Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methodology
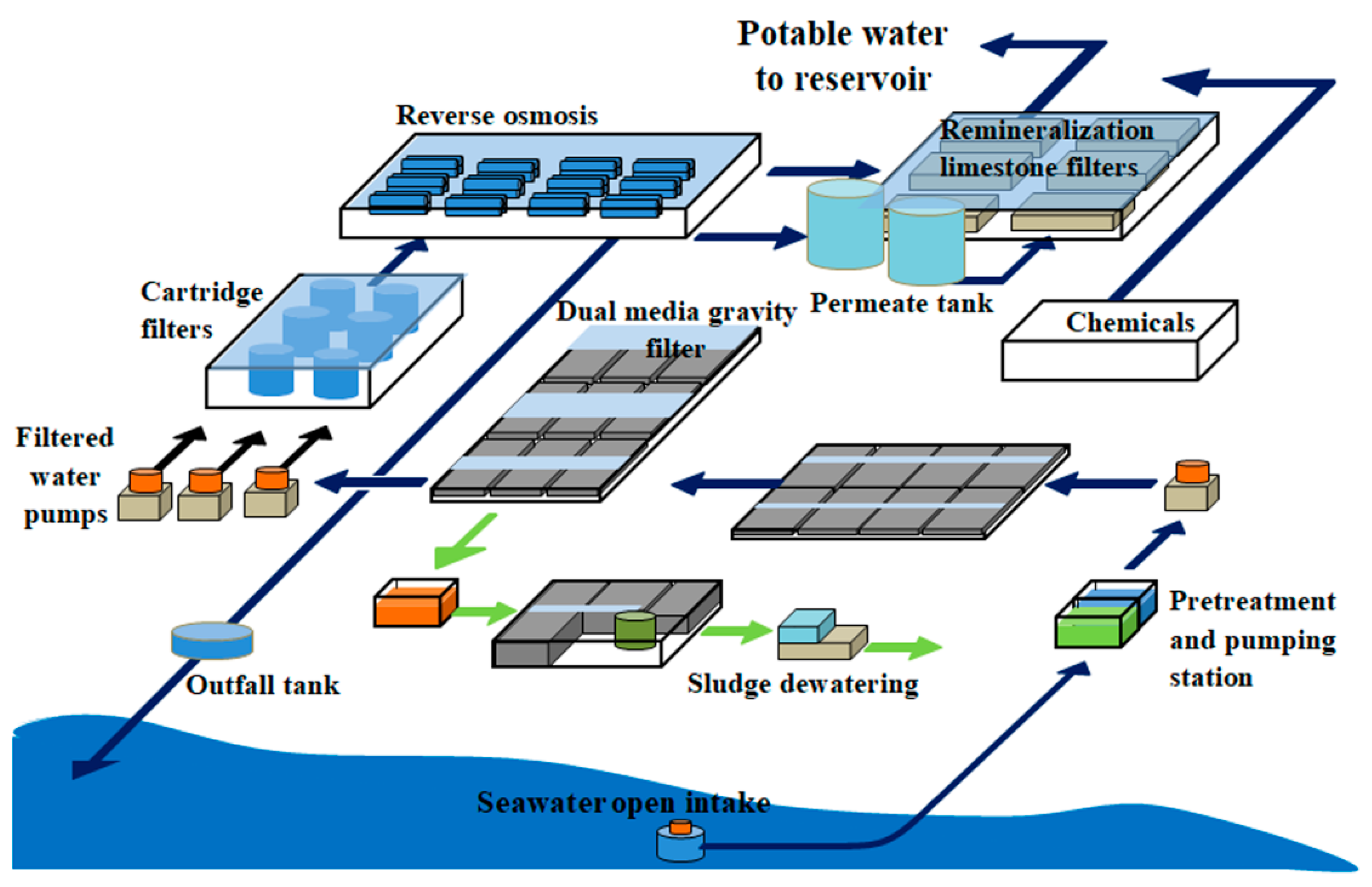
2.1. Plant Description and Location
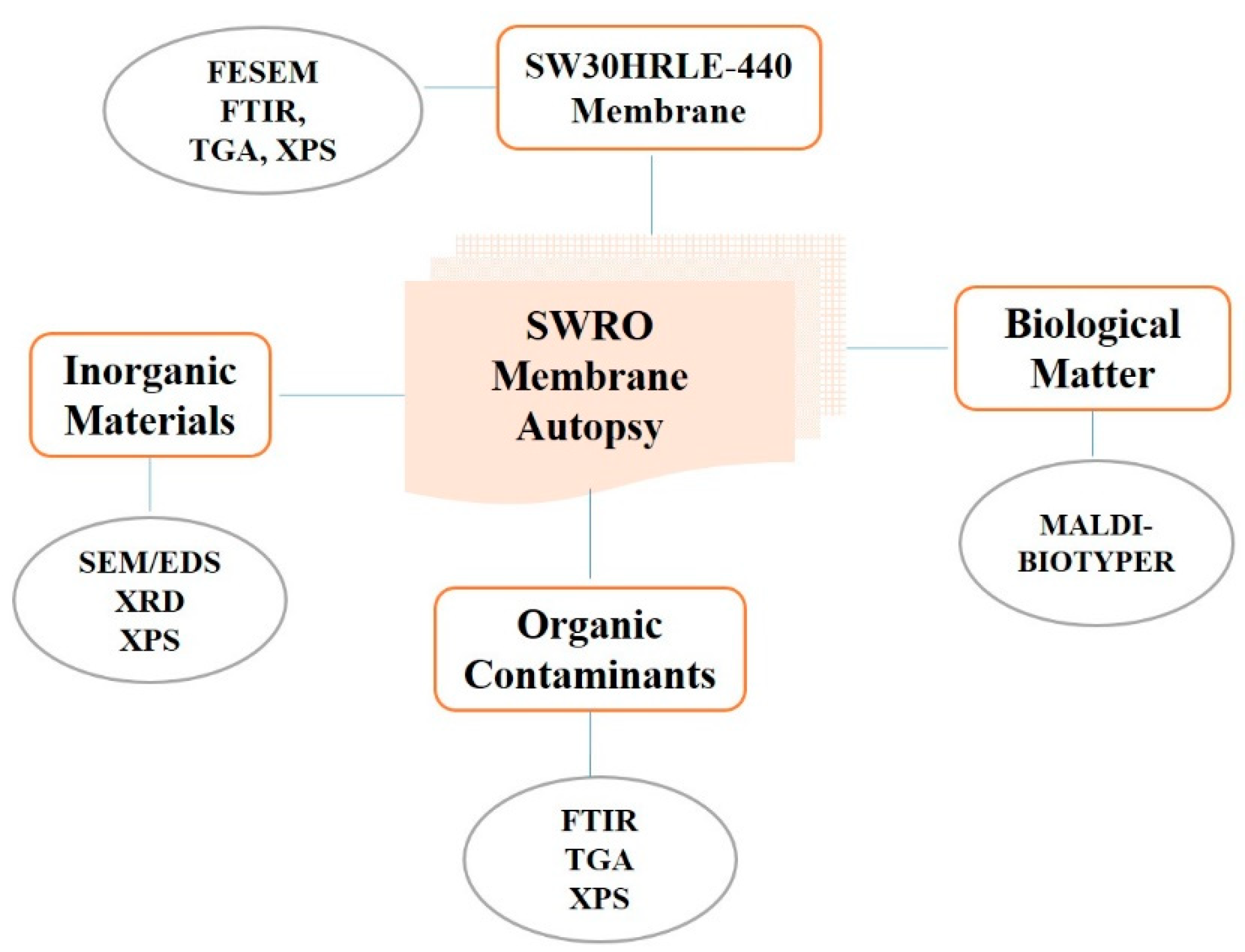
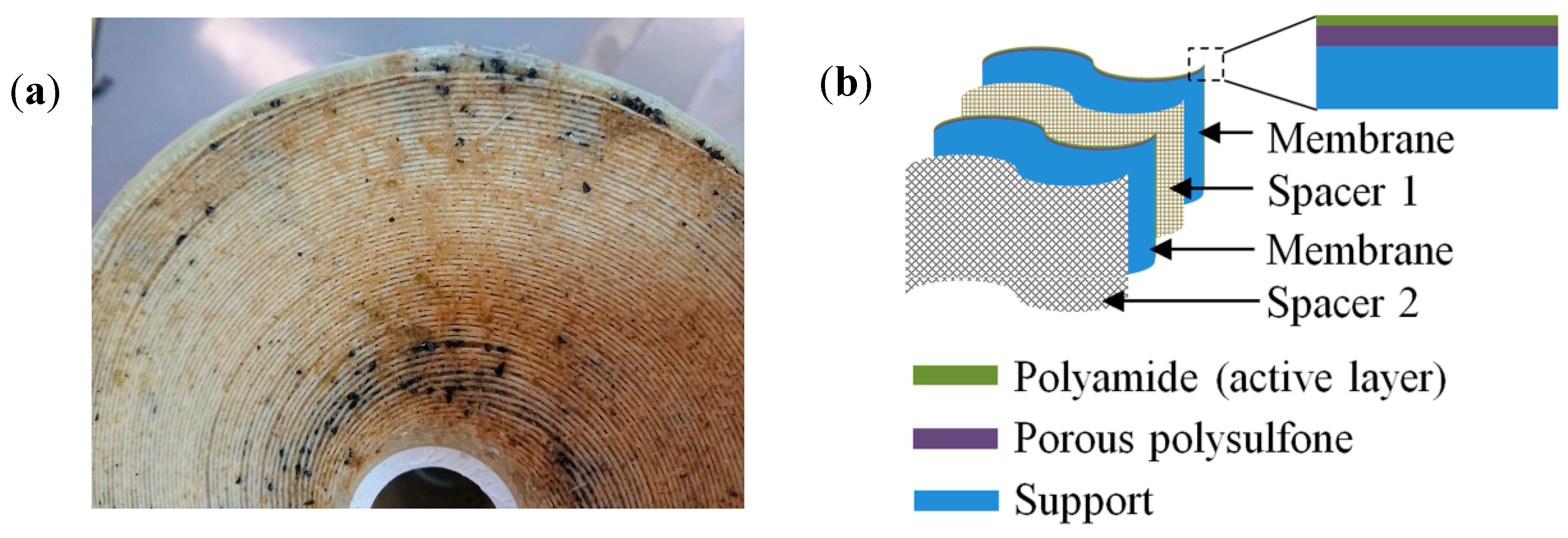
2.2. RO Membrane Autopsy
2.3. Membrane Samples: Cleaning and Storage
2.4. Membrane Samples Characterization
2.5. Bacteria Isolation and Identification
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Optical Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
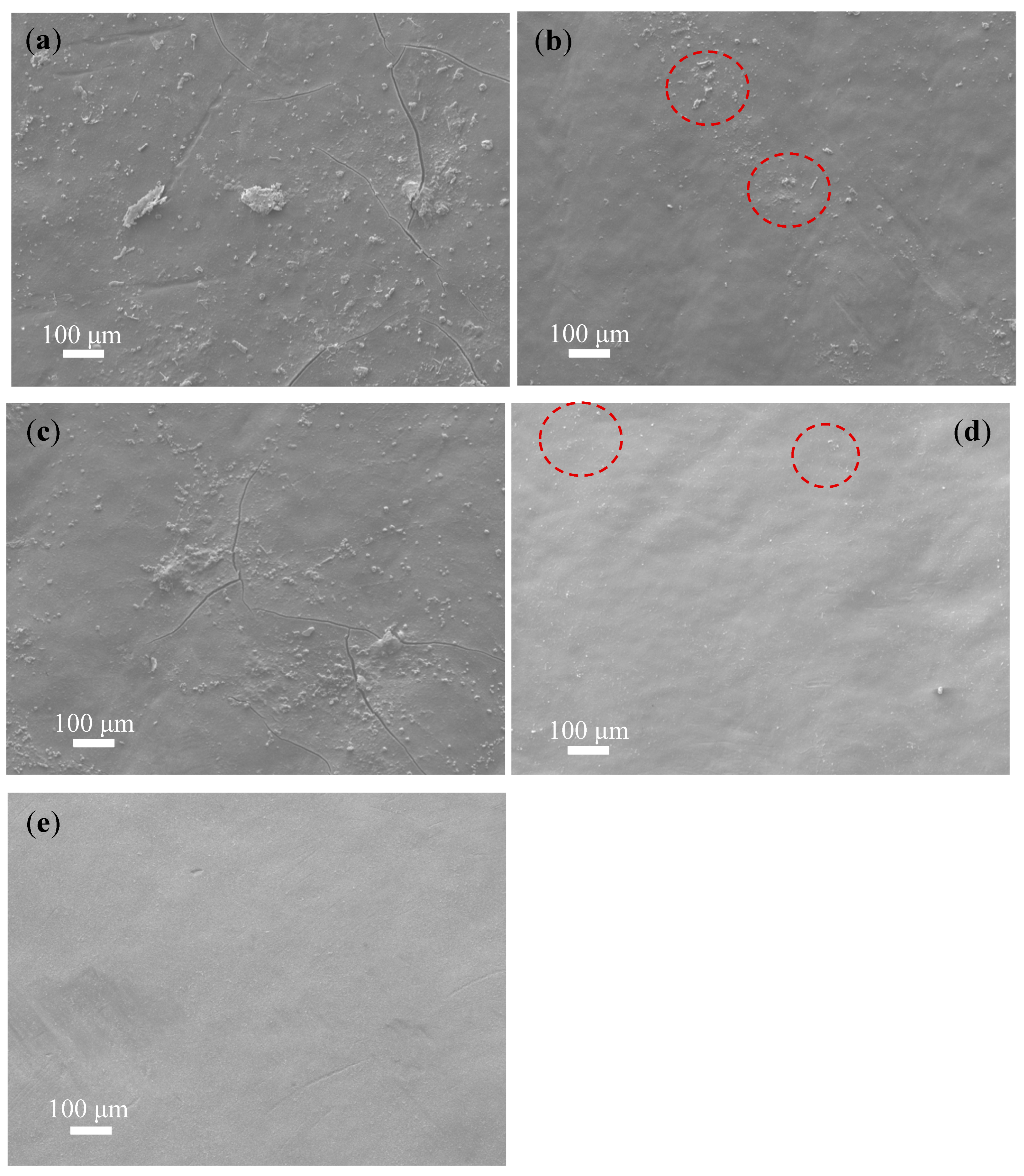
3.2. FESEM Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
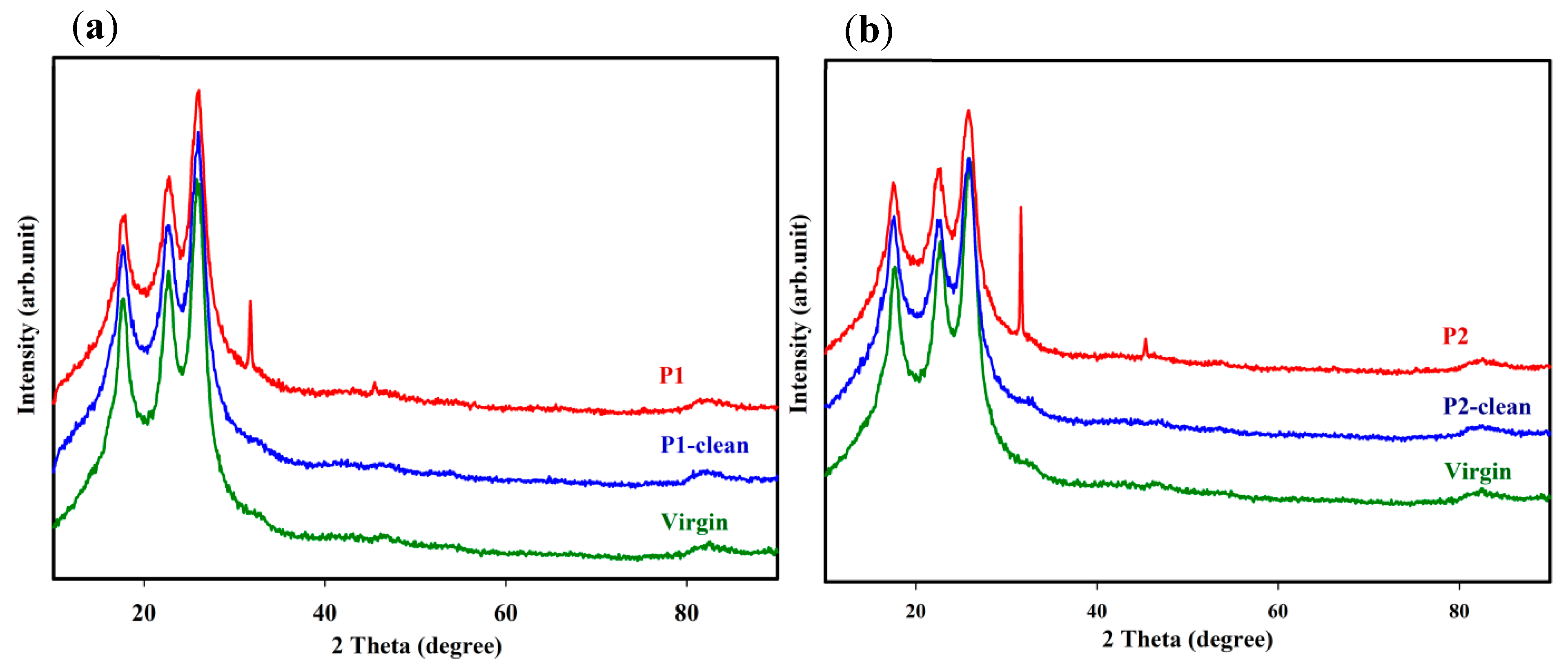
3.3. XRD Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
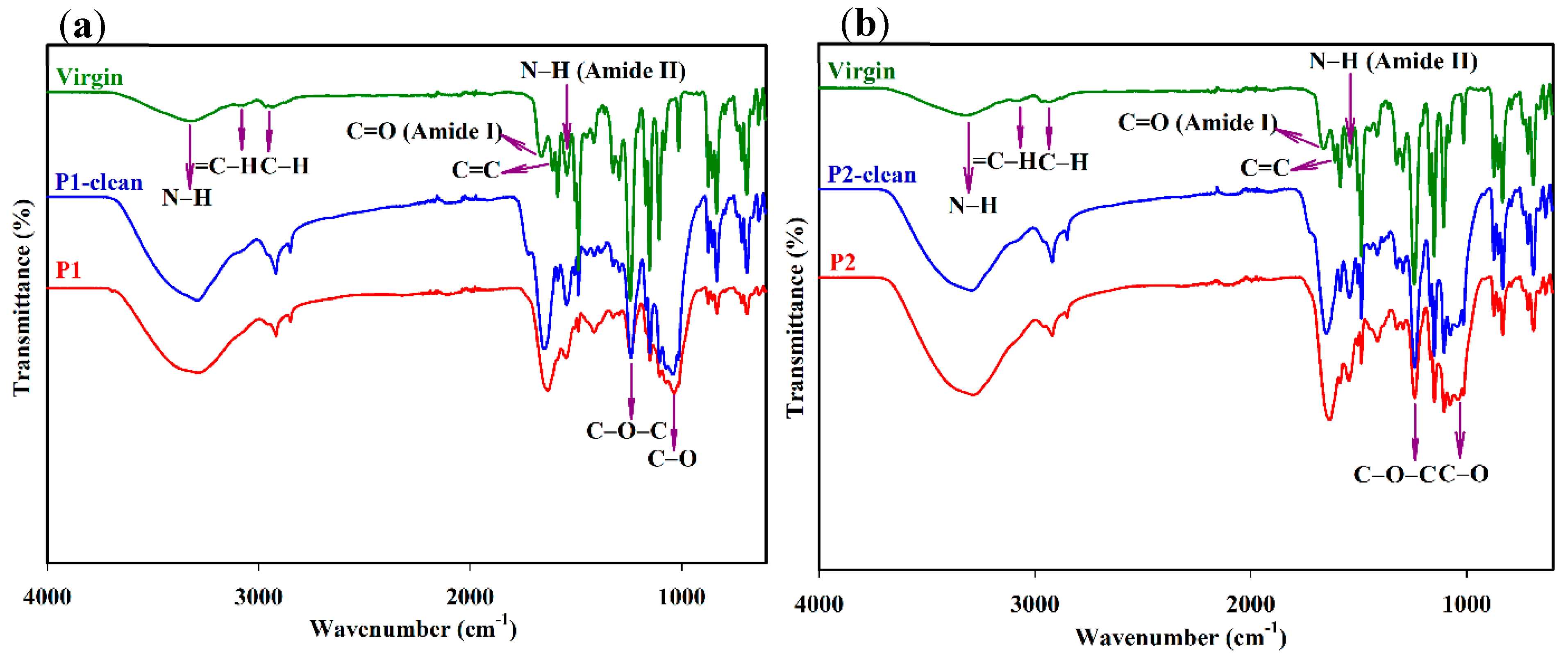
3.4. FTIR Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
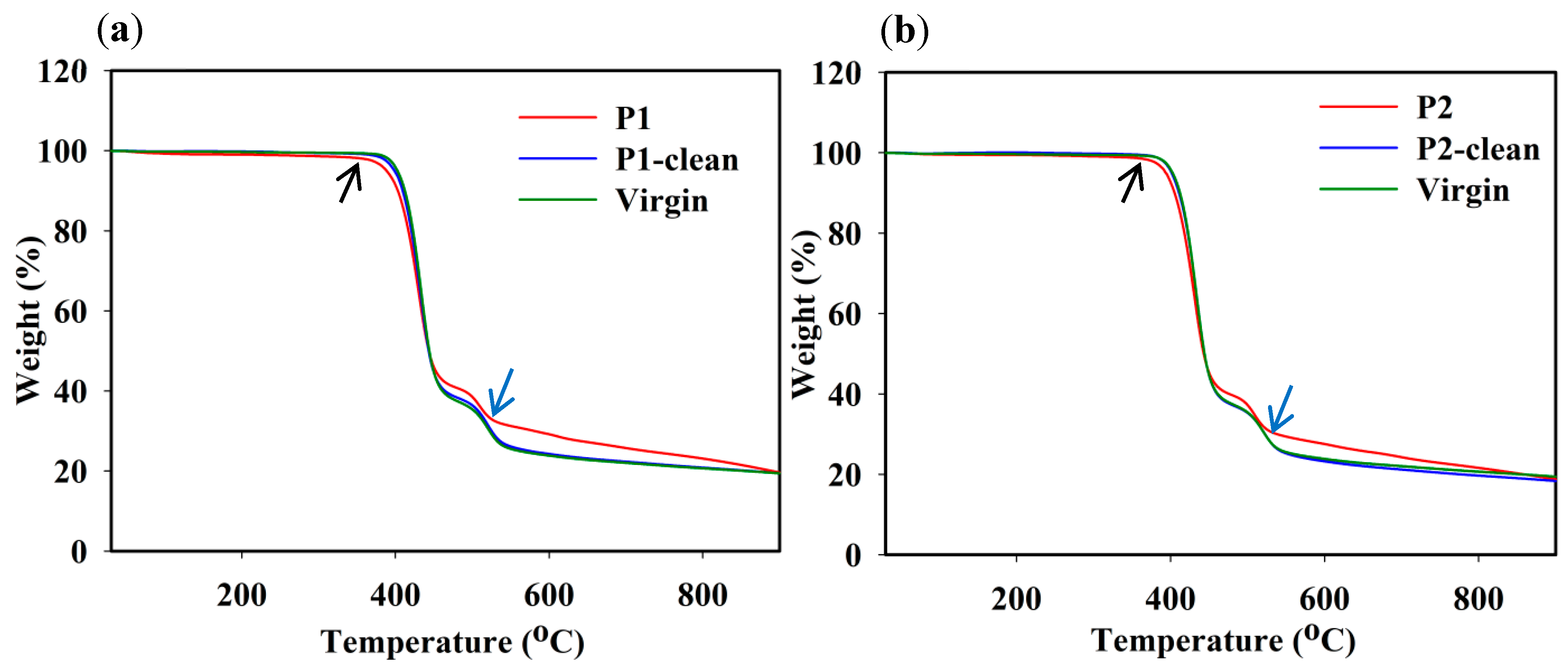
3.5. TGA Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
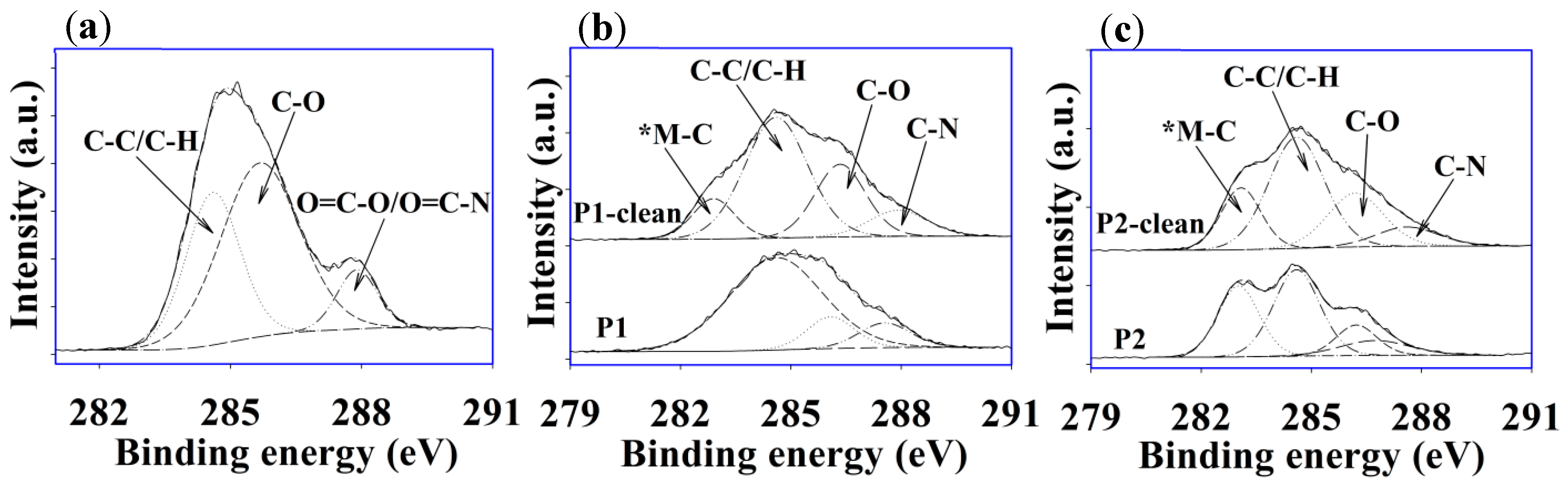
3.6. XPS Analysis of Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
3.7. Bacteria on Fouled and Cleaned Membranes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goh, P.S.; Liang, Y.Y.; Ismail, A.F. Energy Efficient Seawater Desalination: Strategies and Opportunities. Energy Technol. 2021, 9, 2100008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon, F.; Ramos, A. Performance Analysis of a Full-Scale Desalination Plant with Reverse Osmosis Membranes for Irrigation. Membranes 2021, 11, 774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, S. Desalination technology in South Korea: A comprehensive review of technology trends and future outlook. Membranes 2022, 12, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrar, I.; Naji, O.; Sharif, A.; Malekizadeh, A.; Alhawari, A.; Alanezi, A.A.; Altaee, A. A review of fouling mechanisms, control strategies and real-time fouling monitoring techniques in forward osmosis. Water 2019, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abushaban, A.; Salinas-Rodriguez, S.G.; Kapala, M.; Pastorelli, D.; Schippers, J.C.; Mondal, S.; Goueli, S.; Kennedy, M.D. Monitoring biofouling potential using ATP-based bacterial growth potential in SWRO pre-treatment of a full-scale plant. Membranes 2020, 10, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Triñanes, P.; Chairopoulou, M.A.; Campos, L.C. Investigating reverse osmosis membrane fouling and scaling by membrane autopsy of a bench scale device. Environ. Technol. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, Z. Membrane Processes for Water and Wastewater Treatment: Study and Modeling of Interactions between Membrane and Organic Matter. Ph.D. Thesis, Ecole Centrale Paris, Chatenay-Malabry, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.; Hong, S. Nano-colloidal fouling mechanisms in seawater reverse osmosis process evaluated by cake resistance simulator-modified fouling index nanofiltration. Desalination 2014, 343, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvi, A.G.I.; Al-Rasheed, R.; Javeed, M.A. Studies on organic foulants in the seawater feed of reverse osmosis plants of SWCC. Desalination 2000, 132, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, S.; Allen, A.; Koutsos, V.; Semião, A.J. Influence of organic fouling layer characteristics and osmotic backwashing conditions on cleaning efficiency of RO membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 616, 118604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanagaraj, P.; Mohamed, I.M.; Huang, W.; Liu, C. Membrane fouling mitigation for enhanced water flux and high separation of humic acid and copper ion using hydrophilic polyurethane modified cellulose acetate ultrafiltration membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 150, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, S.A.; Balz, A.; Abert, M.; Pronk, W. Characterisation of aquatic humic and non-humic matter with size-exclusion chromatography—Organic carbon detection—Organic nitrogen detection (LC-OCD-OND). Water Res. 2011, 45, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Naidu, G.; Vollprecht, R.; Leiknes, T.; Vigneswaran, S. In-depth analyses of organic matters in a full-scale seawater desalination plant and an autopsy of reverse osmosis membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 162, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, A.W.; Amin, I.N.H.M. Fouling of ultrafiltration membrane during adsorption of long chain fatty acid in glycerine solutions. Sains Malays. 2013, 42, 827–836. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, T.; Roddick, F.A.; Fan, L. Biofouling of water treatment membranes: A review of the underlying causes, monitoring techniques and control measures. Membranes 2012, 2, 804–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Xie, P.; Shang, R.; Ma, J. Removal of Microcystis aeruginosa by UV-activated persulfate: Performance and characteristics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, F.A.A.; Alam, J.; Shukla, A.K.; Alhoshan, M.; Ansari, M.A.; Al-Masry, W.A.; Rehman, S.; Alam, M. Evaluation of antibacterial and antifouling properties of silver-loaded GO polysulfone nanocomposite membrane against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and BSA protein. React. Funct. Polym. 2019, 140, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.; Mulcahy, D.; Zou, L.; Kim, I.S. A short review of membrane fouling in forward osmosis processes. Membranes 2017, 7, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Asadollahi, M.; Bastani, D.; Musavi, S.A. Enhancement of surface properties and performance of reverse osmosis membranes after surface modification: A review. Desalination 2017, 420, 330–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, M.A.; Chellam, S. Reverse osmosis fouling during pilot-scale municipal water reuse: Evidence for aluminum coagulant carryover. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Kim, S.J.; Moon, J.; Cho, J. Combined coagulation-disk filtration process as a pretreatment of ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis membrane for wastewater reclamation: An autopsy study of a pilot plant. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1803–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayache, C.; Manes, C.; Pidou, M.; Croue, J.-P.; Gernjak, W. Microbial community analysis of fouled reverse osmosis membranes used in water recycling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.; Bolto, B.; Gray, S.; Hoang, M.; Ostarcevic, E. An autopsy study of a fouled reverse osmosis membrane element used in a brackish water treatment plant. Water Res. 2007, 41, 3915–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vrouwenvelder, J.; van der Kooij, D. Diagnosis of fouling problems of NF and RO membrane installations by a quick scan. Desalination 2003, 153, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Tay, K.G. Performance prediction of a long crossflow reverse osmosis membrane channel. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 281, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, E.M.; Elimelech, M. Cake-enhanced concentration polarization: A new fouling mechanism for salt-rejecting membranes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 5581–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, P.G.; McArthur, S.L.; McLean, K.M.; Griesser, H.J. Physicochemical properties of polysaccharide coatings based on grafted multilayer assemblies. Langmuir 2002, 18, 2483–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, N.P.; del Vigo, F.; Chesters, S.; Armstrong, M.; Wilson, R.; Fazel, M. A study of the physical and chemical damage on reverse osmosis membranes detected by autopsies. In Proceedings of the International Desalination Association World Congress on Desalination and Water Reuse, Tianjin, China, 20–25 October 2013; pp. 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Tang, C.Y. Dissect the role of particle size through collision-attachment simulations for colloidal fouling of RO/NF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 638, 119679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Elimelech, M. Synergistic effects in combined fouling of a loose nanofiltration membrane by colloidal materials and natural organic matter. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 278, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pacheco, R.; Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Teli, S.B.; García-Calvo, E. Transformation of end-of-life RO membranes into NF and UF membranes: Evaluation of membrane performance. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 495, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landaburu-Aguirre, J.; García-Pacheco, R.; Molina, S.; Rodríguez-Sáez, L.; Rabadán, J.; García-Calvo, E. Fouling prevention, preparing for re-use and membrane recycling. Towards circular economy in RO desalination. Desalination 2016, 393, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahbakhsh, J.; Vatanpour, V.; Khoshnam, M.; Zargar, M. Recent advancements in the application of new monomers and membrane modification techniques for the fabrication of thin film composite membranes: A review. React. Funct. Polym. 2021, 166, 105015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, B.O. Membrane autopsy study to characterize fouling type of RO membrane used in an industrial zone wastewater reuse plant. Desalination 2022, 529, 115648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, M.; Nada, T.; Amin, S.; Anwar, T.; Mohamed, A.A. Characterization of fouling for a full-scale seawater reverse osmosis plant on the Mediterranean sea: Membrane autopsy and chemical cleaning efficiency. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2002, 16, 100704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Arnaouty, M.B.; Ghaffar, A.M.A.; Eid, M.; Aboulfotouh, M.E.; Taher, N.H.; Soliman, E.-S. Nano-modification of polyamide thin film composite reverse osmosis membranes by radiation grafting. J. Radiat. Res. Appl. Sci. 2018, 11, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bao, N.; Miao, X.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xiuyan, J.; Zheng, X. Novel Synthesis of Plasmonic Ag/AgCl@TiO2 Continues Fibers with Enhanced Broadband Photocatalytic Performance. Catalysts 2017, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laqbaqbi, M.; Sanmartino, J.A.; Khayet, M.; García-Payo, C.; Chaouch, M. Fouling in Membrane Distillation, Osmotic Distillation and Osmotic Membrane Distillation. Appl. Sci. 2017, 7, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafi, H.Z.; Matin, A.; Akhtar, S.; Gleason, K.K.; Zubair, S.M.; Khan, Z. Organic fouling in surface modified reverse osmosis membranes: Filtration studies and subsequent morphological and compositional characterization. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián-Martel, N.; Sadhwani, J.J.; Malamis, S.; Ochsenkühn-Petropoulou, M. Structural and chemical characterization of long-term reverse osmosis membrane fouling in a full scale desalination plant. Desalination 2012, 305, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Al-Sulaimi, S.; Farooque, A.M. Characterization of new and fouled SWRO membranes by ATR/FTIR spectroscopy. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashfaq, M.Y.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Qiblawey, H.; Zouari, N. Evaluating the effect of antiscalants on membrane biofouling using FTIR and multivariate analysis. Biofouling 2019, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Ahn, C.H.; Hong, S.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Baek, Y.; Yoon, J. Evaluation of surface properties of reverse osmosis membranes on the initial biofouling stages under no filtration condition. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 351, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karime, M.; Bouguecha, S.; Hamrouni, B. RO membrane autopsy of Zarzis brackish water desalination plant. Desalination 2008, 220, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.; Shafi, H.; Khan, Z.; Khaled, M.; Yang, R.; Gleason, K.; Rehman, F. Surface modification of seawater desalination reverse osmosis membranes: Characterization studies & performance evaluation. Desalination 2014, 343, 128–139. [Google Scholar]
- Idarraga-Mora, J.A.; Lemelin, M.A.; Weinman, S.T.; Husson, S.M. Effect of short-term contact with C1–C4 monohydric alcohols on the water permeance of MPD-TMC thin-film composite reverse osmosis membranes. Membranes 2019, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, A.U.H.; Khan, Z.; Aljundi, I.H. Improved hydrophilicity and anti-fouling properties of polyamide TFN membrane comprising carbide derived carbon. Desalination 2017, 420, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.Y.; Kwon, Y.-N.; Leckie, J.O. Effect of membrane chemistry and coating layer on physiochemical properties of thin film composite polyamide RO and NF membranes: I. FTIR and XPS characterization of polyamide and coating layer chemistry. Desalination 2009, 242, 149–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fettkenhauer, C.; Wang, X.; Kailasam, K.; Antonietti, M.; Dontsova, D. Synthesis of efficient photocatalysts for water oxidation and dye degradation reactions using CoCl2 eutectics. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21227–21232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhojani, G.; Kumar, S.B.; Saha, N.K.; Haldar, S. Membrane biofouling by chlorine resistant Bacillus spp.: Effect of feedwater chlorination on bacteria and membrane biofouling. Biofouling 2018, 34, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Iftikhar, M.A.; Leiknes, T. Draft Genome Sequences of Three Bacillus Species Isolated from Biofouled Reverse-Osmosis Membranes. Microbiol. Resour. Announc. 2020, 9, e00413-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Concentration (ppm) Raw Water | Product Water |
|---|---|---|
| TDS (mg/L) pH Cond (µS/cm) | 39,000–42,000 8.3 ± 0.2 55,714 to 60,000 | <500 mg/L 8.15 to 8.2 891 |
| Cations Potassium (K) Sodium (Na) Magnesium (Mg) Calcium (Ca) | 408 mg/L 11,100 mg/L 1340 mg/L 435 mg/L | <0.1 mg/L 138 mg/L 2.3 mg/L 15 mg/L |
| Anions SO4−2 F− Chloride as Cl− HCO−3 | 3340 mg/L 2.74 mg/L 22,200 mg/L 168 mg/L | <5.0 mg/L <0.8 & >0.60 mg/L <250 mg/L |
| Boron | 5.26 | <2.4 mg/L |
| Peaks | Peak Assignments and Features | References |
|---|---|---|
| 1040 cm−1 | C-O stretching, polysaccharides | Rahman et al. [42], Ashfaq et al. [43] |
| 1243 cm−1 | C-O-C, asymmetric stretching, polysulfone support layer | Shafi et al. [40] |
| 1544 cm−1 | N-H stretching, amide II band | Melián-Martel et al. [41], Matin et al. [46] |
| 1609 cm−1 | C=C ring vibration, polyamide layer | Melián-Martel et al. [41], Matin et al. [46] |
| 1664 cm−1 | C=O, amide I band, protein | Melián-Martel et al. [41], Matin et al. [46] |
| 1484–1410 cm−1 | aliphatic C-H deformation, C-O stretching, and O-H deformation of phenol | Tran et al. [24] |
| 2900–3000 cm−1 | aliphatic C-H stretching vibration | Lee et al. [44] |
| 3030–3090 cm−1 | aromatic =C-H stretching vibration | Lee et al. [44] |
| 3300 cm−1 | free and hydrogen bond N-H stretching, O-H stretching vibration | Melián-Martel et al. [41], Idarraga-Mora et al. [47] |
| 600–800 cm−1 | fatty acid, protein | Ashfaq et al. [43] |
| 2900–3300 cm−1 | polysaccharides | Ashfaq et al. [43] |
| Sample | Strain Code | Bacterial Species | Mean Score Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| P1 fouled | P1 11 | Unidentified | 1.40 |
| P1 fouled | P1 12 | Bacillus cereus | 2.12 |
| P1 fouled | P1 2-2 | Bacillus cereus | 2.11 |
| P1 fouled | P1 3-1 | Bacillus cereus | 1.87 |
| P1 fouled | P1 3-2 | Bacillus cereus | 2.12 |
| P2 fouled | P2 11 | Bacillus flexus | 1.73 |
| P2 fouled | P2 12 | Bacillus cereus | 2.14 |
| P2 fouled | P2 21 | Bacillus marisflavi | 1.73 |
| P2 fouled | P2 22 | Bacillus cereus | 1.67 |
| P2 fouled | P2 2-4 | Bacillus marisflavi | 1.72 |
| P1-clean | No isolates | No isolates | |
| P2-clean | P2 Cl-2 | Bacillus cereus | 2.02 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Abri, M.; Kyaw, H.H.; Al-Ghafri, B.; Myint, M.T.Z.; Dobretsov, S. Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman. Membranes 2022, 12, 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070671
Al-Abri M, Kyaw HH, Al-Ghafri B, Myint MTZ, Dobretsov S. Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):671. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070671
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Abri, Mohammed, Htet Htet Kyaw, Buthayna Al-Ghafri, Myo Tay Zar Myint, and Sergey Dobretsov. 2022. "Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman" Membranes 12, no. 7: 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070671
APA StyleAl-Abri, M., Kyaw, H. H., Al-Ghafri, B., Myint, M. T. Z., & Dobretsov, S. (2022). Autopsy of Used Reverse Osmosis Membranes from the Largest Seawater Desalination Plant in Oman. Membranes, 12(7), 671. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070671








