A Novel Hybrid Reactor of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis Coupling with Activated Sludge Process for Simultaneously Treating Concentrated Seawater Brine and Wastewater and Recovering Energy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Feed and Draw Solutions
2.2. Experimental Set-Up and Operating Conditions
2.3. Membrane Properties and Orientation
2.4. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Performance of PRO-MBR at Two Different Membrane Orientations
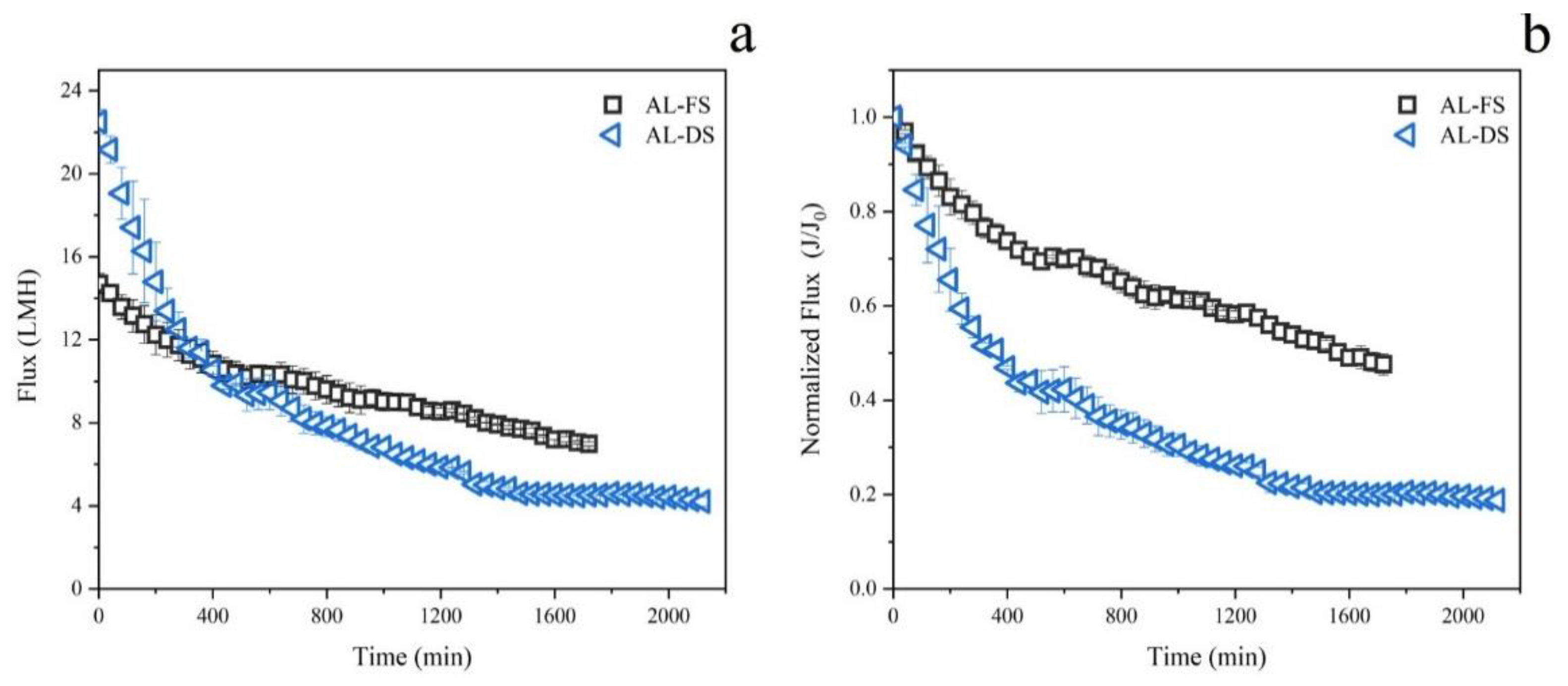
3.1.1. Water Flux
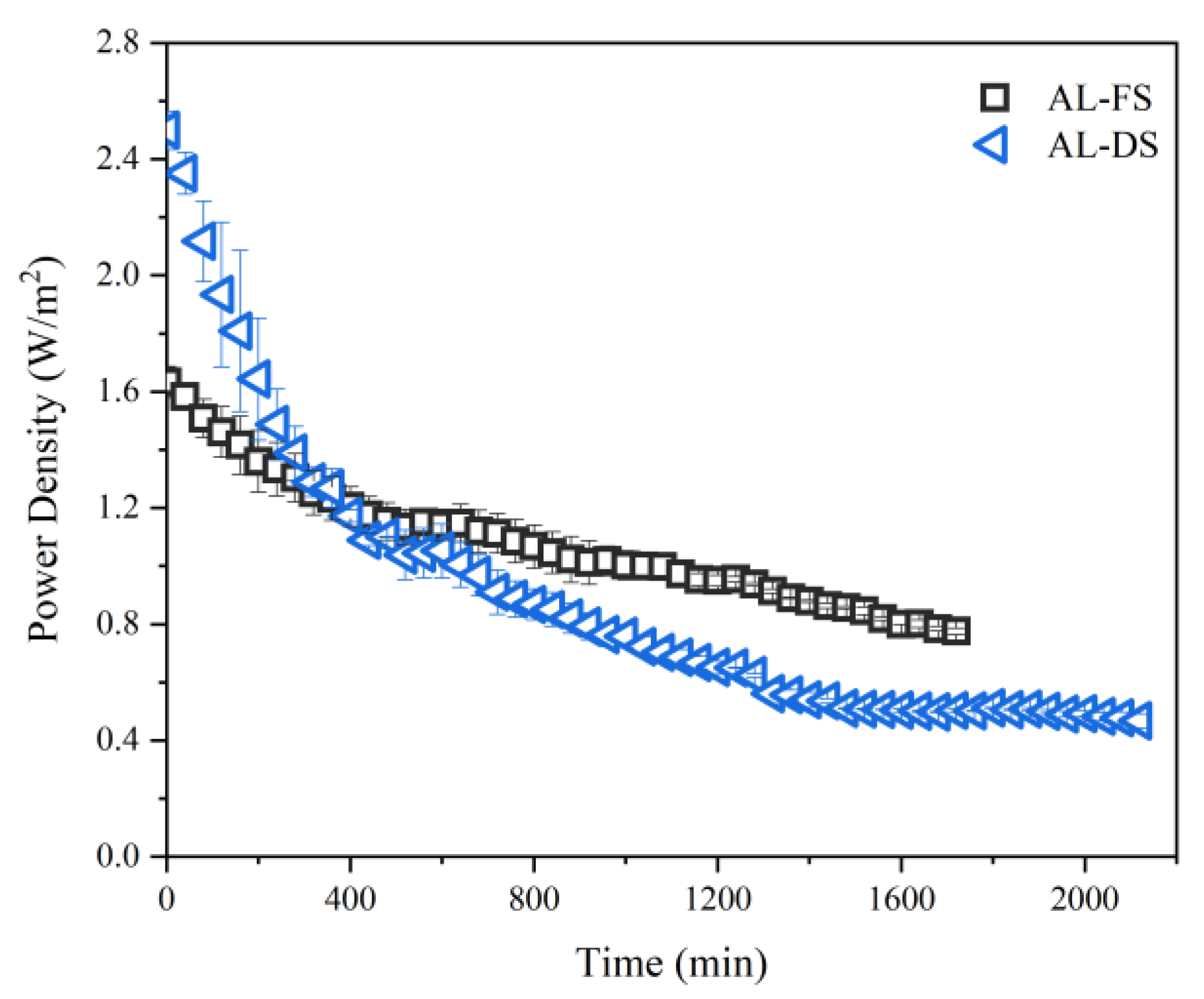
3.1.2. Power Density
3.1.3. Contaminant Removal
3.2. Membrane Fouling of PRO-MBR at Two Different Membrane Orientations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shannon, M.A.; Bohn, P.W.; Elimelech, M.; Georgiadis, J.G.; Marinas, B.J.; Mayes, A.M. Science and technology for water purification in the coming decades. Nature 2008, 452, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menachem, E.; Phillip, W.A. The Future of Seawater Desalination: Energy, Technology, and the Environment. Science 2011, 333, 712–717. [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee, L.F.; Lawler, D.F.; Freeman, B.D.; Marrot, B.; Moulin, P. Reverse osmosis desalination: Water sources, technology, and today’s challenges. Water Res. 2009, 43, 2317–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, Y.J.; Goh, K.; Kurihara, M.; Wang, R. Seawater desalination by reverse osmosis: Current development and future challenges in membrane fabrication—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 629, 119292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charcosset, C. Classical and Recent Developments of Membrane Processes for Desalination and Natural Water Treatment. Membranes 2022, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khawaji, A.D.; Kutubkhanah, I.K.; Wie, J.-M. Advances in seawater desalination technologies. Desalination 2008, 221, 47–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsarayreh, A.A.; Al-Obaidi, M.A.; Al-Hroub, A.M.; Patel, R.; Mujtaba, I.M. Evaluation and minimisation of energy consumption in a medium-scale reverse osmosis brackish water desalination plant. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 248, 119220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritzmann, C.; Löwenberg, J.; Wintgens, T.; Melin, T. State-of-the-art of reverse osmosis desalination. Desalination 2007, 216, 1–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, H.; Fussmann, K.E.; Rahav, E.; Bar Zeev, E. Chronic effects of brine discharge form large-scale seawater reverse osmosis desalination facilities on benthic bacteria. Water Res. 2019, 151, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Bruggen, B.; Lejon, L.; Vandecasteele, C. Reuse, Treatment, and Discharge of the Concentrate of Pressure-Driven Membrane Processes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 3733–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mericq, J.P.; Laborie, S.; Cabassud, C. Vacuum membrane distillation of seawater reverse osmosis brines. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5260–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramani, A.; Jacangelo, J.G. Treatment technologies for reverse osmosis concentrate volume minimization: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 472–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, M.; Mohammadi, T. High-salinity water desalination using VMD. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 149, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinetti, C.R.; Childress, A.E.; Cath, T.Y. High recovery of concentrated RO brines using forward osmosis and membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 331, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Ng, H.Y. Concentration of brine by forward osmosis: Performance and influence of membrane structure. Desalination 2008, 224, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.F.; Chung, T.-S. Energy recovery by pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) in SWRO–PRO integrated processes. Appl. Energy 2016, 162, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajraktari, N.; Hélix-Nielsen, C.; Madsen, H.T. Pressure retarded osmosis from hypersaline sources—A review. Desalination 2017, 413, 65–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.I.; Kim, J.; Shon, H.K.; Hong, S. Pressure retarded osmosis (PRO) for integrating seawater desalination and wastewater reclamation: Energy consumption and fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 483, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.L.; Li, X.; Chung, T.-S. The forward osmosis-pressure retarded osmosis (FO-PRO) hybrid system: A new process to mitigate membrane fouling for sustainable osmotic power generation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 559, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, M.L.; Liu, S.Y.; Wang, X.H. Pressure retarded osmosis coupled with activated sludge process for wastewater treatment: Performance and fouling behaviors. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 307, 123224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Tian, J.; Song, L.; Gao, S.; Shi, W.; Cui, F. Dynamic changes of the fouling layer in forward osmosis based membrane processes for municipal wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Gao, B.; Yue, Q.; Liu, S.; Shon, H.K. Effect of high salinity on the performance of forward osmosis: Water flux, membrane scaling and removal efficiency. Desalination 2016, 378, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altaee, A.; Sharif, A. Pressure retarded osmosis: Advancement in the process applications for power generation and desalination. Desalination 2015, 356, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mi, B.; Elimelech, M. Organic fouling of forward osmosis membranes: Fouling reversibility and cleaning without chemical reagents. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 348, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Influence of concentrative and dilutive internal concentration polarization on flux behavior in forward osmosis. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zou, L.; Mulcahy, D. Effects of membrane orientation on process performance in forward osmosis applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 382, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alturki, A.; McDonald, J.; Khan, S.J.; Hai, F.I.; Price, W.E.; Nghiem, L.D. Performance of a novel osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) system: Flux stability and removal of trace organics. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 113, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Loong, W.L.C.; Chou, S.; Tang, C.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Membrane biofouling and scaling in forward osmosis membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 403–404, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, G.T.; McCutcheon, J.R.; Elimelech, M. Internal concentration polarization in forward osmosis: Role of membrane orientation. Desalination 2006, 197, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chang, V.W.C.; Tang, C.Y. Osmotic membrane bioreactor (OMBR) technology for wastewater treatment and reclamation: Advances, challenges, and prospects for the future. J. Membrane Sci. 2016, 504, 113–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, F. Performance of anaerobic forward osmosis membrane bioreactor (AnOMBR) for dissolved gases transfer and energy recovery. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 235, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Tang, C.Y.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Ren, Y. Development of a novel anaerobic membrane bioreactor simultaneously integrating microfiltration and forward osmosis membranes for low-strength wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 527, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, L.N.; de Brouwer, J.F.C.; Almeida, J.S.; Stal, L.J.; Xavier, J.B. Analysis of a marine phototrophic biofilm by confocal laser scanning microscopy using the new image quantification software PHLIP. BMC Ecol. 2006, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuan, B.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Li, X.; Yu, G. In situ observation of the growth of biofouling layer in osmotic membrane bioreactors by multiple fluorescence labeling and confocal laser scanning microscopy. Water Res. 2015, 75, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Ren, Y.; She, Q. Effect of driving force on the performance of anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactors: New insight into enhancing water flux of FO membrane via controlling driving force in a two-stage pattern. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 569, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Jia, J.; Miao, H.; Ruan, W.; Wang, X. Performance improvement and biofouling mitigation in osmotic microbial fuel cells via in situ formation of silver nanoparticles on forward osmosis membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, M. Secret underneath: Fouling of membrane support layer in anaerobic osmotic membrane bioreactor (AnOMBR). J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 614, 118530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
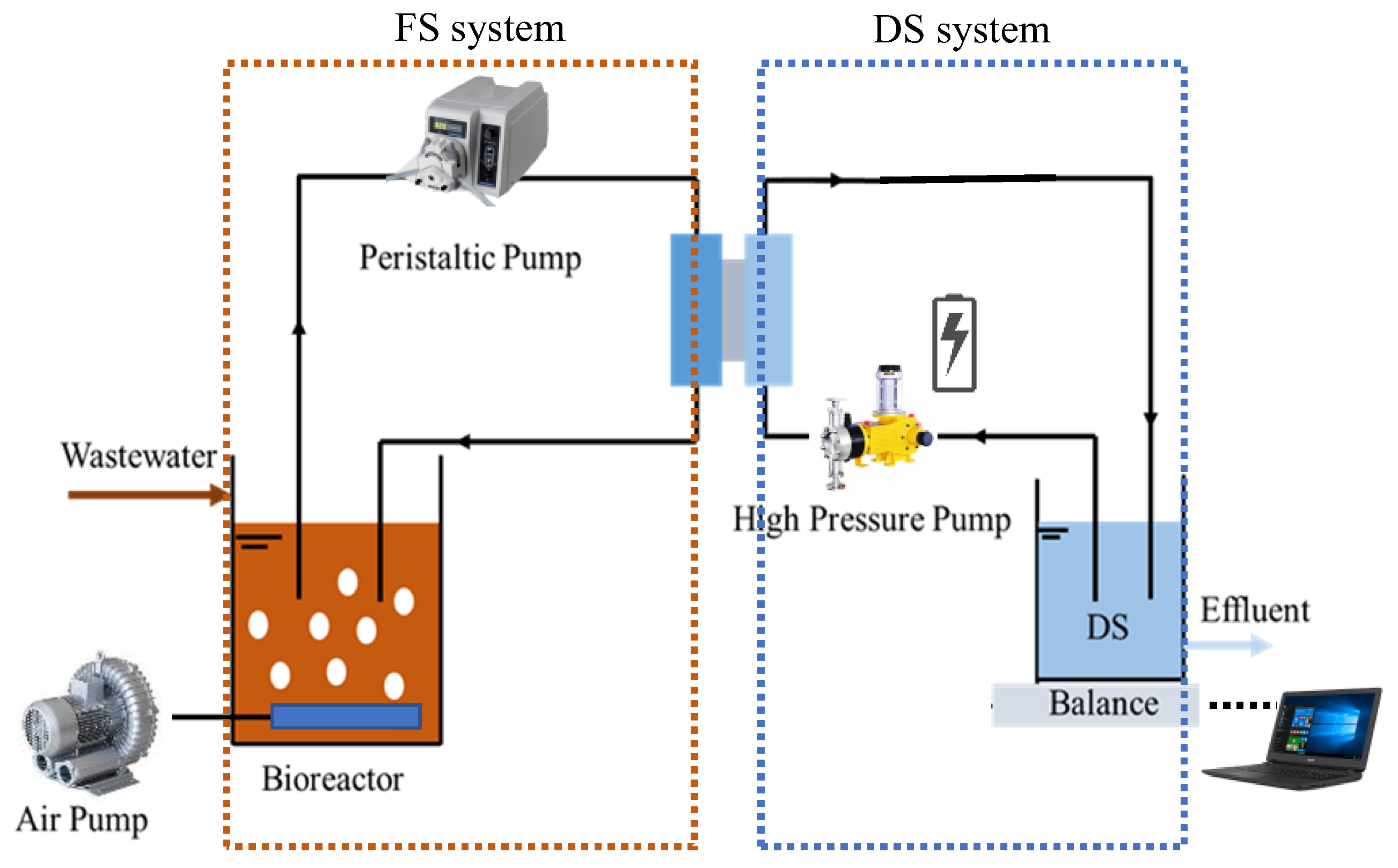

| Components | Concentration (mg/L) | Components | Concentration (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 230.0 | Ammonium bicarbonate | 170.0 |
| Beef extract | 20.0 | Potassium dihydrogen Phosphate | 28.0 |
| Fish meal peptone | 60.0 | Ferric chloride | 1.0 |
| Sodium acetate (anhydrous) | 40.0 | Calcium chloride (anhydrous) | 1.2 |
| Sodium bicarbonate | 198.0 | Magnesium chloride (hexahydrate) | 2.4 |
| Components | Concentration (g/L) | Osmotic Pressure (atm) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaCl | 49.06 | 39.65 | 58.71 |
| MgCl2 | 22.22 | 15.44 | 26.59 |
| Na2SO4 | 8.18 | 3.27 | 9.79 |
| CaCl2 | 2.32 | 1.36 | 2.78 |
| KCl | 1.39 | 0.87 | 1.66 |
| NaHCO3 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.48 |
| Total | 83.57 | 52.60 | 100 |
| AL-DS | AL-FS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| TOC | Influent Concentration (mg/L) | 75.3 ± 4.56 | 75.87 ± 3.73 |
| Concentration in sludge supernatant (mg/L) | 1.35 ± 0.57 | 1.65 ± 0.85 | |
| Concentration in FO permeate (mg/L) | 4.68 ± 2.45 | 3.38 ± 2.51 | |
| Removal rate (%) | 93.78 ± 3.25 | 95.55 ± 3.31 | |
| TP | Influent Concentration (mg/L) | 5.75 ± 0.08 | 5.33 ± 0.09 |
| Concentration in sludge supernatant (mg/L) | 5.79 ± 0.05 | 5.35 ± 0.10 | |
| Concentration in FO permeate (mg/L) | 0.04 ± 0.02 | 0.07 ± 0.04 | |
| Removal rate (%) | 99.30 ± 0.16 | 98.62 ± 0.79 | |
| NH4+-N | Influent Concentration (mg/L) | 27.48 ± 0.13 | 30.70 ± 0.23 |
| Concentration in sludge supernatant (mg/L) | 0.53 ± 0.04 | 0.18 ± 0.10 | |
| Concentration in FO permeate (mg/L) | 0.32 ± 0.07 | 0.13 ± 0.02 | |
| Removal rate (%) | 98.84 ± 0.27 | 99.59 ± 0.07 | |
| TN | Influent Concentration (mg/L) | 30.19 ± 0.20 | 33.91 ± 0.25 |
| Concentration in sludge supernatant (mg/L) | 52.88 ± 0.89 | 56.26 ± 0.27 | |
| Concentration in FO permeate (mg/L) | 0.97 ± 0.07 | 0.62 ± 0.28 | |
| Removal rate (%) | 96.78 ± 0.03 | 98.17 ± 0.81 |
| Membrane Orientation | TS (g/m2) | VS (g/m2) | VS/TS (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AL-FS | 7.61 ± 0.82 | 5.31 ± 0.47 | 69.74 ± 1.28 |
| AL-DS | 17.65 ± 1.57 | 9.35 ± 2.03 | 52.93 ± 6.84 |
| α-D-glucopyranose Polysaccharides (μm3/μm2) | β-D-glucopyranose Polysaccharides (μm3/μm2) | Protein (μm3/μm2) | Total Cells (μm3/μm2) | Thickness (μm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AL-FS | 1.17 ± 0.10 | 2.70 ± 0.38 | 0.93 ± 0.06 | 2.92 ± 0.32 | 34.69 ± 1.33 |
| AL-DS | 1.01 ± 0.07 | 4.13 ± 0.01 | 1.18 ± 0.03 | 0.76 ± 0.15 | 39.11 ± 0.49 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Chu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Lai, W.; Zhao, P.; Wang, X. A Novel Hybrid Reactor of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis Coupling with Activated Sludge Process for Simultaneously Treating Concentrated Seawater Brine and Wastewater and Recovering Energy. Membranes 2022, 12, 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040380
Ding J, Zhou Q, Zhou Z, Chu W, Jiang Y, Lai W, Zhao P, Wang X. A Novel Hybrid Reactor of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis Coupling with Activated Sludge Process for Simultaneously Treating Concentrated Seawater Brine and Wastewater and Recovering Energy. Membranes. 2022; 12(4):380. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040380
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Jiaxin, Qian Zhou, Zixun Zhou, Wenyu Chu, Yao Jiang, Wei Lai, Pin Zhao, and Xinhua Wang. 2022. "A Novel Hybrid Reactor of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis Coupling with Activated Sludge Process for Simultaneously Treating Concentrated Seawater Brine and Wastewater and Recovering Energy" Membranes 12, no. 4: 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040380
APA StyleDing, J., Zhou, Q., Zhou, Z., Chu, W., Jiang, Y., Lai, W., Zhao, P., & Wang, X. (2022). A Novel Hybrid Reactor of Pressure-Retarded Osmosis Coupling with Activated Sludge Process for Simultaneously Treating Concentrated Seawater Brine and Wastewater and Recovering Energy. Membranes, 12(4), 380. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12040380







