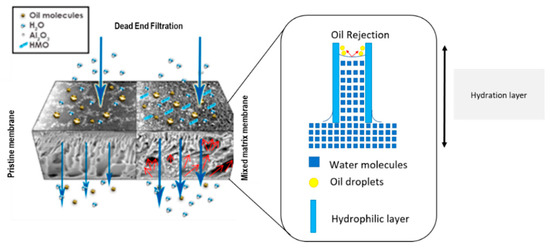
Xylem-Inspired Hydrous Manganese Dioxide/Aluminum Oxide/Polyethersulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Dope Solution
2.3. UF Mixed Matrix Membrane (MMM) Preparation
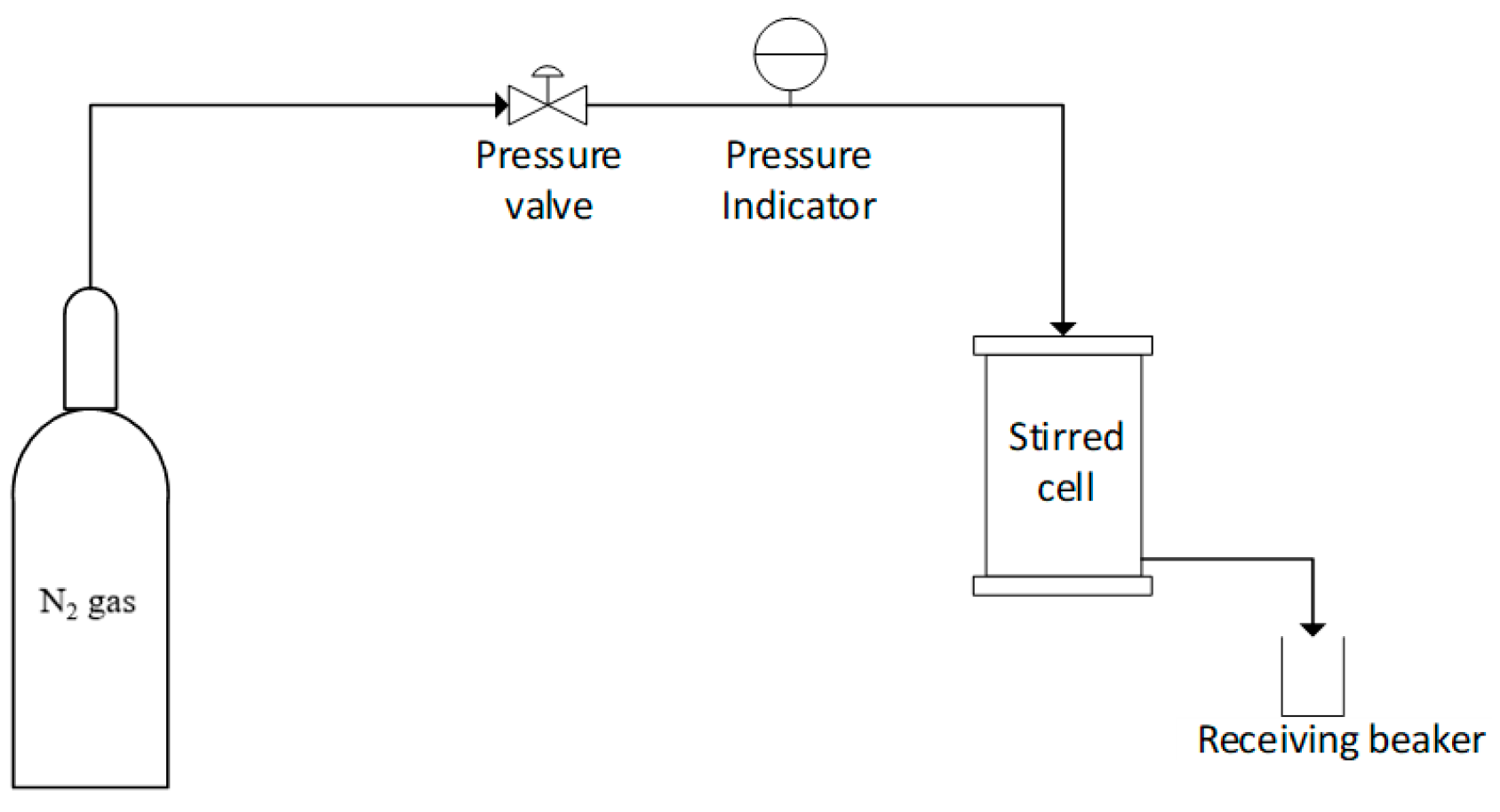
2.4. Membrane Separation Experiments
2.4.1. Synthetic Oily Wastewater Preparation
2.4.2. Ultrafiltration of Synthetic Oily Wastewater
2.5. Membrane Physicochemical Characterization
2.5.1. Membrane Morphology
2.5.2. Membrane Porosity and Pore Size Measurement
2.5.3. Membrane Wettability
2.5.4. Membrane Spectral Analysis
2.5.5. HMO Nanoparticle Diffraction Analysis
3. Results
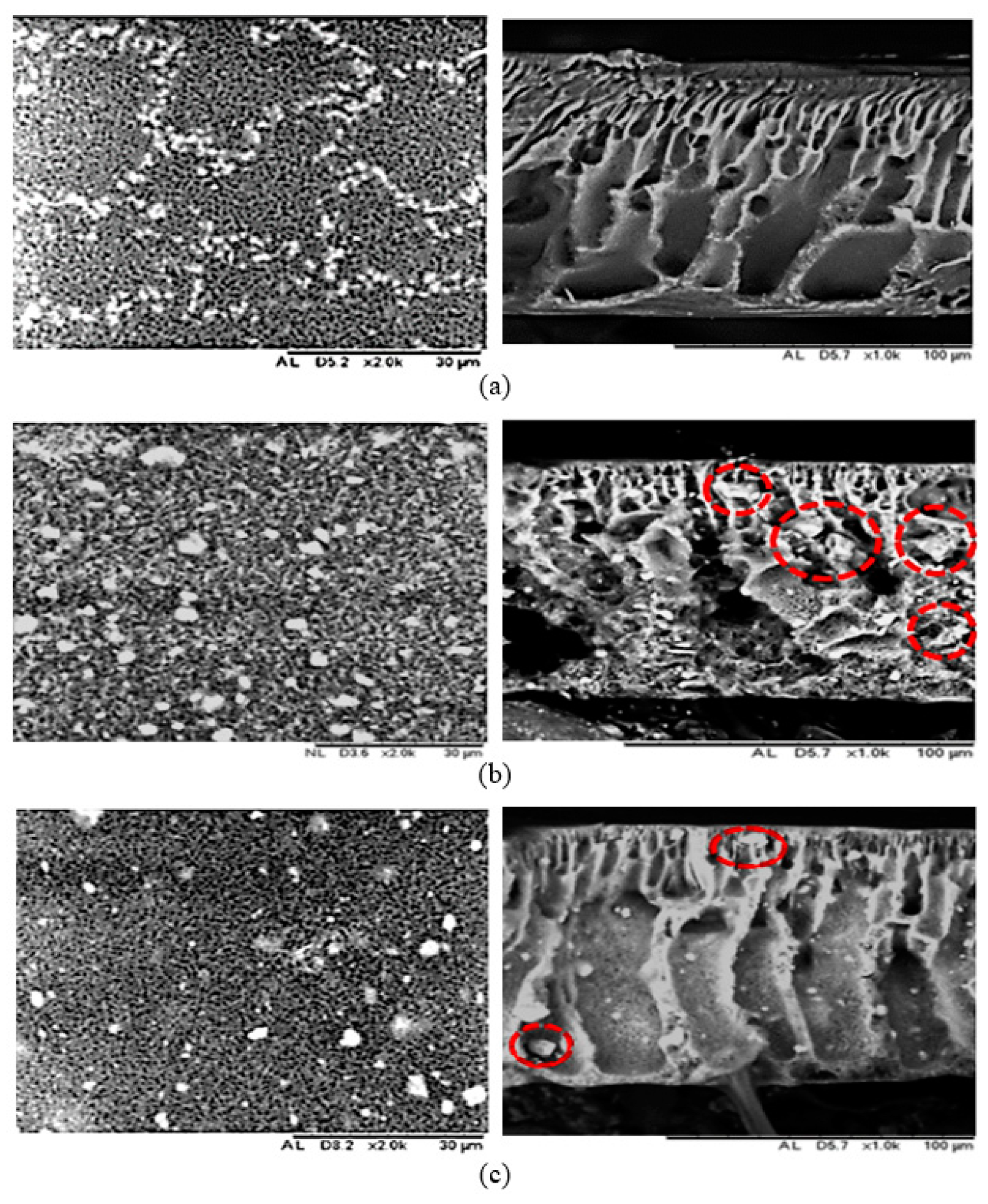
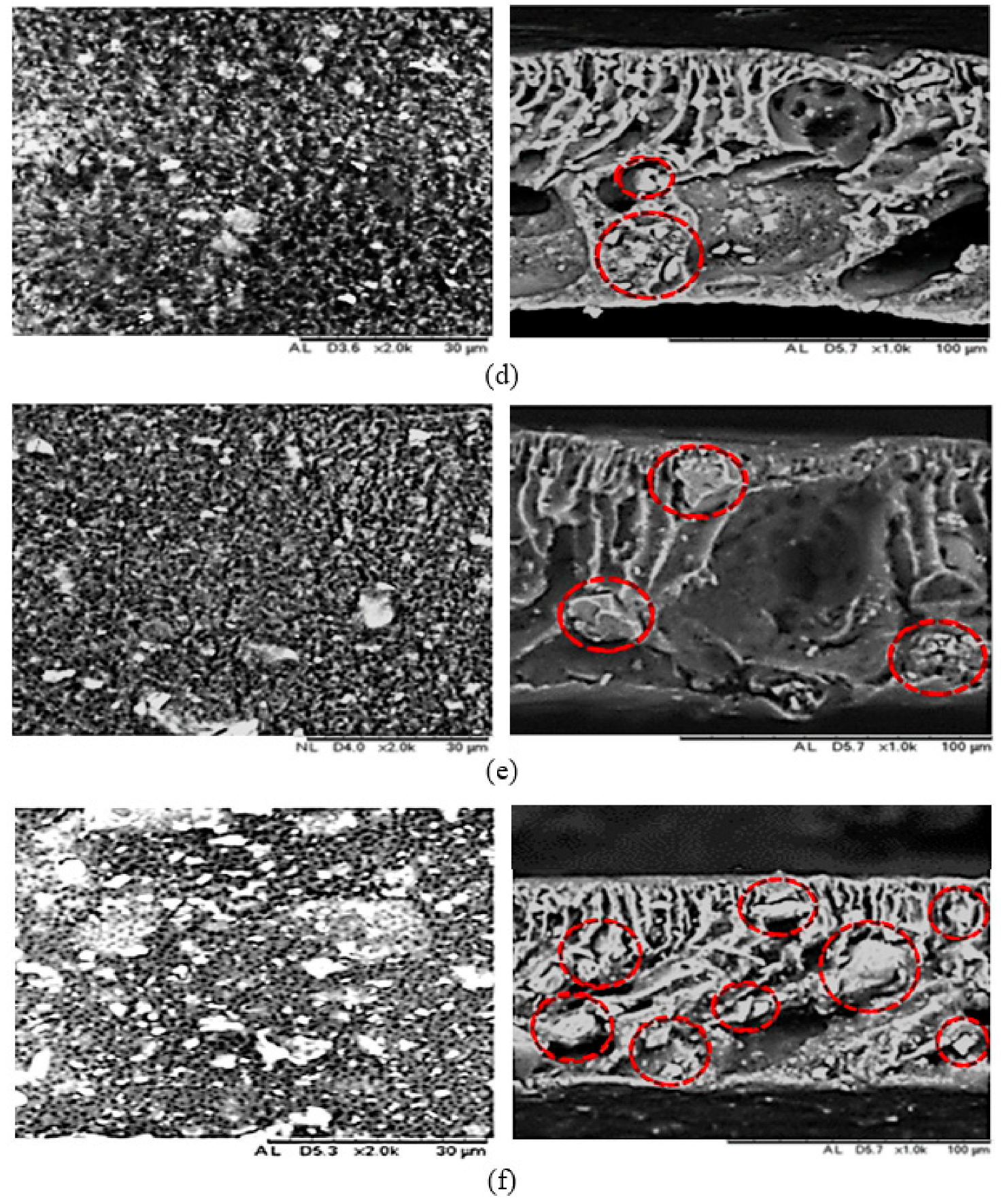
3.1. Membrane Morphological Analysis
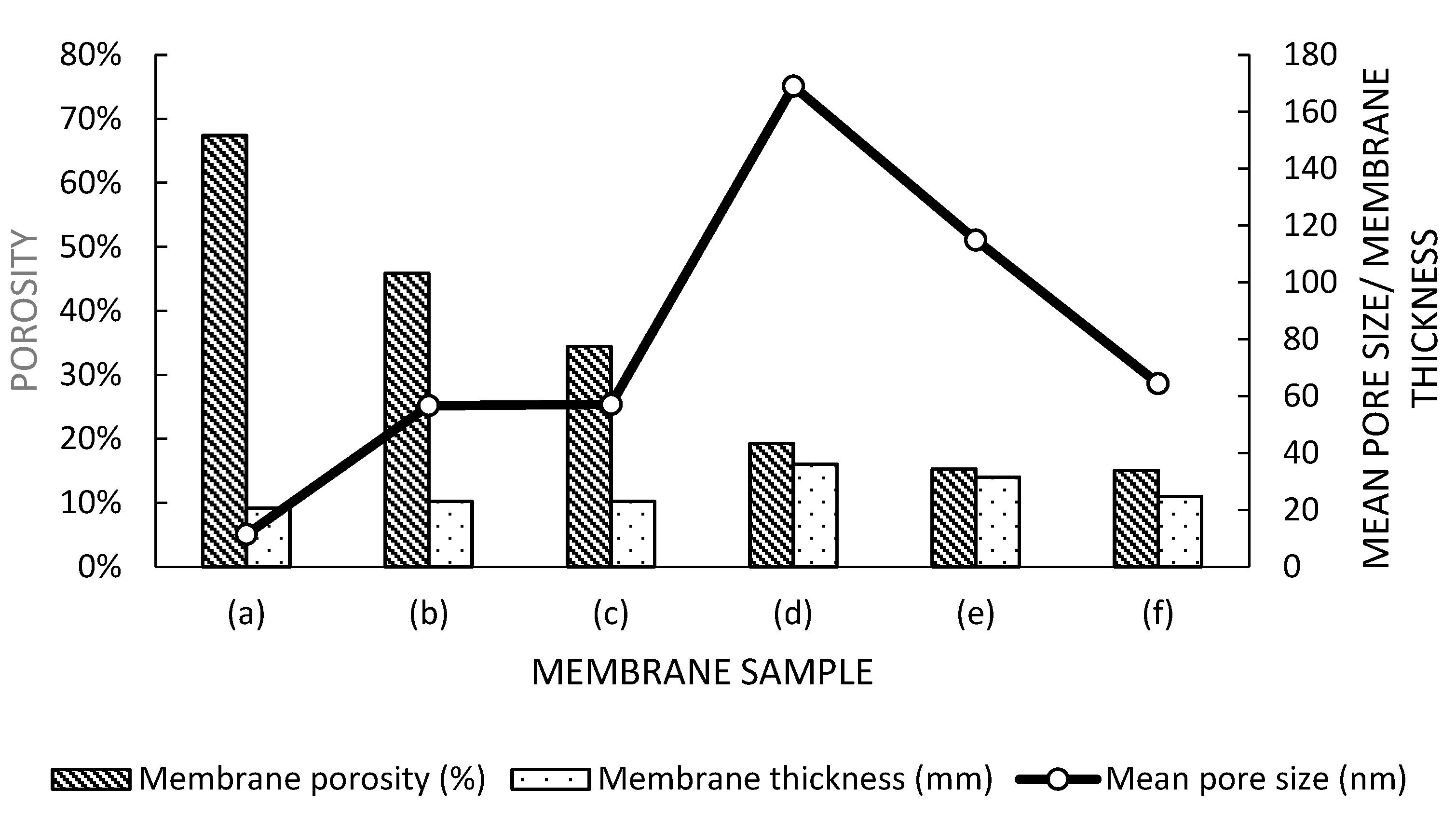
3.2. Porosity and Pore Size Analysis
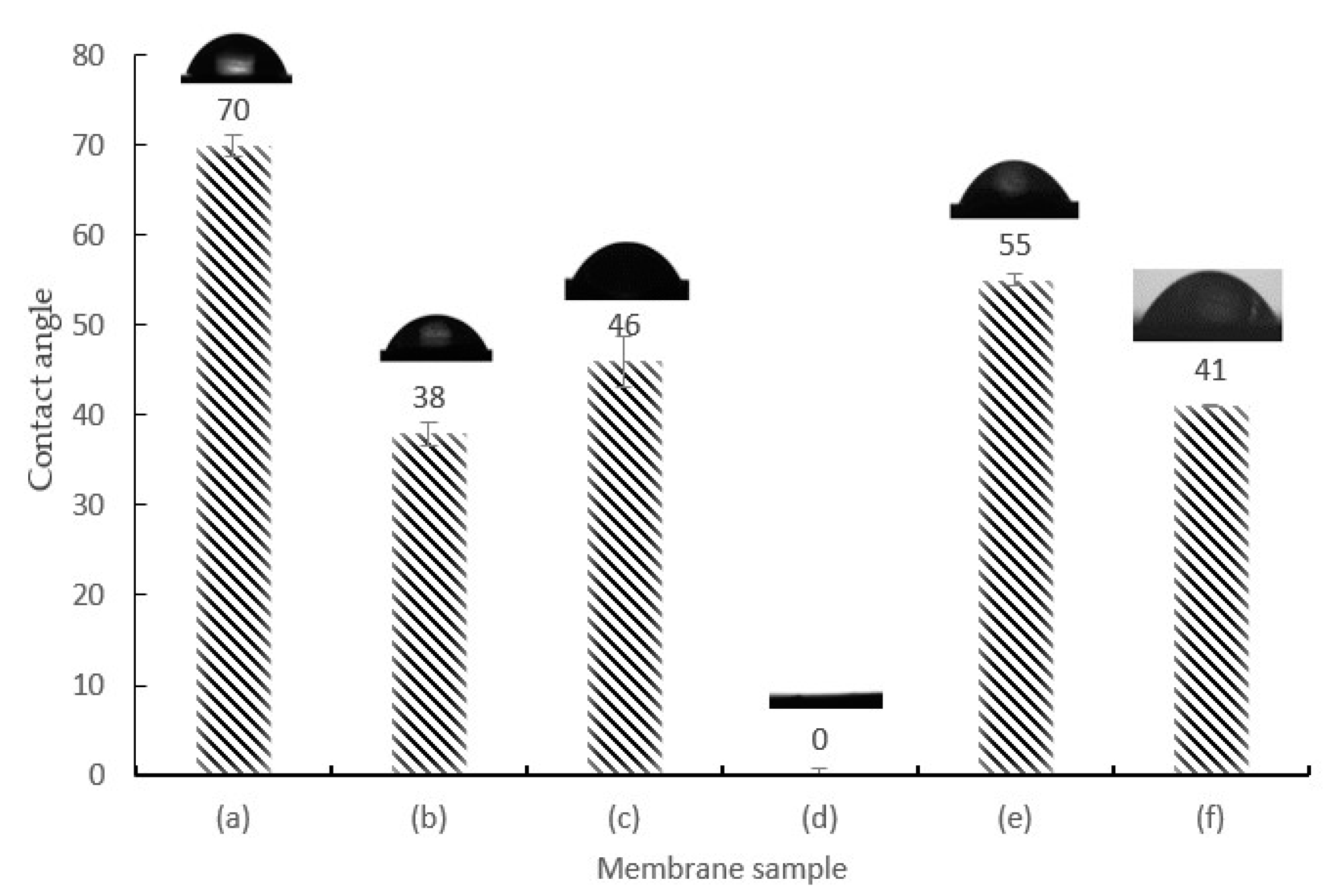
3.3. Wettability Analysis
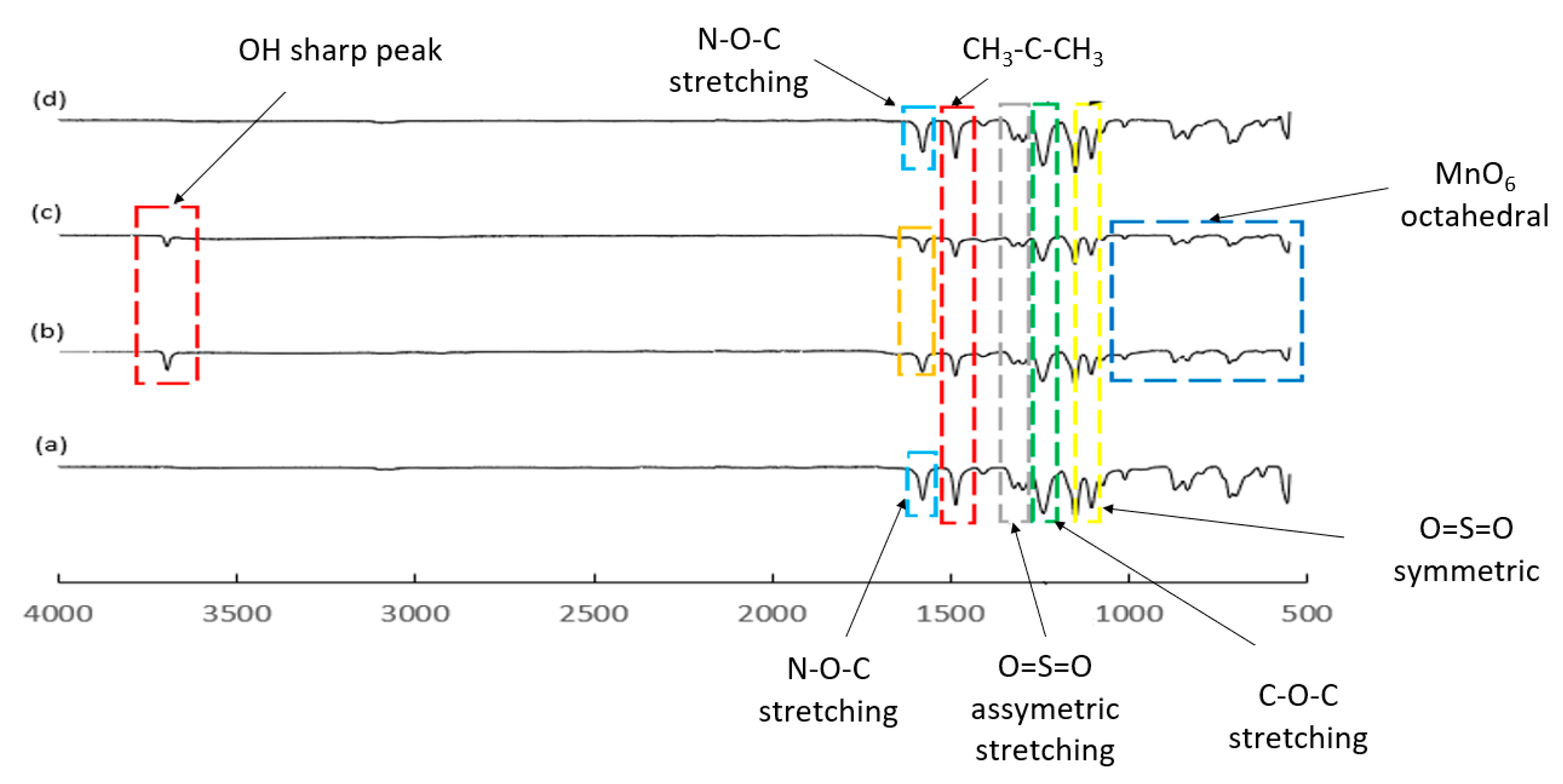
3.4. Spectral Analysis
3.5. Energy Dispersion X-ray (EDX) Analysis
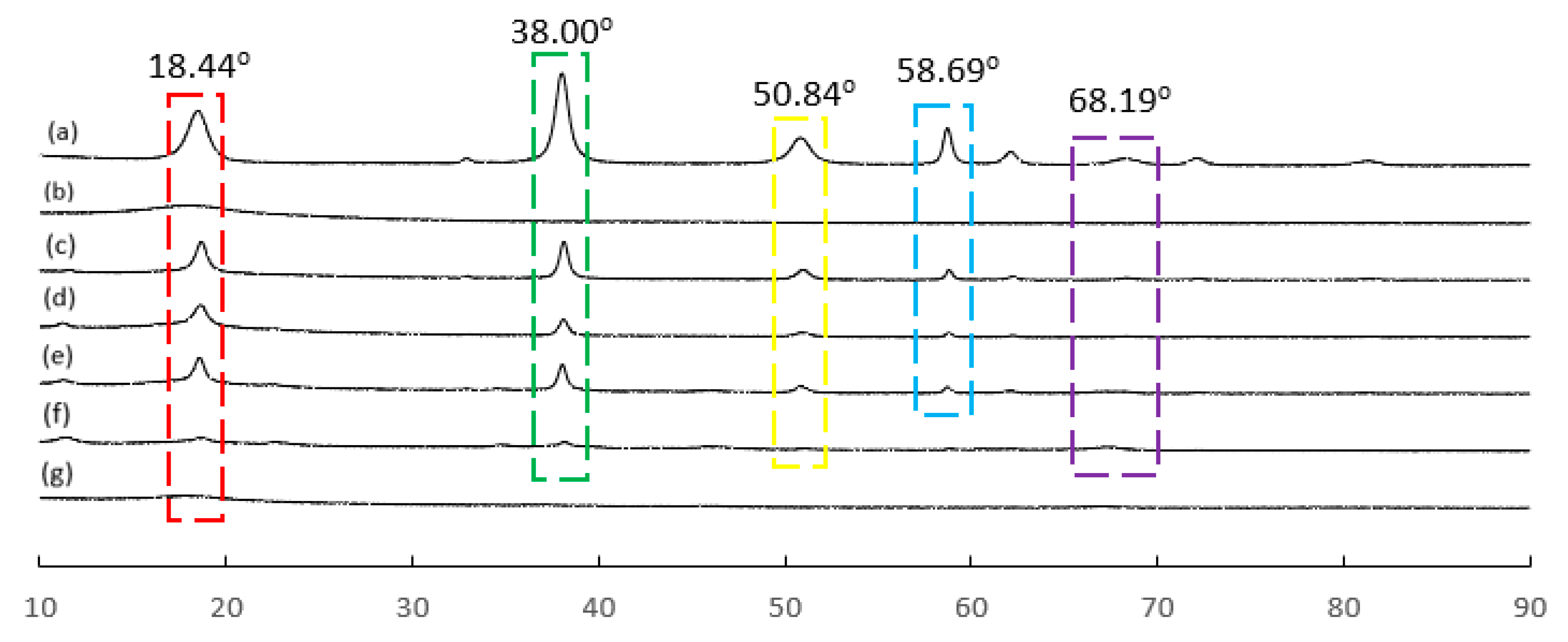
3.6. XRD Diffraction Analysis
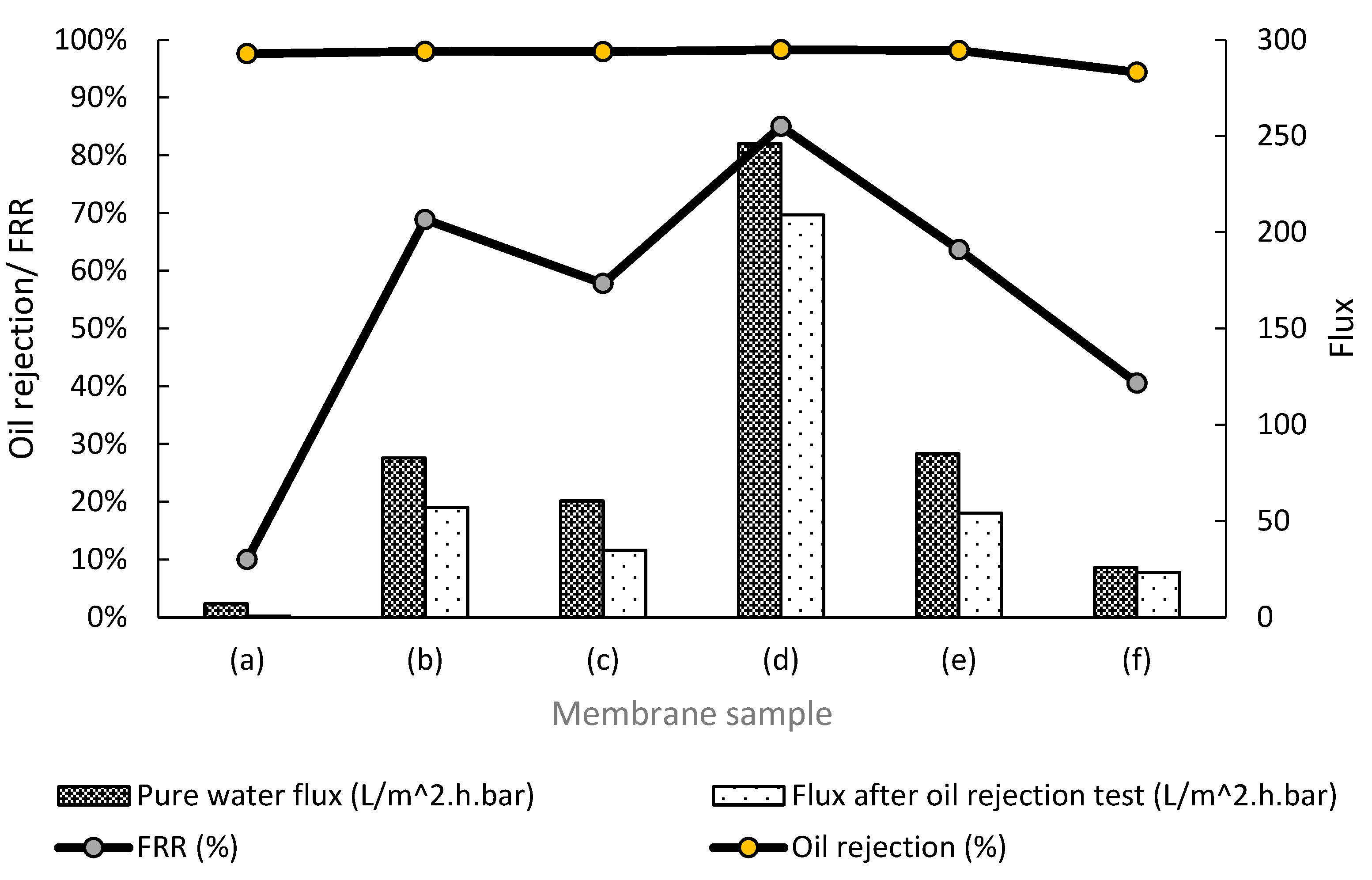
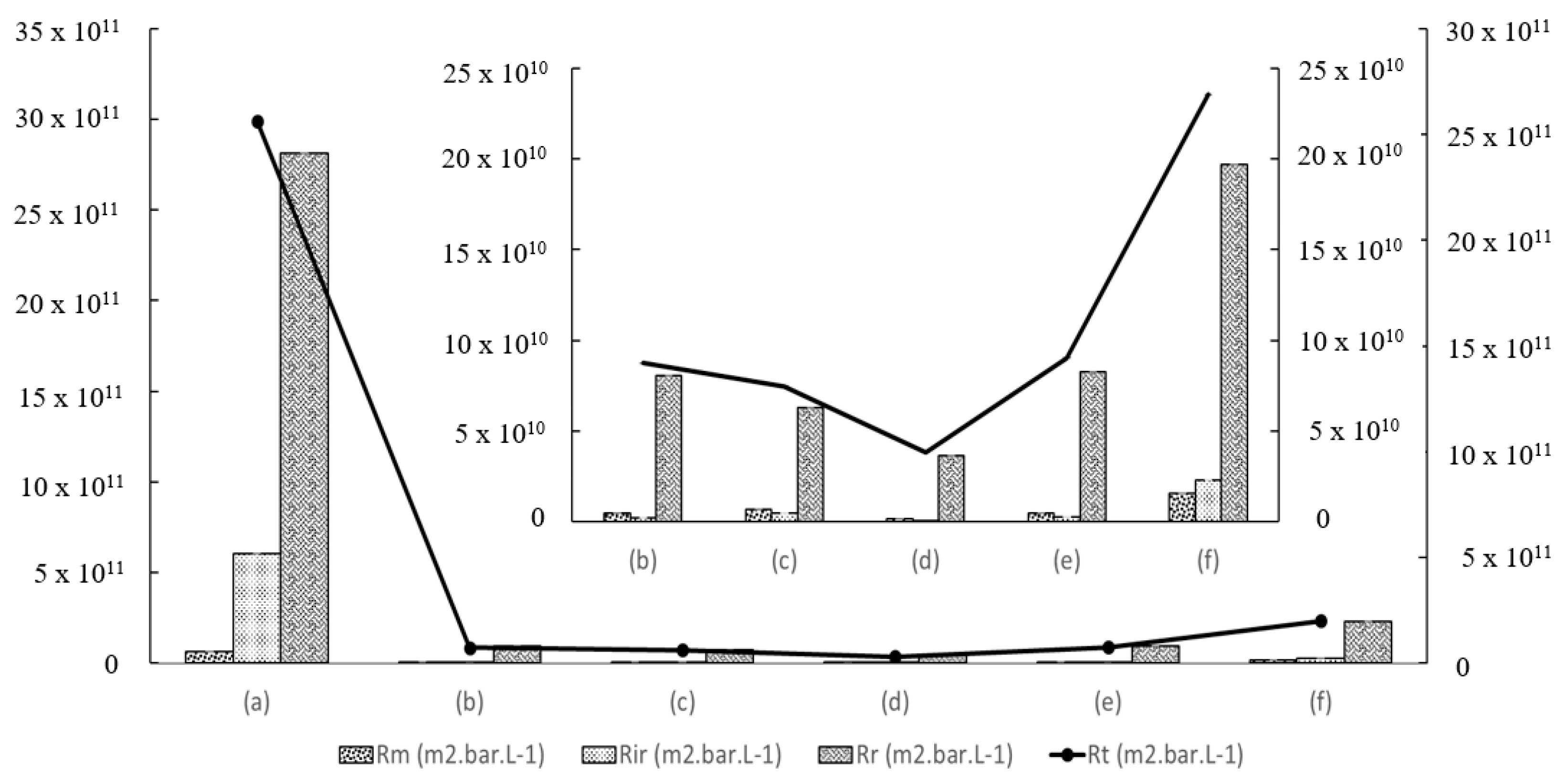
3.7. Membrane Separation Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kundu, P.; Mishra, I.M. Treatment and reclamation of hydrocarbon-bearing oily wastewater as a hazardous pollutant by different processes and technologies: A state-of-the-art review. Rev. Chem. Eng. 2019, 35, 73–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Koirala, N.; Mukherjee, D.; Lee, K.; Zhao, M. Tween 20 Stabilized Conventional Heavy Crude Oil-In-Water Emulsions Formed by Mechanical Homogenization. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Han, M.; He, F. A review of treating oily wastewater. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1913–S1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, J.; De Amorim, P.; Jos, I.; Costa, D.S. Oily Wastewater Treatment: Methods, Challenges, and Trends. Process 2022, 10, 743. [Google Scholar]
- Koga, T. Strict environmental requirements. Hydrocarb. Eng. 2008, 13, 55–58. [Google Scholar]
- Aloulou, H.; Attia, A.; Aloulou, W.; Chakraborty, S.; Baklouti, L.; Dammak, L. Statistical Simulation, a Tool for the Process Optimization of Oily Wastewater by Crossflow Ultrafiltration. 2022. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35877879/ (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Liu, S.H.; Tang, C.; She, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, H.; Wu, C. Poly(ionic liquid) copolymer blended polyvinyl chloride ultrafiltration membranes with simultaneously improved persistent hydrophilicity and pore uniformity. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 295, 121270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawi, N.S.M.; Lau, W.J.; Yusof, N.; Said, N.; Ismail, A. Enhancing Water Flux and Antifouling Properties of PES Hollow Fiber Membranes via Incorporation of Surface-functionalized Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 97, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhsan, S.N.W.; Yusof, N.; Nawi, N.I.M.; Bilad, M.R.; Shamsuddin, N.; Aziz, F.; Ismail, A.F. Halloysite nanotube-ferrihydrite incorporated polyethersulfone mixed matrix membrane: Effect of nanocomposite loading on the antifouling performance. Polymers 2021, 13, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.S.; Yusob, M.H.M.; Lau, W.J.; Gohari, R.J.; Emadzadeh, D.; Ismail, A.F.; Goh, P.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Arzhandi, M.R.D. Novel mixed matrix membranes incorporated with dual-nanofillers for enhanced oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 178, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi Gohari, R.; Halakoo, E.; Nazri, N.A.M.; Lau, W.J.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Improving performance and antifouling capability of PES UF membranes via blending with highly hydrophilic hydrous manganese dioxide nanoparticles. Desalination 2014, 335, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, T.S.; Jiang, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Kulprathipanja, S. Mixed matrix membranes (MMMs) comprising organic polymers with dispersed inorganic fillers for gas separation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2007, 32, 483–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraisammy, V.; Lai, G.S.; Kartohardjono, S.; Lau, W.J.; Chong, K.C.; Lai, S.O.; Hasbullah, H.; Ismail, A.F. Synthesis and Characterization of Mixed Matrix Membranes Incorporated with Hydrous Manganese Oxide Nanoparticles for Highly Concentrated Oily Solution Treatment. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, W.Y.; Ahmad, A.L.; Dina, N. Antifouling and antibacterial evaluation of ZnO/MWCNT dual nano fi ller polyethersulfone mixed matrix membrane. J. Environ. Manage. 2019, 249, 109358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohades Mojtahedi, Y.; Mehrnia, M.R.; Homayoonfal, M. Treatment Fabrication of Al2O3/PSf nanocomposite membranes: Efficiency comparison of coating and blending methods in modification of filtration performance. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6736–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maximous, N.; Nakhla, G.; Wong, K.; Wan, W. Optimization of Al2O3/PES membranes for wastewater filtration. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 73, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmgar, K.; Saljoughi, E.; Mousavi, S.M. Preparation and Characterization of a Novel Hydrophilic PVDF/PVA/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Membrane for Removal of As (V) from Aqueous Solutions. Polym. Compos. 2018, 40, 2452–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugiah, P.S.; Oh, P.C.; Lau, K.K. Concatenation of carbonaceous nanofillers for mixed matrix membrane development. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 458, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugiah, P.S.; Oh, P.C.; Lau, K.K. Collegial effect of carbonaceous hybrid fillers in mixed matrix membrane development. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 135, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Nuñez, C.; Döbeli, M.; Michler, J.; Utke, I. Reaction and Growth Mechanisms in Al2O3 deposited via Atomic Layer Deposition: Elucidating the Hydrogen Source. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8690–8703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portehault, D.; Cassaignon, S.; Nassif, N.; Baudrin, E.; Jolivet, J.P. A core-corona hierarchical manganese oxide and its formation by an aqueous soft chemistry mechanism. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 6441–6444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, D. A Simple Nanocellulose Coating for Self-Cleaning upon Water Action: Molecular Design of Stable Surface Hydrophilicity. Angew. Chemie-Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9053–9057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawamura, Y. Magnesium sulfate: Chemical and technical assessment. Methods 2007, 4, 4–8. [Google Scholar]
- Parida, K.M.; Kanungo, S.B.; Sant, B.R. Studies on MnO2-I chemical composition, microstructure and other characteristics of some synthetic MnO2 of various crystalline modifications. Electrochim. Acta 1981, 26, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.J.; Oh, P.C.; Chew, T.L.; Ahmad, A.L. Antiwettability enhancement of PVDF-HFP membrane via superhydrophobic modification by SiO2 nanoparticles. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2019, 22, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Husaini, I.S.; Yusoff, A.R.M.; Lau, W.J.; Ismail, A.F.; Al-Abri, M.Z.; Al-Ghafri, B.N.; Wirzal, M.D.H. Fabrication of polyethersulfone electrospun nanofibrous membranes incorporated with hydrous manganese dioxide for enhanced ultrafiltration of oily solution. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 212, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamshidi Gohari, R.; Halakoo, E.; Lau, W.J.; Kassim, M.A.; Matsuura, T.; Ismail, A.F. Novel polyethersulfone (PES)/hydrous manganese dioxide (HMO) mixed matrix membranes with improved anti-fouling properties for oily wastewater treatment process. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 17587–17596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, M.J.; Oh, P.C.; Chew, T.L.; Ahmad, A.L. Preparation of Polydimethylsiloxane-SiO2/PVDF-HFP Mixed Matrix Membrane of Enhanced Wetting Resistance for Membrane Gas Absorption. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 244, 116543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arahman, N.; Maimun, T.; Bilad, M.R. Fabrication Of Polyethersulfone Membranes Using Nanocarbon As Additive. Int. J. GEOMATE 2018, 15, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adilah Rosnan, N.; Haan, T.Y.; Mohammad, A.W. The effect of ZnO loading for the enhancement of PSF/ZnO-GO mixed matrix membrane performance. Sains Malays. 2018, 47, 2035–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei-DashtArzhandi, M.; Ismail, A.F.; Bakeri, G.; Hashemifard, S.A.; Matsuura, T. Effect of hydrophobic montmorillonite on PVDF and PEI hollow fiber membranes in gas-liquid contacting process: A comparative study. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 103811–103821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, H.L.; Baker, P.G.L.; Iwuoha, E. Metal Nanoparticle Modified Polysulfone Membranes for Use in Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review. J. Surf. Eng. Mater. Adv. Technol. 2012, 02, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peydayesh, M.; Bagheri, M.; Mohammadi, T.; Bakhtiari, O. Fabrication optimization of polyethersulfone (PES)/polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) nanofiltration membranes using Box-Behnken response surface method. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 24995–25008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, S.; Yao, L.; Zhao, Y.; Li, N.; Zheng, Y. Preparation of graphene oxide modified polyamide thin film composite membranes with improved hydrophilicity for natural organic matter removal. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 280, 720–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasrollahi, N.; Aber, S.; Vatanpour, V.; Mahmoodi, N.M. The effect of amine functionalization of CuO and ZnO nanoparticles used as additives on the morphology and the permeation properties of polyethersulfone ultrafiltration nanocomposite membranes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2018, 154, 388–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández, V.; Khayet, M. Evaluation of the surface free energy of plant surfaces: Toward standardizing the procedure. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazirah, S.; Ikhsan, W.; Yusof, N.; Aziz, F.; Misdan, N. Separation and Purification Technology Efficient separation of oily wastewater using polyethersulfone mixed matrix membrane incorporated with halloysite nanotube-hydrous ferric oxide nanoparticle. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naddeo, V.; Balakrishnan, M.; Choo, K.-H. Frontiers in Water-Energy-Nexus—Nature-Based Solutions, Advanced Technologies and Best Practices for Environmental Sustainability: Proceedings of the 2nd WaterEnergyNexus Conference, November 2018, Salerno, Italy; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020.
- Huang, S.; Ras, R.H.A.; Tian, X. ScienceDirect Antifouling membranes for oily wastewater treatment: Interplay between wetting and membrane fouling. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 36, 90–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhou, Z.; Xie, A.; Meng, M.; Cui, Y.; Liu, S.; Lu, J.; Zhou, S.; Yan, Y.; Dong, H. Bio-inspired fabrication of superhydrophilic nanocomposite membrane based on surface modification of SiO2 anchored by polydopamine towards effective oil-water emulsions separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 209, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brião, V.B.; Seguenka, B.; Zanon, C.D.; Milani, A. Cake formation and the decreased performance of whey ultrafiltration. Acta Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ismail, N.H.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Awang, N.A.; Ahmad, S.Z.N.; Rosman, N.; Sazali, N.; Ismail, A.F. PVDF/HMO ultrafiltration membrane for efficient oil/water separation. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2019, 208, 1563–5201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Membrane | Element (wt %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | S | Al | Mn | |
| PES 0 | 62.70 | 22.93 | 14.37 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| PES 1 | 52.59 | 38.91 | 7.89 | 0.00 | 0.61 |
| PES 2 | 50.21 | 39.33 | 8.76 | 0.97 | 0.73 |
| PES 3 | 45.22 | 39.68 | 8.82 | 5.35 | 0.94 |
| PES 4 | 46.14 | 38.46 | 8.65 | 6.47 | 0.27 |
| PES 5 | 51.43 | 25.32 | 7.97 | 15.28 | 0.00 |
| Additives | Filler Loading | Water Contact Angle | Membrane Performance * | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVP/HMO | 10.00% | 58.7° | PWF:210; R:93 | [42] |
| PVP/HMO | 23.08% | 16.4° | PWF:573.2; R:94; FRR:75 | [27] |
| PVP/HMO/TiO2 | 23.08% | <10° | PWF:29; R:99; FRR:91.5 | [10] |
| HMO/Al2O3 | 23.35% | PWF:245.95; R:98.27; FRR:85 | This work |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, T.S.; Oh, P.C.; Toh, M.J.; Yap, Y.K.; Te, Q.Y. Xylem-Inspired Hydrous Manganese Dioxide/Aluminum Oxide/Polyethersulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090860
Yun TS, Oh PC, Toh MJ, Yap YK, Te QY. Xylem-Inspired Hydrous Manganese Dioxide/Aluminum Oxide/Polyethersulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment. Membranes. 2022; 12(9):860. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090860
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Teng Sam, Pei Ching Oh, Moau Jian Toh, Yun Kee Yap, and Qin Yi Te. 2022. "Xylem-Inspired Hydrous Manganese Dioxide/Aluminum Oxide/Polyethersulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment" Membranes 12, no. 9: 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090860
APA StyleYun, T. S., Oh, P. C., Toh, M. J., Yap, Y. K., & Te, Q. Y. (2022). Xylem-Inspired Hydrous Manganese Dioxide/Aluminum Oxide/Polyethersulfone Mixed Matrix Membrane for Oily Wastewater Treatment. Membranes, 12(9), 860. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090860