Retention and Fouling during Nanoparticle Filtration: Implications for Membrane Purification of Biotherapeutics
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticle Feed Solution Preparation
2.2. Modified Hydrophobic Interaction Chromatography
2.3. Nanoparticle Filtration
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Nanoparticle Characterization
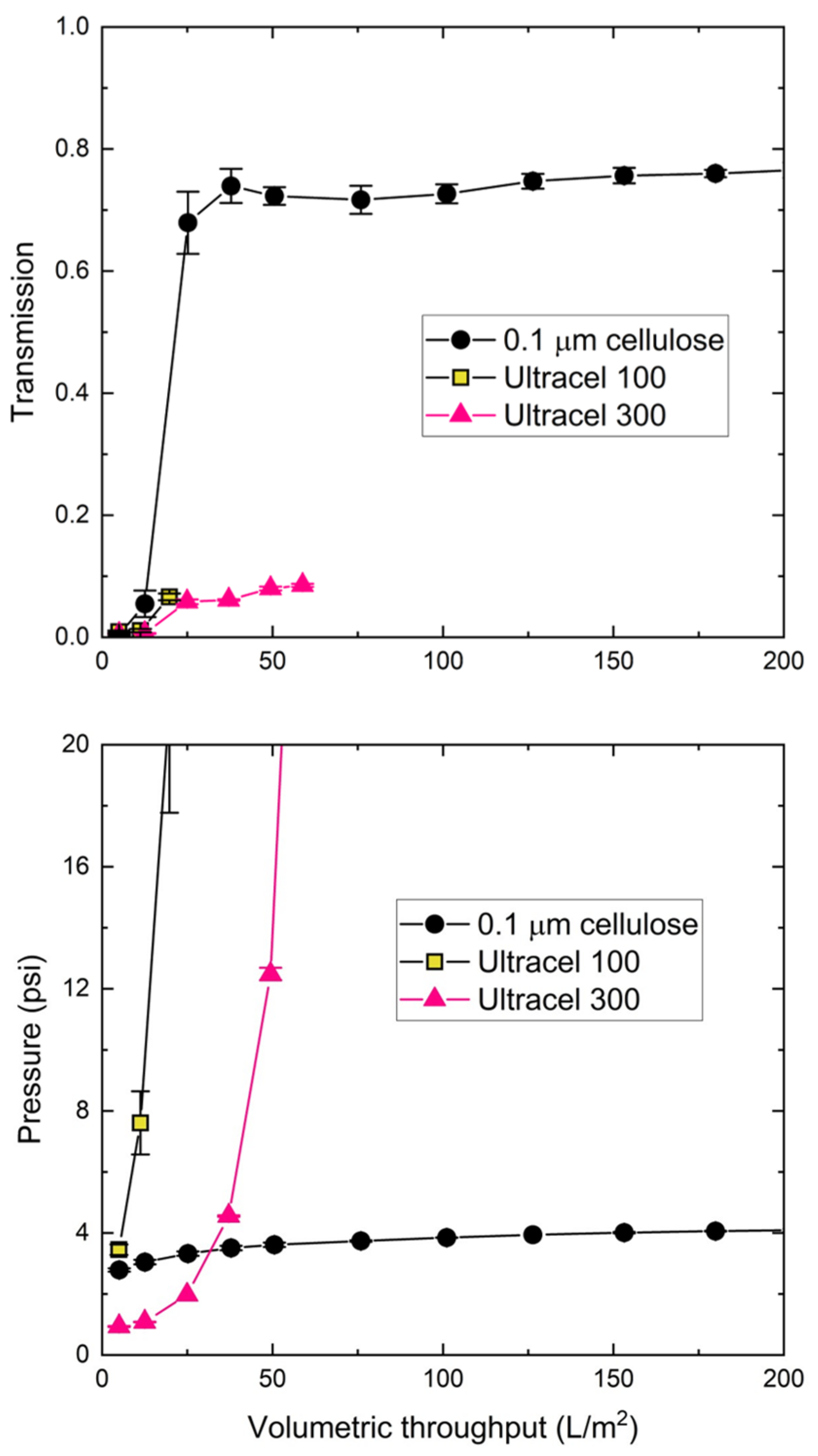
3.2. Nanoparticle Filtration
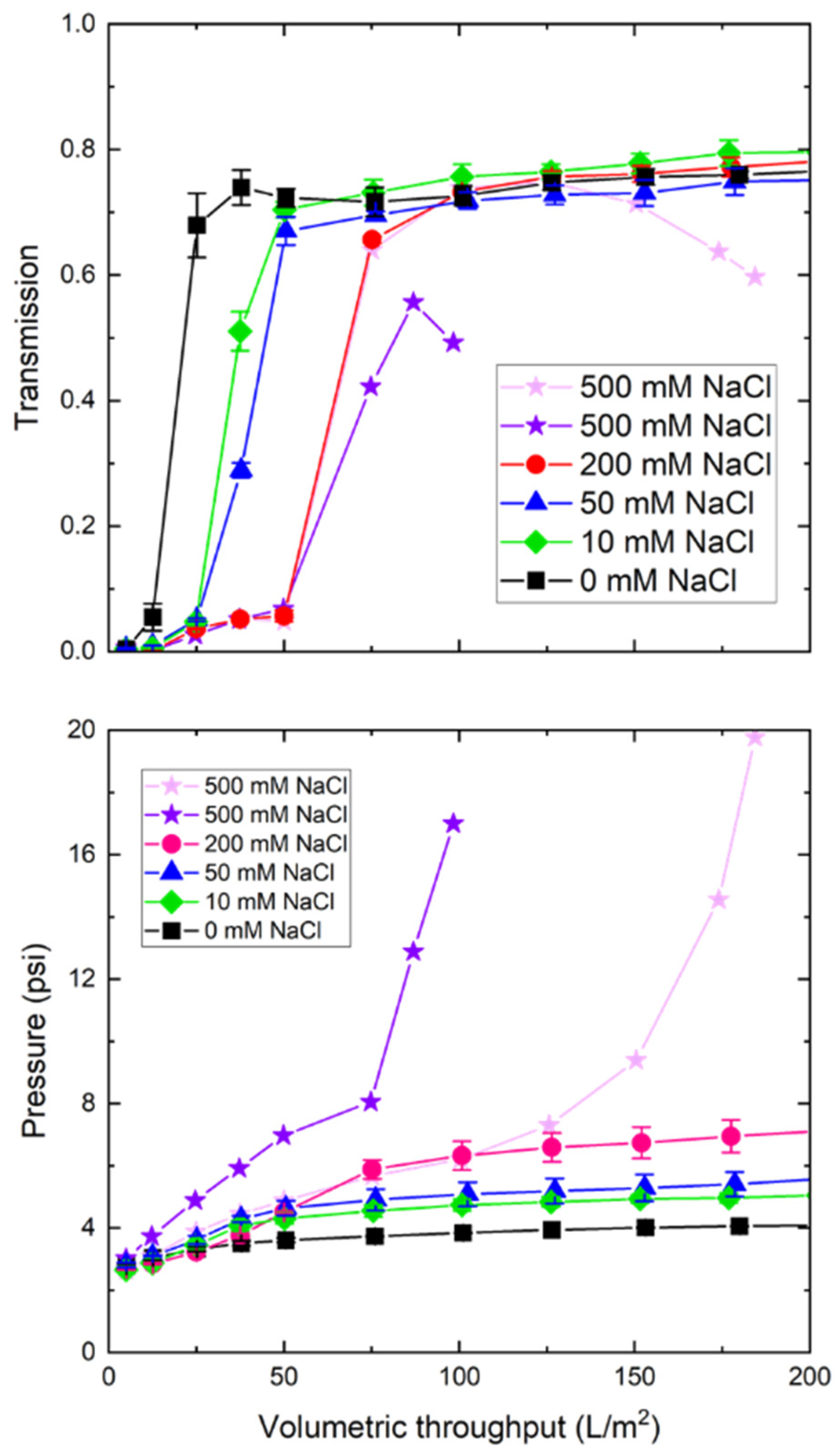
3.3. Buffer Effects
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hou, X.; Zaks, T.; Langer, R.; Dong, Y. Lipid nanoparticles for mRNA delivery. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2021, 6, 1078–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milone, M.C.; O’Doherty, U. Clinical use of lentiviral vectors. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1529–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tai, P.W.L.; Gao, G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 358–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A.A.; Toth, I.; Hussein, W.M.; Moyle, P.M. Advances in targeted gene delivery. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2019, 16, 588–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, R.; Du, K.; Liu, Q.; Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z. Nano iron–copper alloys for tumor ablation: Efficiently amplified oxidative stress through acid response. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 14438–14446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, N.; Ma, W.; Kristopeit, A.; Wang, S.-C.; Zydney, A.L. Enhancing the performance of sterile filtration for viral vaccines and model nanoparticles using an appropriate prefilter. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 674, 120264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bos, G.W.; Trullas-Jimeno, A.; Jiskoot, W.; Crommelin, D.J.A.; Hennink, W.E. Sterilization of poly(dimethylamino) ethyl methacrylate-based gene transfer complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2000, 211, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, J.F. Product-Related Impurities in Clinical-Grade Recombinant AAV Vectors: Characterization and Risk Assessment. Biomedicines 2014, 2, 80–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, B.; Bak, H.; Tustian, A.D. Moving from the bench towards a large scale, industrial platform process for adeno-associated viral vector purification. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 3199–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnon, P.; Leskovec, M.; Prebil, S.D.; Žigon, R.; Štokelj, M.; Raspor, A.; Peljhan, S.; Štrancar, A. Removal of empty capsids from adeno-associated virus preparations by multimodal metal affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2021, 1649, 462210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reimer, C.B.; Baker, R.S.; Van Frank, R.M.; Newlin, T.E.; Cline, G.B.; Anderson, N.G. Purification of large quantities of influenza virus by density gradient centrifugation. J. Virol. 1967, 1, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joshi, P.; Bernier, A.; Moço, P.D.; Schrag, J.; Chahal, P.S.; Kamen, A. Development of a scalable and robust AEX method for enriched rAAV preparations in genome-containing VCs of serotypes 5, 6, 8, and 9. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2021, 21, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, R.H.; Yang, L.; Kotin, R.M. Chromatography-based purification of adeno-associated virus. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 434, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunkumar, A.; Singh, N. Ultrafiltration behavior of recombinant adeno associated viral vectors used in gene therapy. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 620, 118812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peixoto, C.; Ferreira, T.B.; Sousa, M.F.Q.; Carrondo, M.J.T.; Alves, P.M. Towards purification of adenoviral vectors based on membrane technology. Biotechnol. Prog. 2008, 24, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Hir, M.; Wyart, Y.; Georges, G.; Lamoine, L.S.; Sauvade, P.; Moulin, P. Effect of salinity and nanoparticle polydispersity on UF membrane retention fouling. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 405–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jassby, D.; Chae, S.R.; Hendren, Z.; Wiesner, M. Membrane filtration of fullerene nanoparticle suspensions: Effects of derivatization, pressure, electrolyte species and concentration. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 346, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Reis, R.; Zydney, A.L. Bioprocess membrane technology. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 297, 16–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, N.L.; Berguig, G.Y.; Karim, O.A.; Cortesio, C.L.; de Angelis, R.; Khan, A.A.; Gold, D.; Maga, J.A.; Bhat, V.S. Comprehensive characterization and quantification of adeno associated vectors by size exclusion chromatography and multi-angle light scattering. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, L.; Fernandes, D.; Hussain, M.T.; Kaszuba, M.; Stenson, J.; Markova, N. Characterization of Recombinant Adeno-Associated Viruses (rAAVs) for Gene Therapy Using Orthogonal Techniques. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, N.; Ma, W.; Kristopeit, A.; Wang, S.C.; Zydney, A.L. Evaluating nanoparticle hydrophobicity using analytical membrane hydrophobic interaction chromatography. Anal. Chem. 2022. Submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, J.; Hou, J.; Song, H. Comparison of humic acid rejection and flux decline during filtration with negatively charged and uncharged ultrafiltration membranes. Water Res. 2011, 45, 473–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, S.; Zydney, A.L. High resolution protein separations using affinity ultrafiltration with small charged ligands. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hait, S.K.; Moulik, S.P. Determination of critical micelle concentration (CMC) of nonionic surfactants by donor-acceptor interaction with lodine and correlation of CMC with hydrophile-lipophile balance and other parameters of the surfactants. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2001, 4, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


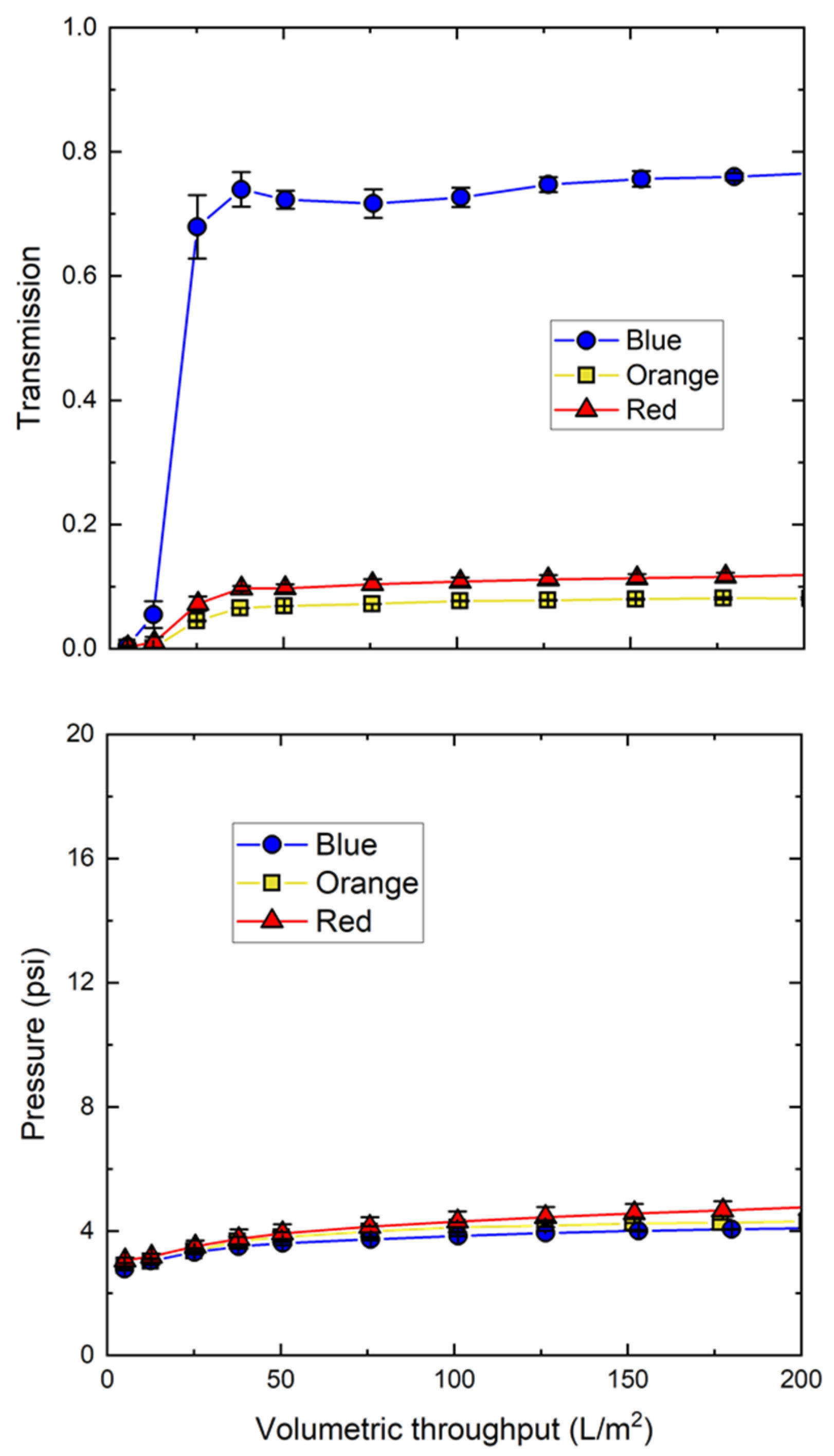

| Emission Wavelength | Z-Average Diameter | Zeta Potential | MHIC Retention | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blue | 419 nm | 34 ± 2 nm | −15 ± 1 mV | 2/8/13 min |
| Orange | 614 nm | 35 ± 1 nm | −15 ± 1 mV | 13 min |
| Red | 630 nm | 35 ± 1 nm | −14 ± 1 mV | ND |
| 0.1 μm | Biomax 100 | Biomax 300 | Biomax 500 | Ultracel 100 | Ultracel 300 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pore diameter dp (nm) | 100 | 13 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 32 ± 2 | 9.0 ± 0.2 | 20 ± 1 |
| Throughput at 10 psi (L/m2) | >200 | 23 | 24 | >200 | 13 | 46 |
| Average Transmission | 74% | 5% | 13% | 79% | 3% | 5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chu, L.-K.; Wickramasinghe, S.R.; Qian, X.; Zydney, A.L. Retention and Fouling during Nanoparticle Filtration: Implications for Membrane Purification of Biotherapeutics. Membranes 2022, 12, 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030299
Chu L-K, Wickramasinghe SR, Qian X, Zydney AL. Retention and Fouling during Nanoparticle Filtration: Implications for Membrane Purification of Biotherapeutics. Membranes. 2022; 12(3):299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030299
Chicago/Turabian StyleChu, Liang-Kai, S. Ranil Wickramasinghe, Xianghong Qian, and Andrew L. Zydney. 2022. "Retention and Fouling during Nanoparticle Filtration: Implications for Membrane Purification of Biotherapeutics" Membranes 12, no. 3: 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030299
APA StyleChu, L.-K., Wickramasinghe, S. R., Qian, X., & Zydney, A. L. (2022). Retention and Fouling during Nanoparticle Filtration: Implications for Membrane Purification of Biotherapeutics. Membranes, 12(3), 299. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12030299








