Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane with a Polyvinylpyrrolidone Additive for Tofu Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Combination with the Coagulation–Flocculation Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Membrane Preparation
2.2. Instrumentation for Membrane Characterization
2.3. Pretreatment of Tofu Wastewater
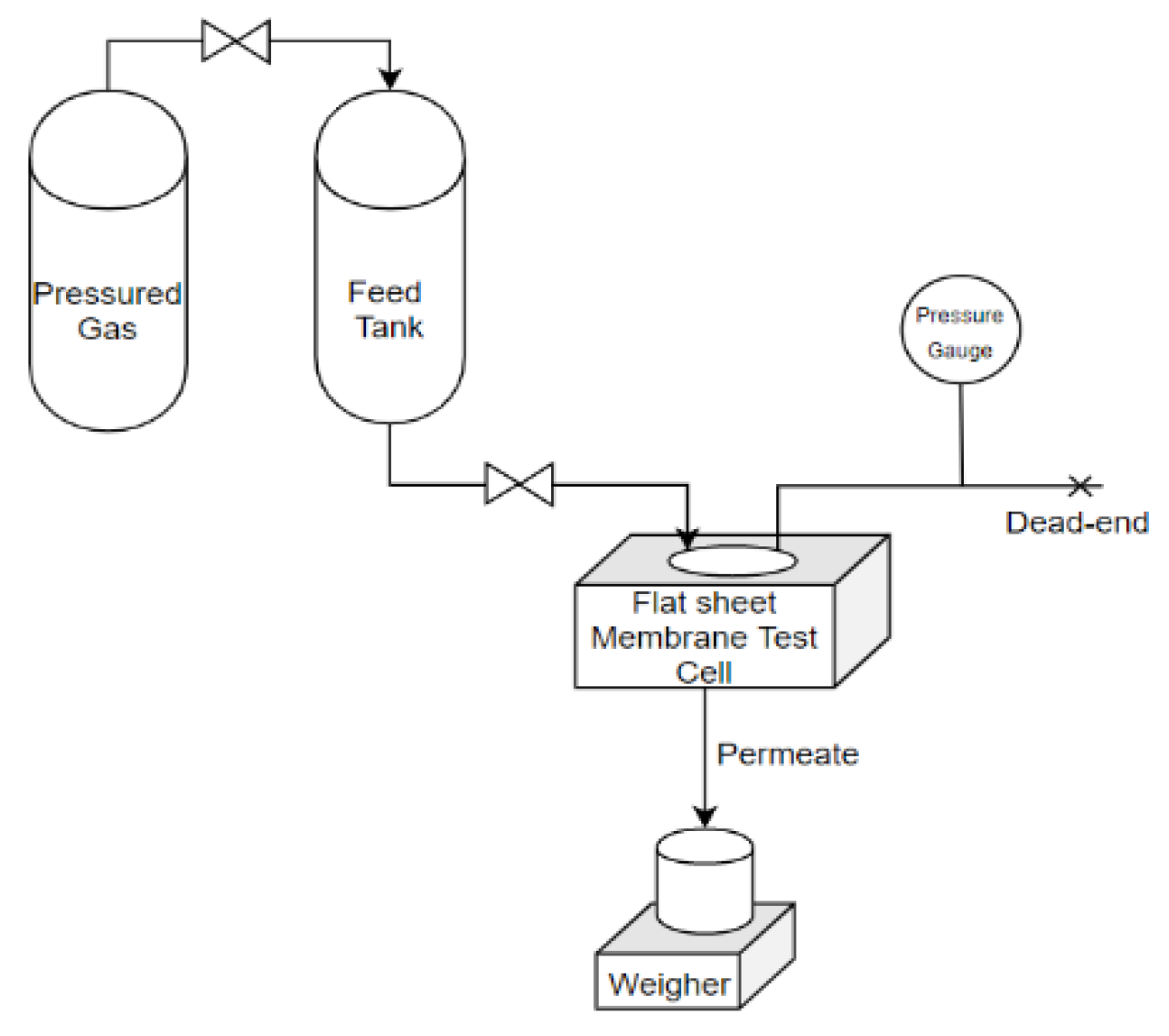
2.4. Ultrafiltration Process
3. Results and Discussion
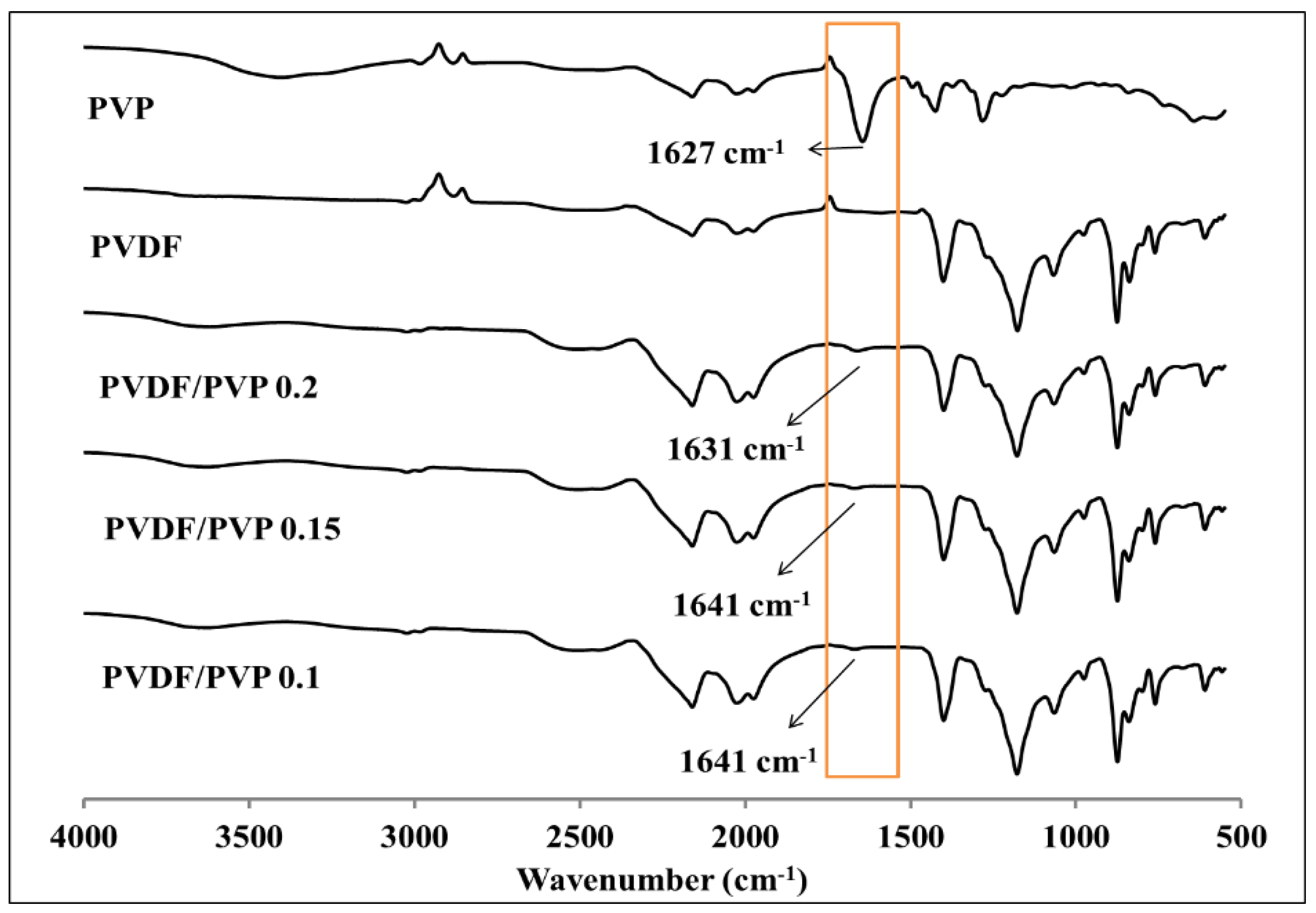
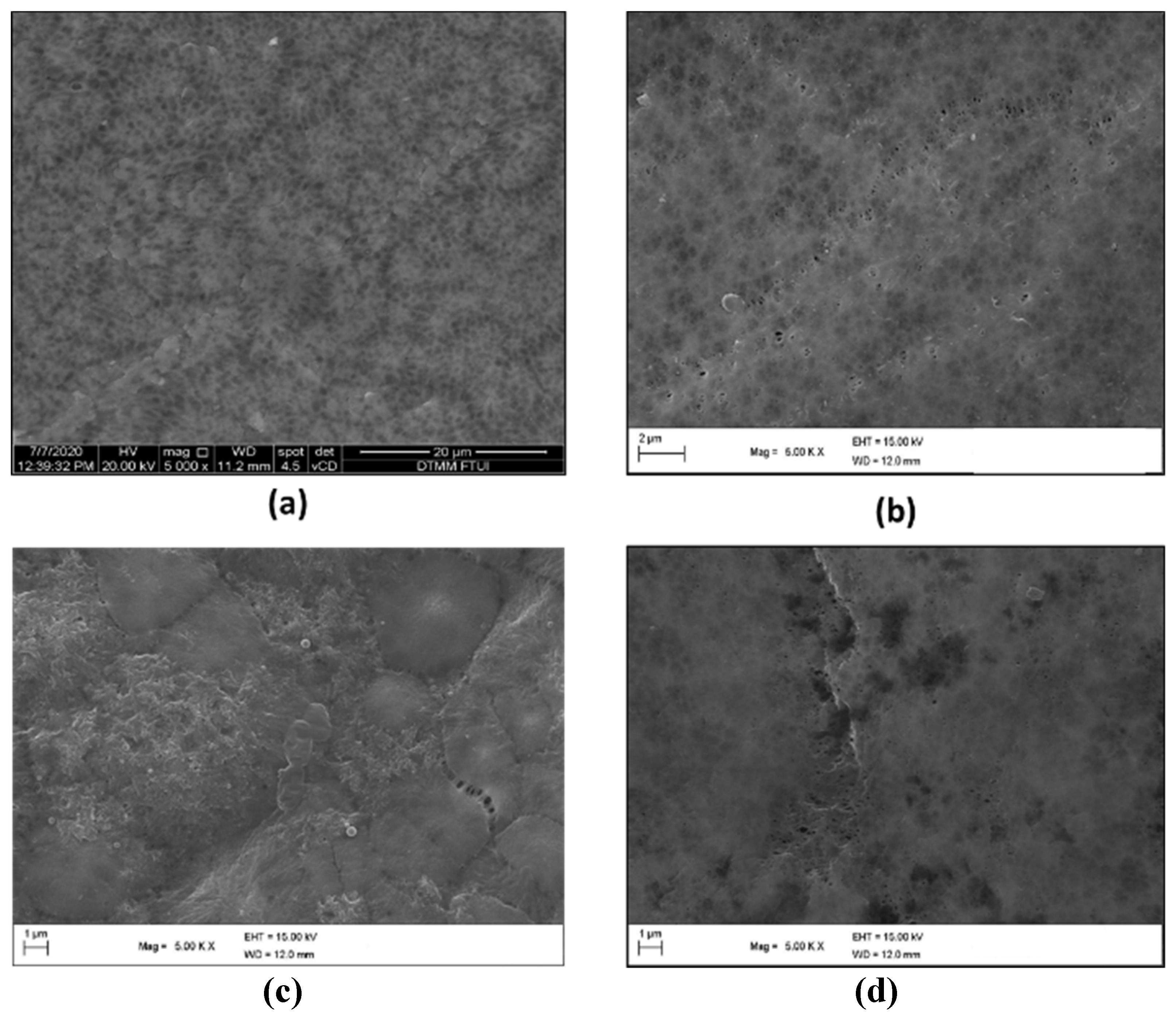
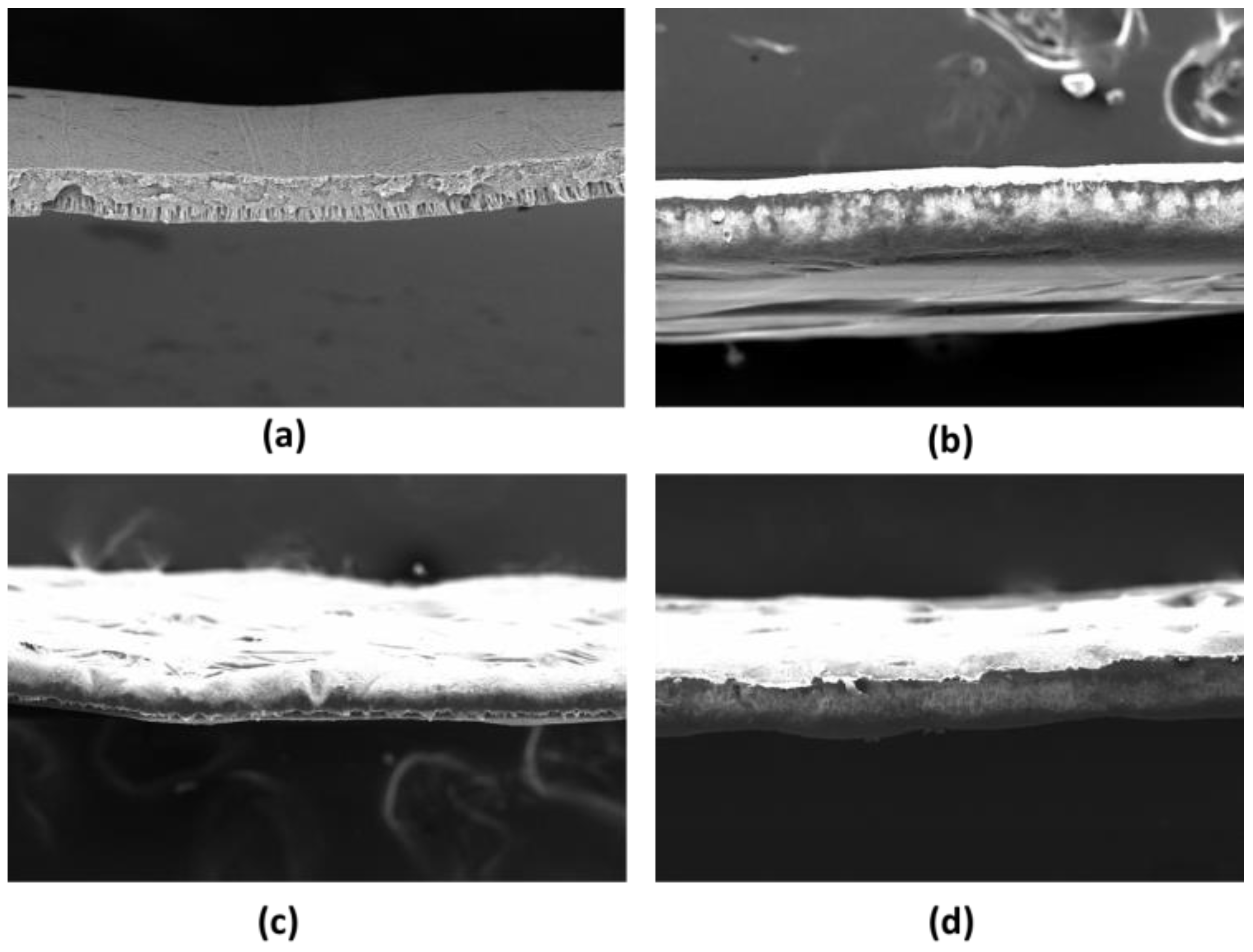
3.1. Membrane Characterization
3.2. Pretreatment Process
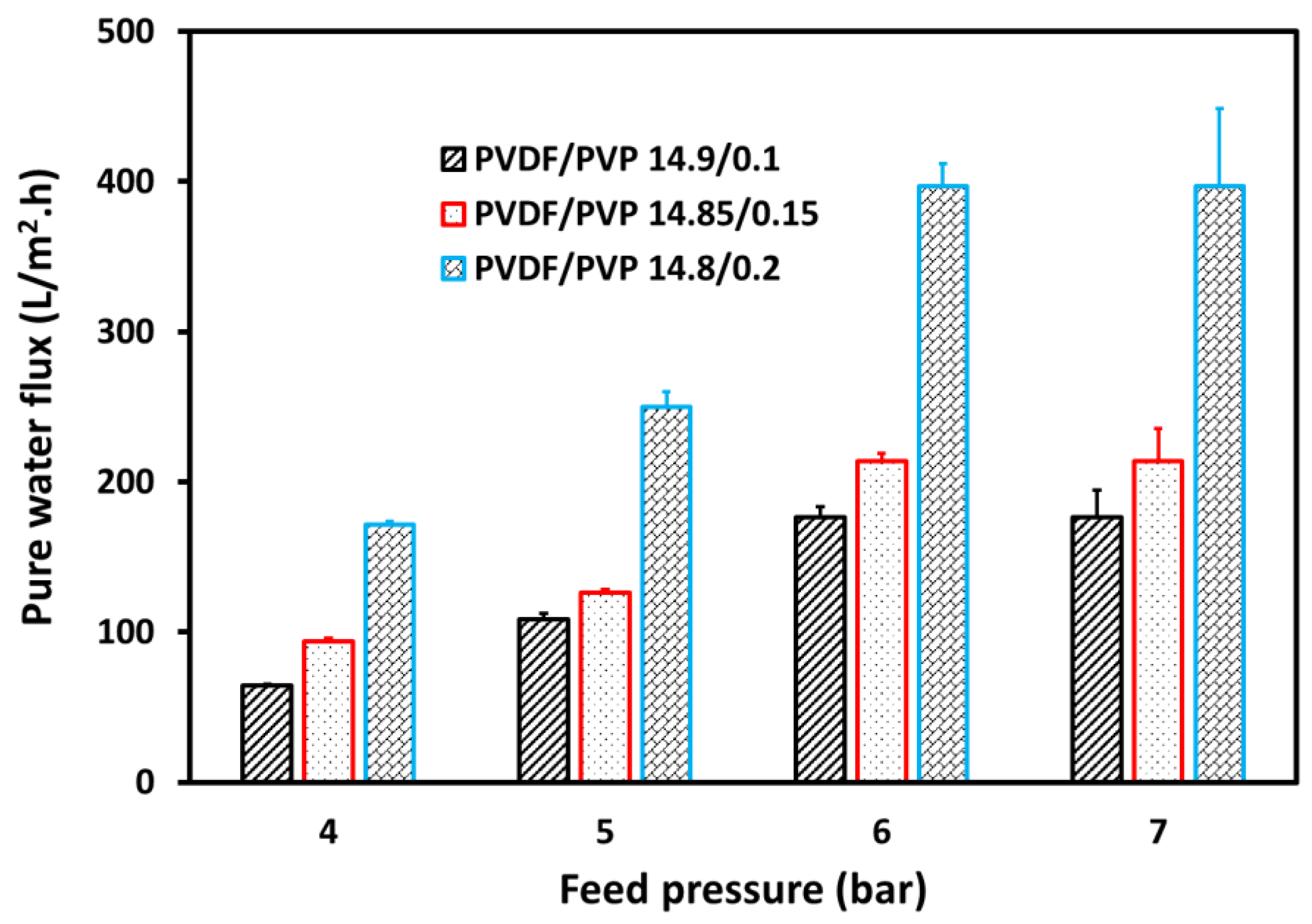
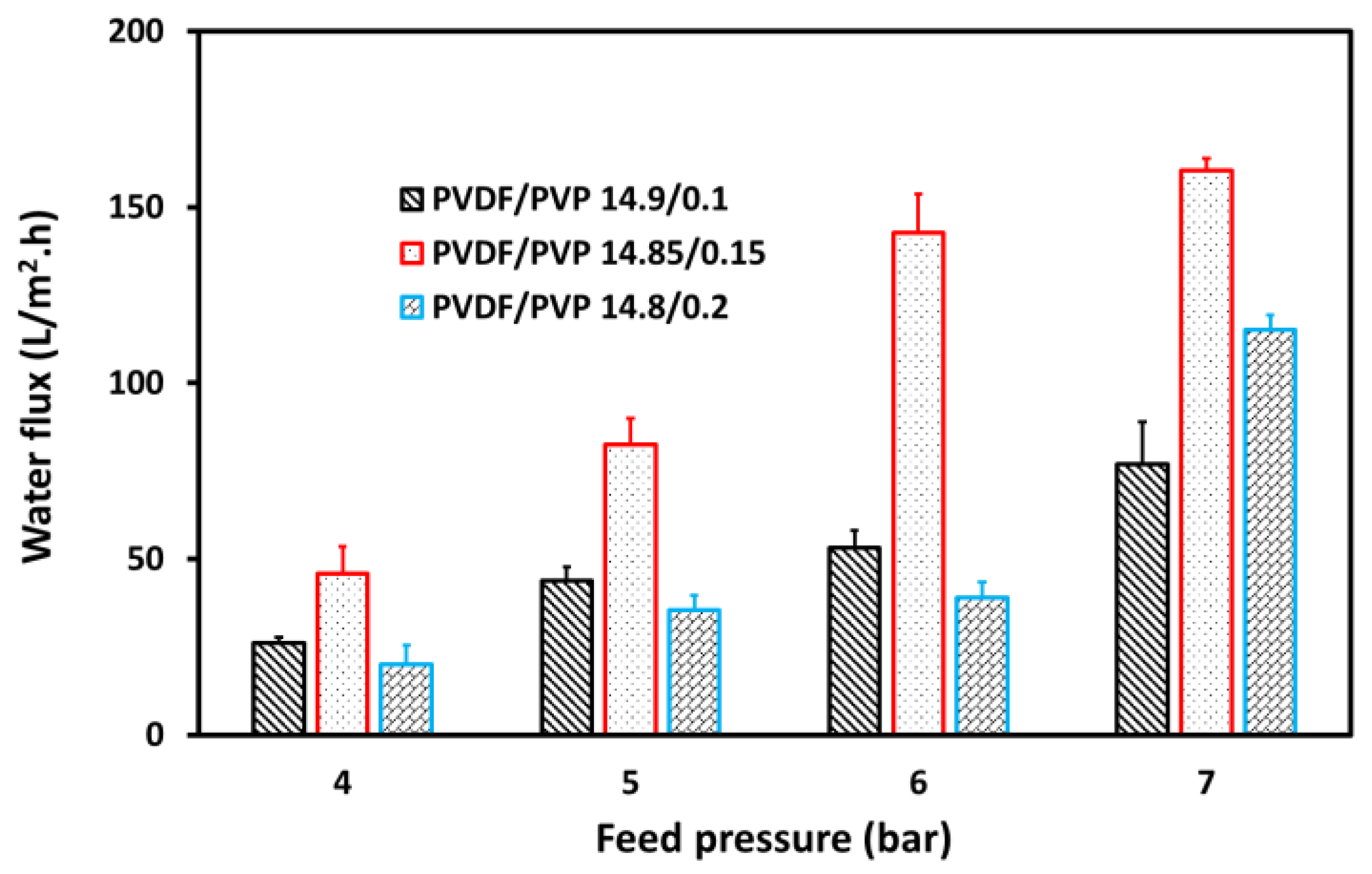
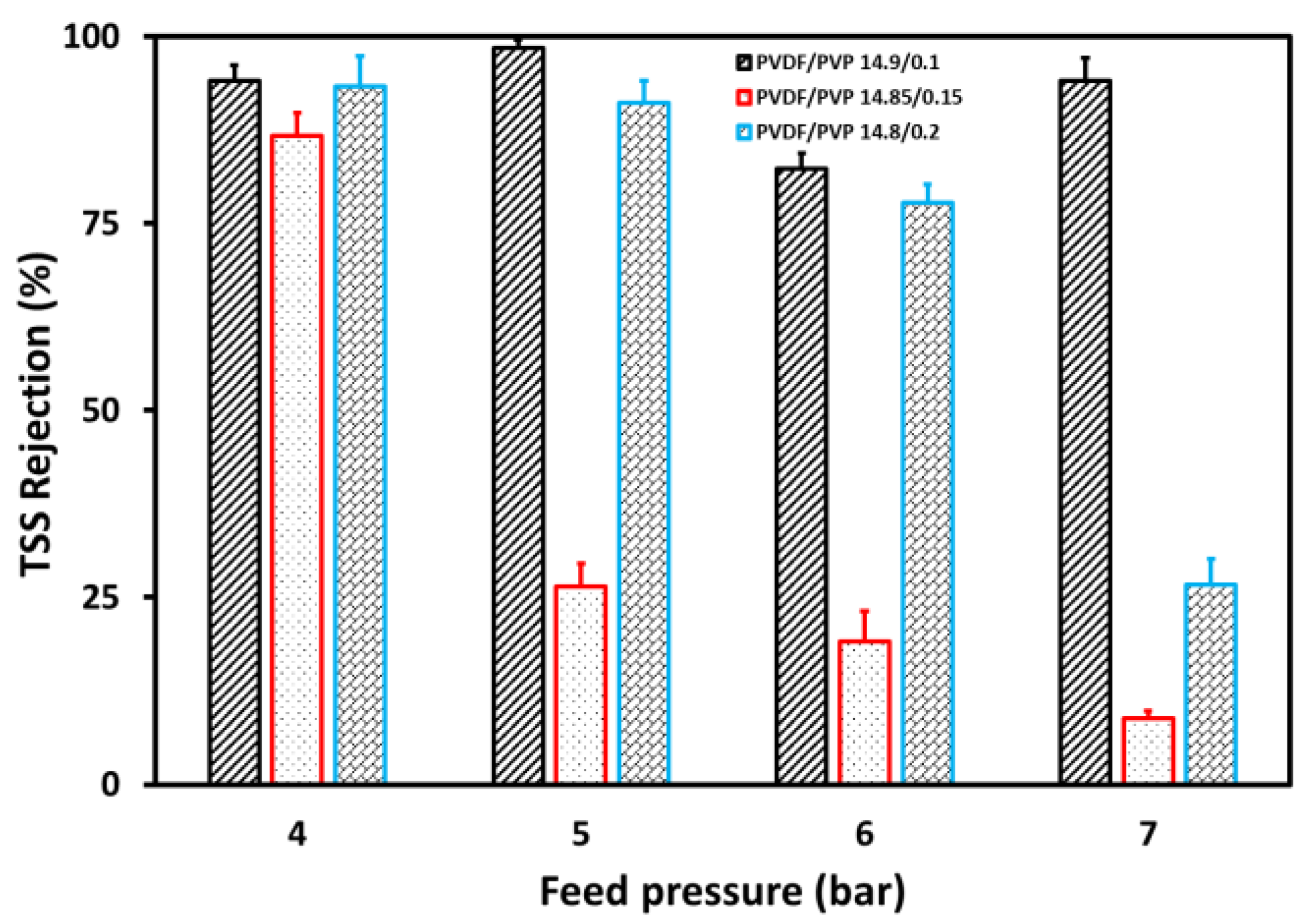
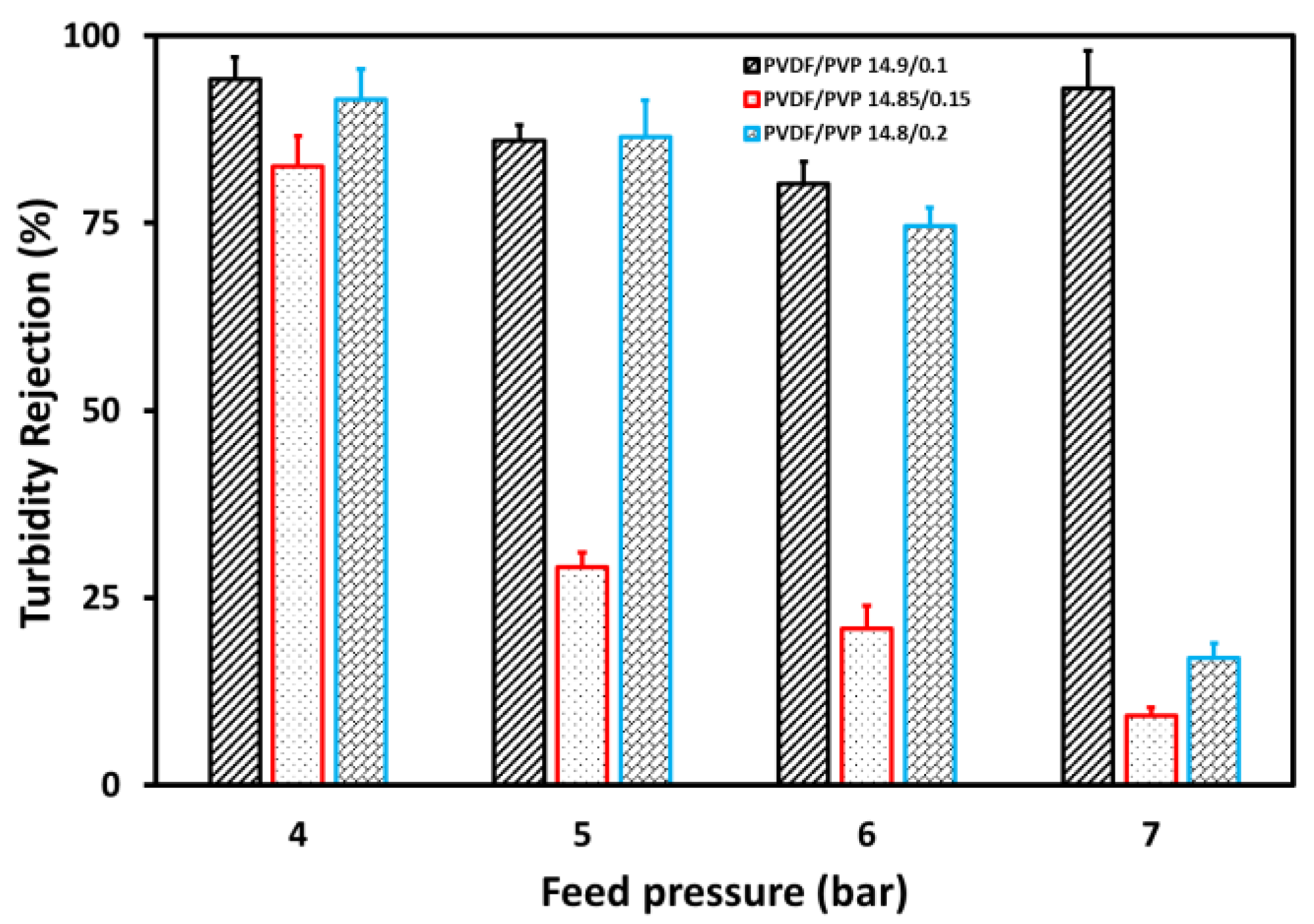
3.3. Separation Process
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, S.-K.; Wang, X.; Miao, J.; Tian, Y.-T. Tofu whey wastewater is a promising basal medium for microalgae culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 253, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaiman, D.K.; Ashby, R.D.; Crocker, N.V. Bioprocess for hydrolysis of galacto-oligosaccharides in soy molasses and tofu whey by recombinant Pseudomonas chlororaphis. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 24, 101529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, T.; Shen, N.; Yu, Z.-W.; Zeng, R.J. Hydraulic retention time affects stable acetate production from tofu processing wastewater in extreme-thermophilic (70 °C) mixed culture fermentation. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matemu, A.O.; Kayahara, H.; Murasawa, H.; Nakamura, S. Importance of size and charge of carbohydrate chains in the preparation of functional glycoproteins with excellent emulsifying properties from tofu whey. Food Chem. 2009, 114, 1328–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choe, U.; Mustafa, A.M.; Zhang, X.; Sheng, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, K. Effects of hydrothermal pretreatment and bamboo hydrochar addition on anaerobic digestion of tofu residue for biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 336, 125279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-S.; Lee, D.-Y. Fermentative hydrogen production from tofu-processing waste and anaerobic digester sludge using microbial consortium. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S48–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Gao, B.; Su, M.; Dai, C.; Huang, L.; Zhang, C. Integrated biorefinery strategy for tofu wastewater biotransformation and biomass valorization with the filamentous microalga Tribonema minus. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.-J.; Dini, J.; Lavandier, C.; Rupasinghe, H.; Faulkner, H.; Poysa, V.; Buzzell, D.; DeGrandis, S. Effects of processing on the content and composition of isoflavones during manufacturing of soy beverage and tofu. Process Biochem. 2002, 37, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Hao, N.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, L.; Jiang, L.; Sui, X. Valorization of soy whey wastewater: How epigallocatechin-3-gallate regulates protein precipitation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 15504–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Kumabe, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Takeuchi, H.; Xie, Y.; Hasegawa, T. Hydrolysis behavior of tofu waste in hot compressed water. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 39, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Tong, Q. Lactobacillus delbrueckii is the key functional microorganism of natural fermented tofu sour water involved in the traditional coagulation of Chinese Huizhou Mao-tofu. LWT 2020, 131, 109706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-K.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y.-T.; Cui, Y.-H. Nutrient recovery from tofu whey wastewater for the economical production of docosahexaenoic acid by Schizochytrium sp. S31. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktariany, A.; Kartohardjono, S. Effect of Coagulant Dosage on Tofu Industry Wastewater Treatment in Combination with Ultrafiltration Process Using Polysulfone Membrane; E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Bali, Indonesia, 2018; p. 04004. [Google Scholar]
- Regulation of the Minister of Environment. Regulation of the Minister of Environment of the Republic of Indonesia Number 5 of 2014 Concerning Wastewater Quality Standards; Regulation of the Minister of Environment: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2014.
- Chua, J.-Y.; Liu, S.-Q. Soy whey: More than just wastewater from tofu and soy protein isolate industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, L.S.; Kartohardjono, S. The Combined Process of Coagulation-Flocculation and Membrane Separations to Treat Wastewater from Tofu Industry; AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Padang, Indonesia, 2020; p. 030010. [Google Scholar]
- Purnawan, I.; Febriasari, A.; Setyaputra, B.; Yolandini, T.T.; Windriyo, M.J.; Karamah, E.F.; Kartohardjono, S. Combined Process of Ozonation and Membrane Processes to Treat Wastewater from Batik Industry; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2020; p. 012003. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, X.; Zuo, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, B. Enhanced biogas production and in situ ammonia recovery from food waste using a gas-membrane absorption anaerobic reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 292, 121864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Febriasari, A.; Purnawan, I.; Chalid, M.; Ismojo, I.; Kartohardjono, S. A Direct Comparison Between Poly (vinylidene) Flouride and Polysulfone Flat Sheet Membrane; Characterization and Mechanical Strength; IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2020; p. 012002. [Google Scholar]
- Barambu, N.U.; Bilad, M.R.; Bustam, M.A.; Kurnia, K.A.; Othman, M.H.D.; Nordin, N.A.H.M. Development of membrane material for oily wastewater treatment: A review. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2020, 12, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Wang, D.; Sun, X.; Jiang, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, L. Surface modified by green synthetic of Cu-MOF-74 to improve the anti-biofouling properties of PVDF membranes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 411, 128524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortaheb, H.; Salehi, M.B.; Rajabzadeh, M. Optimized hybrid PVDF/graphene membranes for enhancing performance of AGMD process in water desalination. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 99, 407–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, V.K.; Voicu, S.I. Recent advances in cellulose and chitosan based membranes for water purification: A concise review. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 146, 148–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.Y.; Arning, A. Performance comparison between polyvinylidene fluoride and polytetrafluoroethylene hollow fiber membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. Membranes 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeow, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, K. Isothermal phase diagrams and phase-inversion behavior of poly (vinylidene fluoride)/solvents/additives/water systems. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 2150–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimethylacetamide (DMAc). Available online: https://www.eastman.com/Pages/ProductHome.aspx?product=71103648 (accessed on 17 September 2021).
- Wahab, M.; Muchtar, S.; Arahman, N.; Mulyati, S.; Riza, M. The Effects of Solvent Type on the Performance of Flat Sheet Polyethersulfone/Brij58 Membranes; IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Aceh, Indonesia, 2019; p. 012119. [Google Scholar]
- Febriasari, A.; Ananto, A.H.; Suhartini, M.; Kartohardjono, S. Polysulfone–Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone Blend Polymer Composite Membranes for Batik Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontananova, E.; Jansen, J.C.; Cristiano, A.; Curcio, E.; Drioli, E. Effect of additives in the casting solution on the formation of PVDF membranes. Desalination 2006, 192, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Hassan, A.R. Preparation, characterization and performance studies of active pvdf ultrafiltration-surfactants membranes containing PVP as additive. Malays. J. Anal. Sci. 2016, 20, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygmohammdi, F.; Kazerouni, H.N.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Hazrati, H.; Yegani, R. Preparation and characterization of PVDF/PVP-GO membranes to be used in MBR system. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2020, 154, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Liu, M.-Q.; Guo, J.-H.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Li, B.-B.; Li, D.-Y. Preparation and characterization of PDMS-PVDF hydrophobic microporous membrane for membrane distillation. Desalination 2015, 370, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simone, S.; Figoli, A.; Criscuoli, A.; Carnevale, M.; Rosselli, A.; Drioli, E. Preparation of hollow fibre membranes from PVDF/PVP blends and their application in VMD. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasin, S.; Filippov, A. Hydrodynamic permeability of the membrane as a system of rigid particles covered with porous layer (cell model). Colloid J. 2004, 66, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusworo, T.D.; Ariyanti, N.; Utomo, D.P. Effect of nano-TiO2 loading in polysulfone membranes on the removal of pollutant following natural-rubber wastewater treatment. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 35, 101190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikooe, N.; Saljoughi, E. Preparation and characterization of novel PVDF nanofiltration membranes with hydrophilic property for filtration of dye aqueous solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 413, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathia, N.; Kartohardjono, S. Effects of Trans-Membrane-Pressure on Tofu Industry Wastewater Treatment through Ultrafiltration and Reverse Osmosis Processes; AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: Padang, Indonesia, 2020; p. 030009. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, C.H.; Oh, K.Y.; Kim, S.K.; Yeo, J.G.; Sharma, P. Pervaporative seawater desalination using NaA zeolite membrane: Mechanisms of high water flux and high salt rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 371, 226–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doraisammy, V.; Lai, G.S.; Kartohardjono, S.; Lau, W.J.; Chong, K.C.; Lai, S.O.; Hasbullah, H.; Ismail, A.F. Synthesis and characterization of mixed matrix membranes incorporated with hydrous manganese oxide nanoparticles for highly concentrated oily solution treatment. Can. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 96, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.P.; Mou, H.; Wang, L.K.; Matsuura, T.; Wei, Y. Membrane separation: Basics and applications. In Membrane and Desalination Technologies; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2011; pp. 271–332. [Google Scholar]
- Hurwitz, G.; Guillen, G.R.; Hoek, E.M. Probing polyamide membrane surface charge, zeta potential, wettability, and hydrophilicity with contact angle measurements. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadi, M.; Jafarzadeh, Y.; Yegani, R.; Kazemi, S. PVDF membranes embedded with PVP functionalized nanodiamond for pharmaceutical wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2018, 140, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, I.; Kartohardjono, S. Effect of pH of Coagulant on the Treatment of Wastewater from Tofu Industry; E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Bali, Indonesia, 2018; p. 04006. [Google Scholar]
- Sabarudin, B.T.; Kartohardjono, S. The Combination of Coagulation-Flocculation and Membrane Processes to Minimize Pollution of Tofu Wastewater. Evergreen 2020, 7, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| PVDF (g) | DMAc (mL) | PVP (g) | Code |
|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 85 | - | PVDF |
| 14.9 | 85 | 0.1 | PVDF/PVP 0.1 |
| 14.85 | 85 | 0.15 | PVDF/PVP 0.15 |
| 14.8 | 85 | 0.2 | PVDF/PVP 0.2 |
| Parameter | Water Contact Angle |
|---|---|
| PVDF Pristine | 73.45° ± 0.5° |
| PVDF/PVP 14.8/0.2 | 55° ± 2.1° |
| PVDF/PVP 14.85/0.15 | 61° ± 2.3° |
| PVDF/PVP 14.9/0.1 | 66° ± 3.5° |
| Membrane | Thickness (µm) | Porosity (ε, %) | Avarage Pore Size (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF Pristine | 65.23 | 9.23 ± 1.5 | Un-identified |
| PVDF/PVP 0.1 | 139.8 | 32.01 ± 0.4 | 14.9 |
| PVDF/PVP 0.15 | 51.11 | 79.41 ± 0.9 | 6.7 |
| PVDF/PVP 0.2 | 77.78 | 93.59 ± 1.3 | 5.9 |
| Parameter | Before Pre-Treatment | After Pre-Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| pH | 4.01 | 6.78 ± 0.21 |
| TSS (mg/L) | 501 | 56.5 ± 1.2 |
| TDS (mg/L) | 833 | 1820 ± 190 |
| Turbidity (FAU) | 594 | 72.5 ± 2.75 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Purnawan, I.; Angputra, D.; Debora, S.C.; Karamah, E.F.; Febriasari, A.; Kartohardjono, S. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane with a Polyvinylpyrrolidone Additive for Tofu Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Combination with the Coagulation–Flocculation Process. Membranes 2021, 11, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120948
Purnawan I, Angputra D, Debora SC, Karamah EF, Febriasari A, Kartohardjono S. Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane with a Polyvinylpyrrolidone Additive for Tofu Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Combination with the Coagulation–Flocculation Process. Membranes. 2021; 11(12):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120948
Chicago/Turabian StylePurnawan, Irfan, Derryadi Angputra, Septiana Crista Debora, Eva Fathul Karamah, Arifina Febriasari, and Sutrasno Kartohardjono. 2021. "Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane with a Polyvinylpyrrolidone Additive for Tofu Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Combination with the Coagulation–Flocculation Process" Membranes 11, no. 12: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120948
APA StylePurnawan, I., Angputra, D., Debora, S. C., Karamah, E. F., Febriasari, A., & Kartohardjono, S. (2021). Polyvinylidene Fluoride Membrane with a Polyvinylpyrrolidone Additive for Tofu Industrial Wastewater Treatment in Combination with the Coagulation–Flocculation Process. Membranes, 11(12), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11120948







