Ion Concentration Polarization in Branched Microchannels: Effect of Membrane Thickness and Applied Voltage
Abstract
1. Introduction
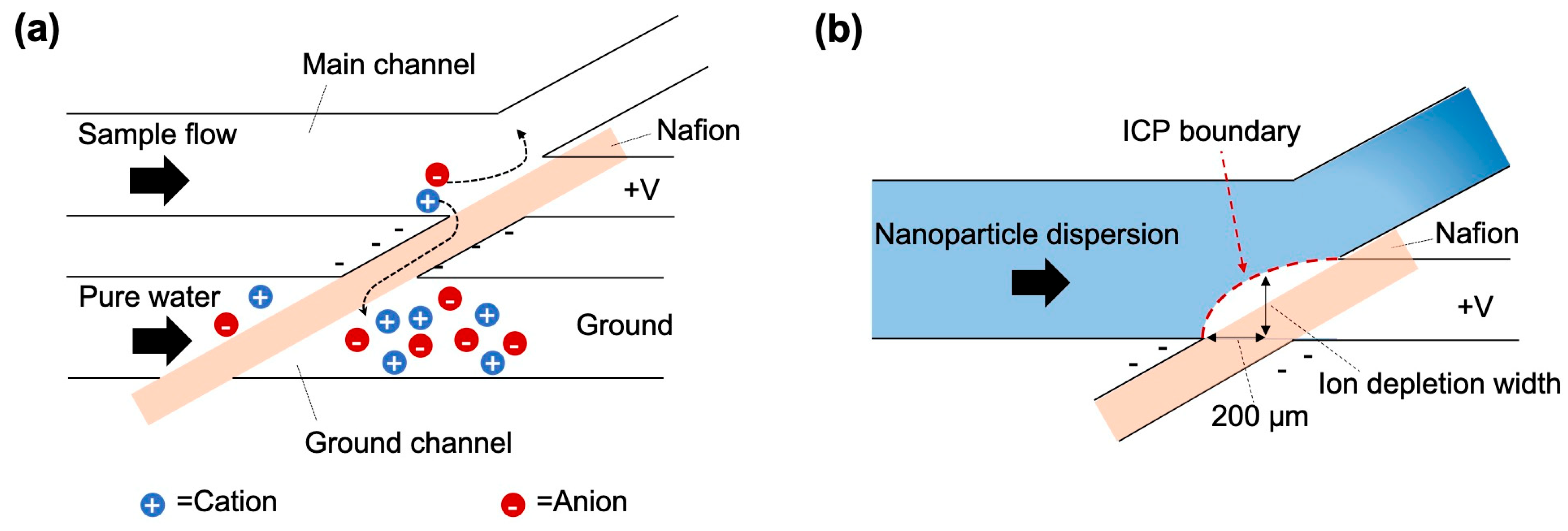
2. Theory
3. Materials and Methods
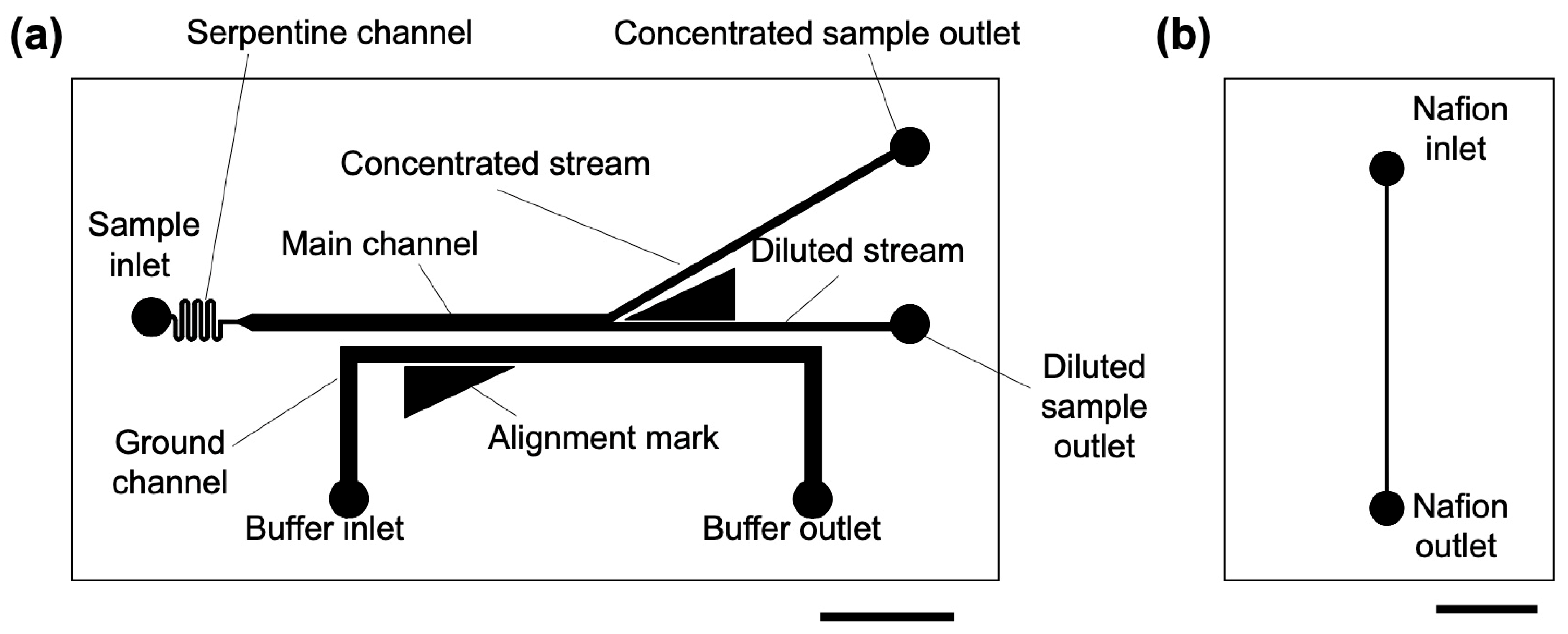
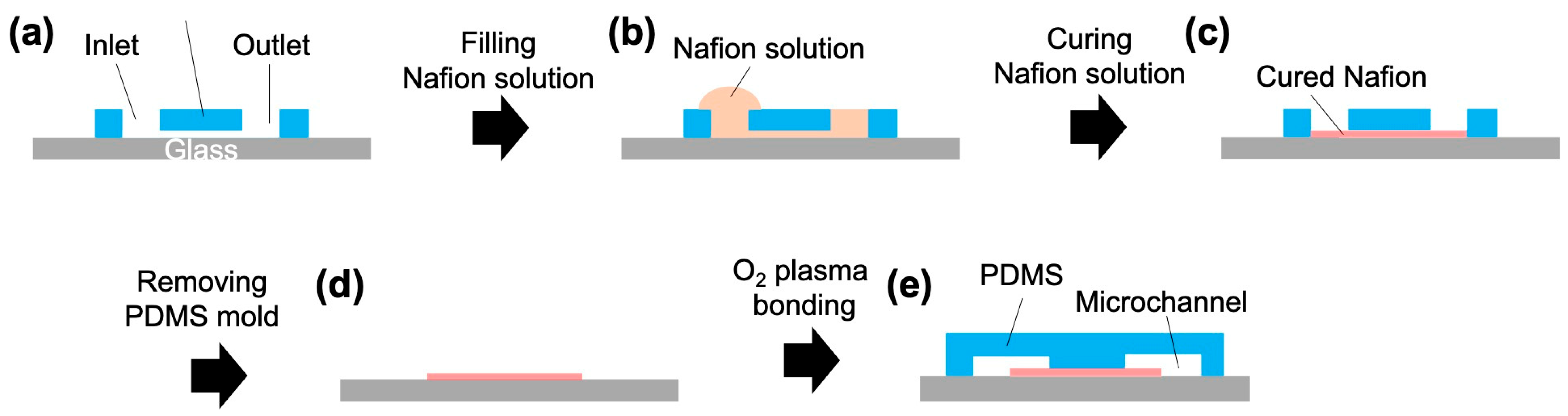
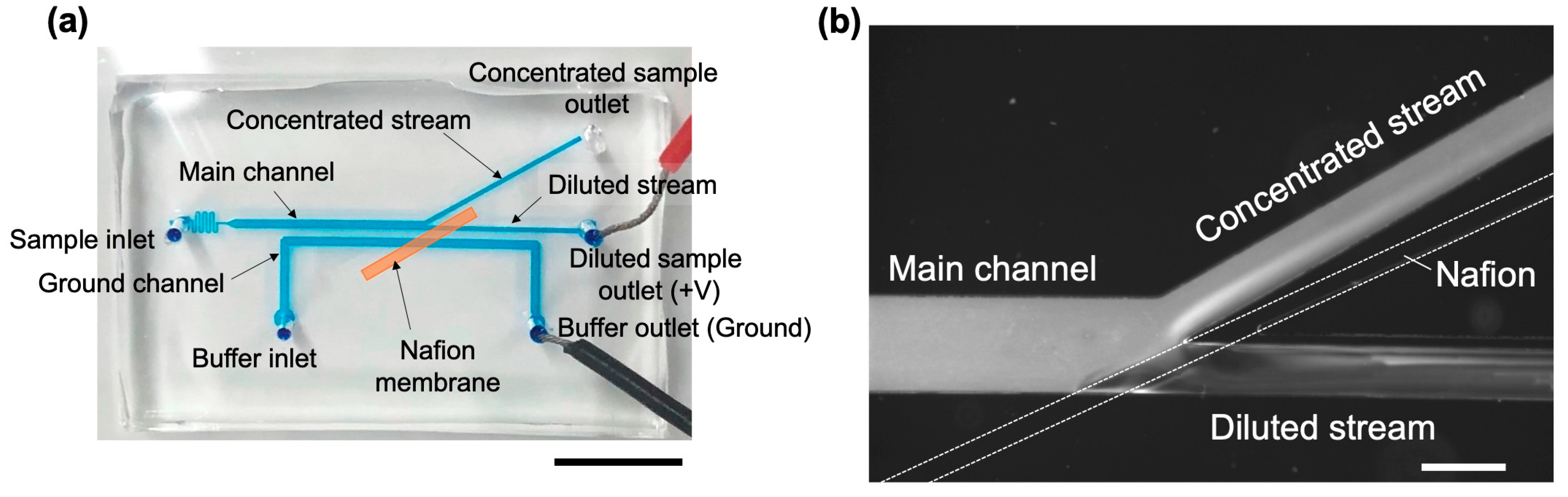
3.1. Design and Fabrication of Microchannels for ICP
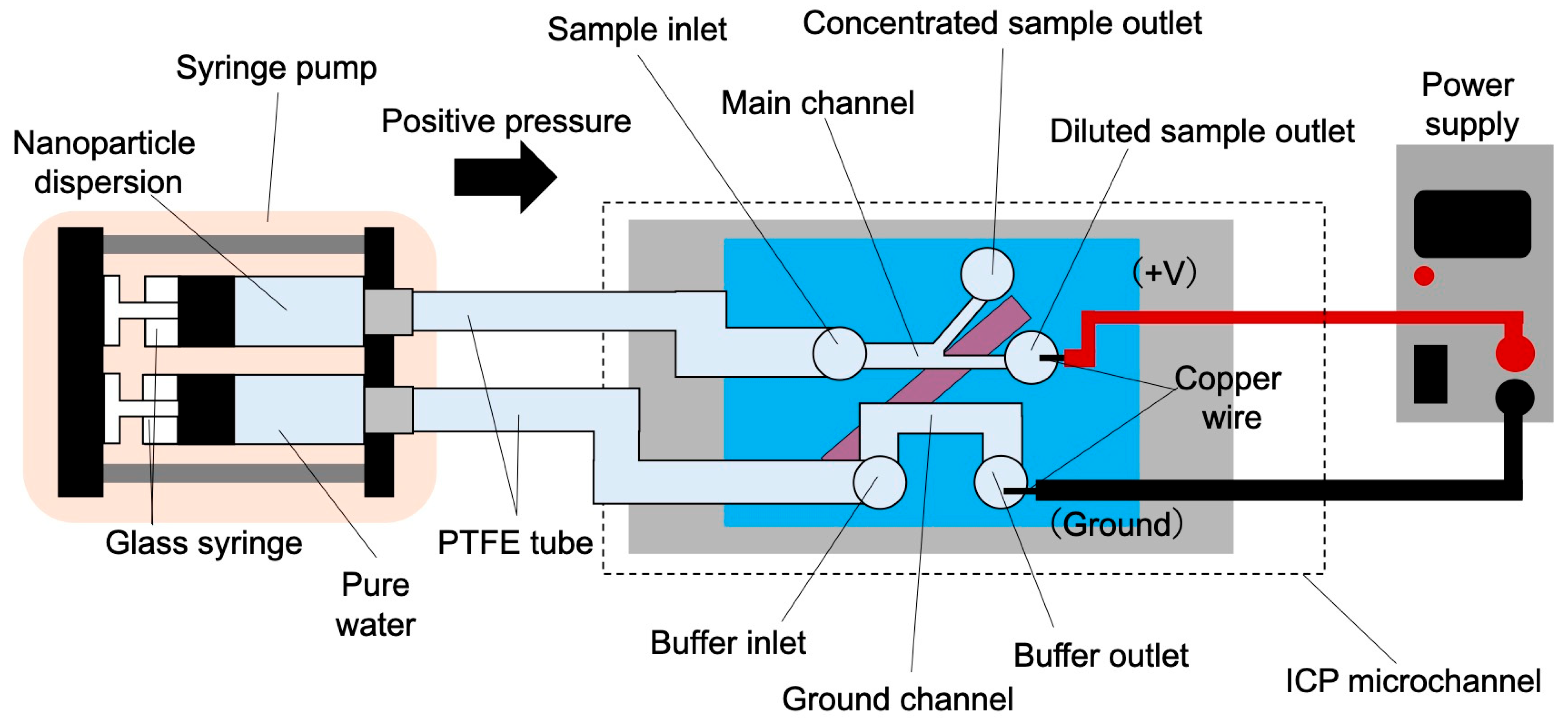
3.2. Microfluidic System
3.3. Measurement and Observation
4. Results and Discussion
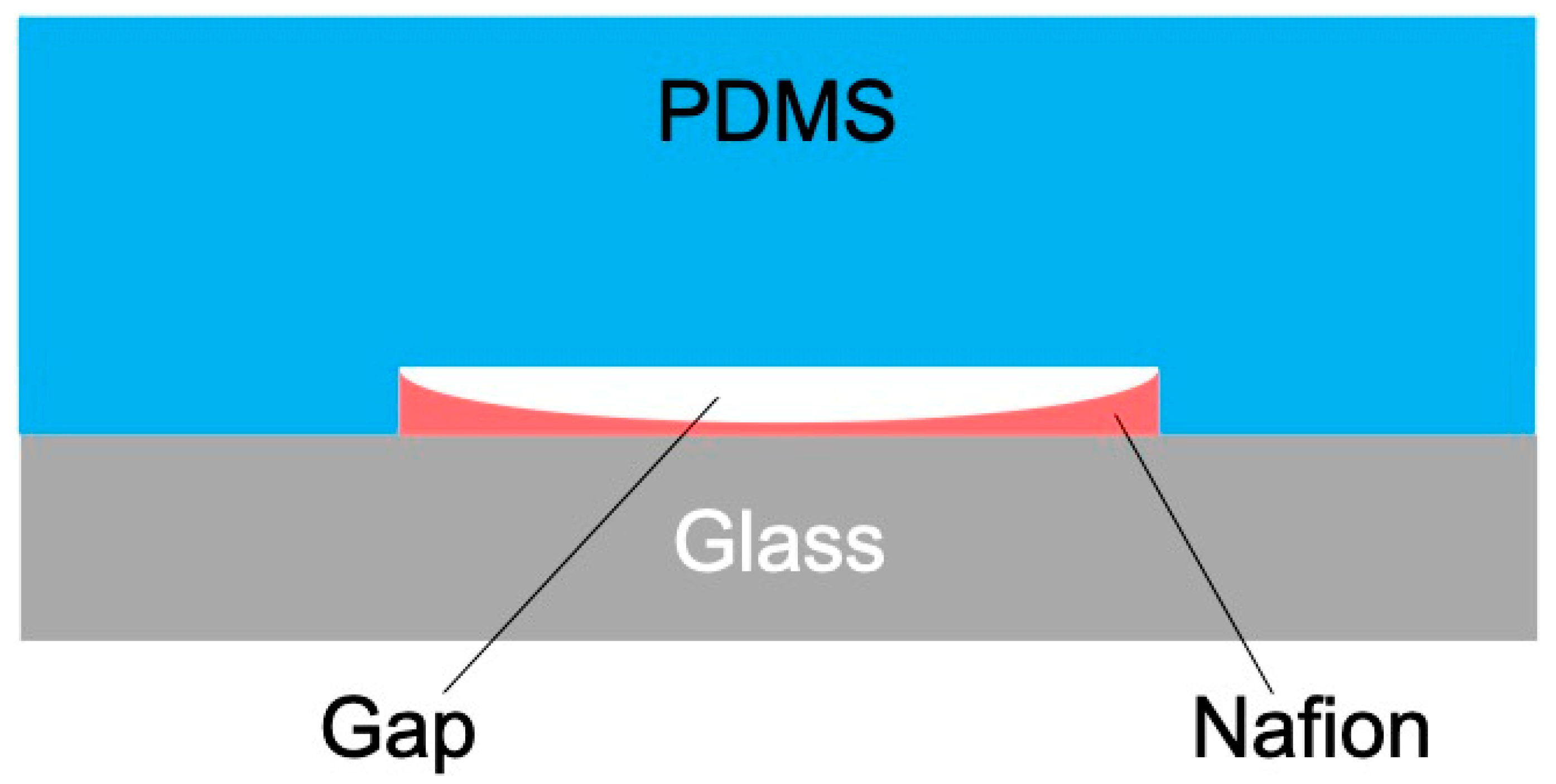
4.1. Nafion Membrane Morphology
4.2. Effects of Various Parameters on ICP
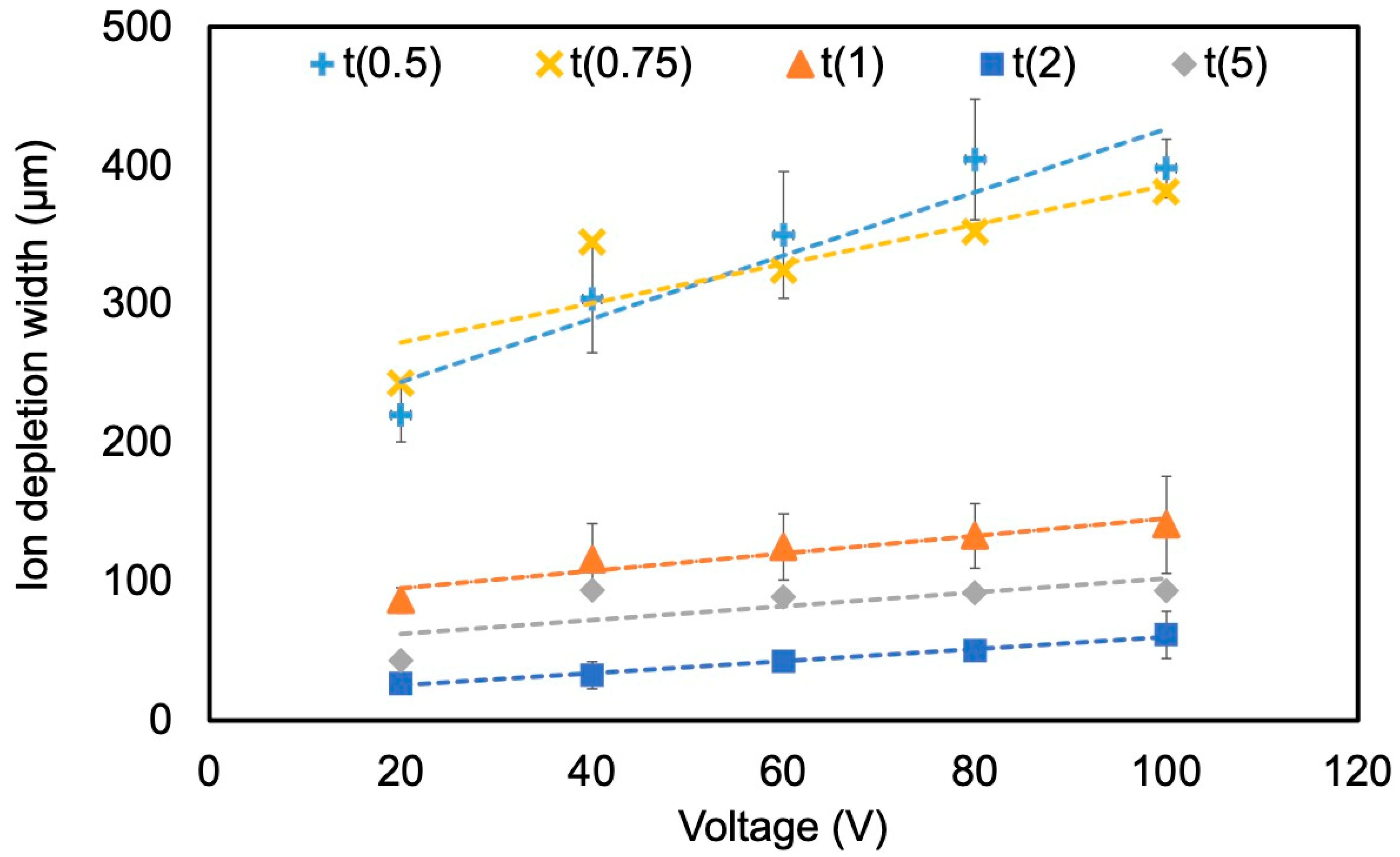
4.2.1. Effect of Voltage and Nafion Membrane Thickness
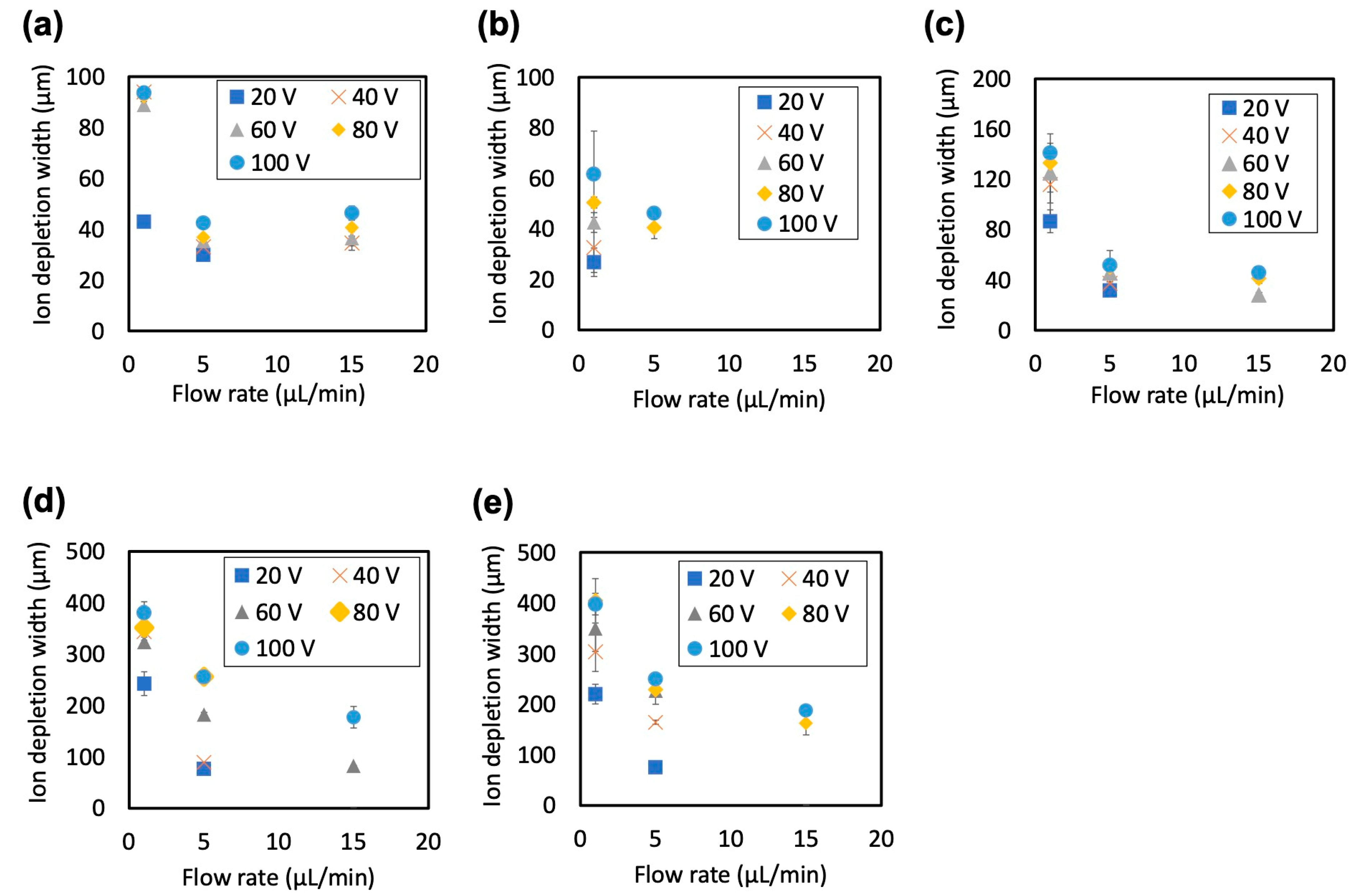
4.2.2. Effect of Flow Rate and Nafion Membrane Thickness
4.2.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Parameters
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, S.J.; Song, Y.-A.; Han, J. Nanofluidic concentration devices for biomolecules utilizing ion concentration polarization: Theory, fabrication, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Anand, R.K. Recent advancements in ion concentration polarization. Analyst 2016, 141, 3496–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, R.; Kim, S.J.; Han, J. Continuous-Flow Biomolecule and Cell Concentrator by Ion Concentration Polarization. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 7348–7355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, I.; Lee, H.; Kim, S.J. Ion Concentration Polarization by Bifurcated Current Path. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-C.; Stevens, A.L.; Han, J. Million-fold Preconcentration of Proteins and Peptides by Nanofluidic Filter. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 4293–4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Song, Y.-A.; Han, J. Multiplexed proteomic sample preconcentration device using surface-patterned ion-selective membrane. Lab A Chip 2008, 8, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, S.H.; Song, Y.-A.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, M.; Han, J.; Kang, K.H. Nanofluidic preconcentration device in a straight microchannel using ion concentration polarization. Lab A Chip 2012, 12, 4472–4482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yang, R. Effects of microchannel geometry on preconcentration intensity in microfluidic chips with straight or convergent–divergent microchannels. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Chiu, P.-H.; Weng, C.-H.; Yang, R.-J. Preconcentration of diluted mixed-species samples following separation and collection in a micro–nanofluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.A.; Wu, L.D.; Tannenbaum, S.R.; Wishnok, J.S.; Han, J. Tunable Membranes for Free-Flow Zone Electrophoresis in PDMS Microchip Using Guided Self-Assembly of Silica Microbeads. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 11695–11699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.M.; Nosrati, R.; Gabriel, M.C.S.; Zini, A.; Sinton, D. Direct DNA Analysis with Paper-Based Ion Concentration Polarization. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 13913–13919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Choi, J.; Jeong, E.; Baek, S.; Kim, H.C.; Chae, J.-H.; Koh, Y.; Seo, S.W.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, S.J. dCas9-mediated Nanoelectrokinetic Direct Detection of Target Gene for Liquid Biopsy. Nano Lett. 2018, 18, 7642–7650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mogi, K.; Hayashida, K.; Yamamoto, T. Damage-less Handling of Exosomes Using an Ion-depletion Zone in a Microchannel. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 875–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Ko, S.H.; Kang, K.H.; Han, J. Direct seawater desalination by ion concentration polarization. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knust, K.N.; Hlushkou, D.; Anand, R.K.; Tallarek, U.; Crooks, R.M. Electrochemically Mediated Seawater Desalination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 8107–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacDonald, B.D.; Gong, M.M.; Zhang, P.; Sinton, D. Out-of-plane ion concentration polarization for scalable water desalination. Lab A Chip 2013, 14, 681–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, B.; Chi, J.; Liu, H. Fabric-Based Ion Concentration Polarization for Pump-Free Water Desalination. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 6, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzina, B.; Anand, R.K. Continuous micellar electrokinetic focusing of neutral species driven by ion concentration polarization. Lab A Chip 2019, 19, 2233–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.; Lee, H.; Kang, K.H.; Lim, G. Ion concentration polarization-based continuous separation device using electrical repulsion in the depletion region. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, H.; Otahara, R.; Mogi, K.; Hayase, M.; Torii, T.; Mekaru, H. Rapid Prototyping of a Nanoparticle Concentrator Using a Hydrogel Molding Method. Polymers 2021, 13, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, D.-T.; Yang, C.; Nguyen, N.-T. Fabrication of nanoporous junctions using off-the-shelf Nafion membrane. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2015, 25, 115019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jia, M.; Kim, T. Ion concentration polarization in a single and open microchannel induced by a surface-patterned perm-selective film. Analyst 2012, 138, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Yoon, S.; Nam, H.; Woo, H.; Choi, W.; Kim, G.H.; Lim, G. Chemical-Free Rapid Lysis of Blood Cells in a Microfluidic Device Utilizing Ion Concentration Polarization. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitriou, V.A.; Segerink, L.I.; Eijkel, J.C.T. Free Flow Ion Concentration Polarization Focusing (FF-ICPF). Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4866–4874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, V.-T.; Pham, V.-S. Multiphysics analytical and numerical studies of biomolecule preconcentration utilizing ion concentration polarization: A case study of convergent microchannels. Anal. 2024, 149, 2252–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peramune, U.; Ahmed, Z.; Anand, R.K. Ion concentration polarization focusing at a millimeter-scale microbead junction: Towards higher volumetric throughput. Lab A Chip 2025, 25, 3495–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, A.T.K.; Pudasaini, S.; Ahmed, S.S.U.; Phan, D.T.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C. Rapid pre-concentration of in a microfluidic paper-based device using ion concentration polarization. Electrophoresis. 2020, 41, 867–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Whitesides, G.M. Soft Lithography. Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci. 1998, 28, 153–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirama, H.; Otahara, R.; Kano, S.; Hayase, M.; Mekaru, H. Characterization of Nanoparticle Adsorption on Polydimethylsiloxane-Based Microchannels. Sensors 2021, 21, 1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probstein, R.F. Physicochemical Hydrodynamics: An Introduction: Wiley; 1994. ISBN: 978-0471010111.
- Schoch, R.B.; Han, J.Y.; Renaud, P. Transport phenomena in nanofluidics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2008, 80, 839–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
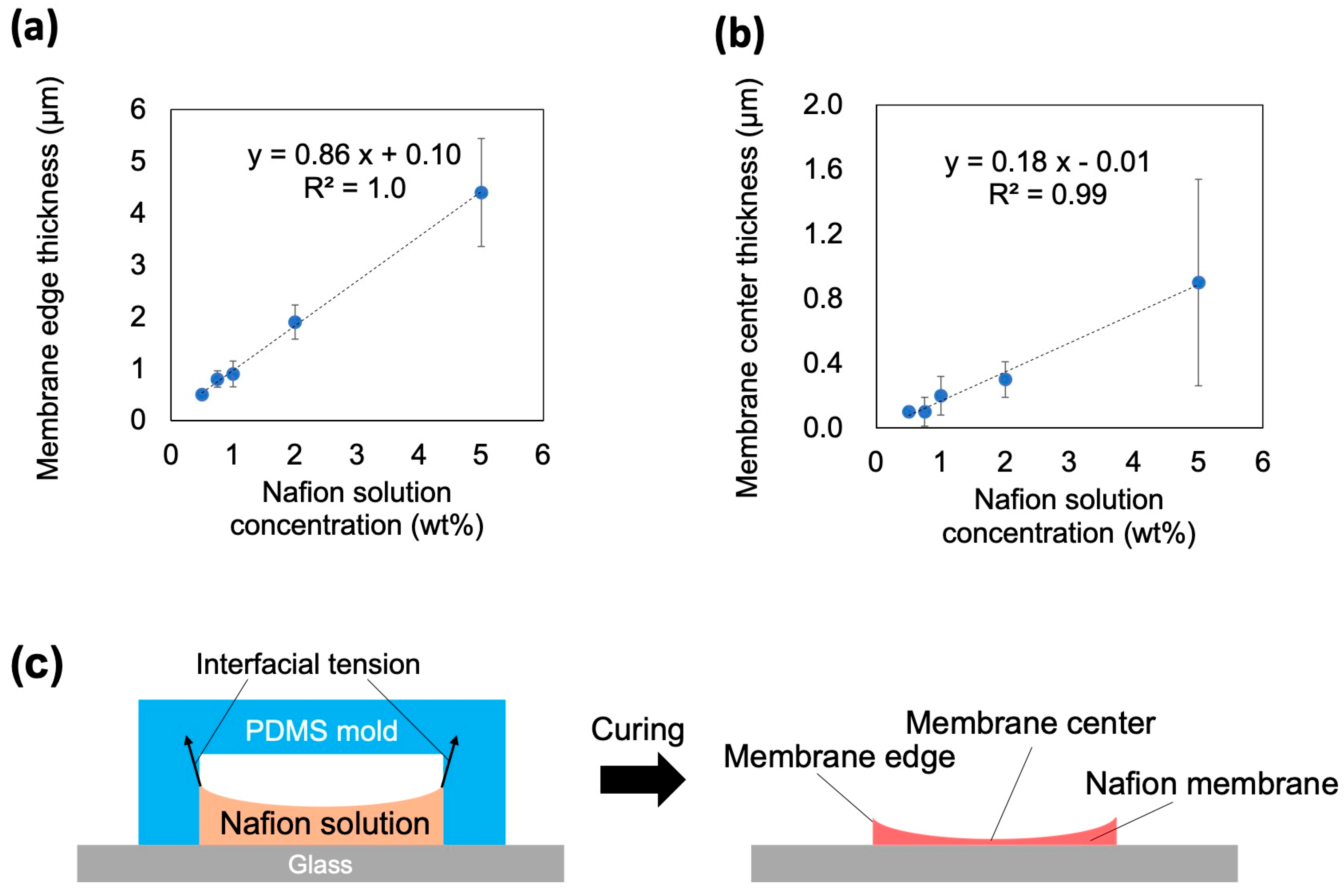
| x | tc(x) | te(x) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.1 ± 0.02 | 0.5 ± 0.05 |
| 0.75 | 0.1 ± 0.09 | 0.8 ± 0.16 |
| 1 | 0.2 ± 0.12 | 0.9 ± 0.25 |
| 2 | 0.3 ± 0.11 | 1.9 ± 0.33 |
| 5 | 0.9 ± 0.64 | 4.4 ± 1.04 |
| Parameter | Range Tested | Baseline | IDW Change (Fold) | IDW Change (%) | Slope (ΔY/ΔX) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage | 20 → 100 V | 20 V | 2.3× | +130 | 0.44 µm/V |
| Membrane thickness | t(5) → t(0.5) | t(2) | 4.4× | +1166 | −69 µm/wt% |
| Flow rate | 1 → 15 µL/min | 1 µL/min | 0.1× | −173 | −3.3 µm/(µL/min) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirama, H.; Hayase, M. Ion Concentration Polarization in Branched Microchannels: Effect of Membrane Thickness and Applied Voltage. Membranes 2025, 15, 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090278
Hirama H, Hayase M. Ion Concentration Polarization in Branched Microchannels: Effect of Membrane Thickness and Applied Voltage. Membranes. 2025; 15(9):278. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090278
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirama, Hirotada, and Masanori Hayase. 2025. "Ion Concentration Polarization in Branched Microchannels: Effect of Membrane Thickness and Applied Voltage" Membranes 15, no. 9: 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090278
APA StyleHirama, H., & Hayase, M. (2025). Ion Concentration Polarization in Branched Microchannels: Effect of Membrane Thickness and Applied Voltage. Membranes, 15(9), 278. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes15090278






