Effect of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA), on the Internal Structure, Fouling Characteristics, and Dye Rejection Mechanism of PVDF Membranes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
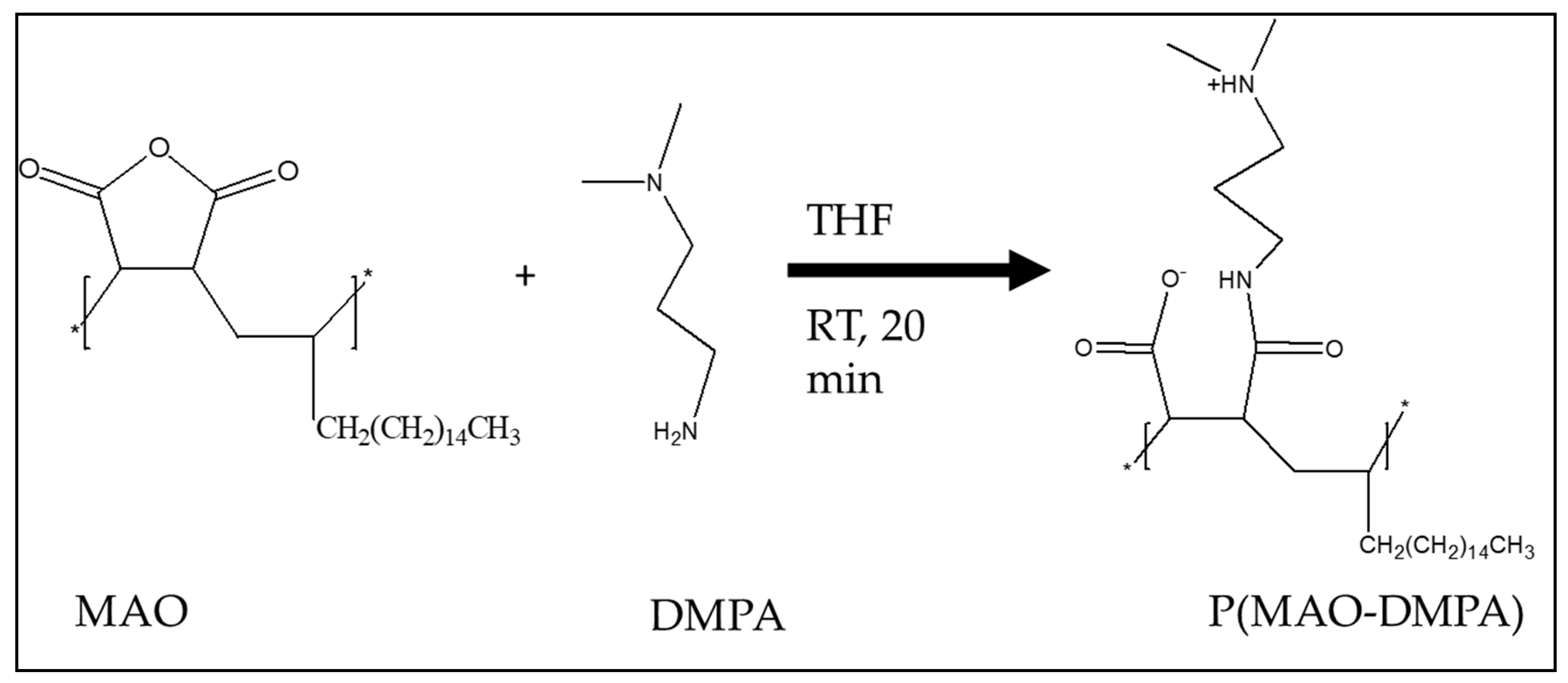
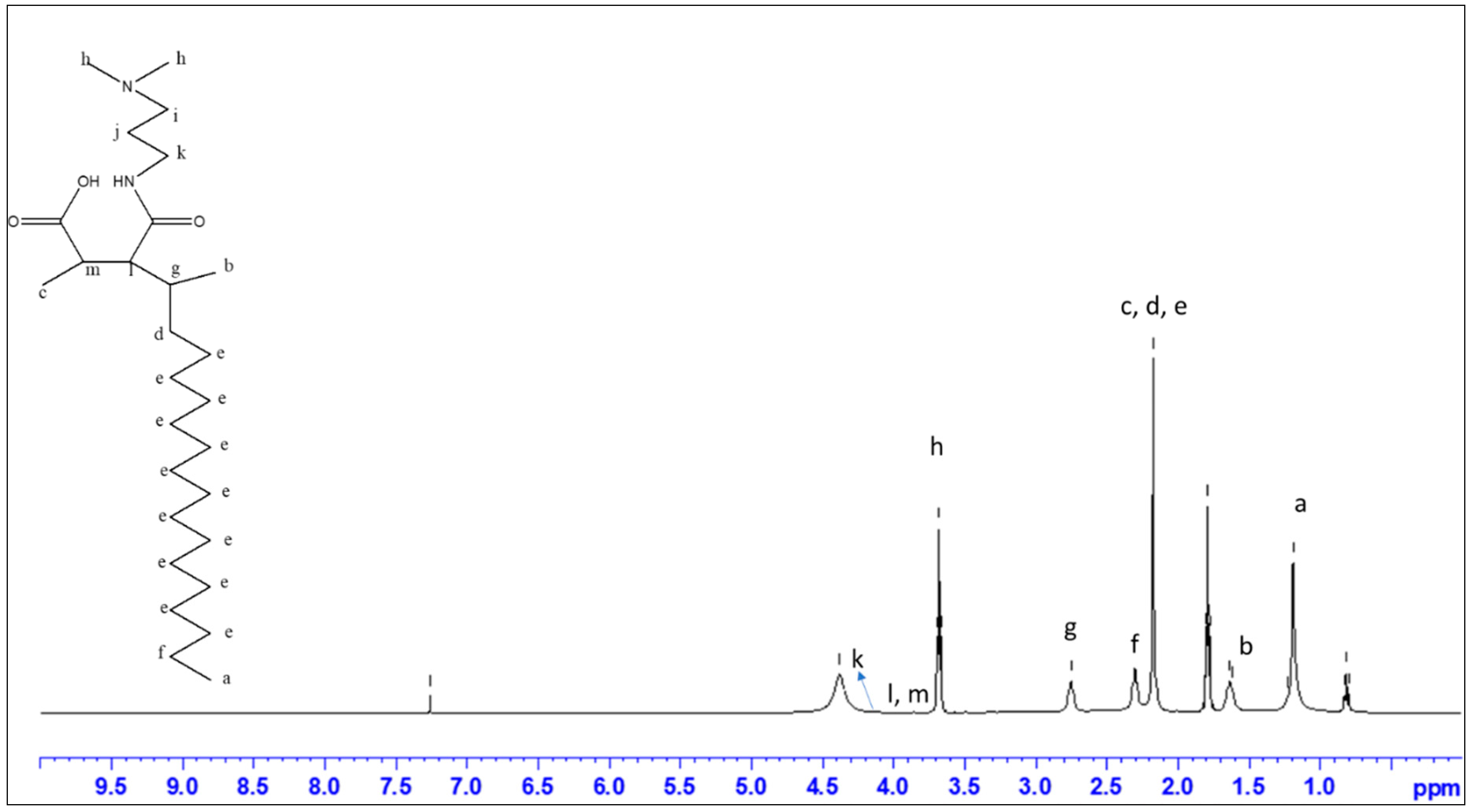
2.2. Synthesis of p(MAO-DMPA)
2.3. Preparation of Membranes
2.4. Characterization of the Membranes
2.5. Membrane Performance Assessment
3. Results and Discussion
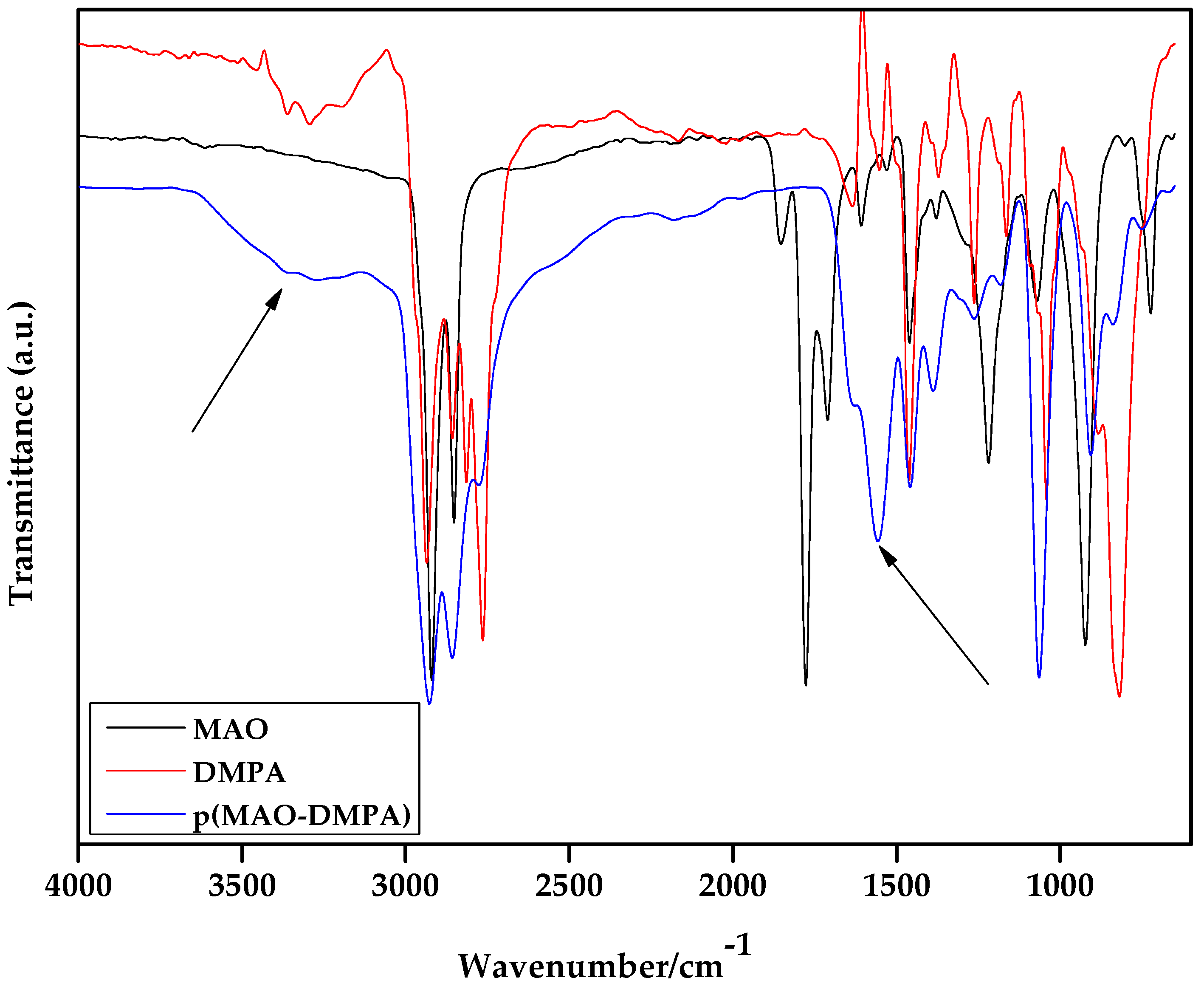
3.1. Characterization of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA)
3.2. Characterization and Membrane Performance of the Ultrafiltration Membranes
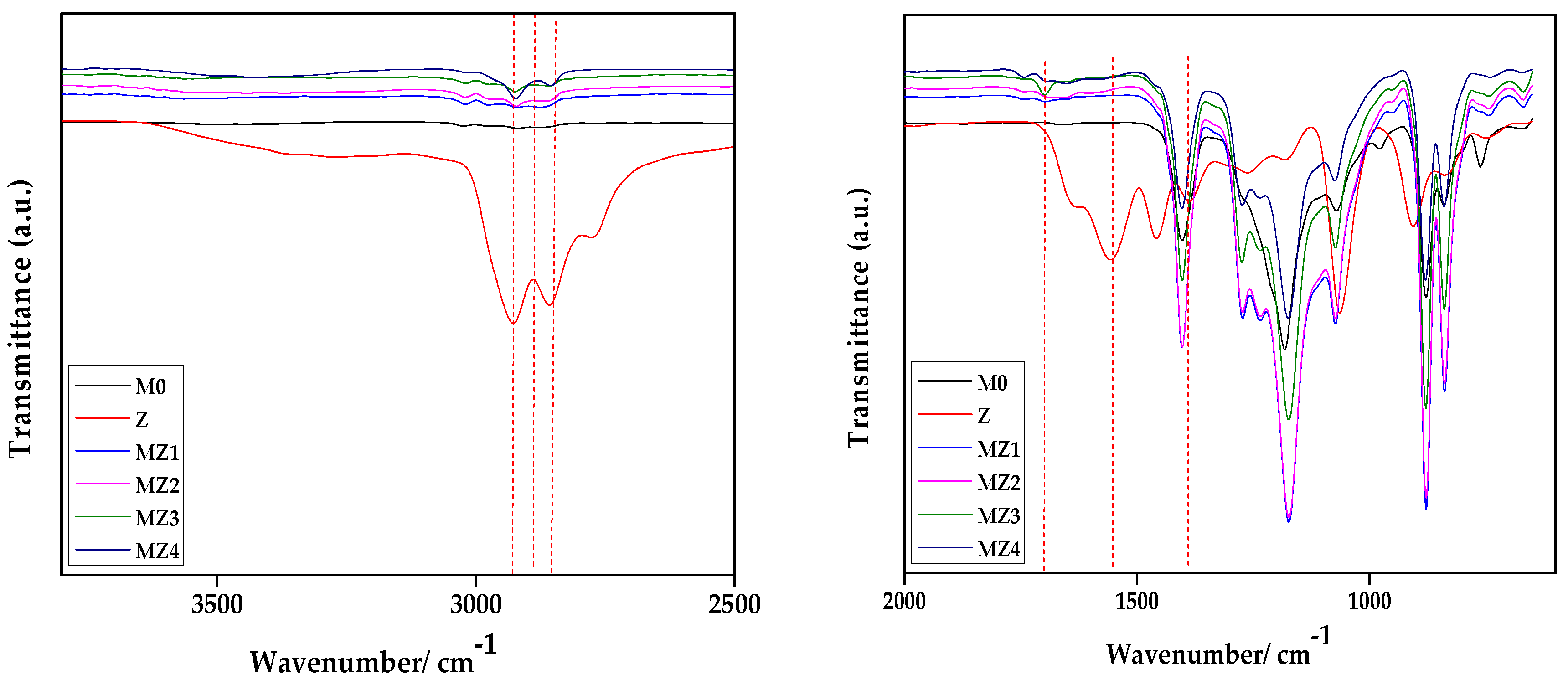
3.2.1. FTIR Analysis
3.2.2. SEM Analysis
3.2.3. AFM Analysis
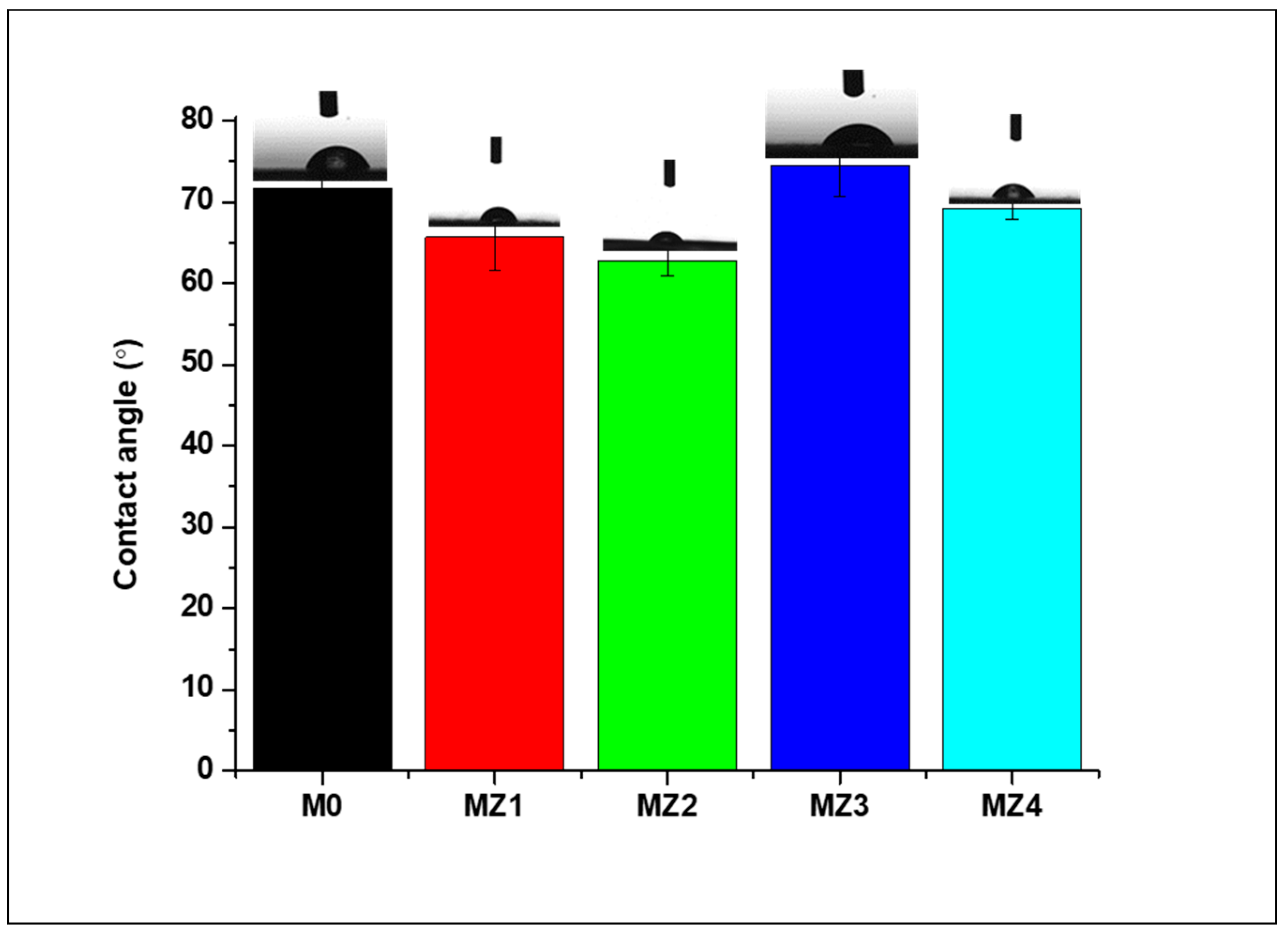
3.2.4. Water Contact Angle Analysis
3.2.5. Water Uptake and Porosity Studies
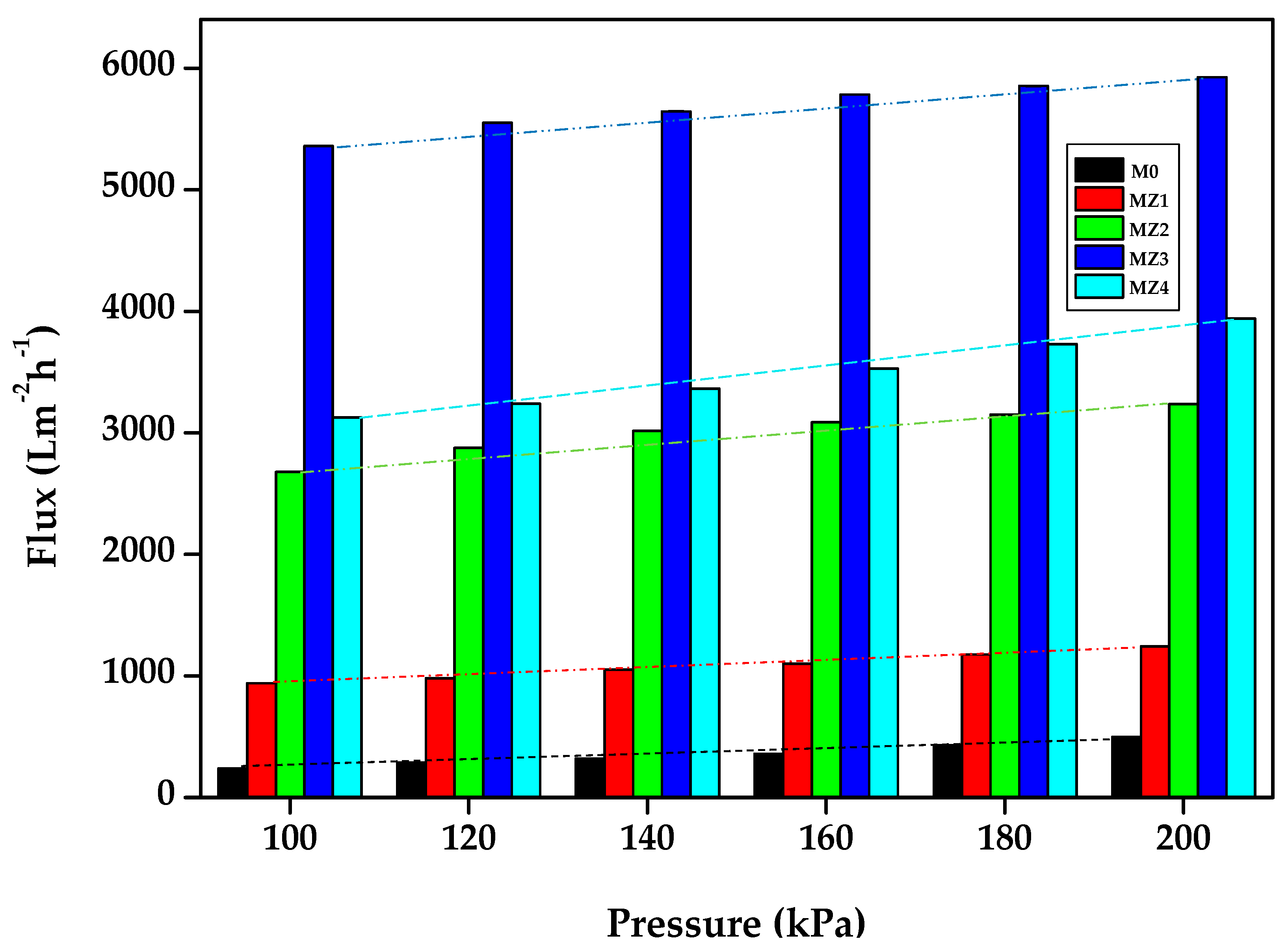
3.3. Membrane Permeation Flux
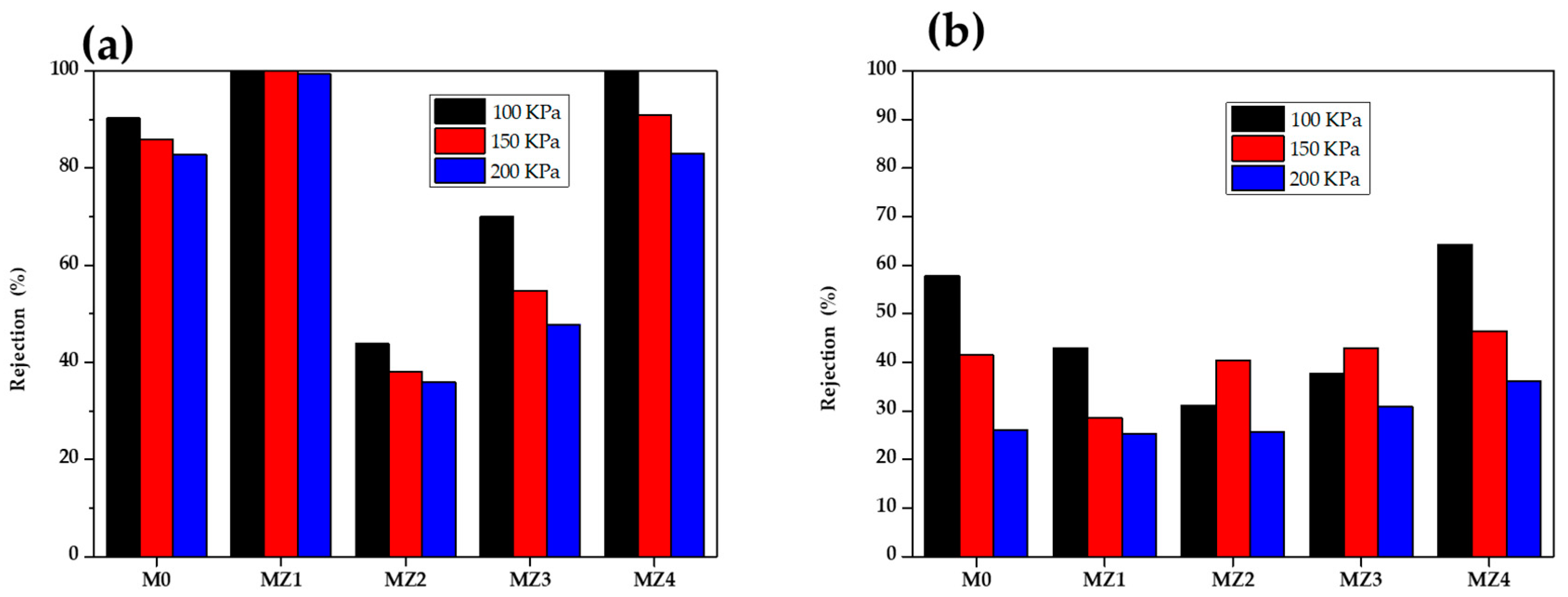
3.4. Dye Rejection Studies
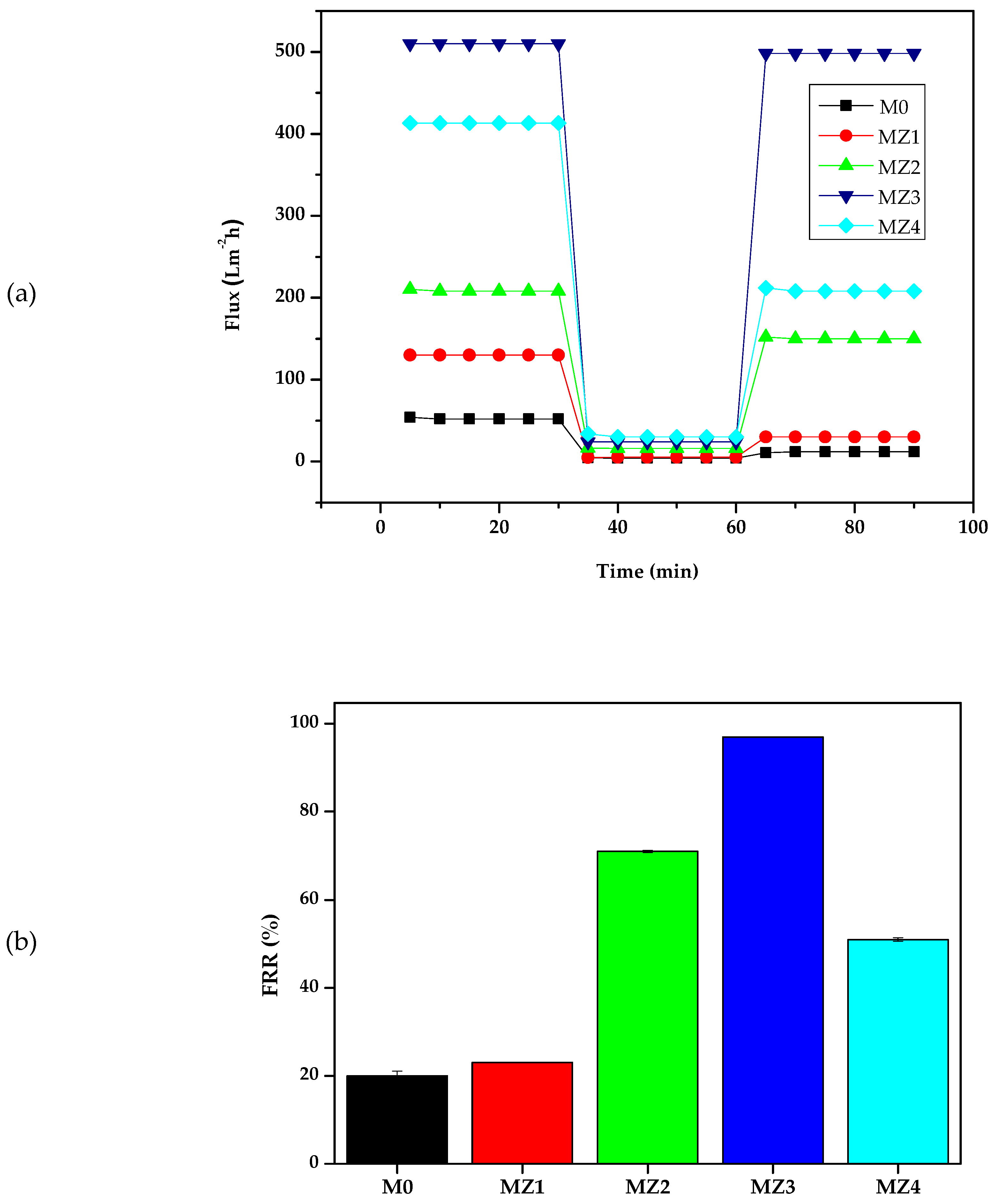
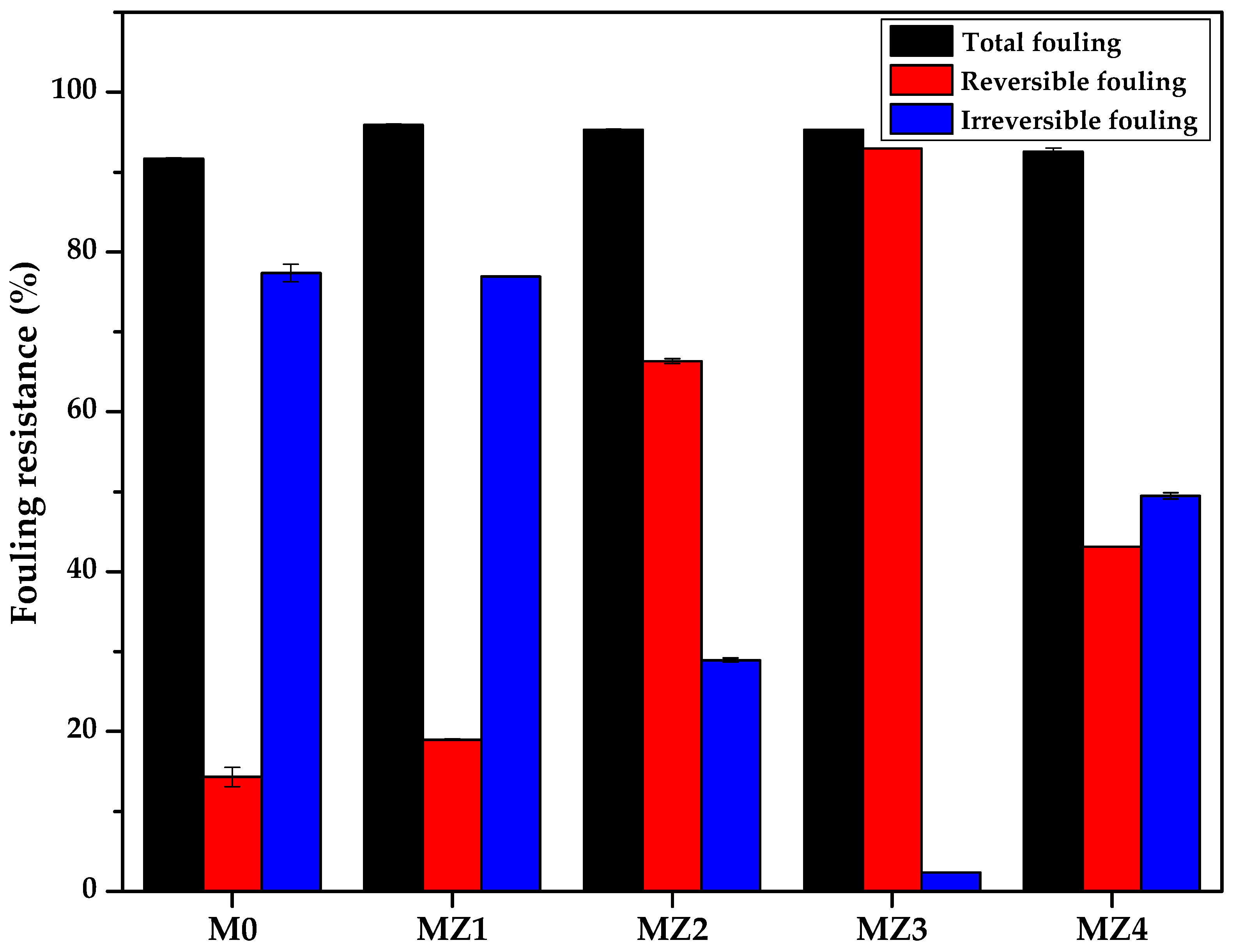
3.5. Antifouling Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, S.; Khajuria, R. Penicillium Enzymes for the Textile Industry. In New and Future Developments in Microbial Biotechnology and Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 201–215. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R. Characterization and Treatment of Textile Wastewater; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, B.-J.; Jiang, W.-L.; Dong, Y.; Liu, Z.-X.; Dong, Y. Post-Synthetic Polymerization of UiO-66-NH2 Nanoparticles and Polyurethane Oligomer toward Stand-Alone Membranes for Dye Removal and Separation. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10565–10571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Liao, B.-Q.; Shen, L.; Lin, H. A conductive PVDF-Ni membrane with superior rejection, permeance and antifouling ability via electric assisted in-situ aeration for dye separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 581, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhetha, T.; Moutloali, R. Antifouling properties of Cu(tpa)@GO/PES composite membranes and selective dye rejection. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 554, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Shen, L.; Lin, H.; Liao, B.-Q.; Wu, G.; Wu, G. Novel conductive membranes breaking through the selectivity-permeability trade-off for Congo red removal. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahe, D.; Heidari, A. A Review on Separation Techniques of Graphene Oxide (GO)/Base on Hybrid Polymer Membranes for Eradication of Dyes and Oil Compounds: Recent Progress in Graphene Oxide (GO)/Base on Polymer Membranes-Related Nanotechnologies. Clin. Med Rev. Case Rep. 2018, 5, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Vashi, R.T. Characterization and column adsorptive treatment for cod and color removal using activated neem leaf powder from textile wastewater. J. Urban Environ. Eng. 2015, 9, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.; Patra, A.S.; Ghorai, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Mahato, V.; Sarkar, S.; Singh, R.P. Efficient and rapid adsorption characteristics of templating modified guar gum and silica nanocomposite toward removal of toxic reactive blue and Congo red dyes. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahrim, A.; Tizaoui, C.; Hilal, N. Coagulation with polymers for nanofiltration pre-treatment of highly concentrated dyes: A review. Desalination 2011, 266, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-R.; Kim, E.-J.; Kim, Y.-M.; Murugesan, K.; Kim, J.; Chang, Y.-S. Use of grape seed and its natural polyphenol extracts as a natural organic coagulant for removal of cationic dyes. Chemosphere 2009, 77, 1090–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, N.; Reetha, D.; Saranraj, P. Biological degradation of Reactive dyes by using bacteria isolated from dye effluent contaminated soil. Middle East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 17, 1695–1700. [Google Scholar]
- Punzi, M.; Anbalagan, A.; Börner, R.A.; Svensson, B.-M.; Jonstrup, M.; Mattiasson, B. Degradation of a textile azo dye using biological treatment followed by photo-Fenton oxidation: Evaluation of toxicity and microbial community structure. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 270, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.L.; Xu, L.J. Advanced Oxidation Processes for Wastewater Treatment: Formation of Hydroxyl Radical and Application. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 42, 251–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidheesh, P.; Zhou, M.; Oturan, M.A. An overview on the removal of synthetic dyes from water by electrochemical advanced oxidation processes. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 210–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katheresan, V.; Kansedo, J.; Lau, S.Y. Efficiency of various recent wastewater dye removal methods: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 4676–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagub, M.T.; Sen, T.K.; Afroze, S.; Ang, H. Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 209, 172–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, X.; Vo, T.; Ngo, H.; Guo, W.; Nguyen, T. Multicriteria assessment of advanced treatment technologies for micropollutants removal at large-scale applications. Sci. Total. Environ. 2016, 563, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Du, P.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H.; Cheng, X.; Chang, B.; Wang, Z. Advances in microbial fuel cells for wastewater treatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 71, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Ye, W.; Baltaru, M.-C.; Tang, Y.P.; Bernstein, N.J.; Gao, P.; Balta, S.; Vlad, M.; Volodin, A.; Sotto, A.; et al. Tight ultrafiltration membranes for enhanced separation of dyes and Na2SO4 during textile wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuli, B.; Mahlambi, M.; Ngila, C.J.; Moutloali, R. Polysulfone Ultrafiltration Membranes Modified with Carbon-Coated Alumina Supported NiTiO2 Nanoparticles for Water Treatment: Synthesis, Characterization and Application. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2019, 5, 222–232. [Google Scholar]
- Aroon, M.; Ismail, A.; Matsuura, T.; Montazer-Rahmati, M. Performance studies of mixed matrix membranes for gas separation: A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 75, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Huang, W.-Y.; Hsiao, S.-W.; Chinnathambi, A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Chen, H.; Zheng, J.; Chang, Y. Zwitterionic Modifications for Enhancing the Antifouling Properties of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Membranes. Langmuir 2016, 32, 4113–4124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, G.-D.; Cao, Y.-M. Application and modification of poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) membranes—A review. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 463, 145–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlotman, D.E.; Ngila, C.J.; Ndlovu, T.; Malinga, S.P. Hyperbranched Polymer Integrated Membrane for the Removal of Arsenic (III) in Water. J. Membr. Sci. Res. 2018, 4, 53–62. [Google Scholar]
- Venault, A.; Chang, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-C.; Chang, H.-Y.; Bouyer, D.; Lee, K.-R.; Chang, Y. Surface zwitterionization of PVDF VIPS membranes for oil and water separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 563, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takht, M.; Kargari, A. New Advances in Membrane Technology. In Advanced Technologies; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Mosikatsi, B.E.; Mabuba, N.; Malinga, S.P. Thin film composite membranes consisting of hyperbranched polyethylenimine (HPEI)-cysteamine layer for cadmium removal in water. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 30, 100686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ong, Y.K.; Li, F.Y.; Sun, S.-P.; Zhao, B.-W.; Liang, C.-Z.; Chung, T.-S. Nanofiltration hollow fiber membranes for textile wastewater treatment: Lab-scale and pilot-scale studies. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2014, 114, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkhomashi, N.; Al-Hamarneh, I.F.; Almasoud, F.I. Determination of natural radioactivity in irrigation water of drilled wells in northwestern Saudi Arabia. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1928–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, L.Y.; Mohammad, A.W.; Leo, C.P.; Hilal, N. Polymeric membranes incorporated with metal/metal oxide nanoparticles: A comprehensive review. Desalination 2013, 308, 15–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Chae, H.-R.; Won, Y.J.; Lee, K.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, H.H.; Kim, I.-C.; Lee, J.-M. Graphene oxide nanoplatelets composite membrane with hydrophilic and antifouling properties for wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 448, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaisamy, R.; Mohan, D.R.; Rajendran, M. Polyurethane and sulfonated polysulfone blend ultrafiltration membranes. I. Preparation and characterization studies. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 254, 129–140. [Google Scholar]
- Malaisamy, R.; Mohan, D.R.; Rajendran, M. Polyurethane and sulfonated polysulfone blend ultrafiltration membranes: II. Application studies. Polym. Int. 2003, 52, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Xu, R.; Lü, Z.; Yu, S.; Liu, M.; Gao, C. Enhanced both perm-selectivity and fouling resistance of poly(piperazine-amide) nanofiltration membrane by incorporating sericin as a co-reactant of aqueous phase. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 523, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fan, X.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Constructing a zwitterionic ultrafiltration membrane surface via multisite anchorage for superior long-term antifouling properties. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 40126–40134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.-L.; An, Q.-F.; Weng, X.-D.; Hung, W.-S.; Lee, K.-R.; Gao, C.-J. Microstructure and performance of zwitterionic polymeric nanoparticle/polyamide thin-film nanocomposite membranes for salts/organics separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, M.; Sadeghi, M.; Chenar, M.P. Improving antifouling performance of PAN hollow fiber membrane using surface modification method. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2015, 55, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Su, Y.; Chen, W.; Peng, J.; Jiang, Z. Grafting perfluoroalkyl groups onto polyacrylonitrile membrane surface for improved fouling release property. J. Membr. Sci. 2012, 415, 824–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Gao, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhan, X.; Chen, F. Enhanced oil-fouling resistance of poly(ether sulfone) membranes by incorporation of novel amphiphilic zwitterionic copolymers. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 7532–7543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Chung, T.-S.; Han, G.; Chung, T.-S. Novel thin-film composite nanofiltration membranes consisting of a zwitterionic co-polymer for selenium and arsenic removal. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 555, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Tian, M.; Hou, J.; Wang, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Surface zwitterionic functionalized graphene oxide for a novel loose nanofiltration membrane. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 1980–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yin, Y.; Cao, L.; Wu, H. Zwitterionic functionalized “cage-like” porous organic frameworks for nanofiltration membrane with high efficiency water transport channels and anti-fouling property. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 548, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, M.; He, C. Antifouling performance of poly(lysine methacrylamide)-grafted PVDF microfiltration membrane for solute separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 171, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, M.; He, C. Antifouling PVDF membrane grafted with zwitterionic poly(lysine methacrylamide) brushes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61434–61442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, D.; Pei, X.F.; Zhang, W.; Jin, J. A novel zwitterionic polyelectrolyte grafted PVDF membrane for thoroughly separating oil from water with ultrahigh efficiency. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5758–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, A.; Went, M.; Prager, A. Membrane Functionalization with Hyperbranched Polymers. Materials 2016, 9, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arumugham, T.; Kaleekkal, N.J.; Doraiswamy, M. Development of new hybrid ultrafiltration membranes by entanglement of macromolecular PPSU-SO3H chains: Preparation, morphologies, mechanical strength, and fouling resistant properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Matsuyama, H. Preparation of antifouling poly(vinylidene fluoride) membranes via different coating methods using a zwitterionic copolymer. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ngo, H.-H.; Li, J. A mini-review on membrane fouling. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 122, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.-C.; Yeh, L.-C.; Venault, A.; Tsai, S.-C.; Hsu, C.-H.; Dizon, G.V.; Huang, Y.-T.; Higuchi, A.; Chang, Y. Controlling the zwitterionization degree of alternate copolymers for minimizing biofouling on PVDF membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 565, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Zhang, X.; Ma, X. The surface tunability and dye separation property of PVDF porous membranes modified by P(MMA-b-MEBIm-Br): Effect of poly(ionic liquid) brush lengths. J. Polym. Res. 2020, 27, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shan, M.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Niu, J.; Zhou, B.; Qian, X. Organosilane-functionalized graphene oxide for enhanced antifouling and mechanical properties of polyvinylidene fluoride ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 458, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziya, K.; Dlamini, B.C.; Malinga, S.P. Hyperbranched polymer nanofibrous membrane grafted with silver nanoparticles for dual antifouling and antibacterial properties against Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. React. Funct. Polym. 2020, 148, 104494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.; Wakeman, R. Membrane fouling and alternative techniques for its alleviation. Membr. Technol. 2000, 2000, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaram, H.S.; Han, X.; Nowinski, A.K.; Ella-Menye, J.R.; Wimbish, C.; Marek, P.; Senecal, K.; Jiang, S. One-step dip coating of zwitterionic sulfobetaine polymers on hydrophobic and hydrophilic surfaces. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 6664–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Liu, Y.; He, M.; Su, Y.; Zhao, X.; Elimelech, M.; Jiang, Z. Antifouling membranes for sustainable water purification: Strategies and mechanisms. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 5888–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahkaramipour, N.; Tran, T.; Ramanan, S.; Lin, H. Membranes with Surface-Enhanced Antifouling Properties for Water Purification. Membranes 2017, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, J.; Bhuvana, S.; Boodhoo, K.; Anbharasi, V.; Singh, G. Synthesis and characterization of PEG-Ag immobilized PES hollow fiber ultrafiltration membranes with long lasting antifouling properties. J. Membr. Sci. 2014, 454, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, D.-Y.; Xu, Y.-Y.; Xu, W.; Zou, H. The influence of PEG molecular weight on morphologies and properties of PVDF asymmetric membranes. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2008, 26, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahkaramipour, N.; Ramanan, S.N.; Fister, D.; Park, E.; Venna, S.R.; Sun, H.; Cheng, C.; Lin, H. Facile Grafting of Zwitterions onto the Membrane Surface to Enhance Antifouling Properties for Wastewater Reuse. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 9202–9212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damodaran, V.B.; Murthy, N.S. Bio-inspired strategies for designing antifouling biomaterials. Biomater. Res. 2016, 20, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, C.; Sun, S.; Zhang, K.; Jiang, S.; Zhan, C. Molecular level studies on interfacial hydration of zwitterionic and other antifouling polymers in situ. Acta Biomater. 2016, 40, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhang, D.; Xie, S.; Chang, Y.; Yang, J.; Wu, J.; Xu, L.; Zheng, J. Fundamentals and applications of zwitterionic antifouling polymers. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2019, 52, 403001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaraj, A.P.J.; Bhuvana, S.; Anbharasi, V.; Ayyanar, N.; Boodhoo, K.V.K.; Singh, G. Self-cleaning Metal Organic Framework (MOF) based ultra filtration membranes—A solution to bio-fouling in membrane separation processes. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6555. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; He, C. Efficient Preparation of Super Antifouling PVDF Ultrafiltration Membrane with One Step Fabricated Zwitterionic Surface. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 17947–17953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Shaikh, A.R.; Kakihana, Y.; Sun, Y.; Matsuyama, H. Effect of type of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) based amphiphilic copolymer on antifouling properties of copolymer/poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF) blend membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 514, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dizon, G.V.; Venault, A. Direct in-situ modification of PVDF membranes with a zwitterionic copolymer to form bi-continuous and fouling resistant membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2018, 550, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, P.; Dudchenko, A.V.; Mauter, M.S.; Asatekin, A. Zwitterionic copolymer additive architecture affects membrane performance: Fouling resistance and surface rearrangement in saline solutions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 4829–4846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.L.; Ideris, N.; Ooi, B.S.; Low, S.C.; Ismail, A. Synthesis of polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) membranes for protein binding: Effect of casting thickness. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 128, 3438–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekambaram, K.; Doraisamy, M. Surface modification of PVDF nanofiltration membrane using Carboxymethylchitosan-Zinc oxide bionanocomposite for the removal of inorganic salts and humic acid. Colloids Surfaces A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 525, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khumalo, N.P.; Nthunya, L.N.; De Canck, E.; Derese, S.; Verliefde, A.R.; Kuvarega, A.T.; Mamba, B.B.; Mhlanga, S.D.; Dlamini, D.S. Congo red dye removal by direct membrane distillation using PVDF/PTFE membrane. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 211, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaner, P.; Rubakh, E.; Kim, D.H.; Asatekin, A. Zwitterion-containing polymer additives for fouling resistant ultrafiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2017, 533, 141–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Rao, T.S.; Isloor, A.M.; Ibrahim, G.P.S.; Inamuddin; Ismail, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Asiri, A.M. Use of cellulose acetate/polyphenylsulfone derivatives to fabricate ultrafiltration hollow fiber membranes for the removal of arsenic from drinking water. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalik-Klimczak, A.; Gierycz, P. Scaling of nanofiltration membranes used for chromium(III) ions recovery from salt solutions. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 3135–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.-X.; Huang, X.-C.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.-M.; Tang, C.Y. A thin-film nanocomposite nanofiltration membrane prepared on a support with in situ embedded zeolite nanoparticles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.-S.; Mi, Y.-F.; Zhao, F.-Y.; Ji, Y.-L.; An, Q.-F.; Gao, C.-J. Zwitterions functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes/polyamide hybrid nanofiltration membranes for monovalent/divalent salts separation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2018, 206, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Q.; Sun, W.-D.; Zhao, Q.; Ji, Y.-L.; Gao, C.-J. Study on a novel nanofiltration membrane prepared by interfacial polymerization with zwitterionic amine monomers. J. Membr. Sci. 2013, 431, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, K.; Gondal, M. Removal of hazardous Rhodamine dye from water by adsorption onto exhausted coffee ground. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2017, 21, S120–S127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotlhao, K.; Lawal, I.A.; Moutloali, R.M.; Klink, M.J. Antifouling Properties of Silver-Zinc Oxide Polyamide Thin Film Composite Membrane and Rejection of 2-Chlorophenol and 2,4-Dichlorophenol. Membranes 2019, 9, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le-Clech, P.; Chen, V.; Fane, T.A.G. Fouling in membrane bioreactors used in wastewater treatment. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 284, 17–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akther, N.; Phuntsho, S.; Chen, Y.; Ghaffour, N.; Shon, H. Recent advances in nanomaterial-modified polyamide thin-film composite membranes for forward osmosis processes. J. Membr. Sci. 2019, 584, 20–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, K.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Relation between membrane characteristics and performance in nanofiltration. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 310, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussu, K.; Belpaire, A.; Volodin, A.; Van Haesendonck, C.; Van Der Meeren, P.; Vandecasteele, C.; Van Der Bruggen, B. Influence of membrane and colloid characteristics on fouling of nanofiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2007, 289, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijesh, A.; Krishnan, P.A.; Isloor, A.M.; Shyma, P. Fabrication of PPSU/PANI Hollow Fiber Membranes for Humic Acid Removal; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020. [Google Scholar]



| Description | Membrane ID | PVDF (wt.%) | PEG (wt.%) | P(MAO-DMPA) (wt.%) | NMP (wt.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M0 | PVDF/PEG | 16.00 | 2.00 | ------ | 82.00 |
| MZ1 | PVDF/PEG/Z1 | 16.00 | 2.00 | 0.50 | 81.50 |
| MZ2 | PVDF/PEG/Z2 | 16.00 | 2.00 | 1.00 | 81.00 |
| MZ3 | PVDF/PEG/Z3 | 16.00 | 2.00 | 1.50 | 80.50 |
| MZ4 | PVDF/PEG/Z4 | 16.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 80.00 |
| Membranes | Water Uptake (%) | Porosity (%) | Pore Size (um) | Thickness (µm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MZ0 | 320 | 2.08 | 0.342 | 92.12 |
| MZ1 | 554 | 2.71 | 0.235 | 97.18 |
| MZ2 | 982 | 4.21 | 0.169 | 94.40 |
| MZ3 | 567 | 3.10 | 0.150 | 96.01 |
| MZ4 | 765 | 2.30 | 0.156 | 129.11 |
| Membranes | Roughness Parameters | |
|---|---|---|
| Ra (nm) | Rq (nm) | |
| M0 | 37.8 | 46.8 |
| MZ1 | 60.7 | 77.4 |
| MZ2 | 56.2 | 78.8 |
| MZ3 | 54.1 | 71.7 |
| MZ4 | 28.3 | 34.3 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gaxela, N.N.; Nomngongo, P.N.; Moutloali, R.M. Effect of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA), on the Internal Structure, Fouling Characteristics, and Dye Rejection Mechanism of PVDF Membranes. Membranes 2020, 10, 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110323
Gaxela NN, Nomngongo PN, Moutloali RM. Effect of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA), on the Internal Structure, Fouling Characteristics, and Dye Rejection Mechanism of PVDF Membranes. Membranes. 2020; 10(11):323. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110323
Chicago/Turabian StyleGaxela, Nelisa Ncumisa, Philiswa Nosizo Nomngongo, and Richard Motlhaletsi Moutloali. 2020. "Effect of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA), on the Internal Structure, Fouling Characteristics, and Dye Rejection Mechanism of PVDF Membranes" Membranes 10, no. 11: 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110323
APA StyleGaxela, N. N., Nomngongo, P. N., & Moutloali, R. M. (2020). Effect of the Zwitterion, p(MAO-DMPA), on the Internal Structure, Fouling Characteristics, and Dye Rejection Mechanism of PVDF Membranes. Membranes, 10(11), 323. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes10110323








