The Suitability of Latex Particles to Evaluate Critical Process Parameters in Steric Exclusion Chromatography
Abstract
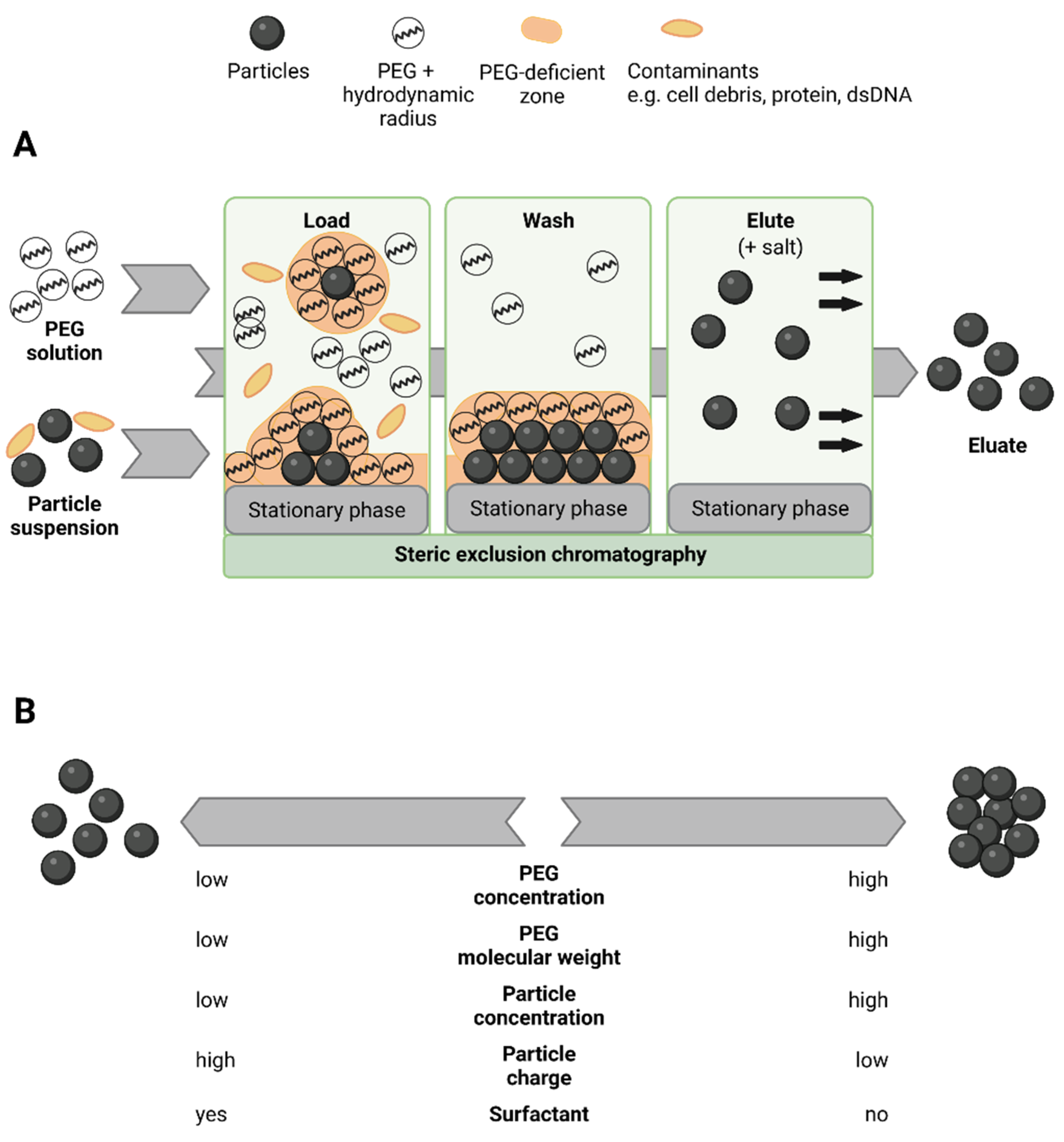
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Polystyrene Calibration Particles Characterization
2.2. Steric Exclusion Chromatography
3. Results
3.1. Polystyrene Particle Characterization
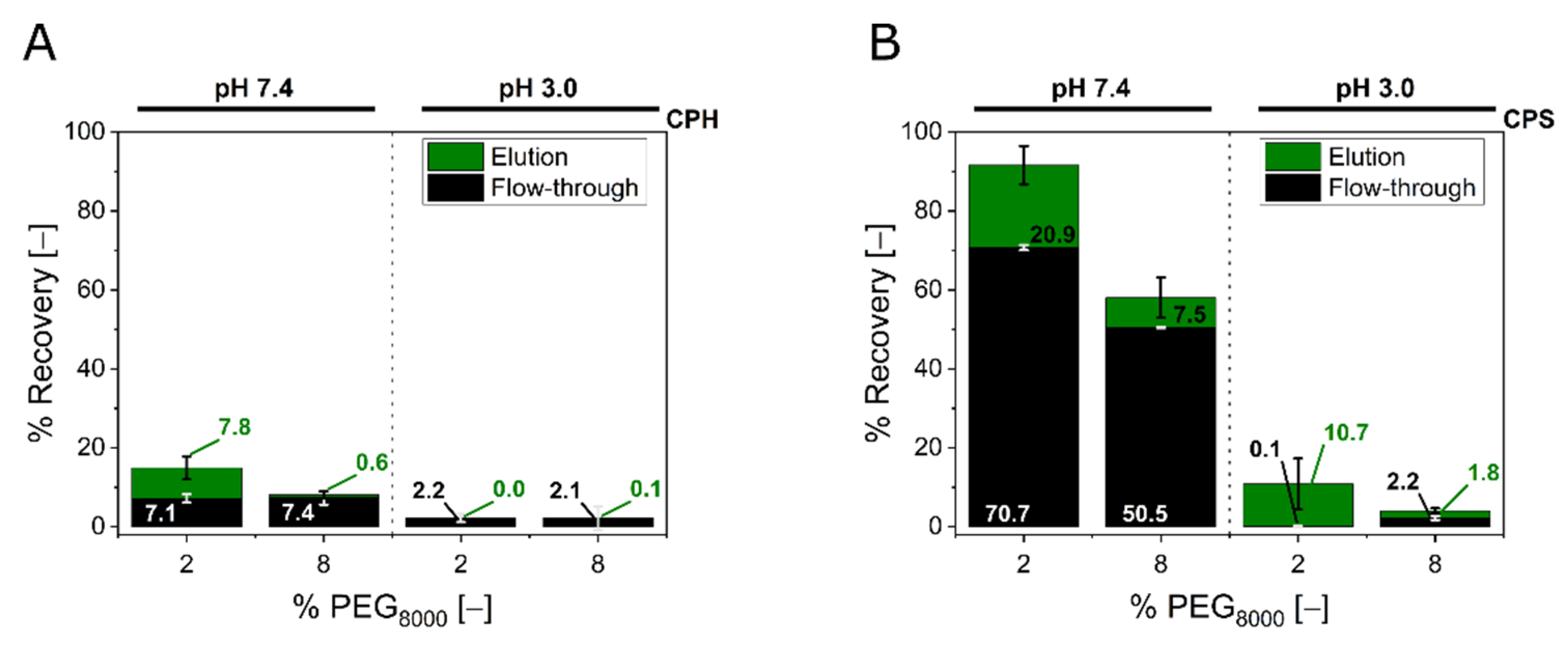
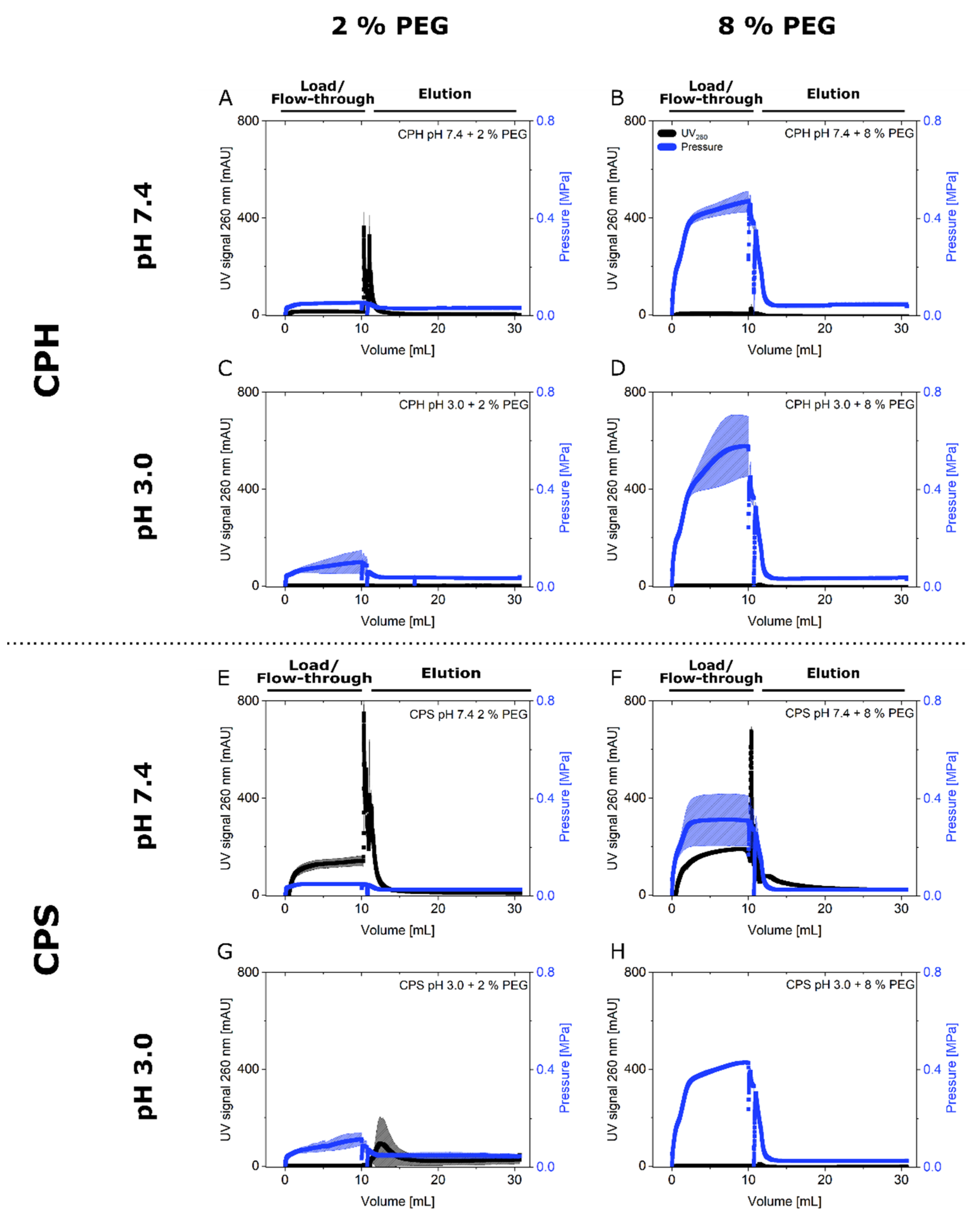
3.2. Steric Exclusion Chromatography with Polystyrene Particles
4. Discussion
4.1. Particle Characterization
4.2. Steric Exclusion Chromatography
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, J.; Gan, H.T.; Latiff, S.M.A.; Chuah, C.; Lee, W.Y.; Yang, Y.-S.; Loo, B.; Ng, S.K.; Gagnon, P. Principles and Applications of Steric Exclusion Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1270, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, P.; Toh, P.; Lee, J. High Productivity Purification of Immunoglobulin G Monoclonal Antibodies on Starch-Coated Magnetic Nanoparticles by Steric Exclusion of Polyethylene Glycol. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1324, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minton, A.P. Molecular crowding: Analysis of effects of high concentrations of inert cosolutes on biochemical equilibria and rates in terms of volume exclusion. In Energetics of Biological Macromolecules Part B; Ackers, G.K., Johnson, M.L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1998; pp. 127–149. ISBN 9780121821968. [Google Scholar]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Mechanism of poly(ethylene glycol) interaction with proteins. Biochemistry 1985, 24, 6756–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.C.; Lee, L.L. Preferential Solvent Interactions Between Proteins and Polyethylene Glycols. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Großhans, S.; Wang, G.; Hubbuch, J. Water on Hydrophobic Surfaces: Mechanistic Modeling of Polyethylene Glycol-Induced Protein Precipitation. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2019, 42, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sukenik, S.; Sapir, L.; Harries, D. Balance of enthalpy and entropy in depletion forces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arakawa, T.; Gagnon, P. Excluded Cosolvent in Chromatography. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2297–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K.; Uversky, V.N. What macromolecular crowding can do to a protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 23090–23140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lothert, K.; Offersgaard, A.F.; Pihl, A.F.; Mathiesen, C.K.; Jensen, T.B.; Alzua, G.P.; Fahnøe, U.; Bukh, J.; Gottwein, J.M.; Wolff, M.W. Development of a downstream process for the production of an inactivated whole hepatitis C virus vaccine. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemb, T.; Leontidis, E. Equilibrium in soft-matter systems under the influence of competing forces. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 493–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. Preferential interactions of proteins with salts in concentrated solutions. Biochemistry 1982, 21, 6545–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levanova, A.; Poranen, M.M. Application of Steric Exclusion Chromatography on Monoliths for Separation and Purification of RNA Molecules. J. Chromatogr. A 2018, 1574, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Bai, S.; Tao, S.-P.; Sun, Y. Evaluation of Steric Exclusion Chromatography on Cryogel Column for the Separation of Serum Proteins. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1333, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lothert, K.; Sprick, G.; Beyer, F.; Lauria, G.; Czermak, P.; Wolff, M.W. Membrane-Based Steric Exclusion Chromatography for the Purification of a Recombinant Baculovirus and its Application for Cell Therapy. J. Virol. Methods 2020, 275, 113756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothert, K.; Pagallies, F.; Eilts, F.; Sivanesapillai, A.; Hardt, M.; Moebus, A.; Feger, T.; Amann, R.; Wolff, M.W. A scalable downstream process for the purification of the cell culture-derived Orf virus for human or veterinary applications. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothert, K.; Pagallies, F.; Feger, T.; Amann, R.; Wolff, M.W. Selection of chromatographic methods for the purification of cell culture-derived Orf virus for its application as a vaccine or viral vector. J. Biotechnol. 2020, 323, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal-Gallardo, P.; Börner, K.; Pieler, M.M.; Sonntag-Buck, V.; Obr, M.; Bejarano, D.; Wolff, M.W.; Kräusslich, H.-G.; Reichl, U.; Grimm, D. Single-use capture purification of adeno-associated viral gene transfer vectors by membrane-based steric exclusion chromatography. Hum. Gene Ther. 2021, 32, 959–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marichal-Gallardo, P.; Pieler, M.M.; Wolff, M.W.; Reichl, U. Steric Exclusion Chromatography for Purification of Cell Culture-Derived Influenza A Virus Using Regenerated Cellulose Membranes and Polyethylene Glycol. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1483, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giesler, J.; Weirauch, L.; Thöming, J.; Baune, M.; Pesch, G.R. Separating microparticles by material and size using dielectrophoretic chromatography with frequency modulation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Beeck, J.O.; de Malsche, W.; Vangelooven, J.; Gardeniers, H.; Desmet, G. Hydrodynamic chromatography of polystyrene microparticles in micropillar array columns. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 6077–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meder, F.; Daberkow, T.; Treccani, L.; Wilhelm, M.; Schowalter, M.; Rosenauer, A.; Mädler, L.; Rezwan, K. Protein adsorption on colloidal alumina particles functionalized with amino, carboxyl, sulfonate and phosphate groups. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 1221–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Tu, K.-J.; Deng, J.-P.; Lo, Y.-S.; Wu, C.-H. Markedly Enhanced Surface Hydroxyl Groups of TiO2 Nanoparticles with Superior Water-Dispersibility for Photocatalysis. Materials 2017, 10, 566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sthoer, A.P.A.; Tyrode, E.C. Anion Specific Effects at Negatively Charged Interfaces: Influence of Cl-, Br-, I-, and SCN- on the Interactions of Na+ with the Carboxylic Acid Moiety. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 12384–12391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Pons Royo, M.C.; Beulay, J.-L.; Valery, E.; Jungbauer, A.; Satzer, P. Mode and dosage time in polyethylene glycol precipitation process influences protein precipitate size and filterability. Process BioChem. 2022, 114, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.F.L.; Merlin, J.; Narayana, P.A.L. Electrostatic Interactions Between Diffuse Soft Multi-layered (Bio)Particles: Beyond Debye–Hückel Approximation and Deryagin Formulation. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 1037–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, J.F.; Gaboriaud, F. Progress in electrohydrodynamics of soft microbial particle interphases. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 15, 184–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dika, C.; Duval, J.F.L.; Francius, G.; Perrin, A.; Gantzer, C. Isoelectric PoInt. is an Inadequate Descriptor of MS2, Phi X 174 and PRD1 Phages Adhesion on Abiotic Surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 446, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langlet, J.; Gaboriaud, F.; Gantzer, C.; Duval, J.F.L. Impact of Chemical and Structural Anisotropy on the Electrophoretic Mobility of Spherical Soft Multilayer Particles: The Case of Bacteriophage MS2. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 3293–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dika, C.; Ly-Chatain, M.H.; Francius, G.; Duval, J.; Gantzer, C. Non-DLVO Adhesion of F-Specific RNA Bacteriophages to Abiotic Surfaces: Importance of Surface Roughness, Hydrophobic and Electrostatic Interactions. Colloid Surf. A 2013, 435, 178–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faille, C.; Lemy, C.; Allion-Maurer, A.; Zoueshtiagh, F. Evaluation of the hydrophobic properties of latex microspheres and Bacillus spores. Influence of the particle size on the data obtained by the MATH method (microbial adhesion to hydrocarbons). Colloid Surf. B 2019, 182, 110398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, H.; Tarabara, V.V. Charge, size distribution and hydrophobicity of viruses: Effect of propagation and purification methods. J. Virol. Methods 2018, 256, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eilts, F.; Steger, M.; Lothert, K.; Wolff, M.W. The Suitability of Latex Particles to Evaluate Critical Process Parameters in Steric Exclusion Chromatography. Membranes 2022, 12, 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050488
Eilts F, Steger M, Lothert K, Wolff MW. The Suitability of Latex Particles to Evaluate Critical Process Parameters in Steric Exclusion Chromatography. Membranes. 2022; 12(5):488. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050488
Chicago/Turabian StyleEilts, Friederike, Marleen Steger, Keven Lothert, and Michael W. Wolff. 2022. "The Suitability of Latex Particles to Evaluate Critical Process Parameters in Steric Exclusion Chromatography" Membranes 12, no. 5: 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050488
APA StyleEilts, F., Steger, M., Lothert, K., & Wolff, M. W. (2022). The Suitability of Latex Particles to Evaluate Critical Process Parameters in Steric Exclusion Chromatography. Membranes, 12(5), 488. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12050488






