Recent Advances on the Fabrication of Antifouling Phase-Inversion Membranes by Physical Blending Modification Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Membrane Technology
1.2. Preparation of Porous Membranes via the Phase-Inversion Processes
1.3. Membrane Fouling and Fouling Mitigation Techniques
1.4. Modification Techniques for Antifouling
1.5. Objectives of the Article
2. Antifouling Materials for Polymeric Membranes
2.1. Polymer/Organic-Based Additives
2.1.1. Poly(ethylene glycol) and Its Derivatives
2.1.2. Poly(vinylpyrrolidone)
2.1.3. Cellulose Nanocrystals
2.1.4. Poly(vinyl alcohol)
2.1.5. Poly(acrylic acid)
2.1.6. Polydopamine
2.1.7. Amphiphilic Copolymers
2.1.8. Zwitterionic Additives
2.1.9. Nature Derived Biopolymers
2.1.10. Concluding Remarks on the Use of Polymeric Additives
2.2. Metal-Based Additives
2.2.1. Metallic Additives
2.2.2. Biphasic Metals
2.2.3. Bimetallic Oxides
2.3. Ceramic-Based Additives
2.4. Carbon Allotropes and Porous Nanomaterials
2.4.1. Carbon Allotropes
2.4.2. Porous Nanomaterials
2.4.3. Concluding Remarks on the Use of Inorganic Nanoparticles (Metal-Based, Ceramic-Based, Carbon Allotropes and Porous Nanomaterials)
2.5. Hybrid Nanomaterials
3. Blending of Additives into the Polymer Matrix and Its Effect on Membrane Morphology
3.1. Influence of the Antifouling Additive on the Morphology of Liquid-Induced Phase Separation Membranes
3.2. Influence of the Antifouling Additive on the Morphology of Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Membranes
3.3. Influence of the Antifouling Additive on the Morphology of Thermal Induced Phase Separation Membranes
4. Assessments of Antifouling Properties of Modified Membranes through Blending Approach
4.1. Hydrophilicity Tests
4.2. Static Fouling Tests
| Class of Additive | Matrix Polymer | Antifouling Additive | Process | Water Contact Angle (o) | Pore Size (nm) | Porosity (%) | Pure Water Permeance * (L/m2·h·bar) | Flux Recovery Ratio (%) | Foulant Adsorption a or Rejection r (% or (μg/cm2) d) | Ref. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin | Modified | Virgin | Modified | Virgin | Modified | Virgin | Modified | Virgin | Modified | Virgin | Modified | |||||
| Polymer/organic-based | CA | PAA | LIPS | 71.5 | 25.0 | 12.9 | 9.6 | 44.6 | 75.6 | 15.3 | 19.0 | 88.2 | 97.6 | r HA (95.7) | r HA (99.9) | [108] |
| PEI | PVP | VIPS | 96.4 | 56.1 | 28.5 | 50.4 | 4.2 | 13.6 | 4.8 | 36.8 | 69.6 | 81.0 | a BSA (170.0) d | a BSA (80.0) d | [94] | |
| PES | CNC | LIPS | 66.0 | 43.0 | 12.0 | 9.0 | - | - | 33.3 | 60.9 | 51.0 | 90.0 | r BSA (93.0) | r BSA (97.0) | [100] | |
| PES | PAN | LIPS | 68.4 | 56.8 | - | - | - | - | 24.6 | 55.6 | 57.9 | 86.1 | r BSA (93.8) | r BSA (87.1) | [371] | |
| PES | PAN/PEG | LIPS | 68.4 | - | - | - | - | - | 24.6 | 202.2 | 57.9 | 90.7 | r BSA (93.8) | r BSA (81.4) | [371] | |
| PES | PVA | LIPS | 79.0 | 63.0 | 11.2 | 34.9 | 54.2 | 65.5 | - | 131.5 | 52.0 | 92.6 | r BSA (81.0) | r BSA (61.2) | [106] | |
| PES | PVP | LIPS | - | - | - | - | - | - | c 72.0 | 1219.5 | c 80.8 | 98.5 | - | r HA (95.0) | [43] | |
| PLA | PVP | LIPS | 82.1 | 34.1 | 88.6 | 42.9 | 79.2 | 57.1 | 185.7 | 19.3 | 57.0 | 93.0 | r BSA (57.0) | r BSA (92.0) | [358] | |
| PSf | PEG400 | LIPS | 87.7 | 79.8 | - | - | 18.7 | 48.4 | 0.8 | 420.0 | - | - | - - | r BSA (90.0)/ r Pepsin (73.0) | [42] | |
| PSf | zP(S-r-4VP) | LIPS | 120.0 | 100.0 | 6.3 | 10.4 | 73.2 | 74.1 | 5.7 | 11.7 | 40.0 | 63.0 | r BSA (80.8) | r BSA (95.6) | [120] | |
| PSf | PEGMA | VIPS | 63.0 | 27.0 | 9.3 | 10.8 | 80.8 | 73.6 | 110.0 | 512.0 | 67.6 | 84.5 | a BSA (15.1) d | a BSA (4.0) d | [372] | |
| PVC | Lignin | LIPS | 106.7 | 41.5 | 19.7 | 25.5 | 76.0 | 84.9 | 111.6 | 347.7 | 20.4 | 92.3 | r HA (73.0) | r HA (98.9) | [142] | |
| 38.1 | 81.3 | r Oil (68.1) | r Oil (97.4) | |||||||||||||
| PVDF | SPANI | LIPS | 92.0 | 29.0 | - | - | - | - | 97.2 | 160.0 | 66.2 | 99.2 | r BSA (90.0)/a BSA (30.0) d | r BSA (95.0)/a BSA (3.0) d | [124] | |
| PVDF | CNC | LIPS | 81.3 | 74.0 | 84.5 | 155.0 | 9.8 | 206.9 | 71.6 | 82.5 | r BSA (83.3) | r BSA (88.2) | [98] | |||
| PVDF | MPC-derivative | VIPS | 137.3 | 113.7 | 108.1 | 155.8 | 72.0 | 76.3 | c 1087 | 1143 | c 17 | 42 | - | - | [122] | |
| PVDF | MPC-derivative | VIPS | 137 | 114 | 30 | 20 | 72 | 70 | c ≈900 | ≈900 | c 17 | 38 | - | - | [373] | |
| PVDF | PS-b-PEGMA | LIPS | 85.0 | - | 25.5 | 51.8 | 64.3 | 79.8 | 43.3 | 58.3 | 56.0 | 91.0 | a FN (100.0)/a γ-globulin (100.0)/a HAS (100.0) | a FN (19.0)/a γ-globulin (35.0)/a HAS (29.0) | [41] | |
| PVDF | PS-b-PEGMA | VIPS | 122 | 118 | 260 | 820 | 72 | 79 | 5000 | 13,000 | ≈10 | ≈82 | a FN (100.0)/a BSA (100.0)/a LY (100.0) | a FN (≈30)/a BSA (≈5)/a LY (≈15) | [153] | |
| PVDF | PS-b-PEGMA | VIPS | 122 | 118 | 260 | 820 | 72 | 79 | 5000 | 10,000 | ≈25 | ≈76.9 | r MA (>99.7) | r MA (>99.7) | [153] | |
| PVDF | PVA | LIPS | 72.2 | 69.0 | 25.3 | 100.4 | 62.8 | 57.6 | 38.1 | 47.5 | 83.0 | 86.0 | r BSA (35.0) | r BSA (5.2) | [107] | |
| PVDF | PVDF-g-PSBMA | LIPS | 89.0 | 67.0 | - | - | - | - | 121.9 | 239.1 | 51.5 | 81.2 | a BSA (110.0) d | a BSA (40.0) d | [118] | |
| PVDF | PS-r-PEGMA | VIPS | 140.0 | 47.0 | 583.0 | 513.0 | 75.4 | 71.9 | - | - | 16.0 | 29.0 | rE. coli (92.5) | rE. coli (99.0) | [374] | |
| PVDF | PS-r-PEGMA | TIPS | 135.7 | 70.0 | ≈210 | ≈210 | - | - | ≈2400 | ≈2400 | ≈45 | 74.0 | a BSA (75.0) | a BSA (18.0) | [365] | |
| PVDF | SM-derivative | VIPS | 145.0 | 67.0 | 510.0 | 430.0 | 57.0 | 62.0 | ≈9000 | ≈12,000 | 36.0 | 90.0 | a BSA (100) | a BSA (35) | [363] | |
| PVDF | PS-r-PEGMA-r-PSBMA | VIPS | 129.0 | 102.0 | 140.0 | 70.0 | 66.5 | 72.9 | 1223.0 | 1146.0 | 66.0 | 91.0 | a BSA (100)/a FN (100) | a BSA (12)/a FN (15) | [117] | |
| PVDF | PS-r-PEGMA-r-PSBAA | VIPS | 140.0 | 112.0 | ≈299 | ≈80 | 67 | 55 | c 2000 | 1100 | 53 | 73 | rE. coli (83.5)/a FN (100)/a blood (100) | rE. coli (89.6)/a FN (20)/a blood (20) | [123] | |
| PVDF | PMAA-r-PEGMA-r-SBMA | VIPS | 139.0 | 90.0 | 560.0 | 150.0 | 70.0 | 62.0 | c 2500 | 900.0 | - | 54.0 | a FN (100)/a E. coli (100)/a blood (100) | a FN (12)/a E. coli (5.6)/a blood (5.1) | [116] | |
| PVDF | zP(S-r-4VP) | VIPS | ≈143 | ≈132 | 250 | 100 | ≈75 | ≈60 | c ≈625 | ≈1900 | 12.0 | 69.0 | aE. coli (100)/a blood (100) | aE. coli (15)/a blood (10) | [119] | |
| Metal-based | BCM | ZrO2 | LIPS | 41.9 | 33.6 | 36.5 | 39.3 | 77.3 | 79.8 | 286.1 | 321.5 | 65.0 | 90.6 | r BSA (71.6) | r BSA (91.2) | [181] |
| PAN | SiO2-DOPA | LIPS | 68.0 | 32.0 | - | - | 51.7 | 77.1 | 426.7 | 1075.0 | 49.0 | 75.0 | r BSA (94.0) | r BSA (98.8) | [239] | |
| PES | Fe2O3-Mn2O3 | LIPS | 73.0 | 67.0 | 40.0 | 45.5 | 58.0 | 74.0 | 208.0 | 396.0 | 64.0 | 77.0 | r BSA (97.0) | r BSA (96.0) | [231] | |
| PES | ZrO2 | LIPS | 73.6 | 52.3 | - | - | - | - | 8.2 | 83.6 | 54 | 97.2 | r BSA (97.2) | r BSA (92.7) | [179] | |
| PES | ZnO-NP | LIPS | 77.9 | 60.0 | - | - | 61.0 | 69.0 | 7.8 | 12.0 | 39.0 | 74.1 | - | - | [82] | |
| ZnO-NR | LIPS | 77.9 | 54.0 | - | - | 61.0 | 71.0 | 7.8 | 12.5 | 39.0 | 70.2 | |||||
| PVC | ZnO | LIPS | 67.5 | 54.5 | 9.3 | 12.1 | 67.9 | 79.8 | 106.5 | 201.0 | 69.3 | 91.8 | r BSA (90.2) | r BSA (97.5) | [236] | |
| PVDF | SiO2@GO | TIPS | - | - | 41.2 | 20.1 | - | - | 268.5 | 182.6 | 48.0 | 95.0 | r BSA (63.5) | r BSA (91.7) | [366] | |
| PVDF | TiO2/PEG | LIPS | 74.4 | 69.0 | 87.0 | 86.0 | 52.9 | 48.6 | 72.8 | 73.1 | - | - | - | - | [38] | |
| PVDF | TiO2 | LIPS | 85.4 | 70.2 | - | - | - | - | 158.0 | 350.0 | 47.5 | 88.2 | r BSA (57.0) | r BSA (95.0) | [190] | |
| PVDF | ZrO2-g-PACMO | LIPS | 93.0 | 66.0 | 31.6 | 17.0 | 77.6 | 58.4 | 36.2 | 82.4 | 38.0 | 97.0 | r Oil (74.9) | r Oil (99.9) | [180] | |
| Carbon allotropes | PEES | GO | LIPS | 96.4 | 72.3 | 45.6 | 72.7 | 43.2 | 65.6 | 30.7 | 53.9 | 62.5 | 83.2 | - | - | [345] |
| PES ** | GO | LIPS | 91.0 | 67.0 | 3.0 | 5.1 | 52.1 | 58.5 | 25.0 | 225.0 | - | - | - | - | [304] | |
| GO | LIPS | 85.0 | 72.0 | 6.6 | 8.6 | 29.1 | 61.0 | 239.6 | 305.2 | |||||||
| PVC | PP-MWCNTs | LIPS | 67.7 | 61.2 | 4.2 | 4.3 | 77.5 | 84.0 | 30.0 | 37.5 | 64.8 | 70.6 | r BSA (96.0) | r BSA (98.0) | [302] | |
| PVC | GQDs | LIPS | 65.0 | 73.0 | 2.84 | 3.01 | 57.2 | 55.3 | 12.2 | 19.1 | 68.8 | >80.0 | r BSA (>98.0) | r BSA (>98.0) | [308] | |
| PVDF | CNDs | LIPS | 76.8 | 65.3 | 23.8 | 33.1 | 47.6 | 63.7 | 49 | 171 | 35 | 85 | r BSA (>85.0) | r BSA (>95.0) | [288] | |
| PVDF | GO | LIPS | 71.0 | 70.0 | 70.0 | 115.0 | 47.5 | 52.5 | 137.0 | 203.5 | - | - | - | - | [304] | |
| PVDF | GO | LIPS | 74.2 | 70.2 | 484.0 | 1034.0 | 59.0 | 80.0 | 47 | 94 | - | - | r DOC (8.65) | r DOC (11.30) | [305] | |
| PVDF | GO/TiO2 | LIPS | 79.0 | 61.0 | 48.1 | 65.2 | 69.6 | 83.1 | 158.1 | 487.8 | 43.0 | 71.1 | r BSA (80.0) | r BSA (92.5) | [369] | |
| PVDF | O-MWCNT | TIPS | 106.8 | 98.0 | - | - | 84.5 | 83.8 | 270.7 | 164.5 | - | 82.7 | r BSA (68.5) | r BSA (90.8) | [23] | |
4.2.1. Protein Adsorption Tests
4.2.2. Cell Attachment Tests
4.3. Dynamic Fouling Tests
4.4. Oil Fouling Tests
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCM | Bamboo cellulose membrane |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CA | Cellulose acetate |
| CB | Carboxybetaine |
| CNC | Cellulose nanocrystal |
| CND | Carboxylated nanodiamond |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| DOPA | Dopamine |
| EPS | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| FN | Fibrinogen |
| FRR | Flux recovery ratio |
| GN | Graphene |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| GQDs | Graphene quantum dots |
| HA | Humic acid |
| HC | Hydration capacity |
| HSA | Human serum albumin |
| LY | Lysozyme |
| MA | Microalgae |
| MF | Microfiltration |
| MMM | Mixed matrix membrane |
| MPC | 2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine |
| MWCNT | Multiwalled carbon nanotubes |
| NF | Nanofiltration |
| OMWCNT | Oxidized multi-wall carbon nanotube |
| PAA | Poly (acrylic acid) |
| PACMO | Poly(N-acryloylmorpholine) |
| PAN | Polyacrylonitrile |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| PC | Phosphorylcholine |
| PE | Polyethylene |
| PEES | Poly(ether ether sulfone) |
| PEG | Poly(ethylene glycol) |
| PEGMA | Poly(ethylene Glycol) Methyl Ether Methacrylate |
| PEI | Polyetherimide |
| PES | Poly(ether sulfone) |
| PLA | Polylactic acid |
| PP | Polypropylene |
| PS | Polystyrene |
| PSBMA | Poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) |
| PSf | Polysulfone |
| PTFE | Polytetrafluoroethylene |
| PVA | Poly(vinyl alcohol) |
| PVC | Poly(vinyl chloride) |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| PVP | Polyvinylpyrrolidone |
| PWF | Pure water flux |
| rGO | Reduced graphene oxide |
| Rir | Irreversible flux ratio |
| Rr | Reversible flux ratio |
| Rt | Total flux ratio |
| RO | Reverse osmosis |
| SB | Sulfobetaine |
| SBAA | Sulfobetaine methacrylamide |
| SBMA | Sulfobetaine methacrylate |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| SM | Styrene maleic anhydride |
| SPANI | Sulfonated polyaniline |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| WCA | Water contact angle |
| ZnO-NP | Zinc oxide nanoparticles |
| ZnO-NR | Zinc oxide nanorods |
| zP(S-r-4VP) | Zwitterionic poly(styrene-random-4-vinylpyrridine) |
References
- Zahid, M.; Rashid, A.; Akram, S.; Rehan, Z.A.; Razzaq, W. A comprehensive review on polymeric nano-composite membranes for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.-M.; Lai, J.-Y. Recent advances in preparation and morphology control of polymeric membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Eng. 2013, 2, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, W.L.; Lau, W.J.; Tan, Y.H.; Mahmoudi, E.; Mohammad, A.W. An Overview on Development of Membranes Incorporating Branched Macromolecules for Water Treatment. Sep. Purif. Rev. 2021, 52, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajid, M.; Jillani, S.M.S.; Baig, N.; Alhooshani, K. Layered double hydroxide-modified membranes for water treatment: Recent advances and prospects. Chemosphere 2022, 287, 132140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Lu, D.; Harris, T.A.L.; Escobar, I.C. Polymers and solvents used in membrane fabrication: A review focusing on sustainable membrane development. Membranes 2021, 11, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, P. Enhanced morphology and hydrophilicity of PVDF flat membrane with modified CaCO3@SMA additive via thermally induced phase separation method. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 107, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, B.; Zhan, W.; Lina, C. Cellulose acetate (CA) hybrid membrane prepared by phase inversion method combined with chemical reaction with enhanced permeability and good anti-fouling property. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obotey Ezugbe, E.; Rathilal, S. Membrane technologies in wastewater treatment: A review. Membranes 2020, 10, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Field, R. Fundamentals of pressure-driven membrane separation processes. In Membrane Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.; Elam, J.W.; Darling, S.B. Membrane materials for water purification: Design, development, and application. Environ. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2016, 2, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Gestel, T.; Doyen, W.; Leysen, R. A review of pressure-driven membrane processes in wastewater treatment and drinking water production. Environ. Prog. 2003, 22, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggay, I.V.; Chang, Y.; Venault, A.; Dizon, G.V.; Wu, C.-J. Functionalized porous filtration media for gravity-driven filtration: Reviewing a new emerging approach for oil and water emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 117983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez, B.; Rosal, R. A critical review of membrane modification techniques for fouling and biofouling control in pressure-driven membrane processes. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulivand, H.; Shahbazi, A.; Vatanpour, V. Fabrication and characterization of a high-flux and antifouling polyethersulfone membrane for dye removal by embedding Fe3O4-MDA nanoparticles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 145, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, E.S.; Sabirova, T.M.; Tretyakova, N.A.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Figoli, A.; Salih, I.K. A mini-review of enhancing ultrafiltration membranes (UF) for wastewater treatment: Performance and stability. Chem. Eng. 2021, 5, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-L.; Yin, M.-J.; An, Q.-F.; Gao, C.-J. Recent developments in polymeric nano-based separation membranes. Fundam. Res. 2021, 2, 254–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Guria, C.; Mandal, A. Synthesis, characterization and performance studies of polysulfone/bentonite nanoparticles mixed-matrix ultra-filtration membranes using oil field produced water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, X. A review on microporous polyvinylidene fluoride membranes fabricated via thermally induced phase separation for MF/UF application. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 639, 119759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remanan, S.; Sharma, M.; Bose, S.; Das, N.C. Recent advances in preparation of porous polymeric membranes by unique techniques and mitigation of fouling through surface modification. Chem. Sel. 2018, 3, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.; Venault, A.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Bouyer, D.; Drioli, E.; Kiadeh, N.T.H. Investigating the potential of membranes formed by the vapor induced phase separation process. J. Memb. Sci 2020, 597, 117601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Hassankiadeh, N.T.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, J.M.; Woo, K.T.; Sanguineti, A.; Arcella, V.; Lee, Y.M.; Drioli, E. Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane preparation with an environmental diluent via thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichi Sawada, S.; Ursino, C.; Galiano, F.; Simone, S.; Drioli, E.; Figoli, A. Effect of citrate-based non-toxic solvents on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane preparation via thermally induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 493, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-P.; Lang, W.-Z.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.-J. Preparation and characterizations of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/oxidized multi-wall carbon nanotube membranes with bi-continuous structure by thermally induced phase separation method. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, A.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, C.; Zhang, Y. Effect of micro-sized SiO2-particle on the performance of PVDF blend membranes via TIPS. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 360, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Lan, X.; Hu, Q.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Mao, J. Antifouling strategies based on super-phobic polymer materials. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 157, 106285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huisman, I.H.; Prádanos, P.; Hernández, A. The effect of protein–protein and protein–membrane interactions on membrane fouling in ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2000, 179, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunil, K.; Sherugar, P.; Rao, S.; Lavanya, C.; Balakrishna, G.R.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Padaki, M. Prolific approach for the removal of dyes by an effective interaction with polymer matrix using ultrafiltration membrane. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Tian, Z.; Wang, H.; Qin, S.; Qin, Q.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Z. Fabrication of ultrafiltration membrane surface with synergistic anti-fouling effect of “dispersion-impedance” and anti-fouling mechanism of dye. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 121028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hairom, N.H.H.; Mohammad, A.W.; Kadhum, A.A.H. Nanofiltration of hazardous Congo red dye: Performance and flux decline analysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadhim, R.J.; Al-Ani, F.H.; Al-Shaeli, M.; Alsalhy, Q.F.; Figoli, A. Removal of dyes using graphene oxide (GO) mixed matrix membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Huang, S.; Venna, S.R.; Lin, H. Rightsizing nanochannels in reduced graphene oxide membranes by solvating for dye desalination. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 12649–12655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Sotto, A.; Li, J.; Van der Bruggen, B. Progress and perspectives for synthesis of sustainable antifouling composite membranes containing in situ generated nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 524, 502–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasir, A.; Masood, F.; Yasin, T.; Hameed, A. Progress in polymeric nanocomposite membranes for wastewater treatment: Preparation, properties and applications. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 79, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, S.K.; Yong, W.F. Recent Progress of Zwitterionic Materials as Antifouling Membranes for Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, and Reverse Osmosis. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2021, 3, 4390–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonawane, S.; Thakur, P.; Sonawane, S.H.; Bhanvase, B.A. Nanomaterials for membrane synthesis: Introduction, mechanism, and challenges for wastewater treatment. In Handbook of Nanomaterials for Wastewater Treatment; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 537–553. [Google Scholar]
- Sile-Yuksel, M.; Tas, B.; Koseoglu-Imer, D.Y.; Koyuncu, I. Effect of silver nanoparticle (AgNP) location in nanocomposite membrane matrix fabricated with different polymer type on antibacterial mechanism. Desalination 2014, 347, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Z. Enhanced antifouling behaviours of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane modified through blending with nano-TiO2/polyethylene glycol mixture. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 345, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowry, G.V.; Gregory, K.B.; Apte, S.C.; Lead, J.R. Transformations of nanomaterials in the environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 6893–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezakazemi, M.; Amooghin, A.E.; Montazer-Rahmati, M.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Matsuura, T. State-of-the-art membrane based CO2 separation using mixed matrix membranes (MMMs): An overview on current status and future directions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 817–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Ballad, M.R.B.; Liu, Y.-H.; Aimar, P.; Chang, Y. Hemocompatibility of PVDF/PS-b-PEGMA membranes prepared by LIPS process. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 477, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Shi, F.; Ma, J.; Wu, M.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C. Effect of PEG additive on the morphology and performance of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. Desalination 2011, 272, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Kim, H.; Jung, J.; Jo, S.; Choi, H. Influence of extreme concentrations of hydrophilic pore-former on reinforced polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes for reduction of humic acid fouling. Chemosphere 2017, 179, 194–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodadadi, F.; Mansourianfar, M.; Bozorg, A. Application of Dextran to Manipulate Formation Mechanism, Morphology, and Performance of Ultrafiltration Membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 183, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Aprilia, S.; Muchtar, S.; Syamsuddin, Y.; Rosnelly, C.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Samsuri, S.; Ismail, N.M. Fabrication of Polyvinylidene Difluoride Membrane with Enhanced Pore and Filtration Properties by Using Tannic Acid as an Additive. Polymers 2022, 14, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhang, D.; Shao, Z.; Han, B.; Lv, Y.; Gao, K.; Peng, X. Superior effect of TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibrils (TOCNs) on the performance of cellulose triacetate (CTA) ultrafiltration membrane. Desalination 2014, 332, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Zhang, K. Modification of PES membrane with Ag–SiO2: Reduction of biofouling and improvement of filtration performance. Desalination 2014, 336, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadari, S.; Rahimi, M.; Zinadini, S. Removal of heavy metal from aqueous medium using novel high-performance, antifouling, and antibacterial nanofiltration polyethersulfone membrane modified with green synthesized Ni-doped Al2O3. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 2424–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vani, B.; Shivakumar, M.; Kalyani, S.; Sridhar, S. TiO2 nanoparticles incorporated high-performance polyphenyl sulfone mixed matrix membranes for ultrafiltration of domestic greywater. Iran. Polym. J. 2021, 30, 917–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganjali, M.R.; Badiei, A.; Mouradzadegun, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Munir, M.T.; Habibzadeh, S.; Saeb, M.R.; Koyuncu, I. Erbium (III) molybdate as a new nanofiller for fabrication of antifouling polyethersulfone membranes. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.; Afshari, M.; Fazlali, A.; Farahani, S.K.; Bandehali, S.; Van der Bruggen, B.; Bagheripour, E. Mixed matrix PES-based nanofiltration membrane decorated by (Fe3O4–polyvinylpyrrolidone) composite nanoparticles with intensified antifouling and separation characteristics. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2019, 147, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Hu, T.-T.; Han, X.-L.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, J.-D. Fabrication of Cu(OH)2 nanowires blended Poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membranes for oil-water separation. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 612–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Bagheripour, E.; Ansari, M. Adapting the performance and physico-chemical properties of PES nanofiltration membrane by using of magnesium oxide nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2017, 34, 1774–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, H.; Shao, J.; Bai, H.; Liu, L.; He, Y. Inherent porous structure modified by titanium dioxide nanoparticle incorporation and effect on the fouling behavior of hybrid Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrnia, M.R.; Mojtahedi, Y.M.; Homayoonfal, M. What is the concentration threshold of nanoparticles within the membrane structure? A case study of Al2O3/PSf nanocomposite membrane. Desalination 2015, 372, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Vatanpour, V. Preparation and characterization of emulsion poly (vinyl chloride)(EPVC)/TiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 472, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.; Lin, R.; Yue, X. Preparation and properties of Fe3+/PVDF-PMMA catalytic membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 3909–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.S.; Khataee, A.R.; Salehi, E.; Zinadini, S.; Monfared, H.A. TiO2 embedded mixed matrix PES nanocomposite membranes: Influence of different sizes and types of nanoparticles on antifouling and performance. Desalination 2012, 292, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keskin, B.; Mehrabani, S.A.N.; Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Teber, O.O.; Khataee, A.; Orooji, Y.; Koyuncu, I. Development of Ti2AlN MAX phase/cellulose acetate nanocomposite membrane for removal of dye, protein and lead ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghankar, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Tavakolmoghadam, M.; Tofighy, M.A. Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Nanoclays (Cloisite 30B and Palygorskite) Mixed Matrix Membranes with Improved Performance and Antifouling Properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 12078–12091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.M.; El-Zahhar, A.A. Novel cellulose acetate propionate-halloysite composite membranes with improved permeation flux, salt rejection, and antifouling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2526–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Zhou, S.; Li, M.; Xue, A.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Yang, D. PVDF/palygorskite composite ultrafiltration membranes: Effects of nano-clay particles on membrane structure and properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 181, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Guria, C.; Mandal, A. Synthesis, characterization and performance studies of mixed-matrix poly (vinyl chloride)-bentonite ultrafiltration membrane for the treatment of saline oily wastewater. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2018, 116, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Vatanpour, V. Effect of solvent type on the physicochemical properties and performance of NLDH/PVDF nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Yuan, F.; Zhang, H.; Xia, S. Preparation and characterization of hydrophilic and antifouling poly (ether sulfone) ultrafiltration membranes modified with Zn–Al layered double hydroxides. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, R.J.; Korminouri, F.; Lau, W.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T.; Chowdhury, M.; Halakoo, E.; Gohari, M.J. A novel super-hydrophilic PSf/HAO nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for efficient separation of oil/water emulsion. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 150, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, A.; Gholami, F.; Nazari, S.; Dolatshah, M. Preparation of antifouling and antibacterial polyvinylidene fluoride membrane by incorporating functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 103042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Li, L.; Pei, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, F.; Li, J. PVDF/MOFs mixed matrix ultrafiltration membrane for efficient water treatment. Front. Chem. 2022, 10, 985750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemade, P.R.; Ganjare, A.V.; Ramesh, K.; Rakte, D.M.; Vaishnavi, P.; Thapa, G. Low fouling sulphonated carbon soot-polysulphone membranes for rapid dehydration of stabilized oil-water emulsions. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anjum, T.; Tamime, R.; Khan, A.L. Mixed-matrix membranes comprising of polysulfone and porous UiO-66, Zeolite 4A, and their combination: Preparation, removal of humic acid, and antifouling properties. Membranes 2020, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Chen, W.; Xu, H.; Yang, W.; Kong, Q.; Wang, A.; Ding, M.; Shang, J. Fabrication of a novel antifouling polysulfone membrane with in situ embedment of mxene nanosheets. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 4659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, M.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Yegani, R.; Kazemi, S. PVDF membranes embedded with PVP functionalized nanodiamond for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Yekavalangi, M.E.; Safarpour, M. Preparation and characterization of nanocomposite PVDF ultrafiltration membrane embedded with nanoporous SAPO-34 to improve permeability and antifouling performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 163, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Pan, J.; Ren, W.; Chen, L.; Huang, L.; Xu, S.; Jiang, Z. Fabrication of antibacterial and self-cleaning CuxP@g-C3N4/PVDF-CTFE mixed matrix membranes with enhanced properties for efficient ultrafiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 659, 120792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Keskin, B.; Mehrabani, S.A.N.; Karimi, H.; Arabi, N.; Behroozi, A.H.; Shokrollahi-far, A.; Gul, B.Y.; Koyuncu, I. Investigation of boron nitride/silver/graphene oxide nanocomposite on separation and antibacterial improvement of polyethersulfone membranes in wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandehali, S.; Moghadassi, A.; Parvizian, F.; Zhang, Y.; Hosseini, S.M.; Shen, J. New mixed matrix PEI nanofiltration membrane decorated by glycidyl-POSS functionalized graphene oxide nanoplates with enhanced separation and antifouling behaviour: Heavy metal ions removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 242, 116745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalamchi, L.; Aber, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Kian, M. Development of an antibacterial and visible photocatalytic nanocomposite microfiltration membrane incorporated by Ag3PO4/CuZnAl NLDH. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 226, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Z.-M.; Yan, X.; Chen, J.; Lang, W.-Z.; Guo, Y.-J. Novel organic-inorganic hybrid polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes with antifouling and antibacterial properties by embedding N-halamine functionalized silica nanospheres. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 52, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Arsuaga, J.M.; Roldan, N.; Martinez, A.; Sotto, A. Effect of amine functionalization of SBA-15 used as filler on the morphology and permeation properties of polyethersulfone-doped ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Jouyandeh, M.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Paziresh, S.; Dehqan, A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Moradi, H.; Mirsadeghi, S.; Badiei, A.; Munir, M.T. Highly antifouling polymer-nanoparticle-nanoparticle/polymer hybrid membranes. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 810, 152228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabi, H.; Ghaemi, N.; Madaeni, S.S.; Daraei, P.; Astinchap, B.; Zinadini, S.; Razavizadeh, S.H. Nano-ZnO embedded mixed matrix polyethersulfone (PES) membrane: Influence of nanofiller shape on characterization and fouling resistance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Guria, C. Progress in the modification of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) membranes: A performance review for wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alpatova, A.; Kim, E.-S.; Sun, X.; Hwang, G.; Liu, Y.; El-Din, M.G. Fabrication of porous polymeric nanocomposite membranes with enhanced anti-fouling properties: Effect of casting composition. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 444, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherazi, T.A.; Azam, S.; Shah, S.H.; Hussain, S.; Naqvi, S.A.R.; Li, S. Zwitterionic analog structured ultrafiltration membranes for high permeate flux and improved anti-fouling performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 643, 120060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carretier, S.; Chen, L.-A.; Venault, A.; Yang, Z.-R.; Aimar, P.; Chang, Y. Design of PVDF/PEGMA-b-PS-b-PEGMA membranes by VIPS for improved biofouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, Y. Upgrading polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes by blending with amphiphilic block copolymers: Beyond surface segregation. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 505, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. Improved antifouling properties of poly (ether sulfone) membrane by incorporating the amphiphilic comb copolymer with mixed poly (ethylene glycol) and poly (dimethylsiloxane) brushes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 8789–8800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Sun, X.; Gao, C. Antifouling polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes with sulfobetaine polyimides as novel additive for the enhancement of both water flux and protein rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggay, I.V.; Yeh, T.-H.; Venault, A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dizon, G.V.; Chang, Y. Tuning the molecular design of random copolymers for enhancing the biofouling mitigation of membrane materials. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Crittenden, J.C. Blended PVC/PVC-g-PEGMA ultrafiltration membranes with enhanced performance and antifouling properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tiraferri, A.; Li, T.; Xie, W.; Chang, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, B. Superwettable PVDF/PVDF-g-PEGMA Ultrafiltration Membranes. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 23450–23459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Tiraferri, A.; Wu, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, B. Improving the Performance of PVDF/PVDF-g-PEGMA Ultrafiltration Membranes by Partial Solvent Substitution with Green Solvent Dimethyl Sulfoxide during Fabrication. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 19799–19807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanagaraj, P.; Nagendran, A.; Rana, D.; Matsuura, T.; Neelakandan, S.; Malarvizhi, K. Effects of polyvinylpyrrolidone on the permeation and fouling-resistance properties of polyetherimide ultrafiltration membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 4832–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Li, D.; Sun, X.; Gao, C. Antifouling polysulfone membranes with an amphiphilic triblock additive. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 285, 126108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatsha, B.; Ngila, J.C.; Moutloali, R.M. Preparation of antifouling polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP 40K) modified polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration (UF) membrane for water purification. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2014, 67, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Huang, W.; Lu, X.; Yan, D.; Chen, S.; Huang, H. Preparation of PVDF porous membranes by using PVDF-g-PVP powder as an additive and their antifouling property. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2012, 81, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, C.; Yang, F. Improvement of antifouling performances for modified PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with hydrophilic cellulose nanocrystal. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Liu, H.; Xiao, H.; Chibante, F.; Ni, Y. Hydrophilic modification of polyester fabric by applying nanocrystalline cellulose containing surface finish. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 91, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Karkooti, A.; Liu, L.; Sadrzadeh, M.; Thundat, T.; Liu, Y.; Narain, R. Fabrication of antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone (PES)/cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) nanocomposite membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, J.; He, M.; Yao, J. Cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: Preparation and characterization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, L. Preparation and characterization of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) composite membranes blended with nano-crystalline cellulose. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2012, 22, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Yang, F. Exploration of permeability and antifouling performance on modified cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membrane with cellulose nanocrystals. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 174, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansor, E.S.; Abdallah, H.; Shaban, A.M. Fabrication of high selectivity blend membranes based on poly vinyl alcohol for crystal violet dye removal. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 103706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmgar, K.; Nasiraee, M. Polyvinyl alcohol-based membranes for filtration of aqueous solutions: A comprehensive review. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2022, 62, 25–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Liu, W.; Ren, J.; Meng, L. Improved antifouling property of poly (ether sulfone) ultrafiltration membrane through blending with poly (vinyl alcohol). Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 18549–18557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.W.; Wang, Q.Y.; Ma, J.X.; Cao, J.; Hu, W.J.; Wu, Z.C. Relationship between polymers compatibility and casting solution stability in fabricating PVDF/PVA membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 537, 263–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ounifi, I.; Guesmi, Y.; Ursino, C.; Santoro, S.; Mahfoudhi, S.; Figoli, A.; Ferjanie, E.; Hafiane, A. Antifouling membranes based on cellulose acetate (CA) blended with poly (acrylic acid) for heavy metal remediation. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Cao, Y.; Kang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, M. Tethering methoxy polyethylene glycols to improve the antifouling property of PSF/PAA-blended membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, E123–E133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, R.A.; Kumar, M.; Khanzada, N.K.; Thomas, N.; Sreedhar, N.; An, A.K.; Arafat, H.A. Hybrid NF and UF membranes tailored using quaternized polydopamine for enhanced removal of salts and organic pollutants from water. Desalination 2022, 539, 115954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulyati, S.; Muchtar, S.; Arahman, N.; Meirisa, F.; Syamsuddin, Y.; Zuhra, Z.; Rosnelly, C.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Mat Nawi, N.I.; Wirzal, M.D.H. One-Pot polymerization of dopamine as an additive to enhance permeability and antifouling properties of polyethersulfone membrane. Polymers 2020, 12, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Macni, C.R.M.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-A.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Mitigating the fouling of mixed-matrix cellulose acetate membranes for oil–water separation through modification with polydopamine particles. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 159, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-H.; Zhu, L.-P.; Zhang, H.-T.; Zhu, B.-K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Improved hydrodynamic permeability and antifouling properties of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes using polydopamine nanoparticles as additives. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 457, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Ibrahim, Y.; Hasan, S.W.; Show, P.L.; Banat, F. Fabrication of novel polyethersulfone (PES) hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with superior permeability and antifouling properties using environmentally friendly sulfonated functionalized polydopamine nanofillers. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 261, 118311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, V.T.; Abdelrasoul, A.; McMartin, D.W. Influence of zwitterionic structure design on mixed matrix membrane stability, hydrophilicity, and fouling resistance: A computational study. J. Mol. Graph. Modell. 2022, 114, 108187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizon, G.V.; Lee, Y.-S.; Venault, A.; Maggay, I.V.; Chang, Y. Zwitterionic PMMA-r-PEGMA-r-PSBMA copolymers for the formation of anti-biofouling bicontinuous membranes by the VIPS process. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 618, 118753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, G.V.; Venault, A. Direct in-situ modification of PVDF membranes with a zwitterionic copolymer to form bi-continuous and fouling resistant membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-H.; Li, M.-Z.; Miao, J.; Wang, J.-B.; Shao, X.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Q. Improved surface property of PVDF membrane with amphiphilic zwitterionic copolymer as membrane additive. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 6398–6405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggay, I.V.; Suba, M.C.A.M.; Aini, H.N.; Wu, C.-J.; Tang, S.-H.; Aquino, R.B.; Chang, Y.; Venault, A. Thermostable antifouling zwitterionic vapor-induced phase separation membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 627, 119227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggay, I.V.B.; Aini, H.N.; Lagman, M.M.G.; Tang, S.-H.; Aquino, R.R.; Chang, Y.; Venault, A. A Biofouling Resistant Zwitterionic Polysulfone Membrane Prepared by a Dual-Bath Procedure. Membranes 2022, 12, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagandran, S.; Goh, P.S.; Ismail, A.F.; Wong, T.-W.; Binti Wan Dagang, W.R.Z. The recent progress in modification of polymeric membranes using organic macromolecules for water treatment. Symmetry 2020, 12, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Ishihara, K.; Chang, Y. Zwitterionic bi-continuous membranes from a phosphobetaine copolymer/Poly(vinylidene fluoride) blend via VIPS for biofouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Zhou, R.-J.; Galeta, T.A.; Chang, Y. Engineering sterilization-resistant and fouling-resistant porous membranes by the vapor-induced phase separation process using a sulfobetaine methacrylamide amphiphilic derivative. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 658, 120760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; He, C. Efficient preparation of super antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with one step fabricated zwitterionic surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17947–17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almaie, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Rasoulifard, M.H.; Dorraji, M.S.S. Novel negatively-charged amphiphilic copolymers of PVDF-g-PAMPS and PVDF-g-PAA to improve permeability and fouling resistance of PVDF UF membrane. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 179, 105386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zeng, B.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Wu, T.; Shen, H.; Luo, W.; Yuan, C.; Xu, Y.; Chen, G. Polyethersulfone microfiltration membrane modified by an amphiphilic dithiolane-containing copolymer for improving anti-protein-fouling performance and rejection of nanoparticles. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2020, 31, 2816–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L. Comb-shaped amphiphilic triblock copolymers blend PVDF membranes overcome the permeability-selectivity trade-off for protein separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 239, 116596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Bhalani, D.V.; Jewrajka, S.K. Surface segregation of segmented amphiphilic copolymer of poly (dimethylsiloxane) and poly (ethylene glycol) on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) blend membrane for oil–water emulsion separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 232, 115940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Yang, C.; Tan, L.; Cui, Z.; Li, W.; Zhang, X. Amphiphilic cellulose for enhancing the antifouling and separation performances of poly (acrylonitrile-co-methyl acrylate) ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 591, 117276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Huang, L.; Shi, M.; Li, W.; Xing, W. Amphiphilic PVDF-g-PDMAPMA ultrafiltration membrane with enhanced hydrophilicity and antifouling properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 48049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Altaee, A.; Déon, S.; Zhou, J. Preparation of novel high permeability and antifouling polysulfone-vanillin membrane. Desalination 2020, 496, 114759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthanareeswaran, G.; Ismail, A. Enhancement of permeability and antibiofouling properties of polyethersulfone (PES) membrane through incorporation of quorum sensing inhibition (QSI) compound. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 72, 200–212. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, S.; Ibrar, I.; Samal, A.K.; Altaee, A.; Déon, S.; Zhou, J.; Ghaffour, N. Preparation of fouling resistant and highly perm-selective novel PSf/GO-vanillin nanofiltration membrane for efficient water purification. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 421, 126744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoerunnisa, F.; Sihombing, M.; Nurhayati, M.; Dara, F.; Triadi, H.A.; Nasir, M.; Hendrawan, H.; Pratiwi, A.; Ng, E.-P.; Opaprakasit, P. Poly (ether sulfone)-based ultrafiltration membranes using chitosan/ammonium chloride to enhance permeability and antifouling properties. Polym. J. 2022, 54, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareei, F.; Bandehali, S.; Hosseini, S.M. Enhancing the separation and antifouling properties of PES nanofiltration membrane by use of chitosan functionalized magnetic nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 38, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T. Synthesis and characterization of novel water soluble derivative of chitosan as an additive for polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 440, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T. Performance improvement of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane using N-succinyl chitosan as additive. Desalination 2013, 318, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.F.; Rashid, S.A.; Matsuura, T. Polysulfone–Chitosan blend ultrafiltration membranes: Preparation, characterization, permeation and antifouling properties. Rsc Adv. 2013, 3, 7855–7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Li, X.; Zhao, X.; Liu, D.; He, C. Preparation and characterization of nano-chitin whisker reinforced PVDF membrane with excellent antifouling property. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 480, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Huan, G.; Xia, W.; Feng, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Y. Preparation and performance optimization of PVDF anti-fouling membrane modified by chitin. J. Polym. Eng. 2018, 38, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colburn, A.; Vogler, R.J.; Patel, A.; Bezold, M.; Craven, J.; Liu, C.; Bhattacharyya, D. Composite membranes derived from cellulose and lignin sulfonate for selective separations and antifouling aspects. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, S.; Liu, W. Properties of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) ultrafiltration membrane improved by lignin: Hydrophilicity and antifouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 575, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, C.; Balakrishna, R.G. Naturally derived polysaccharides-modified PSF membranes: A potency in enriching the antifouling nature of membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavanya, C.; Soontarapa, K.; Jyothi, M.; Balakrishna, R.G. Environmental friendly and cost effective caramel for congo red removal, high flux, and fouling resistance of polysulfone membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shan, C.; Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Yu, L. High hydrophilic antifouling membrane modified with capsaicin-mimic moieties via microwave assistance (MWA) for efficient water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Feng, X.; Hou, J.; Wang, X.; Shan, B.; Yu, L.; Gao, C. Preparation and characterization of a novel polysulfone UF membrane using a copolymer with capsaicin-mimic moieties for improved anti-fouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manawi, Y.; Kochkodan, V.; Mahmoudi, E.; Johnson, D.J.; Mohammad, A.W.; Atieh, M.A. Characterization and separation performance of a novel polyethersulfone membrane blended with acacia gum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Wu, P. Synchronous Engineering for Biomimetic Murray Porous Membranes Using Isocyanate. Nano Lett. 2022, 22, 3077–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H. Improving the antifouling property of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of isocyanate-treated graphene oxide. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9084–9092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, R.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ismail, A.; Shilton, S.J.; Obaid, A.; Fun, H.-K. Probing the morphology and anti-organic fouling behaviour of a polyetherimide membrane modified with hydrophilic organic acids as additives. New J. Chem. 2015, 39, 6141–6150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniei, N.; Ghasemi, N.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Zinadini, S.; Ramezani, M.; Derakhshan, A. Preparation and characterization of a novel antifouling nano filtration poly ethersulfone (PES) membrane by embedding goethite-tannic acid nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Yaoqin, W.; Changmei, S.; Chunnuan, J.; Ying, Z.; Rongjun, Q.; Ying, W. Preparation and properties of PVC-based ultrafiltration membrane reinforced by in-situ synthesized p-aramid nanoparticles. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 642, 119993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Ballad, M.R.B.; Huang, Y.-T.; Liu, Y.-H.; Kao, C.-H.; Chang, Y. Antifouling PVDF membrane prepared by VIPS for microalgae harvesting. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 142, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, B.; Sinha, M.K. Effect of hydrophilic poly (ethylene glycol) methyl ether additive on the structure, morphology, and performance of polysulfone flat sheet ultrafiltration membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosma, V.A.; Beltsios, K.G. Macrovoids in solution-cast membranes: Direct probing of systems exhibiting horizontal macrovoid growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 407, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, F.; Li, J.; Li, B.; Zhao, C. Oxidant-induced dopamine polymerization for multifunctional coatings. Polym. Chem. 2010, 1, 1430–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sreedhar, N.; Thomas, N.; Mavukkandy, M.; Ismail, R.A.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Arafat, H.A. Polydopamine-coated graphene oxide nanosheets embedded in sulfonated poly (ether sulfone) hybrid UF membranes with superior antifouling properties for water treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 433, 133526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Fan, S.; Hu, Y.; Fu, X.; Shao, H.; Zhou, Q. A novel membrane biofouling mitigation strategy of D-amino acid supported by polydopamine and halloysite nanotube. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 579, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Mao, L.; Chen, J.; Li, M. Preparation and characterization of antifouling and antibacterial polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes incorporated with a silver–polydopamine nanohybrid. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Li, S.; Zheng, X.; Zhao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Zhao, Z. Fabrication of novel anti-fouling poly (m-phenylene isophthalamide) ultrafiltration membrane modified with Pluronic F127 via coupling phase inversion and surface segregation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 282, 120106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norde, W. Protein adsorption at solid surfaces: A thermodynamic approach. Pure Appl. Chem. 1994, 66, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwood, J.L. Comprehensive Supramolecular Chemistry II; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, R.; Ma, T.; He, M.; Jiang, Z. Enhanced membrane antifouling and separation performance by manipulating phase separation and surface segregation behaviors through incorporating versatile modifier. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 499, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Hu, Y. Improving the perm-selectivity and anti-fouling property of UF membrane through the micro-phase separation of PSf-b-PEG block copolymers. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 599, 117851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-T.; Venault, A.; Huang, H.Q.; Lee, K.-R.; Chang, Y. Introducing a PEGylated diblock copolymer into PVDF hollow-fibers for reducing their fouling propensity. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2018, 87, 252–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kardela, J.H.; Millichamp, I.S.; Ferguson, J.; Parry, A.L.; Reynolds, K.J.; Aldred, N.; Clare, A.S. Nonfreezable water and polymer swelling control the marine antifouling performance of polymers with limited hydrophilic content. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 29477–29489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morisaku, T.; Watanabe, J.; Konno, T.; Takai, M.; Ishihara, K. Hydration of phosphorylcholine groups attached to highly swollen polymer hydrogels studied by thermal analysis. Polymer 2008, 49, 4652–4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Sundaram, H.S.; Wei, Z.; Li, C.; Yuan, Z. Applications of zwitterionic polymers. React. Funct. Polym. 2017, 118, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laschewsky, A. Structures and synthesis of zwitterionic polymers. Polymers 2014, 6, 1544–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhuang, B.; Yu, J. Functional Zwitterionic Polymers on Surface: Structures and Applications. Chem.-Asian J. 2020, 15, 2060–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ma, J.; Zheng, J.; Dai, R.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Recent advances in nature-inspired antifouling membranes for water purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 432, 134425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bulushia, M.; Al-Hinaic, M.; Al-Obaidanid, S.; Dobrestove, S.; Nxumalog, E.; Al-Abria, M. Antifouling enhancement of polyethersulfone membranes incorporated with silver nanoparticles for bovine serum albumin and humic acid removal. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 243, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhar, F.H.; Harun, Z.; Yusof, K.N.; Alias, S.S.; Hashim, N.; Sazali, E.S. A study of different concentrations of bio-silver nanoparticles in polysulfone mixed matrix membranes in water separation performance. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, S.; Nazar, U.; Ali, J.; Ali, Q.u.A.; Ahmad, N.M.; Sarwar, F.; Waseem, H.; Jamil, S.U.U. Improved antifouling potential of polyether sulfone polymeric membrane containing silver nanoparticles: Self-cleaning membranes. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 1413–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad Rehan, Z.; Gzara, L.; Bahadar Khan, S.; A Alamry, K.; El-Shahawi, M.; H Albeirutty, M.; Figoli, A.; Drioli, E.; M Asiri, A. Synthesis and characterization of silver nanoparticles-filled polyethersulfone membranes for antibacterial and anti-biofouling application. Recent Pat. Nanotechnol. 2016, 10, 231–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Field, R.W.; Zhang, K. Biogenic silver nanocomposite polyethersulfone UF membranes with antifouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 471, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Koutahzadeh, N.; Esfahani, A.R.; Firouzjaei, M.D.; Anderson, B.; Peck, L. A novel gold nanocomposite membrane with enhanced permeation, rejection and self-cleaning ability. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, R.; Gogoi, M.; Borah, H.J.; Ingole, P.G.; Hazarika, S. Biogenic synthesized Pd-nanoparticle incorporated antifouling polymeric membrane for removal of crystal violet dye. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 6139–6146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Lu, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of ZrO2/PES hybrid ultrafiltration membrane with uniform ZrO2 nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 332, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xie, T.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, F. An anti-fouling Poly(vinylidene fluoride) hybrid membrane blended with functionalized ZrO2 nanoparticles for efficient oil/water separation. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 5262–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Tian, F.; Chen, G.; Wang, F.; Weng, R.; Xi, B. Preparation and Characterization of Regenerated Cellulose Membrane Blended with ZrO2 Nanoparticles. Membranes 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.-Z.; Li, X.; Li, J.-S.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Huang, C.; Sun, X.-Y.; Wang, L.-J. In situ preparation and antifouling performance of ZrO2/PVDF hybrid membrane. Acta Phys.-Chim. Sin. 2013, 29, 2592–2598. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Ali, F.A.A.; Alhoshan, M. Efficient soluble anionic dye removal and antimicrobial properties of ZnO embedded-Polyphenylsulfone membrane. Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Sugumaran, J.; Shoparwe, N.F. Antifouling properties of PES membranes by blending with ZnO nanoparticles and NMP–acetone mixture as solvent. Membranes 2018, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarihan, A.; Eren, E. Novel high performanced and fouling resistant PSf/ZnO membranes for water treatment. Membr. Water Treat 2017, 8, 563–574. [Google Scholar]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Aber, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Mahmoodi, N.M. The effect of amine functionalization of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles used as additives on the morphology and the permeation properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration nanocomposite membranes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 154, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Vatanpour, V.; Aber, S. Improving the permeability and antifouling property of PES ultrafiltration membranes using the drying method and incorporating the CuO-ZnO nanocomposite. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 31, 100891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Karami, F.; Farahani, S.K.; Bandehali, S.; Shen, J.; Bagheripour, E.; Seidypoor, A. Tailoring the separation performance and antifouling property of polyethersulfone based NF membrane by incorporating hydrophilic CuO nanoparticles. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzinun, H.; Othman, M.H.D.; Ismail, A.F.; Puteh, M.H.; Rahman, M.A.; Jaafar, J.; Adrus, N.; Hashim, N.A. Antifouling behavior and separation performance of immobilized TiO2 in dual layer hollow fiber membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, Z.; Sethy, N.K.; Kumari, L.; Mishra, P.K.; Verma, B. Antifouling behaviour of PVDF/TiO2 composite membrane: A quantitative and qualitative assessment. Iran. Polym. J. 2019, 28, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsohaimi, I.H.; Kumar, M.; Algamdi, M.S.; Khan, M.A.; Nolan, K.; Lawler, J. Antifouling hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with high selectivity fabricated from polysulfone and sulfonic acid functionalized TiO2 nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 316, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Che Lah, N.F.; Norzli, N.A.; Pang, W.Y. A Contrastive Study of Self-Assembly and Physical Blending Mechanism of TiO2 Blended Polyethersulfone Membranes for Enhanced Humic Acid Removal and Alleviation of Membrane Fouling. Membranes 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.S.; Fakharian Torbati, S.; Alaei Shahmirzadi, M.A.; Tavangar, T. Fabrication, characterization, and performance evaluation of polyethersulfone/TiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes for produced water treatment. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2619–2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, S.B.; Molina, S.; Sotto, A.; Calvo, E.G.A.; Abajob, J.D. Fouling resistant polysulfone–PANI/TiO2 ultrafiltration nanocomposite membranes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2013, 52, 9470–9479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayatzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Fallah, N. Influence of TiO2 nanoparticles loading on permeability and antifouling properties of nanocomposite polymeric membranes: Experimental and statistical analysis. J. Polym. Res. 2019, 26, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Hazrati, M.; Sheydaei, M.; Dehqan, A. Investigation of using UV/H2O2 pre-treatment process on filterability and fouling reduction of PVDF/TiO2 nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 170, 108677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Liu, Y.; Shen, L.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, L.; Lin, H. Magnetic field assisted arrangement of photocatalytic TiO2 particles on membrane surface to enhance membrane antifouling performance for water treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 570, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, A.K.; Shalin, P.; JagadeeshBabu, P. Performance enhancement of polysulfone ultrafiltration membrane using TiO2 nanofibers. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 10506–10514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidsorkhi, H.C.; Riazi, H.; Emadzadeh, D.; Ghanbari, M.; Matsuura, T.; Lau, W.; Ismail, A. Preparation and characterization of a novel highly hydrophilic and antifouling polysulfone/nanoporous TiO2 nanocomposite membrane. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 415706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Yang, Y. Preparation and characterization of PSF-TiO2 hybrid hollow fiber UF membrane by sol–gel method. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behboudi, A.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Yegani, R. Preparation and characterization of TiO2 embedded PVC ultrafiltration membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2016, 114, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fang, X.; Pang, R.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L. Self-assembly of TiO2 nanoparticles around the pores of PES ultrafiltration membrane for mitigating organic fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Fang, X.; Bakzhan, K.; Wang, L.; Van der Bruggen, B. A synergetic analysis method for antifouling behavior investigation on PES ultrafiltration membrane with self-assembled TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbari, A.; Yegani, R.; Pourabbas, B.; Behboudi, A. Analysis of antifouling behavior of high dispersible hydrophilic poly (ethylene glycol)/vinyl functionalized SiO2 nanoparticles embedded polyethylene membrane. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 76, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamari, S.; Shahbazi, A. Biocompatible Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2 nanocomposite as a green nanofiller embedded in PES–nanofiltration membrane matrix for salts, heavy metal ion and dye removal: Long–term operation and reusability tests. Chemosphere 2020, 243, 125282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Development of a hydrophilic PES ultrafiltration membrane containing SiO2@N-Halamine nanoparticles with both organic antifouling and antibacterial properties. Desalination 2013, 326, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, R.; Lin, O.; Zhang, W.; Du, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C. Enhanced hydrophilic and antipollution properties of PES membrane by anchoring SiO2/HPAN nanomaterial. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 7812–7823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Wu, X.; Ma, B.; Zhao, X.; He, C. Enhancing the antifouling property of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/SiO2 hybrid membrane through TIPS method. J. Mater. Sci. 2014, 49, 7797–7808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhao, F.; Liang, X.; Tian, Y. Fabrication of a low-cost nano-SiO2/PVC composite ultrafiltration membrane and its antifouling performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V. Magnetic field-augmented coagulation bath during phase inversion for preparation of ZnFe2O4/SiO2/PES nanofiltration membrane: A novel method for flux enhancement and fouling resistance. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 46, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghandashtani, M.B.; Ashtiani, F.Z.; Karimi, M.; Fouladitajar, A. A novel approach to fabricate high performance nano-SiO2 embedded PES membranes for microfiltration of oil-in-water emulsion. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 349, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Zhou, J. Novel polyethersulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membrane prepared with SiO2-g-(PDMAEMA-co-PDMAPS) and its antifouling performances in oil-in-water emulsion application. Desalination 2015, 365, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadousti, S.; Zokaee Ashtiani, F.; Karimi, M.; Fouladitajar, A. Preparation and characterization of novel PES-(SiO2-g-PMAA) membranes with antifouling and hydrophilic properties for separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2019, 30, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, M.S.; Salim, M.R.; Lau, W.-J. Preparation and characterization of PES/SiO2 composite ultrafiltration membrane for advanced water treatment. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2015, 32, 2319–2329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Lü, Z.; Wei, C.; Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Separation and antifouling properties of hydrolyzed PAN hybrid membranes prepared via in-situ sol-gel SiO2 nanoparticles growth. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 545, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhao, X.; He, C. Zwitterionic SiO2 nanoparticles as novel additives to improve the antifouling properties of PVDF membranes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 53653–53659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Aber, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Mahmoodi, N.M. Development of hydrophilic microporous PES ultrafiltration membrane containing CuO nanoparticles with improved antifouling and separation performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2019, 222, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajau, A.; Motsa, M.; Mamba, B.B.; Mahlangu, O. Leaching of CuO Nanoparticles from PES Ultrafiltration Membranes. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 31797–31809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Karim, A.; Ismail, S.H.; Bayoumy, A.M.; Ibrahim, M.; Mohamed, G.G. Antifouling PES/Cu@Fe3O4 mixed matrix membranes: Quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) modeling and wastewater treatment potentiality. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 407, 126501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankari, S.; Kalaivizhi, R.; Gowriboy, N. Cellulose Acetate (CA) Membrane Tailored with Fe3O4@ZnO Core Shell Nanoparticles: Fabrication, Structural analysis and Its Adsorption Analysis. ChemistrySelect 2021, 6, 2350–2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.S.M.; Lau, W.J.; Yusof, N.; Said, N.; Ismail, A.F. Enhancing water flux and antifouling properties of PES hollow fiber membranes via incorporation of surface-functionalized Fe3O4 nanoparticles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, R.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ananda, K.; Abdullah, M.S.; Ismail, A. Fabrication of a novel hollow fiber membrane decorated with functionalized Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Towards sustainable water treatment and biofouling control. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 4197–4211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirel, E.; Zhang, B.; Papakyriakou, M.; Xia, S.; Chen, Y. Fe2O3 nanocomposite PVC membrane with enhanced properties and separation performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 170–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Demirel, E.; Chen, Y.; Gong, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y. Improving antifouling performance for the harvesting of Scenedesmus acuminatus using Fe2O3 nanoparticles incorporated PVC nanocomposite membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, B.; Yan, Y.; Meng, M. Magnetic induced fabrication of core-shell structure Fe3O4@TiO2 photocatalytic membrane: Enhancing photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and antifouling performance. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Shahsavarifar, S.; Khorshidi, S.; Masteri-Farahani, M. A novel antifouling ultrafiltration membranes prepared from percarboxylic acid functionalized SiO2 bound Fe3O4 nanoparticle (SCMNP-COOOH)/polyethersulfone nanocomposite for BSA separation and dye removal. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2019, 94, 1341–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Rahimi, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Zangeneh, H.; Beygzadeh, M. Novel high flux antifouling nanofiltration membranes for dye removal containing carboxymethyl chitosan coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 349, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ivars, J.; Alcaina-Miranda, M.-I.; Iborra-Clar, M.-I.; Mendoza-Roca, J.-A.; Pastor-Alcañiz, L. Enhancement in hydrophilicity of different polymer phase-inversion ultrafiltration membranes by introducing PEG/Al2O3 nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 128, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazanfari, D.; Bastani, D.; Mousavi, S.A. Preparation and characterization of poly (vinyl chloride)(PVC) based membrane for wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2017, 16, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Hong, H.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Liao, B.-Q. Enhanced permeability and antifouling performance of polyether sulfone (PES) membrane via elevating magnetic Ni@MXene nanoparticles to upper layer in phase inversion process. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 623, 119080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Ouda, M.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Hai, A.; Gnanasundaram, N.; Hasan, S.W.; Banat, F. Surface-engineered polyethersulfone membranes with inherent Fe–Mn bimetallic oxides for improved permeability and antifouling capability. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Leo, C.P.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2013, 308, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigante, M.; Zanini, G.; Avena, M. On the dissolution kinetics of humic acid particles: Effects of pH, temperature and Ca2+ concentration. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 294, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfahani, M.R.; Pallem, V.L.; Stretz, H.A.; Wells, M.J. Humic acid disaggregation with/of gold nanoparticles: Effects of nanoparticle size and pH. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2016, 6, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccolo, A.; Conte, P.; Cozzolino, A. Effects of mineral and monocarboxylic acids on the molecular association of dissolved humic substances. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1999, 50, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Vatanpour, V.; Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Zarrabi, H. Improvement in flux and antifouling properties of PVC ultrafiltration membranes by incorporation of zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2015, 156, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, M.; Arvind, V.; Saikia, K.; Vaidyanathan, V.K. Fabrication of highly permeable and anti-fouling performance of Poly (ether ether sulfone) nanofiltration membranes modified with zinc oxide nanoparticles. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, M.T.; Lesage, G.; Mohammadi, T.; Mericq, J.P.; Mendret, J.; Heran, M.; Faur, C.; Brosillon, S.; Hemmati, M.; Naeimpoor, F. Improved antifouling properties of TiO2/PVDF nanocomposite membranes in UV-coupled ultrafiltration. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.P.; Dubey, N.C.; Subair, R.; Choudhury, S.; Stamm, M. Enhanced hydrophilic and antifouling polyacrylonitrile membrane with polydopamine modified silica nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 4448–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Wang, L.; Zhang, B.; Xie, Y.; Sun, C.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, G. Modification of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane with different shaped α-Fe2O3 nanocrystals for enhanced photocatalytic oxidation performance. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2018, 214, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Moghadassi, A. Influence of the various pore former additives on the performance and characteristics of the bare and EPVC/boehmite nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. Mater. Today Commun. 2019, 21, 100663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farjami, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Moghadassi, A. Effect of nanoboehmite/poly (ethylene glycol) on the performance and physiochemical attributes EPVC nano-composite membranes in protein separation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 156, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Madaeni, S.S.; Rajabi, L.; Zinadini, S.; Derakhshan, A.A. Boehmite nanoparticles as a new nanofiller for preparation of antifouling mixed matrix membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 401, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tian, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. Fabrication of a novel “loose” nanofiltration membrane by facile blending with Chitosan–Montmorillonite nanosheets for dyes purification. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 265, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Devanadera, K.P.O.; Duena, A.N.R.; Luo, Z.-Y.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Millare, J.C.; Aquino, R.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R. Modifying cellulose acetate mixed-matrix membranes for improved oil–water separation: Comparison between sodium and organo-montmorillonite as particle additives. Membranes 2021, 11, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Zahhar, A.A.; Alghamdi, M.M.; Asiri, B.M. Poly (vinyl chloride)-MMT composite membranes with enhanced properties and separation performance. Desalin. Water Treat 2019, 155, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokri, E.; Shahed, E.; Hermani, M.; Etemadi, H. Towards enhanced fouling resistance of PVC ultrafiltration membrane using modified montmorillonite with folic acid. Appl. Clay Sci. 2021, 200, 105906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, T.; Guria, C.; Shekhar, S. Effects of inorganic salts in the casting solution on morphology of poly (vinyl chloride)/bentonite ultrafiltration membranes. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 280, 125805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Dixit, S.; Yadav, V.L. Effect of hydrophilic bentonite nano particle on the performance of polyvinylchloride membrane. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 126415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Chu, H.; Zhou, X.; Wei, Y. Effect of modified attapulgite addition on the performance of a PVDF ultrafiltration membrane. Desalination 2014, 344, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Bharath, G.; Rambabu, K.; Srinivasakannan, C.; Banat, F. Improved permeability and antifouling performance of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membranes tailored by hydroxyapatite/boron nitride nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallem, P.; Ouda, M.; Bharath, G.; Hasan, S.W.; Banat, F. Enhanced water permeability and fouling resistance properties of ultrafiltration membranes incorporated with hydroxyapatite decorated orange-peel-derived activated carbon nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Y.; Zhu, K.; Luan, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.; Na, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, G. Fabrication of hybrid ultrafiltration membranes with improved water separation properties by incorporating environmentally friendly taurine modified hydroxyapatite nanotubes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 577, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lang, W.-Z.; Xu, H.-P.; Yan, X.; Guo, Y.-J. The effects of hydroxyapatite nano whiskers and its synergism with polyvinylpyrrolidone on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 21532–21543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, M.H.D.A.; Vatanpour, V. A comprehensive study on the performance and antifouling enhancement of the PVDF mixed matrix membranes by embedding different nanoparticulates: Clay, functionalized carbon nanotube, SiO2 and TiO2. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 197, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daraei, P.; Ghaemi, N. Synergistic effect of Cloisite 15A and 30B nanofillers on the characteristics of nanocomposite polyethersulfone membrane. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 172, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arkaban, M.; Mahdavian, L.; Arkaban, H. Synthesis of Poly(vinylidene Fluoride)/Modified SBA-15 Nanoparticles Composite Membrane for Water Purification. Silicon 2020, 12, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandehali, S.; Parvizian, F.; Ruan, H.; Moghadassi, A.; Shen, J.; Figoli, A.; Adeleye, A.S.; Hilal, N.; Matsuura, T.; Drioli, E. A planned review on designing of high-performance nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes for pollutants removal from water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 101, 78–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Sotto, A.; Martín, A.; Kim, J. Preparation and characterization of polyethersulfone mixed matrix membranes embedded with Ti-or Zr-incorporated SBA-15 materials. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2017, 45, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, G.; Zinadini, S.; Rahimi, M.; Shiri, F. Efficient Zn2+, Pb2+, and Ni2+ removal using antifouling mixed matrix nanofiltration membrane with curcumin modified mesoporous Santa Barbara Amorphous-15 (Cur-SBA-15) filler. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Lu, X.; Lu, D.; Wang, P.; Ma, J. Development of a high-performance polysulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membrane using hydrophilic polymer-functionalized mesoporous SBA−15 as filler. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shen, H.; Cui, C.; Hou, L.; Chen, W.; Liu, Q.; Xu, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J. Towards to better permeability and antifouling sulfonated poly (aryl ether ketone sulfone) with carboxyl group ultrafiltration membrane blending with amine functionalization of SBA-15. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 265, 118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amid, M.; Nabian, N.; Delavar, M. Performance evaluation and modeling study of PC blended membranes incorporated with SDS-modified and unmodified halloysite nanotubes in the separation of oil from water. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Huang, W.; Zhang, Y. High-flux, antibacterial ultrafiltration membranes by facile blending with N-halamine grafted halloysite nanotubes. Rsc Adv. 2015, 5, 6666–6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grylewicz, A.; Szymański, K.; Darowna, D.; Mozia, S. Influence of Polymer Solvents on the Properties of Halloysite-Modified Polyethersulfone Membranes Prepared by Wet Phase Inversion. Molecules 2021, 26, 2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, N.; Ahzi, S.; Kochkodan, V. Polysulfone/halloysite composite membranes with low fouling properties and enhanced compaction resistance. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 199, 105873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.; Kochkodan, V.; Zekri, A.; Ahzi, S. Polysulfone membranes embedded with halloysites nanotubes: Preparation and properties. Membranes 2019, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Mi, Z.; Jin, S.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Zhao, X.; Zhou, H.; Chen, C. The influence of sulfonated hyperbranched polyethersulfone-modified halloysite nanotubes on the compatibility and water separation performance of polyethersulfone hybrid ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 557, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; He, Y.; Zeng, G.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhou, L.; Peng, L.; Sengupta, A. High-flux PVDF membrane incorporated with β-cyclodextrin modified halloysite nanotubes for dye rejection and Cu (II) removal from water. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2018, 29, 2704–2714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, M. Enhanced antifouling performance of halloysite nanotubes (HNTs) blended poly (vinyl chloride)(PVC/HNTs) ultrafiltration membranes: For water treatment. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 63, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozia, S.; Grylewicz, A.; Zgrzebnicki, M.; Darowna, D.; Czyżewski, A. Investigations on the properties and performance of mixed-matrix polyethersulfone membranes modified with halloysite nanotubes. Polymers 2019, 11, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouda, M.; Hai, A.; Krishnamoorthy, R.; Govindan, B.; Othman, I.; Kui, C.C.; Choi, M.Y.; Hasan, S.W.; Banat, F. Surface tuned polyethersulfone membrane using an iron oxide functionalized halloysite nanocomposite for enhanced humic acid removal. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Yang, E.; Park, H.; Choi, H. Fabrication of functionalized halloysite nanotube blended ultrafiltration membranes for high flux and fouling resistance. Environ. Eng. Res. 2019, 25, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan Ikhsan, S.N.; Yusof, N.; Mat Nawi, N.I.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Aziz, F.; Ismail, A.F. Halloysite nanotube-ferrihydrite incorporated polyethersulfone mixed matrix membrane: Effect of nanocomposite loading on the antifouling performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; He, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, C.; Bai, J.; Zhou, X.; Li, J.; Wang, Y. Fabrication of green poly (L-lactic acid) hybrid membrane through incorporation of functionalized natural halloysite nanotubes. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2022, 97, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H. Improving the antifouling property of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of dextran grafted halloysite nanotubes. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 237, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Yu, Z. Novel polyvinylidene fluoride nanofiltration membrane blended with functionalized halloysite nanotubes for dye and heavy metal ions removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, G.; He, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Zhang, L.; Shi, H.; Yu, Z. Preparation of a novel Poly(vinylidene fluoride) ultrafiltration membrane by incorporation of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-grafted halloysite nanotubes for oil/water separation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Z.; Wang, L.; Liu, C.; Yang, C.; Lin, G.; Liu, S.; Jia, K.; Liu, X. Interfacial coordination mediated surface segregation of halloysite nanotubes to construct a high-flux antifouling membrane for oil-water emulsion separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Khataee, A. Development of a novel high-flux PVDF-based ultrafiltration membrane by embedding Mg-Al nanolayered double hydroxide. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 41, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balcik, C.; Ozbey-Unal, B.; Cifcioglu-Gozuacik, B.; Keyikoglu, R.; Karagunduz, A.; Khataee, A. Fabrication of PSf nanocomposite membranes incorporated with ZnFe layered double hydroxide for separation and antifouling aspects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 285, 120354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, W.; Lu, Z.; Ao, X.; Li, S. Ceramic nanocomposite membranes and membrane fouling: A review. Water Res. 2020, 175, 115674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morihama, A.C.D.; Mierzwa, J.C. Clay nanoparticles effects on performance and morphology of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seshasayee, M.; Yu, Z.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Das, D. Preparation of nanoclay embedded polymeric membranes for the filtration of natural organic matter (NOM) in a circular crossflow filtration system. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dlamini, D.S.; Li, J.; Mamba, B.B. Critical review of montmorillonite/polymer mixed-matrix filtration membranes: Possibilities and challenges. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 168, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koulivand, H.; Shahbazi, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Rahmandoost, M. Novel antifouling and antibacterial polyethersulfone membrane prepared by embedding nitrogen-doped carbon dots for efficient salt and dye rejection. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 111, 110787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koulivand, H.; Shahbazi, A.; Vatanpour, V.; Rahmandoust, M. Development of carbon dot-modified polyethersulfone membranes for enhancement of nanofiltration, permeation and antifouling performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 230, 115895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, S.; Zhou, S.; Fane, A.G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Enhancing water permeability and fouling resistance of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes with carboxylated nanodiamonds. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 556, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinpour, S.; Azimian-Kivi, M.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Yegani, R. Pharmaceutical wastewater treatment using polypropylene membranes incorporated with carboxylated and PEG-grafted nanodiamond in membrane bioreactor (MBR). Water Environ. J. 2021, 35, 1249–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, S.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Huang, S.; Fane, A.G.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Carboxylated Nanodiamond-enhanced photocatalytic membranes with improved antifouling and self-cleaning properties. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 3538–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahida, S.; Siddiqa, A.; Salim, N.; Qaisar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Farooq, U.; Shanableh, A.; Elboughdiri, N.; Kolsi, L.; Bouazzi, Y. Fabrication and characterization of nanocomposite membranes for the rejection of textile dye. Inorg. Nano-Met. Chem. 2022, 97, 1676–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Naeeni, R.S.E.; Ghadimi, A.; Karami, A.; Sadatnia, B. Effect of detonation nanodiamond on the properties and performance of polyethersulfone nanocomposite membrane. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2018, 90, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajibadea, T.F.; Xuc, J.; Tiana, H.; Guanc, L.; Zhanga, K. O-MWCNT/PAN/PVDF ultrafiltration membranes with boosted properties for oil and water separation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 224, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudaib, B.; Gomes, V.; Shi, J.; Zhou, C.; Liu, Z. Poly(vinylidene fluoride)/polyaniline/MWCNT nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for natural organic matter removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 190, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huhn-Ibarra, M.J.; Loría-Bastarrachea, M.I.; Duarte-Aranda, S.; Montes-Luna, A.d.J.; Ortiz-Espinoza, J.; González-Díaz, M.O.; Aguilar-Vega, M. PPSU dual layer hollow fiber mixed matrix membranes with functionalized MWCNT for enhanced antifouling, salt and dye rejection in water treatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e53203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irfan, M.; Basri, H.; Irfan, M.; Lau, W.-J. An acid functionalized MWCNT/PVP nanocomposite as a new additive for fabrication of an ultrafiltration membrane with improved anti-fouling resistance. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 95421–95432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, F.; Xie, C.; Zhu, L.; Shan, B. PMWCNT/PVDF ultrafiltration membranes with enhanced antifouling properties intensified by electric field for efficient blood purification. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 576, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsamanesh, M.; Mansourpanah, Y.; Dadkhah Tehrani, A. Improving the efficacy of PES-based mixed matrix membranes incorporated with citric acid–amylose-modified MWCNTs for HA removal from water. Polym. Bull. 2021, 78, 1293–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Water desalination via novel positively charged hybrid nanofiltration membranes filled with hyperbranched polyethyleneimine modified MWCNT. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 69, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, Z.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Zinadini, S. Preparation of high antibiofouling amino functionalized MWCNTs/PES nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for application in membrane bioreactor. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 29, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J.; Yuan, H.; Lu, J. Doubly modified MWCNTs embedded in polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration membrane and its anti-fouling performance. J. Polym. Eng. 2022, 42, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, N.; Vatanpour, V. Fouling decline and retention increase of polyvinyl chloride nanofiltration membranes blended by polypyrrole functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotubes. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 23, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, M.R.; Delnavaz, M.; Vatanpour, V.; Farahbakhsh, J. Effect of blending polypyrrole coated multiwalled carbon nanotube on desalination performance and antifouling property of thin film nanocomposite nanofiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenpour, S.; Leaper, S.; Shokri, J.; Alberto, M.; Gorgojo, P. Effect of graphene oxide in the formation of polymeric asymmetric membranes via phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 641, 119924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Ni, M. Preparation of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes with graphene oxide addition for natural organic matter removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 473, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, N.; Priestley, R.C.E.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X. The effect of reduction degree of GO nanosheets on microstructure and performance of PVDF/GO hybrid membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 501, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; He, Z.; Gong, H.; He, L. Recent advances in oil-water separation materials with special wettability modified by graphene and its derivatives: A review. Chem. Eng. Process.-Process Intensif. 2022, 170, 108678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Masteri-Farahani, M.; Mosleh, N.; Ganjali, M.R.; Badiei, A.; Pourbashir, E.; Mashhadzadeh, A.H.; Munir, M.T.; Mahmodi, G. Anti-fouling and permeable polyvinyl chloride nanofiltration membranes embedded by hydrophilic graphene quantum dots for dye wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, H.D.; Makwana, P.; Sharma, S. Biofouling of polysulfone and polysulfone-graphene oxide nanocomposite membrane and foulant removal. Mater. Res. Express 2018, 5, 065322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wang, S.; Han, X.; Wang, Y.; Hua, X.; Li, J. Chitosan-functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced permeability and antifouling of ultrafiltration membranes. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2018, 41, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, Y.; Kye, H.; Yang, W.S.; Kang, J.-W. Comparing graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide as blending materials for polysulfone and polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkooti, A.; Yazdi, A.Z.; Chen, P.; McGregor, M.; Nazemifard, N.; Sadrzadeh, M. Development of advanced nanocomposite membranes using graphene nanoribbons and nanosheets for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 560, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashidi, R.; Khakpour, S.; Masoumi, S.; Jafarzadeh, Y. Effects of GO-PEG on the performance and structure of PVC ultrafiltration membranes. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2022, 177, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vatanpour, V.; Khadem, S.S.M.; Dehqan, A.; Al-Naqshabandi, M.A.; Ganjali, M.R.; Hassani, S.S.; Rashid, M.R.; Saeb, M.R.; Dizge, N. Efficient removal of dyes and proteins by nitrogen-doped porous graphene blended polyethersulfone nanocomposite membranes. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 127892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Xie, Q.; Wu, C.; Shen, L.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, G.; Lu, Y.; Shao, W. A facile approach to enhance performance of PVDF-matrix nanocomposite membrane via manipulating migration behavior of graphene oxide. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 590, 117268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, S.; Han, N.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Liu, H.; Yan, X.; Zhang, X. Fluffy-like amphiphilic graphene oxide (f-GO) and its effects on improving the antifouling of PAN-based composite membranes. Desalination 2022, 527, 115575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimipour, H.; Shahbazi, A.; Vatanpour, V. Fouling decline and retention increase of polyethersulfone membrane by incorporating melamine-based dendrimer amine functionalized graphene oxide nanosheets (GO/MDA). J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salim, A.; Abbas, M.A.; Khan, I.A.; Khan, M.Z.; Javaid, F.; Mushtaq, S.; Batool, M.; Yasir, M.; Khan, A.L.; Khan, A.U. Graphene oxide incorporated polyether sulfone nanocomposite antifouling ultrafiltration membranes with enhanced hydrophilicity. Mater. Res. Express 2022, 9, 075503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Xu, X.; Chen, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, F. Highly effective antifouling performance of PVDF/graphene oxide composite membrane in membrane bioreactor (MBR) system. Desalination 2014, 340, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, F.; Chai, Y. A Membrane with Strong Resistance to Organic and Biological Fouling Using Graphene Oxide and D-Tyrosine as Modifiers. Membranes 2022, 12, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, N.; Mahdavi, H. Nanofiltration composite membranes of polyethersulfone and graphene oxide and sulfonated graphene oxide. Adv. Polym. Technol. 2018, 37, 3529–3541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczak, E.; Blus, M. Polymer membranes from polyvinylidene fluoride or cellulose acetate improved graphene oxide used in the UF process. Desalin. Water Treat. 2021, 214, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, H.; Umar, M.; Ullah, A.; Razzaq, H.; Zia, K.M.; Liu, X. Polyvinylidene fluoride nanocomposite super hydrophilic membrane integrated with Polyaniline-Graphene oxide nano fillers for treatment of textile effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.V.; Ngo, T.H.A.; Do, K.D.; Nguyen, M.N.; Dang, N.T.T.; Nguyen, T.T.H.; Vien, V.; Vu, T.A. Preparation and characterization of a hydrophilic polysulfone membrane using graphene oxide. J. Chem. 2019, 2019, 3164373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhouzaam, A.; Qiblawey, H. Synergetic effects of dodecylamine-functionalized graphene oxide nanoparticles on antifouling and antibacterial properties of polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 42, 102120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Cui, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Mo, Y.; Dlamini, D.S.; Wang, H.; He, B.; Li, J.; Matsuyama, H. Ultra-low graphene oxide loading for water permeability, antifouling and antibacterial improvement of polyethersulfone/sulfonated polysulfone ultrafiltration membranes. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, A.; Mahdavi, H. Zwitterionic-functionalized GO/PVDF nanocomposite membranes with improved anti-fouling properties. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Lv, W.; Zhang, C.; Li, Z.; Su, R.; Qi, W.; Yang, Q.-H.; He, Z. High-performance ultrafiltration membranes based on polyethersulfone–graphene oxide composites. Rsc Adv. 2013, 3, 21394–21397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.T.; Ao, D.; Lu, M.C.; Chang, N. Alteration of the morphology of polyvinylidene fluoride membrane by incorporating MOF-199 nanomaterials for improving water permeation with antifouling and antibacterial property. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2020, 67, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Huo, X.; Fan, S.; Zhao, K.; Yu, S.; Tan, X. Design and synthesis of Al-MOF/PPSU mixed matrix membrane with pollution resistance. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 29, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samari, M.; Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.A.; Jafarzadeh, M.; Gholami, F. Designing of a novel polyethersulfone (PES) ultrafiltration (UF) membrane with thermal stability and high fouling resistance using melamine-modified zirconium-based metal-organic framework (UiO-66-NH2/MOF). Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 251, 117010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rameesha, L.; Rana, D.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Nagendran, A. Efficacy of MOF-199 in improvement of permeation, morphological, antifouling and antibacterial characteristics of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes. New J. Chem. 2022, 46, 7638–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Alam, J.; Ali, F.A.A.; Alhoshan, M. A highly permeable zinc-based MOF/polyphenylsulfone composite membrane with elevated antifouling properties. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5231–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, H.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, G.; Cui, M. Hydrophilic modification and anti-fouling properties of PVDF ultrafiltration membrane via blending of nano-particle MIL-101 MOFs. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostructures (DJNB) 2021, 16, 515–526. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadipouya, S.; Mousavi, S.A.; Shokrgozar, A.; Mousavi, D.V. Improving dye removal and antifouling performance of polysulfone nanofiltration membranes by incorporation of UiO-66 metal-organic framework. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Li, J.; Fan, M.; Han, M.; Liu, Z.; Li, Z.; Kong, F. Metal organic framework UiO-66 incorporated ultrafiltration membranes for simultaneous natural organic matter and heavy metal ions removal. Environ. Res. 2022, 208, 112651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadnezhad, F.; Feyzi, M.; Zinadini, S. A novel Ce-MOF/PES mixed matrix membrane; synthesis, characterization and antifouling evaluation. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 71, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasekaran, G.; Balaguru, S.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Das, D.B. Removal of hazardous material from wastewater by using metal organic framework (MOF) embedded polymeric membranes. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2019, 54, 434–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinothkumar, K.; Jyothi, M.S.; Lavanya, C.; Sakar, M.; Valiyaveettil, S.; Balakrishna, R.G. Strongly co-ordinated MOF-PSF matrix for selective adsorption, separation and photodegradation of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 132561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, F.; Zinadini, S.; Zinatizadeh, A.; Abbasi, A. TMU-5 metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as a novel nanofiller for flux increment and fouling mitigation in PES ultrafiltration membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 194, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Tang, H.; Liu, D.; Huang, T.; Zhu, L. Application of ZIF-67 as a crosslinker to prepare sulfonated polysulfone mixed-matrix membranes for enhanced water permeability and separation properties. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yin, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Huang, T.; Fang, S.; Zhu, K.; Xie, Z. Fabrication of ZIF-67@PVDF ultrafiltration membrane with improved antifouling and separation performance for dye wastewater treatment via sulfate radical enhancement. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 279, 119755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, F.; Nxumalo, E.; Krause, R.; Hoek, E.; Mamba, B. Application of polysulfone/cyclodextrin mixed-matrix membranes in the removal of natural organic matter from water. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2014, 67, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austria, H.F.; Subrahmanya, T.M.; Setiawan, O.; Widakdo, J.; Chiao, Y.-H.; Hung, W.-S.; Wang, C.-F.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. A review on the recent advancements in graphene-based membranes and their applications as stimuli-responsive separation materials. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 21510–21531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Nithya, D.; Doraisamy, M. Exploring the effects of graphene oxide concentration on properties and antifouling performance of PEES/GO ultrafiltration membranes. High Perform. Polym. 2018, 30, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Al-Juhani, A.A.; Al-Hamouz, O.C.; Laoui, T.; Khan, Z.; Atieh, M.A. Preparation and properties of nanocomposite polysulfone/multi-walled carbon nanotubes membranes for desalination. Desalination 2015, 367, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.; Murthy, C.N. Studies on the porosity control of MWCNT/polysulfone composite membrane and its effect on metal removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 437, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.-J.; Maggay, I.V.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chen, W.; Chang, Y.; Hu, C.; Venault, A. Removal of tetracycline by a photocatalytic membrane reactor with MIL-53 (Fe)/PVDF mixed-matrix membrane. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 451, 138990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, Y. Novel superhydrophilic antifouling PVDF-BiOCl nanocomposite membranes fabricated via a modified blending-phase inversion method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, H.; Zeinalipour, N.; Kerachian, M.A.; Heidari, A.A. Preparation of high-performance PVDF mixed matrix membranes incorporated with PVDF-g-PMMA copolymer and GO@SiO2 nanoparticles for dye rejection applications. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 46, 102560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri, K.S.; Nair, A.K.; Babu, P.J. Synthesis and characterization of silver decorated polysulfone/cellulose acetate hybrid ultrafiltration membranes using functionalized TiO2 nanoparticles. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 76, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisay, E.J.; Veréb, G.; Pap, Z.; Gyulavári, T.; Ágoston, Á.; Kopniczky, J.; Hodúr, C.; Arthanareeswaran, G.; Arumugam, G.K.S.; László, Z. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic PVDF-TiO2/CNT/BiVO4 hybrid nanocomposite ultrafiltration membrane for dairy wastewater treatment. Chemosphere 2022, 307, 135589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, H.; Zeinalipour, N.; Heidari, A.A. Fabrication of PVDF mixed matrix nanofiltration membranes incorporated with TiO2 nanoparticles and an amphiphilic PVDF-g-PMMA copolymer. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, e52740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhou, S.; Li, M.; Xue, A.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, W.; Xing, W. PVDF mixed matrix ultrafiltration membrane incorporated with deformed rebar-like Fe3O4–palygorskite nanocomposites to enhance strength and antifouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, M. Preparation of Synthetic Membranes. In Basic Principles of Membrane Technology; Mulder, M., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1996; pp. 71–156. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-M.; Venault, A.; Lai, J.-Y. Chapter 2—Fundamentals of nonsolvent-induced phase separation. In Hollow Fiber Membranes; Chung, T.-S., Feng, Y., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 13–56. [Google Scholar]
- Venault, A.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wu, J.-R.; Yang, H.-S.; Chang, Y.; Lai, J.-Y.; Aimar, P. Low-biofouling membranes prepared by liquid-induced phase separation of the PVDF/polystyrene-b-poly (ethylene glycol) methacrylate blend. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.; Hegab, H.M.; Nassar, L.; Wadi, V.S.; Naddeo, V.; Yousef, A.F.; Banat, F.; Hasan, S.W. Asymmetrical ultrafiltration membranes based on polylactic acid for the removal of organic substances from wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 45, 102510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nainar, M.G.; Jayaraman, K.; Meyyappan, H.K.; Miranda, L.R. Antifouling properties of Poly(vinylidene fluoride)-incorporated cellulose acetate composite ultrafiltration membranes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 2248–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Jumao-as-Leyba, A.J.; Yang, Z.-R.; Carretier, S.; Chang, Y. Formation mechanisms of low-biofouling PVDF/F127 membranes prepared by VIPS process. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 62, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Wu, J.-R.; Chang, Y.; Aimar, P. Fabricating hemocompatible bi-continuous PEGylated PVDF membranes via vapor-induced phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 470, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mat Nawi, N.I.; Chean, H.M.; Shamsuddin, N.; Bilad, M.R.; Narkkun, T.; Faungnawakij, K.; Khan, A.L. Development of hydrophilic PVDF membrane using vapour induced phase separation method for produced water treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Venault, A.; Chang, Y. Facile zwitterionization of polyvinylidene fluoride microfiltration membranes for biofouling mitigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 648, 120348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.-L.; Wang, D.-M.; Deratani, A.; Quémener, D.; Bouyer, D.; Lai, J.-Y. Insight into the preparation of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes by vapor-induced phase separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 361, 154–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Venault, A.; Wang, S.; Shen, Q.; Jia, Y.; Fang, C.; Kato, N.; Chang, Y.; Matsuyama, H. One-step entrapment of a PS-PEGMA amphiphilic copolymer on the outer surface of a hollow fiber membrane via TIPS process using triple-orifice spinneret. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 638, 119712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-K.; Lang, W.-Z.; Miao, W.; Yan, X.; Guo, Y.-J. Preparation and properties of PVDF/SiO2@GO nanohybrid membranes via thermally induced phase separation method. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 511, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, C.; Zheng, J. Surface hydration: Principles and applications toward low-fouling/nonfouling biomaterials. Polymer 2010, 51, 5283–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, C.; Song, X.; Su, B.; Mandal, B.; Prasad, B.; Gao, X.; Gao, C. Graphene quantum dots-doped thin film nanocomposite polyimide membranes with enhanced solvent resistance for solvent-resistant nanofiltration. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6527–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wu, T.; Shi, J.; Teng, K.; Wang, W.; Ma, M.; Li, J.; Qian, X.; Li, C.; Fan, J. Photocatalytic antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes based on synergy of graphene oxide and TiO2 for water treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.F.; Banerjee, P.; Mayes, A.M. Preparation of Protein-Resistant Surfaces on Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Membranes via Surface Segregation. Macromolecules 1999, 32, 1643–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirilargani, M.; Sabetghadam, A.; Mohammadi, T. Polyethersulfone/polyacrylonitrile blend ultrafiltration membranes with different molecular weight of polyethylene glycol: Preparation, morphology and antifouling properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-J.; Song, H.-M.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z.-X.; Zhao, C.-T.; Xue, Q.-J.; Guo, X.-P. Microstructures and performances of pegylated polysulfone membranes from an in situ synthesized solution via vapor induced phase separation approach. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 515, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Venault, A.; Huang, Y.-T.; Wu, B.-W.; Chou, C.-J.; Ishihara, K.; Chang, Y. Toward Antibiofouling PVDF Membranes. Langmuir 2019, 35, 6782–6792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Aini, H.N.; Galeta, T.A.; Chang, Y. Using the Dimethyl Sulfoxide Green Solvent for the Making of Antifouling PEGylated Membranes by the Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Process. J. Membr. Sci. Lett. 2022, 2, 100025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanis-Kanbur, M.B.; Tamilselvam, N.R.; Chew, J.W. Membrane fouling mechanisms by BSA in aqueous-organic solvent mixtures. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2022, 108, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramwit, P. Introduction to biomaterials for wound healing. In Wound Healing Biomaterials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, M.; Bahrami, S.; Ravari, S.B.; Zangabad, P.S.; Mirshekari, H.; Bozorgomid, M.; Shahreza, S.; Sori, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Albumin nanostructures as advanced drug delivery systems. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1609–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.-F.; Zhu, L.-P.; Jiang, J.-H.; Yi, Z.; Zhu, B.-K.; Xu, Y.-Y. Enhancing the antifouling and antimicrobial properties of poly (ether sulfone) membranes by surface quaternization from a reactive poly (ether sulfone) based copolymer additive. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 13952–13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chiang, C.-H.; Chang, H.-Y.; Hung, W.-S.; Chang, Y. Graphene oxide/PVDF VIPS membranes for switchable, versatile and gravity-driven separation of oil and water. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zacharia, N.S. Surface functionalization for a nontextured liquid-infused surface with enhanced lifetime. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 5892–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Liu, C.; Xu, W.; Liu, G.; Xiao, K.; Zhao, H.-Z. Interpenetrating network nanoarchitectonics of antifouling Poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes for oil–water separation. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 31865–31876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Dasgupta, J.; Adhikari, U.; Sikder, J. Tuning permeation characteristics of cellulose acetate membrane embedded with raw and amine-functionalized silicon carbide nanoparticle for oil-water separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2021, 41, 102019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, F.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Masoumi, S.; Rostamizadeh, M. Oil-in-water emulsion separation by PVC membranes embedded with GO-ZnO nanoparticles. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Guzman, M.R.; Andra, C.K.A.; Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Dizon, G.V.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Lee, K.-R. Increased performance and antifouling of mixed-matrix membranes of cellulose acetate with hydrophilic nanoparticles of polydopamine-sulfobetaine methacrylate for oil-water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K. Blood-Compatible Surfaces with Phosphorylcholine-Based Polymers for Cardiovascular Medical Devices. Langmuir 2019, 35, 1778–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, B.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Lin, S.; Shen, J. Facile surface modification of silicone rubber with zwitterionic polymers for improving blood compatibility. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2013, 33, 3865–3874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, T.; Lu, T.; Xie, Y.; Zhao, W.-F.; Sun, S.-D.; Zhao, C.-S. Zwitterionic polymer functionalization of polysulfone membrane with improved antifouling property and blood compatibility by combination of ATRP and click chemistry. Acta Biomater. 2016, 40, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Mao, L.; Matindi, C.N.; Liu, G.; He, J.; Cui, Z.; Ma, X.; Fang, K.; Wu, B.; Mamba, B.B. Tailoring the micro-structure of PVC/SMA-g-PEG blend ultrafiltration membrane with simultaneously enhanced hydrophilicity and toughness by in situ reaction-controlled phase inversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 653, 120545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elakkiya, S.; Arthanareeswaran, G. Evaluation of membrane tailored with biocompatible halloysite–polyaniline nanomaterial for efficient removal of carcinogenic disinfection by–products precursor from water. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lan, Y.; Yang, K.; Wang, R.; Cheng, L.; Gao, C. Antifouling modification of PVDF membranes via in situ mixed-charge copolymerization and TiO2 mineralization. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Tang, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, C. Highly dual antifouling and antibacterial ultrafiltration membranes modified with silane coupling agent and capsaicin-mimic moieties. Polymers 2020, 12, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, W.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Li, J. EVOH in situ fibrillation and its effect of strengthening, toughening and hydrophilic modification on PVDF hollow fiber microfiltration membrane via TIPS process. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 5971–5987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.-J.; Song, H.-M.; Wang, G.; Zeng, Z.-X.; Xue, Q.-J. Dual stimuli-responsive polysulfone membranes with interconnected networks by a vapor-liquid induced phase separation strategy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 531, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zheng, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, X.; Zhu, J.; He, C. Low-fouling PES membranes fabricated via in situ copolymerization mediated surface zwitterionicalization. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 2248–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Xu, J.; Tang, Y.; Hou, J.; Yu, L.; Gao, C. A novel long-lasting antifouling membrane modified with bifunctional capsaicin-mimic moieties via in situ polymerization for efficient water purification. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 10352–10362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, M.; Liu, J. Fabrication of a mixed matrix membrane with in situ synthesized quaternized polyethylenimine nanoparticles for dye purification and reuse. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 690–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Wu, M.B.; Xiang, T.; Wang, R.; Sun, S.D.; Zhao, C.S. Antifouling and blood-compatible poly (ether sulfone) membranes modified by zwitterionic copolymers via In situ crosslinked copolymerization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, M.; Liu, F.; Xue, L. Persistently hydrophilic microporous membranes based on in situ cross-linking. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 474, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Pang, R.; Li, J.; Sun, X.; Shen, J.; Han, W.; Wang, L. In situ formation of Ag nanoparticles in PVDF ultrafiltration membrane to mitigate organic and bacterial fouling. Desalination 2013, 324, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-Y.; Xu, Z.-L.; Yang, H.; Wei, Y.-M.; Wu, W.-Z. Fabrication and characterization of PVDF membranes via an in situ free radical polymerization method. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 97, 296–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Hydrophilicity and crystallization behavior of PVDF/PMMA/TiO2 (SiO2) composites prepared by in situ polymerization. J. Polym. Res. 2012, 19, 9862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Liu, F.; Xue, L. Hydrophilic Poly(vinylidene fluoride)(PVDF) membrane by in situ polymerisation of 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) and micro-phase separation. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 9131–9137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shi, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, H. Preparation of hydrophilic PVDF/PPTA blend membranes by in situ polycondensation and its application in the treatment of landfill leachate. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 346, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Mu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Na, R.; Xu, W.; Wang, G. Mixed matrix membranes decorated with in situ self-assembled polymeric nanoparticles driven by electrostatic interaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 7859–7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-P.; Yu, Y.-H.; Lang, W.-Z.; Yan, X.; Guo, Y.-J. Hydrophilic modification of polyvinyl chloride hollow fiber membranes by silica with a weak in situ sol–gel method. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 13733–13742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patala, R.; Mahlangu, O.T.; Nyoni, H.; Mamba, B.B.; Kuvarega, A.T. In Situ Generation of Fouling Resistant Ag/Pd Modified PES Membranes for Treatment of Pharmaceutical Wastewater. Membranes 2022, 12, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.-h.; Li, Y.-m.; Gu, G.-w. Chemical composition of organic matters in domestic wastewater. Desalination 2010, 262, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulan, D.R.; Hamidah, U.; Komarulzaman, A.; Rosmalina, R.T.; Sintawardani, N. Domestic wastewater in Indonesia: Generation, characteristics and treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 32397–32414. [Google Scholar]
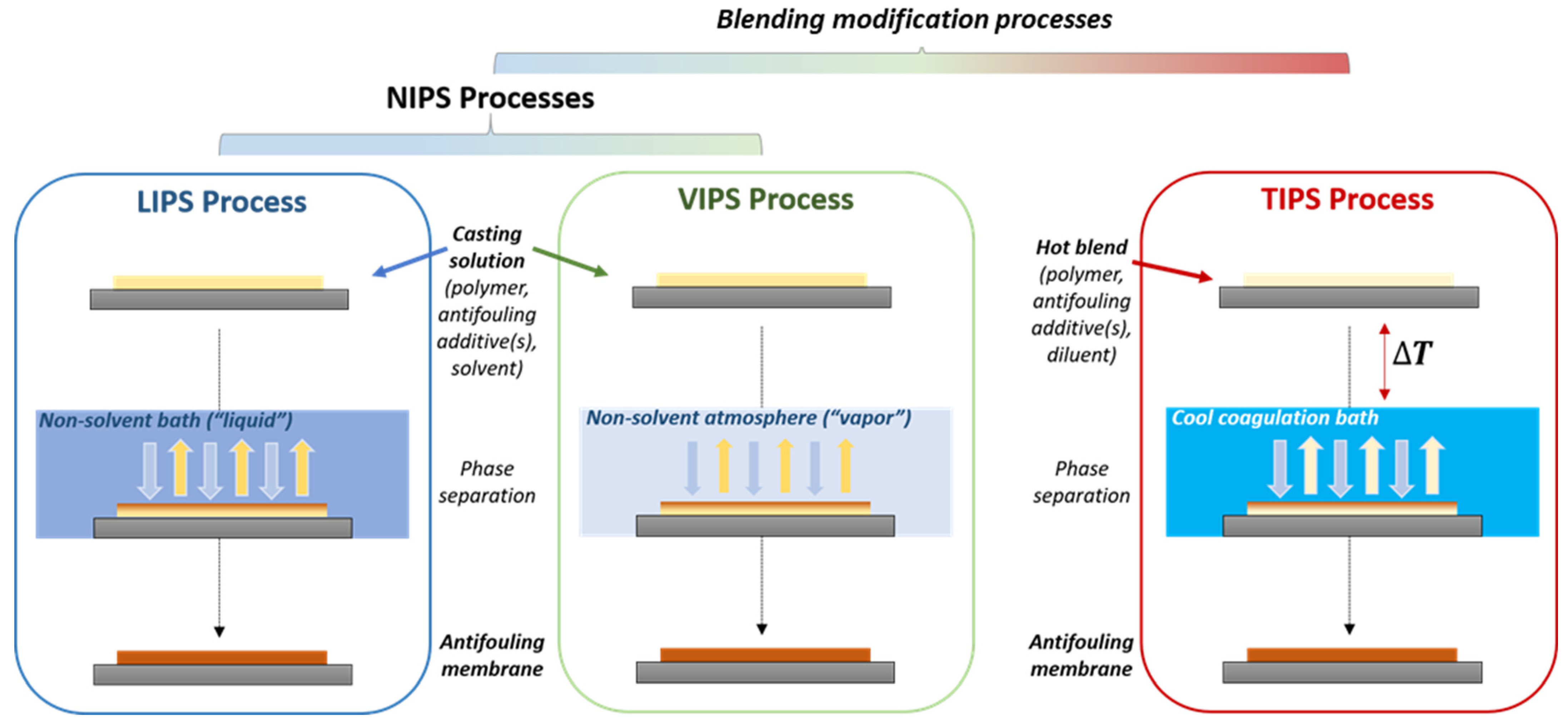
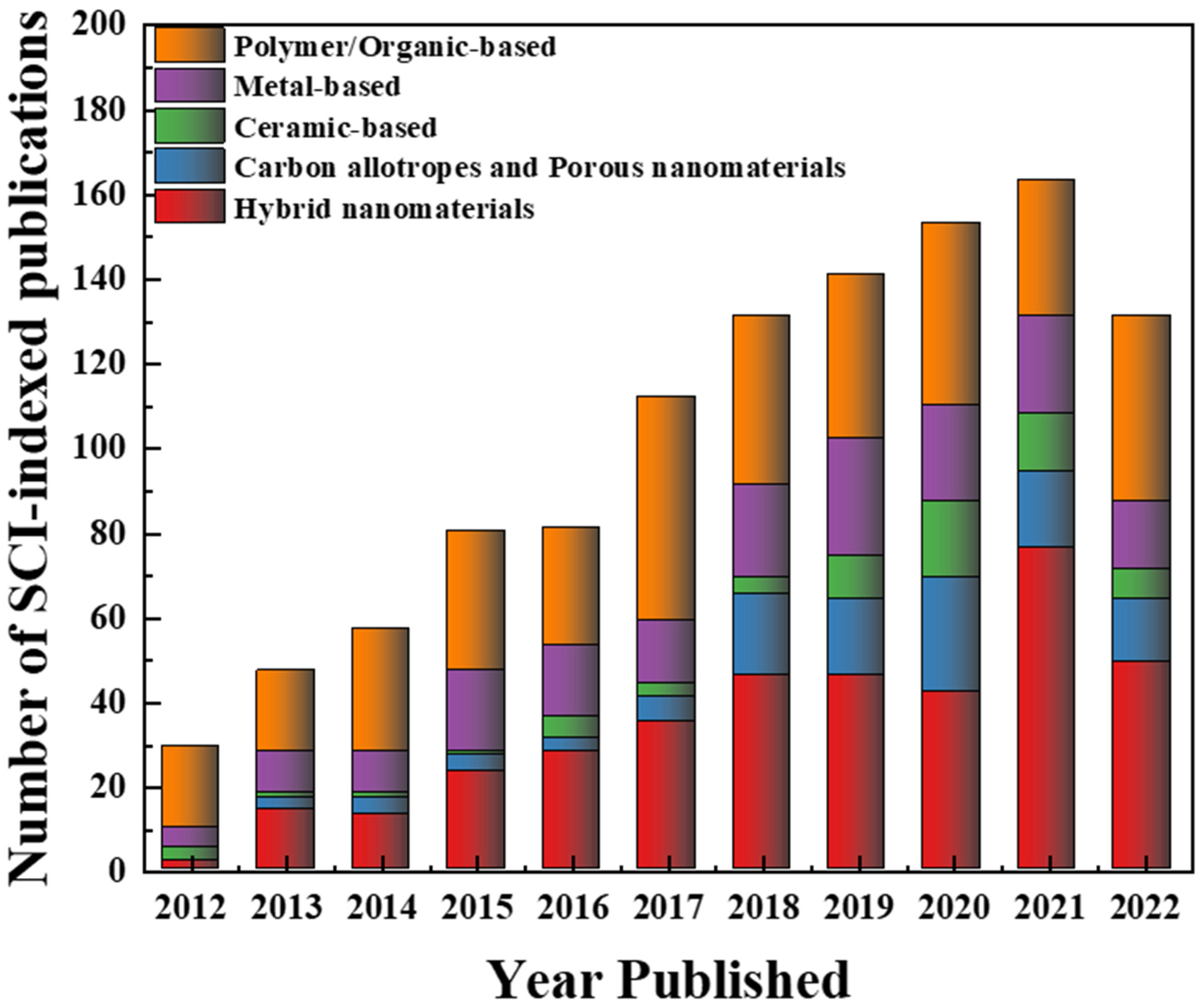
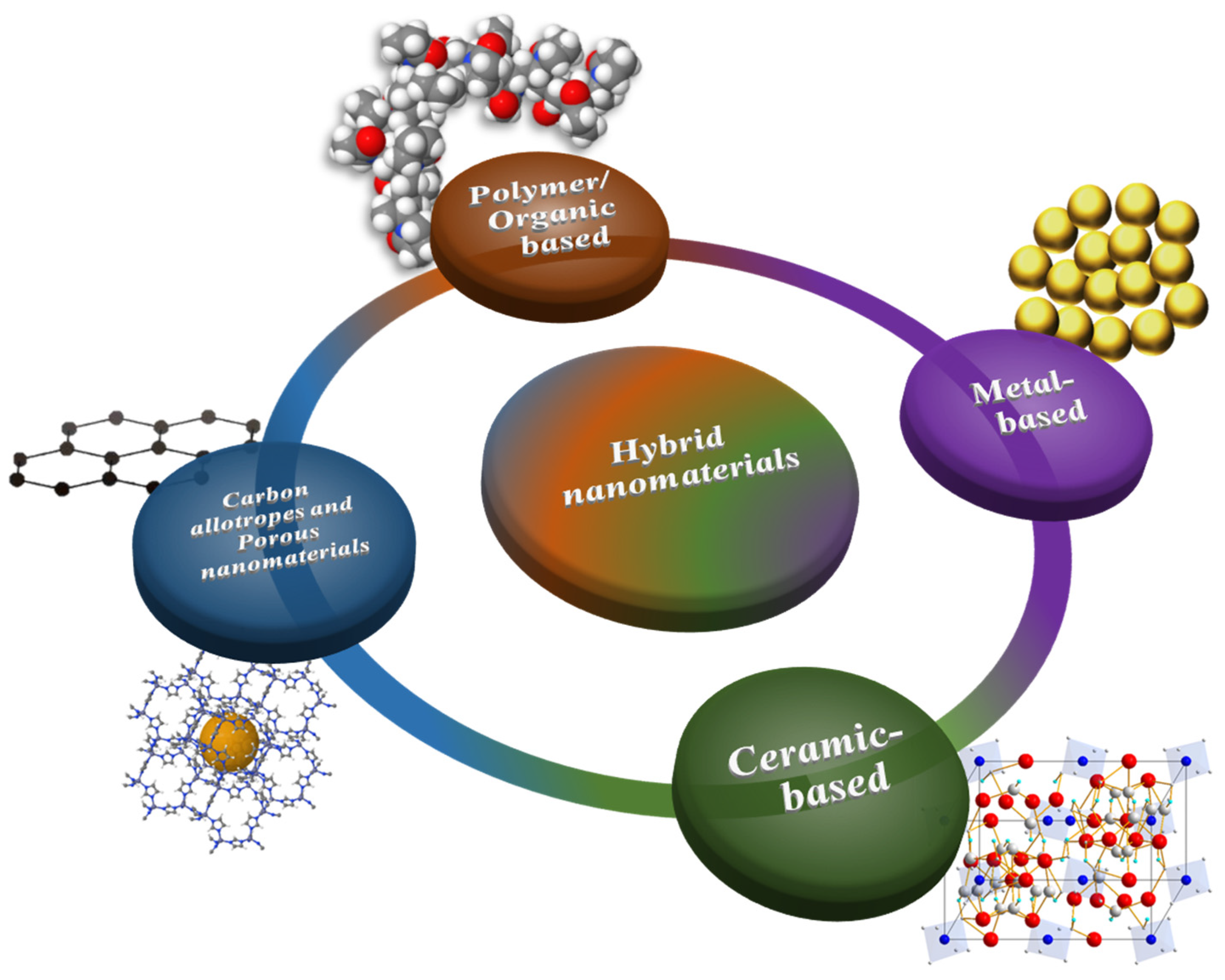
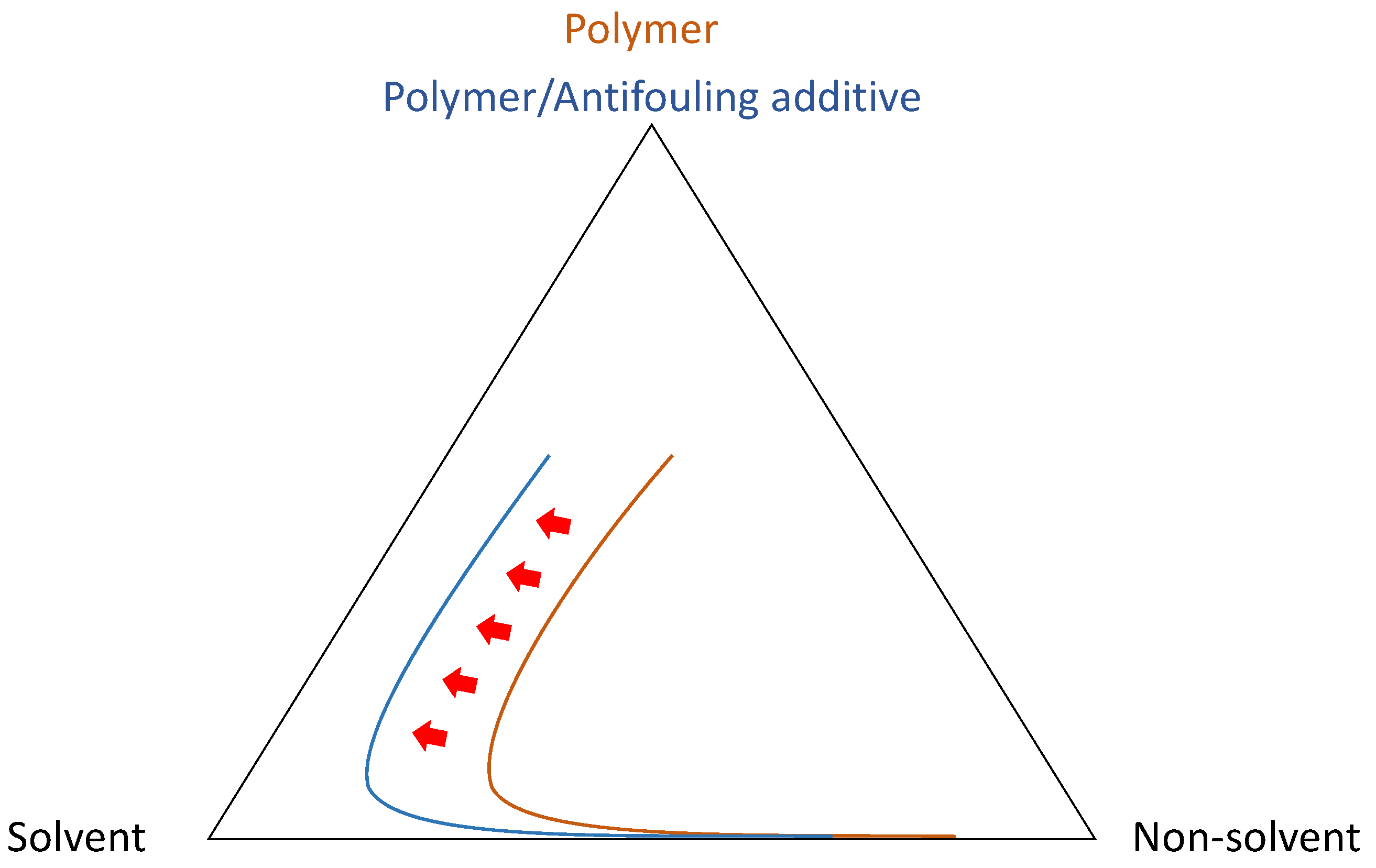
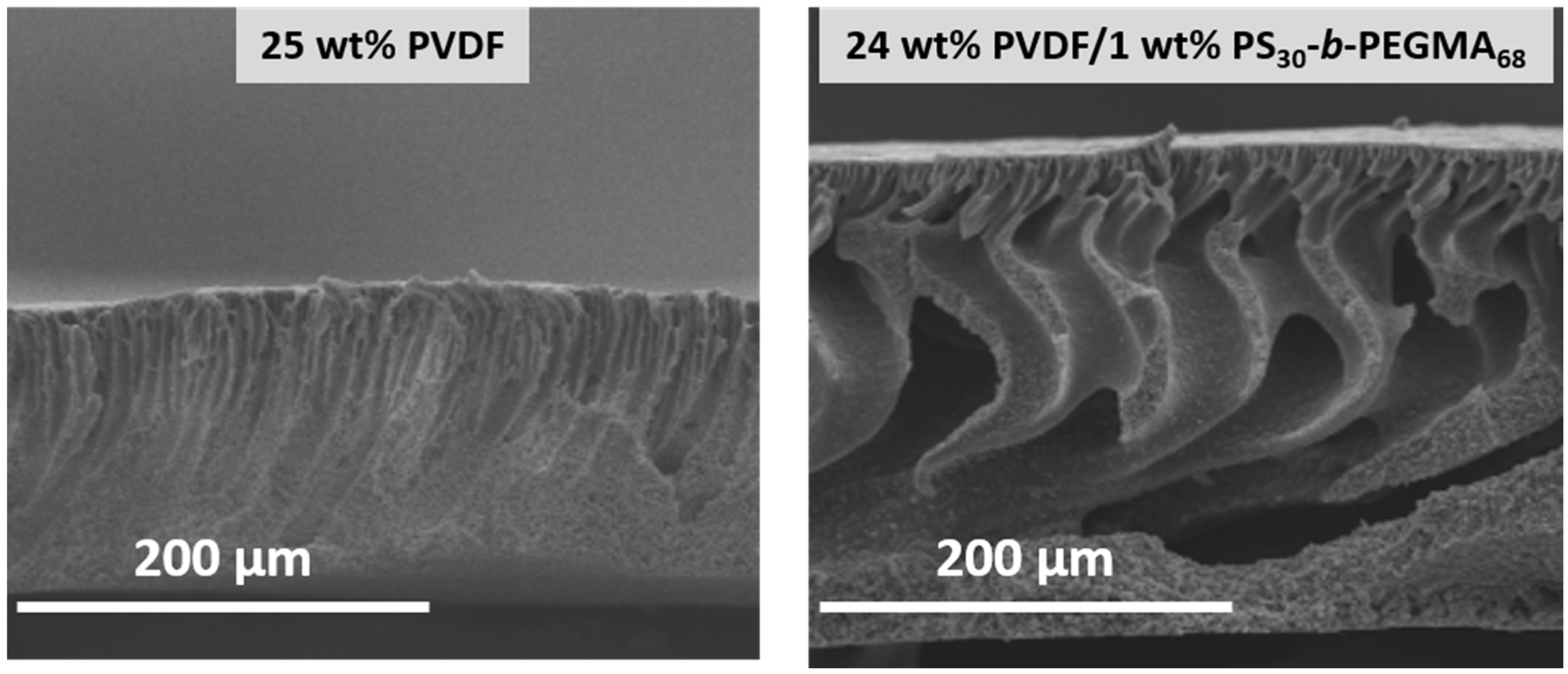
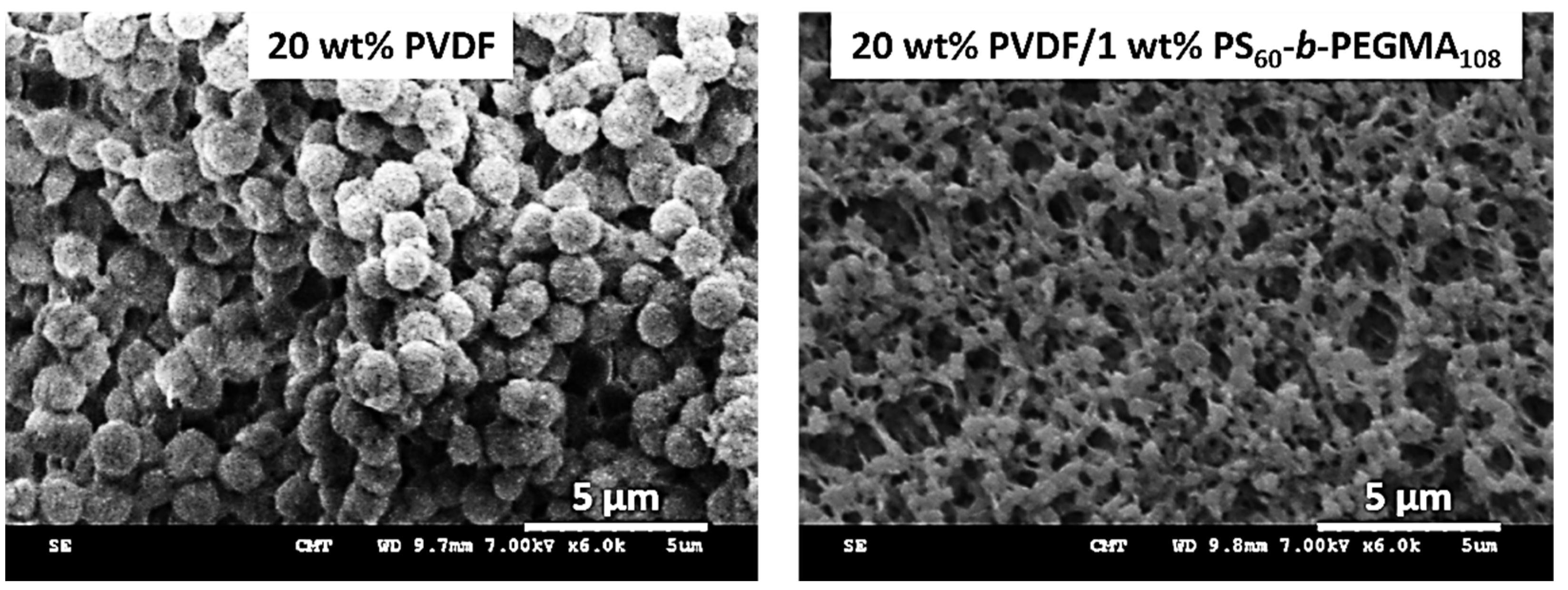
| Polymer/Organic-Based Additives | Materials | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Hydrophilic or amphiphilic | Poly(ethylene glycol) and its derivatives | [1,41,42,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93] |
| Poly(vinylpyrrolidone) | [43,94,95,96,97] | |
| Cellulose nanocrystals | [98,99,100,101,102,103] | |
| Poly(vinyl alcohol) | [104,105,106,107] | |
| Poly(acrylic acid) | [44,108,109] | |
| Polydopamine | [110,111,112,113,114] | |
| Zwitterion/amphiphilic zwitterion | [115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124] | |
| Amphiphilic copolymer | [95,125,126,127,128,129,130] | |
| Nature-derived biopolymers | Vanillin | [131,132,133] |
| Chitosan | [134,135,136,137,138] | |
| Chitin | [139,140] | |
| Lignin | [141,142] | |
| Lignocellulose | [143] | |
| Caramel | [144] | |
| Capsaicin | [145,146] | |
| Acacia gum | [147] | |
| Isocyanate | [148,149] | |
| Organic acids | [45,150,151] | |
| p-aramid | [152] |
| Metal-Based Additives | Materials | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Metallic | Ag and bio-derived Ag | [172,173,174,175,176] |
| Au | [177] | |
| Pd | [178] | |
| Biphasic metals | ZrO2 | [179,180,181,182] |
| ZnO | [183,184,185,186,187,188] | |
| TiO2 | [38,58,189,190,191,192,193,194,195,196,197,198,199,200,201,202,203] | |
| SiO2 | [204,205,206,207,208,209,210,211,212,213,214,215,216] | |
| CuO | [186,187,188,217,218] | |
| Fe2O3, Fe3O4 | [14,51,205,219,220,221,222,223,224,225,226,227] | |
| Al2O3 | [55,228,229] | |
| MXenes | [230] | |
| Bimetallic oxides | Fe-Mn oxide | [231] |
| Ceramic-Based Additives | Materials | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Nanoclay | Boehmite | [241,242,243] |
| Montmorillonite | [244,245,246,247] | |
| Bentonite | [63,248,249] | |
| Attapulgite | [250] | |
| Hydroxyappatite | [251,252,253,254] | |
| Goethite | [151] | |
| Cloisite 15A and 30B | [60,255,256] | |
| Pyrochlores | [255] | |
| SBA-15 | [257,258,259,260,261,262] | |
| Halloysite | [158,263,264,265,266,267,268,269,270,271,272,273,274,275,276,277,278,279] | |
| Layered double hydroxide | [64,65,280,281] |
| Carbon Allotropes and Porous Nanomaterials | Materials | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon allotropes | Carbon quantum dot | [286,287] |
| Nanodiamond | [72,288,289,290,291,292] | |
| Carbon nanotubes | [293,294,295,296,297,298,299,300,301,302,303] | |
| Graphene and its derivatives | [157,304,305,306,307,308,309,310,311,312,313,314,315,316,317,318,319,320,321,322,323,324,325,326,327,328] | |
| Porous nanomaterials | Metal-organic framework | [68,70,329,330,331,332,333,334,335,336,337,338,339,340] |
| Zeolites/ZIF | [73,341,342] | |
| Cyclodextrin | [343] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Geleta, T.A.; Maggay, I.V.; Chang, Y.; Venault, A. Recent Advances on the Fabrication of Antifouling Phase-Inversion Membranes by Physical Blending Modification Method. Membranes 2023, 13, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010058
Geleta TA, Maggay IV, Chang Y, Venault A. Recent Advances on the Fabrication of Antifouling Phase-Inversion Membranes by Physical Blending Modification Method. Membranes. 2023; 13(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeleta, Tesfaye Abebe, Irish Valerie Maggay, Yung Chang, and Antoine Venault. 2023. "Recent Advances on the Fabrication of Antifouling Phase-Inversion Membranes by Physical Blending Modification Method" Membranes 13, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010058
APA StyleGeleta, T. A., Maggay, I. V., Chang, Y., & Venault, A. (2023). Recent Advances on the Fabrication of Antifouling Phase-Inversion Membranes by Physical Blending Modification Method. Membranes, 13(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010058









