Removal of Ni(II) Ions by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Film via Laser Ablation in Liquid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
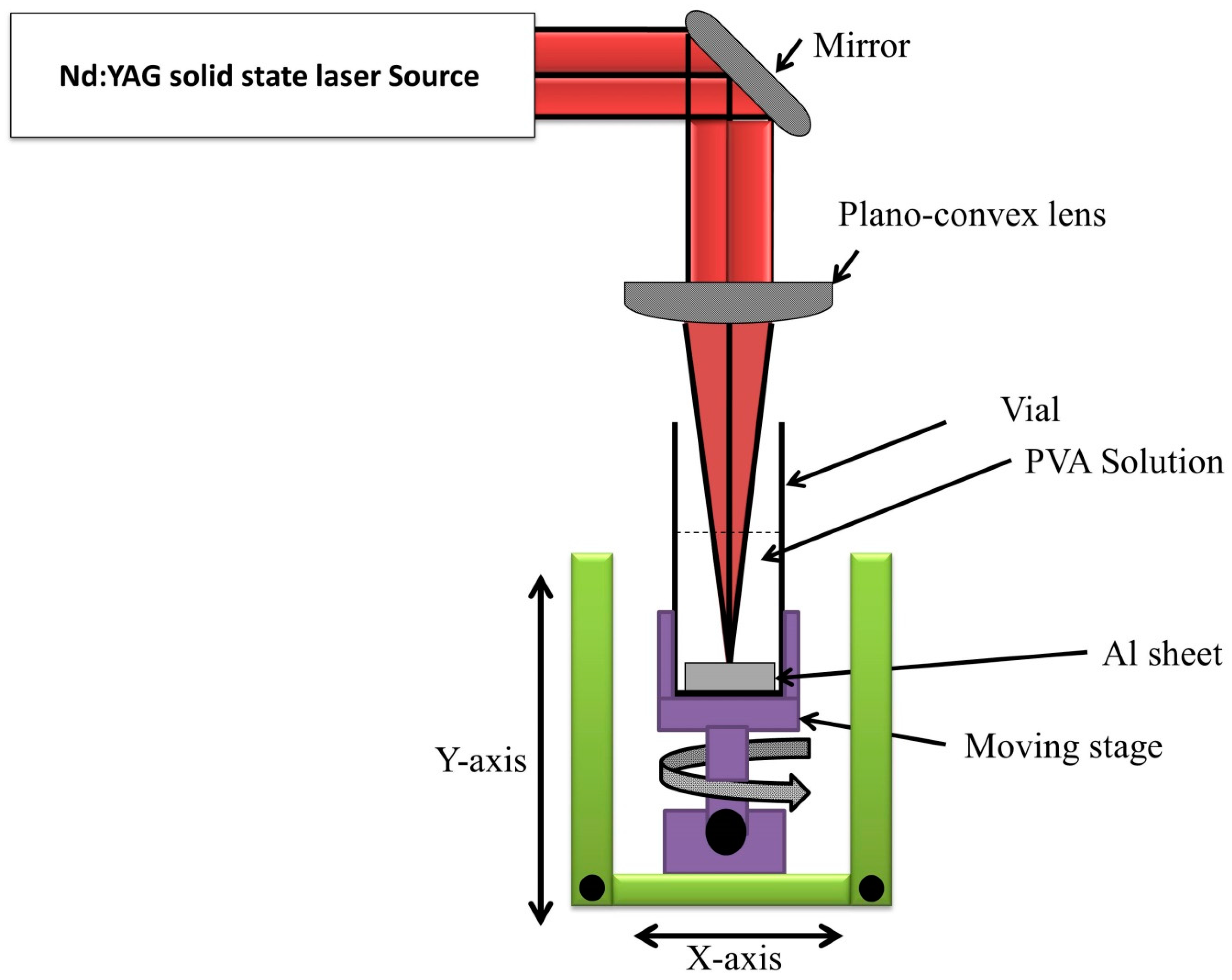
2. Materials and Experimental Work
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of PVA Solution
2.3. Preparation of Al2O3-PVA Composite
2.4. Investigation Techniques
2.5. Adsorption Study
3. Result and Discussion
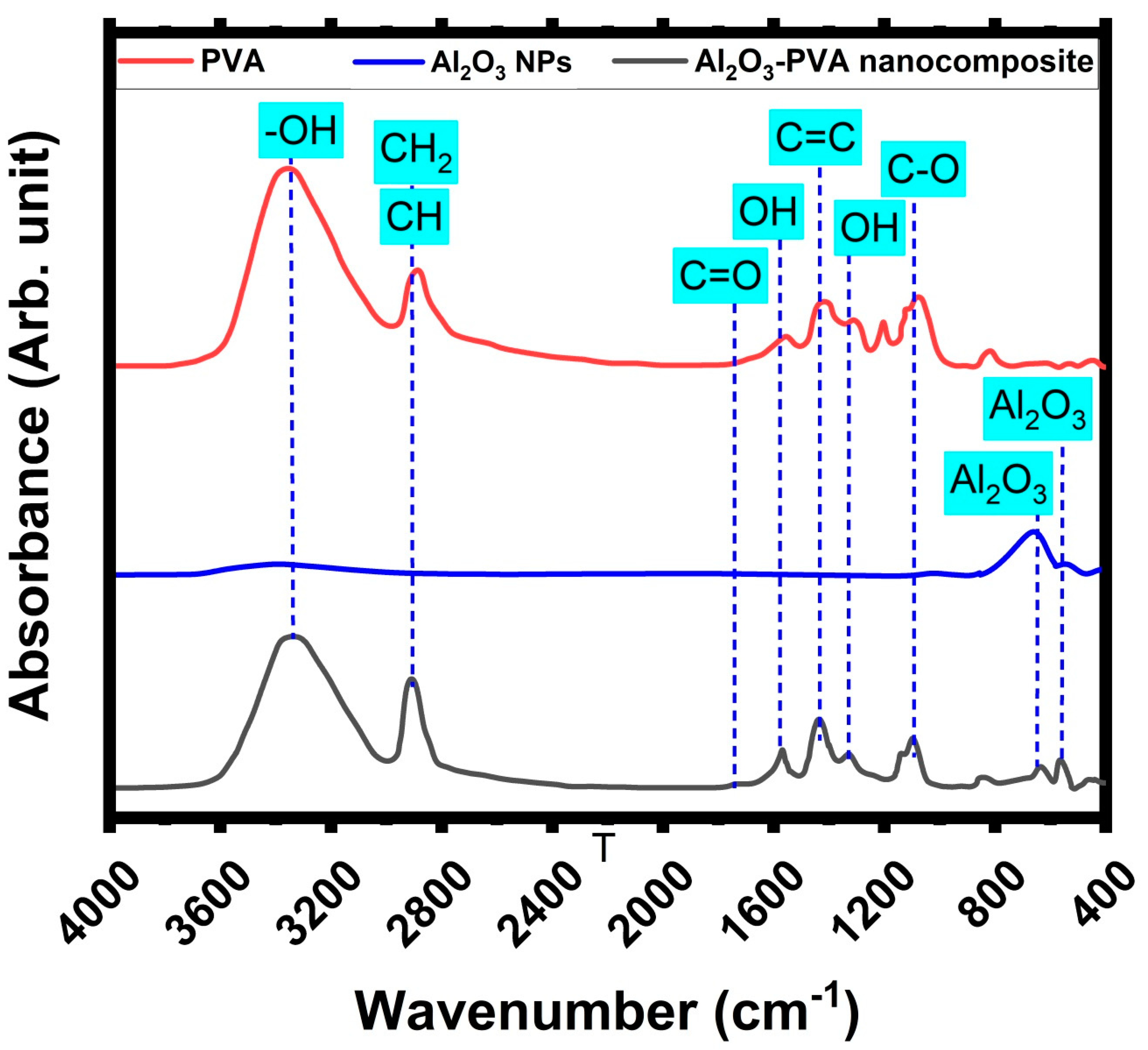
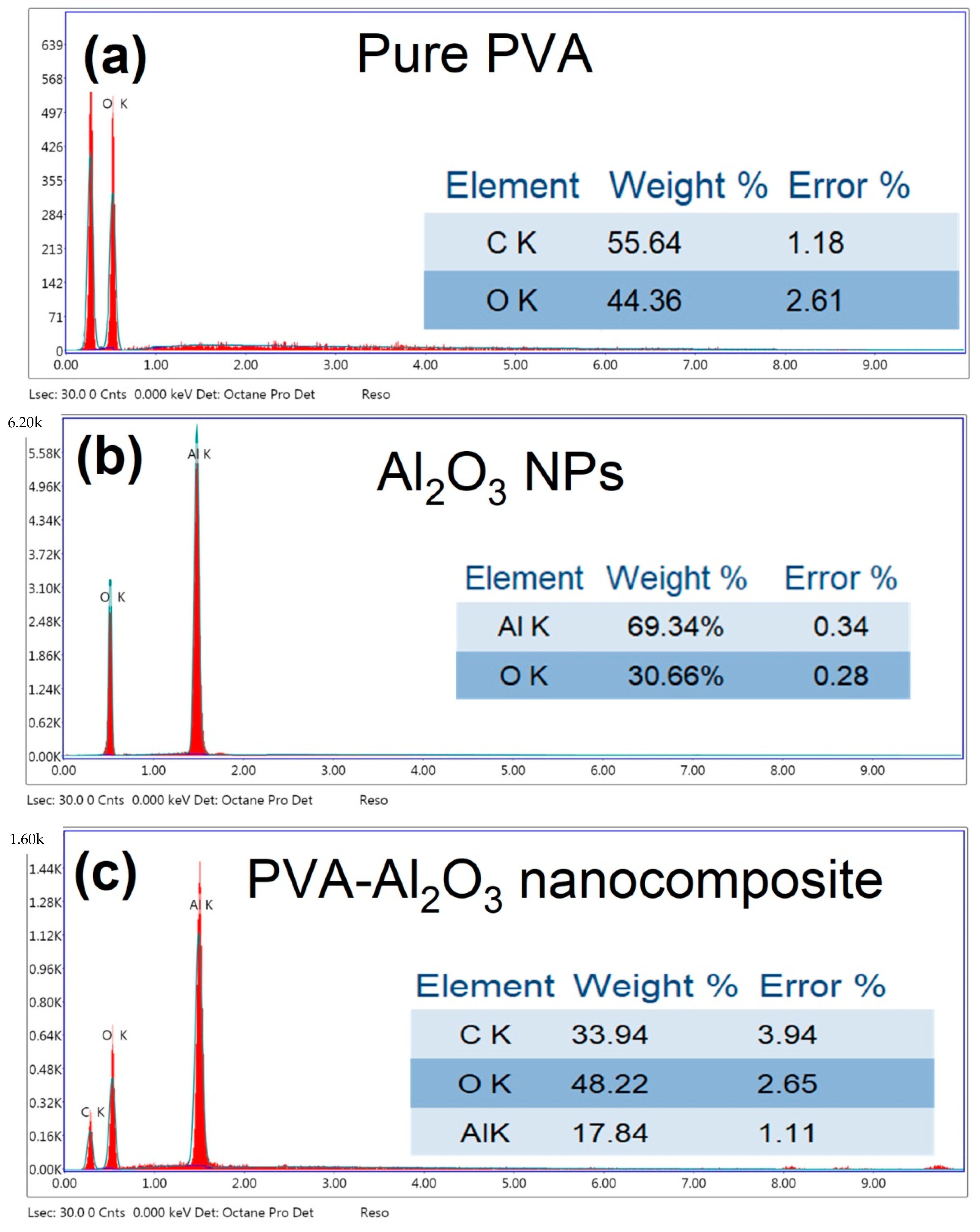
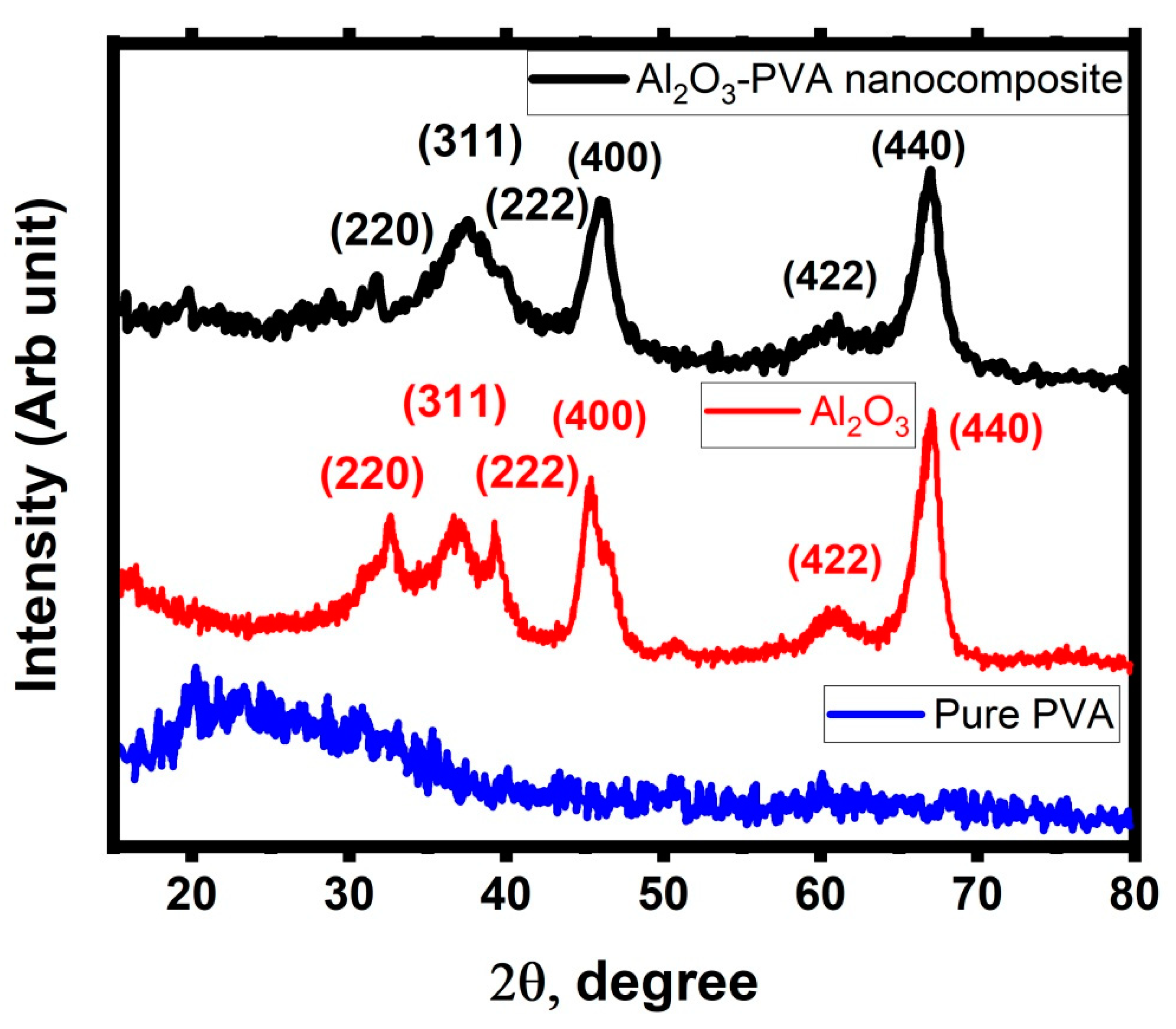
3.1. Investigation of the Prepared Al2O3-PVA Nanocomposite
3.2. Adsorption Process
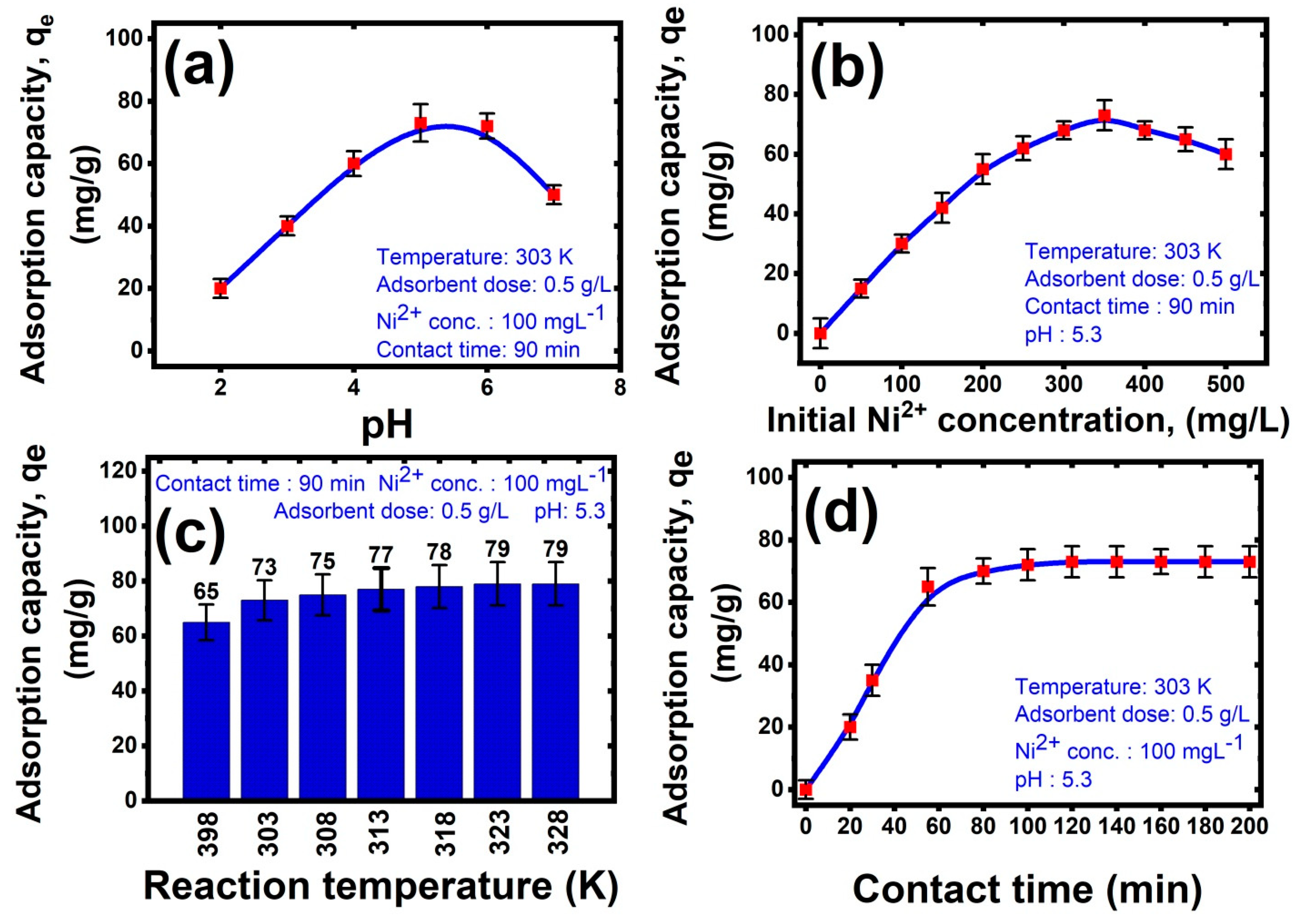
3.2.1. Effect of pH
- At pH values higher than 6, the excess of alkaline –OH group has a greater tendency to combine with Ni2+ and form Ni(OH)2 participated, causing the adsorption to be diminished.
- At pH values in the range 5–6, the surface charge of the hybrid nanocomposite turned to a negative charge due to the medium having a low acidic concentration, increasing the coordination between positively charged metal ions (Ni2+) and Al2O3-PVA nanocomposite by electrostatic attraction, leading to reach the maximum adsorption capacity. The results were consistent with Ni2+ adsorption on Al2O3-PVA nanocomposite as mentioned in the previous work [57].
- At pH values lower than 5, the decrease in nickel adsorption capability at lower pH levels is related to protonation of the Al2O3-PVA nanocomposite by the acidic medium and the water molecules converted from H2O to H3O+, leading to a decrease in the number of charge carriers in the hybrid membrane for metal adsorption. In addition, competition for adsorption sites on the PVA structure created between H+ and Al2+ make an electrostatic repulsion between them [58,59,60,61].
3.2.2. Effect of Initial Pollutant Concentration
3.2.3. Effect of Temperature
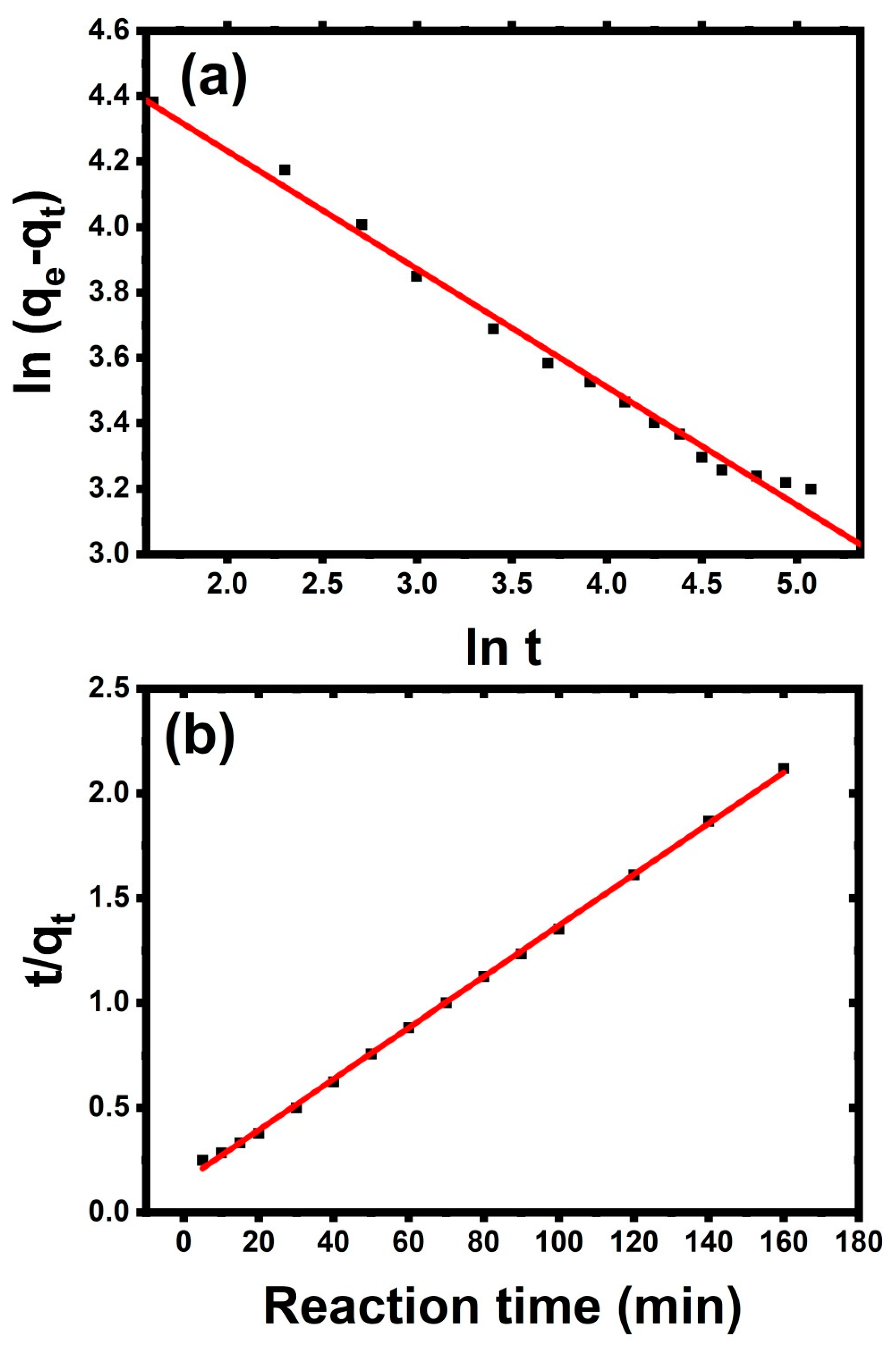
3.2.4. Effect of Contact Time
3.3. Mechanism of Adsorption Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Altowyan, A.S.; Toghan, A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Pashameah, R.A.; Mwafy, E.A.; Alrefaee, S.H.; Mostafa, A.M. Removal of methylene blue dye from aqueous solution using carbon nanotubes decorated by nickel oxide nanoparticles via pulsed laser ablation method. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 198, 110268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kadhi, N.S.; Pashameah, R.A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alrefaee, S.H.; Alamro, F.S.; Faqih, H.H.; Mwafy, E.A.; Mostafa, A.M. Preparation of NiO/MWCNTs nanocomposite and its application for cadmium ion removal from aqueous solutions. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 19, 1961–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwafy, E.A.; Mostafa, A.M. Tailored MWCNTs/SnO2 decorated cellulose nanofiber adsorbent for the removal of Cu (II) from waste water. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2020, 177, 109172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkallas, F.H.; Toghan, A.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alrefaee, S.H.; Pashameah, R.A.; Alrebdi, T.A.; Mwafy, E.A.; Mstafa, A.M. Catalytic performance of NiO nanoparticles decorated carbon nanotubes via one-pot laser ablation method against methyl orange dye. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 3336–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaleh, B.; Nasrollahzadeh, M.; Mohazzab, B.F.; Eslamipanah, M.; Sajjadi, M.; Ghafuri, H. State-of-the-art technology: Recent investigations on laser-mediated synthesis of nanocomposites for environmental remediation. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 10389–10425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, B.; Chen, Y. Conductive WO3-x@ CNT networks for efficient Li-S batteries. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 892, 012027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y. Designed synthesis of ultrafine NiO nanocrystals bonded on a three dimensional graphene framework for high-capacity lithium-ion batteries. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 9901–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; You, X.; Zhang, M.; Walle, M.D.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.-N. 3D well-interconnected NiO–graphene–carbon nanotube nanohybrids as high-performance anode materials for Li-ion batteries. J. Nanopart. Res. 2016, 18, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ni, S.; Lv, X.; Yang, X.; Duan, S. Preparation of NiO–Ni/natural graphite composite anode for lithium ion batteries. J. Alloy. Compd. 2013, 553, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Huang, J.; Wang, M.; Huang, M.; Wang, Y. The fate and long-term toxic effects of NiO nanoparticles at environmental concentration in constructed wetland: Enzyme activity, microbial property, metabolic pathway and functional genes. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, A.R.; Correia, A.A.; Rasteiro, M.G. Heavy Metals Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Multiwall Carbon Nanotubes: Effect of MWCNTs Dispersion. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egbosiuba, T.C.; Abdulkareem, A.S.; Kovo, A.S.; Afolabi, E.A.; Tijani, J.O.; Bankole, M.T.; Bo, S.; Roos, W.D. Adsorption of Cr(VI), Ni(II), Fe(II) and Cd(II) ions by KIAgNPs decorated MWCNTs in a batch and fixed bed process. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carolin, C.F.; Kumar, P.S.; Saravanan, A.; Joshiba, G.J.; Naushad, M. Efficient techniques for the removal of toxic heavy metals from aquatic environment: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2782–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, R.; Pelalak, R.; Pishnamazi, M.; Marjani, A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Sarkar, S.M.; Shirazian, S. A novel and facile green synthesis method to prepare LDH/MOF nanocomposite for removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II). Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsalani, N.; Bazazi, S.; Abuali, M.; Jodeyri, S. A new method for preparing ZnO/CNT nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic degradation of malachite green under visible light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2020, 389, 112207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareesh, K.; Sunitha, D.V.; Dhole, S.D.; Bhoraskar, V.N.; Phase, D.M.; Williams, J. One-step gamma radiation aided diffusion of Ag-Au alloy nanoparticles into polycarbonate and its application towards the reduction of 4-Nitrophenol. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2019, 162, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alwan, S.H.; Alshamsi, H.A. In situ synthesis NiO/F-MWCNTs nanocomposite for adsorption of malachite green dye from polluted water. Carbon Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwafy, E.A.; Gaafar, M.S.; Mostafa, A.M.; Marzouk, S.Y.; Mahmoud, I.S. Novel laser-assisted method for synthesis of SnO2/MWCNTs nanocomposite for water treatment from Cu (II). Diam. Relat. Mater. 2021, 113, 108287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhong, A.; Jin, Y. Removal capacity and adsorption mechanism of heat-treated palygorskite clay for methylene blue. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 174, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taherian, Z.; Shahed Gharahshiran, V.; Khataee, A.; Meshkani, F.; Orooji, Y. Comparative study of modified Ni catalysts over mesoporous CaO-Al2O3 support for CO2/methane reforming. Catal. Commun. 2020, 145, 106100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghihinezhad, M.; Baghdadi, M.; Shahin, M.S.; Torabian, A. Catalytic ozonation of real textile wastewater by magnetic oxidized g-C3N4 modified with Al2O3 nanoparticles as a novel catalyst. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 283, 120208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudin, M.; Carles, P.; Laborde, E.; Champeaux, C.; Dumas-Bouchiat, F. A dual nanosecond-pulsed laser setup for nanocomposite synthesis—Ag nanoparticles in Al2O3/VO2 matrix. J. Appl. Phys. 2019, 125, 054301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, H.R.; Kapoor, S.; Patel, Y.; Ngai, K.; Levin, K.; Germanov, Y.; Krishtopa, L.; Kroeker, S.; Goel, A. Composition-structure-property relationships in Li2O–Al2O3–B2O3 glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2018, 502, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Saniger, J.; Castaño, V.M. Characterization of the mechanical properties of polyacrylic acid-metal oxide concretes. Mater. Lett. 1992, 14, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, A.B.G.; Alkallas, F.H.; Ziouche, A.; Boukhachem, A.; Ghamnia, M.; Elhouichet, H. Structural Defect Impact on Changing Optical Response and Raising Unpredicted Ferromagnetic Behaviour in (111) Preferentially Oriented Nanocrystalline NiO Films. Crystals 2022, 12, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Fang, D.; Pang, Z.; Luo, B.; Kuang, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Shen, Q.; Ji, F. Immobilization of powdery calcium silicate hydrate via PVA covalent cross-linking process for phosphorus removal. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 645, 937–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Abidin, Z.H.Z.; Chowdhury, F.; Arof, A.K. A high efficiency chlorophyll sensitized solar cell with quasi solid PVA based electrolyte. Int. J. Photoenergy 2016, 2016, 3685210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.; Basit, M.; Ahmad, M.; Raza, Z.A. Structural and Band Structure Investigation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Incorporated PVA Nanocomposite Films. Res. Sq. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Menazea, A.A. Polyvinyl Alcohol/Silver nanoparticles film prepared via pulsed laser ablation: An eco-friendly nano-catalyst for 4-nitrophenol degradation. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1212, 128125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X. Deposition of Au nanoparticles on PDA-functionalized PVA beads as a recyclable catalyst for degradation of organic pollutants with NaBH4 in aqueous solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 793, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElFaham, M.M.; Okil, M.; Mostafa, A.M. Fabrication of magnesium metallic nanoparticles by liquid-assisted laser ablation. JOSA B 2020, 37, 2620–2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Mwafy, E.A. The effect of laser fluence for enhancing the antibacterial activity of NiO nanoparticles by pulsed laser ablation in liquid media. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2020, 14, 100382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Mwafy, E.A. Laser-assisted for preparation Ag/CdO nanocomposite thin film: Structural and optical study. Opt. Mater. 2020, 107, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.M.; Mwafy, E.A. Synthesis of ZnO/CdO thin film for catalytic degradation of 4-nitrophenol. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1221, 128872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, J.; Lombard, J.; Dujardin, C.; Ledoux, G.; Merabia, S.; Amans, D.J.A.P.L. Dynamical study of bubble expansion following laser ablation in liquids. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 074104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, L. Characteristics of γ-Al2O3 nanoparticles generated by continuous-wave laser ablation in liquid. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 101, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piriyawong, V.; Thongpool, V.; Asanithi, P.; Limsuwan, P. Preparation and characterization of alumina nanoparticles in deionized water using laser ablation technique. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riahi, A.; Khamlich, S.; Balghouthi, M.; Khamliche, T.; Doyle, T.B.; Dimassi, W.; Guizani, A.; Maaza, M. Study of thermal conductivity of synthesized Al2O3-water nanofluid by pulsed laser ablation in liquid. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 304, 112694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari Eskandari, M.; Shafyei, A.; Karimzadeh, F. One-step fabrication of Au@Al2O3 core-shell nanoparticles by continuous-wave fiber laser ablation of thin gold layer on aluminum surface: Structural and optical properties. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menazea, A.A.; Mostafa, A.M.; Al-Ashkar, E.A. Effect of nanostructured metal oxides (CdO, Al2O3, Cu2O) embedded in PVA via Nd:YAG pulsed laser ablation on their optical and structural properties. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1203, 127374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElFaham, M.M.; Okil, M.; Mostafa, A.M. Effects of post-laser irradiation on the optical and structure properties of Al2O3 nanoparticles produced by laser ablation. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 128, 153104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Fu, Y.; Ai, H.; Fu, M.-L.; Yuan, B. Removal of phosphate at low concentration from water by porous PVA/Al2O3 composites. Environ. Technol. 2022, 43, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman Khan, M.M.; Akter, M.; Amin, M.K.; Younus, M.; Chakraborty, N. Synthesis, Luminescence and Thermal Properties of PVA–ZnO–Al2O3 Composite Films: Towards Fabrication of Sunlight-Induced Catalyst for Organic Dye Removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2018, 26, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, Z.; Khalili, R.; Ali Zazouli, M. Surface modified polythiophene/Al2O3 and polyaniline/Al2O3 nanocomposites using poly (vinyl alcohol) for the removal of heavy metal ions from water: Kinetics, thermodynamic and isotherm studies. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 84, 182–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukwevho, N.; Gusain, R.; Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Kumar, N.; Waanders, F.; Ray, S.S. Removal of naphthalene from simulated wastewater through adsorption-photodegradation by ZnO/Ag/GO nanocomposite. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 81, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menazea, A.A.; Ezzat, H.A.; Omara, W.; Basyouni, O.H.; Ibrahim, S.A.; Mohamed, A.A.; Tawfik, W.; Ibrahim, M.A. Chitosan/graphene oxide composite as an effective removal of Ni, Cu, As, Cd and Pb from wastewater. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2020, 1189, 112980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulfiqar, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Mafize, A.A.; Kahar, N.A.M.A.; Johari, K.; Rabat, N.E. Efficient Removal of Pb(II) from Aqueous Solutions by Using Oil Palm Bio-Waste/MWCNTs Reinforced PVA Hydrogel Composites: Kinetic, Isotherm and Thermodynamic Modeling. Polymers 2020, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inagaki, M.; Fujita, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Oshida, K.; Iwata, H.; Konno, H. Formation of graphite crystals at 1000–1200°C from mixtures of vinyl polymers with metal oxides. Carbon 2001, 39, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaei, B.; Miri, R.; Bazyari, A.; Thompson, L.T. Asphaltene adsorption on MgO, CaO, SiO2, and Al2O3 nanoparticles synthesized via the Pechini-type Sol−Gel method. Fuel 2022, 321, 124136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hema, M.; Selvasekarapandian, S.; Arunkumar, D.; Sakunthala, A.; Nithya, H.F.T.I.R. FTIR, XRD and ac impedance spectroscopic study on PVA based polymer electrolyte doped with NH4X (X = Cl, Br, I). J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darwish, A.M.; Eisa, W.H.; Shabaka, A.A.; Talaat, M.H. Synthesis of nano-cadmium sulfide by pulsed laser ablation in liquid environment. Spectrosc. Lett. 2015, 48, 638–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, P.; Vuksanović, M.M.; Mitrić, M.; Stojanović, D.B.; Kojović, A.; Rogan, J.R.; Jančić-Heinemann, R. Electrospun alumina fibers doped with ferric and magnesium oxides. Sci. Sinter. 2018, 50, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, D.; Gautam, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Shukla, B.K.; Shankar, V.; Krishna, V. Citric acid coated magnetic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and application in removal of Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2014, 4, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Phosphorus removal from wastewater using nano-particulates of hydrated ferric oxide doped activated carbon fiber prepared by Sol–Gel method. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 200–202, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Mishra, S. Synthesis, characterization and removal of Cd(II) using Cd(II)-ion imprinted polymer. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 164, 1547–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, A.N.; Billingham, N.C. Characterisation and oxidative degradation of a room-temperature vulcanised poly(dimethylsiloxane) rubber. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2001, 73, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwafy, E.A.; Mostafa, A.M. Efficient removal of Cu (II) by SnO2/MWCNTs nanocomposite by pulsed laser ablation method. Nano-Struct. Nano-Objects 2020, 24, 100591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, C.; Wu, D.; Kong, H. Removal and recovery of phosphate from water by activated aluminum oxide and lanthanum oxide. Powder Technol. 2015, 269, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, E.M.; Petit, C. Towards the use of metal–organic frameworks for water reuse: A review of the recent advances in the field of organic pollutants removal and degradation and the next steps in the field. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 22484–22506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acelas, N.Y.; Martin, B.D.; López, D.; Jefferson, B. Selective removal of phosphate from wastewater using hydrated metal oxides dispersed within anionic exchange media. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubey, S.; Banerjee, S.; Upadhyay, S.N.; Sharma, Y.C. Application of common nano-materials for removal of selected metallic species from water and wastewaters: A critical review. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 240, 656–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, R.; Guo, L.; Zou, X.; Li, J.; Hao, Z.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Zeng, X.; Lu, Y.F. Background removal in soil analysis using laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy combined with standard addition method. Opt. Express 2016, 24, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, P.; Tang, L.; Tang, J.; Zeng, G.; Huang, B.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Deng, Y.; Ma, L. Catalytic reduction–adsorption for removal of p-nitrophenol and its conversion p-aminophenol from water by gold nanoparticles supported on oxidized mesoporous carbon. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 469, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Xu, J.; Bu, X.-H. Recent advances about metal–organic frameworks in the removal of pollutants from wastewater. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 378, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arizavi, A.; Mirbagheri, N.S.; Hosseini, Z.; Chen, P.; Sabbaghi, S. Efficient removal of naphthalene from aqueous solutions using a nanoporous kaolin/Fe3O4 composite. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 17, 1991–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, S.; Nasreen, S.; Haroon, A.; Ashraf, M.A. Synhesis of Silver and Copper Nanoparticles from Plants and Application as Adsorbents for Naphthalene decontamination. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 27, 1016–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Fu, Q.; Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J. Highly-effective removal of Pb by co-pyrolysis biochar derived from rape straw and orthophosphate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Composite | Organic Pollutants/Heavy Metals | Efficacy |
|---|---|---|
| Al2O3-PVA [42] | phosphate | 95% |
| PVA–ZnO–Al2O3 [43] | MB | 100% |
| Polythiophene/PVA/Al2O3 [44] | Pb(II), | 97.3% |
| Zn(II), | 89.4% | |
| Cd(II) | 95.8% | |
| Polyaniline/PVA/Al2O3 [44] | Pb(II), | 89.78% |
| Zn(II), | 84.9% | |
| Cd(II) | 79.2% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alkallas, F.H.; Ahmed, H.A.; Alrebdi, T.A.; Pashameah, R.A.; Alrefaee, S.H.; Alsubhe, E.; Trabelsi, A.B.G.; Mostafa, A.M.; Mwafy, E.A. Removal of Ni(II) Ions by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Film via Laser Ablation in Liquid. Membranes 2022, 12, 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070660
Alkallas FH, Ahmed HA, Alrebdi TA, Pashameah RA, Alrefaee SH, Alsubhe E, Trabelsi ABG, Mostafa AM, Mwafy EA. Removal of Ni(II) Ions by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Film via Laser Ablation in Liquid. Membranes. 2022; 12(7):660. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070660
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlkallas, Fatemah H., Hoda A. Ahmed, Tahani A. Alrebdi, Rami Adel Pashameah, Salhah H. Alrefaee, Emaan Alsubhe, Amira Ben Gouider Trabelsi, Ayman M. Mostafa, and Eman A. Mwafy. 2022. "Removal of Ni(II) Ions by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Film via Laser Ablation in Liquid" Membranes 12, no. 7: 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070660
APA StyleAlkallas, F. H., Ahmed, H. A., Alrebdi, T. A., Pashameah, R. A., Alrefaee, S. H., Alsubhe, E., Trabelsi, A. B. G., Mostafa, A. M., & Mwafy, E. A. (2022). Removal of Ni(II) Ions by Poly(Vinyl Alcohol)/Al2O3 Nanocomposite Film via Laser Ablation in Liquid. Membranes, 12(7), 660. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12070660









