Local and Global Changes in Brain Metabolism during Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Surgical Procedure
2.3. PET Imaging and Analysis
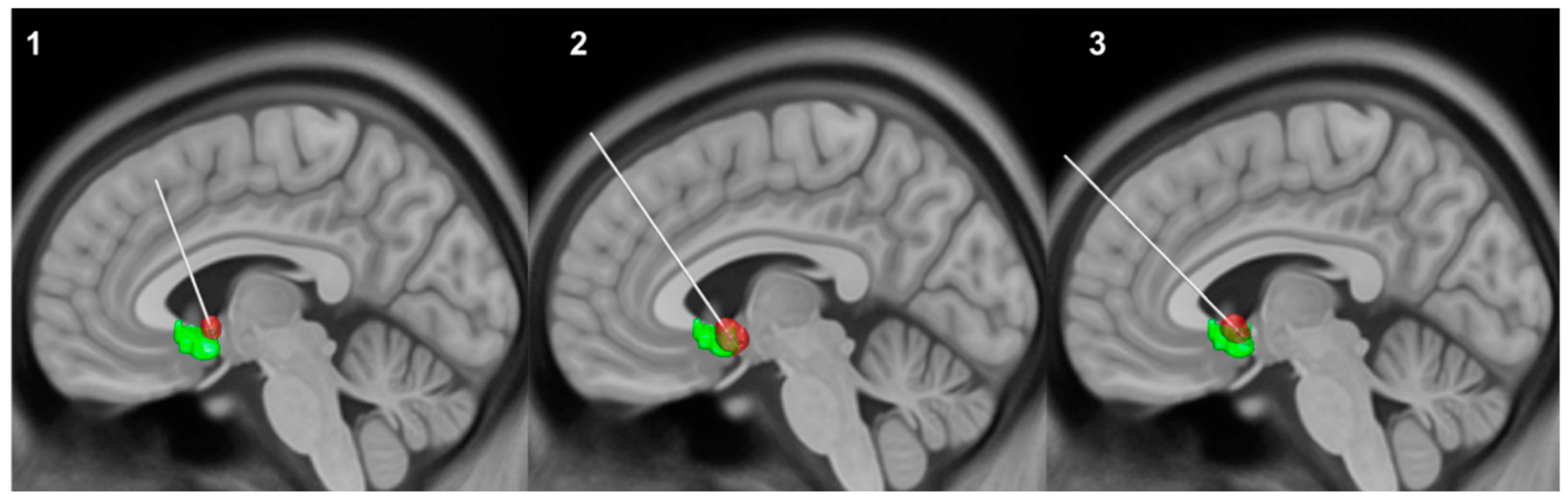
2.4. Reconstruction of Volume of Tissue Activated
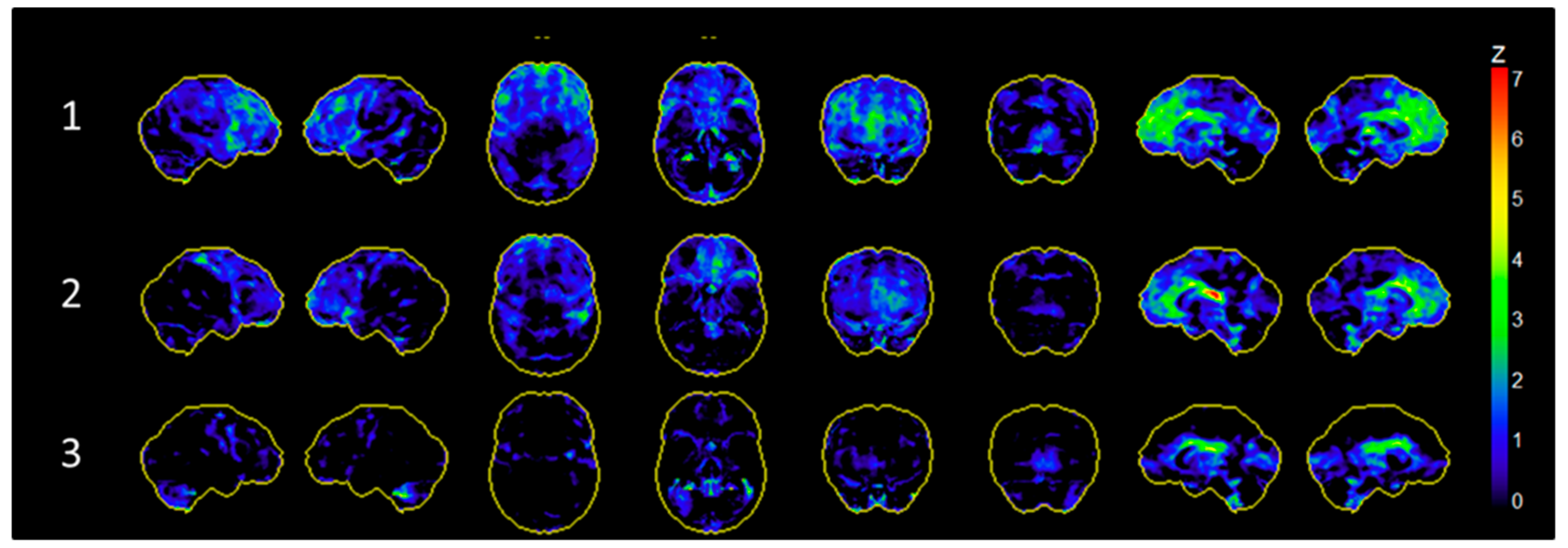
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ruscio, A.M.; Stein, D.J.; Chiu, W.T.; Kessler, R.C. The epidemiology of obsessive-compulsive disorder in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Mol. Psychiatry 2010, 15, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mian, M.K.; Campos, M.; Sheth, S.A.; Eskandar, E.N. Deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Past, present, and future. Neurosurg. Focus 2010, 29, E10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldermann, J.C.; Melzer, C.; Zapf, A.; Kohl, S.; Timmermann, L.; Tittgemeyer, M.; Huys, D.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kühn, A.A.; Horn, A.; et al. Connectivity Profile Predictive of Effective Deep Brain Stimulation in Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 85, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, F.A.; Asaad, W.F.; Foote, K.D.; Anderson, W.S.; Rees Cosgrove, G.; Baltuch, G.H.; Beasley, K.; Reymers, D.E.; Oh, E.S.; Targum, S.D.; et al. Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the fornix for Alzheimer’s disease: Surgical safety in the ADvance trial. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oswal, A.; Beudel, M.; Zrinzo, L.; Limousin, P.; Hariz, M.; Foltynie, T.; Litvak, V.; Brown, P. Deep brain stimulation modulates synchrony within spatially and spectrally distinct resting state networks in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2016, 139, 1482–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figee, M.; Luigjes, J.; Smolders, R.; Valencia-Alfonso, C.E.; van Wingen, G.; de Kwaasteniet, B.; Mantione, M.; Ooms, P.; de Koning, P.; Vulink, N.; et al. Deep brain stimulation restores frontostriatal network activity in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Nat. Neurosci. 2013, 16, 386–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, D.D.; Chou, T.; Corse, A.K.; Arulpragasam, A.R.; Widge, A.S.; Cusin, C.; Evans, K.C.; Greenberg, B.D.; Haber, S.N.; Deckersbach, T. Acute deep brain stimulation changes in regional cerebral blood flow in obsessive-compulsive disorder. J. Neurosurg. 2016, 125, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sturm, V.; Lenartz, D.; Koulousakis, A.; Treuer, H.; Herholz, K.; Klein, J.C.; Klosterkötter, J. The nucleus accumbens: A target for deep brain stimulation in obsessive-compulsive- and anxiety-disorders. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003, 26, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suetens, K.; Nuttin, B.; Gabriels, L.; van Laere, K. Differences in Metabolic Network Modulation Between Capsulotomy and Deep-Brain Stimulation for Refractory Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 951–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huys, D.; Kohl, S.; Baldermann, J.C.; Timmermann, L.; Sturm, V.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Kuhn, J. Open-label trial of anterior limb of internal capsule–nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation for obsessive-compulsive disorder: Insights gained. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, A.C.; Collins, D.L.; Mills, S.R.; Brown, E.D.; Kelly, R.L.; Peters, T.M. 3D statistical neuroanatomical models from 305 MRI volumes. In Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE Conference Record Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 October 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Della Rosa, P.A.; Cerami, C.; Gallivanone, F.; Prestia, A.; Caroli, A.; Castiglioni, I.; Gilardi, M.C.; Frisoni, G.; Friston, K.; Ashburner, J.; et al. A Standardized [18F]-FDG-PET Template for Spatial Normalization in Statistical Parametric Mapping of Dementia. Neuroinformatics 2014, 12, 575–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Landeau, B.; Papathanassiou, D.; Crivello, F.; Etard, O.; Delcroix, N.; Mazoyer, B.; Joliot, M. Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 2002, 15, 273–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minoshima, S.; Frey, K.A.; Koeppe, R.A.; Foster, N.L.; Kuhl, D.E. A diagnostic approach in Alzheimer’s disease using three-dimensional stereotactic surface projections of fluorine-18-FDG PET. J. Nucl. Med. 1995, 36, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vollmar, S.; Čížek, J.; Sué, M.; Klein, J.; Jacobs, A.H.; Herholz, K. VINCI—“Volume Imaging in Neurological Research, Co-Registration and ROIs included”. In Forschung und Wissenschaftliches Rechnen 2003; Kremer, K., Macho, V., Eds.; Forschung and wissenschaftliches Rechnen: Göttingen, Germany, 2004; Volume GWDG, pp. 115–131. [Google Scholar]
- Horn, A.; Li, N.; Dembek, T.A.; Kappel, A.; Boulay, C.; Ewert, S.; Tietze, A.; Husch, A.; Perera, T.; Neumann, W.J.; et al. Lead-DBS v2: Towards a comprehensive pipeline for deep brain stimulation imaging. Neuroimage 2019, 184, 293–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horn, A.; Reich, M.; Vorwerk, J.; Li, N.; Wenzel, G.; Fang, Q.; Schmitz-Hübsch, T.; Nickl, R.; Kupsch, A.; Volkmann, J.; et al. Connectivity Predicts deep brain stimulation outcome in Parkinson disease. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 82, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Zhan, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zuo, C.; Sun, B. Modified fluorodeoxyglucose metabolism in motor circuitry by subthalamic deep brain stimulation. Stereotact. Funct. Neurosurg. 2017, 95, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.J.; Oh, J.S.; Moon, H.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, M.S.; Chung, S.J.; Kim, J.S.; Jeon, S.R. Parkinson Disease-Related Pattern of Glucose Metabolism Associated With the Potential for Motor Improvement After Deep Brain Stimulation. Neurosurgery 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, J.; Hardenacke, K.; Lenartz, D.; Gruendler, T.; Ullsperger, M.; Bartsch, C.; Mai, J.K.; Zilles, K.; Bauer, A.; Matusch, A.; et al. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus basalis of Meynert in Alzheimer’s dementia. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agnesi, F.; Connolly, A.T.; Baker, K.B.; Vitek, J.L.; Johnson, M.D. Deep Brain Stimulation Imposes Complex Informational Lesions. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, C.C.; Grill, W.M.; Sherman, D.L.; Thakor, N. V Cellular Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation: Model-Based Analysis of Activation and Inhibition Cellular Effects of Deep Brain Stimulation: Model-Based Analysis of Activation and Inhibition. J. Neurophysiol. 2004, 91, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McIntyre, C.C.; Anderson, R.W. Deep brain stimulation mechanisms: The control of network activity via neurochemistry modulation. J. Neurochem. 2016, 139, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiken, S.; Nambu, A. Mechanism of Deep Brain Stimulation: Inhibition, Excitation, or Disruption? Neuroscientist 2015, 22, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brody, A.L.; Saxena, S.; Schwartz, J.M.; Stoessel, P.W.; Maidment, K.; Phelps, M.E.; Baxter, L.R. FDG-PET predictors of response to behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in obsessive compulsive disorder. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 1998, 84, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widge, A.S.; Zorowitz, S.; Basu, I.; Paulk, A.C.; Cash, S.S.; Eskandar, E.N.; Deckersbach, T.; Miller, E.K.; Dougherty, D.D. Deep brain stimulation of the internal capsule enhances human cognitive control and prefrontal cortex function. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, P.; Banks, G.P.; Pathak, Y.J.; Sheth, S.A. Connectivity-based parcellation of the anterior limb of the internal capsule. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2017, 38, 6107–6117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tastevin, M.; Spatola, G.; Régis, J.; Lançon, C.; Richieri, R. Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of obsessive-compulsive disorder: Current perspectives. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2019, 15, 1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casquero-Veiga, M.; García-García, D.; Desco, M.; Soto-Montenegro, M.A.L. Understanding deep brain stimulation: In vivo metabolic consequences of the electrode insertional effect. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holiga, Š.; Mueller, K.; Möller, H.E.; Urgošík, D.; Růžička, E.; Schroeter, M.L.; Jech, R. Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging of the subthalamic microlesion and stimulation effects in Parkinson’s disease: Indications of a principal role of the brainstem. NeuroImage Clin. 2015, 9, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Subject | Sex | Age at Surgery | Preoperative Y-BOCS | Postoperative Y-BOCS | Stimulation Settings | Medication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Male | 47 | 28 | 15 | 3−, 2−, c+; 11−, 10−, C+; 130 Hz; 3.3V; 120µs | Clomipramine 225mg/d Quetiapine 400mg/d |
| 2 | Male | 45 | 37 | 31 | 2−,1−, c+;10−,9−, c+; 130 Hz; 4.8V; 150µs | Venlafaxine 225mg/d Mirtazapine 30mg/d |
| 3 | Female | 54 | 34 | 33 | 3−, 2−, c+; 11−, 10−, C+; 130 Hz; 4.2V; 90µs | Fluoxetine 80mg/d |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldermann, J.C.; Bohn, K.P.; Hammes, J.; Schüller, C.B.; Visser-Vandewalle, V.; Drzezga, A.; Kuhn, J. Local and Global Changes in Brain Metabolism during Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9090220
Baldermann JC, Bohn KP, Hammes J, Schüller CB, Visser-Vandewalle V, Drzezga A, Kuhn J. Local and Global Changes in Brain Metabolism during Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Brain Sciences. 2019; 9(9):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9090220
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldermann, Juan Carlos, Karl Peter Bohn, Jochen Hammes, Canan Beate Schüller, Veerle Visser-Vandewalle, Alexander Drzezga, and Jens Kuhn. 2019. "Local and Global Changes in Brain Metabolism during Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder" Brain Sciences 9, no. 9: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9090220
APA StyleBaldermann, J. C., Bohn, K. P., Hammes, J., Schüller, C. B., Visser-Vandewalle, V., Drzezga, A., & Kuhn, J. (2019). Local and Global Changes in Brain Metabolism during Deep Brain Stimulation for Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder. Brain Sciences, 9(9), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci9090220




