Effect of Different Influent Conditions on Biomass Production and Nutrient Removal by Aeration Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor (ICFB-MMBR) System for Mariculture Wastewater Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor System
2.2. Operation of Internal Circulating Fluidized Bed Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor
2.2.1. Source and Culture of Microalgae
2.2.2. The Composition of Simulated Mariculture Wastewater
2.2.3. The Experimental Method
2.3. Water Sample Collection and Determination Method
2.3.1. Collection and Biomass Determination of Microalgae
2.3.2. Water Quality Analysis Method
3. Results
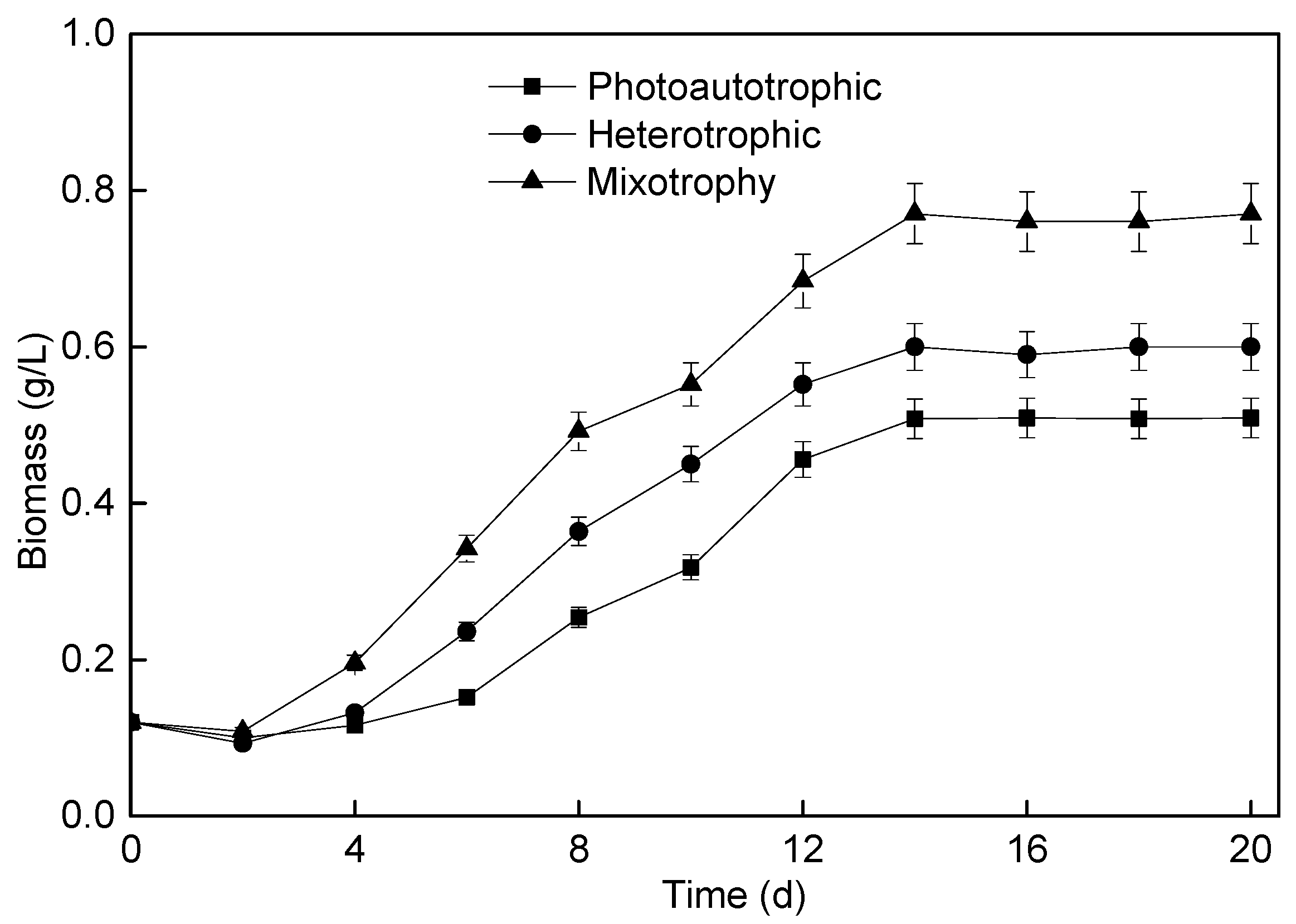
3.1. Effect of Different Culture Modes on Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor Perforamence
3.1.1. P. helgolandica tsingtaoensis Growth
3.1.2. Nutrient Removal
3.2. Effect of Different Influent TOC Concentration on Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor Performance
3.2.1. P. helgolandica tsingtaoensis Growth
3.2.2. Nutrient Removal
3.2.3. TOC Removal
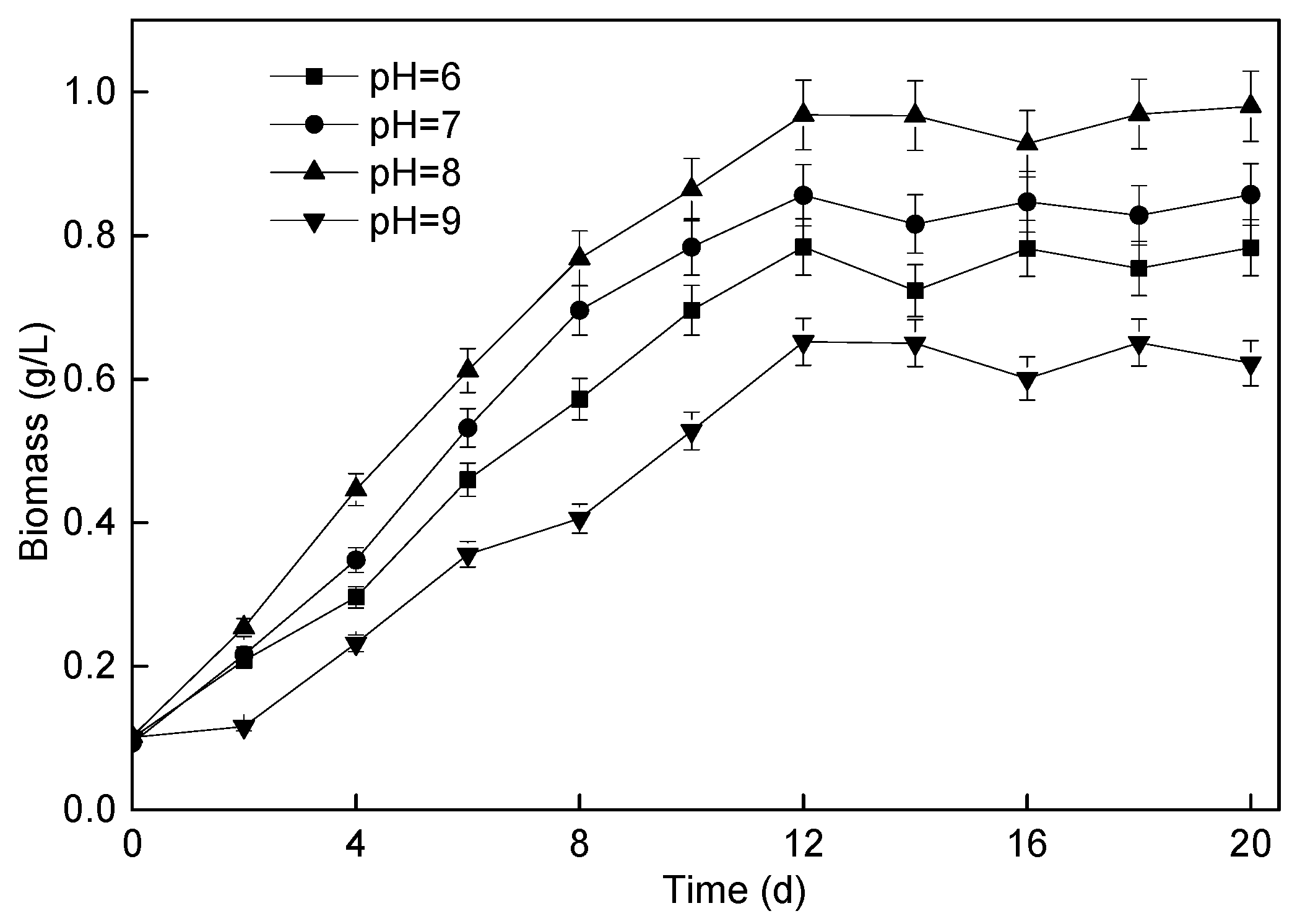
3.3. Effect of Different Influent pH on Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor Performance
3.3.1. P. helgolandica tsingtaoensis Growth
3.3.2. Nutrient Removal
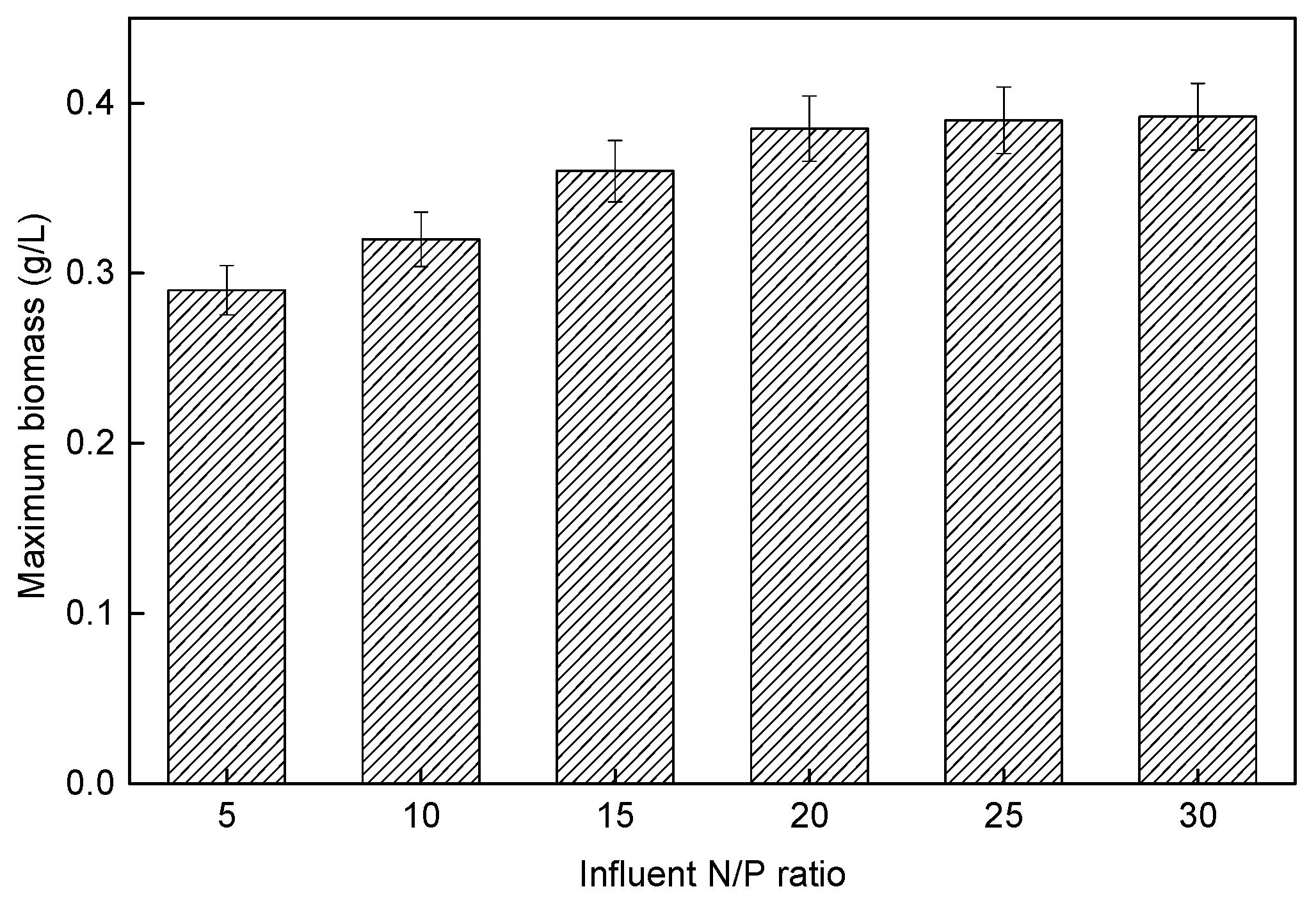
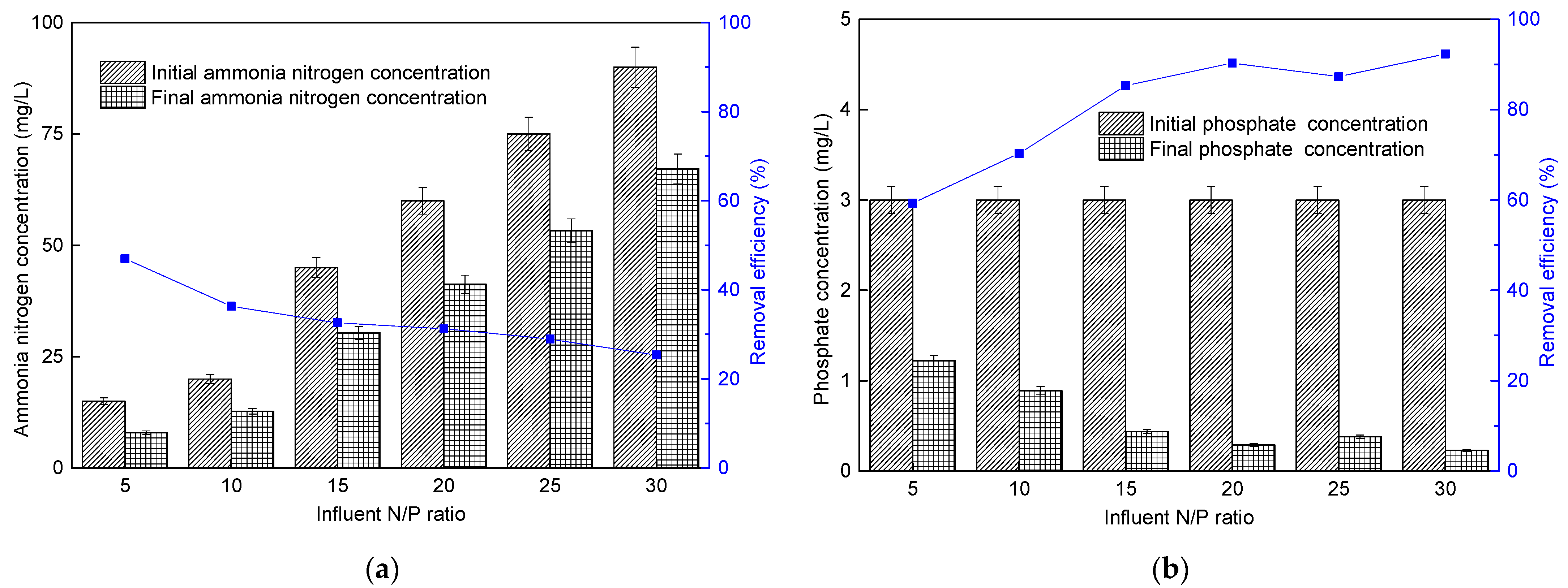
3.4. Effect of Different Influent N/P Ratios on Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor Performance
3.4.1. P. helgolandica tsingtaoensis Growth
3.4.2. Nutrient Removal
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Xu, X.-R.; Liu, S.-S.; Sun, K.-F.; Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.G. Steroids in marine aquaculture farms surrounding Hailing Island, South China: Occurrence, bioconcentration, and human dietary exposure. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Jiang, Y. The Evolution of Mariculture Structures and Environmental Effects in China. J. Coast. Res. 2018, 83, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentry, R.R.; Ruff, E.O.; Lester, S.E. Temporal patterns of adoption of mariculture innovation globally. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.-H.; Zeng, G.-M.; Feng, L.-J.; Liu, J.-z.; Liu, M.; Cai, H.-w. Continuous microalgae cultivation in aquaculture wastewater by a membrane photobioreactor for biomass production and nutrients removal. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 92, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Qiu, L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Xie, K. Recent development of scale marine aquaculture wastewater treatment. In Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering, Shenzhen, China, 20–21 December 2015; Atlantis Press: Paris, France, 2016; pp. 496–499. [Google Scholar]
- Jiaqi, S.; Lifen, L.; Fenglin, Y. Successful bio-electrochemical treatment of nitrogenous mariculture wastewater by enhancing nitrogen removal via synergy of algae and cathodic photo-electro-catalysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Liu, L.; Wei, L.; Huang, X.; Liu, C. Recycling of rural abandoned constructed wetlands: Mariculture wastewater treatment. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2021, 11, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Peng, Y.Y.; Li, C.; Yang, G.J.; Deng, Y.B.; Xue, B.; Guo, Y.M. Simultaneous nutrient removal and biomass/lipid production by Chlorella sp in seafood processing wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640, 943–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Pei, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Chen, S.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z. Microalgae nourished by mariculture wastewater aids aquaculture self-reliance with desirable biochemical composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 278, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, X.; Zhang, Z.; Guo, L.; Liao, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jin, C.; Gao, M.; She, Z.; Wang, G. Integrating acidogenic fermentation and microalgae cultivation of bacterial-algal coupling system for mariculture wastewater treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 320, 124335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo, H.N.P.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.; Chang, S.W.; Nguyen, D.D.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, X. Microalgae for saline wastewater treatment: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 50, 1224–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinandan, S.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Megharaj, M. Nutrient removal and biomass production: Advances in microalgal biotechnology for wastewater treatment. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2018, 38, 1244–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Yang, H.L.; Li, C.; Peng, Y.Y.; Lu, M.M.; Jin, W.H.; Bao, J.J.; Guo, Y.M. Effect of organic carbon to nitrogen ratio in wastewater on growth, nutrient uptake and lipid accumulation of a mixotrophic microalgae Chlorella sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Malik, S.; Zhu, H.; Xu, J.; Nawaz, M.Z.; Nawaz, S.; Alam, A.; Mehmood, M.A. Cultivating microalgae in wastewater for biomass production, pollutant removal, and atmospheric carbon mitigation; a review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 704, 135303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Qiu, S.; Tremblay, D.; Viner, K.; Champagne, P.; Jessop, P.G. Centrate wastewater treatment with Chlorella vulgaris: Simultaneous enhancement of nutrient removal, biomass and lipid production. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 342, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, G.; Li, J.; Chen, S.Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.T.; Li, A.M. Response of performance and ammonia oxidizing bacteria community to high salinity stress in membrane bioreactor with elevated ammonia loading. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liang, S.K.; Zhang, Y. The ecological competition and grazing reverse the effects of sulfamethoxazole on plankton: A case study on characterizing community-level effect. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 17283–17288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burford, M.A.; Thompson, P.J.; McIntosh, R.P.; Bauman, R.H.; Pearson, D.C. Nutrient and microbial dynamics in high-intensity, zero-exchange shrimp ponds in Belize. Aquaculture 2003, 219, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ju, Z.Y.; Deng, D.F.; Dominy, W. A defatted microalgae (Haematococcus pluvialis) meal as a protein ingredient to partially replace fishmeal in diets of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei, Boone, 1931). Aquaculture 2012, 354, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhukova, N.V.; Kharlamenko, V.I. Sources of essential fatty acids in the marine microbial loop. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 17, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, H.X.; Li, J.; Chen, P.; Chang, Z.Q.; Shen, M.M.; Zhao, F.Z. Cultivation of green algae Platymonas helgolandica in rearing water enhances the growth performance and resistance of Litopenaeus vannamei against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Aquac. Int. 2017, 25, 1279–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Fan, X.L.; Yang, Z.M.; Wang, H.Y.; Yang, D.W.; Guo, R.B. Characterization of H-2 photoproduction by a new marine green alga, Platymonas helgolandica var. tsingtaoensis. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 38–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Peng, W.; Zhang, M.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Zhang, Y. A review on anaerobic membrane bioreactors: Applications, membrane fouling and future perspectives. Desalination 2013, 314, 169–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neoh, C.H.; Noor, Z.Z.; Mutamim, N.S.A.; Lim, C.K. Green technology in wastewater treatment technologies: Integration of membrane bioreactor with various wastewater treatment systems. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 283, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bagheri, M.; Mirbagheri, S.A. Critical review of fouling mitigation strategies in membrane bioreactors treating water and wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 258, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijing, L.D.; Woo, Y.C.; Choi, J.S.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.H.; Shon, H.K. Fouling and its control in membrane distillation—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 475, 215–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.; Hwang, Y.; Shin, H.; Lee, W. Effects of salinity on the characteristics of biomass and membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 141, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Panswad, T.; Anan, C. Specific oxygen, ammonia, and nitrate uptake rates of a biological nutrient removal process treating elevated salinity wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 1999, 70, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.; Sumanasekera, D.; Ibrahim, S.; Lubberding, H.; Hooijmans, C.; Gijzen, H.; van Loosdrecht, M. Long term effects of salt on activity, population structure and floc characteristics in enriched bacterial cultures of nitrifiers. Water Res. 2006, 40, 1377–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppens, J.; Lindeboom, R.; Muys, M.; Coessens, W.; Alloul, A.; Meerbergen, K.; Lievens, B.; Clauwaert, P.; Boon, N.; Vlaeminck, S.E. Nitrification and microalgae cultivation for two-stage biological nutrient valorization from source separated urine. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 211, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Lee, Y.Y.; Scherr, D.; Senger, R.S.; Li, Y.; He, Z. Mitigating nutrient accumulation with microalgal growth towards enhanced nutrient removal and biomass production in an osmotic photobioreactor. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valizadeh, K.; Davarpanah, A. Design and construction of a micro-photo bioreactor in order to dairy wastewater treatment by micro-algae: Parametric study. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2019, 42, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Guo, Z.S.; Mei, J.X.; Liang, Z.L.; Li, Z.P.; Hou, X.G. Investigation into the Novel Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor with Internal Circulating Fluidized Bed for Marine Aquaculture Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2020, 10, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsenpour, S.F.; Hennige, S.; Willoughby, N.; Adeloye, A.; Gutierrez, T. Integrating micro-algae into wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 142168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eriksen, N.T. The technology of microalgal culturing. Biotechnol. Lett. 2008, 30, 1525–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resdi, R.; Lim, J.S.; Kamyab, H.; Lee, C.T.; Hashim, H.; Mohamad, N.; Ho, W.S. Review of microalgae growth in palm oil mill effluent for lipid production. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2016, 18, 2347–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Li, S.; Hu, T.; Nugroho, Y.K.; Yin, Z.; Hu, D.; Chu, R.; Mo, F.; Liu, C.; Hiltunen, E. Effects of nitrogen source heterogeneity on nutrient removal and biodiesel production of mono- and mix-cultured microalgae. Energy Convers. Manag. 2019, 201, 112144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, M.; Hu, B.; Zhou, W.G.; Li, Y.C.; Chen, P.; Ruan, R. Mutual influence of light and CO2 on carbon sequestration via cultivating mixotrophic alga Auxenochlorella protothecoides UMN280 in an organic carbon-rich wastewater. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, J.; Champagne, P.; Hall, G. Multivariate statistical analysis of water chemistry conditions in three wastewater stabilization ponds with algae blooms and pH fluctuations. Water Res. 2016, 96, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschlößl, T.; Steinmann, C.; Schleypen, P.; Melzer, A. Constructed wetlands for effluent polishing of lagoons. Water Res. 1998, 32, 2639–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Huang, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, W.; Wan, M.; Shen, G.; Wang, J. Enhanced lipid productivity of Chlorella pyrenoidosa through the culture strategy of semi-continuous cultivation with nitrogen limitation and pH control by CO2. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 136, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, K.J. How Critical Is The Critical N:P Ratio?1. J. Phycol. 2002, 38, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.T.; Hu, G.K. Effect of nitrogen to phosphorus ratios on cell proliferation in marine micro algae. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E.; Daufresne, T.; Levin, S.A. Optimal nitrogen-to-phosphorus stoichiometry of phytoplankton. Nature 2004, 429, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausmeier, C.A.; Litchman, E.; Daufresne, T.; Levin, S.A. Phytoplankton stoichiometry. Ecol. Res. 2008, 23, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.M.; Cheng, L.H.; Xu, X.H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.L. Enhanced lipid production of Chlorella vulgaris by adjustment of cultivation conditions. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 6797–6804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phukan, M.M.; Chutia, R.S.; Konwar, B.K.; Kataki, R. Microalgae Chlorella as a potential bio-energy feedstock. Appl. Energy 2011, 88, 3307–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevigne-Itoiz, E.; Fuentes-Grunewald, C.; Gasol, C.M.; Garces, E.; Alacid, E.; Rossi, S.; Rieradevall, J. Energy balance and environmental impact analysis of marine microalgal biomass production for biodiesel generation in a photobioreactor pilot plant. Biomass Bioenergy 2012, 39, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms: I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.; Duan, P.; Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Lin, L.; Li, M. Comparison of monoculture and mixed culture (Scenedesmus obliquus and wild algae) for C, N, and P removal and lipid production. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 20961–20968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabilil, M.S.; Agus, S.E. Biomass Composition of Microalgae Local Mixed Culture using POME (Palm Oil Mill Effluent) Medium. Res. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 16, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, B.K. The Estimation of Algal Yield Parameters Associated with Mixotrophic and Photoheterotrophic Growth under Batch Cultivation. Biomass 1989, 18, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Miao, X.L.; Wu, Q.Y. High quality biodiesel production from a microalga Chlorella protothecoides by heterotrophic growth in fermenters. J. Biotechnol. 2006, 126, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Qiang, H.; Shimizu, K. Energetics and carbon metabolism during growth of microalgal cells under photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and cyclic light-autotrophic/dark-heterotrophic conditions. Biochem. Eng. J. 2000, 6, 87–102. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Sarkany, N.; Cui, Y. Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnol. Lett. 2009, 31, 1043–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheirsilp, B.; Torpee, S. Enhanced growth and lipid production of microalgae under mixotrophic culture condition: Effect of light intensity, glucose concentration and fed-batch cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 110, 510–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.V.; Suárez-Muñoz, M.; Trebuch, L.M.; Verbraak, P.J.; Van de Waal, D.B. Toward an ecologically optimized N: P recovery from wastewater by microalgae. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, R.; Qin, L.; Feng, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, S. The joint effect of ammonium and pH on the growth of Chlorella vulgaris and ammonium removal in artificial liquid digestate. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 325, 124690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nzayisenga, J.C.; Eriksson, K.; Sellstedt, A. Mixotrophic and heterotrophic production of lipids and carbohydrates by a locally isolated microalga using wastewater as a growth medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 257, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecina, M.; Nadal, G.; Solà, C.; Prat, J.; Cairó, J.J. Optimization of ferric chloride concentration and pH to improve both cell growth and flocculation in Chlorella vulgaris cultures. Application to medium reuse in an integrated continuous culture bioprocess. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 216, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, A.; Mendoza, J.L.; Guzmán, J.L.; Berenguel, M.; Acién, F.G.; Dormido, S. Effective utilization of flue gases in raceway reactor with event-based pH control for microalgae culture. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karam, A.L.; McMillan, C.C.; Lai, Y.-C.; de los Reyes, F.L., III; Sederoff, H.W.; Grunden, A.M.; Ranjithan, R.S.; Levis, J.W.; Ducoste, J. Construction and Setup of a Bench-scale Algal Photosynthetic Bioreactor with Temperature, Light, and pH Monitoring for Kinetic Growth Tests. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2017, 124, e55545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, R.; Gao, S.; Lopez, P.A.; Ogden, K.L. Effects of pH on cell growth, lipid production and CO2 addition of microalgae Chlorella sorokiniana. Algal Res. 2017, 28, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Zheng, Z. Effects of various LED light wavelengths and intensities on the performance of purifying synthetic domestic sewage by microalgae at different influent C/N ratios. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 51, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, M.S. Metabolic response of the halotolerant green alga Dunaliella bardawil to nitrogen: Phosphorus ratios in batch culture. Folia Microbiol. 1997, 42, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darley, W.M. Algal biology: A physiological approach. Br. Med. J. 1983, 2, 984. [Google Scholar]






| System Parameters | Culture Modes | Influent TOC (mg/L) | pH | Influent Ammonia (mg/L) | Influent Phosphate (mg/L) | Operation Time (days) | HRT | Flux (L/m2·h) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Run 1 | Photoautotrophic | 60 | 7.5 | 15 | 3 | 20 | 1 | 3.9 | 25 |
| Heterotrophic | |||||||||
| Mixotrophy | |||||||||
| Run 2 | Mixotrophy | 40 | 7.5 | 15 | 3 | 20 | 1 | 3.9 | 25 |
| 80 | |||||||||
| 120 | |||||||||
| Run 3 | Mixotrophy | 120 | 6.0 | 15 | 3 | 20 | 1 | 3.9 | 25 |
| 7.0 | |||||||||
| 8.0 | |||||||||
| 9.0 | |||||||||
| Run 4 | Mixotrophy | 120 | 8.0 | 15 | 3 | 20 | 3 | 1.3 | 25 |
| 30 | |||||||||
| 45 | |||||||||
| 60 | |||||||||
| 75 | |||||||||
| 90 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ding, Y.; Wang, S.; Ma, H.; Ma, B.; Guo, Z.; You, H.; Mei, J.; Hou, X.; Liang, Z.; Li, Z. Effect of Different Influent Conditions on Biomass Production and Nutrient Removal by Aeration Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor (ICFB-MMBR) System for Mariculture Wastewater Treatment. Membranes 2021, 11, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110874
Ding Y, Wang S, Ma H, Ma B, Guo Z, You H, Mei J, Hou X, Liang Z, Li Z. Effect of Different Influent Conditions on Biomass Production and Nutrient Removal by Aeration Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor (ICFB-MMBR) System for Mariculture Wastewater Treatment. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110874
Chicago/Turabian StyleDing, Yi, Shiyuan Wang, Hang Ma, Binyu Ma, Zhansheng Guo, Hong You, Junxue Mei, Xuguang Hou, Zhenlin Liang, and Zhipeng Li. 2021. "Effect of Different Influent Conditions on Biomass Production and Nutrient Removal by Aeration Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor (ICFB-MMBR) System for Mariculture Wastewater Treatment" Membranes 11, no. 11: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110874
APA StyleDing, Y., Wang, S., Ma, H., Ma, B., Guo, Z., You, H., Mei, J., Hou, X., Liang, Z., & Li, Z. (2021). Effect of Different Influent Conditions on Biomass Production and Nutrient Removal by Aeration Microalgae Membrane Bioreactor (ICFB-MMBR) System for Mariculture Wastewater Treatment. Membranes, 11(11), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110874






