A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Impact of Traditional Cleaning Methods on the Chemical Structure of IEMs
3. Water Content and Exchange Capacity of Fouled IEMs
4. Transport Characteristics of Fouled IEMs
4.1. Modelling
4.2. Interpretation of Experimental Data Using a Microheterogeneous Model
5. Effect of Fouling on IEMs Behavior in an Electric Field
5.1. Theoretical Background
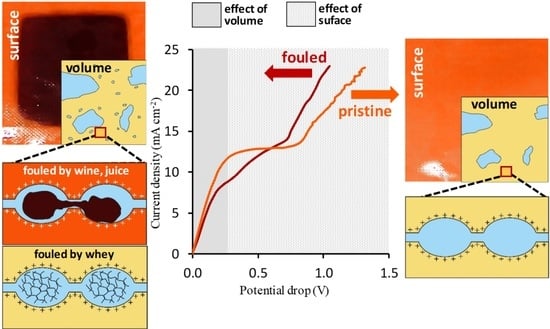
5.2. Voltammetry
5.3. Chronopotentiometry
5.4. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
6. Non-Destructive Methods of Membrane Fouling Control
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AEM | Anion-exchange membrane |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CEM | Cation-exchange membrane |
| ChP | Chronopotentiogramm |
| CVC | Current–voltage characteristic |
| EC | Electroconvection |
| ED | Electrodialysis |
| EDS | Energy dispersive X-ray spectrometry |
| EIS | Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (spectrum) |
| FO | Forward osmosis |
| IEC | Ion exchange capacity |
| NF | Nanofiltration |
| PEF | Pulsed electric field |
| PP | Polyphenol |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| RNA | Ribonucleic acid |
| RO | Reverse osmosis |
| SECM | Scanning electrochemical microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| UF | Ultrafiltration |
| WS | Water splitting |
| XRD | X-ray diffraction |
References
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Bazinet, L.; Xu, T. Electrodialysis-Based Separation Technologies in the Food Industry; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 349–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, J. Membrane separation processes for enrichment of bovine and caprine milk oligosaccharides from dairy byproducts. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 3667–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazinet, L.; Geoffroy, T.R. Electrodialytic processes: Market overview, membrane phenomena, recent developments and sustainable strategies. Membranes 2020, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, F.; Fernandes, C.; Liu, G.; Wu, D.; Chen, G.; Halim, R.; Liu, J.; Deng, H. Comparative study on tartaric acid production by two-chamber and three-chamber electro-electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 263, 118403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameira dos Santos, P.; de Pinho, M.N. Wine tartaric stabilization by electrodialysis and its assessment by the saturation temperature. J. Food Eng. 2003, 59, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Rayess, Y.; Mietton-Peuchot, M. Membrane Technologies in Wine Industry: An Overview. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56, 2005–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kattan Readi, O.M. Membranes in the Biobased Economy: Electrodialysis of Amino Acids for the Production of Biochemical; Universiteit Twente: Enschede, The Netherlands, 2013; p. 176. ISBN 978-94-6108-414-9. [Google Scholar]
- Shaposhnik, V.A.; Eliseeva, T.V. Barrier effect during the electrodialysis of ampholytes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 161, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hülber-Beyer, É.; Bélafi-Bakó, K.; Nemestóthy, N. Low-waste fermentation-derived organic acid production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis—An overview. Chem. Pap. 2021, 75, 5223–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, R. Electric field effects on proton transfer between ionizable groups and water in ion exchange membranes. Electrochim. Acta 1984, 29, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pärnamäe, R.; Mareev, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Melnikov, S.; Sheldeshov, N.; Zabolotskii, V.; Hamelers, H.V.M.; Tedesco, M. Bipolar membranes: A review on principles, latest developments, and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 617, 118538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.-T.; Adha, R.S.; Lee, C.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, I.S. Quantifying the influence of divalent cations mass transport on critical flux and organic fouling mechanism of forward osmosis membrane. Desalination 2021, 512, 115146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Amoudi, A.; Lovitt, R.W. Fouling strategies and the cleaning system of NF membranes and factors affecting cleaning efficiency. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 303, 4–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Bhuvanesh, E.; Chattopadhyay, S. Physicochemical interactions of organic acids influencing microstructure and permselectivity of anion exchange membrane. Colloid Surface A 2018, 560, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kononenko, N.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Fomenko, M.; Volfkovich, Y. Porous structure of ion exchange membranes investigated by various techniques. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2017, 246, 196–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pismenskaya, N.; Sarapulova, V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Kononenko, N.; Fomenko, M.; Nikonenko, V. Concentration dependences of diffusion permeability of anion-exchange membranes in sodium hydrogen carbonate, monosodium phosphate and potassium hydrogen tartrate solutions. Membranes 2019, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Chen, Q.; Lu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, P. Electrodialysis with porous membrane for bioproduct separation: Technology, features, and progress. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pismenskaya, N.; Sarapulova, V.; Klevtsova, A.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Adsorption of anthocyanins by cation and anion exchange resins with aromatic and aliphatic polymer matrices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langevin, M.-E.; Bazinet, L. Ion-exchange membrane fouling by peptides: A phenomenon governed by electrostatic interactions. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 369, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwal, S.; Doyen, A.; Bazinet, L. Characterization of protein, peptide and amino acid fouling on ion-exchange and filtration membranes: Review of current and recently developed methods. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Fouling on ion-exchange membranes: Classification, characterization and strategies of prevention and control. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2016, 229, 34–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Perreault, V.; Mikhaylin, S.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Bazinet, L.; Dammak, L. Identification of phenolic compounds and their fouling mechanisms in ion-exchange membranes used at an industrial scale for wine tartaric stabilization by electrodialysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 233, 115995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreault, V.; Sarapulova, V.; Tsygurina, K.; Pismenskaya, N.; Bazinet, L. Understanding of adsorption and desorption mechanisms of anthocyanins and proanthocyanidins on heterogeneous and homogeneous cation-exchange membranes. Membranes 2021, 11, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sholokhova, A.Y.; Eliseeva, T.V.; Voronyuk, I.V. Sorption of vanillin by highly basic anion exchangers under dynamic conditions. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 2018, 92, 2048–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, P.J.; Bird, M.R.; Rogers, D.; Wright, C.J. Measurement of polyphenol-membrane interaction forces during the ultrafiltration of black tea liquor. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Aspect. 2009, 335, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L. A review on ion-exchange membranes fouling and antifouling during electrodialysis used in food industry: Cleanings and strategies of prevention. Chem. Afr. 2020, 3, 609–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Ghalloussi, R.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D. Structure and properties of heterogeneous and homogeneous ion-exchange membranes subjected to ageing in sodium hypochlorite. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 452, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, H.; Irfan, M.; Xu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Y. Electrodialytic Desalination of Tobacco Sheet Extract: Membrane Fouling Mechanism and Mitigation Strategies. Membranes 2020, 10, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Xie, S.; Hu, Z.; Wu, G.; Morrison, L.; Croot, P.; Zhan, X. Nutrient recovery from pig manure digestate using electrodialysis reversal: Membrane fouling and feasibility of long-term operation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chon, K.; Jeong, N.; Rho, H.; Nam, J.Y.; Jwa, E.; Cho, J. Fouling characteristics of dissolved organic matter in fresh water and seawater compartments of reverse electrodialysis under natural water conditions. Desalination 2020, 496, 114478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafari, M.; Mohona, T.M.; Su, L.; Lin, H.; Plata, D.L.; Xiong, B.; Dai, N. Effects of peracetic acid on aromatic polyamide nanofiltration membranes: A comparative study with chlorine. Env. Sci. Water Res. Technol. 2021, 7, 306–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyer, F.; Laurinonyte, J.; Zwijnenburg, A.; Stams, A.J.; Plugge, C.M. Membrane fouling and chemical cleaning in three full-scale reverse osmosis plants producing demineralized water. J. Eng. 2017, 2017, 6356751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Šímová, H.; Kysela, V.; Černín, A. Demineralization of natural sweet whey by electrodialysis at pilot-plant scale. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 14, 170–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Qiu, L.; Yu, S.; Yang, H.; Li, L.; Ye, Y.; Liu, G. Effects of alkaline cleaning on the conversion and transformation of functional groups on ion-exchange membranes in polymer-flooding wastewater treatment: Desalination performance, fouling behavior, and mechanism. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 14430–14440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aumeier, B.M.; Yüce, S.; Wessling, M. Temperature enhanced backwash. Water Res. 2018, 142, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Tremblay, A.Y. Membrane regeneration and filtration modeling in treating oily wastewaters. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Elimelech, M. Salt cleaning of organic-fouled reverse osmosis membranes. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1134–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilyeva, V.I.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Akberova, E.M.; Nebavskaya, K.A. Effect of thermomechanical treatment on the surface morphology and hydrophobicity of heterogeneous ion exchange membranes. Rus. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 88, 1293–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, S.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, M.-K.; Yun, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Stability of composite anion exchange membranes with various functional groups and their performance for energy conversion. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pine, S.H. The base-promoted rearrangements of quaternary ammonium salts. Org. React. 2011, 403–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merle, G.; Wessling, M.; Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2011, 377, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Grande, D. Ageing of ion-exchange membranes in oxidant solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 69, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizutani, Y.; Yamane, R.; Motomura, H. Studies of ion exchange membranes. XXII. Semicontinuous preparation of ion exchange membranes by the “Paste Method”. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1965, 38, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higa, M.; Tanaka, N.; Nagase, M.; Yutani, K.; Kameyama, T.; Takamura, K.; Kakihana, Y. Electrodialytic properties of aromatic and aliphatic type hydrocarbonbased anion-exchange membranes with various anion-exchange groups. Polymer 2014, 55, 3951–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sata, T. Ion Exchange Membranes: Preparation, Characterization, Modification and Application; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2004; p. 314, ISBN-13: 978-0854045907. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, S.; Taniguchi, I.; Yasukawa, M.; Kakihana, Y.; Higa, M. Effect of alkali treatment on the mechanical properties of anion-exchange membranes with a poly(vinyl chloride) backing and binder. Membranes 2020, 10, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.; Takumi, N.; Kakihana, Y.; Higa, M. Alkali attack on cation-exchange membranes with polyvinyl chloride backing and binder: Comparison with anion-exchange membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, S.; Yasukawa, H.; Kakihana, Y.; Higa, M. Alkali attack on anion exchange membranes with PVC backing and binder: Effect on performance and correlation between them. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 573, 85–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minsker, K.S.; Zaikov, G.E. Achievements and research tasks for polyvinylchloride aging and stabilization. J. Vinyl Add. Technol. 2001, 7, 222–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalkina, O.A.; Tsygurina, K.A.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Mareev, S.A.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Evolution of current–voltage characteristics and surface morphology of homogeneous anion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis desalination of alkali metal salt solutions. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amato, L.; Gilbert, M.; Caswell, A. Degradation studies of crosslinked polyethylene. II Aged in water. Plast. Rubber Compos. 2005, 34, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Henry, J.L.; Garton, A. Thermal oxidation of polyethylene in aqueous environments. Polym. Prepr. ACS 1989, 30, 183–184. [Google Scholar]
- Helfferich, F. Ion. Exchange; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1962; p. 624. ISBN 0-486-68784-8. [Google Scholar]
- Audinos, R. Fouling of ion-selective membranes during electrodialysis of grape must. J. Membr. Sci. 1989, 41, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araya-Farias, M.; Bazinet, L. Effect of calcium and carbonate concentrations on anionic membrane fouling during electrodialysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 296, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persico, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Doyen, A.; Firdaous, L.; Hammami, R.; Chevalier, M.; Flahaut, C.; Dhulster, P.; Bazinet, L. Formation of peptide layers and adsorption mechanisms on a negatively charged cation-exchange membrane. J. Colloid Interface 2017, 508, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Mikhaylin, S.; Doyen, A.; Firdaous, L.; Hammami, R.; Bazinet, L. How peptide physicochemical and structural characteristics affect anion-exchange membranes fouling by a tryptic whey protein hydrolysate. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 520, 914–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Grande, D. Evolution of anion-exchange membrane properties in a full scale electrodialysis stack. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 446, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghalloussi, R.; Garcia-Vasquez, W.; Chaabane, L.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Deabate, S.V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Nikonenko, V.; Grande, D. Ageing of ion-exchange membranes in electrodialysis: A structural and physicochemical investigation. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 436, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Porozhnyy, M.; Nevakshenova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V. Characterization and cleaning of anion-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis of polyphenol-containing food industry solutions; comparison with cation-exchange membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 210, 636–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bdiri, M.; Dammak, L.; Chaabane, L.; Larchet, C.; Hellal, F.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Cleaning of cation-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis for food industry by chemical solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 199, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmai, A.; Sarapulova, V.; Sharafan, M.; Melkonian, K.; Rusinova, T.; Kozmai, Y.; Pismenskaya, N.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of anion-exchange membrane amx-sb fouled by red wine components. Membranes 2021, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belashova, E.D.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Sistat, P.; Pourcelly, G. Current-voltage characteristic of anion-exchange membrane in monosodium phosphate solution. Modelling and experiment. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 542, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapulova, V.; Nevakshenova, E.; Nebavskaya, X.; Kozmai, A.; Aleshkina, D.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N. Characterization of bulk and surface properties of anion-exchange membranes in initial stages of fouling by red wine. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 559, 170–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Auclair, B.; Parchikov, S.; Nikonenko, V. A simplified procedure for ion-exchange membrane characterization. New J. Chem. 2004, 28, 1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Abdu, S.; Wessling, M. Selectivity of ion exchange membranes: A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 429–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, N.P.; Kononenko, N.A.; Dyomina, O.A.; Gnusin, N.P. Characterization of ion-exchange membrane materials: Properties vs structure. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2008, 139, 3–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabolotsky, V.I.; Nikonenko, V.V. Effect of structural membrane inhomogeneity on transport properties. J. Membr. Sci. 1993, 79, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnusin, N.P.; Berezina, N.P.; Shudrenko, A.A.; Ivina, A.P. Electrolyte diffusion across ion-exchange membranes. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. A 1994, 68, 506–510. [Google Scholar]
- Sedkaoui, Y.; Szymczyk, A.; Lounici, H.; Arous, O. A new lateral method for characterizing the electrical conductivity of ion-exchange membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2016, 507, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lteif, R.; Dammak, L.; Larchet, C.; Auclair, B. Conductivité électrique membranaire: Étude de l’effet de la concentration, de la nature de l’électrolyte et de la structure membranaire. Eur. Polym. J. 1999, 35, 1187–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpenko, L.V.; Demina, O.A.; Dvorkina, G.A.; Parshikov, S.B.; Larchet, C.; Auclair, B.; Berezina, N.P. Comparative study of methods used for the determination of electroconductivity of ion-exchange membranes. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2001, 37, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareev, S.A.; Butylskii, D.Y.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V.V. Geometrical heterogeneity of homogeneous ion-exchange Neosepta membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnusin, N.P.; Berezina, N.P.; Kononenko, N.A.; Dyomina, O.A. Transport structural parameters to characterize ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 243, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuan, L.X.; Mertens, D.; Buess-Herman, C. The two-phase model of structure microheterogeneity revisited by the study of the CMS cation exchange membrane. Desalination 2009, 240, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porozhnyy, M.V.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Huguet, P.; Deabate, S.; Nikonenko, V.V. Mathematical modeling of concentration dependences of electric conductivity and diffusion permeability of anion-exchange membranes soaked in wine. Petrol. Chem. 2017, 57, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalkina, O.A.; Tsygurina, K.A.; Melnikova, E.D.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Catalytic effect of ammonia-containing species on water splitting during electrodialysis with ion-exchange membranes. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 299, 946–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalkina, O.; Tsygurina, K.; Melnikova, E.; Mareev, S.; Moroz, I.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N. Partial fluxes of phosphoric acid anions through anion-exchange membranes in the course of NaH2PO4 solution electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Talebi, S.; Chen, G.Q.; Freeman, B.; Suarez, F.; Freckleton, A.; Bathurst, K.; Kentish, S.E. Fouling and in-situ cleaning of ion-exchange membranes during the electrodialysis of fresh acid and sweet whey. J. Food Eng. 2019, 246, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintossi, D.; Saakes, M.; Borneman, Z.; Nijmeijer, K. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy of a reverse electrodialysis stack: A new approach to monitoring fouling and cleaning. J. Power Sources 2019, 444, 227302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Jia, H.; Wang, J.; Wen, H.; Li, J. Characterization of fouling and concentration polarization in ion exchange membrane by in-situ electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 594, 117443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galama, A.H.; Vermaas, D.A.; Veerman, J.; Saakes, M.; Rijnaarts, H.H.M.; Post, J.W.; Nijmeijer, K. Membrane resistance: The effect of salinity gradients over a cation exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 467, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, K.S.; Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Scarazzato, T.; Bernardes, A.M.; Espinosa, D.C.R.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Investigation of ion-exchange membranes by means of chronopotentiometry: A comprehensive review on this highly informative and multipurpose technique. Adv. Colloid Interfac. 2021, 293, 102439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teorell, T. Studies on the “diffusion effect” upon ionic distribution. Some theoretical considerations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1935, 21, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, K.H.; Sievers, J.-F. La perméabilité des membranes I. Théorie de la perméabilité ionique. Helv. Chim. Acta 1936, 19, 649–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gierke, T.; Munn, G.; Wilson, F. Morphology in Nafion perfluorinated membrane products, as determined by wide- and small-angle X-ray studies. J. Polymer Sci. Part. B. 1981, 19, 1687–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreuer, K.D.J. On the development of proton conducting polymer membranes for hydrogen and methanol fuel cells. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geise, G.M.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Fundamental water and salt transport properties ofpolymeric materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Equilibrium ion partitioning between aqueous salt solutions and inhomogeneous ion exchange membranes. Desalination 2018, 446, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Luo, H.; Geise, G.M. Specific co-ion sorption and diffusion properties influence membrane permselectivity. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 492–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fridman-Bishop, N.; Freger, V. What makes aromatic polyamide membranes superior: New insights into ion transport and membrane structure. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 540, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippov, A.N.; Kononenko, N.A.; Demina, O.A. Diffusion of electrolytes of different natures through the cation-exchange membrane. Colloid J. 2017, 79, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnusin, N.P.; Zabolotskii, V.I.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Meshechkov, A.I. Development of the generalized conductance principle to the description of transfer phenomena in disperse systems under the acting of different forces. Rus. J. Phys. Chem. 1980, 54, 1518–1522. [Google Scholar]
- Golubenko, D.V.; Safronova, E.Y.; Ilyin, A.B.; Shevlyakov, N.V.; Tverskoi, V.A.; Pourcelly, G.; Yaroslavtsev, A.B. Water state and ionic conductivity of grafted ion exchange membranes based on polyethylene and sulfonated polystyrene. Mendeleev Commun. 2017, 27, 380–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Effect of fixed charge group concentration on equilibrium ion sorption in ion exchange membranes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4638–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamcev, J.; Sujanani, R.; Jang, E.-S.; Yan, N.; Moe, N.; Paul, D.R.; Freeman, B.D. Salt concentration dependence of ionic conductivity in ion exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 547, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoiruddin, K.; Ariono, D.; Subagjo, S.; Wenten, I.G. Structure and transport properties of polyvinyl chloride-based heterogeneous cation-exchange membrane modified by additive blending and sulfonation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 873, 114304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niftaliev, S.I.; Kozaderova, O.A.; Kim, K.B. Electroconductance of heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes in aqueous salt solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 794, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasil’eva, V.I.; Akberova, E.M.; Kostylev, D.V.; Tzkhai, A.A. Diagnostics of the structural and transport properties of an anion-exchange membrane MA-40 after use in electrodialysis of mineralized natural waters. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 153–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choy, T.C. Effective Medium Theory: Principles and Applications; Oxford Science Publication: Oxford, UK, 1999; p. 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaroslavtsev, A.B.; Nikonenko, V.V. Ion-exchange membrane materials: Properties, modification, and practical application. Nanotechnol. Russ. 2009, 4, 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larchet, C.; Nouri, S.; Auclair, B.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Application of chronopotentiometry to determine the thickness of diffusion layer adjacent to an ion-exchange membrane under natural convection. Adv. Colloid Interface 2008, 139, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porozhnyy, M.; Huguet, P.; Cretin, M.; Safronova, E.; Nikonenko, V. Mathematical modeling of transport properties of proton-exchange membranes containing immobilized nanoparticles. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy. 2016, 41, 15605–15614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukhovets, A.; Eliseeva, T.; Oren, Y. Fouling of anion-exchange membranes in electrodialysis of aromatic amino acid solution. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 364, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevakshenova, E.E.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Application of sodium chloride solutions to regeneration of anion-exchange membranes used for improving grape juices and wines. Membr. Membr. Technol. 2019, 1, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.; You, F.; Yu, S.; Li, L.; Zhao, D. Mechanisms of chemical cleaning of ion exchange membranes: A case study of plant-scale electrodialysis for oily wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, D.; Bazinet, L. Effect of membrane type on cation migration during green tea electromigration and equivalent mass transported calculation. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 275, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, D.; Araya-Farias, M.; Tremblay, A.; Bazinet, L. Electromigration feasibility of green tea catechins. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 254, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.S. Wine Science: Principles and Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; p. 751. ISBN 9780123736468. [Google Scholar]
- Ribéreau-Gayon, P.; Glories, Y.; Maujean, A.; Dubourdieu, D. Handbook of Enology: The Chemistry of Wine, Stabilization and Treatments; John Wiley & Sons Ltd: Chichester, UK, 2006; p. 451. ISBN 0-470-01037-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hong, M.-K.; Han, S.-D.; Shim, J.; Moon, S.-H. Analysis of fouling potential in the electrodialysis process in the presence of an anionic surfactant foulant. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Jaegher, B.; De Schepper, W.; Verliefde, A.; Nopens, I. Enhancing mechanistic models with neural differential equations to predict electrodialysis fouling. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 259, 118028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkessa, Y.W.; Lang, Q.; Yan, B.; Kuang, S.; Mao, D.; Shu, L.; Zhang, Y. Anion exchange membrane organic fouling and mitigation in salt valorization process from high salinity textile wastewater by bipolar membrane electrodialysis. Desalination 2019, 465, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Wang, X.; Nie, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, S. Study on the recovery of ionic liquids from dilute effluent by electrodialysis method and the fouling of cation-exchange membrane. Sci. China Chem. 2013, 56, 1811–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Buzzi, D.C.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Ortega, E.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenório, J.A.S.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Sulfuric acid recovery from acid mine drainage by means of electrodialysis. Desalination 2014, 343, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strathmann, H. Electrodialysis, a mature technology with a multitude of new applications. Desalination 2010, 264, 268–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-T.; Kammermeyer, K. Membranes in Separation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1975; p. 559. ISBN 047193268X. [Google Scholar]
- Zabolotskii, V.I.; El’nikova, L.E.; Shel’deshov, N.V.; Alekseev, A.V. Precision method for measuring ionic transport numbers in ion-exchange membranes. Sov. Electrochem. 1988, 23, 1516–1519. [Google Scholar]
- Nikonenko, V.V.; Mareev, S.A.; Pis’menskaya, N.D.; Uzdenova, A.M.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Urtenov, M.K.; Pourcelly, G. Effect of electroconvection and its use in intensifying the mass transfer in electrodialysis. Russ. J. Electrochem. 2017, 53, 1122–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, A.; Wang, K.M. electroconvection near electrochemical interfaces: Experiments, modeling, and computation. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 2020, 52, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovalenko, A.V.; Wessling, M.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Mareev, S.A.; Moroz, I.A.; Evdochenko, E.; Urtenov, M.K. Space-Charge breakdown phenomenon and spatio-temporal ion concentration and fluid flow patterns in overlimiting current electrodialysis. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 636, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Water dissociation reaction generated in an ion exchange membrane. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 350, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeva, M.A.; Gil, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Dammak, L.; Kononenko, N.A.; Larchet, C.; Grande, D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Mitigation of membrane scaling in electrodialysis by electroconvection enhancement, pH adjustment and pulsed electric field application. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 549, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylin, S.; Nikonenko, V.; Pismenskaya, N.; Pourcelly, G.; Choi, S.; Kwon, H.J.; Han, J.; Bazinet, L. How physico-chemical and surface properties of cation-exchange membrane affect membrane scaling and electroconvective vortices: Influence on performance of electrodialysis with pulsed electric field. Desalination 2016, 393, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.D.; Pokhidnia, E.V.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V.V. Can the electrochemical performance of heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes be better than that of homogeneous membranes? J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 566, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabolotskii, V.I.; Shel’deshov, N.V.; Gnusin, N.P. Dissociation of water molecules in systems with ion-exchange membranes. Rus. Chem. Rev. 1988, 57, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareev, S.A.; Evdochenko, E.; Wessling, M.; Kozaderova, O.A.; Niftaliev, S.I.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V. A comprehensive mathematical model of water splitting in bipolar membranes: Impact of the spatial distribution of fixed charges and catalyst at bipolar junction. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 603, 118010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonenko, V.; Urtenov, M.; Mareev, S.; Pourcelly, G. Mathematical modeling of the effect of water splitting on ion transfer in the depleted diffusion layer near an ion-exchange membrane. Membranes 2020, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mafé, S.; Ramírez, P.; Alcaraz, A. Electric field-assisted proton transfer and water dissociation at the junction of a fixed-charge bipolar membrane. Chem. Phys. Lett. 1998, 294, 406–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobreshova, O.; Novikova, L.; Kulintsov, P.; Balavadze, E. Amino acids and water electrotransport through cation-exchange membranes. Desalination 2002, 149, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aristov, I.V.; Bobreshova, O.V.; Kulintsov, P.I.; Zagorodnykh, L.A. Transfer of amino acids through a membrane/solution interface in the presence of heterogeneous chemical protonation reaction. Rus. J. Electrochem. 2001, 37, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Evdochenko, E.; Bär, J.; Garcia-Gabaldon, M.; Wessling, M.; Perez-Herranz, V. Tracking homogeneous reactions during electrodialysis of organic acids via EIS. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 595, 117592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.D.; Rybalkina, O.A.; Kozmai, A.E.; Tsygurina, K.A.; Melnikova, E.D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Generation of H+ and OH− ions in anion-exchange membrane/ampholyte-containing solution systems: A study using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 601, 117920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y. Ion Exchange Membranes Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; p. 522. ISBN 9780444633194. [Google Scholar]
- Mishchuk, N.A. Polarization of systems with complex geometry. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, I. Electroconvection at an electrically inhomogeneous permselective interface. Phys. Fluids A 1991, 3, 2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, I.; Zaltzman, B. Electro-osmotically induced convection at a permselective membrane. Phys. Rev. E 2000, 62, 2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebavskaya, K.A.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Sabbatovskiy, K.G.; Sobolev, V.D.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Sistat, P.; Cretin, M.; Nikonenko, V.V. Impact of ion exchange membrane surface charge and hydrophobicity on electroconvection at underlimiting and overlimiting currents. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.M.; Wessling, M.; Mani, A. On the dynamical regimes of pattern-accelerated electroconvection. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zyryanova, S.; Mareev, S.; Gil, V.; Korzhova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Sarapulova, V.; Rybalkina, O.; Boyko, E.; Larchet, C.; Dammak, L.; et al. How electrical heterogeneity parameters of ion-exchange membrane surface affect the mass transfer and water splitting rate in electrodialysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zabolotsky, V.I.; Novak, L.; Kovalenko, A.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Urtenov, M.H.; Lebedev, K.A.; But, A.Y. Electroconvection in systems with heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes. Pet. Chem. 2017, 57, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balster, J.; Yildirim, M.H.; Stamatialis, D.F.; Ibanez, R.; Lammertink, R.G.H.; Jordan, V.; Wessling, M. Morpholgy and microtopology of cation-exchange polymers and the origin of the overlimiting current. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 2152–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindstrand, V.; Sundström, G.; Jönsson, A.S. Fouling of electrodialysis membranes by organic substances. Desalination 2000, 128, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, E.J.; Pfromm, P.H. Capacitance spectroscopy to characterize organic fouling of electrodialysis membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 1999, 162, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindstrand, V.; Jönsson, A.-S.; Sundström, G. Organic fouling of electrodialysis membranes with and without applied voltage. Desalination 2000, 130, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Choi, J.H.; Yeon, K.H.; Moon, S.H. An approach to fouling characterization of an ion-exchange membrane using current-voltage relation and electrical impedance spectroscopy. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 294, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloň, T.; Polezhaev, P.; Vobecká, L.; Slouka, Z. Fouling of a heterogeneous anion-exchange membrane and single anion-exchange resin particle by ssDNA manifests differently. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 572, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, C.R.; Benvenuti, T.; da Trindade, C.D.M.; Rodrigues, M.A.S.; Zoppas-Ferreira, J.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Bernardes, A.M. Electrodialysis for the tertiary treatment of municipal wastewater: Efficiency of ion removal and ageing of ion exchange membranes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5855–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, G.; Virtanen, T.; Ferrando, M.; Güell, C.; Lipnizki, F.; Kallioinen, M. A review of in situ real-time monitoring techniques for membrane fouling in the biotechnology, biorefinery and food sectors. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 588, 117221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-J.; Hong, M.-K.; Han, S.-D.; Cho, S.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Fouling of an anion exchange membrane in the electrodialysis desalination process in the presence of organic foulants. Desalination 2009, 238, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Moon, S.-H. Effects of electrolytes on the transport phenomena in a cation-exchange membrane. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2001, 238, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaltzman, B.; Rubinstein, I. Electro-osmotic slip and electroconvective instability. J. Fluid Mech. 2007, 579, 173–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.; Wang, K.; Schiffbauer, J.; Mani, A. Confinement effects on electroconvective instability. Electrophoresis 2016, 38, 702–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belashova, E.D.; Kharchenko, O.A.; Sarapulova, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Effect of protolysis reactions on the shape of chronopotentiograms of a homogeneous anion-exchange membrane in NaH2PO4 solution. Petrol. Chem. 2017, 57, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-H.; Moon, S.-H. Pore size characterization of cation-exchange membranes by chronopotentiometry using homologous a mine ions. J. Membr. Sci. 2001, 191, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.-J.; Kang, M.-S.; Kim, S.-H.; Cho, J.; Moon, S.-H. Characterization of LDPE/polystyrene cation exchange membranes prepared by monomer sorption and UV radiation polymerization. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 223, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audinos, R.; Jacquet-Battault, F.; Moutounet, M. Study of the variation in time of the transport properties of electrodialysis permselective membranes fouled by polyphenols of grape must. J. Chim. Phys. Chim. Biol. 1985, 82, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maruyama, T.; Katoh, S.; Nakajima, M.; Nabetani, H. Mechanism of bovine serum albumin aggregation during ultrafiltration. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2001, 75, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, W.; Wu, P. Fast proton conduction in denatured bovine serum albumin coated nafion membranes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interface 2018, 10, 39768–39776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kammerer, J.; Boschet, J.; Kammerer, D.R.; Carle, R. Enrichment and fractionation of major apple flavonoids, phenolic acids and dihydrochalcones using anion exchange resins. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 44, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubinstein, I.; Zaltzman, B. Equilibrium electroconvective instability. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2015, 114, 114502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Korzhova, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Lopatin, D.; Baranov, O.; Dammak, L.; Nikonenko, V. Effect of surface hydrophobization on chronopotentiometric behavior of an AMX anion-exchange membrane at overlimiting currents. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.S. Electrochemical Systems; Prentice-Hall: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1972; p. 432, ISBN-10: 027596356X. [Google Scholar]
- Belashova, E.; Mikhaylin, S.; Pismenskaya, N.; Nikonenko, V.; Bazinet, L. Impact of cation-exchange membrane scaling nature on the electrochemical characteristics of membrane system. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 189, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freijanes, Y.; Barragán, V.M.; Muñoz, S. Chronopotentiometric study of a Nafion membrane in presence of glucose. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 510, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahi, V.K.; Thampy, S.K.; Rangarajan, R. Chronopotentiometric studies on dialytic properties of glycine across ion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 203, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-S.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Choi, Y.-J.; Moon, S.-H. Electrodialytic separation characteristics of large molecular organic acid in highly water-swollen cation-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 222, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarale, R.K.; Shahi, V.K.; Thampy, S.K.; Rangarajan, R. Studies on electrochemical characterization of polycarbonate and polysulfone based heterogeneous cation-exchange membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2004, 61, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarazzato, T.; Barros, K.S.; Benvenuti, T.; Siqueira Rodrigues, M.A.; Romano Espinosa, D.C.; Moura Bernardes, A.; Amado, F.D.R.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Achievements in electrodialysis process for wastewater and water treatment. Curr. Trends Future Dev. (Bio-) Membr. 2020, 5, 127–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerche, D.; Wolf, H. Quantitative characterisation of current-induced diffusion layers at cation-exchange membranes. I. Investigations of temporal and local behaviour of concentration profile at constant current density. Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. 1975, 2, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mareev, S.A.; Butylskii, D.Y.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V. Chronopotentiometry of ion-exchange membranes in the overlimiting current range. Transition time for a finite-length diffusion layer: Modeling and experiment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 500, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titorova, V.D.; Mareev, S.A.; Gorobchenko, A.D.; Gil, V.V.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Sabbatovskii, K.G.; Pismenskaya, N.D. Effect of current-induced co-ion transfer on the shape of chronopotentiograms of cation-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2021, 624, 119036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Buzzi, D.C.; Garcia-Gabaldon, M.; Bernardes, A.M.; Tenorio, J.A.S.; Perez-Herranz, V. Ion transport through homogeneous and heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes in single salt and multicomponent electrolyte solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 466, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barros, K.S.; Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Perez-Herranz, V.; Espinosa, D.C.R. A three-stage chemical cleaning of ion-exchange membranes used in the treatment by electrodialysis of wastewaters generated in brass electroplating industries. Desalination 2020, 492, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Garcia-Gabaldon, M.; Perez-Herranz, V. Mass transfer phenomena during electrodialysis of multivalent ions: Chemical equilibria and overlimiting currents. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Effect of the equilibria of multivalent metal sulfates on the transport through cation-exchange membranes at different current regimes. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 443, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pismenskaya, N.; Igritskaya, K.; Belova, E.; Nikonenko, V.; Pourcelly, G. Transport properties of ion-exchange membrane systems in LysHCl solutions. Desalination 2006, 200, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gally, C.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Ortega, E.M.; Bernardes, A.M.; Pérez-Herranz, V. Chronopotentiometric study of the transport of phosphoric acid anions through an anion-exchange membrane under different pH values. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 238, 116421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, K.S.; Martí-Calatayud, M.C.; Ortega, E.M.; Perez-Herranz, V.; Espinosa, D.C.R. Chronopotentiometric study on the simultaneous transport of EDTA ionic species and hydroxyl ions through an anion-exchange membrane for electrodialysis applications. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 879, 114782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerdoumi, R.; Chatta, H.; Mellahi, D.; Oulmi, K.; Ferhat, M.; Ourari, A. Chronopotentiometric evaluation of enhanced counter-ion transport through anion exchange membranes in electromembrane processes. Desalin. Water Treat. 2017, 78, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-S.; Choi, J.-H.; Woo, J.-J.; Moon, S.-H. An electrical impedance spectroscopic (EIS) study on transport characteristics of ion-exchange membrane systems. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 300, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; Wang, Z.; Shi, F.; Liu, H. Investigations on the interfacial capacitance and the diffusion boundary layer thickness of ion exchange membrane using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 502, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golubenko, D.; Karavanova, Y.; Yaroslavtsev, A. Effects of the surface layer structure of the heterogeneous ion-exchange membranes on their impedance. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 777, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Garcia, I.; Kotoka, F.; Portugal, C.A.M.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Characterization of poly(Acrylic) acid-modified heterogenous anion exchange membranes with improved monovalent permselectivity for RED. Membranes 2020, 10, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, S.; Cao, H.; Xu, B.; Zhao, Z.; Cao, R.; Chang, J.; Duan, F.; Wen, H. Anion exchange nanocomposite membranes modified with graphene oxide and polydopamine: Interfacial structure and antifouling applications. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Długołęcki, P.; Ogonowski, P.; Metz, S.J.; Saakes, M.; Nijmeijer, K.; Wessling, M. On the resistances of membrane, diffusion boundary layer and double layer in ion-exchange membrane transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2010, 349, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sistat, P.; Kozmai, A.; Pismenskaya, N.; Larchet, C.; Pourcelly, G.; Nikonenko, V. Low-frequency impedance of an ion-exchange membrane system. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 6380–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozmai, A.E.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Mareev, S.A.; Belova, E.I.; Sistat, P. Use of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for determining the diffusion layer thickness at the surface of ion-exchange membranes. Petrol. Chem. 2012, 52, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, H.D.; Dibiani, R. Experimental and theoretical investigations of steady and transient states in systems of ion exchange bipolar membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 228, 17–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kniaginicheva, E.; Pismenskaya, N.; Melnikov, S.; Belashova, E.; Sistat, P.; Cretin, M.; Nikonenko, V. Water splitting at an anion-exchange membrane as studied by impedance spectroscopy. J. Membr. Sci. 2015, 496, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slouka, Z.; Senapati, S.; Yan, Y.; Chang, H.-C. Charge inversion, water splitting, and vortex suppression due to DNA sorption on ion-selective membranes and their ion-current signatures. Langmuir 2013, 29, 8275–8283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloň, T.; Slouka, Z. Overlimiting behavior of surface-modified heterogeneous anion-exchange membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 610, 118291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino-Garcia, I.; Velizarov, S. New insights into the definition of membrane cleaning strategies to diminish the fouling impact in ion exchange membrane separation processes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 277, 119445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbaton-Baguena, M.J.; Alvarez-Blanco, S.; Vincent-Vela, M.C. Cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes fouled with BSA by means of saline solutions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 125, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, O.M.; Markham, K.R. Flavonoids: Chemistry, Biochemistry and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; p. 1256. ISBN 9780849320217. [Google Scholar]
- Petrus, H.B.; Li, H.; Chen, V.; Norazman, N. Enzymatic cleaning of ultrafiltration membranes fouled by protein mixture solutions. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 325, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilad, M.R.; Baten, M.; Pollet, A.; Courtin, C.; Wouters, J.; Verbiest, T.; Vankelecom, I.F.J. A novel in-situ enzymatic cleaning method for reducing membrane fouling in membrane bioreactors (MBRs). Indones. J. Sci. Technol. 2016, 1, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bdiri, M.; Bensghaier, A.; Chaabane, L.; Kozmai, A.; Baklouti, L.; Larchet, C. Preliminary study on enzymatic-based cleaning of cation-exchange membranes used in electrodialysis system in red wine production. Membranes 2019, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nichka, V.S.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Bazinet, L. Fouling mitigation by optimizing flow rate and pulsed electric field during bipolar membrane electroacidification of caseinate solution. Membranes 2021, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkel, A.; Ashrafi, A.M. An investigation on the application of pulsed electrodialysis reversal in whey desalination. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pelletier, S.; Serre, É.; Mikhaylin, S.; Bazinet, L. Optimization of cranberry juice deacidification by electrodialysis with bipolar membrane: Impact of pulsed electric field conditions. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 186, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoiruddin, K.; Ariono, D.; Subagjo, S.; Wenten, I.G. Improved anti-organic fouling of polyvinyl chloride-based heterogeneous anion-exchange membrane modified by hydrophilic additives. J. Water Proc. Eng. 2021, 41, 102007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Pan, J.; Wei, B.; Feng, J.; Liao, S.; Li, X.; Yu, Y. Anti-fouling anion exchange membrane for electrodialysis fabricated by in-situ interpenetration of the ionomer to gradient cross-linked network of Ca-Na alginate. Desalination 2021, 505, 115005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, D.; Van der Bruggen, B. Modification of an anion exchange membrane based on rapid mussel-inspired deposition for improved antifouling performance. Colloid. Surface. A 2021, 615, 126267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariono, D.; Subagjo, D.; Wenten, I.G. Surface modification of ion-exchange membranes: Methods, characteristics, and performance. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Ladewig, B.P.; Yao, Z. A comprehensive review on the synthesis and applications of ion exchange membranes. Chemosphere 2021, 282, 130817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ran, J.; Wu, L.; He, Y.B.; Yang, Z.J.; Wang, Y.M.; Jiang, C.X.; Ge, L.; Bakangura, E.; Xu, T.W. Ion exchange membranes: New developments and applications. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 522, 267–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotoka, F.; Merino-Garcia, I.; Velizarov, S. Surface modifications of anion exchange membranes for an improved reverse electrodialysis process performance: A review. Membranes 2020, 10, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larchet, C.; Zabolotsky, V.I.; Pismenskaya, N.D.; Nikonenko, V.V.; Tskhay, A.; Tastanov, K.; Pourcelly, G. Comparison of different ED stack conceptions when applied for drinking water production from brackish waters. Desalination 2008, 222, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlowski, S.; Crespo, J.G.; Velizarov, S. Profiled ion exchange membranes: A comprehensible review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]











| AEM Soaking Duration, h | f2app | f2 | f2s | fcp | d/d (h = 0) | IECsw (mmol cm−3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.11 | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 2.30 |
| 24 | 0.087 | 0.09 | 0.07 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 1.02 | 1.95 |
| 100 | 0.084 | 0.12 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 1.44 | 1.05 | 1.84 |
| 500 | 0.073 | 0.16 | 0.06 | 0.1 | 1.47 | 1.08 | 1.77 |
| 750 | 0.071 | 0.18 | 0.05 | 0.13 | 1.74 | 1.08 | 1.72 |
| 1000 | 0.069 | 0.20 | 0.045 | 0.155 | 1.88 | 1.08 | 1.70 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pismenskaya, N.; Bdiri, M.; Sarapulova, V.; Kozmai, A.; Fouilloux, J.; Baklouti, L.; Larchet, C.; Renard, E.; Dammak, L. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences. Membranes 2021, 11, 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110811
Pismenskaya N, Bdiri M, Sarapulova V, Kozmai A, Fouilloux J, Baklouti L, Larchet C, Renard E, Dammak L. A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences. Membranes. 2021; 11(11):811. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110811
Chicago/Turabian StylePismenskaya, Natalia, Myriam Bdiri, Veronika Sarapulova, Anton Kozmai, Julie Fouilloux, Lassaad Baklouti, Christian Larchet, Estelle Renard, and Lasâad Dammak. 2021. "A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences" Membranes 11, no. 11: 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110811
APA StylePismenskaya, N., Bdiri, M., Sarapulova, V., Kozmai, A., Fouilloux, J., Baklouti, L., Larchet, C., Renard, E., & Dammak, L. (2021). A Review on Ion-Exchange Membranes Fouling during Electrodialysis Process in Food Industry, Part 2: Influence on Transport Properties and Electrochemical Characteristics, Cleaning and Its Consequences. Membranes, 11(11), 811. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11110811