Enhanced Nanofiltration Process of Thin Film Composite Membrane Using Dodecyl Phenol Ethoxylate and Oleic Acid Ethoxylate for Oilfield Calcite Scale Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthetic Produced Water
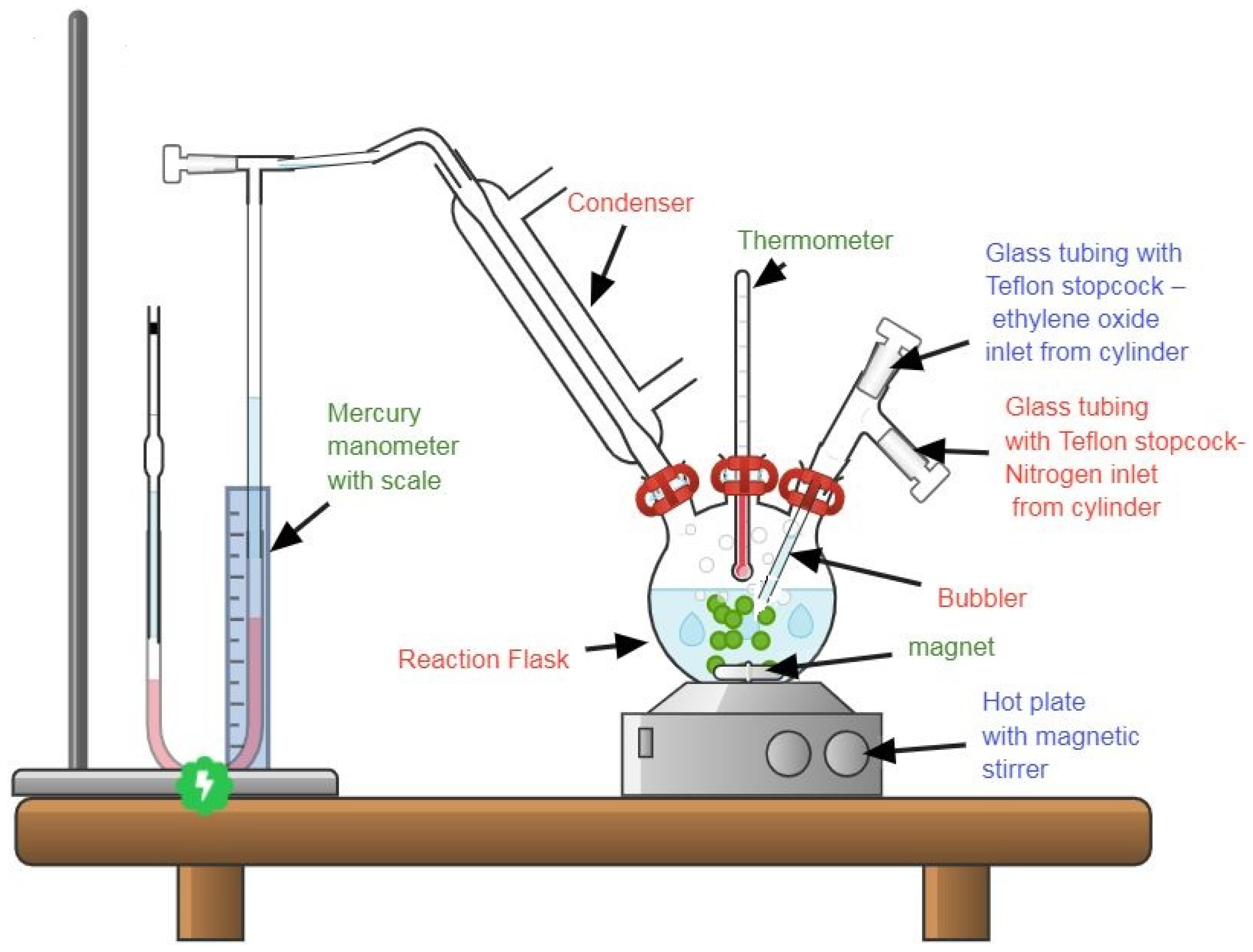
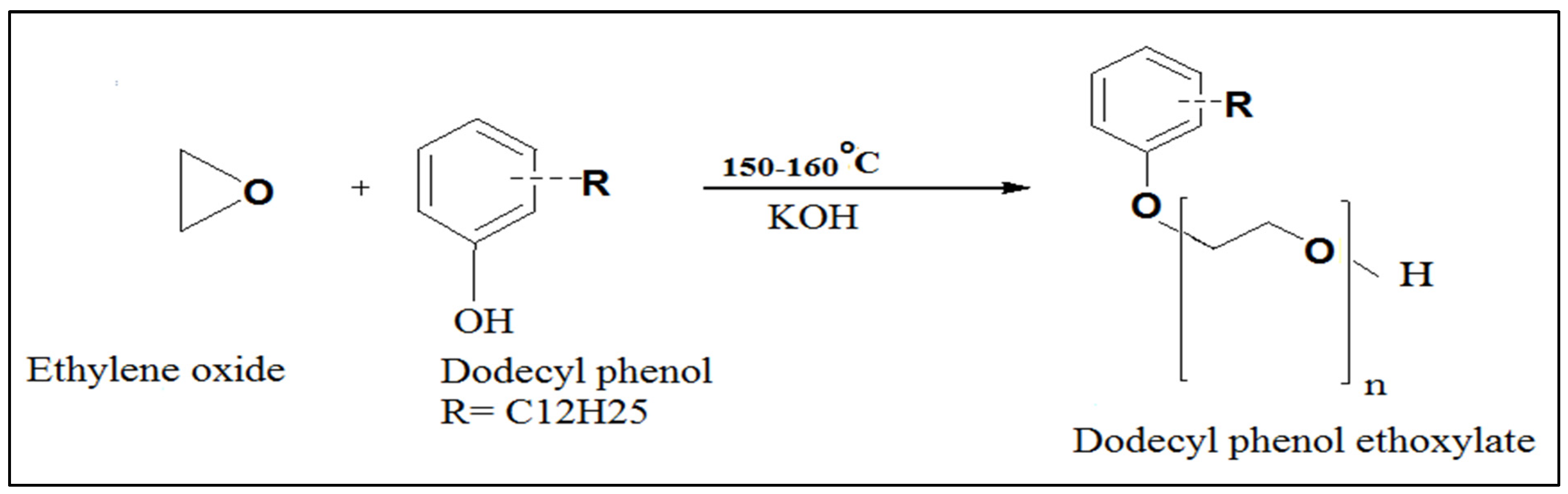
2.3. Scale Inhibitors Preparation
2.4. Thin-Film Composite Nanofiltration Membrane Prepration (TFCNF)
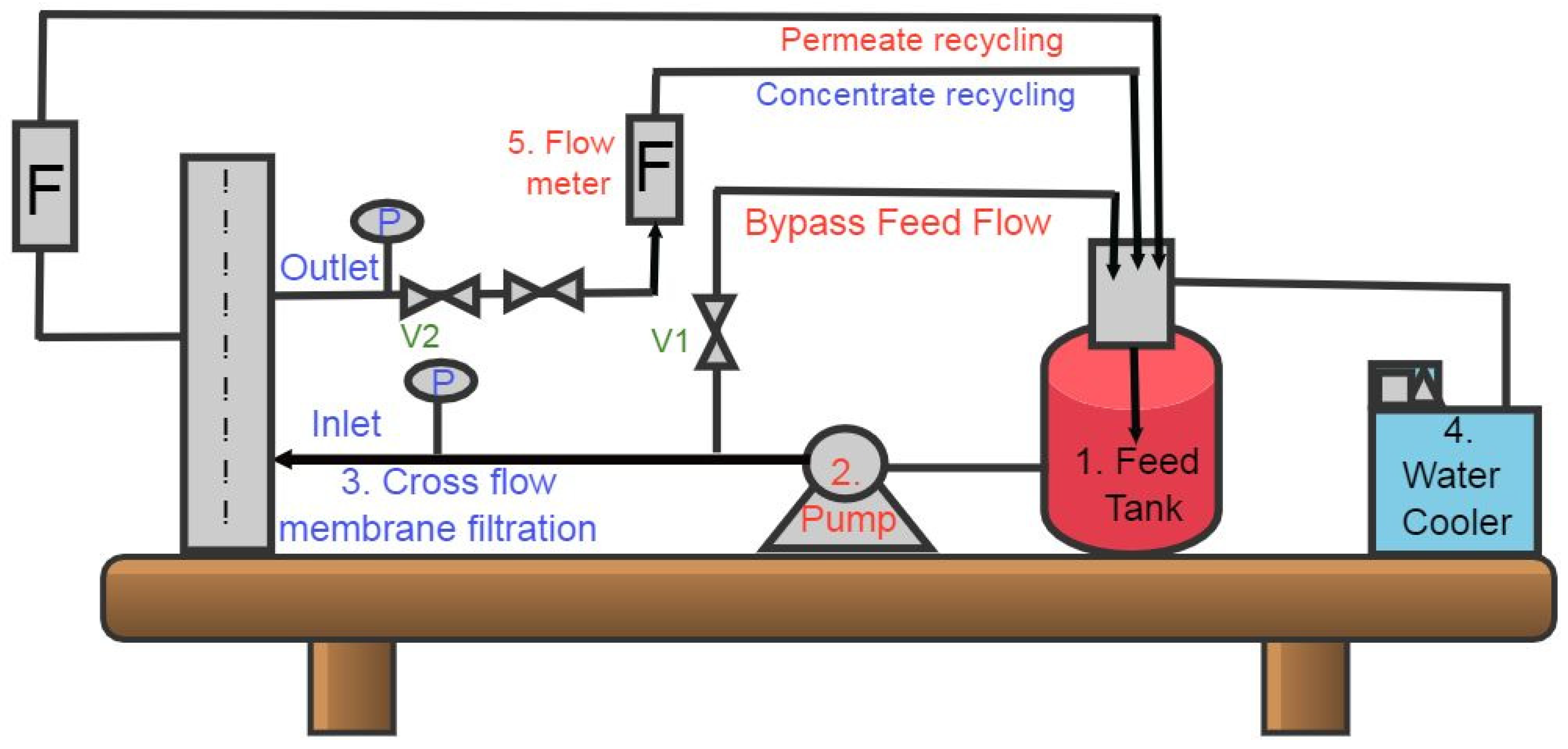
2.5. Experiments of TFCNF Membrane Antiscaling
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Scale Inhibitors and Membrane Characterization
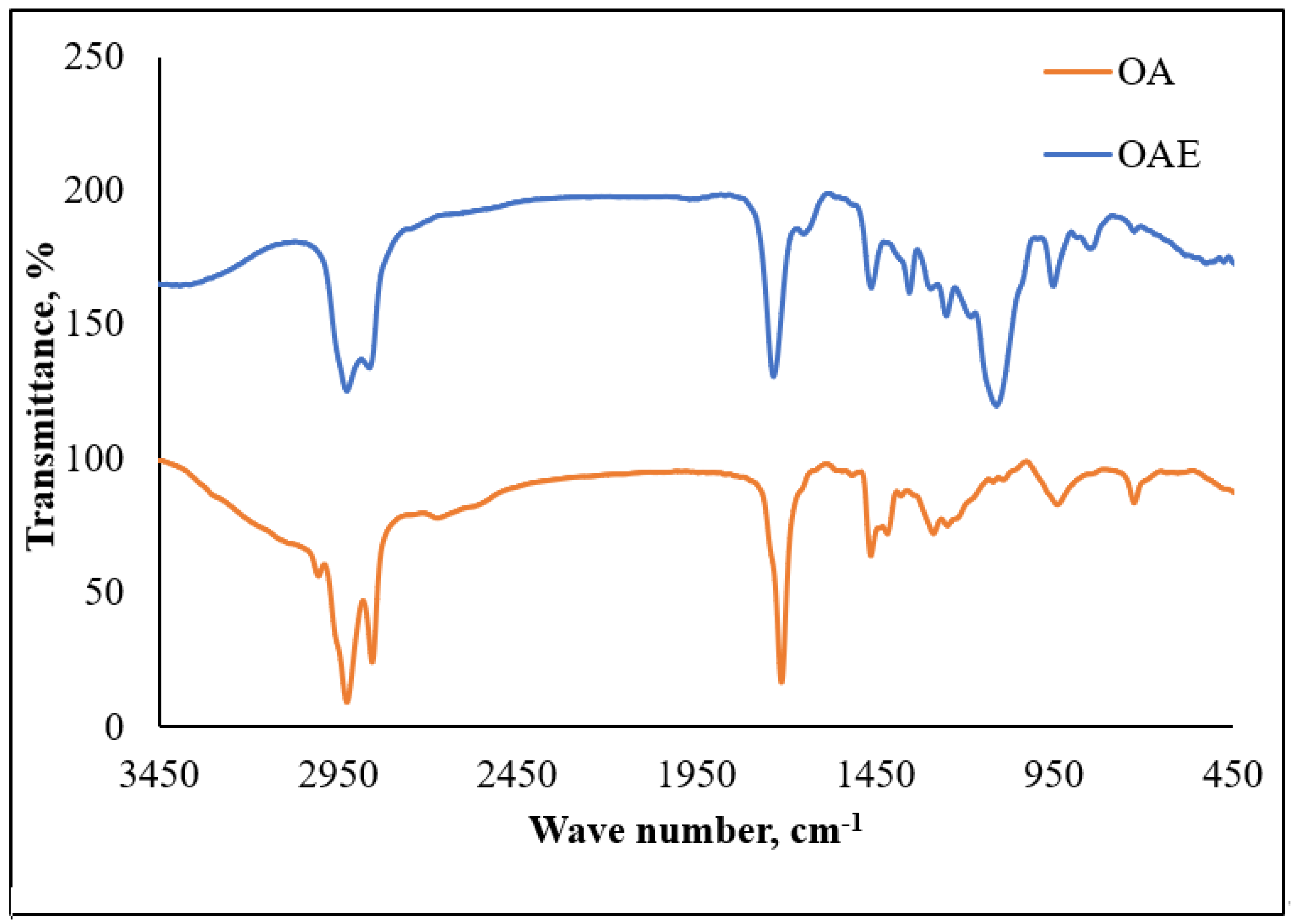
3.1.1. FT-IR of Scale Inhibitors
3.1.2. H-NMR for Scale Inhibitors
3.2. Membrane Scaling Evaluation
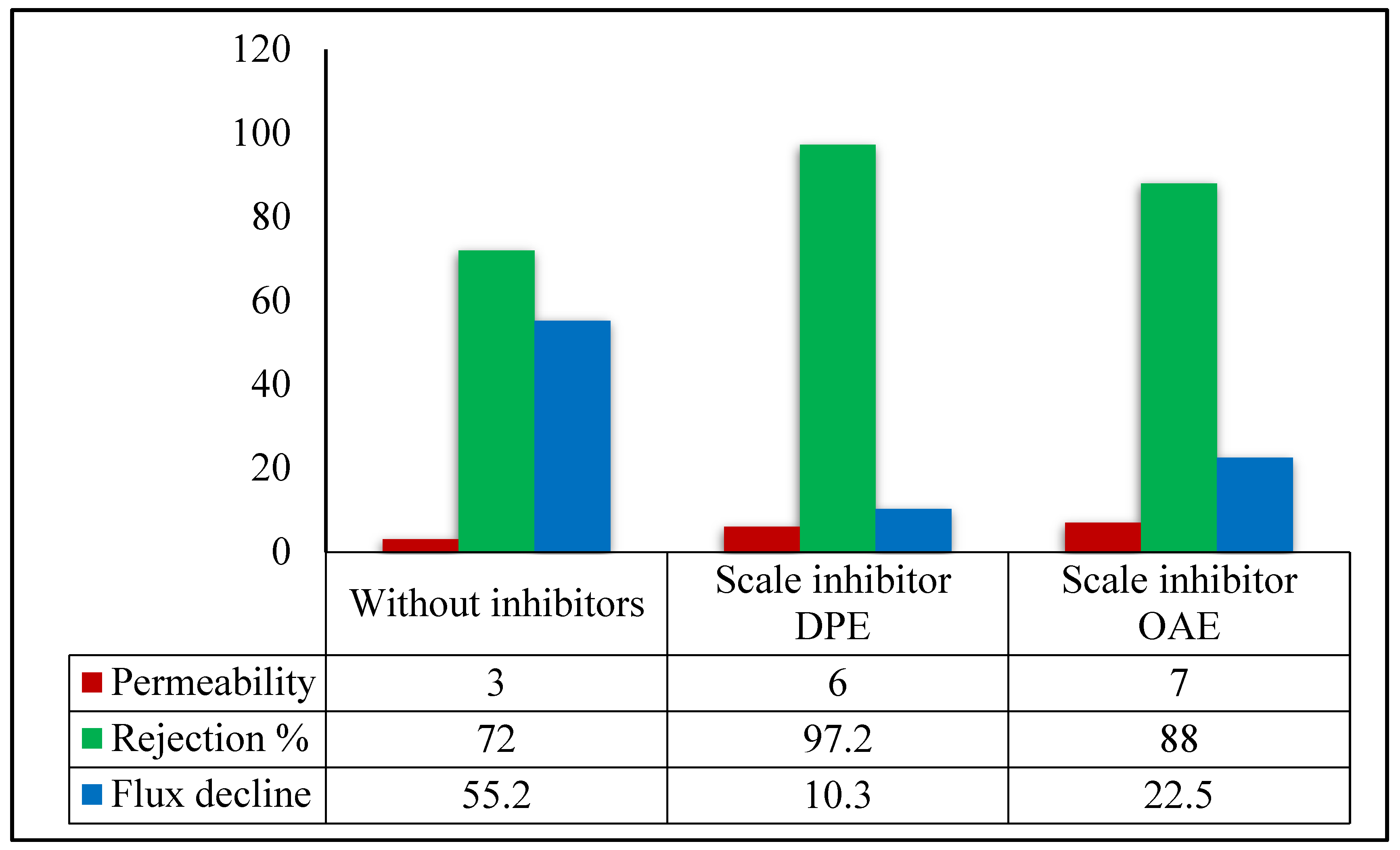
3.2.1. Permeability, Salt Rejection, and Permeate Flux Decline
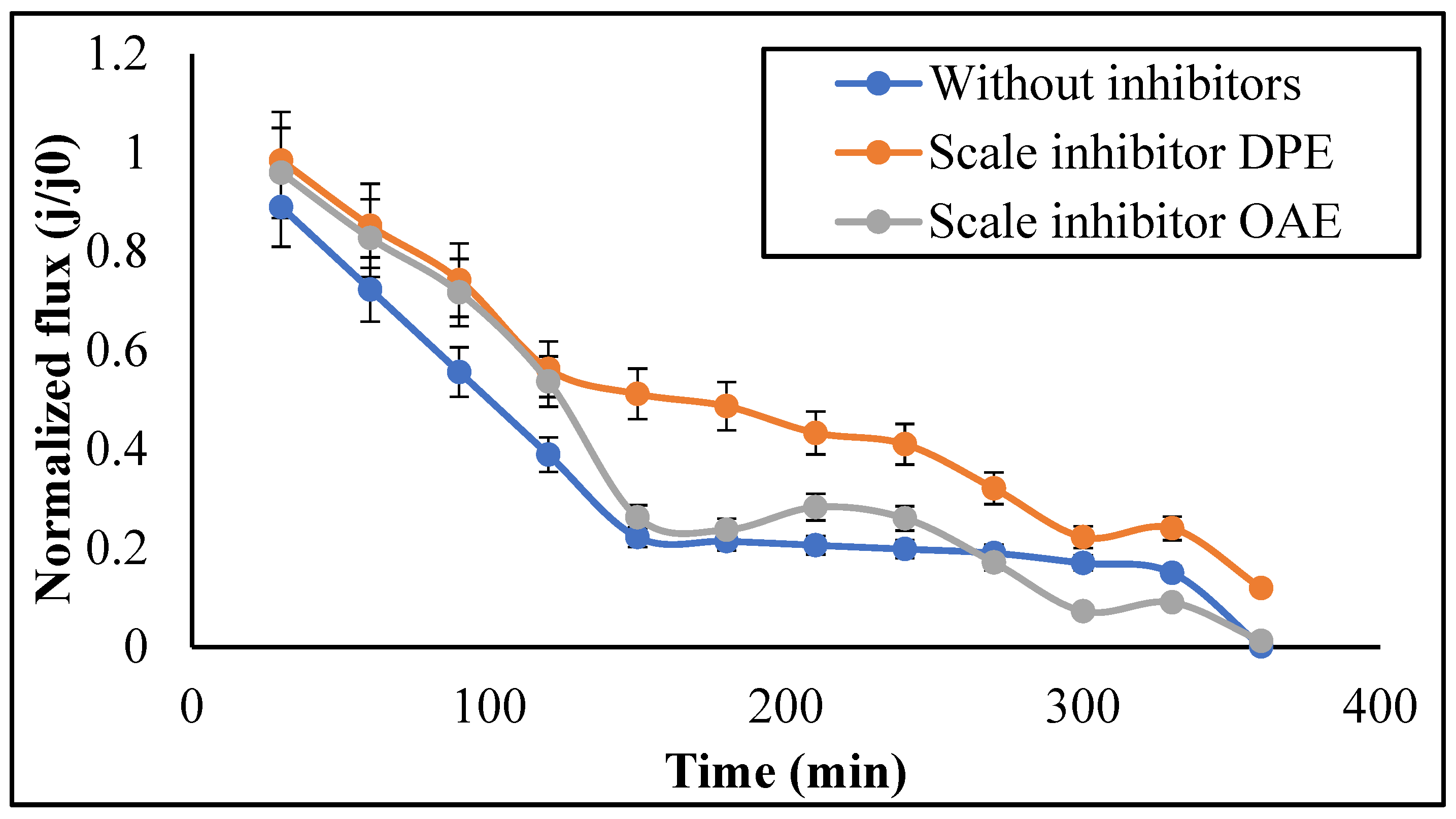
3.2.2. Permeate Flux
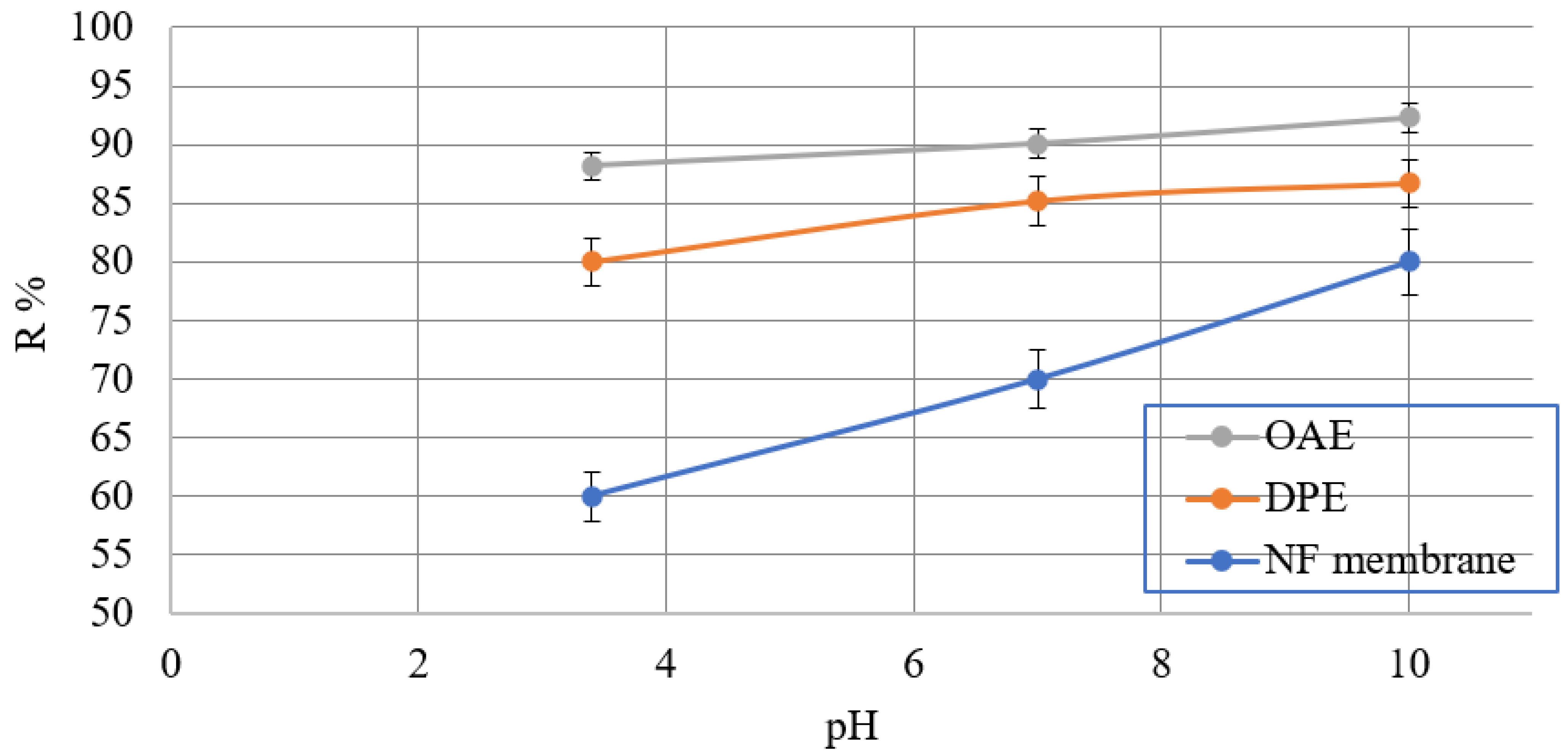
3.2.3. Effect of pH Value on Calcite Scale Formation
3.3. Simulation of CaCO3 Scaled Membrane
3.3.1. ESEM for Inhibited Scaled TFCNF Membrane after Injection the Scale Inhibitors
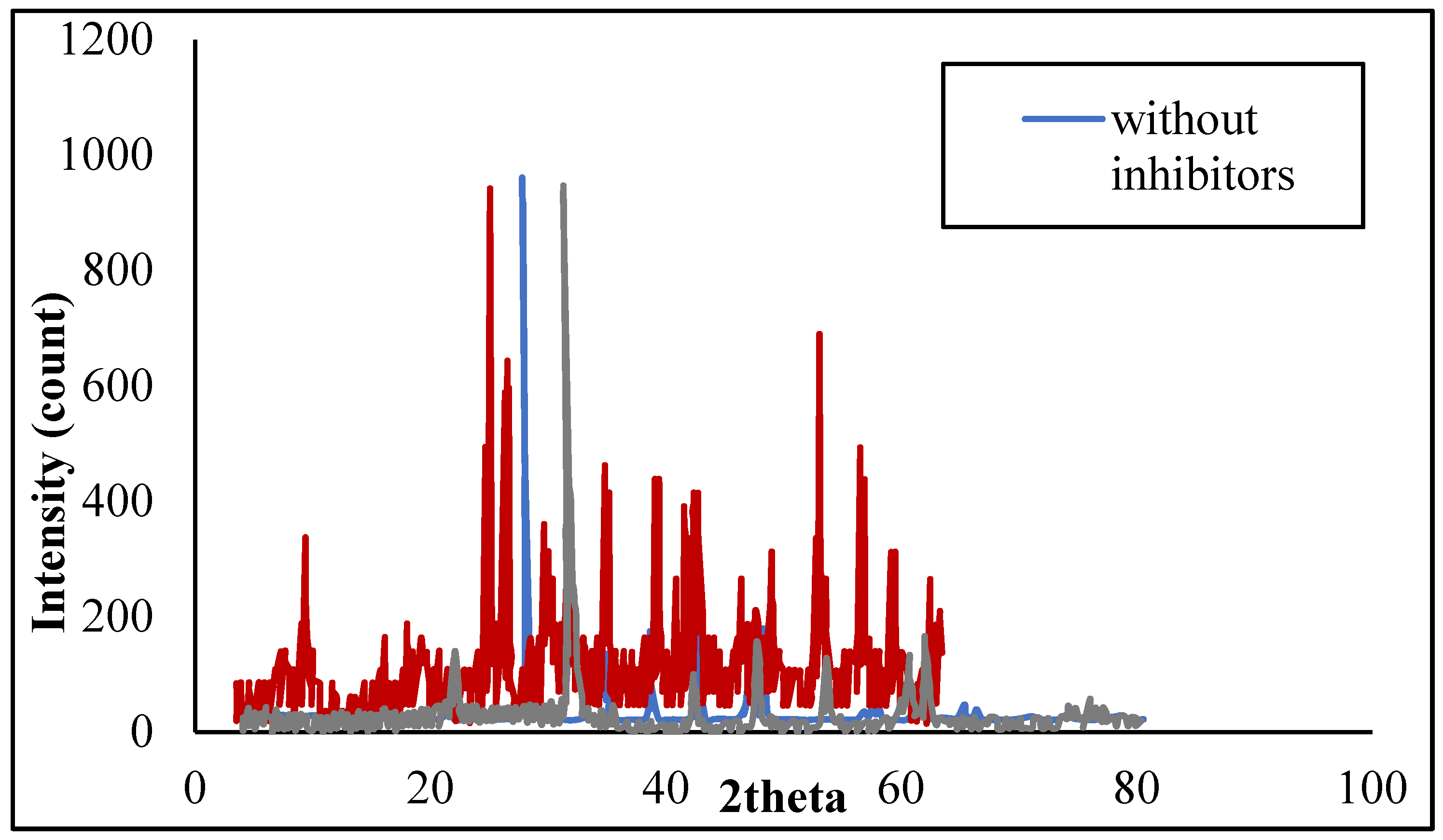
3.3.2. XRD Spectra of the Inhibited ScaledTFCNF Membrane
3.3.3. FTIR Spectra of CaCO3 Scaled Membrane
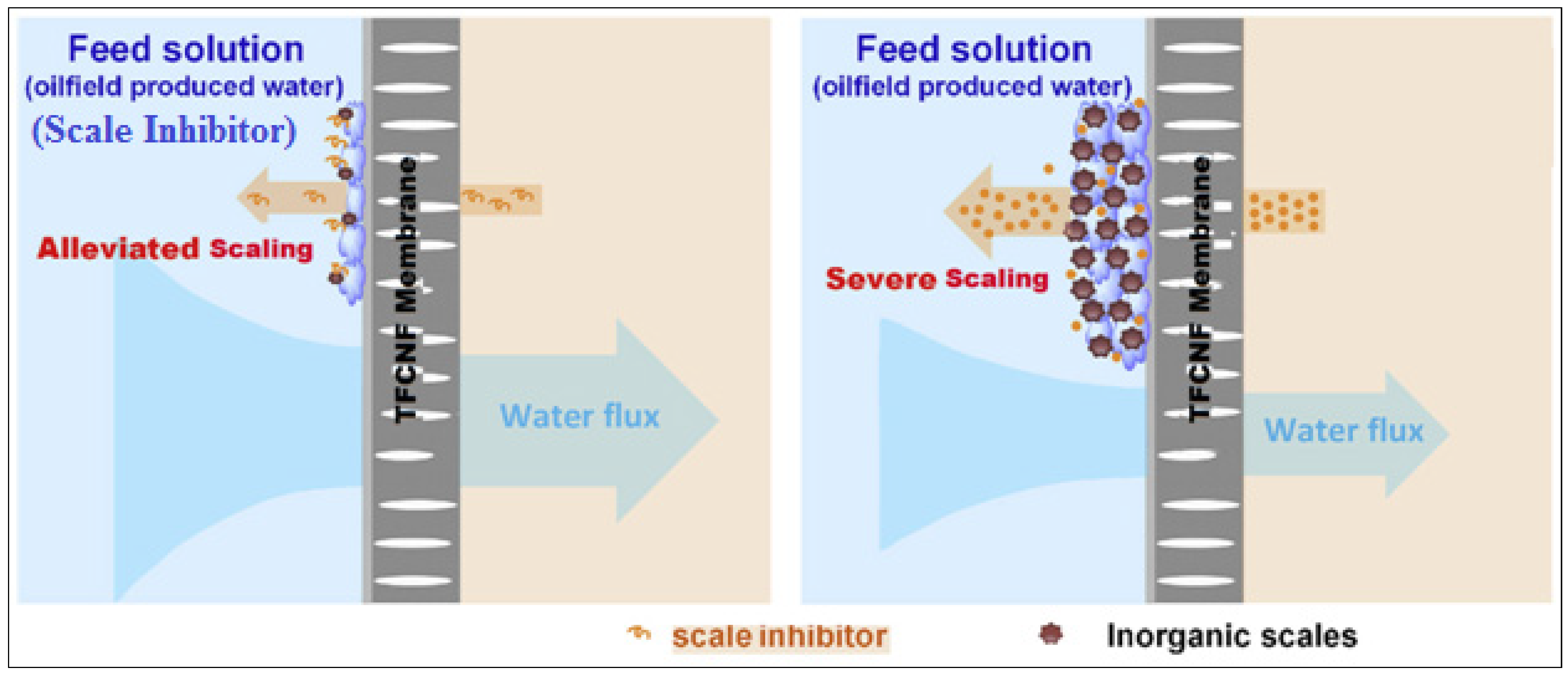
3.3.4. Mechanism of Membrane Scaling Control with S.I. DPE and OAE
3.4. Comparison of OAE and DPE with Other Scale Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| S.I. | Scale Inhibitor |
| NF | Nanoafiltration |
| TFCNF | Thin-film composite nanofiltration membrane |
| FT-IR | Forior transform IR |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
| ESEM | Environmental scanning electron |
| DP | Dodecyl phenol |
| DPE | Dodecyl phenol ethoxylate |
| OA | Oleic acid |
| OAE | Oleic acid ethoxylate |
| PW | Produced water |
| Na2CO3 | Sodium carbonate |
| CaCl2 | Calcium chloride |
| DMAc | Dimethyl-acetamide |
| DCM | Dichloromethane |
| OcA | Octylamine |
| OcDA | Octadecylamine |
| PVDF | Poly-vinylidene fluoride |
| AA-APEC | Acrylic acid allylpolyethoxy carboxylate |
| CM-QAOC | Carboxymethyl quaternary ammonium oligochitosan |
| PASP/Cs | Polyaspartic acid/chitosan |
| PAA | Polyacrylic acid |
| CG | Chitosan biguanidine hydrochloride |
References
- Nasiri, M.; Jafari, I. Produced water from oil-gas plants: A short review on challenges and opportunities. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2017, 61, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coday, B.D.; Xu, P.; Beaudry, E.G.; Herron, J.; Lampi, K.; Hancock, N.T.; Cath, T.Y. The sweet spot of forward osmosis: Treatment of produced water, drilling wastewater, and other complex and difficult liquid streams. Desalination 2014, 333, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhru’l-Razi, A.; Pendashteh, A.; Abdullah, L.C.; Biak, D.R.A.; Madaeni, S.S.; Abidin, Z.Z. Review of technologies for oil and gas produced water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 530–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyeneyin, B. Introduction to the hydrocarbon composite production system. In Developments in Petroleum Science; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 63, pp. 11–128. [Google Scholar]
- Moghadasi, J.; Jamialahmadi, M.; Müller-Steinhagen, H.; Sharif, A. Formation damage due to scale formation in porous media resulting from water injection. In Proceedings of the SPE International Symposium and Exhibition on Formation Damage Control, Lafayette, LA, USA, 18–20 February 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Capodaglio, A.; Callegari, A.; Cecconet, D.; Molognoni, D. Sustainability of decentralized wastewater treatment technologies. Water Pract. Technol. 2017, 12, 463–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Song, C.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Feng, X. Membrane technology coupled with electrochemical advanced oxidation processes for organic wastewater treatment: Recent advances and future prospects. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 376, 120909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morillo, J.; Usero, J.; Rosado, D.; El Bakouri, H.; Riaza, A.; Bernaola, F.-J. Comparative study of brine management technologies for desalination plants. Desalination 2014, 336, 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.S. Factors affecting natural organic matter (NOM) and scaling fouling in NF membranes: A review. Desalination 2010, 259, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, J.A.; Vanneste, J.; Cath, T.Y. Membrane distillation for concentration of hypersaline brines from the Great Salt Lake: Effects of scaling and fouling on performance, efficiency, and salt rejection. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 170, 78–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashfaq, M.Y.; Al-Ghouti, M.A.; Zouari, N. Functionalization of reverse osmosis membrane with graphene oxide to reduce both membrane scaling and biofouling. Carbon 2020, 166, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qingfeng, Y. Inhibition of CaCO3 scaling in reverse osmosis system by zinc ion. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2006, 14, 178–183. [Google Scholar]
- LI, Y.; ZHOU, B.; SHI, Y.; Wang, X. Survey of researches on reveres osmosis scale inhibitor. Ind. Water Treat. 2004, 24, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, W.; Wang, F.Y.; Xia, M.Z.; Wang, F. Synthesis and its scale inhibition effect of green scale inhibitor polyepoxysuccinic acid. J. Chem. Ind. Eng. China 2006, 57, 2207. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzi, M.; Hosny, R.; El-Sayed, M.; Fathy, M.; Moghny, T.A. Evaluation of scale inhibitors performance under simulated flowing field conditions using dynamic tube blocking test. Int. J. Chem. Sci. 2016, 14, 16–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sousa, M.F.; Bertran, C.A. New methodology based on static light scattering measurements for evaluation of inhibitors for in bulk CaCO3 crystallization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 420, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, M.K.; Choi, Y.-G. The comparative study for scale inhibition on surface of RO membranes in wastewater reclamation: CO2 purging versus three different antiscalants. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 546, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosny, R.; Fathy, M.; Ramzi, M.; Moghny, T.A.; Desouky, S.E.; Shama, S.A. Treatment of the oily produced water (OPW) using coagulant mixtures. Egypt. J. Pet. 2016, 25, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hilal, N.; Ogunbiyi, O.O.; Miles, N.J.; Nigmatullin, R. Methods employed for control of fouling in MF and UF membranes: A comprehensive review. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 1957–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjad, Z.; Demadis, K.D. Mineral Scales and Deposits: Scientific and Technological Approaches; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Zoubi, H.; Rieger, A.; Steinberger, P.; Pelz, W.; Haseneder, R.; Härtel, G. Optimization study for treatment of acid mine drainage using membrane technology. Sep. Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 2004–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knoell, T.; Patel, M.; Neely, T.; Dunivin, W.; Owens, E. Identifying, evaluating, and implementing antiscalants in RO reuse applications. IDA J. Desalination Water Reuse 2011, 3, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinthaki, A.; Demadis, K.D. Chemical methods for scaling control. In Corrosion and Fouling Control in Desalination Industry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 307–342. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, G.-G.; Williams, B.; Kookana, R. Environmental fate of alkylphenols and alkylphenol ethoxylates—A review. Environ. Int. 2002, 28, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, G.F. Bacterial biodegradation of ethoxylated surfactants. Pestic. Sci. 1993, 37, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakat, Y.M.A.; Ibrahim, V. Surfactants with Natural Hydrophobic Tails Polyoxyethylenated Cholesterol-Surface Tension and CMC. J. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 6, 1273–1290. [Google Scholar]
- Longman, G.F. Analysis of Detergents and Detergent Products; Wiley: London, UK, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Tyman, J.H.; Bruce, I.E. Synthesis and characterization of polyethoxylate surfactants derived from phenolic lipids. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2003, 6, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Alberto, M.; Gorgojo, P.; Szekely, G.; Budd, P.M. High-flux PIM-1/PVDF thin film composite membranes for 1-butanol/water pervaporation. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 529, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Curcio, E.; Fontananova, E.; Di Profio, G.; Drioli, E. Influence of the structural properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes on the heterogeneous nucleation rate of protein crystals. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 12438–12445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ang, M.B.M.Y.; Tang, C.-L.; De Guzman, M.R.; Maganto, H.L.C.; Caparanga, A.R.; Huang, S.-H.; Tsai, H.-A.; Hu, C.-C.; Lee, K.-R.; Lai, J.-Y. Improved performance of thin-film nanofiltration membranes fabricated with the intervention of surfactants having different structures for water treatment. Desalination 2020, 481, 114352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhabiles, O.; Galiano, F.; Marino, T.; Mahmoudi, H.; Lounici, H.; Figoli, A. Preparation and characterization of TiO2-PVDF/PMMA blend membranes using an alternative non-toxic solvent for UF/MF and photocatalytic application. Molecules 2019, 24, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Chen, J.; Hong, H.; Wang, A.; Lin, H. Pollutant removal and membrane fouling in an anaerobic submerged membrane bioreactor for real sewage treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 69, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xu, G.-R.; Das, R. Inorganic scaling in reverse osmosis (RO) desalination: Mechanisms, monitoring, and inhibition strategies. Desalination 2019, 468, 114065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y. Composite Fouling of Calcium Sulfate and Calcium Carbonate in a Dynamic Seawater Reverse Osmosis Unit; University of New South Wales: Sydney, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Piyadasa, C.; Ridgway, H.F.; Yeager, T.R.; Stewart, M.B.; Pelekani, C.; Gray, S.R.; Orbell, J.D. The application of electromagnetic fields to the control of the scaling and biofouling of reverse osmosis membranes—A review. Desalination 2017, 418, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua-Anusorn, W.; St Pierre, T. Pathological biomineralization of iron. In Biomineralization-Medical Aspects of Solubility; John Wiley and Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006; pp. 219–267. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, D.; Zhang, P.; Kan, A.T.; Fu, G.; Alsaiari, H.A.; Tomson, M.B. Control placement of scale inhibitors in the formation with stable Ca-DTPMP nanoparticle suspension and its transport in porous medium. In Proceedings of the SPE International Oilfield Scale Conference, Aberdeen, UK, 28–29 May 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, S.A.; Haladu, S.A.; Mazumder, M.A.; Al-Muallem, H.A. Synthesis of a terpolymer and a tetrapolymer using monomers of diallylamine salts and SO2 and their application as antiscalants. Iran. Polym. J. 2016, 25, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, K.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, G.; Wang, H.; Yao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Sun, W.; Wu, W. A multicarboxyl antiscalant for calcium phosphate and calcium carbonate deposits in cooling water systems. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 52, 7258–7264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.; Jin, X.; Sun, D.; Wang, D.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J.; Han, X. Preparation of modified oligochitosan and evaluation of its scale inhibition and fluorescence properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-El-Khalek, D.; Abd-El-Nabey, B.; Abdel-kawi, M.A.; Ramadan, S. Investigation of a novel environmentally friendly inhibitor for calcium carbonate scaling in cooling water. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 2870–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Chen, T.; Zhou, S. Synthesis of polyaspartic acid/chitosan graft copolymer and evaluation of its scale inhibition and corrosion inhibition performance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2015, 10, 9513–9527. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, X.; Fu, C.; Li, N.; Zheng, F.; Yang, W.; Yang, X. Performance of a non-phosphorus antiscalant on inhibition of calcium-sulfate precipitation. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maher, Y.A.; Ali, M.E.A.; Salama, H.E.; Sabaa, M.W. Preparation, characterization and evaluation of chitosan biguanidine hydrochloride as a novel antiscalant during membrane desalination process. Arab. J. Chem. 2020, 13, 2964–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Concentration of Ions (mg/L) | Density(g/cc) | 1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 2000 | pH | 7.81 |
| Cl− | 3437.46 | TDS | 6447.55 |
| Ca2+ | 400 | Salinity | 6010 |
| HCO3− | 610 | Alkalinity as HCO3− (mg/L) | 599.53 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Mhyawi, S.R.; Mubarak, M.F.; Hosny, R.; Amine, M.; Abdelraheem, O.H.; Zayed, M.A.; Ragab, A.H.; El Shahawy, A. Enhanced Nanofiltration Process of Thin Film Composite Membrane Using Dodecyl Phenol Ethoxylate and Oleic Acid Ethoxylate for Oilfield Calcite Scale Control. Membranes 2021, 11, 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110855
Al-Mhyawi SR, Mubarak MF, Hosny R, Amine M, Abdelraheem OH, Zayed MA, Ragab AH, El Shahawy A. Enhanced Nanofiltration Process of Thin Film Composite Membrane Using Dodecyl Phenol Ethoxylate and Oleic Acid Ethoxylate for Oilfield Calcite Scale Control. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):855. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110855
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Mhyawi, Saedah R., Mahmoud F. Mubarak, Rasha Hosny, Manal Amine, Omnia H. Abdelraheem, M. A. Zayed, Ahmed H. Ragab, and Abeer El Shahawy. 2021. "Enhanced Nanofiltration Process of Thin Film Composite Membrane Using Dodecyl Phenol Ethoxylate and Oleic Acid Ethoxylate for Oilfield Calcite Scale Control" Membranes 11, no. 11: 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110855
APA StyleAl-Mhyawi, S. R., Mubarak, M. F., Hosny, R., Amine, M., Abdelraheem, O. H., Zayed, M. A., Ragab, A. H., & El Shahawy, A. (2021). Enhanced Nanofiltration Process of Thin Film Composite Membrane Using Dodecyl Phenol Ethoxylate and Oleic Acid Ethoxylate for Oilfield Calcite Scale Control. Membranes, 11(11), 855. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110855









