Cryo-EM Structure of Mechanosensitive Channel YnaI Using SMA2000: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
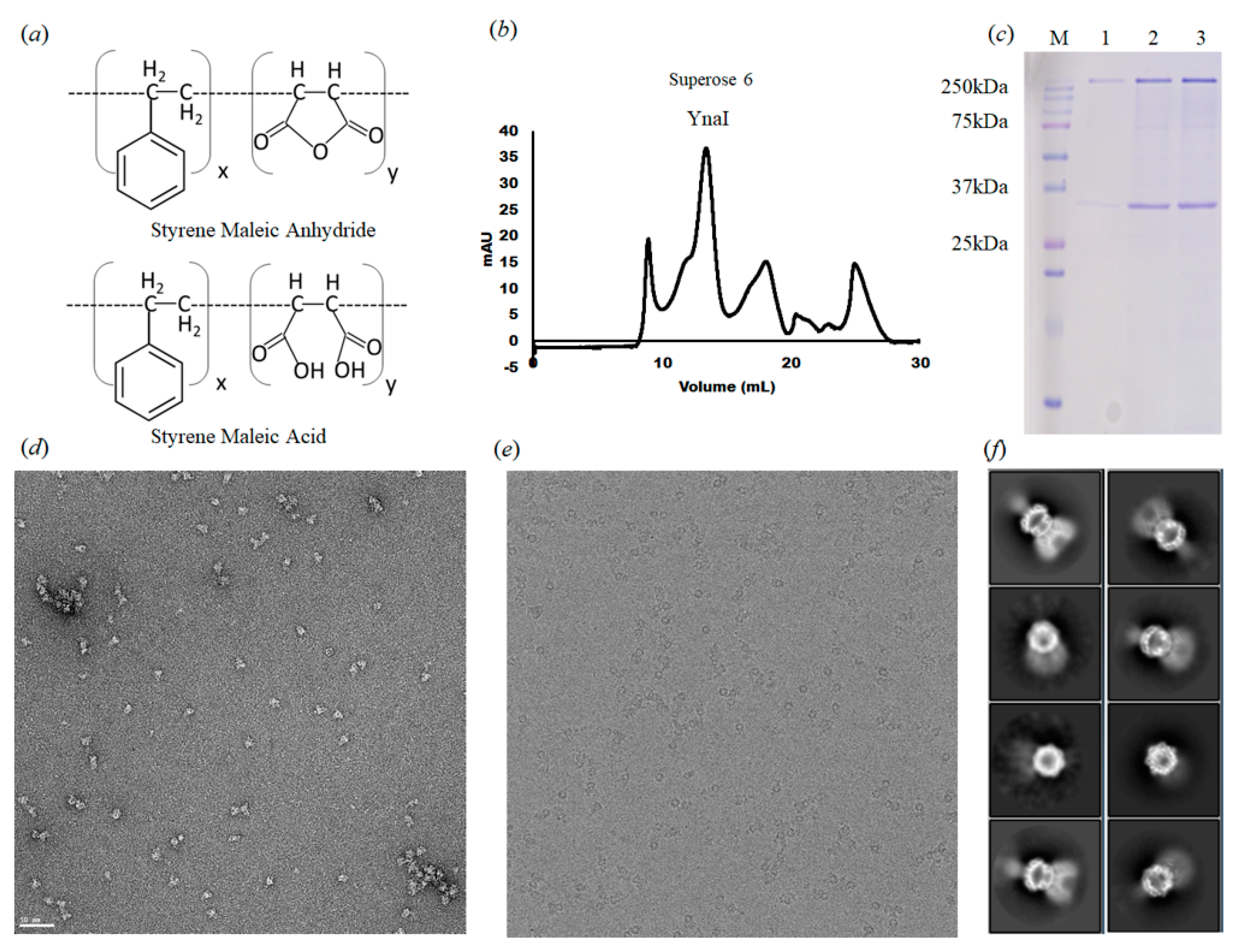
2.1. Protein Expression and Purification for Cryo-EM
2.2. Negative-Stain Electron Microscopy
2.3. Cryo-EM Specimen Preparation, Data Collection, and 3D EM Map Reconstruction
2.4. Atomic Modeling, Refinement, and Validation
2.5. YnaI Structural Comparison
2.6. HINT Lipid-Protein Analysis
3. Results
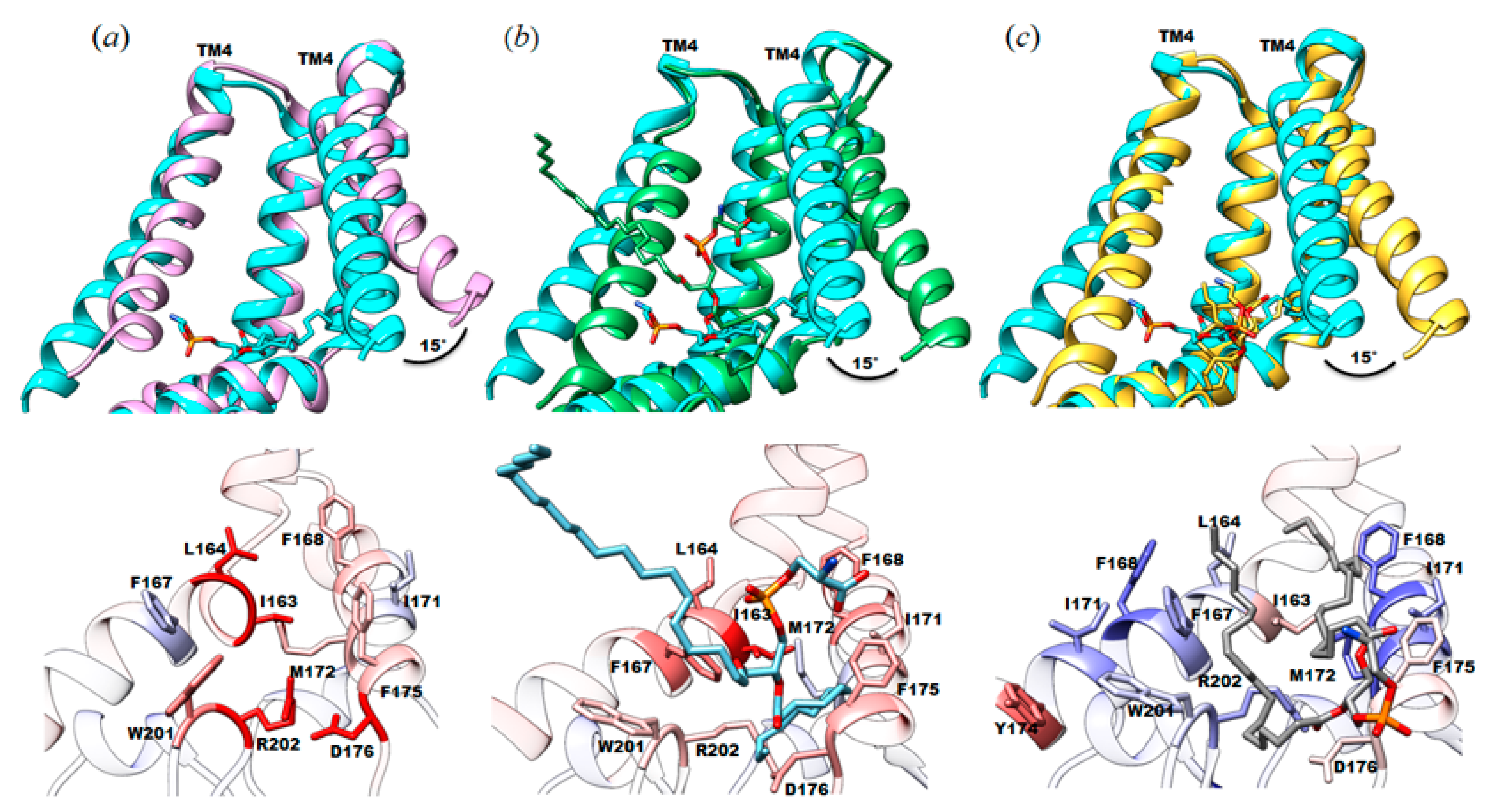
3.1. The Structure of YnaI Solubilized with SMA2000 Shows Native Lipids Bound at the Juxtamembrane
3.2. Protein-Lipid Interactions Affect Channel Conformation at the Juxtamembrane
4. Discussion
4.1. Native Lipids Alter the Structure’s Morphology in the Membrane-Soluble Region Interface of YnaI
4.2. Limitation of SMA Copolymer
4.3. The Need for a Large Membrane-Active Polymer Library for High-Resolution Structure Determination of Membrane Proteins
4.4. Structural Study of Membrane Proteins Using SMA Copolymers Should Be Accompanied by Functional Validation
4.5. Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids Using Samples from SMA Copolymer Prepared Samples Should Be Accompanied by Structural Validation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cox, C.D.; Bavi, N.; Martinac, B. Bacterial Mechanosensors. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2018, 80, 71–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, T.; Rasmussen, A. Bacterial Mechanosensitive Channels. Subcell. Biochem. 2018, 87, 83–116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blount, P.; Iscla, I. Life with Bacterial Mechanosensitive Channels, from Discovery to Physiology to Pharmacological Target. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2020, 84, e00055-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, M.D.; Black, S.; Rasmussen, T.; Rasmussen, A.; Stokes, N.R.; Stephen, T.-L.; Miller, S.; Booth, I.R. Characterization of three novel mechanosensitive channel activities in Escherichia coli. Channels 2012, 6, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levina, N.; Totemeyer, S.; Stokes, N.R.; Louis, P.; Jones, M.; Booth, I.R. Protection of Escherichia coli cells against extreme turgor by activation of MscS and MscL mechanosensitive channels: Identification of genes required for MscS activity. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumann, U.; Edwards, M.D.; Rasmussen, T.; Bartlett, W.; Van West, P.; Booth, I.R. YbdG in Escherichia coli is a threshold-setting mechanosensitive channel with MscM activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12664–12669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Booth, I.R.; Rasmussen, T.; Edwards, M.D.; Black, S.; Rasmussen, A.; Bartlett, W.; Miller, S. Sensing bilayer tension: Bacterial mechanosensitive channels and their gating mechanisms. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malcolm, H.; Maurer, J. The Mechanosensitive Channel of Small Conductance (MscS) Superfamily: Not Just Mechanosensitive Channels Anymore. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balleza, D. Mechanical properties of lipid bilayers and regulation of mechanosensitive function From biological to biomimetic channels. Channels 2012, 6, 220–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Battle, A.; Ridone, P.; Bavi, N.; Nakayama, Y.; Nikolaev, Y.; Martinac, B. Lipid–protein interactions: Lessons learned from stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 1744–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Sokabe, M.; Yoshimura, K. Lipid-Protein Interaction of the MscS Mechanosensitive Channel Examined by Scanning Mutagenesis. Biophys. J. 2006, 91, 2874–2881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powl, A.M.; East, A.J.M.; Lee, A.G. Lipid−Protein Interactions Studied by Introduction of a Tryptophan Residue: The Mechanosensitive Channel MscL. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 14306–14317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blount, P.; Yuezhou, L.; Moe, P.C.; Iscla, I. Mechanosensitive Channels Gated by Membrane Tension: Bacteria and beyond. Mechanosensitive Ion Channels. Mechanosensitive Ion Channels; Kiseleva, K.I., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, D.; Blount, P. Phosphatidylinositol Is Crucial for the Mechanosensitivity of Mycobacterium tuberculosis MscL. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 5415–5420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, B.; Bavi, N.; Lu, A.; Park, Y.; Perozo, E. Molecular basis of force-from-lipids gating in the mechanosensitive channel MscS. eLife 2019, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Daday, C.; Gu, R.-X.; Cox, C.D.; Martinac, B.; de Groot, B.L.; Walz, T. Visualization of the mechanosensitive ion channel MscS under membrane tension. Nat. Cell Biol. 2021, 590, 509–514. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y. Be Cautious with Crystal Structures of Membrane Proteins or Complexes Prepared in Detergents. Crystals 2020, 10, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhou, Q.; An, J.; Hildebrandt, E.; Aleksandrov, L.A.; Kappes, J.C.; DeLucas, L.J.; Riordan, J.R.; Urbatsch, I.L.; et al. Membrane protein stability can be compromised by detergent interactions with the extramembranous soluble domains. Protein Sci. 2014, 23, 769–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chipot, C.; Dehez, F.; Schnell, J.R.; Zitzmann, N.; Pebay-Peyroula, E.; Catoire, L.J.; Miroux, B.; Kunji, E.; Veglia, G.; Cross, T.A.; et al. Perturbations of Native Membrane Protein Structure in Alkyl Phosphocholine Detergents: A Critical Assessment of NMR and Biophysical Studies. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 3559–3607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, C.Q.; Zhuo, W.; Ge, J.; Jun, L.; Gao, N.; Li, Y.; Yang, M. A binding-block ion selective mechanism revealed by a Na/K selective channel. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, H. Mechanosensitive channel YnaI has lipid-bound extended sensor paddles. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flegler, V.J.; Rasmussen, A.; Rao, S.; Wu, N.; Zenobi, R.; Sansom, M.S.P.; Hedrich, R.; Rasmussen, T.; Böttcher, B. The MscS-like channel YnaI has a gating mechanism based on flexible pore helices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 28754–28762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, W.; Fu, Z.; Xu, G.G.; Grassucci, R.A.; Zhang, Y.; Frank, J.; Hendrickson, W.A.; Guo, Y. Structure and activity of lipid bilayer within a membrane-protein transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 12985–12990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suloway, C.; Pulokas, J.; Fellmann, D.; Cheng, A.; Guerra, F.; Quispe, J.; Stagg, S.; Potter, C.S.; Carragher, B. Automated molecular microscopy: The new Leginon system. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 151, 41–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.Q.; Palovcak, E.; Armache, J.-P.; Verba, K.A.; Cheng, Y.; Agard, S.Q. MotionCor2: Anisotropic correction of beam-induced motion for improved cryo-electron microscopy. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohou, A.; Grigorieff, N. CTFFIND4: Fast and accurate defocus estimation from electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 2015, 192, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zivanov, J.; Nakane, T.; Forsberg, B.O.; Kimanius, D.; Hagen, W.J.; Lindahl, E.; Scheres, S.H. New tools for automated high-resolution cryo-EM structure determination in RELION-3. eLife 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucukelbir, A.; Sigworth, F.J.; Tagare, H.D. Quantifying the local resolution of cryo-EM density maps. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 63–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.; Cowtan, K.D. Features and development ofCoot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.-W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2019, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Huang, C.C.; Ferrin, T.E. Tools for integrated sequence-structure analysis with UCSF Chimera. BMC Bioinform. 2006, 7, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, A.; Kellogg, G.E. Hydrophobicity—Shake Flasks, Protein Folding and Drug Discovery. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, G.E.; Abraham, D.J. Hydrophobicity: Is LogP(o/w) more than the sum of its parts? Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000, 35, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroeck, K.G.; Qiu, W.; Catalano, C.; Trinh, T.K.H.; Guo, Y. Native Cell Membrane Nanoparticles System for Membrane Protein-Protein Interaction Analysis. J. Vis. Exp. 2020, 2020, e61298. [Google Scholar]
- Morein, S.; Andersson, A.-S.; Rilfors, L.; Lindblom, G. Wild-type Escherichia coli Cells Regulate the Membrane Lipid Composition in a “Window” between Gel and Non-lamellar Structures. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 6801–6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellogg, G.E.; Fornabaio, M.; Spyrakis, F.; Lodola, A.; Cozzini, P.; Mozzarelli, A.; Abraham, D.J. Getting it right: Modeling of pH, solvent and "nearly" everything else in virtual screening of biological targets. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2004, 22, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, N.A.; Sept, D.; Joseph, S.; Holst, M.J.; McCammon, J.A. Electrostatics of nanosystems: Application to microtubules and the ribosome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 10037–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anishkin, A.; Loukin, S.H.; Teng, J.; Kung, C. Feeling the hidden mechanical forces in lipid bilayer is an original sense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7898–7905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinac, B.; Bavi, N.; Ridone, P.; Nikolaev, Y.A.; Martinac, A.D.; Nakayama, Y.; Rohde, P.R.; Bavi, O. Tuning ion channel mechanosensitivity by asymmetry of the transbilayer pressure profile. Biophys. Rev. 2018, 10, 1377–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridone, P.; Grage, S.L.; Patkunarajah, A.; Battle, A.R.; Ulrich, A.S.; Martinac, B. ‘Force-from-lipids’ gating of mechanosensitive channels modulated by PUFAs. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2018, 79, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bass, R.B.; Strop, P.; Barclay, M.; Rees, D.C. Crystal Structure of Escherichia coli MscS, a Voltage-Modulated and Mechanosensitive Channel. Science 2002, 298, 1582–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Black, S.S.; Edwards, M.D.; Miller, S.; Morrison, E.L.; Bartlett, W.; Dong, C.; Naismith, J.H.; Booth, I.R. The Structure of an Open Form of an E. coli Mechanosensitive Channel at 3.45 A Resolution. Science 2008, 321, 1179–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y. Detergent-free systems for structural studies of membrane proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2021, 49, 1361–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacCallum, J.L.; Tieleman, D.P. Hydrophobicity scales: A thermodynamic looking glass into lipid–protein interactions. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelman, D.M. Membranes are more mosaic than fluid. Nat. Cell Biol. 2005, 438, 578–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulamhussein, A.A.; Uddin, R.; Tighe, B.J.; Poyner, D.R.; Rothnie, A.J. A comparison of SMA (styrene maleic acid) and DIBMA (di-isobutylene maleic acid) for membrane protein purification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autzen, H.E.; Julius, D.; Cheng, Y. Membrane mimetic systems in CryoEM: Keeping membrane proteins in their native environment. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2019, 58, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Catalano, C.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, W.; Zhang, D.; McDermott, A.; Guo, Y.; Blount, P. A native cell membrane nanoparticles system allows for high-quality functional proteoliposome reconstitution. BBA Adv. 2021, 1, 100011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Microscope | Titan Krios (FEI) |
|---|---|
| Voltage (kV) | 300 |
| Detector | Gatan K2 SUMMIT |
| Nominal magnification | 22,500 |
| Electron exposure (e- Å-2) | 56.18 |
| Defocus range (µm) | −0.1–3.1 |
| Pixel size (Å2 per pixel) | 1.07 |
| Dose rate (e-/s/pixel) | 7.02 |
| Exposure time (s) | 8 |
| Movies stacks (no.) | 2155 |
| Boxsize (pixels) | 256 |
| Final particle images (no.) | 142,000 |
| Symmetry imposed | C7 |
| Map resolution | 2.4 Å |
| FSC threshold | 0.143 |
| PDB ID | 7N4T |
|---|---|
| EMDBID | EMD-24177 |
| Non-hydrogen atoms | 12,887 |
| Protein residues | 1603 |
| Ligands | 7 |
| R.m.s. deviations | |
| Bonds (Å) | 0.003 |
| Angles (°) | 0.483 |
| Validation | |
| MolProbity score | 1.72 |
| Clashscore | 5.48 |
| Poor rotamers (%) | 0.22 |
| Ramachandran plot | |
| Most favored (%) | 93.64 |
| Allowed (%) | 6.36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Catalano, C.; Ben-Hail, D.; Qiu, W.; Blount, P.; des Georges, A.; Guo, Y. Cryo-EM Structure of Mechanosensitive Channel YnaI Using SMA2000: Challenges and Opportunities. Membranes 2021, 11, 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110849
Catalano C, Ben-Hail D, Qiu W, Blount P, des Georges A, Guo Y. Cryo-EM Structure of Mechanosensitive Channel YnaI Using SMA2000: Challenges and Opportunities. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):849. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110849
Chicago/Turabian StyleCatalano, Claudio, Danya Ben-Hail, Weihua Qiu, Paul Blount, Amedee des Georges, and Youzhong Guo. 2021. "Cryo-EM Structure of Mechanosensitive Channel YnaI Using SMA2000: Challenges and Opportunities" Membranes 11, no. 11: 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110849
APA StyleCatalano, C., Ben-Hail, D., Qiu, W., Blount, P., des Georges, A., & Guo, Y. (2021). Cryo-EM Structure of Mechanosensitive Channel YnaI Using SMA2000: Challenges and Opportunities. Membranes, 11(11), 849. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110849







