ssPINE: Probabilistic Algorithm for Automated Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid-State NMR Data from Complex Protein Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. ssPINE Algorithm
2.2. Input Files
2.2.1. Preparation of Peak Lists
2.2.2. Protein Sequence
2.3. Output Files
2.4. Data Used in Developing ssPINE
2.4.1. Data from GB1
2.4.2. Other Protein NMR Data
2.5. ssPINE Web Server
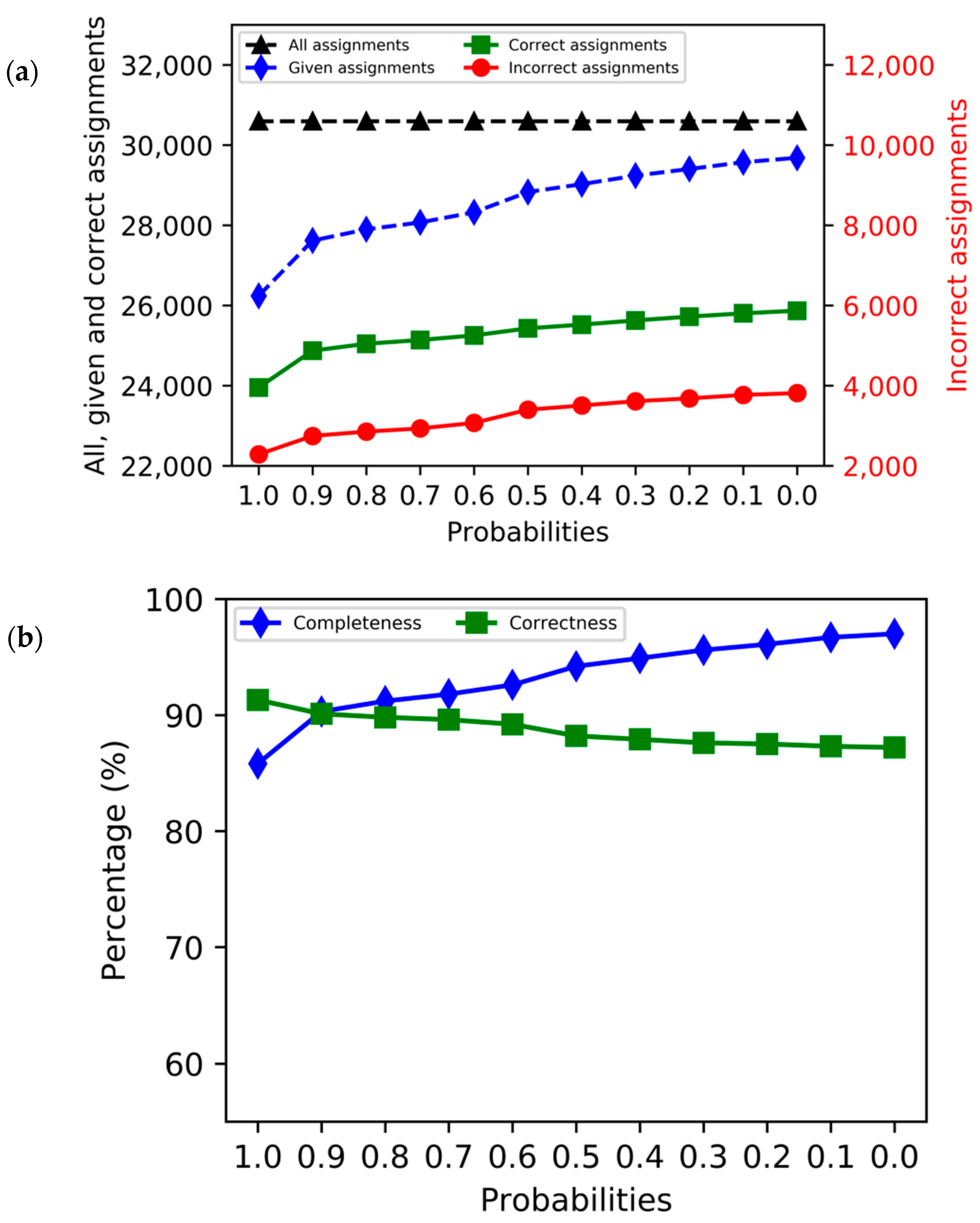
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Web Server Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ilari, A.; Savino, C. Protein Structure Determination by X-ray Crystallography. Bioinformatics 2008, 63–87. [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyoshi, Y. The Structural Study of Membrane Proteins by Electron Crystallography. Adv. Biophys. 1998, 35, 25–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen O áHill, H. Immobilization of Small Proteins in Carbon Nanotubes: High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy Study and Catalytic Activity. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1995, 17, 1803–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Wüthrich, K. The Way to NMR Structures of Proteins. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 923–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shuker, S.B.; Hajduk, P.J.; Meadows, R.P.; Fesik, S.W. Discovering High-Affinity Ligands for Proteins: SAR by NMR. Science 1996, 274, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsisiotis, A.I. NMR Studies of Inhibitor Binding to Metallo-B-Lactamases. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Leicester, Leicester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kempf, J.G.; Loria, J.P. Protein Dynamics from Solution NMR. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2002, 37, 187–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovermann, M.; Rogne, P.; Wolf-Watz, M. Protein Dynamics and Function from Solution State NMR Spectroscopy. Q. Rev. Biophys. 2016, 49, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellani, F.; Van Rossum, B.; Diehl, A.; Schubert, M.; Rehbein, K.; Oschkinat, H. Structure of a Protein Determined by Solid-State Magic-Angle-Spinning NMR Spectroscopy. Nature 2002, 420, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, S.A.; Bardiaux, B.; Franks, W.T.; Krabben, L.; Habeck, M.; van Rossum, B.-J.; Linke, D. Membrane-Protein Structure Determination by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy of Microcrystals. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M. Solid-State NMR Determination of 13Cα Chemical Shift Anisotropies for the Identification of Protein Secondary Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 3762–3770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, B. Ultra-High Resolution in MAS Solid-State NMR of Perdeuterated Proteins: Implications for Structure and Dynamics. J. Magn. Reson. 2012, 216, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Angelis, A.A.; Jones, D.H.; Grant, C.V.; Park, S.H.; Mesleh, M.F.; Opella, S.J. NMR Experiments on Aligned Samples of Membrane Proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 394, 350–382. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wi, S.; Frydman, L. An Efficient, Robust New Scheme for Establishing Broadband Homonuclear Correlations in Biomolecular Solid State NMR. ChemPhysChem 2020, 21, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, N.; Iwahara, J.; Koshiba, S.; Tomizawa, T.; Tochio, N.; Güntert, P.; Kigawa, T.; Yokoyama, S. KUJIRA, a Package of Integrated Modules for Systematic and Interactive Analysis of NMR Data Directed to High-Throughput NMR Structure Studies. J. Biomol. NMR 2007, 39, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Assadi, A.H.; Markley, J.L.; Eghbalnia, H.R. Probabilistic Interaction Network of Evidence Algorithm and Its Application to Complete Labeling of Peak Lists from Protein NMR Spectroscopy. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, J.H.; Westler, W.M.; Markley, J.L. PONDEROSA, an Automated 3D-NOESY Peak Picking Program, Enables Automated Protein Structure Determination. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1727–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Stark, J.L.; Markley, J.L. PONDEROSA-C/S: Client–Server Based Software Package for Automated Protein 3D Structure Determination. J. Biomol. NMR 2014, 60, 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Westler, W.M.; Bahrami, A.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Markley, J.L. PINE-SPARKY: Graphical Interface for Evaluating Automated Probabilistic Peak Assignments in Protein NMR Spectroscopy. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 2085–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Bahrami, A.; Dashti, H.T.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Tonelli, M.; Westler, W.M.; Markley, J.L. I-PINE Web Server: An Integrative Probabilistic NMR Assignment System for Proteins. J. Biomol. NMR 2019, 73, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Yu, W.; Kim, S.; Chang, I.; Lee, W.; Markley, J.L. PACSY, a Relational Database Management System for Protein Structure and Chemical Shift Analysis. J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 54, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Lee, Y.; Markley, J.L.; Lee, W. iPick: Multiprocessing Software for Integrated NMR Signal Detection and Validation. J. Magn. Reson. 2021, 328, 106995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Markley, J.L. PINE-SPARKY. 2 for Automated NMR-Based Protein Structure Research. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1586–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Rahimi, M.; Lee, Y.; Chiu, A. POKY: A Software Suite for Multidimensional NMR and 3D Structure Calculation of Biomolecules. Bioinformatics 2021, 37, 3041–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, D.K.; Wang, S.; Markley, J.L.; Veglia, G.; Lee, W. PISA-SPARKY: An Interactive SPARKY Plugin to Analyze Oriented Solid-State NMR Spectra of Helical Membrane Proteins. Bioinformatics 2020, 36, 2915–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.; Tonelli, M.; Markley, J.L. NMRFAM-SPARKY: Enhanced Software for Biomolecular NMR Spectroscopy. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1325–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opella, S.J.; Marassi, F.M. Structure Determination of Membrane Proteins by NMR Spectroscopy. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 3587–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, T.; Manu, V.S.; Weber, D.K.; Veglia, G. PHRONESIS: A One-Shot Approach for Sequential Assignment of Protein Resonances by Ultrafast MAS Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. ChemPhysChem 2022, 23, e202200127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moseley, H.N.; Sperling, L.J.; Rienstra, C.M. Automated Protein Resonance Assignments of Magic Angle Spinning Solid-State NMR Spectra of Β1 Immunoglobulin Binding Domain of Protein G (GB1). J. Biomol. NMR 2010, 48, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, E.; Gath, J.; Habenstein, B.; Ravotti, F.; Székely, K.; Huber, M.; Buchner, L.; Böckmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; Güntert, P. Automated Solid-State NMR Resonance Assignment of Protein Microcrystals and Amyloids. J. Biomol. NMR 2013, 56, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.H.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Comellas, G.; Sperling, L.J.; Tang, M.; Shah, G.J.; Brea, E.J.; Lemkau, L.R.; Rienstra, C.M. Solid-State NMR Analysis of Membrane Proteins and Protein Aggregates by Proton Detected Spectroscopy. J. Biomol. NMR 2012, 54, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, T.; Veglia, G. Multiple Acquisition of Magic Angle Spinning Solid-State NMR Experiments Using One Receiver: Application to Microcrystalline and Membrane Protein Preparations. J. Magn. Reson. 2015, 253, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Yedidia, J.S.; Freeman, W.T.; Weiss, Y. Constructing Free-Energy Approximations and Generalized Belief Propagation Algorithms. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2005, 51, 2282–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, C.; Xia, T.; Billeter, M.; Güntert, P.; Wüthrich, K. The Program XEASY for Computer-Supported NMR Spectral Analysis of Biological Macromolecules. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, R.L.J. Optimizing the Process of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrum Analysis and Computer Aided Resonance Assignment. Ph.D. Thesis, ETH Zurich, Zürich, Switzerland, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Vranken, W.F.; Boucher, W.; Stevens, T.J.; Fogh, R.H.; Pajon, A.; Llinas, M.; Ulrich, E.L.; Markley, J.L.; Ionides, J.; Laue, E.D. The CCPN Data Model for NMR Spectroscopy: Development of a Software Pipeline. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 2005, 59, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eghbalnia, H.R.; Wang, L.; Bahrami, A.; Assadi, A.; Markley, J.L. Protein Energetic Conformational Analysis from NMR Chemical Shifts (PECAN) and Its Use in Determining Secondary Structural Elements. J. Biomol. NMR 2005, 32, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Eghbalnia, H.R.; Bahrami, A.; Markley, J.L. Linear Analysis of Carbon-13 Chemical Shift Differences and Its Application to the Detection and Correction of Errors in Referencing and Spin System Identifications. J. Biomol. NMR 2005, 32, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, E.L.; Akutsu, H.; Doreleijers, J.F.; Harano, Y.; Ioannidis, Y.E.; Lin, J.; Livny, M.; Mading, S.; Maziuk, D.; Miller, Z. BioMagResBank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D402–D408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.; Henrick, K.; Nakamura, H.; Markley, J.L. The Worldwide Protein Data Bank (WwPDB): Ensuring a Single, Uniform Archive of PDB Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, D301–D303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experiment | Dimension | Profile |
|---|---|---|
| CC * | 2D | CX/O(i)-CX/O(i) |
| NCA * | 2D | N(i)-CA(i) |
| NCACB | 2D | N(i)-CA/B(i) |
| NCO * | 2D | N(i)-CO(i − 1) |
| NCACO | 3D | N(i)-CA(i)-CO(i) |
| NCACB | 3D | N(i)-CA(i)-CA/B(i) |
| NCACX * | 3D | N(i)-CA(i)-CX(i) |
| NCOCX * | 3D | N(i)-CO(i − 1)-CX/C(i − 1) |
| NCOCA | 3D | N(i)-CO(i − 1)-CA(i − 1) |
| NCOCACB | 3D | N(i)-CO(i − 1)-CA/B(i − 1) |
| CANCO | 3D | CA(i)-N(i)-CO(i − 1) |
| CANCOCX * | 3D | CA(i)-N(i)-CX/O(i − 1) |
| CANCOCA | 3D | CA(i)-N(i)-CA/O(i − 1) |
| CANCOCACB | 3D | CA(i)-N(i)-CO/A/B(i − 1) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dwarasala, A.; Rahimi, M.; Markley, J.L.; Lee, W. ssPINE: Probabilistic Algorithm for Automated Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid-State NMR Data from Complex Protein Systems. Membranes 2022, 12, 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090834
Dwarasala A, Rahimi M, Markley JL, Lee W. ssPINE: Probabilistic Algorithm for Automated Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid-State NMR Data from Complex Protein Systems. Membranes. 2022; 12(9):834. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090834
Chicago/Turabian StyleDwarasala, Adilakshmi, Mehdi Rahimi, John L. Markley, and Woonghee Lee. 2022. "ssPINE: Probabilistic Algorithm for Automated Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid-State NMR Data from Complex Protein Systems" Membranes 12, no. 9: 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090834
APA StyleDwarasala, A., Rahimi, M., Markley, J. L., & Lee, W. (2022). ssPINE: Probabilistic Algorithm for Automated Chemical Shift Assignment of Solid-State NMR Data from Complex Protein Systems. Membranes, 12(9), 834. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12090834







