Children with Dyslexia Benefit from Short Combined Reading and Motor Training: Objective Measures Assessed by Eye Movements and Postural Sway Recordings
Abstract
1. Introduction
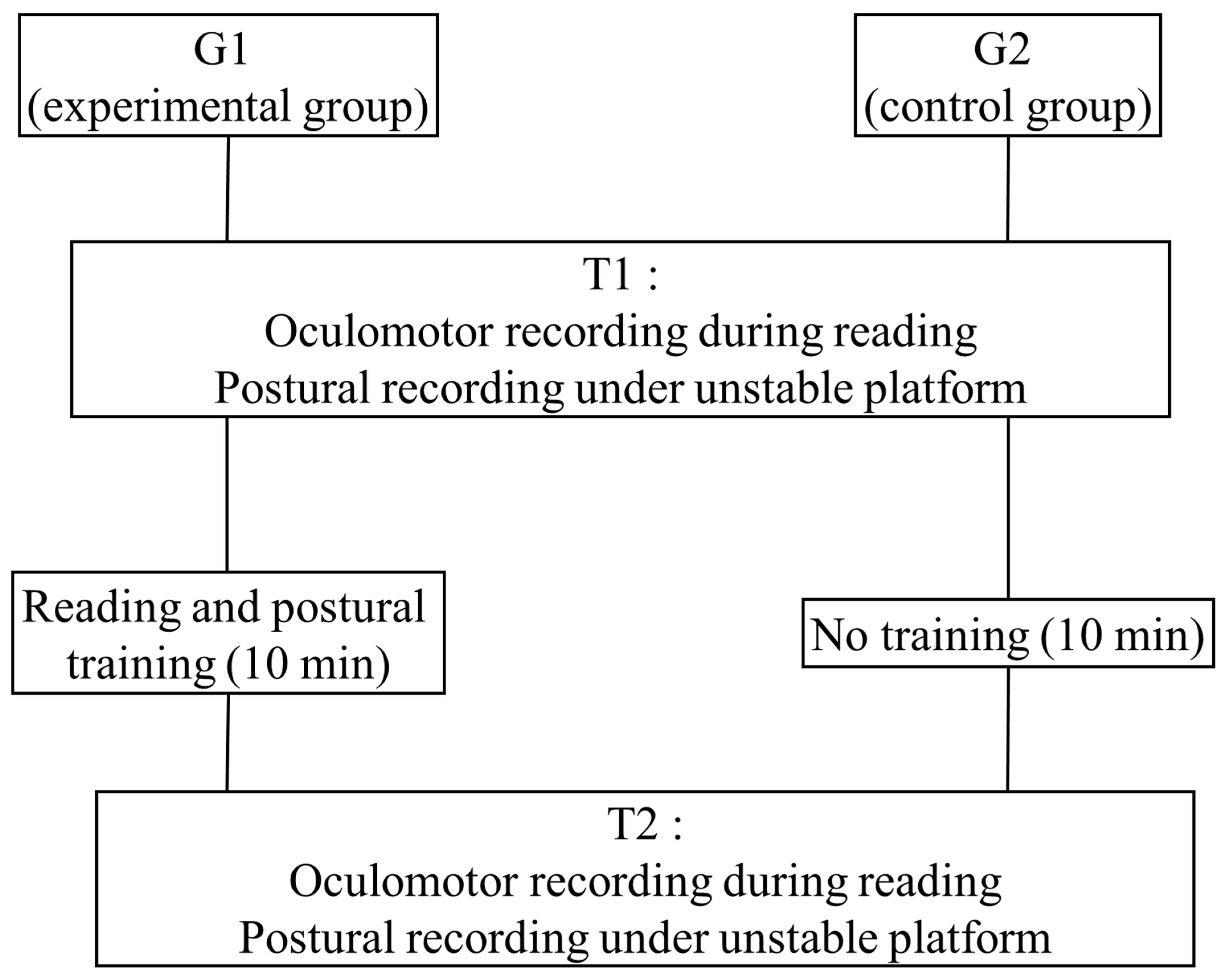
2. Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Oculomotor Recording
2.3. Postural Recording
2.4. Combined Reading and Postural Training Protocol
2.5. Data Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
| Forward Saccades: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | |||
| Number | Amplitude (deg) | Number | Amplitude (deg) | |
| G1 | 66 ± 1 | 2.75 ± 0.20 | 52 ± 2 * | 2.76 ± 0.28 |
| G2 | 70 ± 7 | 2.98 ± 0.33 | 72 ± 9 | 2.90 ± 0.34 |
| Backward saccades: | ||||
| G1 | 24 ± 4 | 2.69 ± 0.19 | 19 ± 3 | 2.85 ± 0.14 |
| G2 | 25 ± 8 | 2.79 ± 0.29 | 26 ± 7 | 2.98 ± 0.16 |
Postural Measures

4. Discussion
4.1. Oculomotor Performances
4.2. Postural Control
4.3. Effect of Combined Reading and Postural Training Protocol
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association APA. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, DSM 5th ed.; American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Goswami, U. Sensory theories of developmental dyslexia: Three challenges for research. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellutino, F.R.; Fletcher, J.M.; Snowling, M.J.; Scanlon, D.M. Specific reading disability (dyslexia): What have we learned in the past four decades? J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry 2004, 45, 2–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J. What is developmental dyslexia? Brain Sci. 2018, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallal, P. Auditory temporal perception, phonics, and reading disabilities in children. Brain Lang. 1980, 9, 182–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brosnan, M.; Demetre, J.; Hamill, S.; Robson, K.; Shepherd, H.; Cody, G. Executive functioning in adults and children with developmental dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 2002, 40, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facoetti, A.; Lorusso, M.L.; Paganoni, P.; Cattaneo, C.; Galli, R.; Mascetti, G.G. The time course of attentional focusing in dyslexic and normally reading children. Brain Cogn. 2003, 53, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, C.; Dubois, M.; Valdois, S. The eye movements of dyslexic children during reading and visual search: Impact of the visual attention span. Vis. Res. 2007, 47, 2521–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J.; Dean, P. Developmental dyslexia: The cerebellar deficit hypothesis. Trends Neurosci. 2001, 24, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, T.; Vernet, P.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; Robichon, F.; Bron, A.; Quercia, P. Static postural control in children with developmental dyslexia. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 403, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, R.L.; Tinkler, S.; Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Striking the right balance: Motor difficulties in children and adults with dyslexia. Dyslexia 2010, 16, 358–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawcett, A.J. Balance and reading are separate symptoms of dyslexia. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 2011, 53, 294–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Moscoso, A.; Acquaviva, E.; Hameau, E.; Delorme, R. Eye movements and postural control in children; biomarkers of neurodevelopmental disorders: Evidences toward new forms of therapeutic intervention? J. Pediatr. Neuropsychol. 2024, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolson, R.I.; Fawcett, A.J. Development of dyslexia: The delayed neural commitment framework. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premeti, A.; Bucci, M.P.; Isel, F. Evidence from ERP and Eye Movements as Markers of Language Dysfunction in Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangwill, O.; Blakemore, C. Dyslexia: Reversal of eye-movements during reading. Neuropsychologia 1972, 10, 371–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlidis, G.T. Do eye movements hold the key to dyslexia? Neuropsychologia 1981, 19, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, K. Do faulty eye movements cause dyslexia? Dev. Neuropsychol. 1985, 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raymond, J.E.; Ogden, N.A.; Fagan, J.E.; Kaplan, B.J. Fixational Instability and Saccadic Eye Movements of Dyslexic Children with Subtle Cerebellar Dysfunction. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1988, 65, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, G.; Stein, J.; Wood, H.; Wood, F. Differences in eye movements and reading problems in dyslexic and normal children. Vis. Res. 1994, 34, 1345–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyona, J.; Olson, R.K. Eye Fixation Patterns Among Dyslexic and Normal Readers: Effects of Word Length and Word Frequency. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. 1995, 21, 1430–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, M.; Di Pace, E.; Judica, A.; Spinelli, D.; Zoccolotti, P. Eye movement patterns in linguistic and non-linguistic tasks in developmental surface dyslexia. Neuropsychologia 1999, 37, 1407–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trauzettel-Klosinski, S.; MacKeben, M.; Reinhard, J.; Feucht, A.; Dürrwächter, U.; Klosinski, G. Pictogram Naming in Dyslexic and Normal Children Assessed by SLO. Vis. Res. 2002, 42, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutzler, F.; Wimmer, H. Eye movements of dyslexic children when reading in a regular orthography. Brain Lang. 2004, 89, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-H.; Jing, J.; Zou, X.-B.; Huang, X.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Q.-X.; Chen, X.-B.; Yang, B.-R.; Yang, S.-Y. Picture perception in Chinese dyslexic children: An eye-movement study. Chin. Med. J. 2009, 122, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Nassibi, N.; Gerard, C.-L.; Bui-Quoc, E.; Seassau, M. Immaturity of binocular saccade coordination in dyslexic children: Evidence from a reading and visual search study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basharpoor, S.; Seif, E.; Daneshvar, S. Computerized Executive Functions Training: The efficacy on reading performance of children with dyslexia. Dyslexia 2024, 30, e1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walda, S.A.E.; van Weerdenburg, M.; Bosman, A.M.T. Working memory training in students with dyslexia: Additional effects to reading and spelling remediation not likely. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2024, 155, 104865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, R.; Dworetsky, A.; Coalson, R.S.; Petersen, S.E.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Rosch, K.S.; Horowitz-Kraus, T. An executive-functions-based reading training enhances sensory-motor systems integration during reading fluency in children with dyslexia. Cereb. Cortex. 2024, 34, bhae166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulème, N.; Gérard, C.-L.; Bucci, M.P. The Effect of Training on Postural Control in Dyslexic Children. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Behzadipour, S.; Pourghayoomi, E.; Joghataei, M.T.; Shirazi, E.; Fawcett, A.J. Evaluating a new verbal working memory-balance program: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial study on Iranian children with dyslexia. BMC Neurosci. 2021, 22, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Behzadipour, S.; Fawcett, A.J.; Joghataei, M.T. Verbal Working Memory-Balance Program Training Alters the Left Fusiform Gyrus Resting-State Functional Connectivity: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study on Children with Dyslexia. Dyslexia 2023, 29, 264–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: Tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdar, C.C.; Cihan, M.; Yücel, D.; Serdar, M.A. Sample Size, Power and Effect Size Revisited: Simplified and Practical Approaches in Pre-Clinical, Clinical and Laboratory Studies. Biochem. Med. 2021, 31, 27–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrie-Muller, C.; Simon, A.-M.; Fournier, S. Langage Oral, Langage Écrit, Mémoire, Attention: L2MA; ECPA: Paris, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Caldani, S.; Gerard, C.L.; Peyre, H.; Bucci, M.P. Visual attentional training affects reading performance in children with reading disabilities: An eye tracking study. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulème, N.; Debue, M.; Spruyt, K.; Vanderveken, C.; De Siati, R.D.; Ortega-Solis, J.; Petrossi, J.; Wiener-Vacher, S.; Bucci, M.P.; Ionescu, E.; et al. Changes of spatial and temporal characteristics of dynamic postural control in children with typical neurodevelopment with age: Results of a multicenter pediatric study. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2018, 113, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- New, B.; Pallier, C.; Ferrand, L.; Matos, R. Une base de données lexicales du français contemporain sur internet: Lexique™//a lexical database for contemporary French: Lexique™. L’année Psychol. 2001, 101, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard-Demanze, L.; Léonard, J.; Dumitrescu, M.; Meller, R.; Magnan, J.; Lacour, M. Static and dynamic posture control in postlingual cochlear implanted patients: Effects of dual-tasking, visual and auditory inputs suppression. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, J.L.; De Losa, L.; Bavin, E.L.; Crewther, S.G. Efficacy of dynamic visuo-attentional interventions for reading in dyslexic and neurotypical children: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2019, 100, 58–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vander Stappen, C.; Dricot, L.; Van Reybroeck, M. RAN training in dyslexia: Behavioral and brain correlates. Neuropsychologia 2020, 146, 107566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bucci, M.P.; Goulème, N.; Stordeur, C.; Acquaviva, E.; Scheid, I.; Lefebvre, A.; Gerard, C.L.; Peyre, H.; Delorme, R. Discriminant validity of spatial and temporal postural index in children with neurodevelopmental disorders. Dev. Cogn. Neurosci. 2017, 61, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razuk, M.; Barela, J.A.; Peyre, H.; Gerard, C.L.; Bucci, M.P. Eye movements and postural control in dyslexic children performing different visual tasks. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hecke, R.; Danneels, M.; Dhooge, I.; Van Waelvelde, H.; Wiersema, J.R.; Deconinck, F.J.; Maes, L. Vestibular function in children with neurodevelopmental disorders: A systematic review. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 3328–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barela, J.A.; Dias, J.L.; Godoi, D.; Viana, A.R.; de Freitas, P.B. Postural control and automaticity in dyslexic children: The relationship between visual information and body sway. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2011, 32, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quercia, P.; Demougeot, L.; Dos Santos, M.; Bonnetblanc, F. Integration of proprioceptive signals and attentional capacity during postural control are impaired but subject to improvement in dyslexic children. Exp. Brain Res. 2011, 209, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, S.; Quercia, P.; Bonnetblanc, F.; Michel, C. Space representation in children with dyslexia and children without dyslexia: Contribution of line bisection and circle centering tasks. Res. Dev. Disabil. 2013, 34, 3997–4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Fawcett, A.J. Cognitive-Motor Training Improves Reading-Related Executive Functions: A Randomized Clinical Trial Study in Dyslexia. Brain Sci. 2024, 14, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Dhia, A.; Bucci, M.P.; Naffeti, C.; Ben Saad, H.; Hammouda, O.; Driss, T. Combined Cognitive and Motor Training Improves Reading, Writing and Motor Coordination in Dyslexic Children. Pediatr. Rep. 2025, 17, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol, L.F.; Budding, D.; Andreasen, N.; D’Arrigo, S.; Bulgheroni, S.; Imamizu, H.; Ito, M.; Manto, M.; Marvel, C.; Parker, K.; et al. Consensus paper: The cerebellum’s role in movement and cognition. Cerebellum 2014, 13, 151–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoodley, C.J.; Schmahmann, J.D. Evidence for topographic organization in the cerebellum of motor control versus cognitive and affective processing. Cortex 2010, 46, 831–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.S.-H.; Kloth, A.D.; Badura, A. The cerebellum, sensitive periods, and autism. Neuron 2014, 83, 518–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| G1 Experimental Group N = 16 Children | G2 Control Group N = 16 Children | |
|---|---|---|
| Age (year) | 10 ± 0.28 | 10.9 ± 0.60 |
| Sex (F/M) | 2/14 | 3/13 |
| ELFE test (words/min) | 64 ± 8 | 66 ± 10 |
| L2MA standard deviation from the mean: | ||
| Oral language | 2.7 | 2.6 |
| Written language | 2.8 | 2.7 |
| Memory | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| Wechsler scale (WISC-V) scores: | ||
| Verbal Comprehension Index | 97 ± 4 | 98 ± 5 |
| Visual Spatial Index | 90 ± 6 | 91 ± 4 |
| Working Memory Index | 95 ± 3 | 96 ± 5 |
| Fluid Reasoning Index | 98 ± 5 | 96 ± 4 |
| Processing Speed Index | 96 ± 6 | 97 ± 7 |
| Total Reading Duration (s) | Durations of Fixations (ms) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | T2 | T1 | T2 | |
| G1 | 45.9 ± 5.15 | 39.9 ± 5.20 | 376 ± 23 | 330 ± 21 |
| G2 | 51.9 ± 4.5 | 54.6 ± 5.1 | 296 ± 24 | 302 ± 25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caldani, S.; Khoury, E.; Delorme, R.; Bucci, M.P. Children with Dyslexia Benefit from Short Combined Reading and Motor Training: Objective Measures Assessed by Eye Movements and Postural Sway Recordings. Brain Sci. 2025, 15, 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111218
Caldani S, Khoury E, Delorme R, Bucci MP. Children with Dyslexia Benefit from Short Combined Reading and Motor Training: Objective Measures Assessed by Eye Movements and Postural Sway Recordings. Brain Sciences. 2025; 15(11):1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111218
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaldani, Simona, Elie Khoury, Richard Delorme, and Maria Pia Bucci. 2025. "Children with Dyslexia Benefit from Short Combined Reading and Motor Training: Objective Measures Assessed by Eye Movements and Postural Sway Recordings" Brain Sciences 15, no. 11: 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111218
APA StyleCaldani, S., Khoury, E., Delorme, R., & Bucci, M. P. (2025). Children with Dyslexia Benefit from Short Combined Reading and Motor Training: Objective Measures Assessed by Eye Movements and Postural Sway Recordings. Brain Sciences, 15(11), 1218. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci15111218





