Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Dope Solutions Preparation
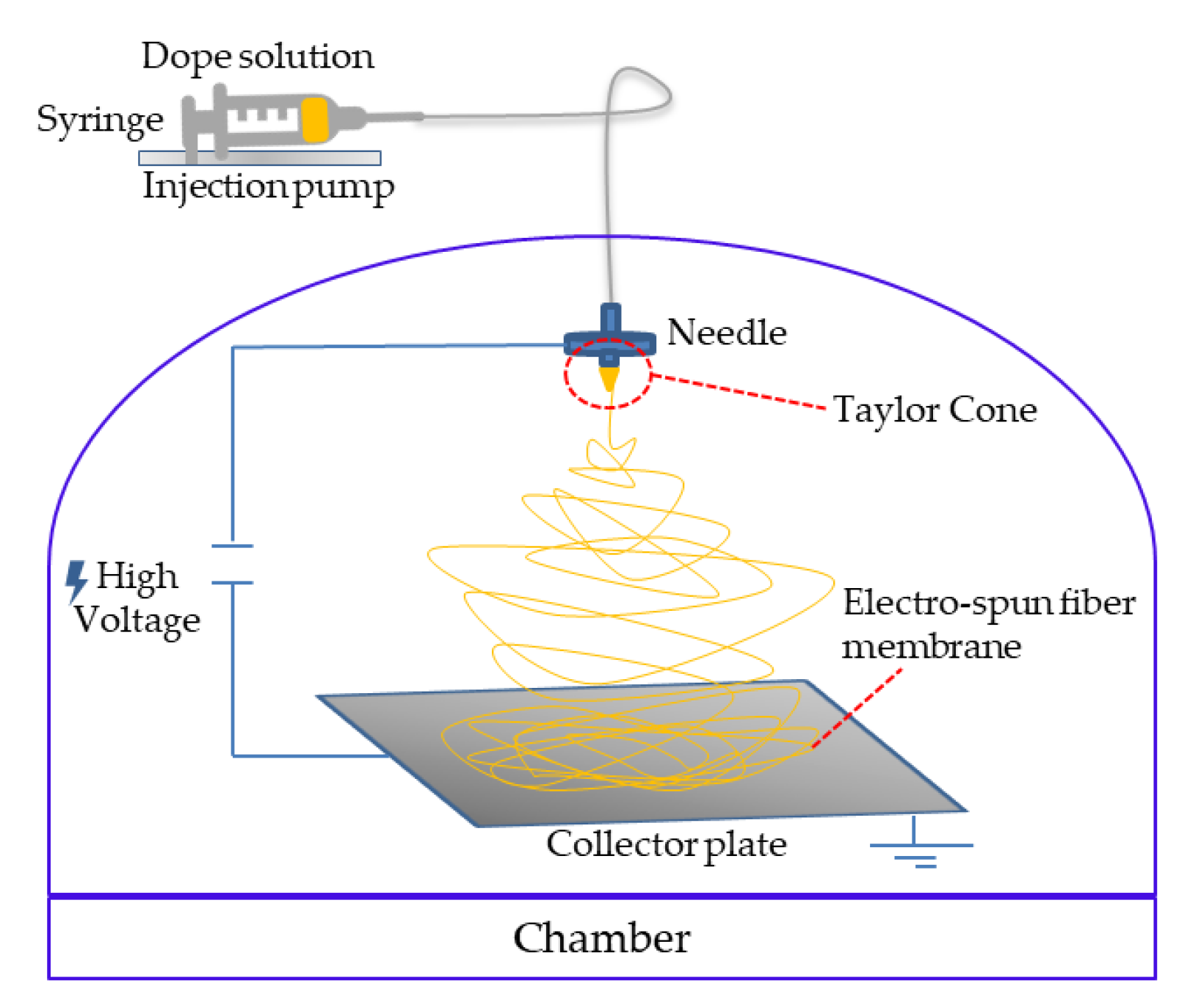
2.3. ENMs Preparation by Electrospinning
2.4. ENM Characterizations
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.4.2. Porosity
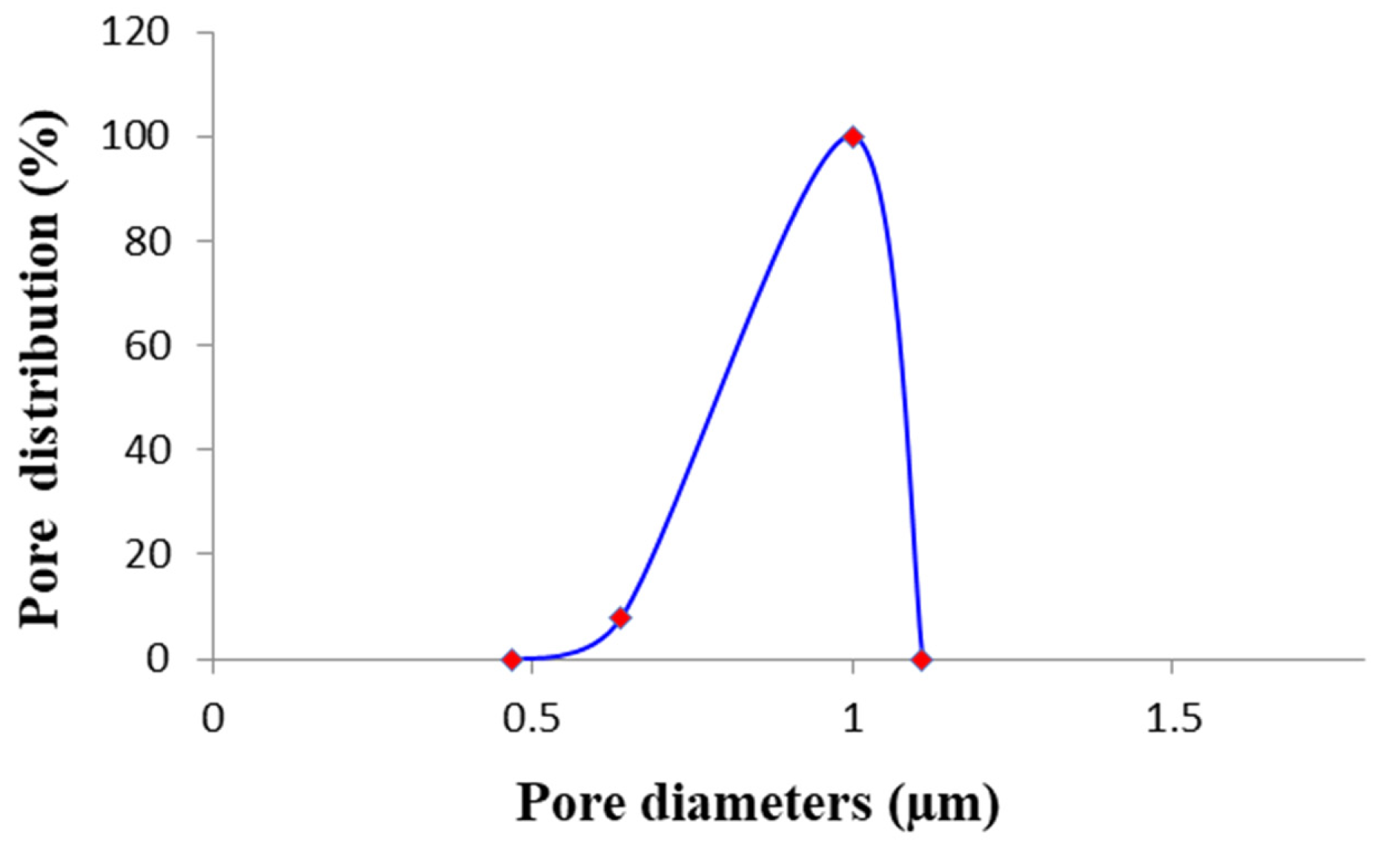
2.4.3. Pore Size
2.4.4. Contact Angle
2.4.5. Thickness
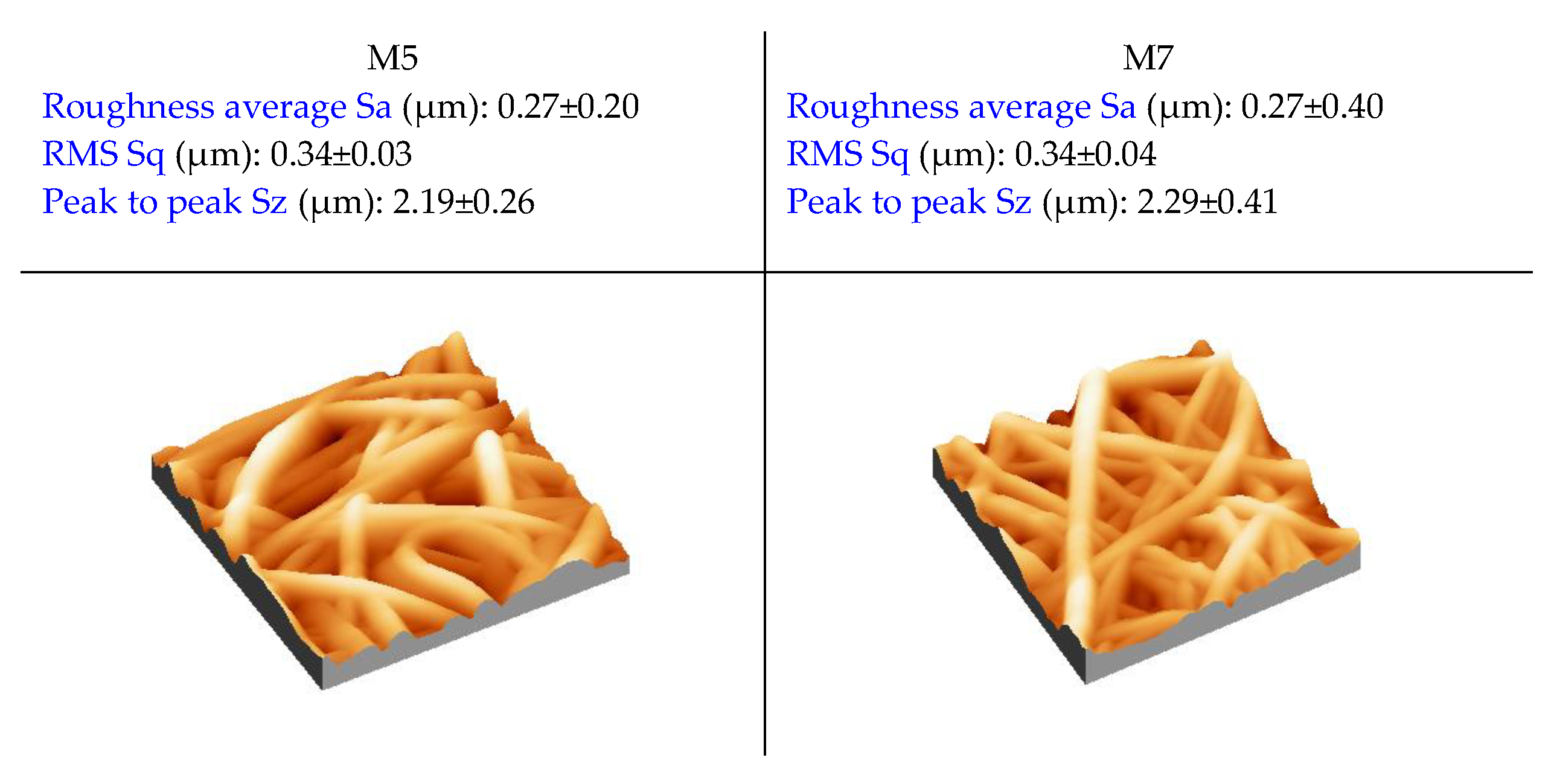
2.4.6. Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
2.4.7. Water Permeability (PWP)
3. Results
3.1. Viscosity Meaurement
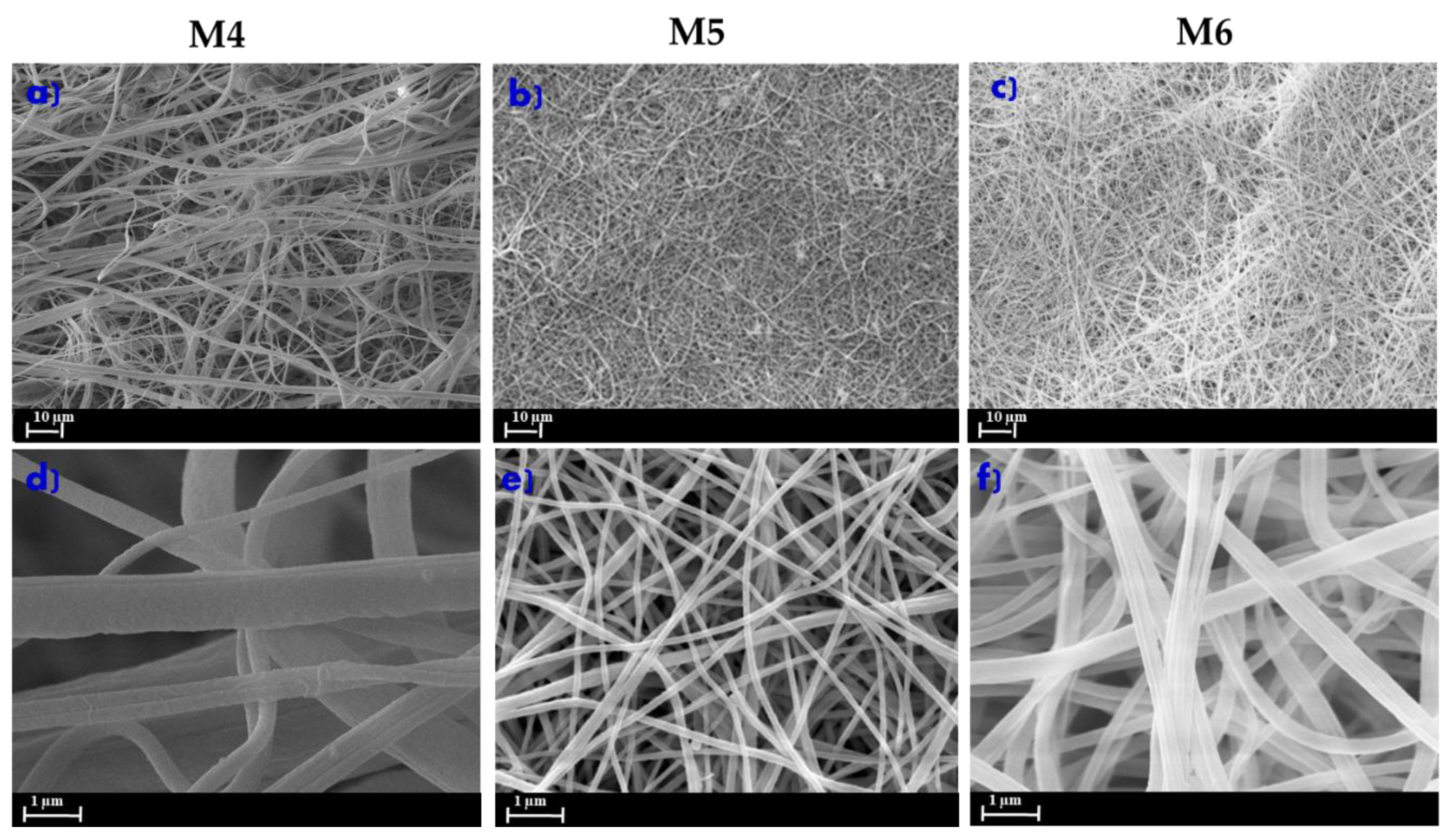
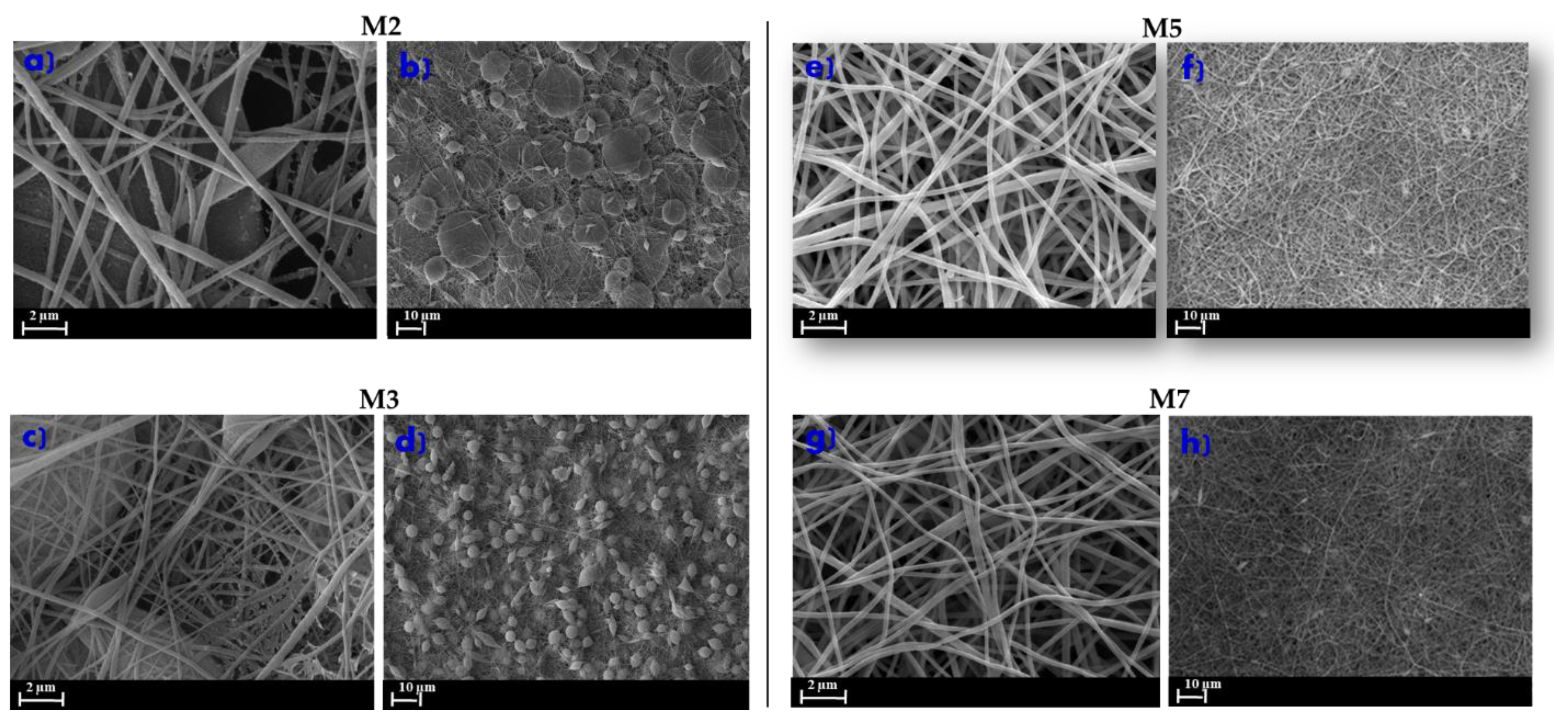
3.2. Morphology of ENMs
3.3. Porosity, Pore Size, Thickness, Contact Angle, and AFM of ENMs
4. Comparison with the Literature
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Figoli, A.; Simone, S.; Drioli, E. Polymeric membranes. In Membrane Fabrication; Hilal, N., Ismail, A.F., Wright, C., Eds.; Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015; pp. 1–42. [Google Scholar]
- Fane, A.G.; Tang, C.Y.; Wang, R. Membrane Technology for Water: Microfiltration, Ultrafiltration, Nanofiltration, and Reverse Osmosis. In Treatise on Water Science; Wilderer, P., Ed.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 4, pp. 301–335. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Loh, C.-H.; Tian, M.; Wang, R.; Fane, A.G. Progress in electrospun polymeric nanofibrous membranes for water treatment: Fabrication, modification and applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 77, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2015, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, D.; Zhu, M.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Q.; Xiong, R.; Huang, C. Green Electrospun Nanofibers and Their Application in Air Filtration. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2018, 303, 1800336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Cheng, Z.; Kang, L.; Chu, M.; Wu, D.; Li, M.; Xie, S. Novel stellate poly (vinylidene fluoride)/polyethersulfone microsphere- nanofiber electrospun membrane with special wettability for oil/water separation. Mater. Lett. 2017, 207, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Hou, D.; Fu, C.; Wang, K.; Wang, J. Fabrication of PVDF nanofibrous hydrophobic composite membranes reinforced with fabric substrates via electrospinning for membrane distillation desalination. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 75, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L. Fouling resistance improvement with a new superhydrophobic electrospun PVDF membrane for seawater desalination. Desalination 2020, 476, 11426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillen, G.R.; Pan, Y.; Li, M.; Hoek, E.M.V. Preparation and characterization of membranes formed by nonsolvent induced phase separation: A review. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3798–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ECHA, Candidate List of Substances of very High Concern for Authorisation, European Chemicals Agency. 2020. Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/ (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Marino, T.; Galiano, F.; Simone, S.; Figoli, A. DMSO EVOLTM as novel non-toxic solvent for polyethersulfone membrane preparation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 14774–14785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerton, F.M. Alternative Solvents for Green Chemistry; Clark, J.H., Kraus, G.A., Eds.; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2009; p. 131. [Google Scholar]
- Figoli, A.; Marino, T.; Simone, S.; Di Nicolò, E.; Li, X.M.; He, T.; Tornaghi, S.; Drioli, E. Towards non-toxic solvents for membrane preparation: A review. Green Chem. 2014, 16, 4034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evenepoel, N.; Wen, S.; Tsehaye, M.T.; Bruggen, B. Van Der Potential of DMSO as greener solvent for PES ultra- and nanofiltration membrane preparation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 46494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimethyl Sulfoxide, Safety Data Sheet, Sigma Aldrich. Available online: www.sigmaaldrich.com (accessed on 13 January 2020).
- Madaeni, S.S.; Bakhtiari, L. Thermodynamic-based predictions of membrane morphology in water/dimethylsulfoxide/polyethersulfone systems. Polymer 2012, 53, 4481–4488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexowsky, C.; Bojarska, M.; Ulbricht, M. Porous poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes with tailored properties by fast and scalable non-solvent vapor induced phase separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2019, 577, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meringolo, C.; Mastropietro, T.F.; Poerio, T.; Fontananova, E.; De Filpo, G.; Curcio, E.; Di Profio, G. Tailoring PVDF Membranes Surface Topography and Hydrophobicity by a Sustainable Two-Steps Phase Separation Process. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 10069–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.J.; Chang, C.L.; Lee, C.K.; Cheng, L.P. Preparation and characterization of microporous PVDF/PMMA composite membranes by phase inversion in water/DMSO solutions. Eur. Polym. J. 2006, 42, 2407–2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enayatzadeh, M.; Mohammadi, T. Morphology and performance of poly (vinylidene fluoride) flat sheet membranes: Thermodynamic and kinetic aspects. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 16–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefi-Oskoui, S.; Khataee, A.; Vatanpour, V. Effect of solvent type on the physicochemical properties and performance of NLDH/PVDF nanocomposite ultrafiltration membranes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 184, 97–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehlage, D.; Böttjer, R.; Grothe, T.; Ehrmann, A. Electrospinning water-soluble/insoluble polymer blends. AIMS Mater. Sci. 2018, 5, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabantina, L.; Klöcker, M.; Wortmann, M.; Mirasol, J.R.; Cordero, T.; Moritzer, E.; Finsterbusch, K.; Ehrmann, A. Stabilization of polyacrylonitrile nanofiber mats obtained by needleless electrospinning using dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent. J. Ind. Text. 2019, 5, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. The electrospinning behavior of poly(vinyl alcohol) in DMSO-water binary solvent mixtures. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102947–102955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rianjanu, A.; Kusumaatmaja, A.; Suyono, E.A.; Triyana, K. Solvent vapor treatment improves mechanical strength of electrospun polyvinyl alcohol nanofibers. Heliyon 2018, 4, e00592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S. Influence of solvents properties on morphology of electrospun polyurethane nanofiber mats. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2014, 25, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wortmann, M.; Frese, N.; Sabantina, L.; Petkau, R.; Kinzel, F.; Gölzhäuser, A.; Moritzer, E.; Hüsgen, B.; Ehrmann, A. New polymers for needleless electrospinning from low-toxic solvents. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Wang, R.; Tian, M.; Qiu, C.; Fane, A.G. Fabrication of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) nanofiber membranes by electro-spinning for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 425–426, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essalhi, M.; Khayet, M. Self-sustained webs of polyvinylidene fluoride electrospun nano-fibers: Effects of polymer concentration and desalination by direct contact membrane distillation. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, C.; Khulbe, K.C.; Tabe, S. Volatile organic compound removal by membrane gas stripping using electro-spun nanofiber membrane. Desalination 2012, 287, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Liu, T.; Liu, Z.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, C.; Feng, X. Microporous CA/PVDF membranes based on electrospun nanofibers with controlled crosslinking induced by solvent vapor. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 512, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.D.; Cao, Y.M. Application and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Vidorreta, I.M.; Sebastian, V.; Moro, A.; Coelhoso, I.M.; Portugal, C.A.M.; Lima, J.C.; Desiderio, G.; Lombardo, G.; Drioli, E.; et al. A non-invasive optical method for mapping temperature polarization in direct contact membrane distillation. J. Memb. Sci. 2017, 536, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, S.; Vidorreta, I.; Coelhoso, I.; Lima, J.C.; Desiderio, G.; Lombardo, G.; Drioli, E.; Mallada, R.; Crespo, J.; Criscuoli, A.; et al. Experimental evaluation of the thermal polarization in direct contact membrane distillation using electrospun nanofiber membranes doped with molecular probes. Molecules 2019, 24, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deitzel, J.; Kleinmeyer, J.; Harris, D.; Beck Tan, N. The effect of processing variables on the morphology of electrospun nanofibers and textiles. Polymer 2001, 42, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Xie, R.; Luo, F.; Faraj, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ju, X.J.; Wang, W.; Chu, L.Y. Preparation of high strength poly(vinylidene fluoride) porous membranes with cellular structure via vapor-induced phase separation. J. Memb. Sci. 2018, 549, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarus, B.; Fadel, N.; Al-Oufy, A.; El-Messiry, M. Effect of polymer concentration on the morphology and mechanical characteristics of electrospun cellulose acetate and poly (vinyl chloride) nanofiber mats. Alex. Eng. J. 2016, 55, 2975–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mit-uppatham, C.; Nithitanakul, M.; Supaphol, P. Ultrafine Electrospun Polyamide-6 Fibers: Effect of Solution Conditions on Morphology and Average Fiber Diameter. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2004, 205, 2327–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, F.; Jirsak, O. The effect of salt on the roller electrospinning of polyurethane nanofibers. Fibers Polym. 2009, 10, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.-H.; Yang, E.-L.; Li, N.; Wang, S.-Y. Effect of different salts on electrospinning of polyacrylonitrile (PAN) polymer solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 103, 3865–3870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirazi, M.J.A.; Bazgir, S.; Shirazi, M.M.A.; Ramakrishna, S. Coalescing filtration of oily wastewaters: Characterization and application of thermal treated, electrospun polystyrene filters. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 5974–5986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, W.K.; Youk, J.H.; Lee, T.S.; Park, W.H. The effects of solution properties and polyelectrolyte on electrospinning of ultrafine poly (ethylene oxide) fibers. Polymer 2004, 45, 2959–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massaglia, G.; Quaglio, M. Semiconducting nanofibers in photoelectrochemistry. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 73, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sheng, J. Preparation and properties of electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2005, 97, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, C.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. Nanofibrous materials and their applications. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2006, 36, 333–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, C.M. Hansen Solubility Parameters: A User’s Handbook. Choice Rev. Online 2000, 37, 3905. [Google Scholar]
- Smallwood, I.M. Solvent Recovery Handbook, 2nd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002; p. 13. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, F.; Galiano, F.; Pedace, F.; Aricò, F.; Figoli, A. Dimethyl Isosorbide As a Green Solvent for Sustainable Ultrafiltration and Microfiltration Membrane Preparation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.J.; Stride, E.; Edirisinghe, M. Mapping the Influence of Solubility and Dielectric Constant on Electrospinning Polycaprolactone Solutions. Macromolecules 2012, 45, 4669–4680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Cui, W.; Li, X.; Jin, Y. Electrospun Fibrous Mats with High Porosity as Potential Scaffolds for Skin Tissue Engineering. Biomacromolecules 2008, 9, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, T.; Russo, F.; Figoli, A. The formation of polyvinylidene fluoride membranes with tailored properties via vapour/non-solvent induced phase separation. Membranes 2018, 8, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iulianelli, A.; Russo, F.; Galiano, F.; Desiderio, G.; Basile, A.; Figoli, A. PLA Easy Fil—White-based membranes for CO2 separation. Greenh. Gases Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalia, B.S.; Guillen-Burrieza, E.; Arafat, H.A.; Hashaikeh, R. Fabrication and characterization of polyvinylidenefluoride-co-hexafluoropropylene (PVDF-HFP) electrospun membranes for direct contact membrane distillation. J. Memb. Sci. 2013, 428, 104–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, X.; Ding, B.; Yu, J.; Qian, J.; Sun, G. Controllable fabrication of soap-bubble-like structured polyacrylic acid nano-nets via electro-netting. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthil, T.; Anandhan, S. Effect of Solvents on the Solution Electrospinning of Poly (styrene-co-acrylonitrile). Testing and Measuring. 2017. Available online: www.kgk-rubberpoint.de (accessed on 18 January 2020).
- Akduman, Ç. PVDF Electrospun Nanofiber Membranes for Microfiltration: The Effect of Pore Size and Thickness on Membrane Performance. Avrupa Bilim ve Teknoloji Dergisi 2019, 16, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Na, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, X. Effect of hot-press on electrospun poly (vinylidene fluoride) membranes. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2008, 48, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, T.; Zhan, Z.; Zuo, W.; Cheng, W.; Xu, B.; Su, Y.; Sun, D. Electrospinning PVDF/EC fibre from a binary solvent system. Int. J. Nanomanuf. 2012, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghafi, H.; Brugo, T.; Minak, G.; Zucchelli, A. The effect of PVDF nanofibers on mode-I fracture toughness of composite materials. Compos. Part B Eng. 2015, 72, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, S.; Johnson, B.; Smith, A.L. Optimizing electrospinning parameters for piezoelectric PVDF nanofiber membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Membrane Code | Solutions | Conditions | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polymer | Solvents | Additive | Electrospinning Parameters | Post-Treatment | |||||
| PVDF 6012 | DMSO | DMF | Acetone | LiCl | Needle-to-Collector Distance | Voltage | Air for 2 h; Water for 24 h and in the Oven at 40 °C | 100 °C in the Oven for 1 h; 130 °C between Two Glass Plates | |
| (wt%) | (v/v) | (v/v) | (v/v) | (wt%) | (cm) | (kV) | |||
| M1 | 8 | - | 6 | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 15 | X | - |
| M2 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | - | 15 | 15 | X | - |
| M3 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | - | 15 | 15 | - | X |
| M4 | 6 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 15 | X | - |
| M5 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 15 | X | - |
| M6 | 10 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 15 | X | - |
| M7 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 15 | - | X |
| M8 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 12 | X | - |
| M9 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 15 | 18 | X | - |
| M10 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 10 | 15 | X | - |
| M11 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 20 | 15 | X | - |
| Dope Solutions | Polymer | Solvents | Additive | Viscosity | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF (wt%) | DMSO (v/v) | DMF (v/v) | Acetone (v/v) | LiCl (wt%) | (cP) | |
| DS1 | 8 | - | 6 | 4 | 0.43 | 87.3 |
| DS2 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | - | 79.4 |
| DS3 | 6 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 49.6 |
| DS4 | 8 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 74.4 |
| DS5 | 10 | 6 | - | 4 | 0.43 | 199.3 |
| Compound | HSPs | Dielectric Constant [48] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ẟT (MPa) | ẟd (MPa) | ẟp (MPa) | ẟh (MPa) | ||
| PVDF [49] | 24.2 | 17.2 | 12.5 | 9.2 | - |
| DMF [49] | 24.9 | 17.4 | 13.7 | 11.3 | 37.3 |
| DMSO [49] | 26.7 | 18.4 | 16.4 | 10.2 | 46.7 |
| Code | Contact Angle (°) | Porosity (%) | Pore Size (µm) | Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M1 | 125 ± 2 | 93 ± 1 | 0.81 ± 0.04 | 69 ± 1 |
| M2 | 123 ± 3 | 74 ± 1 | 2.29 ± 0.03 | 49 ± 2 |
| M3 | 128 ± 1 | 95 ± 1 | 2.26 ± 0.08 | 35 ± 1 |
| M4 | 125 ± 3 | 92 ± 1 | 0.87 ± 0.08 | 65 ± 3 |
| M5 | 125 ± 2 | 93 ± 1 | 0.90 ± 0.08 | 73 ± 1 |
| M6 | 122 ± 2 | 97 ± 1 | 1.03 ± 0.02 | 76 ± 2 |
| M7 | 127 ± 4 | 91 ± 3 | 1.27 ± 0.02 | 54 ± 2 |
| M8 | 126 ± 1 | 95 ± 1 | 1.19 ± 0.04 | 67 ± 1 |
| M9 | 128 ± 1 | 96 ± 1 | 1.06 ± 0.05 | 79 ± 1 |
| M10 | 125 ± 2 | 96 ± 1 | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 42 ± 2 |
| M11 | 114 ± 3 | 94 ± 1 | 0.93 ± 0.03 | 75 ± 1 |
| Solvent 1 | Toxicity 2 | PVDF Conc. (wt.%) | Electrosp. Temp. (°C) | Fiber Appearance | Pore Size | Post Treatment | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DMA | Hazardous | 12–16 | Room temperature | Uniform PVDF nanofibers | 2–5.88 | - | [57] |
| 10–15 | Continuous hot-press-2 layers | Some beads are present at lower concentrations | 0.26–1.49 | Dried at 50 °C for 24 h in the oven | [54] | ||
| DMF | Hazardous | 19 | Continuous hot-press at 145 °C; | Networks with large pores | - | 40-55 °C for 12 h in the oven | [58] |
| 6 | Room temperature | Some beads are present | 0.91–1.12 | Pressed between two flat glass panes and placed at 170 °C in an oven | [29] | ||
| NMP | Hazardous | 16–20 | Room temperature | Beads disappear and there are uniform fibres at lower concentration | - | 100 °C in the oven | [59] |
| DMSO | Less Hazardous | 6–10 | Room temperature | Uniform nanofibers | 0.8–2.29 | Air for 2 h; water for 24 h and at 40 °C in the oven | This work |
| 15 | Room temperature | Some beads are presents | - | - | [60] | ||
| 12 | Room temperature | Uniform nanofiber | 2.4 | Heat treatment | [61] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Russo, F.; Ursino, C.; Avruscio, E.; Desiderio, G.; Perrone, A.; Santoro, S.; Galiano, F.; Figoli, A. Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent. Membranes 2020, 10, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030036
Russo F, Ursino C, Avruscio E, Desiderio G, Perrone A, Santoro S, Galiano F, Figoli A. Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent. Membranes. 2020; 10(3):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030036
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusso, Francesca, Claudia Ursino, Elisa Avruscio, Giovanni Desiderio, Andrea Perrone, Sergio Santoro, Francesco Galiano, and Alberto Figoli. 2020. "Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent" Membranes 10, no. 3: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030036
APA StyleRusso, F., Ursino, C., Avruscio, E., Desiderio, G., Perrone, A., Santoro, S., Galiano, F., & Figoli, A. (2020). Innovative Poly (Vinylidene Fluoride) (PVDF) Electrospun Nanofiber Membrane Preparation Using DMSO as a Low Toxicity Solvent. Membranes, 10(3), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10030036










