The Effect of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Intestinal Injury in Chickens Through RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of OTA-Contaminated Moldy Feed
2.2.1. Activation and Culture of Bacteria
2.2.2. Preparation of Moldy Feed
2.2.3. Determination of OTA Concentration in Moldy Feed
2.3. Animal Research
2.4. HE Staining
2.5. NO Detection
2.6. CCK8 to Determine Cell Viability and Cell Culture with Treatment
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Analysis of Interleukin Index
2.9. Detection of Related Gene Expression
2.10. Western Blotting of Protein Expression
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
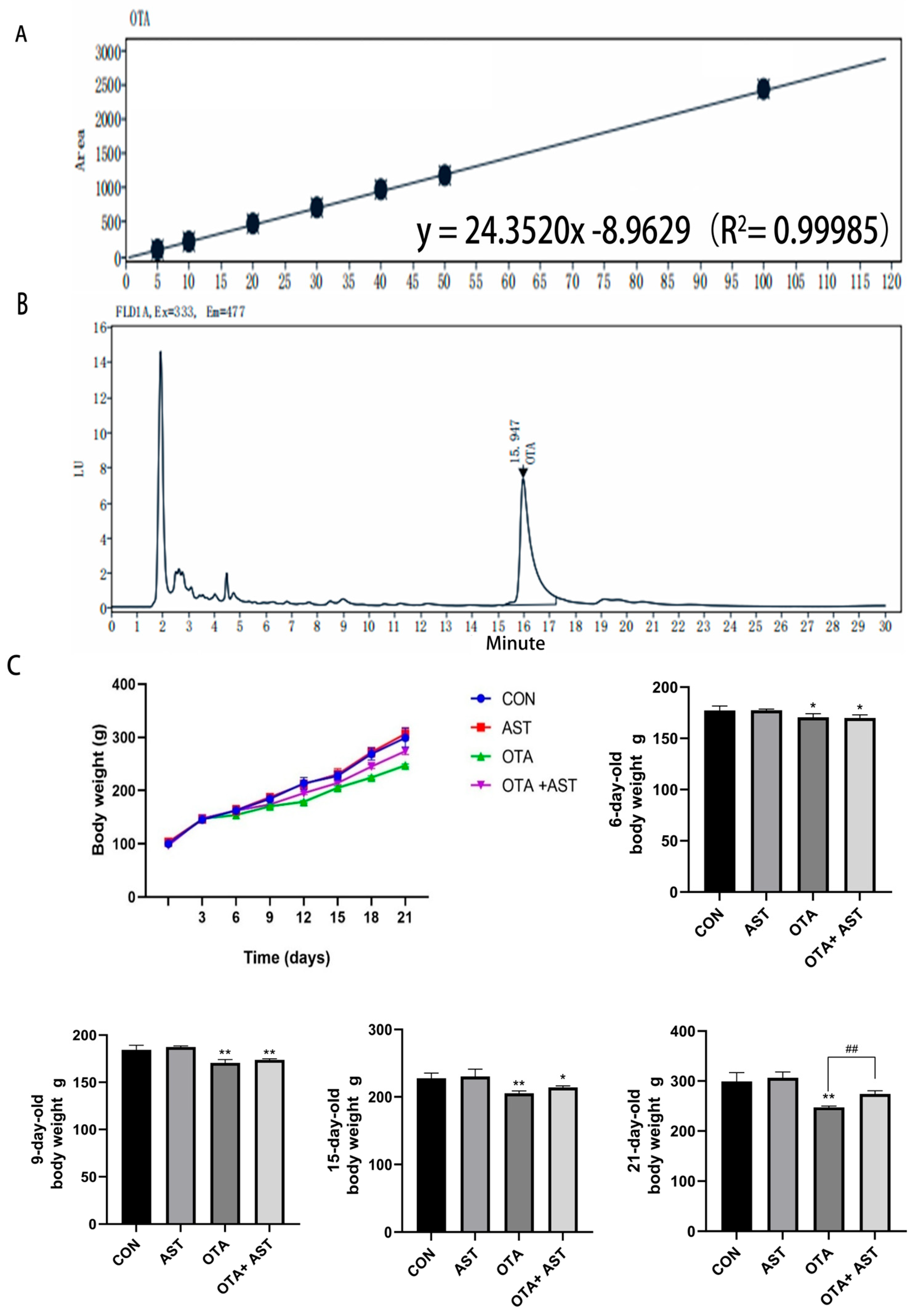
3.1. AST Alleviated the Damage of OTA on Chickens and CSIECs
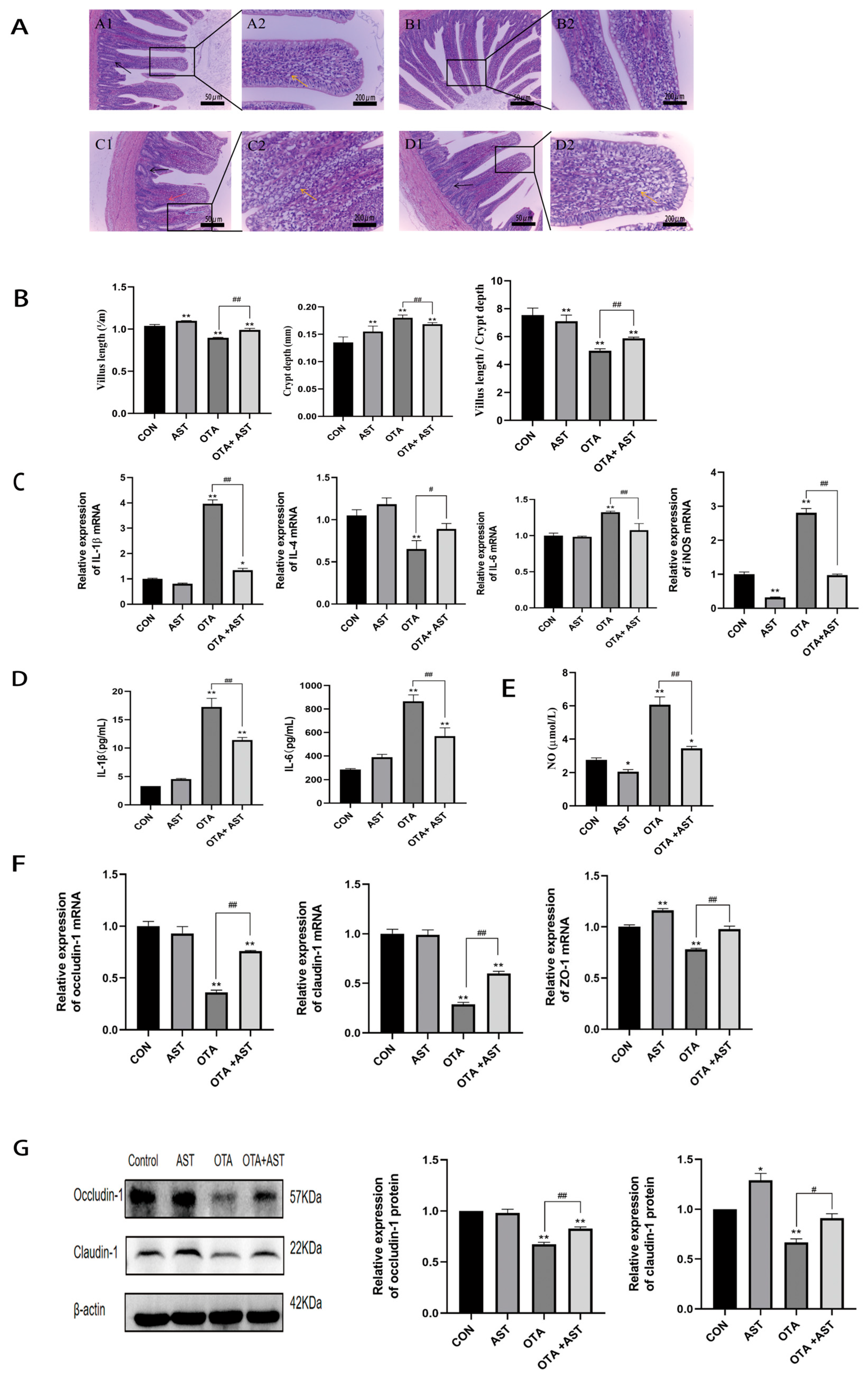
3.2. AST Alleviated the Inflammatory Damage Caused by OTA to the Jejunum of Chickens
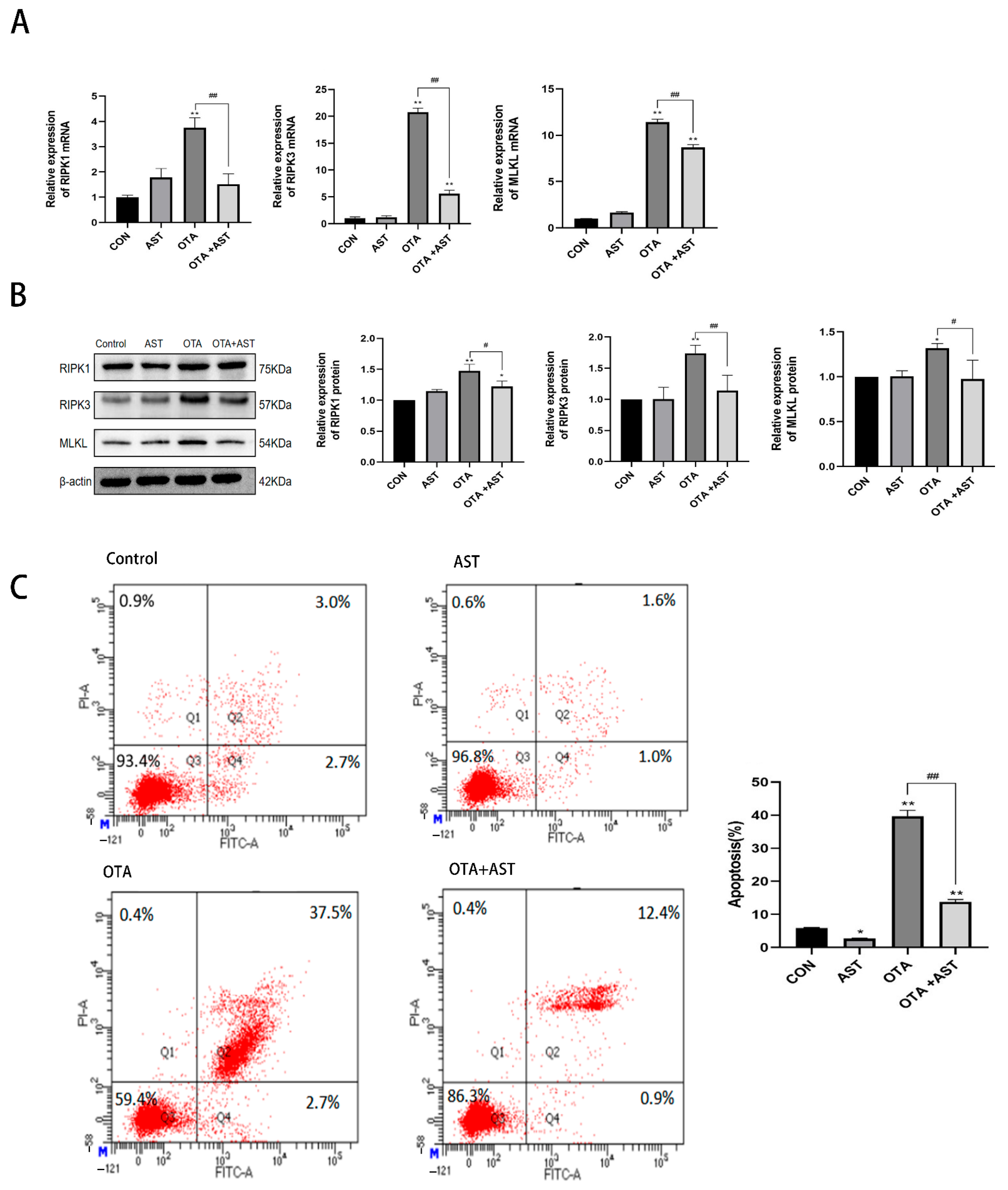
3.3. AST Alleviated OTA-Induced Necroptosis in the Chicken Jejunum by Modulating the RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Signaling Pathway
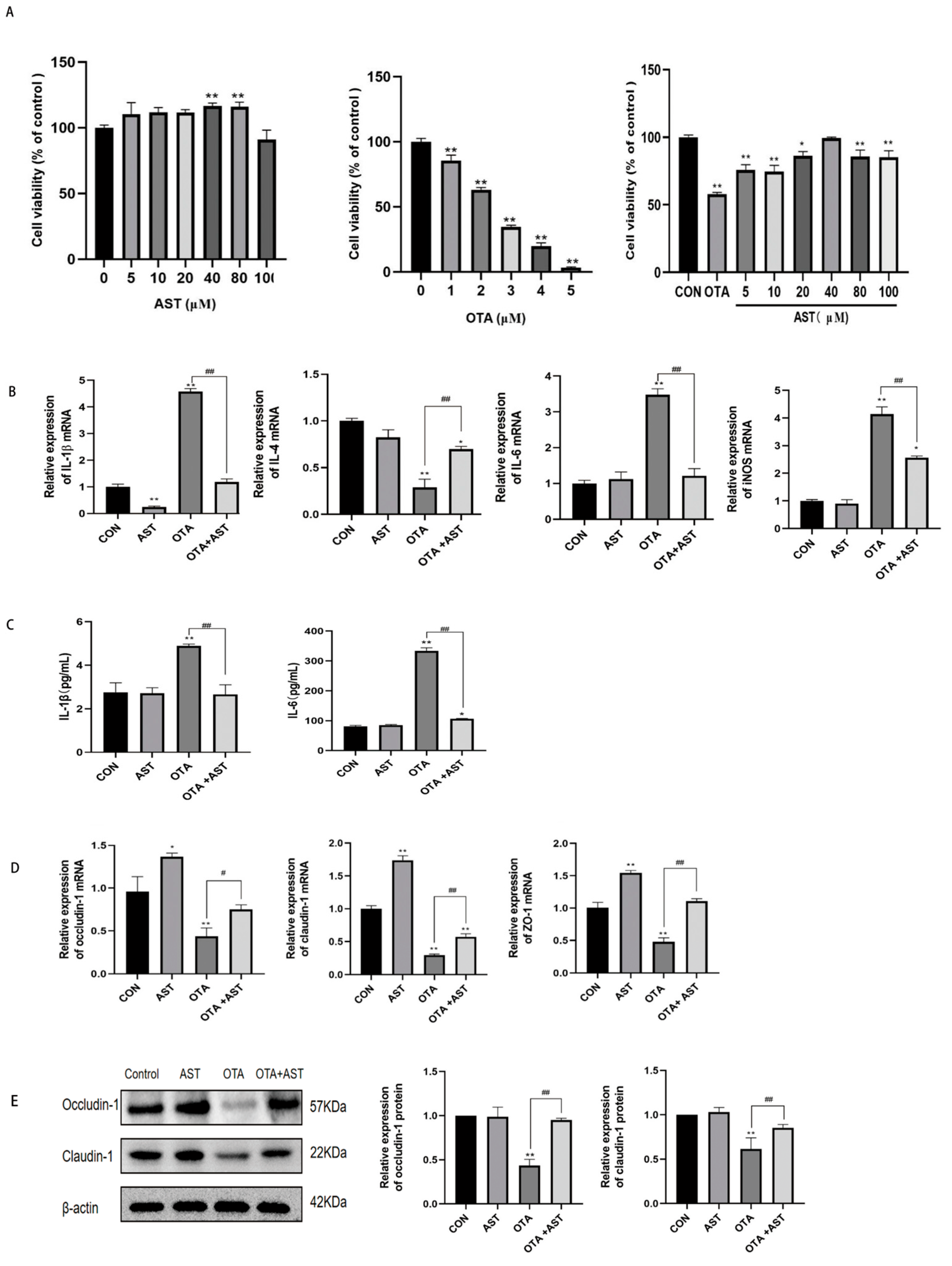
3.4. AST Alleviated the Inflammatory Damage Caused by OTA on CSIECs
3.5. AST Alleviated the Necroptosis of OTA on CSIECs by Interfering with RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway
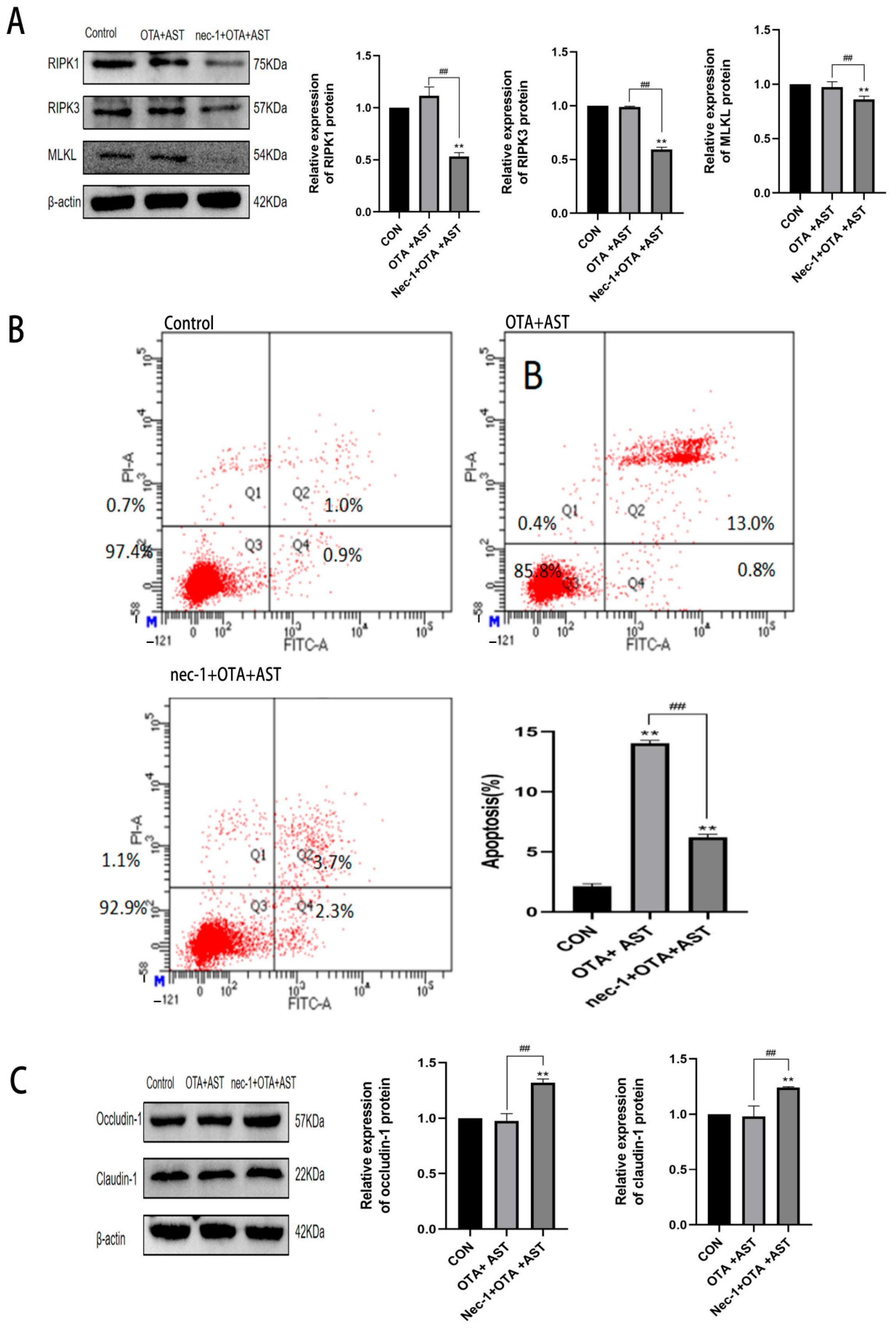
3.6. Nec-1 Promoted the Antagonistic Effect of AST on OTA-Induced Necroptosis and Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jorgensen, K. Survey of pork, poultry, coffee, beer and pulses for ochratoxin A. Food Addit. Contam. 1998, 15, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, L.; Marín, S.; Sanchis, V.; Ramos, A.J. Screening of mycotoxin multicontamination in medicinal and aromatic herbs sampled in Spain. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2009, 89, 1802–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabarani, A.; Zinedine, A.; Bouchriti, N.; Abdennebi, E. Exposure assessment to ochratoxin A through the intake of three cereal derivatives from the Moroccan market. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Sharma, B.; Borah, R.; Haque, S.; Mahmud, M.M.C.; Shah, A.K.; Rawal, D.; Bora, H.; Bui, S. Ochratoxins in food and feed: Occurrence and its impact on human health and management strategies. Toxicon 2020, 187, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, L.T.; Shen, X.; Wei, X.Q.; Huang, X.N.; Liu, Y.J.; Sun, X.L.; Wang, Z.H.; Sun, Y.M.; Xu, Z.L.; et al. Broad-Specificity Immunoassay for Simultaneous Detection of Ochratoxins A, B, and C in Millet and Maize. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4830–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damiano, S.; Longobardi, C.; De Marchi, L.; Piscopo, N.; Meucci, V.; Lenzi, A.; Ciarcia, R. Detection of Ochratoxin A in Tissues of Wild Boars (Sus scrofa) from Southern Italy. Toxins 2025, 17, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, Y.; Katsunuma, Y.; Nunokawa, M.; Minato, H.; Yonemochi, C. Influence of repeated ochratoxin A ingestion on milk production and its carry-over into the milk, blood and tissues of lactating cows. Anim. Sci. J. 2016, 87, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.C.; Pushparaj, K.; Meyyazhagan, A.; Arumugam, V.A.; Pappuswamy, M.; Bhotla, H.K.; Baskaran, R.; Issara, U.; Balasubramanian, B.; Khaneghah, A.M. Ochratoxin A as an alarming health threat for livestock and human: A review on molecular interactions, mechanism of toxicity, detection, detoxification, and dietary prophylaxis. Toxicon 2022, 213, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, A.R.; Balasubramanian, B.; Park, S.; Jha, R.; Andretta, I.; Bakare, A.G.; Kim, I.H. Ochratoxin A: Carryover from animal feed into livestock and the mitigation strategies. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 7, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milani, J.; Heidari, S. Stability of Ochratoxin a During Bread Making Process. J. Food Saf. 2017, 37, e12283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahal, S.; Lee, H.J.; Gu, K.J.; Ryu, D.J. Heat Stability of Ochratoxin A in an Aqueous Buffered Model System. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1748–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duarte, S.C.; Lino, C.M.; Pena, A. Ochratoxin A in feed of food-producing animals: An undesirable mycotoxin with health and performance effects. Vet. Microbiol. 2011, 154, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penagos-Tabares, F.; Todorov, A.; Raj, J.; Farkas, H.; Grubjesic, G.; Jakovcevic, Z.; Cujic, S.; Nedeljkovic-Trailovic, J.; Vasiljevic, M. Multi-Mycotoxin Contamination in Serbian Maize During 2021–2023: Climatic Influences and Implications for Food and Feed Safety. Toxins 2025, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 574/2011 of 16 June 2011 amending Annex I to Directive 2002/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards maximum levels for nitrite, melamine, Ambrosia spp. and carry-over of certain coccidiostats and histomonostats and consolidating Annexes I and II thereto. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2011, L159, 7–24.
- Wang, H.; Zhai, N.H.; Chen, Y.; Fu, C.Y.; Huang, K.H. OTA induces intestinal epithelial barrier dysfunction and tight junction disruption in IPEC-J2 cells through ROS/Ca2+-mediated MLCK activation. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 242, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marin, D.E.; Pistol, G.C.; Gras, M.A.; Palade, M.L.; Taranu, I. Comparative effect of ochratoxin A on inflammation and oxidative stress parameters in gut and kidney of piglets. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 89, 224–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.Y.; Zhang, B.Y.; Dai, Y.Q.; Li, H.Y.; Xu, W.T. A Review: Epigenetic Mechanism in Ochratoxin A Toxicity Studies. Toxins 2017, 9, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafai, S.; Cimbalo, A.; Manyes, L. Evaluation of Dietary Bioactive Agents Against Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A-Induced Duodenal Toxicity in Rats. Foods 2025, 14, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, D.Y.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Wang, H.; Zhai, S.S.; Jiang, X.Z.; Meca, G.; Wang, S.X.; et al. Melatonin alleviates Ochratoxin A-induced liver inflammation involved intestinal microbiota homeostasis and microbiota-independent manner. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 413, 125239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroemer, G.; Galluzzi, L.; Vandenabeele, P.; Abrams, J.; Alnemri, E.S.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Blagosklonny, M.V.; El-Deiry, W.S.; Golstein, P.; Green, D.R.; et al. Classification of cell death: Recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2009. Cell Death Differ. 2009, 16, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holler, N.; Zaru, R.; Micheau, O.; Thome, M.; Attinger, A.; Valitutti, S.; Bodmer, J.L.; Schneider, P.; Seed, B.; Tschopp, J. Fas triggers an alternative, caspase-8-independent cell death pathway using the kinase RIP as effector molecule. Nat. Immunol. 2000, 1, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hitomi, J.; Christofferson, D.E.; Ng, A.; Yao, J.; Degterev, A.; Xavier, R.J.; Yuan, J. Identification of a molecular signaling network that regulates a cellular necrotic cell death pathway. Cell 2008, 135, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Yin, J.; Starovasnik, M.A.; Fairbrother, W.J.; Dixit, V.M. Identification of a novel homotypic interaction motif required for the phosphorylation of receptor-interacting protein (RIP) by RIP3. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 9505–9511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.; Challa, S.; Moquin, D.; Genga, R.; Ray, T.D.; Guildford, M.; Chan, F.K.M. Phosphorylation-Driven Assembly of the RIP1-RIP3 Complex Regulates Programmed Necrosis and Virus-Induced Inflammation. Cell 2009, 137, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Tang, M.B.; Luo, H.Y.; Shi, C.H.; Xu, Y.M. Necroptosis in neurodegenerative diseases: A potential therapeutic target. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Jiang, W.D.; Wu, P.; Liu, Y.; Ren, H.M.; Jin, X.W.; Feng, L.; Zhou, X.Q. Dietary curcumin alleviates intestinal damage induced by ochratoxin A in juvenile grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella): Necroptosis and inflammatory responses. Anim. Nutr. 2024, 18, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Ryu, D.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, H.Y. Ochratoxin A induces hepatic and renal toxicity in mice through increased oxidative stress, mitochondrial damage, and multiple cell death mechanisms. Arch. Toxicol. 2024, 98, 2281–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longobardi, C.; Ferrara, G.; Andretta, E.; Montagnaro, S.; Damiano, S.; Ciarcia, R. Ochratoxin A and Kidney Oxidative Stress: The Role of Nutraceuticals in Veterinary Medicine-A Review. Toxins 2022, 14, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, L.L.; Wang, D.X.; Yin, K.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, H.M.; Guo, T.T.; Li, J.B.; Zhao, H.J.; Xing, M.W. Polystyrene microplastics induce apoptosis in chicken testis via crosstalk between NF-KB and Nrf2 pathways. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2022, 262, 109444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z. A Preliminary Study on Astragalus Polysaccharide Protection of Ochratoxin A-induced Chicken Liver Injury; Jilin University: Changchun, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, E. Astaxanthin as a Medical Food. Funct. Foods Health Dis. 2013, 3, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.X.; Xiong, F. Astaxanthin and its Effects in Inflammatory Responses and Inflammation-Associated Diseases: Recent Advances and Future Directions. Molecules 2020, 25, 5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koller, M.; Muhr, A.; Braunegg, G. Microalgae as versatile cellular factories for valued products. Algal Res. -Biomass Biofuels Bioprod. 2014, 6, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhri, S.; Aneva, I.Y.; Farzaei, M.H.; Sobarzo-Sánchez, E. The Neuroprotective Effects of Astaxanthin: Therapeutic Targets and Clinical Perspective. Molecules 2019, 24, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi, A.; Dargahi, L.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Pourgholami, M.H.; Asgari, A.; Manoochehri, M.; Jorjani, M. Neuroprotective effects of astaxanthin in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Behav. Brain Res. 2017, 329, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.M.; Cai, X.L.; Wen, Q.P. Astaxanthin reduces isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 4073–4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.B.; Cui, R.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, C.; Zhang, J.Y. Astaxanthin alleviated acute lung injury by inhibiting oxidative/nitrative stress and the inflammatory response in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.T.; Zhang, S.Y.; Yang, J.; Qin, C.; Jin, B.; Liang, Z.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Li, L.; Long, M. Protective Effects of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Liver Injury: Effects of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Mitochondrial Fission-Fusion Balance. Toxins 2024, 16, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrenk, D.; Bignami, M.; Bodin, L.; Chipman, J.K.; del Mazo, J.; Grasl-Kraupp, B.; Hogstrand, C.; Hoogenboom, L.; Leblanc, J.C.; Nielsen, E.; et al. Risks for animal health related to the presence of ochratoxin A (OTA) in feed. Efsa J. 2023, 21, e08375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Cafsi, I.; Bjeoui, S.; Rabeh, I.; Nechi, S.; Chelbi, E.; El Cafsi, M.; Ghram, A. Effects of ochratoxin A on membrane phospholipids of the intestine of broiler chickens, practical consequences. Animal 2020, 14, 933–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, D.; Wang, W.C.; Lin, C.X.; Fouad, A.M.; Chen, W.; Xia, W.G.; Wang, S.; Luo, X.; Zhang, W.H.; Yan, S.J.; et al. Effects of curcumin on performance, antioxidation, intestinal barrier and mitochondrial function in ducks fed corn contaminated with ochratoxin A. Animal 2019, 13, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vakili, R.; Zanghaneh, A.; Qharari, F.; Mortzavi, F. Hydroalcoholic Extract of Saffron Petals, Yeast Cell Wall and Bentonite Reduce Contamination Effects with Aflatoxin B1 and Ochratoxin A in Exposed Broilers. Vet. Med. Sci. 2025, 11, e70122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yan, A.; Liu, X.Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, F.F.; Wang, M.Z.; Loor, J.J.; Wang, H.R. Melatonin ameliorates ochratoxin A induced liver inflammation, oxidative stress and mitophagy in mice involving in intestinal microbiota and restoring the intestinal barrier function. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 407, 124489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.W.; Kim, M.O.; Shin, S.; Kwon, W.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kwon, Y.J.; Lee, S.I. Spirobenzofuran Mitigates Ochratoxin A-Mediated Intestinal Adverse Effects in Pigs through Regulation of Beta Defensin 1. Toxics 2024, 12, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakai, S.; Nishida, A.; Ohno, M.; Inatomi, O.; Bamba, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kawahara, M.; Andoh, A. Astaxanthin, a xanthophyll carotenoid, prevents development of dextran sulphate sodium-induced murine colitis. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2019, 64, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assar, D.H.; Abou Asa, S.; El-Abasy, M.A.; Elbialy, Z.; Shukry, M.; Latif, A.A.; BinMowyna, M.N.; Althobaiti, N.A.; El-Magd, M.A. Aspergillus awamori attenuates ochratoxin A-induced renal and cardiac injuries in rabbits by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway and downregulating IL1β, TNFα, and iNOS gene expressions. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 69798–69817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.W.; Shin, S.; Park, J.; Lee, B.R.; Lee, S.I. TLR/MyD88-Mediated Inflammation Induced in Porcine Intestinal Epithelial Cells by Ochratoxin A Affects Intestinal Barrier Function. Toxics 2023, 11, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korhonen, R.; Lahti, A.; Kankaanranta, H.; Moilanen, E. Nitric Oxide Production and Signaling in Inflammation. Curr. Drug Targets-Inflamm. Allergy 2005, 4, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, A.L.; Menconi, M.J.; Unno, N.; Ezzell, R.M.; Casey, D.M.; Gonzalez, P.K.; Fink, M.P. Nitric oxide dilates tight junctions and depletes ATP in cultured Caco-2BBe intestinal epithelial monolayers. Am. J. Physiol. 1995, 268, G361–G373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witthoft, T.; Eckmann, L.; Kim, J.M.; Kagnoff, M.F. Enteroinvasive bacteria directly activate expression of iNOS and NO production in human colon epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, G564–G571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, T.; Sershen, C.L.; May, E.E. Investigating the Role of TNF-α and IFN-γ Activation on the Dynamics of iNOS Gene Expression in LPS Stimulated Macrophages. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soufli, I.; Toumi, R.; Rafa, H.; Touil-Boukoffa, C. Overview of cytokines and nitric oxide involvement in immuno-pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel diseases. World J. Gastrointest. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 7, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Hiraku, Y.; Ma, N.; Kato, T.; Saito, K.; Nagahama, M.; Semba, R.; Kuribayashi, K.; Kawanishi, S. Inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent DNA damage in mouse model of inflammatory bowel disease. Cancer Sci. 2005, 96, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, D.; Yun, T.; Koo, Y.; Chae, Y.; Kang, J.H.; Kang, B.T.; Yang, M.P.; Kim, H. Clinical signs, duodenal histopathological grades, and serum high-mobility group box 1 concentrations in dogs with inflammatory bowel disease. J. Vet. Intern. Med. 2021, 35, 2205–2214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.L.; Fu, Q.J.; Qin, L.L.; Lin, L.Y.; Wu, Q.; Zeng, K.Q.; Wu, J.H.; Cao, Z.Y.; Ou, Y.F. Ochratoxin A induces lung cell PANoptosis through activation of the AIM 2 inflammasome. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2025, 150, 114184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, L.; Liang, P.; Qu, Y.H.; An, T.Y.; Wang, J.H.; Deng, X.N.; Bai, L.Y.; Shen, P.J.; Bai, D.S. Protective effect of astaxanthin against SnS2 nanoflowers induced testes toxicity by suppressing RIPK1-RIPK3-MLKL signaling in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Gene Name | Primer (5′–3′) | Sequence Number |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | F:CCAGCCATGTATGTAGCCATCCAG R:AACACCATCACCAGAGTCCATCAC | NM_205518.2 |
| IL-1β | F:CAGAAGAAGCCTCGCCTGGATTC R:GCCTCCGCAGCAGTTTGGTC | NM_204524.2 |
| IL-6 | F:AAATCCCTCCTCGCCAATCT R:CCCTCACGGTCTTCTCCATAAA | NM_204628.2 |
| IL-4 | F:CTTCCTCAACATGCGTCAGC R:TGAAGTAGTGTTGCCTGCTGC | NM_001007079.2 |
| Occludin | F:CTGCTCTGCCTCATCTGCTTCTTC R:CCATCCGCCACGTTCTTCACC | NM_205128.1 |
| Claudin-1 | F:GACCAGGTGAAGAAGATGCGGATG R:CGAGCCACTCTGTTGCCATACC | NM_001013611.2 |
| ZO-1 | F:TCTTCCTCCTCCCGCTTCTTCAC R:AGAGATGGTGGTGTAGGCAGTGG | XM_040706827.2 |
| RIPK1 | F:GATCACGACTACGAACGAGATGGAC R:AACTGTAGCACCTTTGGAGCCTTG | NM_001397225.1 |
| RIPK3 | F:AACCACATCCTTGACATCCTTCGC R:CACTACAACCTGTGCTGCCTTCTC | XM_046925830.1 |
| MLKL | F:CCATGGGTGGTTCCTCCTTC R:TGGATCTTCCGCACCTTAGC | XM_010717908.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fan, R.; Tian, W.; Jin, B.; Sun, Y.; Long, M.; Yang, S.; Li, P. The Effect of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Intestinal Injury in Chickens Through RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080915
Fan R, Tian W, Jin B, Sun Y, Long M, Yang S, Li P. The Effect of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Intestinal Injury in Chickens Through RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway. Antioxidants. 2025; 14(8):915. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080915
Chicago/Turabian StyleFan, Ruiwen, Wenqi Tian, Bo Jin, Yuhang Sun, Miao Long, Shuhua Yang, and Peng Li. 2025. "The Effect of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Intestinal Injury in Chickens Through RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway" Antioxidants 14, no. 8: 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080915
APA StyleFan, R., Tian, W., Jin, B., Sun, Y., Long, M., Yang, S., & Li, P. (2025). The Effect of Astaxanthin on Ochratoxin A-Induced Intestinal Injury in Chickens Through RIPK1/RIPK3/MLKL Pathway. Antioxidants, 14(8), 915. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox14080915







