Surface Immunogenic Protein of Streptococcus Group B is an Agonist of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and a Potential Immune Adjuvant
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Mice Strains
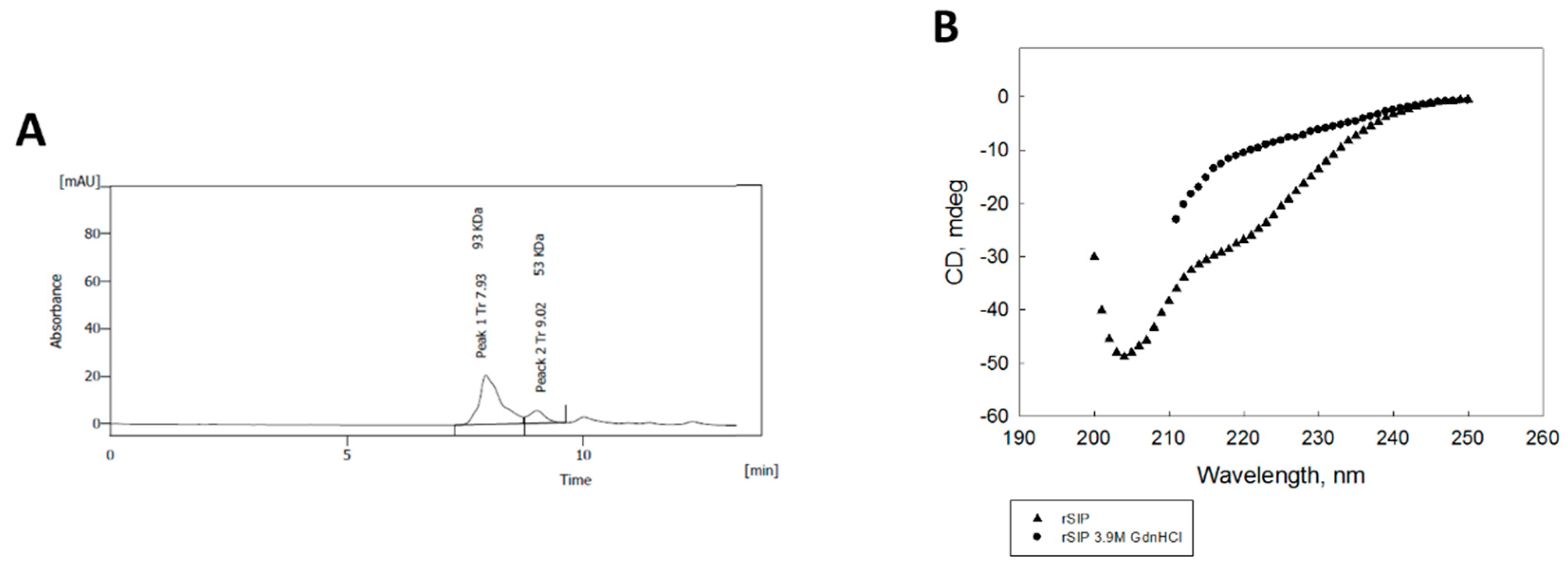
2.3. Purification of Recombinant SIP
2.4. Circular Dichroism Measurements
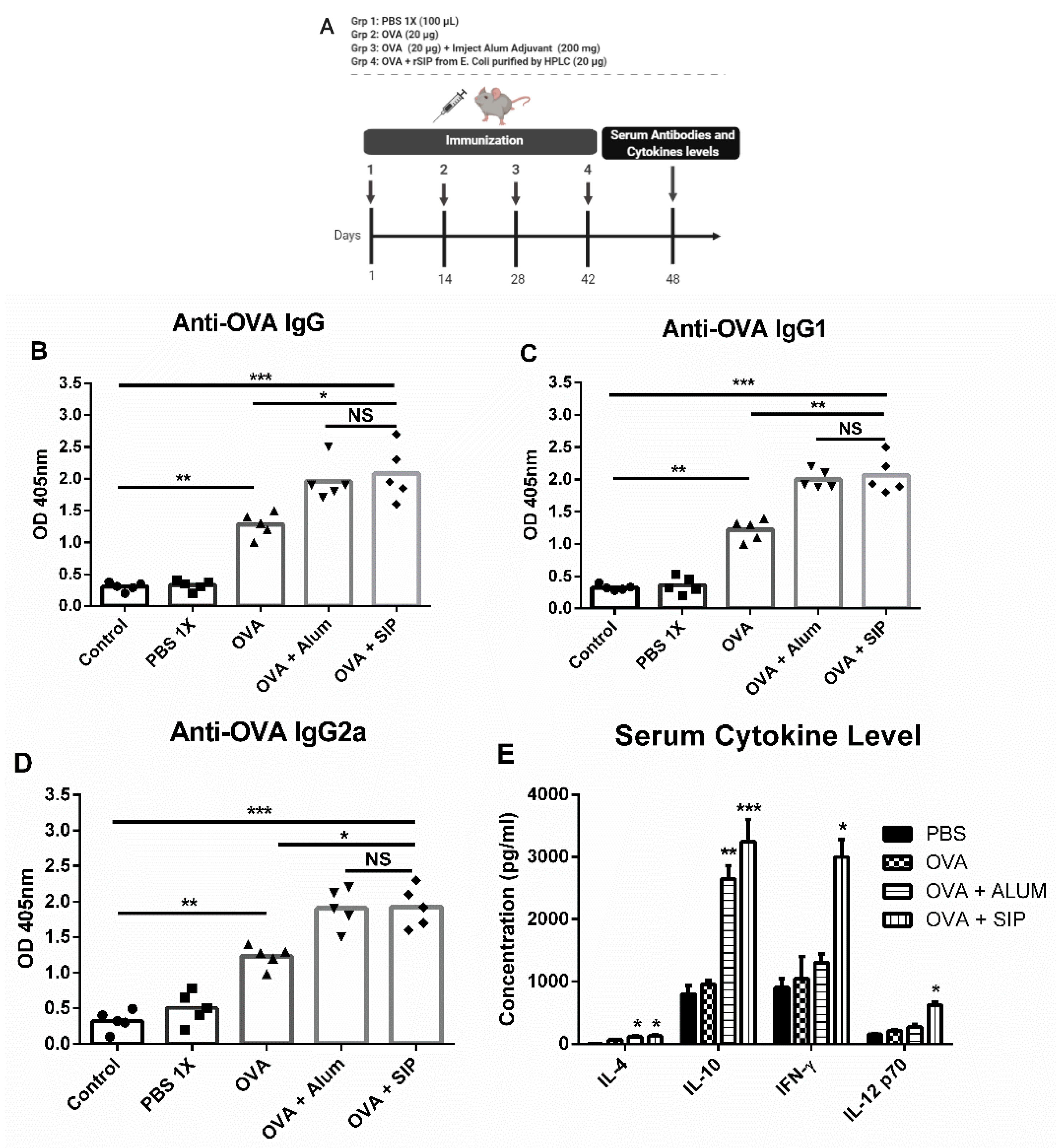
2.5. Animal Immunization
2.6. Measurement of Anti-OVA Specific Antibodies
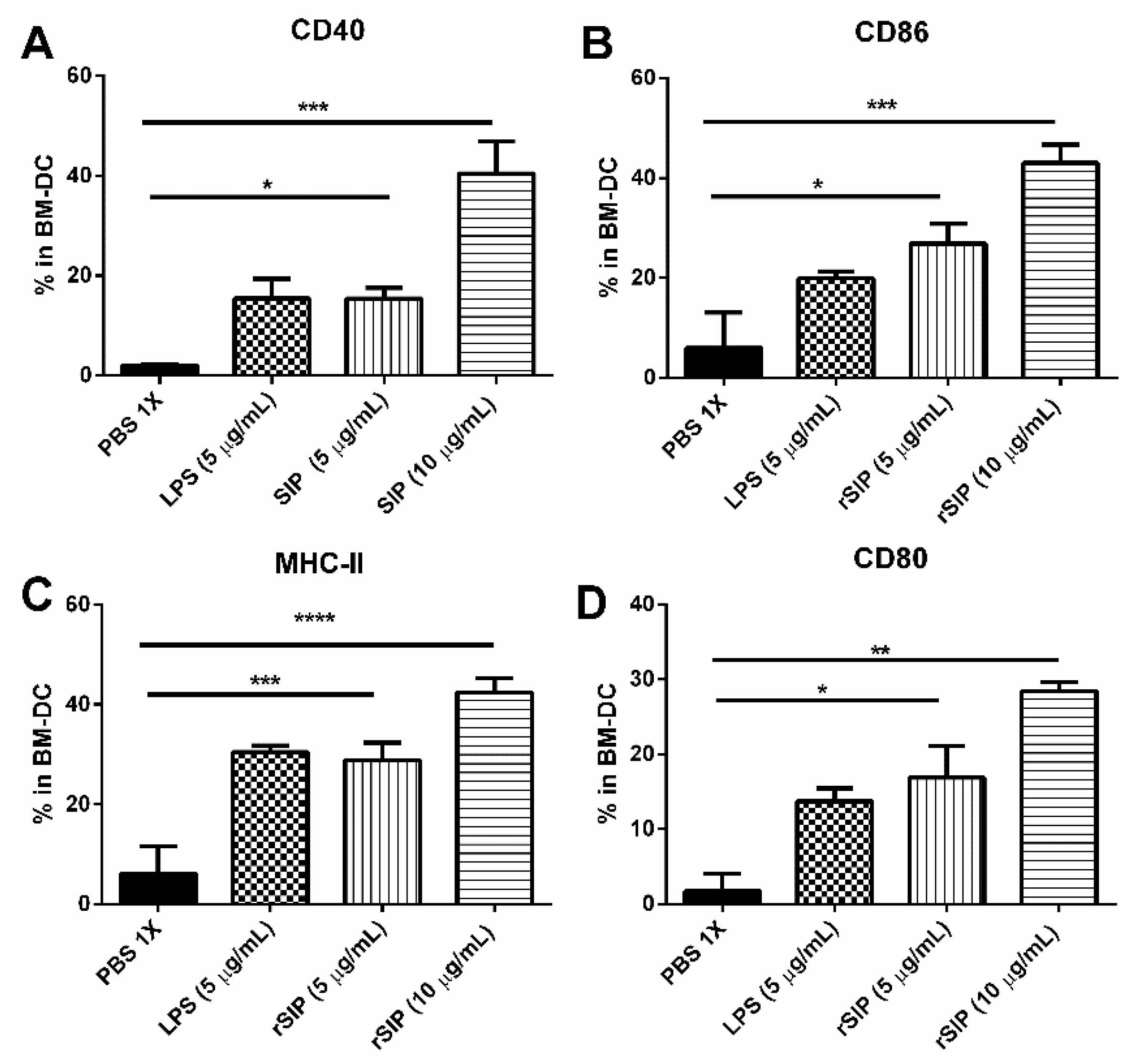
2.7. Bone Marrow Dendritic Cell Culture
2.8. Flow Cytometry Analysis of BM-DC Phenotypic Markers
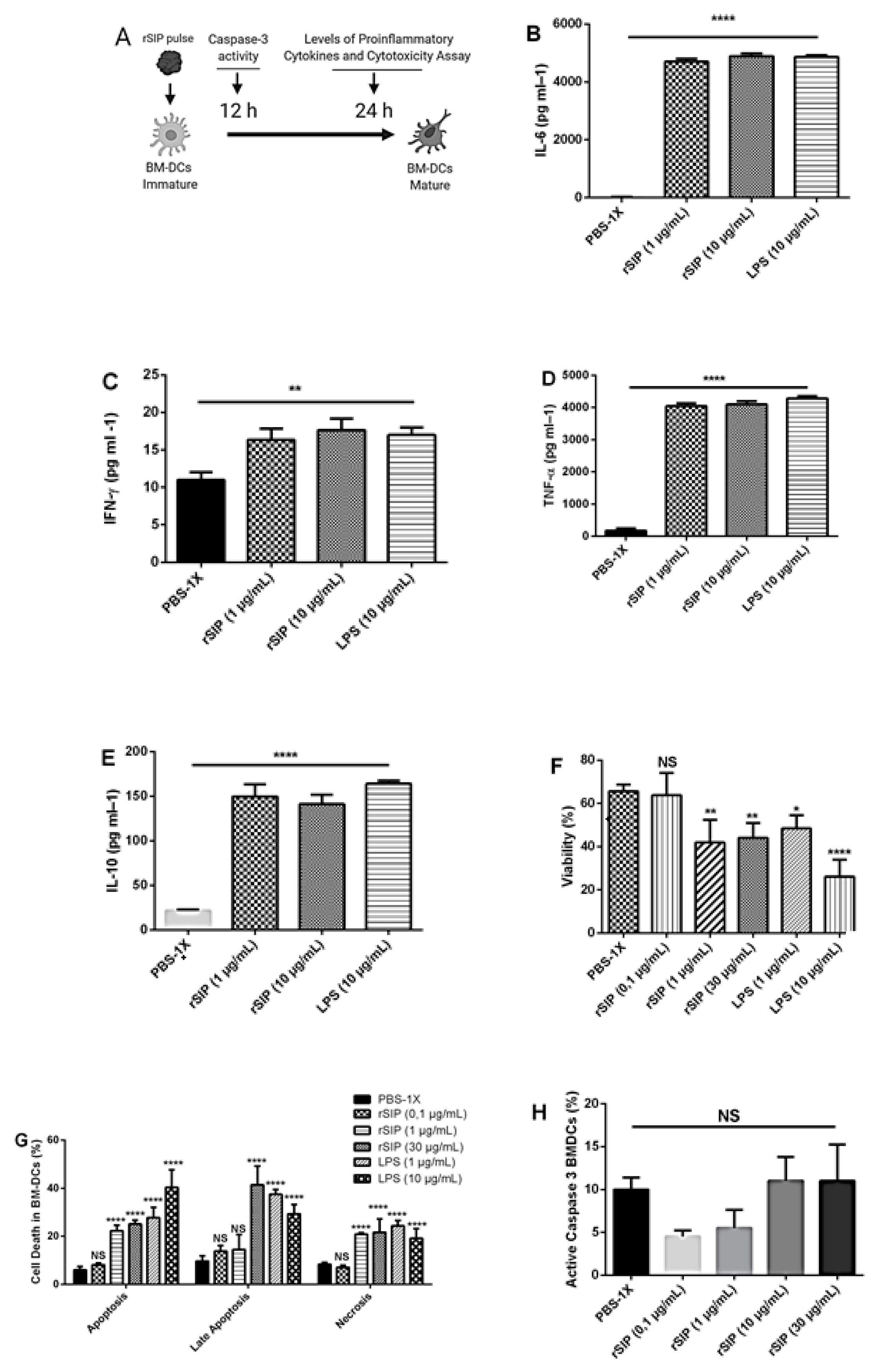
2.9. Measurement of Serum Cytokine Profiles
2.10. Detection of Soluble Cytokines Supernatants of BM-DCs
2.11. Secreted Alkaline Phosphatase Nuclear Factor Kappa-Light-Chain-Enhancer of Activated B Cells (NF-κB) Activity Assays
2.12. Cytotoxicity and Cell Viability Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Surface Immunogenic Protein of GBS Forms a Homodimer with a Principal β-Sheet Secondary Structure
3.2. The Surface Immunogenic Protein of GBS Increases Immunoglobulin Secretion Against OVA Protein
3.3. rSIP of GBS Induces Maturation of Murine Bone Marrow-Derived DCs
3.4. rSIP Promotes the Secretion of Proinflammatory Cytokines from BM-DCs
3.5. Activation Induced Cell Death upon rSIP Stimulation
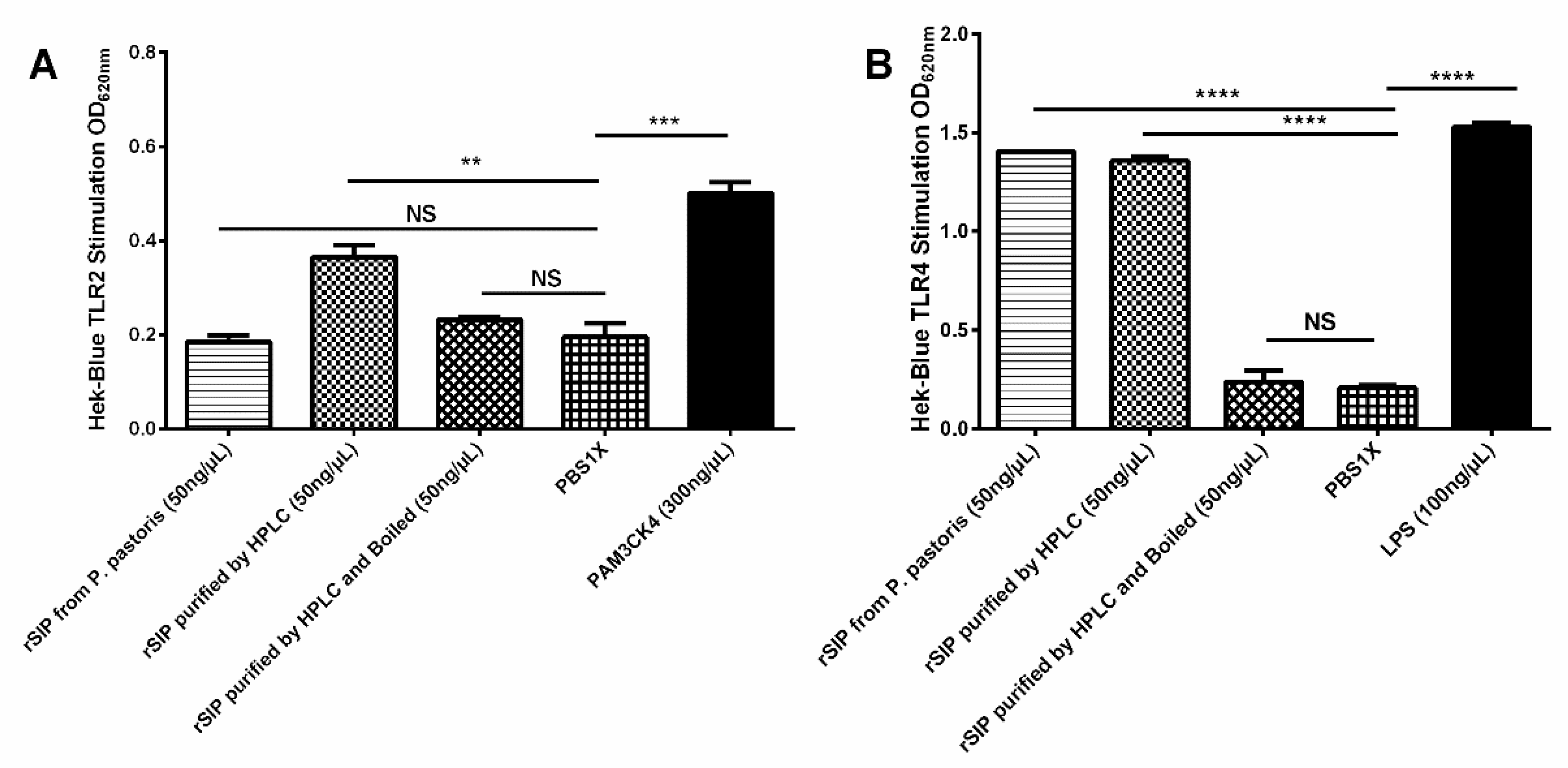
3.6. rSIP Stimulates HEK Blue TLR2 and TLR4
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Gregorio, E.; Rappuoli, R. From empiricism to rational design: A personal perspective of the evolution of vaccine development. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, N.I.; In’t Veld, L.G.H.; Raaijmakers, T.K.; Adema, G.J. Adjuvants enhancing cross-presentation by dendritic cells: The key to more effective vaccines? Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendelac, A.; Medzhitov, R. Adjuvants of immunity: Harnessing innate immunity to promote adaptive immunity. J. Exp. Med. 2002, 195, F19–F23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Sunagar, R.; Gosselin, E.J. Bacterial Protein Toll-Like-Receptor Agonists: A Novel Perspective on Vaccine Adjuvants. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pore, D.; Mahata, N.; Pal, A.; Chakrabarti, M.K. 34 kDa MOMP of Shigella flexneri promotes TLR2 mediated macrophage activation with the engagement of NF-kappaB and p38 MAP kinase signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 47, 1739–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berguer, P.M.; Mundinano, J.; Piazzon, I.; Goldbaum, F.A. A polymeric bacterial protein activates dendritic cells via TLR4. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Jerias, J.I.; Soto, D.A.; Soto, J.A.; Díaz, N.V.; Leyton, Y.Y. The optimisation of the expression of recombinant surface immunogenic protein of group B Streptococcus in Escherichia coli by response surface methodology improves humoral immunity. Mol. Biotechnol. 2018, 60, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, J.A.; Diaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Soto, D.A.; Barrientos, M.J.; Carrión, F.; Kalergis, A.M.; Vasquez, A.E. Cellular immune response induced by surface immunogenic protein with AbISCO-100 adjuvant vaccination decreases group B Streptococcus vaginal colonization. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 111, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Soto, D.A.; Leyton, Y.Y.; Altamirano-Lagos, M.J.; Avendaño, M.J.; Kalergis, A.M.; Vasquez, A.E. Oral vaccine based on a surface immunogenic protein mixed with alum promotes a decrease in Streptococcus agalactiae vaginal colonization in a mouse model. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Torres, A.; Bastias, D.; Pinto, C.; Soto, D.; Avendaño, M.J.; Berrios, J.; Kalergis, A.M.; Vasquez, A. Optimization of the Expression Surface Immunogenic Protein from Group B Streptococcus in Pichia Pastoris by Response Surface Methodology and its Protective Immune Response. 2020; Manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wetzler, L.M.; Massari, P. The PorB porin from commensal Neisseria lactamica induces Th1 and Th2 immune responses to ovalbumin in mice and is a potential immune adjuvant. Vaccine 2008, 26, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, N.; Toyota, H.; Hata, K.; Yagyu, S.; Seki, T.; Harada, M. OVA-bound nanoparticles induce OVA-specific IgG1, IgG2a, and IgG2b responses with low IgE synthesis. Vaccine 2014, 32, 5918–5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.B.; Schnare, M.; Menges, M.; Rössner, S.; Röllinghoff, M.; Schuler, G.; Gessner, A. Differential functions of IL-4 receptor types I and II for dendritic cell maturation and IL-12 production and their dependency on GM-CSF. J. Immunol. 2002, 169, 3574–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.T.; Na, H.; Ryu, H.; Chung, Y. Modulation of dendritic cell activation and subsequent Th1 cell polarization by lidocaine. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, A.C.; Rahavi, S.M.; Fung, S.Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Yang, H.; Lim, C.J.; Turvey, S.E. Combination therapy with proteasome inhibitors and TLR agonists enhances tumour cell death and IL-1β production. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, A.; Rajoria, S.; George, A.L.; Mittelman, A.; Suriano, R.; Tiwari, R.K. Synthetic Toll like receptor-4 (TLR-4) agonist peptides as a novel class of adjuvants. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Doare, K.; Kampmann, B.; Vekemans, J.; Heath, P.T.; Goldblatt, D.; Nahm, M.H. Serocorrelates of protection against infant group B streptococcus disease. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2019, 19, e162–e171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 2011, 34, 637–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Karmakar, S.; Babu, S.P.S. TLR2 and TLR4 mediated host immune responses in major infectious diseases: A review. Braz. J. Infect Dis. 2016, 20, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaman, M.; Toth, I. Immunostimulation by synthetic lipopeptide-based vaccine candidates: Structure-activity relationships. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hood, J.D.; Warshakoon, H.J.; Kimbrell, M.R.; Shukla, N.M.; Malladi, S.S.; Wang, X.; David, S.A. Immunoprofiling toll-like receptor ligands: Comparison of immunostimulatory and proinflammatory profiles in ex vivo human blood models. Hum. Vaccin. 2010, 6, 322–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liljeroos, L.; Malito, E.; Ferlenghi, I.; Bottomley, M.J. Structural and computational biology in the design of immunogenic vaccine antigens. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 156241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolb, J.P.; Casella, C.R.; SenGupta, S.; Chilton, P.M.; Mitchell, T.C. Type I interferon signaling contributes to the bias that Toll-like receptor 4 exhibits for signaling mediated by the adaptor protein TRIF. Sci. Signal. 2014, 7, ra108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosmann, T.R.; Coffman, R.L. TH1 and TH2 cells: Different patterns of lymphokine secretion lead to different functional properties. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1989, 7, 145–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, J.M.; Conacher, M.; Hunter, C.A.; Mohrs, M.; Brombacher, F.; Alexander, J. Aluminium hydroxide adjuvant initiates strong antigen-specific Th2 responses in the absence of IL-4-or IL-13-mediated signaling. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 6448–6454. [Google Scholar]
- Kaisho, T.; Akira, S. Toll-like receptors as adjuvant receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2001, 1589, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Re, F.; Strominger, J.L. Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) and TLR4 differentially activate human dendritic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 37692–37699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agrawal, S.; Agrawal, A.; Doughty, B.; Gerwitz, A.; Blenis, J.; Van Dyke, T.; Pulendran, B. Cutting edge: Different Toll-like receptor agonists instruct dendritic cells to induce distinct Th responses via differential modulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase-mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 4984–4989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horng, T.; Barton, G.M.; Flavell, R.A.; Medzhitov, R. The adaptor molecule TIRAP provides signalling specificity for Toll-like receptors. Nature 2002, 420, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zang, A.; Du, M.; Ma, D.; Yuan, C.; Zhou, C.; Deng, Q. mTOR regulates TLR-induced c-fos and Th1 responses to HBV and HCV vaccines. Virol. Sin. 2015, 30, 174–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, J. Programmed cell death of dendritic cells in immune regulation. Immunol. Rev. 2010, 236, 11–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneke, P.; Dramsi, S.; Mancuso, G.; Chraibi, K.; Pellegrini, E.; Theilacker, C.; Poyart, C. Lipoproteins are critical TLR2 activating toxins in group B streptococcal sepsis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 6149–6158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, S.G.; Hsu, F.C.; Carter, D.; Orr, M.T. The science of vaccine adjuvants: Advances in TLR4 ligand adjuvants. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 41, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Y.L.; Zhao, F.; Shao, J.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Chang, H.; Zhang, Y. Application of built-in adjuvants for epitope-based vaccines. PeerJ 2019, 6, e6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.Y.; Englund, J.A. Maternal immunization. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2014, 59, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto, J.A.; Gálvez, N.; Rivera, C.A.; Palavecino, C.E.; Céspedes, P.F.; Kalergis, A.M. Recombinant BCG vaccines reduce pneumovirus-caused airway pathology by inducing protective cellular and humoral immunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diaz-Dinamarca, D.A.; Manzo, R.A.; Soto, D.A.; Avendaño-Valenzuela, M.J.; Bastias, D.N.; Soto, P.I.; Escobar, D.F.; Vasquez-Saez, V.; Carrión, F.; Pizarro-Ortega, M.S.; et al. Surface Immunogenic Protein of Streptococcus Group B is an Agonist of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and a Potential Immune Adjuvant. Vaccines 2020, 8, 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010029
Diaz-Dinamarca DA, Manzo RA, Soto DA, Avendaño-Valenzuela MJ, Bastias DN, Soto PI, Escobar DF, Vasquez-Saez V, Carrión F, Pizarro-Ortega MS, et al. Surface Immunogenic Protein of Streptococcus Group B is an Agonist of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and a Potential Immune Adjuvant. Vaccines. 2020; 8(1):29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010029
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiaz-Dinamarca, Diego A., Ricardo A. Manzo, Daniel A. Soto, María José Avendaño-Valenzuela, Diego N. Bastias, Paulina I. Soto, Daniel F. Escobar, Valeria Vasquez-Saez, Flavio Carrión, Magdalena S. Pizarro-Ortega, and et al. 2020. "Surface Immunogenic Protein of Streptococcus Group B is an Agonist of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and a Potential Immune Adjuvant" Vaccines 8, no. 1: 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010029
APA StyleDiaz-Dinamarca, D. A., Manzo, R. A., Soto, D. A., Avendaño-Valenzuela, M. J., Bastias, D. N., Soto, P. I., Escobar, D. F., Vasquez-Saez, V., Carrión, F., Pizarro-Ortega, M. S., Wilson, C. A. M., Berrios, J., Kalergis, A. M., & Vasquez, A. E. (2020). Surface Immunogenic Protein of Streptococcus Group B is an Agonist of Toll-Like Receptors 2 and 4 and a Potential Immune Adjuvant. Vaccines, 8(1), 29. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines8010029






