Highly Effective Anti-Organic Fouling Performance of a Modified PVDF Membrane Using a Triple-Component Copolymer of P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz as the Additive
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis and Characterization of the Triple-Component Copolymer Additive
2.3. Membrane Preparation
2.4. Characterization of Prepared Membranes
2.5. Protein Adsorption Test
2.6. Filtration Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of the Triple-Component Copolymer Additives
3.2. Morphologies and Mechanical Strength of Prepared Membranes
3.3. Surface Composition of Prepared Membranes
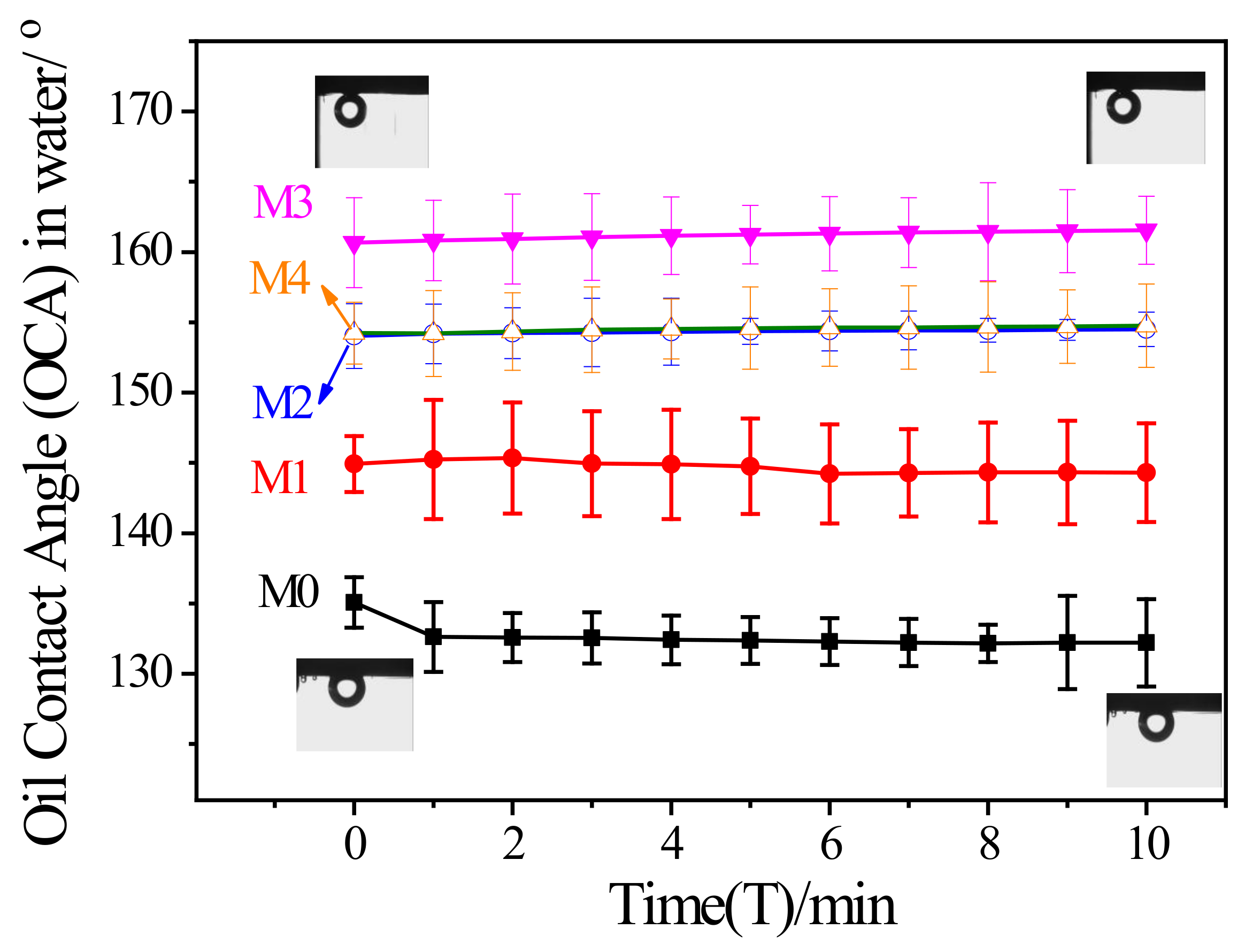
3.4. Membrane Surface Wetting Properties
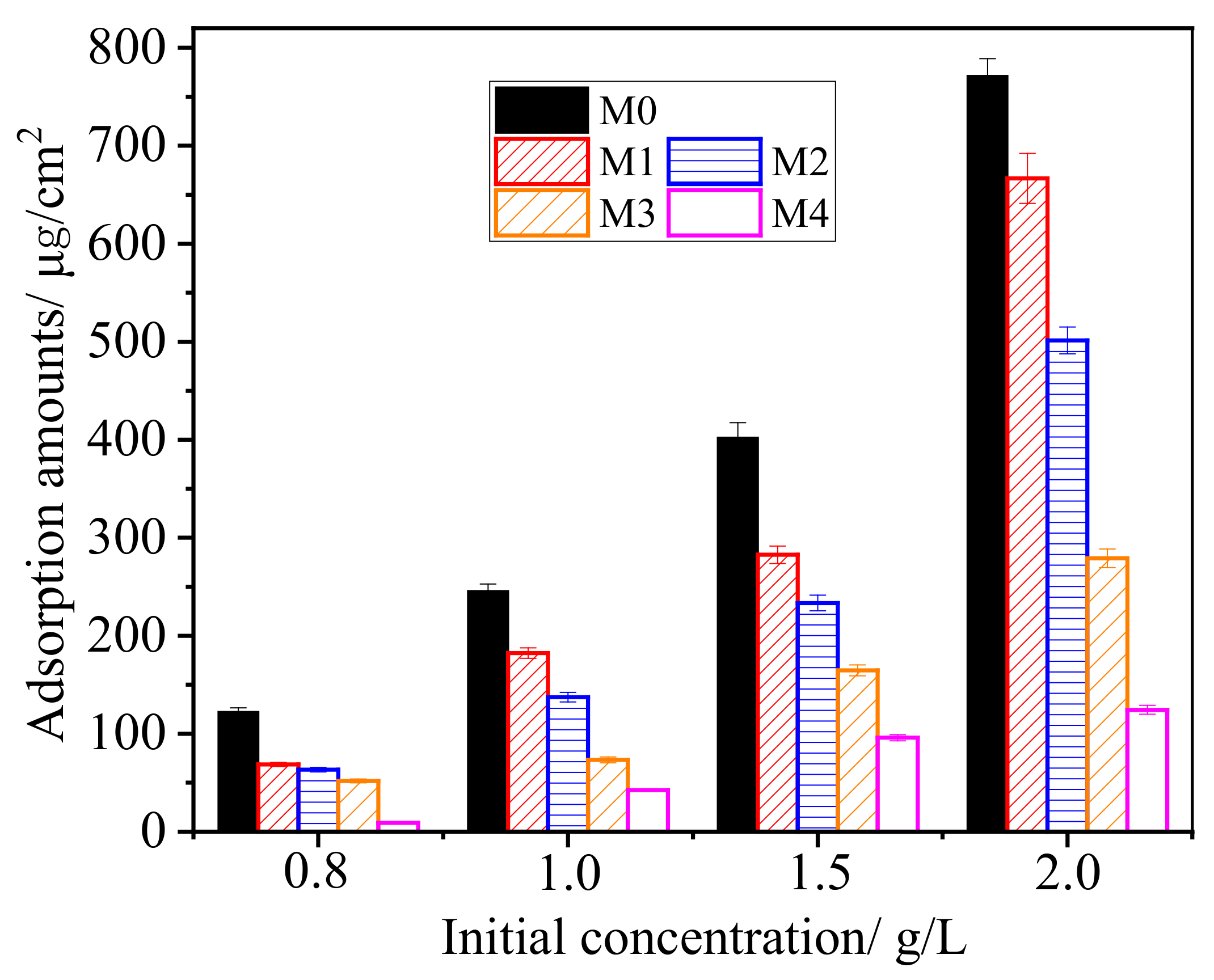
3.5. Adsorption to BSA Protein
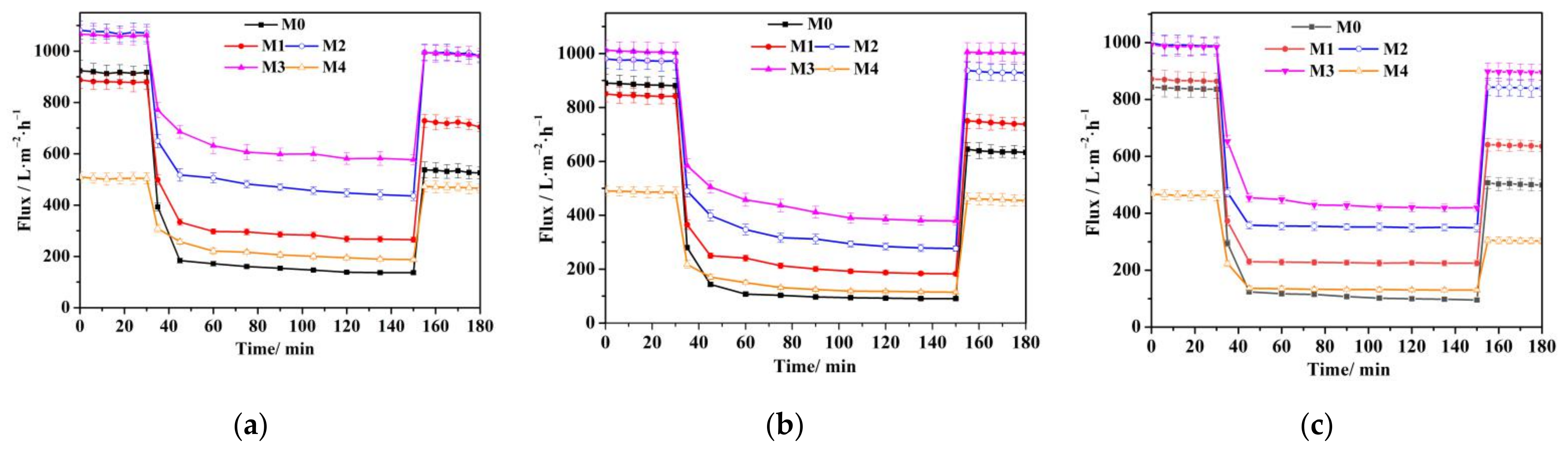
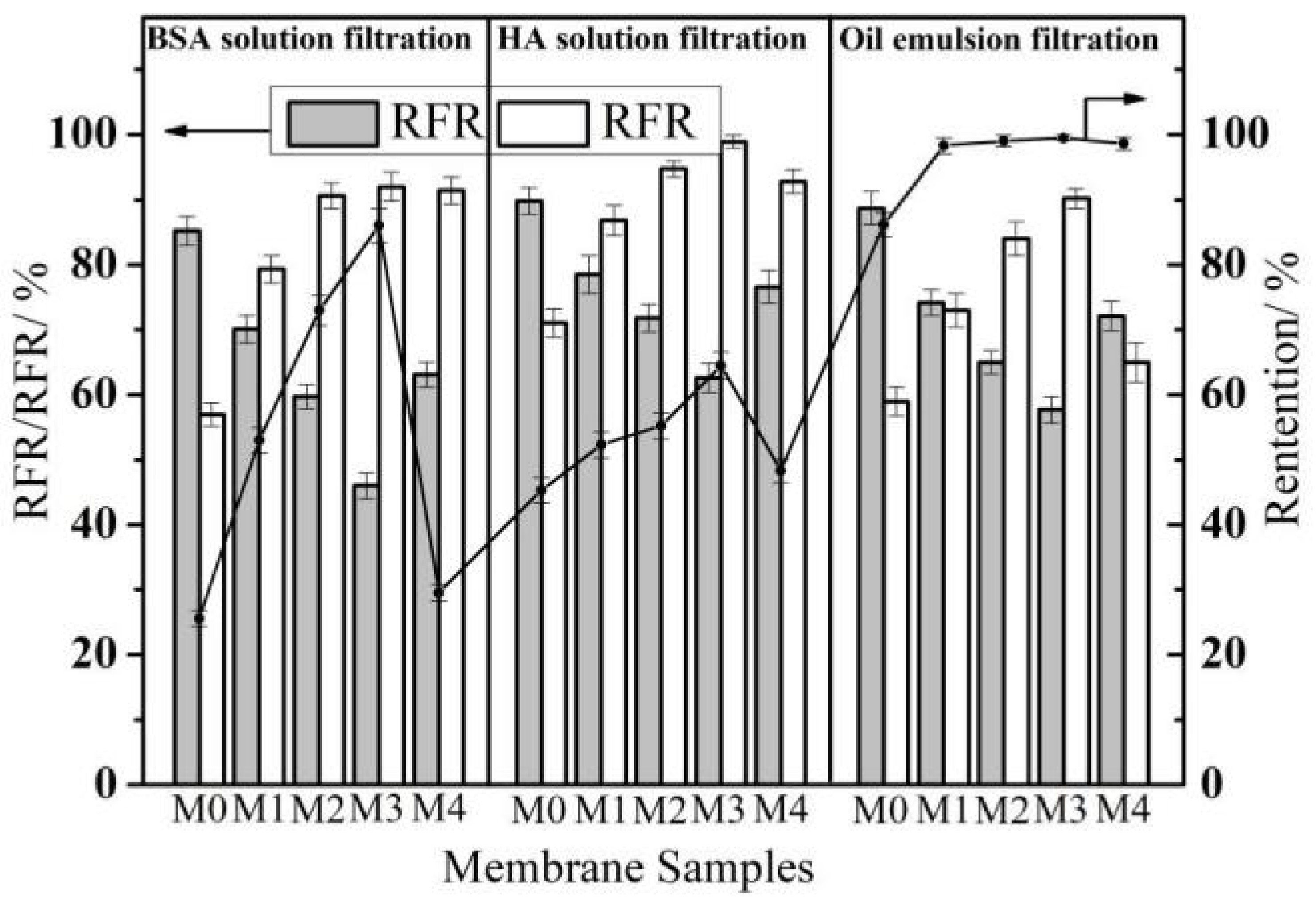
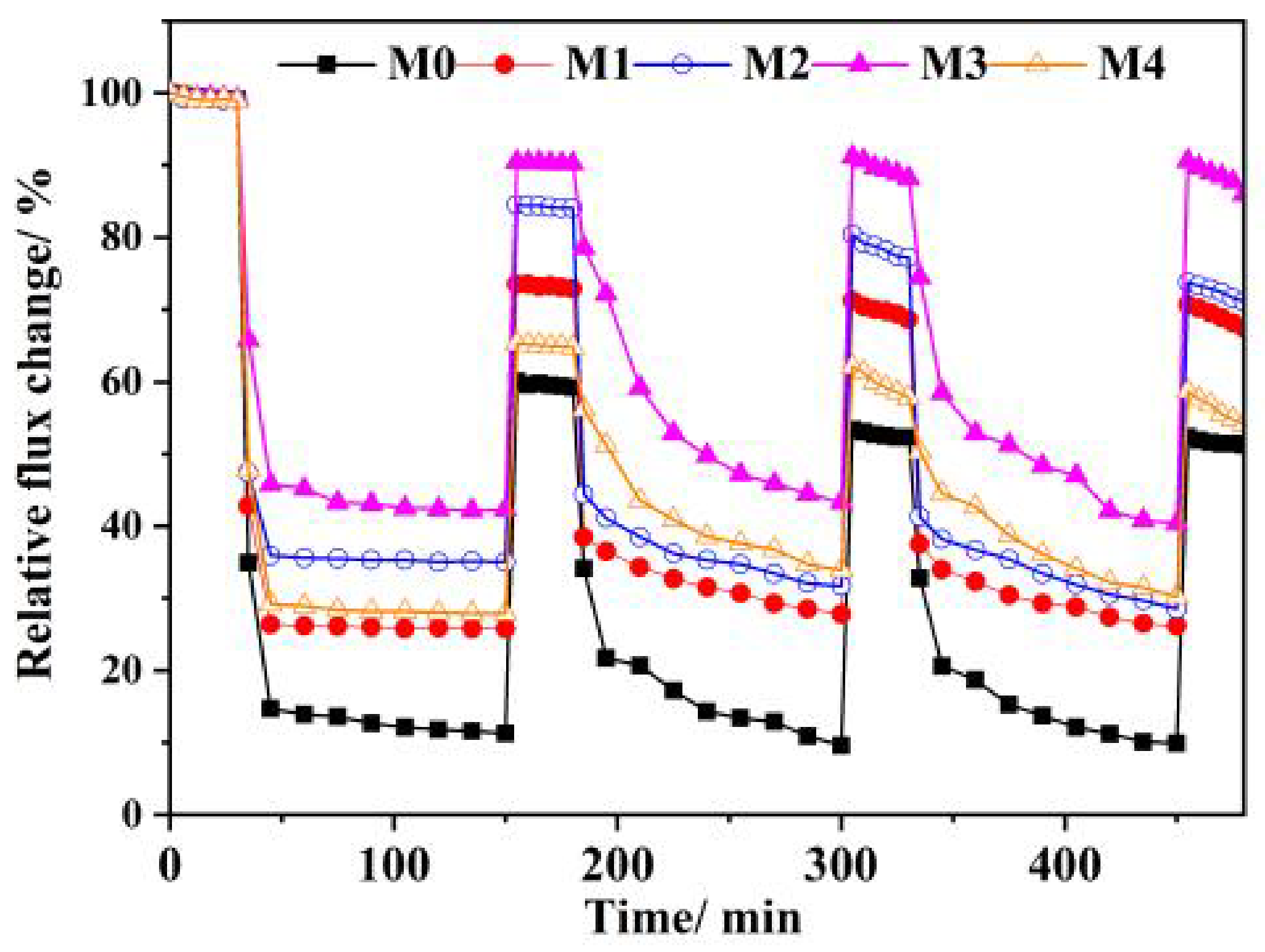
3.6. Anti-Organic Fouling Performance during Filtration Separation Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ulbricht, M. Advanced functional polymer membranes. Polymers 2006, 47, 2217–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.F.; Ma, S.H. Study on fouling and cleaning of PVDF. Membranes 2009, 3, 52–58. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Hashim, N.A.; Liu, Y.; Abed, M.R.M.; Li, K. Progress in the production and modification of PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 375, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Liu, J.X. Pretreatment and membrane hydrophilic modification to reduce membrane fouling. Membranes 2013, 3, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Zhu, T.; Liu, W.; Zhou, R.; Zhou, S.; Wu, R. Ultrafiltration pre-oxidation by boron-doped diamond anode for algae-laden water treatment: Membrane fouling mitigation, interface characteristics and cake layer organic release. Water Rues. 2020, 187, 116435–116444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slagt, J.M.; Henkel, J. Robustness of water systems in industrial applications. Chem. Ing. Tech. 2019, 91, 1395–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chan, R.; Chen, V. Characterization of protein fouling on membranes: Opportunities and challenges. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeva, P.D.; Knoche, T.; Pieper, T.; Ulbricht, M. Cross-flow ultrafiltration of protein solutions through unmodified and surface functionalized polyethersulfone membranes—Effect of process conditions on separation performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohani, M.M.; Mehta, A.; Zydney, A.L. Development of high performance charged ligands to control protein transport through charge-modified ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 362, 434–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, N.H.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Ismail, A.F.; Hasbullah, H.; Yusof, N.; Aziz, F.; Jaafar, J. Hydrophilic polymer-based membrane for oily wasterwater treatment: A review. Sep. Purifi. Technol. 2020, 233, 116007–116024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.P.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, M.; He, C.J. Antifouling performance of poly(lysine methacrylamide)-grafted PVDF microfiltration membrane for solute separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.G.; Wang, H.Z.; Zhang, Y.C.; Li, R.J.; Fabien, B.; Yu, G.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Liao, B.Q. New strategy of grafting hydroxyethyl acrylate (HEA) via γ ray radiation to modify polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membrane: Thermodynamic mechanisms of the improved antifouling performance. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 207, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Yi, S.; Hong, K.D.; Seo, J.H. Copolymerization of zwitterionic carboxybetaine and various hydrophobic groups to optimize antifouling and biocompatible properties. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 96, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, K.C.; Teow, Y.H.; Ang, W.L.; Mohammad, A.W. Novel GO/OMWCNTs mixed-matrix membrane with enhanced antifouling property for palm oil mill effluent treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 177, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.C.; Takahara, A. Synthesis and surface properties of amphiphilic copolymer consisting of hydrophobic perfluorocarbon and hydrpphilic zwitterionic blocks. Polymer 2021, 230, 124029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakihana, Y.; Cheng, L.; Fang, L.F.; Wang, S.Y.; Jeon, S.; Saeki, D.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of positively charged PVDF membranes with improved antibacterial activity by blending modification: Effect of change in membrane surface material properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 533, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Wang, T.; Su, Y.L.; Peng, F.B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, Z. Remarkable reduction of irreversible fouling and improvement of the permeation properties of poly (ether sulfone) ultrafiltration membranes by blending with Pluronic F127. Langmuir 2015, 21, 11856–11862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Ahn, Y.; Jang, M.; Kin, H.J.; Cho, K.Y.; Hwang, S.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Baek, K.Y. Effects of methacrylate based amphiphilic block copolymer additives on ultra filtration PVDF membrane formation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 202, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Cristiano, A.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Effect of additives in the casting solution on the formation of PVDF membranes. Desalination 2006, 192, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, C.S.; Lau, W.J.; Goh, P.S.; Ng, B.C.; Ismail, A.F. Preparation and characterization of PVDF-PVP-TiO2 composite hollow fifiber membranes for oily wastewater treatment using submerged membrane system. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar]
- Uragami, T.; Naito, Y.; Sugihara, M. Studies on synthesis and permeability of special polymer membranes. Polym. Bull. 1981, 4, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.J.; Kim, N.; Lee, Y.T. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/TiO2 organic–inorganic composite membranes for fouling resistance improvement. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 345, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teow, T.H.; Ooi, B.S.; Ahmad, A.L.; Lim, J.K. Investigation of Anti-fouling and UV-Cleaning Properties of PVDF/TiO2 Mixed-Matrix Membrane for Humic Acid Removal. Membranes 2021, 11, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venault, A.; Liu, Y.H.; Wu, J.R.; Yang, H.S.; Chang, Y.; Lai, J.Y.; Aimar, P. Low biofouling membranes prepared by liquid-induced phase separation of the PVDF/polystyrene-b-poly(ethylene glycol) methacrylate blend. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 450, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, X.S.; Li, J.H.; Zhou, Q.; Miao, J.; Zhang, Q. Amphiphilic poly(vinylchloride)-g-poly[poly(ethylene glycol) methylether methacrylate] copolymer for the surface hydrophilicity modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 129, 2472–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.B.; Li, T.; Liu, B.C.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Crittenden, J.C. Blended PVC/PVC-g-PEGMA ultrafiltration membranes with enhanced performance and antifouling properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 455, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.N.; Xiao, C.F.; An, S.L.; Hu, X.Y. Preparation and properties of PVDF/PVA hollow fiber membranes. Desalination 2010, 250, 530–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.Y.; Li, Q.; Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.K.; Wang, X.L. Hydrophilic modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membrane with poly(vinyl pyrrolidone) via a cross-linking reaction. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 304–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Loo, H.E.; Bai, R.B. A novel membrane showing both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties and its non-fouling performances for potential water treatment applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hester, J.F.; Mayes, A.M. Design and performance of foul-resistant poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes prepared in a single-step by surface segregation. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 202, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikita, S.; Shintani, T.; Nakagawa, K.; Matsuyama, H.; Yoshioka, T. Structure contreol of hydrophilized PVDF hollow-fiber membranes using amphiphilic copolymers: PMMA-co-P(HEMA-co-MEA). J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 612, 118421–118429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.X.; Tian, T.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Li, P.; Kong, Y. Synthesis of well-defined amphiphilic block copolymers via AGET ATRP used foe hydrophilic modification of PVDF membrane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42080–42088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Zhang, T.; Xu, Z.G.; Li, X.M.; Zhao, Y. A single colvalently grafted fluorolayer imparts instrinsically hydrophilic foams with simulaneous oleophobicity and hydrophilicity for removing water from oils. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 606, 125380–125387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefi, E.; Ghadimi, M.R.; Amirpoor, S.; Dolati, A. Preparation of new superhydrophobic and hughly oleophobic polyurethane coating with enhanced mechanical durability. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 454, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tang, Z.G.; Park-Lee, K.J.; Hess, D.W.; Breedveld, V. Fabrication of non-fluorinated hydrophilic-oleophobic stainless steel mesh for oil-water separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Sun, M.Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, S.F.; Wu, J.D.; Wang, J.P. Underwater oleophobic PTFE membrane for efficient and reusable emulsion separation and the influence of surface wettability and pore size. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.J.; Gong, X. Special oleopphobic and hydrophilic surfaces: Approaches, mechanism, and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 3759–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikhsan, S.N.W.; Yusof, N.; Aziz, F.; Ismail, A.F.; Jaafar, J.; Salleh, W.N.W.; Misdan, N. Superwetting materials for hydrophilic -oleophobic membrane in oily wastewater treatment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 290, 112565–112578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, Z.P.; Wang, H.Y.; Chen, L. Interaction energy evaluation of the role of solution chemistry and organic foulant composition on polysaccharide fouling of microfiltration membrane bioreactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2013, 104, 1028–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.; Cho, J.; Hoek, E.M.V. Natural organic matter fouling due to foultant-membrane physicochemical interactions. Desalination 2007, 202, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.Z.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Pei, X.F.; Zhang, W.B.; Jin, J. A novel zwitterioic polyelectrolyte grafted PVDF membrane for thoroughly separating oil from water with ultrahigh efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5758–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.J.; Su, Y.L.; Peng, J.M.; Zhao, X.T.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Dong, Y.A.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, Y.G.; Liu, J.Z. Efficient wastewater treatment by membranes through constructing tunable antifouling membrane surfaces. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 6545–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.Y.; Tu, W.T.; Wee, K.; Bai, R.B. Effective and pow fouling oil/water separation by a novel hollow fiber membrane with both hydrophilic and oleophobic surface properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, A.; Pham, V.A.; Matsuura, T.; Santerre, J.P. Development of membranes with low surface energy to reduce the fouling in ultrafiltration applications. J. Membr. Sci. 1997, 131, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cottlieb, H.E.; Koltyar, V.; Nudelman, A. NMR chemical shifts of common laboratory solvents as trace impurities. J. Org. Chem. 1997, 62, 7512–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, H.C.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, P.P.; Ma, J.; Zhai, X.D. Improved separation and antifouling properties of PVDF gravity-diven membranes by blending with amphiphilic muti-armspolymer PPG-Si-PEG. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117148–117158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Ulbricht, M. Novel ultrafiltration membranes with adjustable charge density based on sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) block copolymers and their tunable protein separation performance. Polymer 2014, 55, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, L.; Yu, W.H.; Kang, E.T.; Neoh, K.G. Functional and surface-active membranes from poly(vinylidene fluoride)-graft-poly(acrylic acid) prepared via raft-mediated graft copolymerization. Langmuir 2004, 20, 6032–6040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.J.; Su, Y.L.; Peng, J.M.; Dong, Y.N.; Zhao, X.T.; Jiang, Z.Y. Engineering a robust, versatile amphiphilic membrane surface through forced surface segregation for ultralow flux-decline. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hikita, M.; Tanaka, K.; Nakamura, T.; Kajiyama, T.; Takahara, A. Aggregation states and surface wettability in films of poly(styrene-block-2-perfluorooctyl ethyl acrylate) diblock copolymers synthesized by atom transfer radical polymerization. Langmuir 2004, 20, 5304–5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zheng, Y.M.; Zhai, J.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired super-antiwetting interfaces with special liquid-solid adhesion. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Liu, M.; Chen, L.; Chen, P.; Ma, J.; Han, D.; Jiang, L. Bio-inspires hierarchical macromolecule—Nanoclay hydrogels for robust underwater superoleophobicity. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4826–4830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Sun, Y.L.; Zhao, W.; Li, C.; Hu, Y.H.; Jiang, Z.Y.; Zhu, S.P. Zwitterionic polyethersulfone ultrafiltration membrane with superior antifouling property. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 315, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, L.; Chen, S.; Jiang, S. Molecular simulation study of water interactions with oligo(ethylene glycol)-terminated alkanethiol self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir 2004, 20, 8931–8938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrwerth, S.; Eck, W.; Reinhardt, S.; Grunze, M. Factors that determine the protein resistance of oligoether self-assembled monolayers-internal hydropgilicity, terminal hydrophilicity, and lateral packing density. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 9359–9366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, T.; Trinadh, M.; Babu, P.V.; Sainath, A.V.S.; Reddy, A.V.R. Oil–water emulsion separation using ultrafiltration membranes based on novel blends of poly(vinylidene fluoride) and amphiphilic tri-block copolymer containing carboxylic acid functional group. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 481, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Li, Y. Novel superhydrophilic antifouling PVDF-BiOCl nanocomposite membranes fabricated via a modified blending-phase inversion method. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117656–1176666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolto, B.; Zhang, J.H.; Wu, X.; Xie, Z.L. A review on current development of membranes for oil removal from wastewaters. Membranes 2020, 10, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]

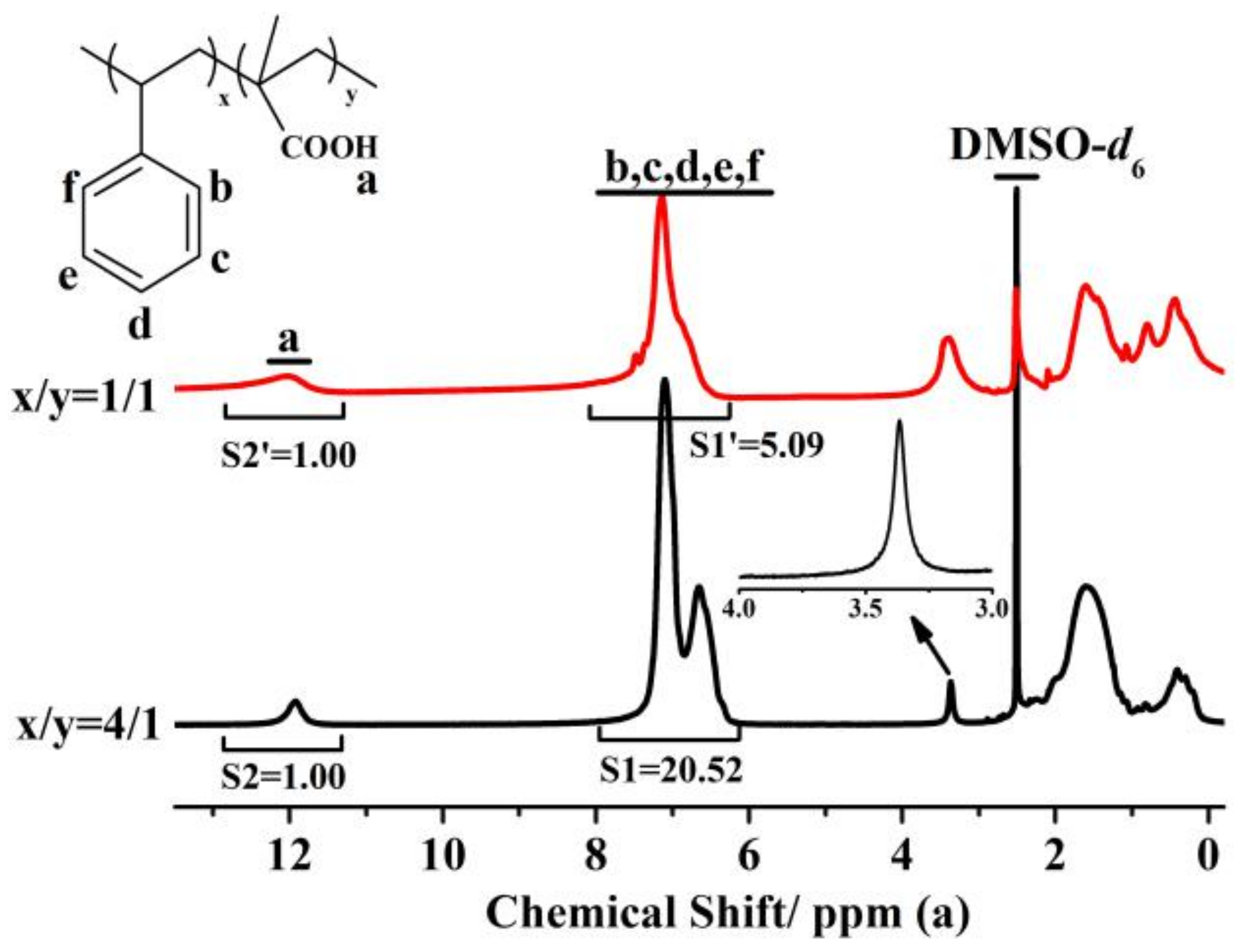
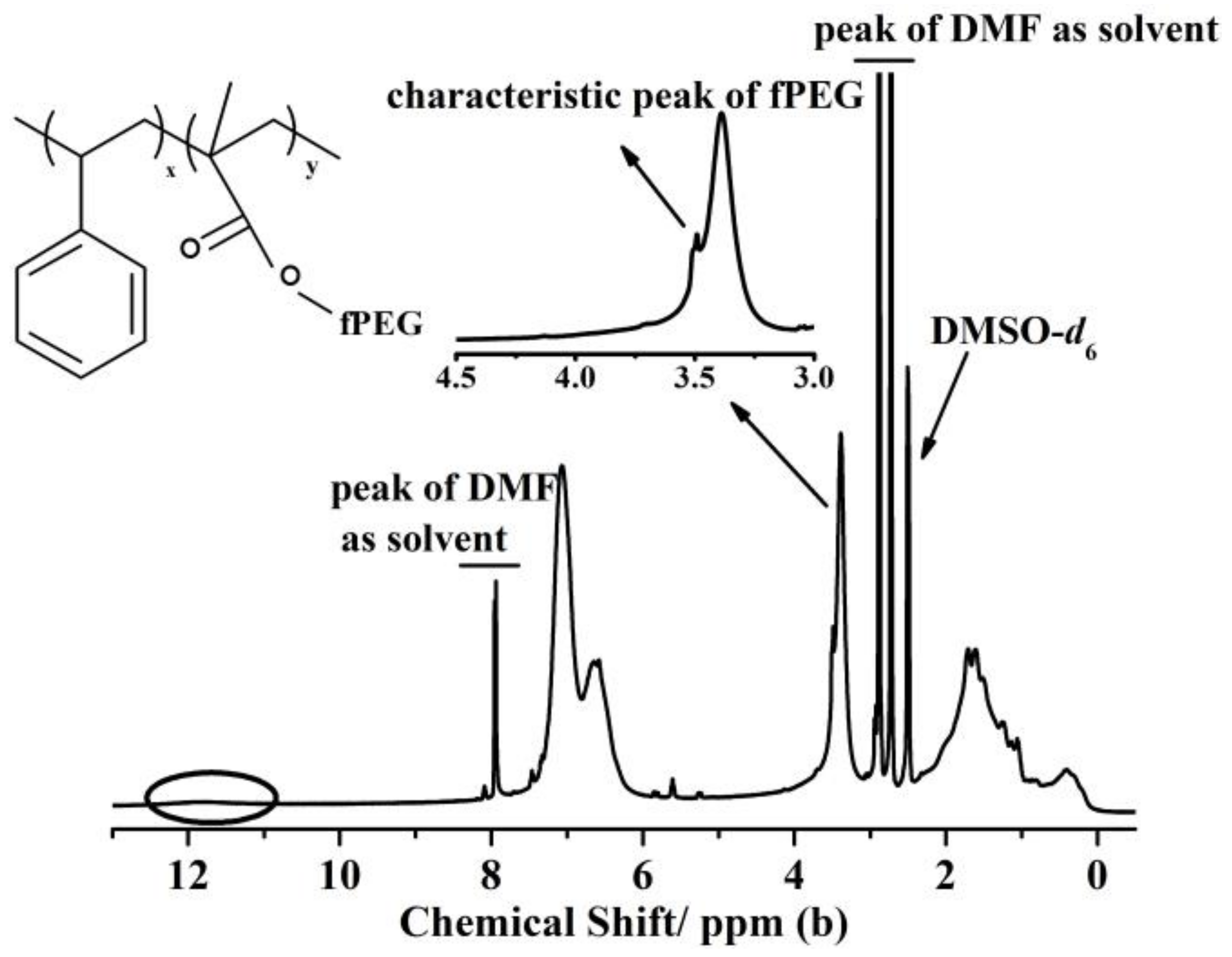
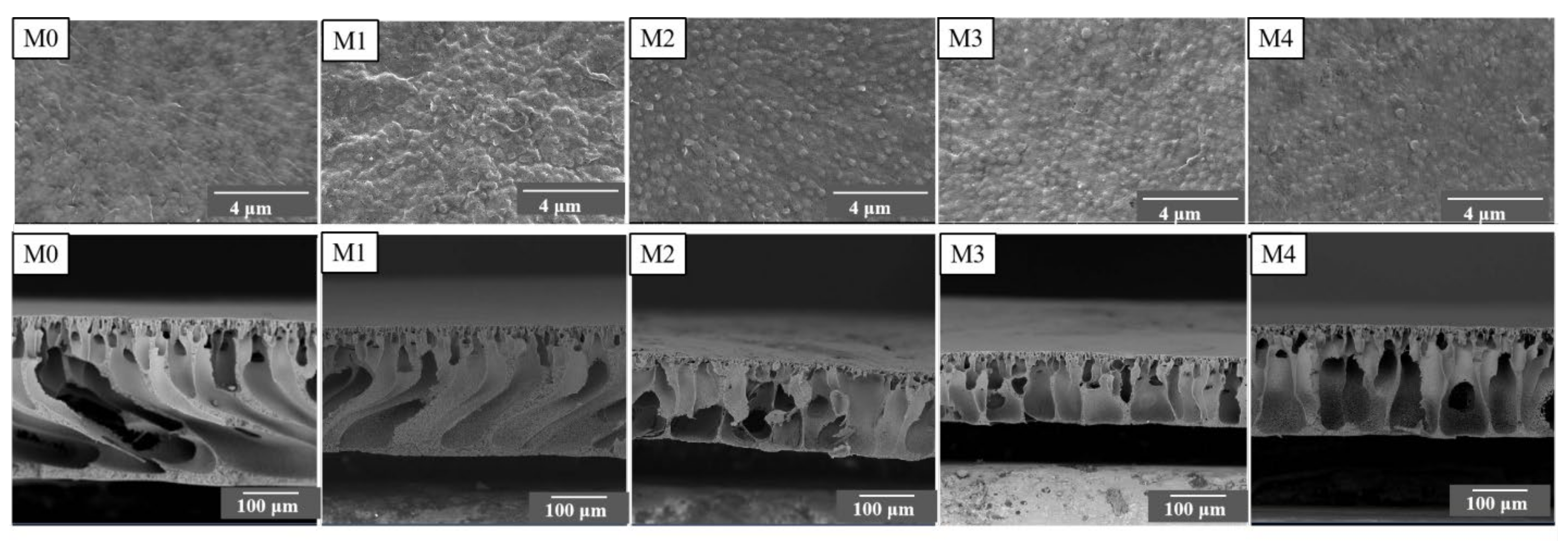
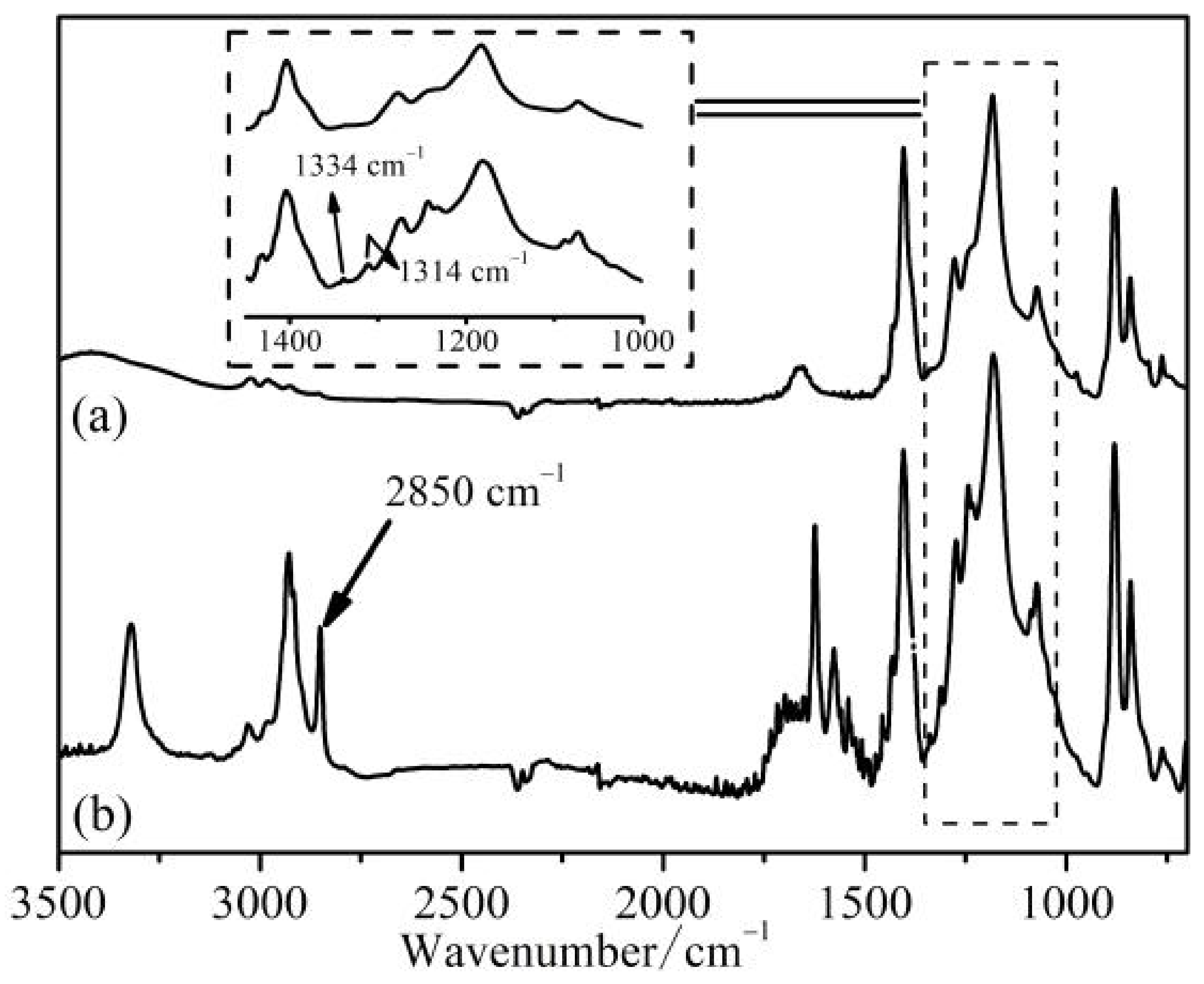
| Parameter | Types of Membranes Samples | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | M1 | M2 | M3 | M4 | |
| Composition of additive polymer | - | P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz (x:y = z at 4:1) | P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz (x:y = z at 4:1) | P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz (x:y = z at 1:1) | P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz (x:y = z at 1:1) |
| PVDF:Additive ratio (in weight) | 10:0 | 9:1 | 7:3 | 9:1 | 7:3 |
| Total content of PVDF and additive in casting solution (wt%) | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 | 18 |
| PVP in casting solution (wt%) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| NMP in casting solution (wt%) | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 | 77 |
| Non-solvent coagulant | H2O | H2O | H2O | H2O | H2O |
| Measured porosity (%) | 60.8 | 64.2 | 72.0 | 78.9 | 73.5 |
| Measured pore size (μm) | 0.229 | 0.279 | 0.320 | 0.424 | 0.302 |
| Measured initial water contact angle (°) | 79.3 ± 2.3 | 63.7 ± 1.6 | 61.7 ± 1.2 | 48.8 ± 1.0 | 59.4 ± 1.2 |
| Measured oil contact angle under water (°) | 135.1 ± 1.8 | 144.9 ± 2.0 | 154.0 ± 2.3 | 160.7 ± 3.2 | 154.2 ± 2.2 |
| Tensile stress (MPa) | 1.58 ± 0.12 | 1.52 ± 0.11 | 0.98 ± 0.05 | 1.08 ± 0.1 | 0.67 ± 0.08 |
| Breaking elongation (%) | 57.10 ± 2.9 | 56.03 ± 2.1 | 19.11 ± 0.80 | 33.94 ± 1.5 | 19.46 ± 0.75 |
| Types of Membranes | Membrane Surface Compositions (Area %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C–C (284.8 eV) | C–H (286.1 eV) | C–O (288.1 eV) | C–F2 (290.7 eV) | C–F3 (291.6 eV) | |
| M0 | 14.00% | 46.38% | 3.42% | 35.95% | 0 |
| M1 | 31.04% | 39.98% | 6.88% | 21.97% | 1.20% |
| M2 | 36.02% | 38.70% | 6.69% | 12.89% | 4.17% |
| M3 | 35.12% | 37.73% | 5.22% | 20.58% | 1.30% |
| M4 | 40.60% | 34.60% | 5.36% | 13.06% | 6.36% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Sun, Y.; Shen, S.; Li, Y.; Bai, R. Highly Effective Anti-Organic Fouling Performance of a Modified PVDF Membrane Using a Triple-Component Copolymer of P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz as the Additive. Membranes 2021, 11, 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120951
Zhou X, Sun Y, Shen S, Li Y, Bai R. Highly Effective Anti-Organic Fouling Performance of a Modified PVDF Membrane Using a Triple-Component Copolymer of P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz as the Additive. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120951
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xiaoji, Yizhuo Sun, Shusu Shen, Yan Li, and Renbi Bai. 2021. "Highly Effective Anti-Organic Fouling Performance of a Modified PVDF Membrane Using a Triple-Component Copolymer of P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz as the Additive" Membranes 11, no. 12: 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120951
APA StyleZhou, X., Sun, Y., Shen, S., Li, Y., & Bai, R. (2021). Highly Effective Anti-Organic Fouling Performance of a Modified PVDF Membrane Using a Triple-Component Copolymer of P(Stx-co-MAAy)-g-fPEGz as the Additive. Membranes, 11(12), 951. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120951







