2018). Recent Advances in Poly(vinylidene fluoride) and Its Copolymers for Lithium-Ion Battery Separators. Membranes, 8(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes8030045