Abstract
Zika virus (ZIKV) is an emerging arthropod-borne virus of major public health concern. ZIKV infection is responsible for congenital Zika disease and other neurological defects. Antibody-mediated virus neutralization is an essential component of protective antiviral immunity against ZIKV. In the present study, we assessed whether our GFP reporter ZIKV derived from African viral strain MR766 could be useful for the development of a flow cytometry neutralization test (FNT), as an alternative to the conventional plaque-reduction neutralization test (PRNT). To improve the efficacy of GFP-expressing MR766, we selected virus variant MR766GFP showing a high level of GFP signal in infected cells. A MR766GFP-based FNT was assayed with immune sera from adult mice that received ZIKBeHMR-2. The chimeric ZIKV clone ZIKBeHMR-2 comprises the structural protein region of epidemic strain BeH819015 into MR766 backbone. We reported that adult mice inoculated with ZIKBeHMR-2 developed high levels of neutralizing anti-ZIKV antibodies. Comparative analysis between MR766GFP-based FNT and conventional PRNT was performed using mouse anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera. Indistinguishable neutralization patterns were observed when compared with PRNT50 and FNT50. We consider that the newly developed MR766GFP-based FNT is a valid format for measuring ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens.
1. Introduction
Mosquito-borne Zika virus (ZIKV) is an emerging flavivirus initially reported in Africa in 1947 [1]. Recently, ZIKV became a public health concern with recent epidemics occurring in Yap islands (2007), French Polynesia (2013), and South America (2015) [2]. During these outbreaks, ZIKV infection was reported to cause severe complications in humans, such as developmental abnormalities in infants and Guillain-Barre syndrome in adults [3]. Also, ZIKV is capable of long-term persistence in human body fluids and sexual transmission of disease has been documented [4,5].
Laboratory diagnosis of ZIKV infection is mainly based on RT-PCR method during the acute phase of the disease [5,6,7,8]. Serological diagnosis of ZIKV infection is obtained at least one week after the onset of the clinical symptoms [5,6]. It is frequently observed that members of flavivirus genus share strong antigenic cross-reactivity making inconclusive serological tests especially in regions where ZIKV and related flaviviruses, such as dengue viruses, co-circulate. To overcome this issue, the detection of antibodies that have neutralizing activity against ZIKV can be achieved to confirm recent infection [8]. Plaque-reduction neutralization test (PRNT) is a widely accepted method to measure neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens [9]. Although PRNT is considered as a “gold standard” assay for flavivirus neutralization, this specific but conventional format is a time-consuming method making difficult the screening of a large number of samples. Noteworthy, virus plaque-based analysis is limited to cultured cell lines, such as green monkey epithelial Vero cells, that permit plaque-forming assay.
New biological tests revisiting the conventional PRNT method are necessary for the rapid measurement of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in large serum series. Consequently, several reporter gene-based methods for neutralizing assays have been recently developed for ZIKV [10,11,12]. Given that reporter systems afford the ability to visualize viral expression inside the infected cells, we generated a GFP reporter ZIKV entitled ZIKVGFP [13]. We demonstrated that ZIKVGFP is a performing tool for the monitoring of ZIKV replication in the host cell as well as the screening of antiviral compounds [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In the present study, we adapted ZIKVGFP for the measurement of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies by flow cytometry analysis. The GFP reporter ZIKV-based flow cytometry neutralization test (FNT) was challenged with serum samples from mice inoculated with ZIKV. Results showed that our newly developed FNT generated ZIKV-neutralizing antibody titers that are equivalent to those obtained with conventional PRNT.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells and Virus
Vero cells (clone E6) and A549Dual cells (Invivogen, Toulouse, France), referred to hereafter as “A549 cells”, were cultured at 37 °C under 5% CO2 atmosphere at 37 °C in MEM Eagle medium, supplemented with 5% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 2 mM L-glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, 100 U/mL penicillin, 0.1 mg/mL streptomycin, and 0.5 µg/mL amphotericin B (PAN Biotech, Aidenbach, Germany). The recombinant ZIKVGFP derived from molecular clone ZIKV MR766MC is described elsewhere [13]. ZIKVGFP and derived viral clone MR766GFP stocks were amplified on Vero cells and titrated by plaque-forming assay on Vero cells, as described elsewhere [21]. Virus titer was expressed as plaque-forming unit per mL (PFU/mL).
2.2. Generation of MR766GFP
Variants of ZIKVGFP were selected using a limiting dilution cloning method. Briefly, Vero cells seeded in 96-well plates (10,000 cells/well) were infected 5 days with ZIKVGFP at the multiplicity of infection (m.o.i) of l0−4. Supernatants of GFP-positive cell monolayers were recovered, and the second round of virus cloning was performed on Vero cells, as described above. Viral clone MR766GFP was selected and then passaged twice on Vero cells to produce a final virus stock for experiments. The infectious titer of the working MR766GFP stock was 7.7 log PFU/mL on Vero cells.
2.3. Focus-Forming Assay
For the focus-forming assay, Vero cells were seeded in 24-well plates. Virus samples were added to the cells for 2 h at 37 °C and then incubated with 0.8% carboxymethylcellulose (CMC). After a 4-day incubation, cell monolayers were fixed with 3.7% formaldehyde (FA) in PBS, followed by permeabilization with 0.15% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min. Cells were incubated with a mouse anti-GFP (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at dilution 1:1000 followed by incubation with HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at dilution 1:2000. Virus plaques were revealed with Vector NovaREDTM peroxidase substrate (Cliniscences Nanterre, France) and counterstained with 0.5% crystal violet in 20% ethanol. Plates were scanned with an Epson scanner (Levallois-Perret, France).
2.4. Mouse Serum Specimens
The protocols and subsequent experiments in mice were ethically approved by the Ethics Committee for Control of Experiments on Animals at the CECEMA (Montpellier, France) with the reference n°036 and by the French Ministère de l’Enseignement Supérieur, de la Recherche et de l’Innovation with reference APAFIS#9137-2017030316134494 v6 (February 28th, 2018) [22,23]. A total of 29 individualized mouse immune serum specimens was selected for this study [23]. The first group of adult BALB/c mice (n = 5) was inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2, a second group (n = 15) received a single dose of 5 log PFU of ZIKBeHMR-2, and a third group (n = 14) received two doses of 5 log PFU of ZIKBeHMR-2 with a 6-week interval. All the serum specimens were heat-inactivated at 56 °C for 30 min.
2.5. Plaque-Reduction Neutralization Test
For the plaque-reduction neutralization test (PRNT), Vero cells were seeded in 24-well plates. Serum samples were 2-fold serially diluted in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS with a starting dilution of 1:50, and incubated with an equal volume of a virus sample containing 100 PFU of MR766GFP for 2 h at 37 °C. The virus-antibody mixture was added on cell monolayers for 2 h at 37 °C and then incubated with 0.8% CMC in growth medium. After a 4-day incubation, cell monolayers were fixed with 3.7% FA in PBS and then stained with 0.5% crystal violet in 20% ethanol. Visible plaques were manually counted. The neutralizing antibody titers were determined as the reciprocal of the last serum dilution that resulted in a 50% residual of infectivity of negative-control serum samples. PRNT50 values were determined from a nonlinear regression analysis.
2.6. Flow Cytometry Assay and Flow Cytometry-Based Neutralization Test
For flow cytometry assay, cells were seeded in 24-well plates. Virus samples were added to the cells for 18 h. Cells were gently harvested by trypsinization, fixed with 3.7% FA in PBS, and permeabilized with 0.15% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min. Samples were incubated with mouse anti-flavivirus E MAb 4G2 at dilution 1:1000 (R&D Biotech, Besançon, France) and then with Alexa 647-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) at dilution 1:1000. Cells were analyzed with a Cytoflex flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Villepinte, France).
For flow cytometry-based neutralization test (FNT), 20,000 cells per well were seeded in 96-well plates. Serum specimens were 2-fold serially diluted in DMEM supplemented with 2% FBS with a starting dilution of 1:50, and incubated with an equal volume of a virus sample containing 20,000 PFU of MR766GFP for 2 h at 37 °C. The virus-antibody mixture was added to the cell monolayers for 20 h. Cells were fixed with 3.7% FA in PBS, and 10,000 cells of each assay were analyzed for GFP expression with a CytoFLEX flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Villepinte, France). The 100% infectivity was obtained with the number of ZIKV-infected cells positive for GFP expression in the absence of serum samples. The neutralizing antibody titer was determined as the serum dilution that resulted in a 50% reduction of GFP expression (FNT50) and was calculated by nonlinear, dose-response regression analysis.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Linear regression was used to determine the correlation, with associated p-value, between PRNT50 values and FNT50 values. Pearson’s correlation coefficients (r) and the coefficient of determination (R²) were determined using Prism software version 7.01 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Generation of Viral Clone MR766GFP for Flow Cytometry Neutralization Test
To generate a more reliable GFP reporter ZIKV for flow cytometry neutralization test, recombinant ZIKVGFP was repeatedly passaged on Vero cells using a limiting dilution cloning method [13]. A single virus clone, hereafter named MR766GFP, was selected for further studies. The progeny virus production of MR766GFP variant in Vero cells was at least 1.5 log higher than for parental ZIKVGFP [13]. Expression of MR766GFP was examined in Vero cells infected at a multiplicity of infection (m.o.i.) of 1 (Figure 1). We observed that most of the virus plaques produced in the focus-forming assay were positively stained by anti-GFP antibody (Figure 1A). Flow-cytometry analysis confirmed that Vero cells positive for GFP expression were recognized by the anti-E mAb 4G2 (Figure 1B). Thus, the MR766GFP variant is a suitable GFP reporter ZIKV for the development of a FNT.
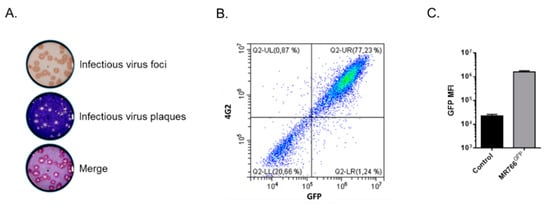
Figure 1.
Characterization of viral clone MR766GFP on Vero cells. In (A), the example of infectious virus foci developed after a focus-forming assay using anti-GFP antibody. To visualize infectious virus plaques, the cell monolayer was counterstained with crystal violet. In (B), cells were infected 24 h with MR766GFP at an m.o.i. of 1. The GFP-positive cells (GFP) stained with anti-E MAb 4G2 (4G2) were analyzed by flow cytometry analysis. In (C), mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of MR766GFP-infected cells (MR766GFP), as determined by flow cytometry analysis. Control: mock-infected Vero cells.
3.2. Comparison Between MR766GFP-Based FNT Assay and Conventional PRNT
We reported that immunocompetent adult mice that received intraperitoneally 5 log PFU of chimeric ZIKV clone ZIKBeHMR-2 developed high titers of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies [23]. ZIKBeHMR-2 is a chimeric clone of ZIKV derived from historical African ZIKV strain MR766 in which the structural protein region was replaced with that of epidemic ZIKV strain BeH819015 of Asian lineage [23]. Noteworthy, the ZIKBeHMR-2 E protein lacks N-glycosylation [23].
The neutralization assays were assessed with a selection of 29 immune sera from adult BALB/c mice that received one or two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2 with an interval of 6 weeks [23]. Immune sera from mice inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 served as negative controls [23]. The serum samples were first subjected to testing by a conventional PRNT method in Vero cells using MR766GFP (Figure 2). As expected, negative control immune sera exhibited no reduction of virus plaque number at the lower dilution tested (1:50). In contrast, immune sera from mice inoculated with ZIKBeHMR-2 showed neutralizing activity against MR766GFP. The serum samples reduced the number of virus plaques in a dilution-dependent manner. In mice that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2, there was a PRNT50 value of 130 (95% Confident Interval (CI): 93–182). After inoculation of a booster dose, the ZIKV-neutralizing antibody titers increased up to 3051 (95% CI: 2251–4136). Thus, a conventional PRNT confirmed the neutralizing activity of anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera against ZIKV.
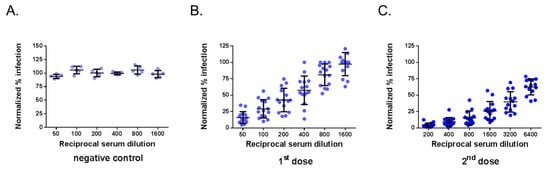
Figure 2.
Plaque-reduction neutralization test on anti-Zika virus immune sera. The neutralizing ability of mouse serum specimens against MR766GFP was determined by plaque-reduction neutralization test (PRNT) on Vero cells. Samples of anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera were tested individually. Serum specimens were two-fold serial diluted starting at a 1:50 dilution. The results are shown normalized to the 100% infection achieved with MR766GFP without serum. In (A), the immune sera of BALB/c mice inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 served as a negative control (negative control). In (B), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) (1st dose). In (C), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) with an interval of 6 weeks (2nd dose).
The mouse serum samples were next assessed by MR766GFP-based FNT. The neutralization tests were performed on Vero cells grown in 96-well plates, and GFP expression was examined 20 h post-infection (Figure 3). By flow-cytometry analysis, the percentage of GFP-positive Vero cells infected with MR766GFP reached 55%. There was no reduction in the percentages of GFP-positive cells using immune sera from mice inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 that served as a negative virus control (Figure 3A). Whereas mouse anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera showed neutralizing activity against MR766GFP in a dilution-dependent manner (Figure 3B,C). In mice (n = 15) that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2, there was a FNT50 value of 117 (95% CI: 81–169). After inoculation of a booster dose, the FNT50 values of immune sera (n = 14) increased up to 2469 (95% CI: 1673–3645).
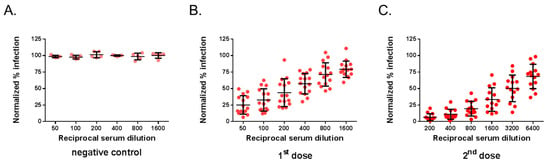
Figure 3.
Flow cytometry neutralization test on Vero cells. The neutralizing ability of mouse serum specimens against ZIKV was determined by flow cytometry neutralization test (FNT) on Vero cells. Samples of anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera were tested individually. Serum specimens were two-fold serial diluted starting at a 1:50 dilution and mixed with an equal volume of virus sample containing 20,000 PFU of MR766GFP. The virus-antibody mixture was added on 20,000 Vero cells grown in 96-well plates. At 20 h post-infection, the percentage of positive cells for GFP expression was determined by flow-cytometry analysis. The number of GFP-positive cells without serum was considered 100% of infectivity. The results were expressed as the percentage of GFP-positive cells in assay relative to that calculated in absence of serum. In (A), the immune sera of BALB/c mice inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 served as a negative control (negative control). In (B), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) (1st dose). In (C), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) with a 6-week interval (2nd dose).
Data fitting between PRNT50 and FNT50 values on anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera revealed a linear relationship (R² = 0.90, p-value <0.0001) between the two assays (Figure 4). This indicates a concordance between conventional PRNT and a FNT method based on a single infection round. Such results support the utilization of MR766GFP-based FNT for measuring ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens.
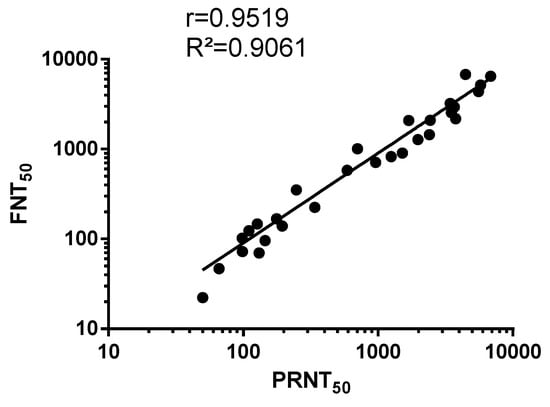
Figure 4.
Scatter plots of PRNT50 and FNT50 values in Vero cells. PRNT: plaque-reduction neutralization test; FNT: flow-cytometry neutralization test. The PRNT50 and FNT50 were determined as the reciprocal of the last serum dilution that resulted in a 50% residual of infectivity of negative-control serum samples.
We next evaluated whether the MR766GFP-based FNT can be performed in human cells that do not support virus plaque assay such as human epithelial A549 cells. To evaluate the performance of our FNT on A549 cells, MR766GFP was incubated with serial dilutions of immune sera from mice inoculated with one or two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2. The virus-antibody mixtures were used to infect A549 cells seeded in 96-well plates. At 20 h post-infection, the GFP expression was observed in infected A549 cells by flow cytometry analysis. The percentage of GFP-positive A549 cells infected with MR766GFP reached 50%. There was a 100% infectivity with immune sera directed against heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 (Figure 5A). We observed that anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera reduced MR766GFP infectivity for A549 cells in a serum dilution-dependent manner (Figure 5B,C). In mice (n = 15) that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2, there was a FNT50 value of 161 (95% CI: 119–216). After inoculation of a booster dose, the FNT50 value of immune sera (n = 14) increased up to 2320 (95% CI: 1507–3570).
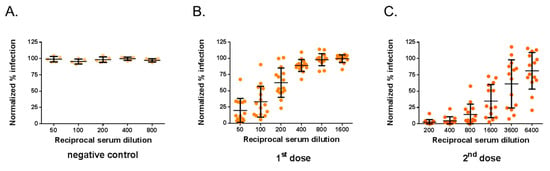
Figure 5.
Flow cytometry neutralization test on A549 cells. The neutralizing ability of mouse serum specimens against ZIKV was determined by FNT on A549 cells. Samples of anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera were tested individually. Serum samples were two-fold serial diluted starting at a 1:50 dilution and mixed with an equal volume of virus sample containing 20,000 PFU of MR766GFP. The virus-antibody mixture was added on 20,000 A549 cells grown in 96-well plates. At 20 h post-infection, the percentage of positive cells for GFP expression was determined by flow-cytometry analysis. The number of GFP-positive cells without serum was considered 100% of infectivity. The results were expressed as the percentage of GFP-positive cells in assay relative to that calculated without serum. In (A), The immune sera of BALB/c mice inoculated with heat-inactivated ZIKBeHMR-2 served as a negative control (negative control). In (B), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received a single dose of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) (1st dose). In (C), immune sera of BALB/c mice that received two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2 (5 log PFU) with a 6-week interval (2nd dose).
As shown in Figure 6, there was a linear relationship (R² = 0.94, p-value <0.0001) between FNT50 performed in Vero and A549 cells. Thus, human epithelial A549 cells are suitable for the measurement of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens based on our newly developed MR766GFP-based FNT.
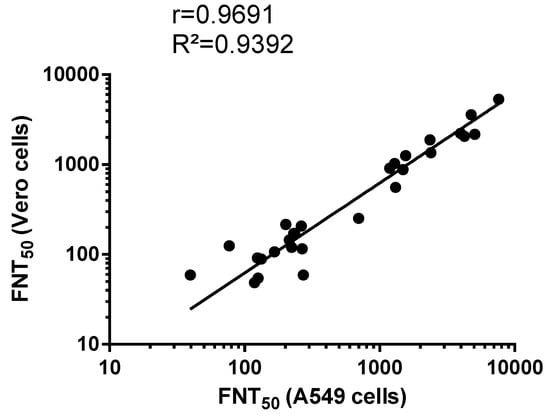
Figure 6.
Scatter plots of FNT50 on Vero and A549 cells. FNT: flow-cytometry neutralization test. The FNT50 were determined as the reciprocal of the last serum dilution that resulted in a 50% residual of infectivity of negative-control serum samples.
4. Discussion
The development of new neutralizing assays that overcome the restrictions presented by the conventional PRNT methods become a priority for ZIKV. To this aim, we took advantage of our previously developed GFP reporter ZIKV (recombinant ZIKVGFP), which had been demonstrated to be a powerful tool for the monitoring of virus replication as well as the screening of antiviral compounds [13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20]. In routine, ZIKVGFP infection is observed by flow cytometry analysis at 18–24 h post-infection based on the GFP signal. In the present study, we identified MR766GFP as a variant of ZIKVGFP exhibiting a greater propensity to produce a GFP signal associated with a higher virus progeny production.
Here, MR766GFP was assayed with serum specimens from adult BALB/c mice inoculated with a chimeric viral clone ZIKBeHMR-2, which contains the structural protein region of epidemic Brazilian ZIKV strain BeH810915 into a MR766 backbone [23]. ZIKBeHMR-2 has a non-glycosylated E protein due to the introduction of a limited number of amino acid substitutions in the E glycan-loop of BeH819015 [23]. The ability of ZIKBeHMR-2 to induce anti-ZIKV antibody production had been validated in adult BALB/c mice immunized by the intraperitoneal route [23]. The serum specimens obtained from mice inoculated with one or two doses of ZIKBeHMR-2 were evaluated for neutralizing antibodies by conventional PRNT. Immunized mice developed anti-ZIKV antibodies that neutralize MR766 with PRNT50 values reaching up to 3500 [23]. Consequently, anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera were suitable for a comparative analysis between our MR766GFP-based FNT and conventional PRNT, the latter being considered as a “gold standard” assay for flavivirus neutralization. FNT was first performed on African green monkey Vero cells which are commonly used for neutralization tests. Vero cells were grown in 96-well-plates. The neutralizing activity of anti-ZIKBeHMR-2 immune sera against ZIKV was estimated within two days. There was a linear correlation between FNT50 and PRNT50 values with R2 coefficient of determination of 0.9. Thus, our newly developed GFP reporter ZIKV-based FNT allows a prompt and reliable detection of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens. A such method was next employed on human epithelial A549 cells, and there was a linear correlation between FNT50s values in A549 and Vero cells with an R2 coefficient of determination of 0.94. We propose that MR766GFP-based FNT is a suitable method for the general measurement of antibody-mediated ZIKV neutralization. Now, it is of paramount importance to estimate our newly developed FNT format for the detection of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies using human serum specimens from Zika patients.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we demonstrated that viral clone MR766GFP is a suitable GFP reporter ZIKV for the identification of ZIKV-neutralizing antibodies in serum specimens by flow-cytometry analysis. The time-saver MR766GFP-based FNT format could provide a reliable platform for measuring antibodies that neutralize ZIKV in a large number of serum specimens without the requirement for plaque-forming formation. Further studies will be necessary to determine whether conventional PRNT method might be replaced by our newly developed MR766GFP-based FNT for epidemiological cohort studies as well as vaccine development on ZIKV.
6. Patent
The viral clone ZIKBeHMR-2 has been described in the patent entitled “Vaccine compositions comprising an attenuated mutant Zika virus” under the number WO2017220748A1 (priority date 2016-06-23).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: E.F., P.D.; Methodology: E.F., P.D.; Formal analysis: E.F., G.G., W.V., P.D.; Investigation: P.D.; Resources: P.D.; Data curation: E.F., W.V., G.G., P.D.; Writing-Original Draft Preparation: E.F., P.D.; Writing-Review and Editing: E.F., W.V., G.G., P.D.; Visualization: P.D., Supervision: P.D.; Project Administration: P.D.; Funding Acquisition: P.D.
Funding
This research was funded by INSERM transfert (ZIKALIVax program) and POE FEDER 2014-20 of the Conseil Régional de La Reunion (ZIKAlert program, N° SYNERGIE RE00001902). EF received funding from FEDER Région Réunion-La Reunion University (ZIKALIVax 2.0 program, N° SYNERGIE RE0012406).
Acknowledgments
We greatly thank M. Roche, M.T. Alvarez-Martinez, and D.J. Arnaud for their assistance in animal experiments. We thank the PIMIT lab members for their interest in this work. We thank Y. Lemonnier and O-F. Cadjee (IRIADE, CHU de la Reunion) for technical assistance and helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Weaver, S.C.; Costa, F.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A.; Ko, A.I.; Ribeiro, G.S.; Saade, G.; Shi, P.-Y.; Vasilakis, N. Zika Virus: History, Emergence, Biology, and Prospects for Control. Antiviral Res. 2016, 130, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatherer, D.; Kohl, A. Zika virus: A previously slow pandemic spreads rapidly through the Americas. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao-Lormeau, V.M.; Blake, A.; Mons, S.; Lastere, S.; Roche, C.; Vanhomwegen, J.; Dub, T.; Baudouin, L.; Teissier, A.; Larre, P.; et al. Guillain-Barré Syndrome outbreak associated with Zika virus infection in French Polynesia: A case-control study. Lancet 2016, 387, 1531–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge-Ranzinger, S.; Morrison, A.C.; Manrique-Saide, P.; Horstick, O. Zika transmission patterns: A meta-review. Trop. Med. Int. Health 2019, 24, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musso, D.; Gubler, D.J. Zika Virus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 29, 487–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Kosoy, O.L.; Laven, J.J.; Velez, J.O.; Lambert, A.J.; Johnson, A.J.; Stanfield, S.M.; Duffy, M.R. Genetic and serologic properties of Zika virus associated with an epidemic, Yap State, Micronesia, 2007. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1232–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanciotti, R.S.; Calisher, C.H.; Gubler, D.J.; Chang, G.J.; Vorndam, A.V. Rapid detection and typing of dengue viruses from clinical samples by using reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1992, 30, 545–551. [Google Scholar]
- Maeda, A.; Maeda, J. Review of diagnostic plaque reduction neutralization tests for flavivirus infection. Vet. J. 2013, 195, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roehrig, J.T.; Hombach, J.; Barrett, A.D.T. Guidelines for Plaque-Reduction Neutralization Testing of Human Antibodies to Dengue Viruses. Viral Immunol. 2008, 21, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Yamanaka, A.; Yato, K.; Yoshii, K.; Watashi, K.; Aizaki, H.; Konishi, E.; Takasaki, T.; Kato, T.; Muramatsu, M.; et al. High-throughput neutralization assay for multiple flaviviruses based on single-round infectious particles using dengue virus type 1 reporter replicon. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, C.; Xie, X.; Ren, P.; Loeffelholz, M.J.; Yang, Y.; Furuya, A.; Dupuis, A.P.; Kramer, L.D.; Wong, S.J.; Shi, P.-Y. A Rapid Zika Diagnostic Assay to Measure Neutralizing Antibodies in Patients. EBioMedicine 2017, 17, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koishi, A.C.; Suzukawa, A.A.; Zanluca, C.; Camacho, D.E.; Comach, G.; Duarte Dos Santos, C.N. Development and evaluation of a novel high-throughput image-based fluorescent neutralization test for detection of Zika virus infection. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2018, 12, e0006342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadea, G.; Bos, S.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Clain, E.; Viranaicken, W.; El-Kalamouni, C.; Mavingui, P.; Desprès, P. A robust method for the rapid generation of recombinant Zika virus expressing the GFP reporter gene. Virology 2016, 497, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Kalamouni, C.; Frumence, E.; Bos, S.; Turpin, J.; Nativel, B.; Harrabi, W.; Wilkinson, D.A.; Meilhac, O.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P.; et al. Subversion of the Heme Oxygenase-1 Antiviral Activity by Zika Virus. Viruses 2018, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clain, E.; Sinigaglia, L.; Koishi, A.C.; Gorgette, O.; Gadea, G.; Viranaicken, W.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Mavingui, P.; Desprès, P.; Nunes Duarte Dos Santos, C.; et al. Extract from Aphloia theiformis, an edible indigenous plant from Reunion Island, impairs Zika virus attachment to the host cell surface. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, J.G.; Koishi, A.C.; Gaudry, A.; Nunes Duarte Dos Santos, C.; Viranaicken, W.; Desprès, P.; El Kalamouni, C. Doratoxylon apetalum, an Indigenous Medicinal Plant from Mascarene Islands, Is a Potent Inhibitor of Zika and Dengue Virus Infection in Human Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clain, E.; Haddad, J.G.; Koishi, A.C.; Sinigaglia, L.; Rachidi, W.; Desprès, P.; Duarte Dos Santos, C.N.; Guiraud, P.; Jouvenet, N.; El Kalamouni, C. The Polyphenol-Rich Extract from Psiloxylon mauritianum, an Endemic Medicinal Plant from Reunion Island, Inhibits the Early Stages of Dengue and Zika Virus Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudry, A.; Bos, S.; Viranaicken, W.; Roche, M.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P.; El-Kalamouni, C. The Flavonoid Isoquercitrin Precludes Initiation of Zika Virus Infection in Human Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwalscappel, B.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P. A Viperin Mutant Bearing the K358R Substitution Lost its Anti-ZIKA Virus Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwalscappel, B.; Tada, T.; Landau, N.R. Toll-like receptor agonist R848 blocks Zika virus replication by inducing the antiviral protein viperin. Virology 2018, 522, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frumence, E.; Roche, M.; Krejbich-Trotot, P.; El-Kalamouni, C.; Nativel, B.; Rondeau, P.; Missé, D.; Gadea, G.; Viranaicken, W.; Desprès, P. The South Pacific epidemic strain of Zika virus replicates efficiently in human epithelial A549 cells leading to IFN-β production and apoptosis induction. Virology 2016, 493, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Clutton, R.E.; Lilley, E.; Hansen, K.E.A.; Brattelid, T. PREPARE: Guidelines for planning animal research and testing. Lab. Anim. 2018, 52, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frumence, E.; Viranaicken, W.; Bos, S.; Alvarez-Martinez, M.-T.; Roche, M.; Arnaud, J.-D.; Gadea, G.; Desprès, P. A Chimeric Zika Virus between Viral Strains MR766 and BeH819015 Highlights a Role for E-glycan Loop in Antibody-mediated Virus Neutralization. Vaccines 2019, 7, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).