Effect of Electrode Morphology on Performance of Ionic Actuators Based on Vat Photopolymerized Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Electrode Preparation
2.3. Membrane Preparation
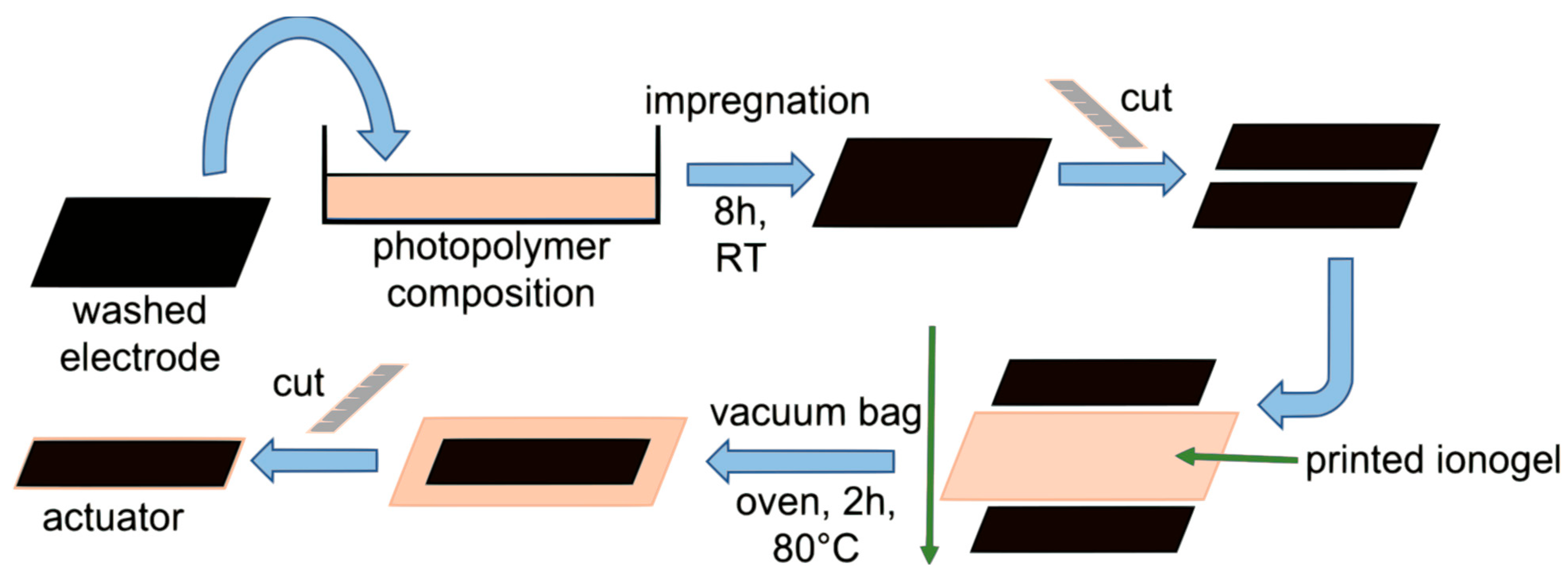
2.4. Actuator Fabrication
2.5. Electrodes Characterization
2.6. Actuator Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Additive on Electrode Properties
3.2. Actuators
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Sugino, T. Ionic Polymer Actuators: Principle, Fabrication and Applications. In Actuators; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahramzadeh, Y.; Shahinpoor, M. A Review of Ionic Polymeric Soft Actuators and Sensors. Soft Robot. 2013, 1, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Yin, G.; Vokoun, D.; Shen, Q.; Lu, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, X.; Yu, M.; Dai, Z. Review on Improvement, Modeling, and Application of Ionic Polymer Metal Composite Artificial Muscle. J. Bionic Eng. 2022, 19, 279–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oguro, K.; Kawami, Y.; Takenaka, H. Bending of an ion-conducting polymer filmelectrode composite by an electric stimulus at low voltage. J. Micromach. Soc. 1992, 5, 27. [Google Scholar]
- Asaka, K.; Oguro, K.; Nishimura, Y.; Mizuhata, M.; Takenaka, H. Bending of Polyelectrolyte Membrane-Platinum Composites by Electric Stimuli I. Response Characteristics to Various Waveforms. Polym. J. 1995, 27, 436–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khursheed, S.; Chaturvedi, S.; Moeed, K. Comparative Study of the Use of IPMC as an Artificial Muscle in Robots Replacing The Motors: A Review. In Proceedings of the TRIBOINDIA-2018 An International Conference on Tribology, Mumbai, India, 13–15 December 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaian, N.; Olsen, Z.J.; Kim, K.J. Ionic Polymer-Metal Composite (IPMC) Artificial Muscles in Underwater Environments: Review of Actuation, Sensing, Controls, and Applications to Soft Robotics. In Bioinspired Sensing, Actuation, and Control in Underwater Soft Robotic Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 117–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Yu, L.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, P.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Y. Ionic Electroactive Polymers Used in Bionic Robots: A Review. J. Bionic Eng. 2018, 15, 765–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, X.L.; Chee, P.S.; Lim, E.H. Ionic Polymer Actuator with Crenellated Structures for MEMs Application. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics (ICSE), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 28–29 July 2020; pp. 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanamori, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Omiya, M. Ionic polymer metal composite (IPMC) for MEMS actuator and sensor. In Proceedings of the ASME 2011 Pacific Rim Technical Conference and Exhibition on Packaging and Integration of Electronic and Photonic Systems, Portland, Oregon, USA, 6–8 July 2011; pp. 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinpoor, M.; Bar-Cohen, Y.; Simpson, J.O.; Smith, J. Ionic polymer-metal composites (IPMCs) as biomimetic sensors, actuators and artificial muscles—A review. Smart Mater. Struct. 1998, 7, R15–R30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newbury, K.M.; Leo, D.J. Linear electromechanical model of ionic polymer transducers—Part I: Model development. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2003, 14, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaakson, P.; Aabloo, A.; Tamm, T. Encapsulation of ionic electroactive polymers: Reducing the interaction with environment. In Electroactive Polymer Actuators and Devices (EAPAD) 2016, Proceedings of the SPIE Smart Structures and Materials + Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 20–24 March 2016; Bar-Cohen, Y., Vidal, F., Eds.; IPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9798, p. 979825. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, M.D.; Leo, D.J.; Wilkes, G.L.; Beyer, F.L.; Pechar, T.W. A model of charge transport and electromechanical transduction in ionic liquid-swollen Nafion membranes. Polymer 2006, 47, 6782–6796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhou, D.; Spinks, G.; Wallace, G.; Forsyth, S.; Forsyth, M.; MacFarlane, D. Use of ionic liquids as electrolytes in electromechanical actuator systems based on inherently conducting polymers. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 2392–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidal, F.; Plesse, C.; Teyssié, D.; Chevrot, C. Long-life air working conducting semi-IPN/ionic liquid based actuator. Synth. Met. 2004, 142, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T.; Asaka, K.; Kosaka, A.; Aida, T. Fully plastic actuator through layer-by-layer casting with ionic-liquid-based bucky gel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 2410–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegranza, C.; Gaillard, L.; Le Letty, R.; Patti, S.; Scolamiero, L.; Toso, M. Actuators for Space Applications: State of the Art and New Technologies. In Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on New Actuators, Bremen, Germany, 23–25 June 2014; pp. 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Punning, A.; Kim, K.J.; Palmre, V.; Vidal, F.; Plesse, C.; Festin, N.; Maziz, A.; Asaka, K.; Sugino, T.; Alici, G.; et al. Ionic electroactive polymer artificial muscles in space applications. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fannir, A.; Temmer, R.; Nguyen, G.T.M.; Cadiergues, L.; Laurent, E.; Madden, J.D.W.; Vidal, F.; Plesse, C. Linear Artificial Muscle Based on Ionic Electroactive Polymer: A Rational Design for Open-Air and Vacuum Actuation. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2019, 4, 1800519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, O.; Shin, T.J.; Park, M.J. Fast low-voltage electroactive actuators using nanostructured polymer electrolytes. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.; Kim, H.; Choi, U.H.; Park, M.J. One-volt-driven superfast polymer actuators based on single-ion conductors. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, O.S.; Babkin, A.V.; Ivanchenko, A.V.; Shachneva, S.S.; Nechausov, S.S.; Alentiev, D.A.; Bermeshev, M.V.; Bulgakov, B.A.; Kepman, A.V. Ionomers Based on Addition and Ring Opening Metathesis Polymerized 5-phenyl-2-norbornene as a Membrane Material for Ionic Actuators. Membranes 2022, 12, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, O.S.; Bulgakov, B.A.; Ivanchenko, A.V.; Shachneva, S.S.; Nechausov, S.S.; Bermeshev, M.V.; Kepman, A.V. Data on synthesis and characterization of sulfonated poly(phenylnorbornene) and polymer electrolyte membranes based on it. Data Brief 2019, 27, 104626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, T. Molecular Ordering of Organic Molten Salts Triggered by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes. Science 2003, 300, 2072–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Asaka, K.; Kiyohara, K.; Sugino, T.; Takeuchi, I.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T. High performance fully plastic actuator based on ionic-liquid-based bucky gel. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5555–5562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terasawa, N.; Asaka, K. Electrochemical and Electromechanical Properties of Activated Multi-walled Carbon Nanotube Polymer Actuator that Surpass the Performance of a Single-walled Carbon Nanotube Polymer Actuator. Mater. Today Proc. 2016, 3, S178–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torop, J.; Palmre, V.; Arulepp, M.; Sugino, T.; Asaka, K.; Aabloo, A. Flexible supercapacitor-like actuator with carbide-derived carbon electrodes. Carbon 2011, 49, 3113–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotal, M.; Kim, J.; Tabassian, R.; Roy, S.; Hiep Nguyen, V.; Koratkar, N.; Oh, I.-K.; Kotal, M.; Kim, J.; Tabassian, R.; et al. Highly Bendable Ionic Soft Actuator Based on Nitrogen-Enriched 3D Hetero-Nanostructure Electrode. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1802464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Fu, R.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, L.; Ming, Y.; Hu, Y.; Lin, H.; Tao, X.; et al. High-performance graphdiyne-based electrochemical actuators. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokubo, H.; Honda, T.; Imaizumi, S.; Dokko, K.; Watanabe, M. Effects of Carbon Electrode Materials on Performance of Ionic Polymer Actuators Having Electric Double-Layer Capacitor Structure. Electrochemistry 2013, 81, 849–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseyev, N.I.; Khmelnitskiy, I.K.; Aivazyan, V.M.; Broyko, A.P.; Korlyakov, A.V.; Luchinin, V.V. Ionic eap actuators with electrodes based on carbon nanomaterials. Polymers 2021, 13, 4137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Takeuchi, I.; Mukai, K.; Asaka, K. Actuator properties of the complexes composed by carbon nanotube and ionic liquid: The effects of additives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 141, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugino, T.; Kiyohara, K.; Takeuchi, I.; Mukai, K.; Asaka, K. Improving the actuating response of carbon nanotube / ionic liquid composites by the addition of conductive nanoparticles. Carbon 2011, 49, 3560–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Farino, C.; Yang, C.; Scott, T.; Browe, D.; Choi, W.; Freeman, J.W.; Lee, H. Soft Robotic Manipulation and Locomotion with a 3D Printed Electroactive Hydrogel. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 17512–17518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrico, J.D.; Kim, K.J.; Leang, K.K. 3D-printed ionic polymer-metal composite soft crawling robot. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; pp. 4313–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCracken, J.M.; Donovan, B.R.; White, T.J. Materials as Machines. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imaizumi, S.; Ohtsuki, Y.; Yasuda, T.; Kokubo, H.; Watanabe, M. Printable polymer actuators from ionic liquid, soluble polyimide, and ubiquitous carbon materials. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 6307–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Cebeci, H.; De Villoria, R.G.; Lin, J.H.; Wardle, B.L.; Zhang, Q.M. High Electromechanical Response of Ionic Polymer Actuators with Controlled-Morphology Aligned Carbon Nanotube/Nafion Nanocomposite Electrodes. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 3266–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morozov, O.S.; Shachneva, S.S.; Bulgakov, B.A.; Babkin, A.V.; Kepman, A.V. Effect of different pore-forming additives on the formation of PVDF microporous membranes for bucky-gel actuator. Eur. Chem. J. 2020, 22, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, O.S.; Shachneva, S.S.; Kepman, A.V. Microporous PVDF ionic membranes for actuator applications prepared with imidazole-based poly(ionic) liquid as a pore forming material. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 683, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrell, A.K.; Del Sesto, R.E.; Baker, S.N.; McCleskey, T.M.; Baker, G.A. The large scale synthesis of pure imidazolium and pyrrolidinium ionic liquids. Green Chem. 2007, 9, 449–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Effect of PMMA on crystallization behavior and hydrophilicity of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/poly(methyl methacrylate) blend prepared in semi-dilute solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 8377–8388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, I.; Asaka, K.; Kiyohara, K.; Sugino, T.; Terasawa, N.; Mukai, K.; Fukushima, T.; Aida, T. Electromechanical behavior of fully plastic actuators based on bucky gel containing various internal ionic liquids. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 1762–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamagawa, H.; Yagasaki, K.; Nogata, F. Mechanical characteristics of ionic polymer-metal composite in the process of self-bending. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 7614–7618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, P.; Lopes, A.C.; Lanceros-Mendez, S. Electroactive phases of poly(vinylidene fluoride): Determination, processing and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 683–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechausov, S.; Ivanchenko, A.; Morozov, O.; Miriyev, A.; Must, I.; Platnieks, O.; Jurinovs, M.; Gaidukovs, S.; Aabloo, A.; Kovač, M.; et al. Data on FTIR, photo-DSC and dynamic DSC of triethylene glycol dimethacrylate and N-vinylpyrrolidone copolymerization in the presence of ionic liquids. Data Brief 2022, 43, 108395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechausov, S.; Ivanchenko, A.; Morozov, O.; Miriyev, A.; Must, I.; Platnieks, O.; Jurinovs, M.; Gaidukovs, S.; Aabloo, A.; Kovač, M.; et al. Effects of ionic liquids and dual curing on vat photopolymerization process and properties of 3d-printed ionogels. Addit. Manuf. 2022, 56, 102895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
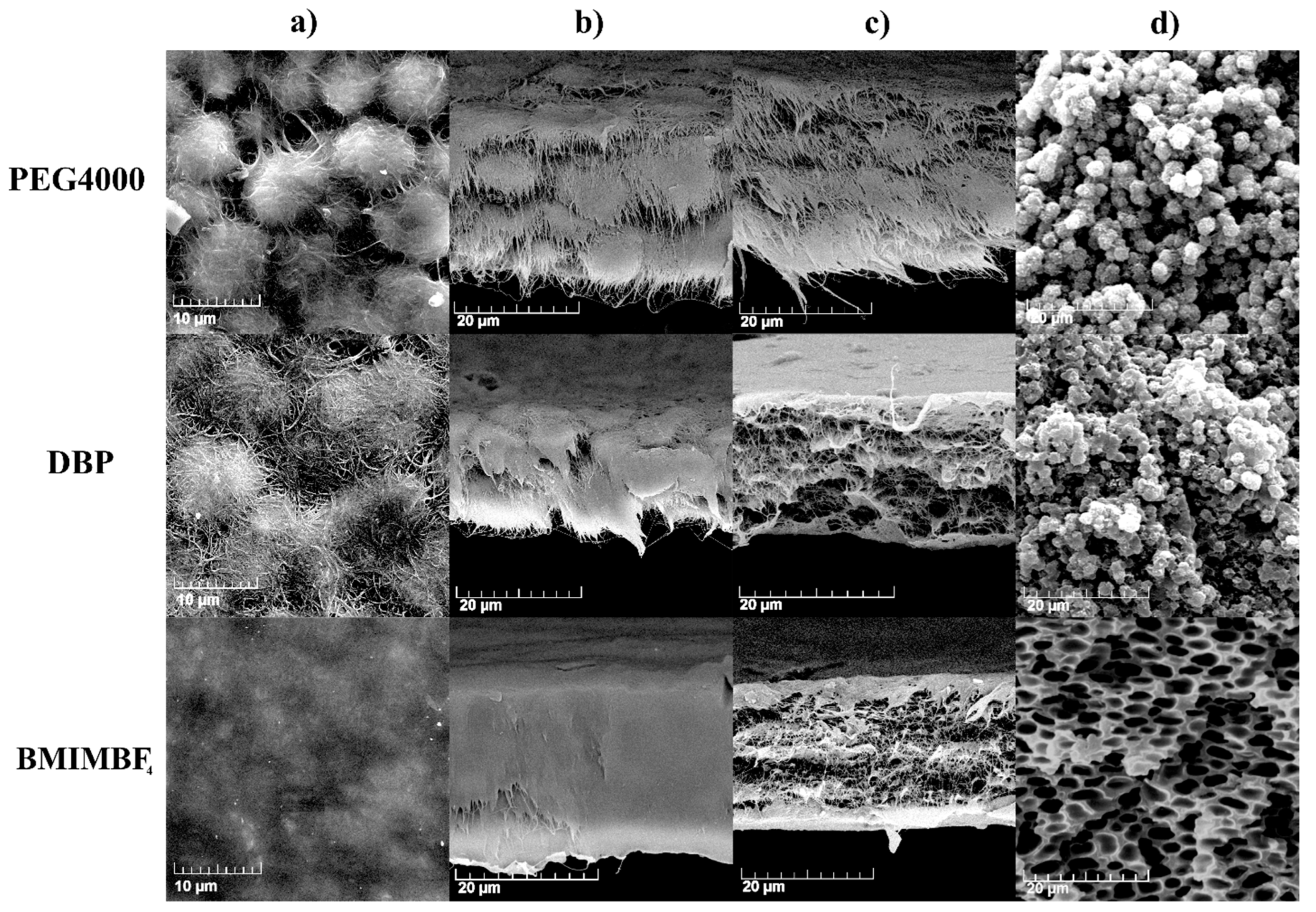
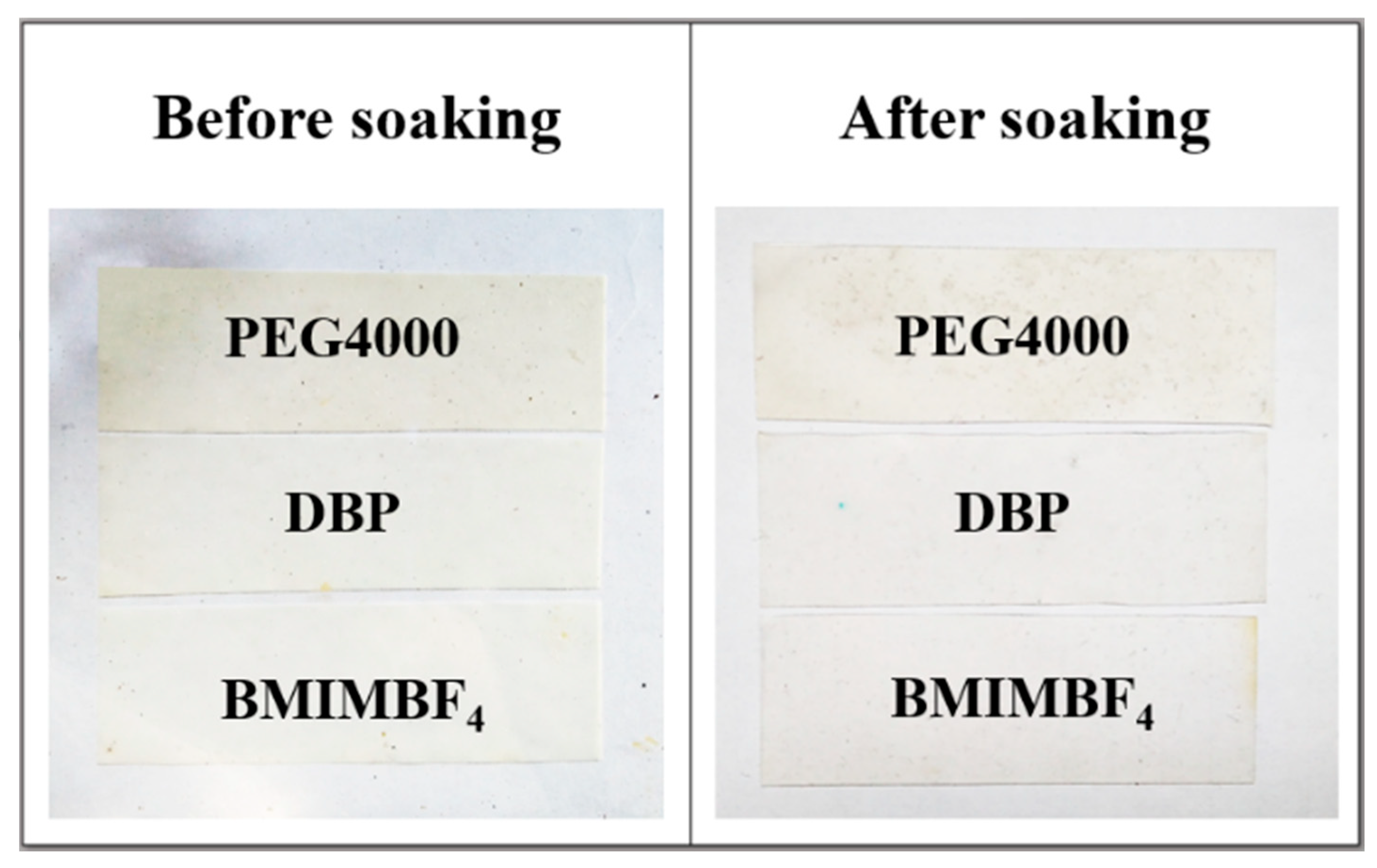
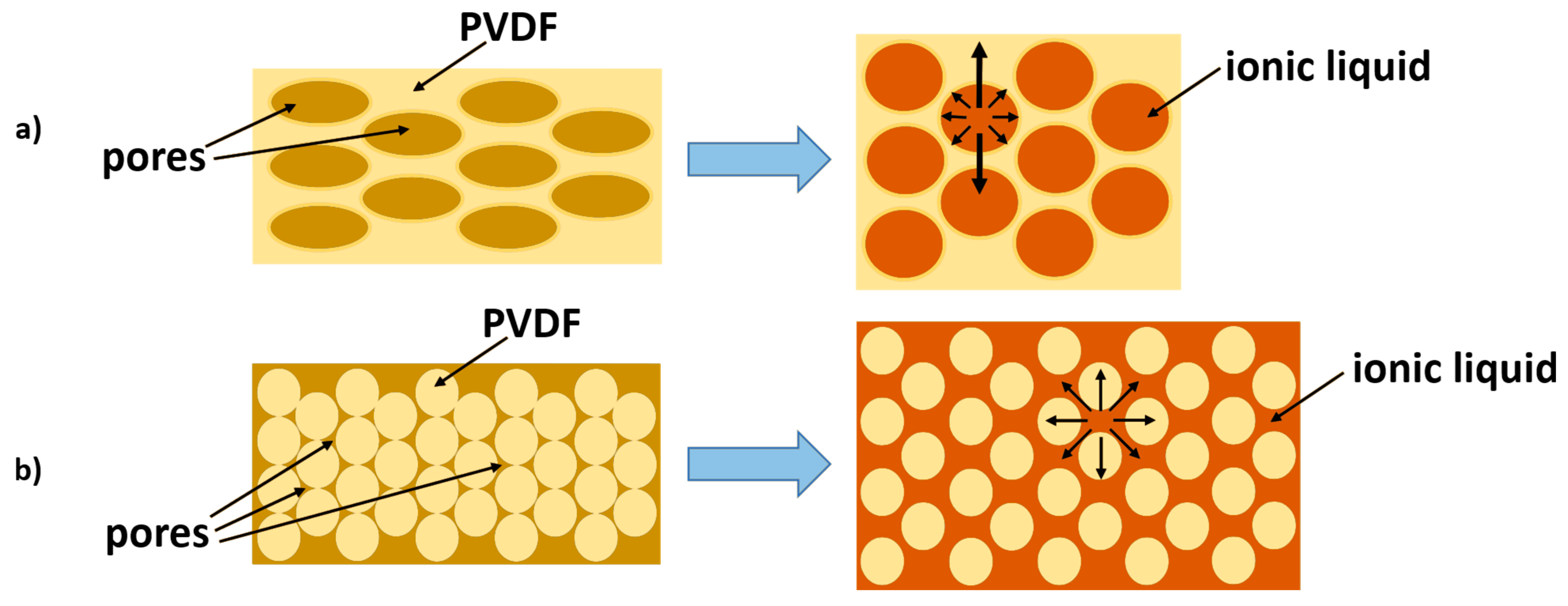

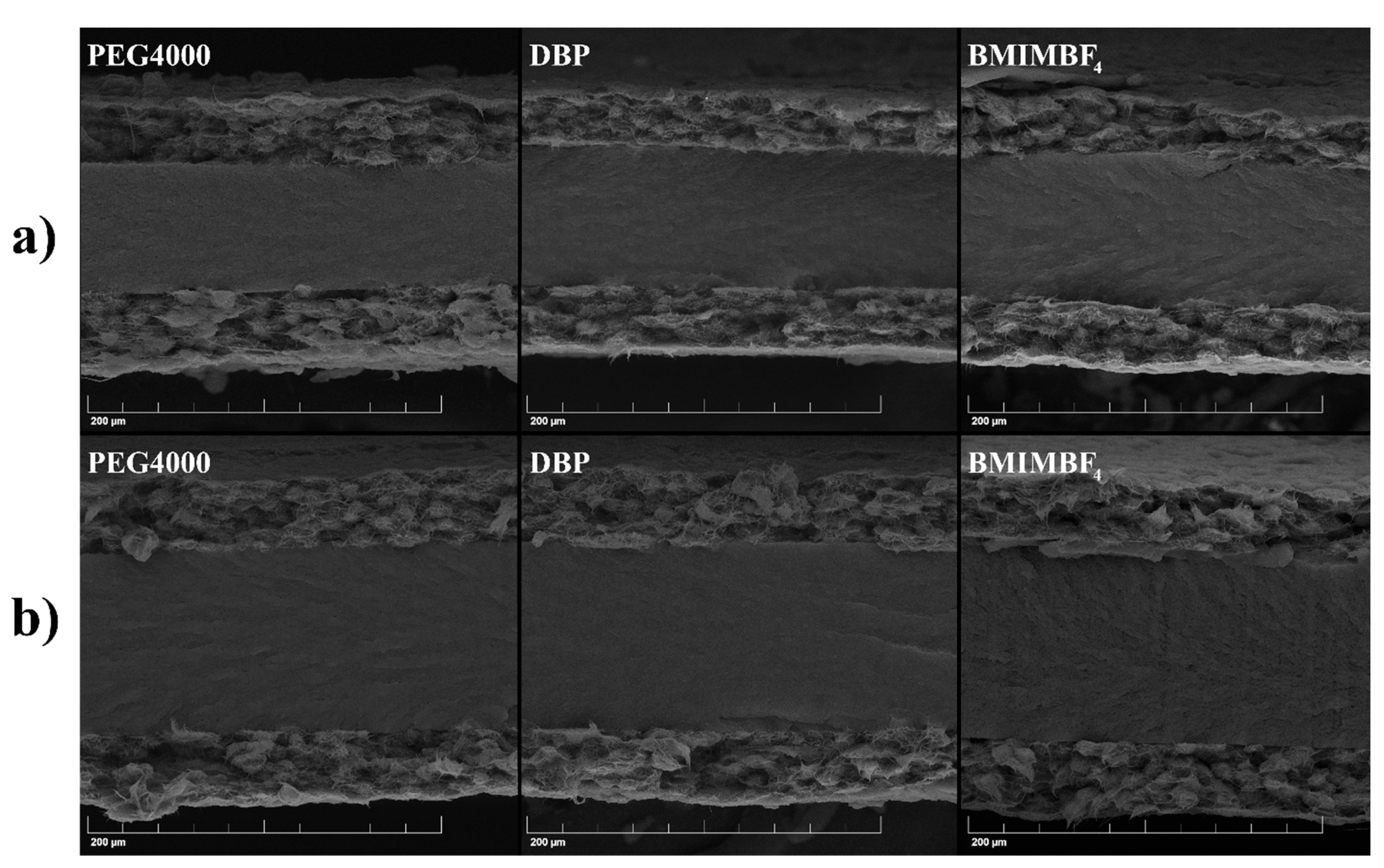

| Additive | Density, g/cm3 | Calculated Mass, mg |
|---|---|---|
| PEG | 1.20 | 237 |
| DBP | 1.05 | 207 |
| BMIMBF4 | 1.21 | 239 |
| Abbreviation | Composition, % Mass. |
|---|---|
| BMIm | BMIMBF4/VP/TEGDMA 50/25/25 |
| OMIm | OMIMBF4/VP/TEGDMA 50/25/25 |
| Additive | Elongation, % | Thickening, % | Volume Increase, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG4000 | 24.2 | 15 | 77.4 |
| DBP | 19.2 | 23 | 74.8 |
| BMIMBF4 | 15.2 | 30 | 72.5 |
| Additive | Porosity, vol. % | Electrolyte Uptake, vol. % | Thickness, μm | ΔH, J/g | Degree of Crystallinity, % | Crystalline Phases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEG4000 | 41.3 | 41.1 | 30 ± 1 | 42.5 | 41 | γ phase |
| DBP | 40.4 | 40.0 | 33 ± 1 | 42.7 | 41 | β + γ phases |
| BMIMBF4 | 39.6 | 39.7 | 31 ± 2 | 40.8 | 39 | β + γ phases |
| Additive | Elongation, % | Thickening, % | Volume Increase, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| PEG4000 | 5 | 17 | 29 |
| DBP | 2 | 24 | 29 |
| BMIMBF4 | 3 | 23 | 30 |
| Abbreviation | σact, mS/cm | σ, mS/cm [48] |
|---|---|---|
| BMIm | 0.24 | 0.19 |
| OMIm | 0.10 | 0.11 |
| Additive | Capacitance, F/g(CNT) | Strain ±3 V, % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMIm | OMIm | BMIm | OMIm | |
| PEG4000 | 43.41 ± 0.23 | 43.43 ± 0.05 | 0.56 | 0.65 |
| DBP | 43.83 ± 0.64 | 42.99 ± 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.47 |
| BMIMBF4 | 42.98 ± 0.23 | 43.46 ± 0.42 | 0.35 | 0.46 |
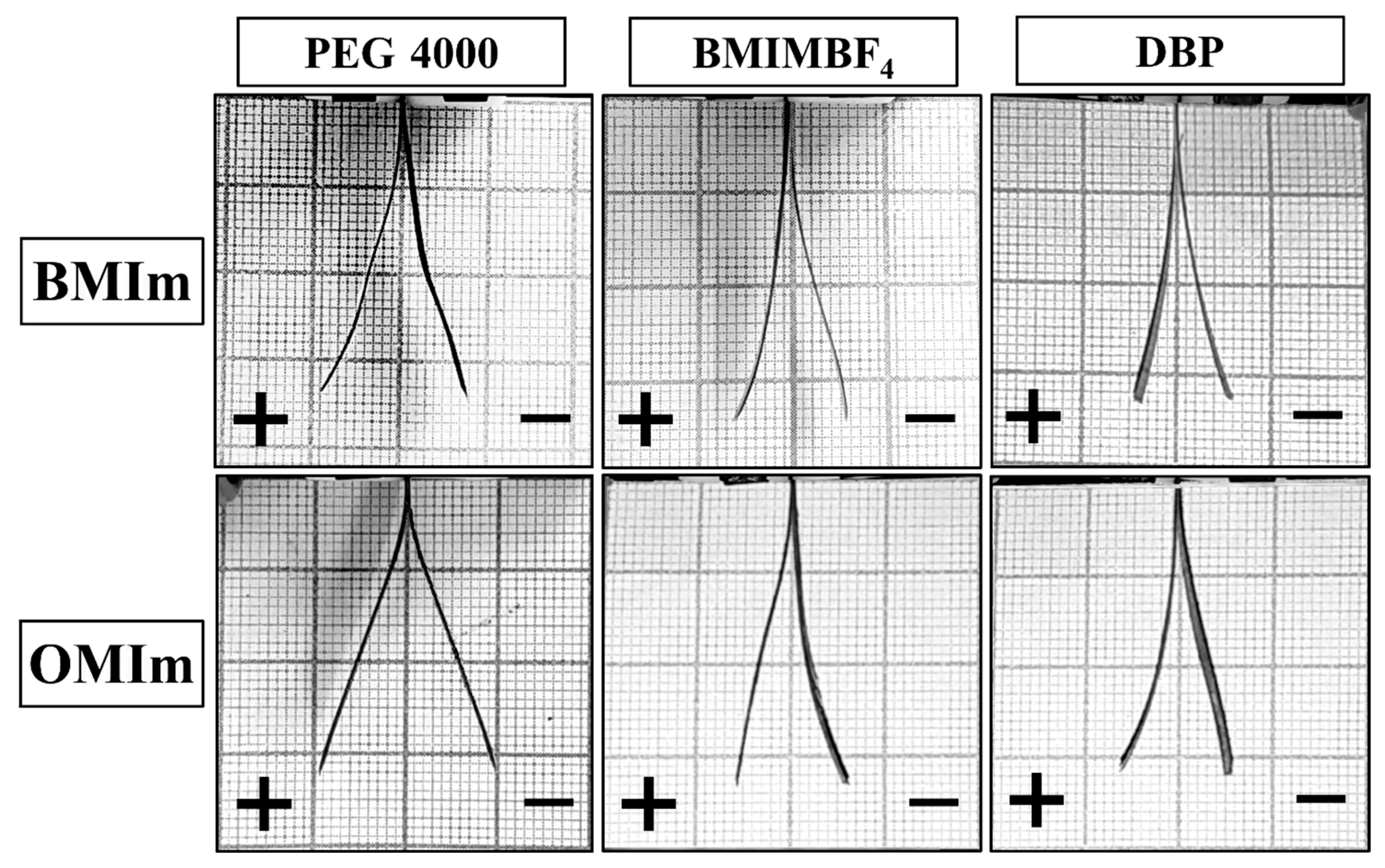
| Additive | Blocking Force, mN | σ, MPa |
|---|---|---|
| PEG4000 | 0.196 | 0.126 |
| DBP | 0.235 | 0.170 |
| BMIMBF4 | 0.274 | 0.263 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Morozov, O.S.; Ivanchenko, A.V.; Nechausov, S.S.; Bulgakov, B.A. Effect of Electrode Morphology on Performance of Ionic Actuators Based on Vat Photopolymerized Membranes. Membranes 2022, 12, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111110
Morozov OS, Ivanchenko AV, Nechausov SS, Bulgakov BA. Effect of Electrode Morphology on Performance of Ionic Actuators Based on Vat Photopolymerized Membranes. Membranes. 2022; 12(11):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111110
Chicago/Turabian StyleMorozov, Oleg S., Anna V. Ivanchenko, Sergey S. Nechausov, and Boris A. Bulgakov. 2022. "Effect of Electrode Morphology on Performance of Ionic Actuators Based on Vat Photopolymerized Membranes" Membranes 12, no. 11: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111110
APA StyleMorozov, O. S., Ivanchenko, A. V., Nechausov, S. S., & Bulgakov, B. A. (2022). Effect of Electrode Morphology on Performance of Ionic Actuators Based on Vat Photopolymerized Membranes. Membranes, 12(11), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes12111110






