Naringenin Inhibits Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Cell Treatments
2.2. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.3. Western Blot
2.4. Detection of Intracellular ROS
2.5. Assessment of Intracellular and Serum Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)/MDA Levels
2.6. Measurement of Intracellular Total Iron
2.7. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
2.8. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
2.9. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
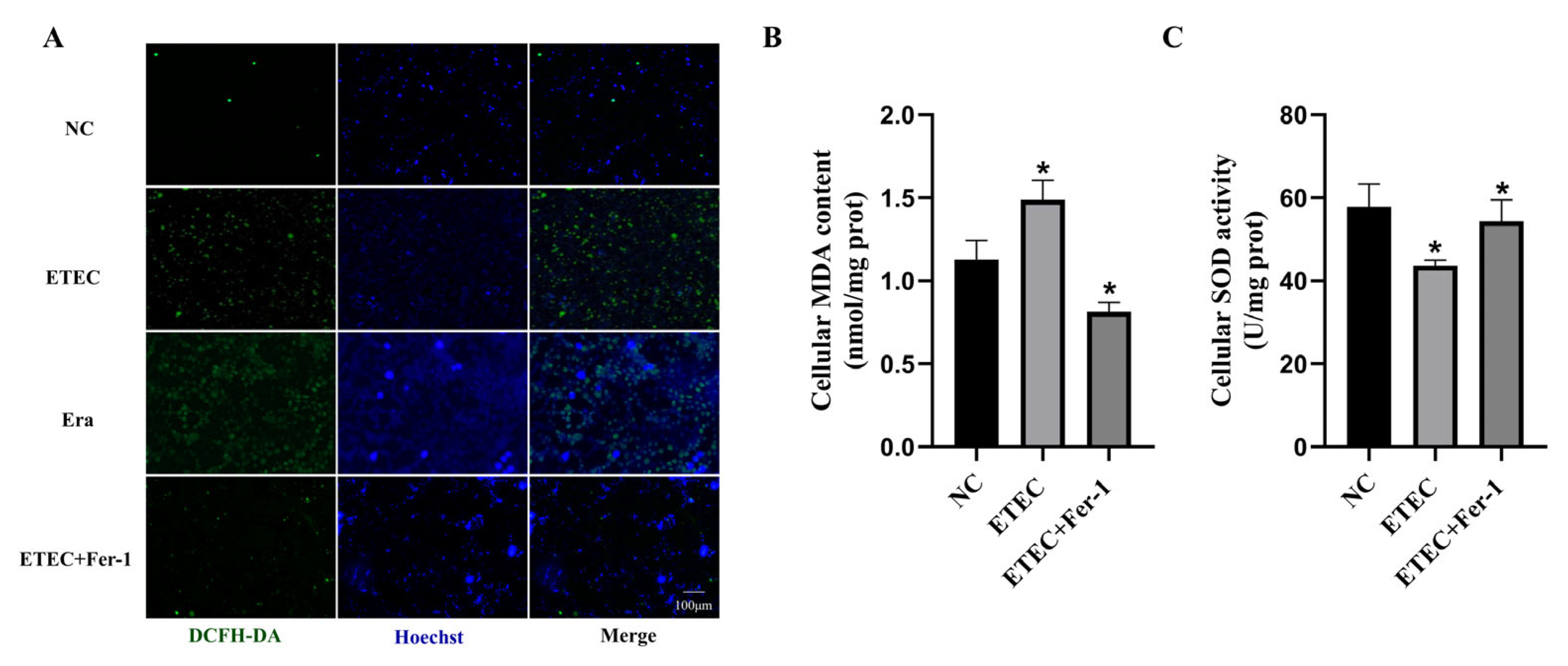
3.1. Infection with ETEC Induces Oxidative Stress in IPEC-J2 Cells
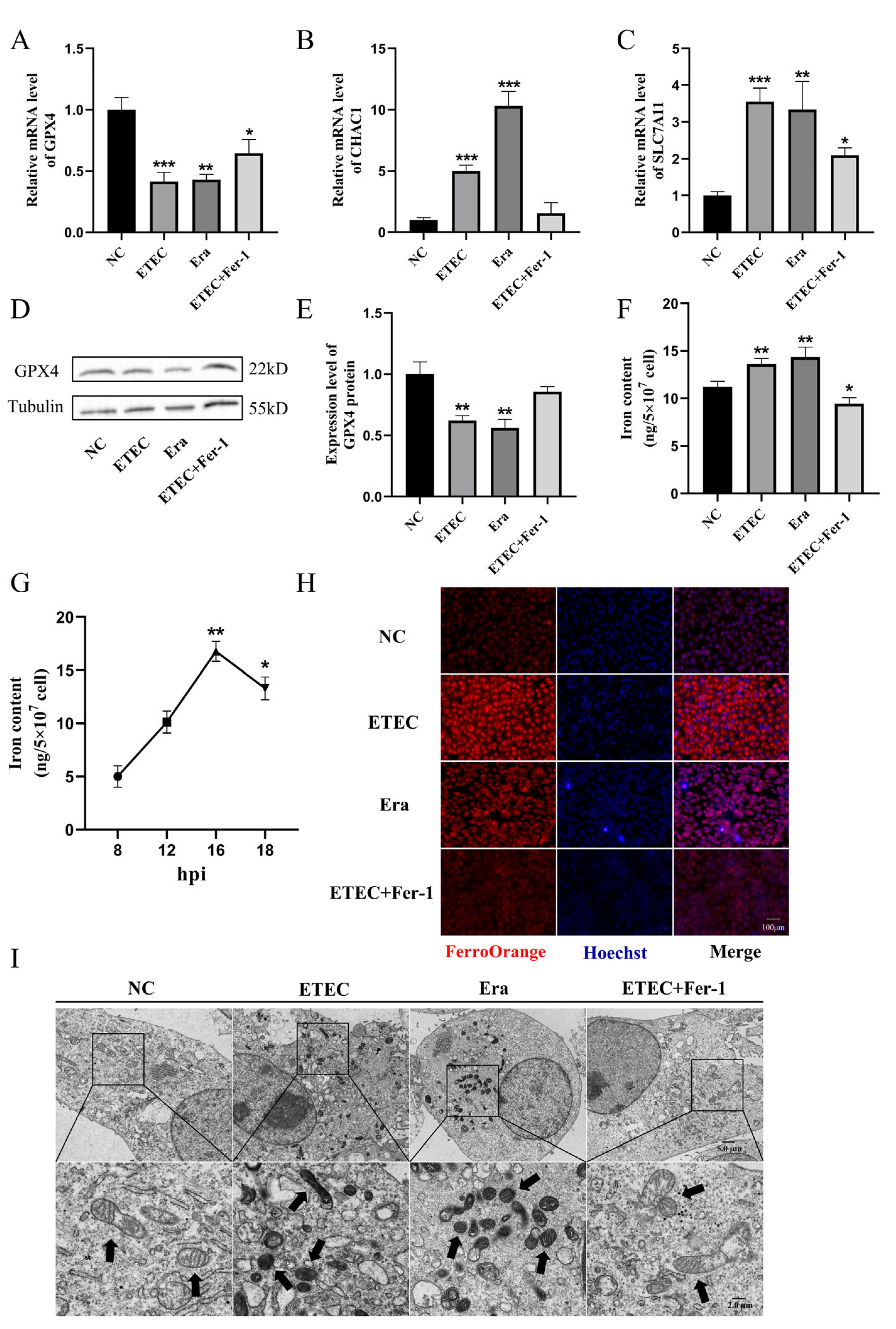
3.2. ETEC Infection Induces Ferroptosis of IPEC-J2 Cells
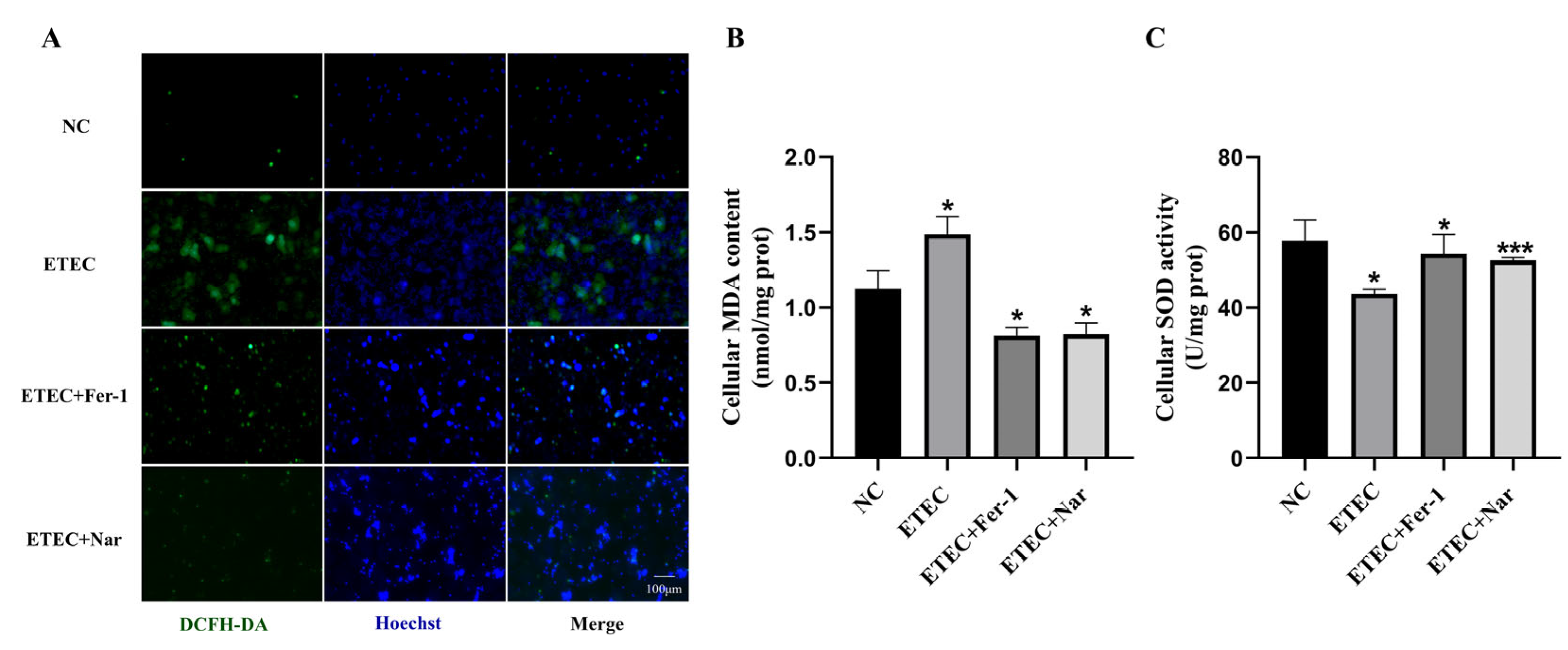
3.3. Nar Alleviates ETEC-Induced Oxidative Stress of IPEC-J2 Cells
3.4. Nar Inhibits ETEC-Induced Ferroptosis of IPEC-J2 Cells
3.5. Analysis of the Action Targets of Nar in the Treatment of Piglet Diarrhea by Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
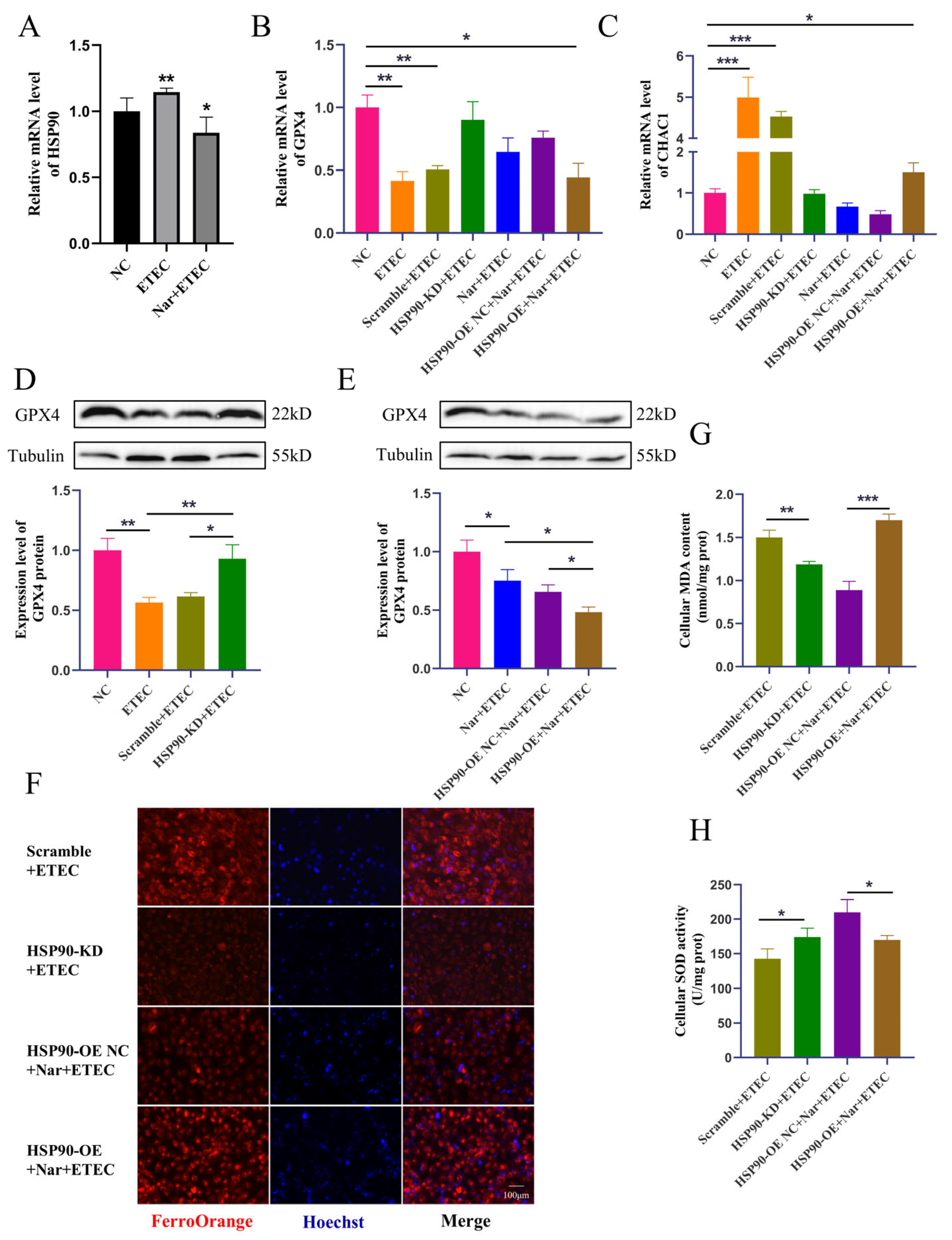
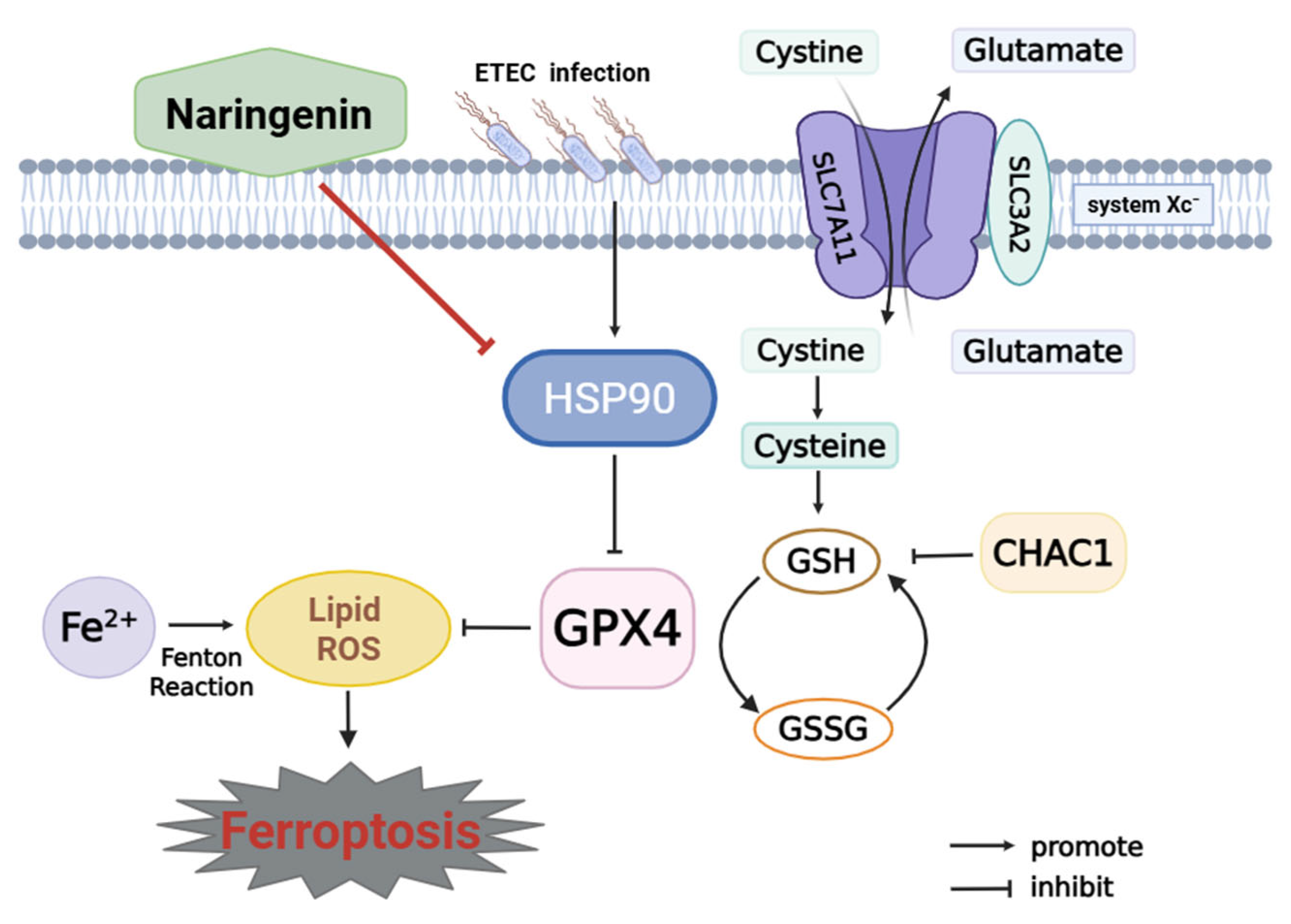
3.6. Nar Inhibits ETEC-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CHAC1 | ChaC glutathione-specific gamma-glutamylcyclotransferase 1 |
| CTD | Comparative toxicogenomics database |
| ETEC | Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli |
| Era | Erastin |
| Fer-1 | Ferrostatin-1 |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GPX4 | Glutathione peroxidase 4 |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| HSP90 | Heat-shock protein 90 |
| HE | Hematoxylin and Eosin |
| IPEC-J2 | Intestinal porcine epithelial cell line-J2 |
| KD | knockdown |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| Nar | Naringenin |
| PWD | Postweaning diarrhea |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| SLC7A11 | Solute carrier family 7 member 11 |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| ZO-1 | Zonula occludens-1 |
References
- Dubreuil, J.D.; Isaacson, R.E.; Schifferli, D.M. Animal Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. EcoSal Plus 2016, 7, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Gu, K.; Wang, F.; Jia, G.; Zhao, H.; Chen, X.; Wu, C.; Zhang, R.; Tian, G.; Cai, J.; et al. Tryptophan Ameliorates Barrier Integrity and Alleviates the Inflammatory Response to Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88 Through the CaSR/Rac1/PLC-γ1 Signaling Pathway in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 748497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Xu, H.; Yang, C.; O, K. Regulation of oxidative stress in the intestine of piglets after enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) infection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2024, 1871, 119711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, R.K.; Basuroy, S.; Rao, V.U.; Karnaky, K.J., Jr.; Gupta, A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem. J. 2002, 368, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, Q.; Mark Evers, B.; Chung, D.H. Oxidative stress-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis is mediated by p38 MAPK. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 350, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Bin, P.; Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Yin, J.; Liu, G.; Tang, Z.; Ren, W. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli infection promotes apoptosis in piglets. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 125, 290–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An Iron-Dependent Form of Nonapoptotic Cell Death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; He, Y.; Lin, L.; Chen, P.; Chen, M.; Zhang, S. The emerging role of ferroptosis in intestinal disease. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; You, J.; Yang, Y.; Li, X. Protective immunity of a Multivalent Vaccine Candidate against piglet diarrhea caused by enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) in a pig model. Vaccine 2018, 36, 723–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Wu, W.; Pang, S.; Pan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, G.; Dudley, E.G. Coimmunization with Two Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (ETEC) Fimbrial Multiepitope Fusion Antigens Induces the Production of Neutralizing Antibodies against Five ETEC Fimbriae (F4, F5, F6, F18, and F41). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e00217-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motallebi, M.; Bhia, M.; Rajani, H.F.; Bhia, I.; Tabarraei, H.; Mohammadkhani, N.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Kasaii, M.S.; Nouri-Majd, S.; Mueller, A.L.; et al. Naringenin: A potential flavonoid phytochemical for cancer therapy. Life Sci. 2022, 305, 120752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, N.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Tan, X.; Liao, B.; Li, P.; Feng, J. Oxidative stress signaling in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy and the potential therapeutic role of antioxidant naringenin. Redox Rep. Commun. Free. Radic. Res. 2023, 28, 2246720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikram, A.; Jayaprakasha, G.K.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Suppression of bacterial cell-cell signalling, biofilm formation and type III secretion system by citrus flavonoids. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 109, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, M.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Tan, Z.; Han, X.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Lv, J.; et al. Naringenin alleviates intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via targeting YAP/STAT3 signaling axis. Phytomedicine: Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 135, 156095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Mao, J.; Ma, D.; Han, X.; Tian, L.; Zhu, Q.; Lu, G.; Yan, X.; et al. Naringenin Alleviates Radiation-Induced Intestinal Injury by Inhibiting TRPV6 in Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2024, 68, e2300745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patankar, J.V.; Becker, C. Cell death in the gut epithelium and implications for chronic inflammation. Nat. reviews. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, Q.; Huang, F.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Long chain PUFA ameliorate ETEC-induced intestinal inflammation and cell injury by modulating pyroptosis and necroptosis signaling pathways in IPEC-1 cells—CORRIGENDUM. Br. J. Nutr. 2022, 128, 991–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Chen, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, S.; Huang, R.; Zhu, G.; Yin, Y.; Ren, W.; Deng, J. GABA attenuates ETEC-induced intestinal epithelial cell apoptosis involving GABA(A)R signaling and the AMPK-autophagy pathway. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 7509–7522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, K.; Zhou, M.; Lv, Q.; He, P.; Qin, X.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y. Protocatechuic acid and quercetin attenuate ETEC-caused IPEC-1 cell inflammation and injury associated with inhibition of necroptosis and pyroptosis signaling pathways. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2023, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Du, M.; Ji, X.; Liu, X.; Zhao, C.; Pang, X.; Jin, E.; Wen, A.; Li, S.; et al. Berberine alleviates ETEC-induced intestinal inflammation and oxidative stress damage by optimizing intestinal microbial composition in a weaned piglet model. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1460127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Du, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhang, T. GPX4-independent ferroptosis-a new strategy in disease’s therapy. Cell Death Discov. 2022, 8, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewerenz, J.; Hewett, S.J.; Huang, Y.; Lambros, M.; Gout, P.W.; Kalivas, P.W.; Massie, A.; Smolders, I.; Methner, A.; Pergande, M.; et al. The cystine/glutamate antiporter system x(c)(-) in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 18, 522–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Pan, J.; Huang, S.; Chen, X.; Chang, A.C.Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Hydrogen sulfide protects cardiomyocytes from doxorubicin-induced ferroptosis through the SLC7A11/GSH/GPx4 pathway by Keap1 S-sulfhydration and Nrf2 activation. Redox Biol. 2024, 70, 103066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Ren, H.; Wang, J.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, L. CHAC1: A master regulator of oxidative stress and ferroptosis in human diseases and cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1458716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Koppula, P.; Gan, B. Regulation of H2A ubiquitination and SLC7A11 expression by BAP1 and PRC1. Cell Cycle 2019, 18, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Zeng, X.A.; Wang, M.S.; Brennan, C.S.; Gong, D. Modification of membrane properties and fatty acids biosynthesis-related genes in Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus: Implications for the antibacterial mechanism of naringenin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calis, Z.; Dasdelen, D.; Baltaci, A.K.; Mogulkoc, R. Naringenin Prevents Inflammation, Apoptosis, and DNA Damage in Potassium Oxonate-Induced Hyperuricemia in Rat Liver Tissue: Roles of Cytochrome C, NF-κB, Caspase-3, and 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2022, 20, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.X.; Yang, X.Y.; Han, B.S.; Hu, Y.Y.; An, T.; Lv, B.H.; Lian, J.; Wang, T.Y.; Bao, X.L.; Gao, L.; et al. Naringenin regulates gut microbiota and SIRT1/PGC-1ɑ signaling pathway in rats with letrozole-induced polycystic ovary syndrome. Biomed. Pharmacother. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 153, 113286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Lin, T.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Song, Z.; Pan, X. Naringenin protects against acute pancreatitis-associated intestinal injury by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation via AhR signaling. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1090261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhao, F.; Li, H.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F. HSP90 mediates the connection of multiple programmed cell death in diseases. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Yu, T.; Zhu, R.; Lu, J.; Ouyang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, Q.; Li, J.; Cui, J.; Jiang, F.; et al. Timosaponin AIII promotes non-small-cell lung cancer ferroptosis through targeting and facilitating HSP90 mediated GPX4 ubiquitination and degradation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 1471–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; She, R.; Mei, Z.; Liu, D.; Ge, J. Crosstalk between ferroptosis and necroptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury and Naotaifang formula exerts neuroprotective effect via HSP90-GCN2-ATF4 pathway. Phytomedicine Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 130, 155399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ouyang, B.; Ning, B.; Wang, Y.; Guo, H.; Pang, Z.; Shen, S. Localized disruption of redox homeostasis boosting ferroptosis of tumor by hydrogel delivery system. Mater. Today Bio 2021, 12, 100154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Symbol | Accession Number | Primer Sequence (5′→3′) | Product Size/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPX4 (pig) | NM_214407.1 | F: CTGCTGGCTACAACGTCAAA R: AGTTCCATTTGTAGCATTTCCCA | 135 |
| CHAC1 (pig) | XM_021084905.1 | F: TCCTTGAAGATTGTGAGGGCT R: CCTCCTTGGTGTCATAGCCA | 126 |
| SLC7A11 (pig) | XM_021101587.1 | F: CCTGGGCAGGAGAAAGTTGT R: AGGACAAGGCTCCAAACAGT | 193 |
| GAPDH (pig) | NM_001206359.1 | F: AACGTGTCGGTTGTGGATCT R: TCACAGGACACAACCTGGTC | 140 |
| HSP90 (pig) | NM_213973.2 | F: AAGACCGGACCCTCACGATA R: AGGCATACTGCTCGTCATCG | 231 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, P.; Liu, K.; Cui, Y.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Hou, Z.; Cui, J.; Chen, N.; Fan, J.; Li, J.; et al. Naringenin Inhibits Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080914
Jiang P, Liu K, Cui Y, Liu P, Wang X, Hou Z, Cui J, Chen N, Fan J, Li J, et al. Naringenin Inhibits Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(8):914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080914
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Pengxin, Kangping Liu, Yanan Cui, Puyu Liu, Xutao Wang, Zijuan Hou, Jiamei Cui, Ning Chen, Jinghui Fan, Jianguo Li, and et al. 2025. "Naringenin Inhibits Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells" Antioxidants 14, no. 8: 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080914
APA StyleJiang, P., Liu, K., Cui, Y., Liu, P., Wang, X., Hou, Z., Cui, J., Chen, N., Fan, J., Li, J., Zuo, Y., & Li, Y. (2025). Naringenin Inhibits Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli-Induced Ferroptosis via Targeting HSP90 in IPEC-J2 Cells. Antioxidants, 14(8), 914. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080914






