Balance Rehabilitation through Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection Criteria
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Quality Assessment
2.4. Data Extraction
2.5. Statistical Analysis
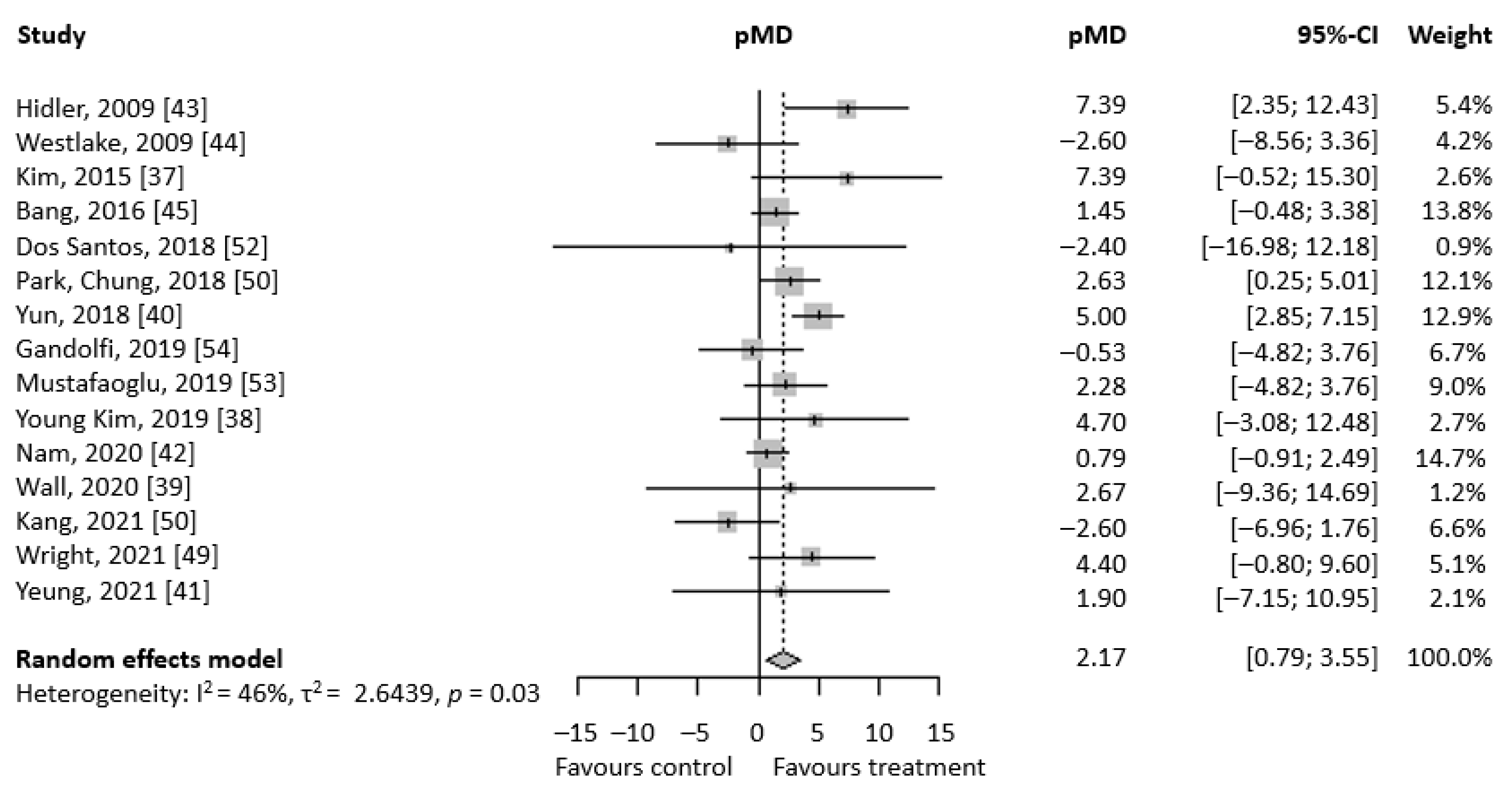
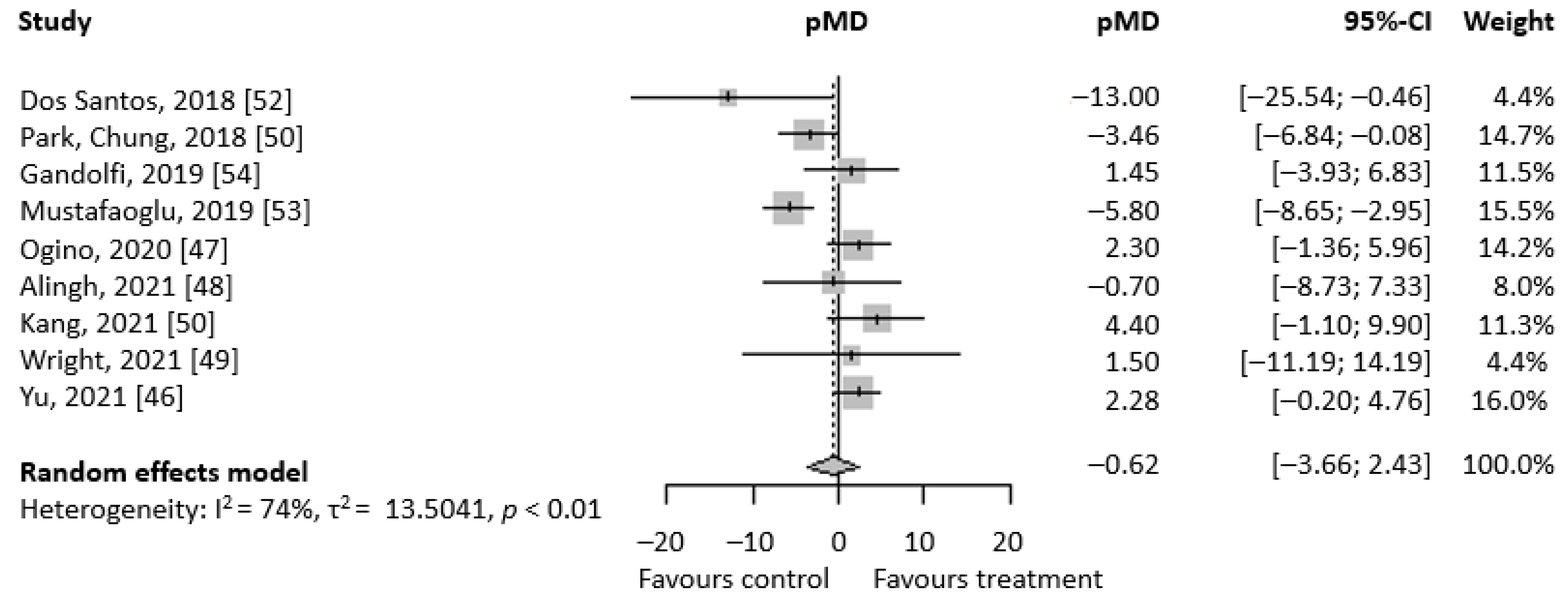
3. Results
3.1. Literature Selection Process
3.2. Primary Analyses
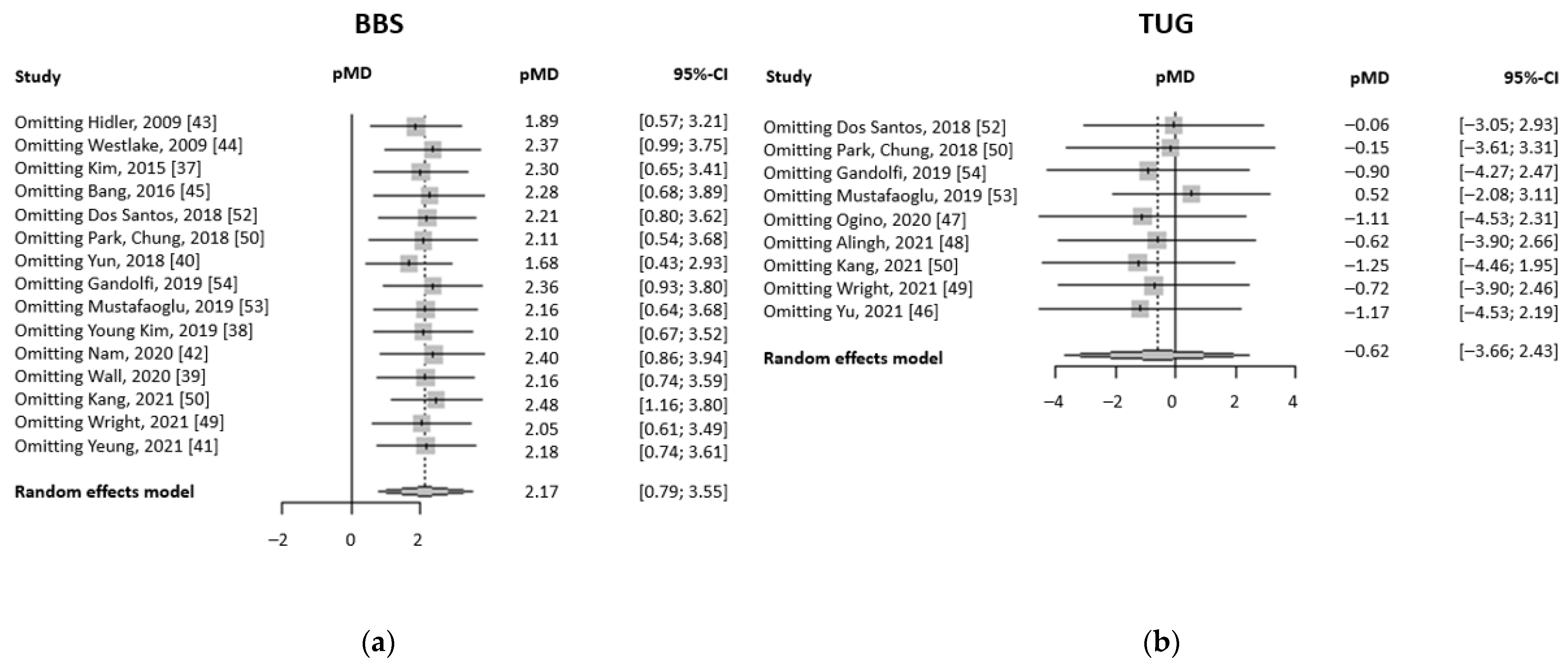
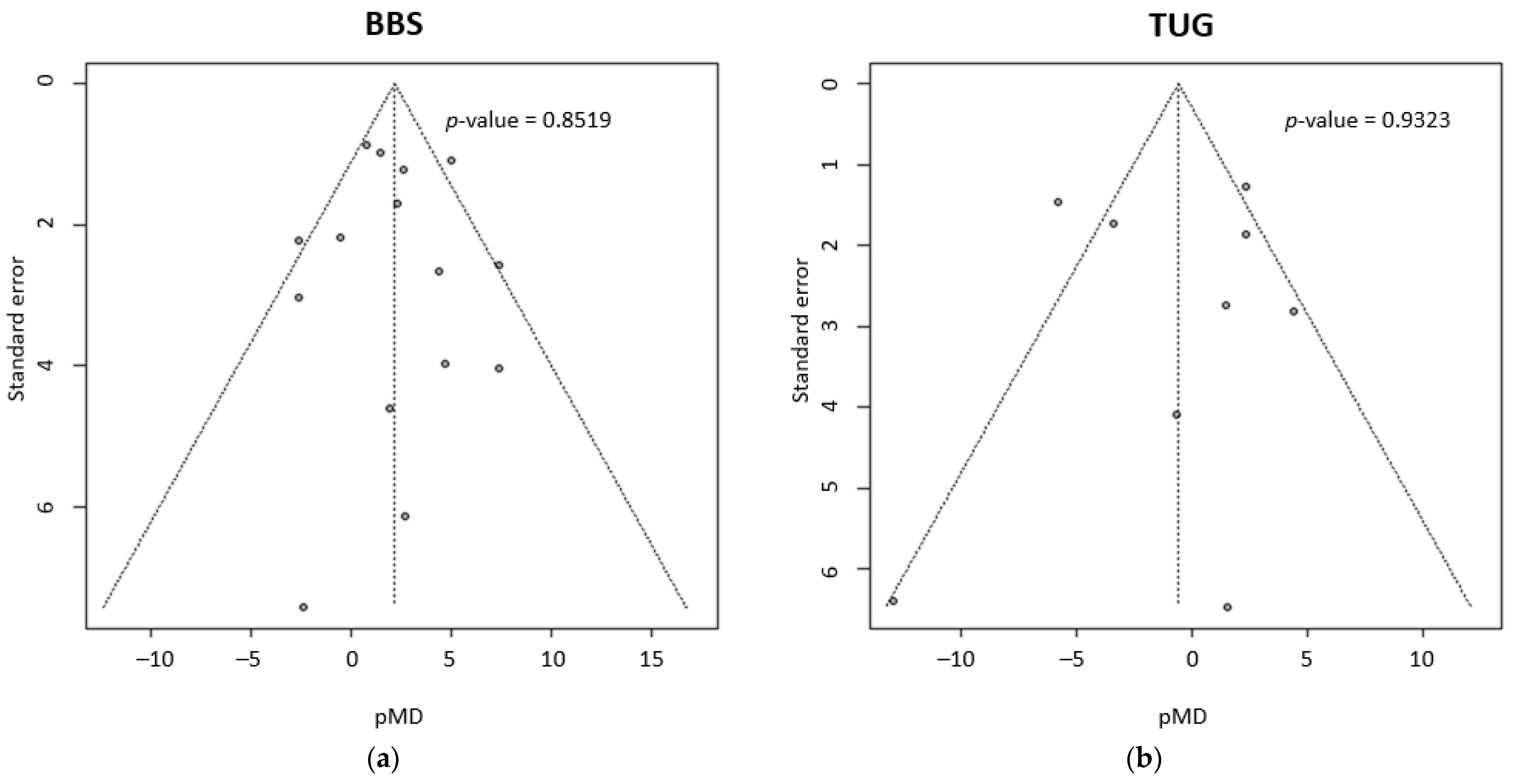
3.3. Supplemental Analyses
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochmah, T.; Rahmawati, I.; Dahlui, M.; Budiarto, W.; Bilqis, N. Economic Burden of Stroke Disease: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.; Esenwa, C. Secondary stroke prevention: Challenges and solutions. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, S.; Candelario-Jalil, E. Emerging neuroprotective strategies for the treatment of ischemic stroke: An overview of clinical and preclinical studies. Exp. Neurol. 2020, 335, 113518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly-Hayes, M.; Beiser, A.; Kase, C.S.; Scaramucci, A.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Wolf, P.A. The influence of gender and age on disability following ischemic stroke: The Framingham study. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2003, 12, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.M.; Tay, M.R.J.; Rajeswaran, D.K.; Tham, S.-L.; Lui, W.L.; Kong, K.H. Changes in muscle architecture on ultrasound in patients early after stroke. NeuroRehabilitation 2021, 49, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Lo, W.L.A.; Mao, Y.R.; Ding, M.H.; Lin, Q.; Li, H.; Zhao, J.L.; Xu, Z.Q.; Bian, R.H.; Huang, D.F. Effect of Virtual Reality on Postural and Balance Control in Patients with Stroke: A Systematic Literature Review. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7309272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.-R.; Chiu, Y.-L.; Chiang, S.-L.; Chen, H.-Y.; Sung, W.-H. Feasibility of a smartphone-based balance assessment system for subjects with chronic stroke. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2018, 161, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques-Sule, E.; Arnal-Gómez, A.; Buitrago-Jiménez, G.; Suso-Martí, L.; Cuenca-Martínez, F.; Espí-López, G.V. Effectiveness of Nintendo Wii and Physical Therapy in Functionality, Balance, and Daily Activities in Chronic Stroke Patients. J. Am. Med. Dir. Assoc. 2021, 22, 1073–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morreale, M.; Marchione, P.; Pili, A.; Lauta, A.; Castiglia, S.F.; Spallone, A.; Pierelli, F.; Giacomini, P. Early versus delayed rehabilitation treatment in hemiplegic patients with ischemic stroke: Proprioceptive or cognitive approach? Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2015, 52, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Aichner, F.; Adelwöhrer, C.; Haring, H.-P. Rehabilitation approaches to stroke. J. Neural Transm. Suppl. 2002, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerbeek, J.; van Wegen, E.; Van Peppen, R.; Van Der Wees, P.J.; Hendriks, E.; Rietberg, M.; Kwakkel, G. What Is the Evidence for Physical Therapy Poststroke? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobkin, B.H.; Dorsch, A. New Evidence for Therapies in Stroke Rehabilitation. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2013, 15, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, P.; Zhang, W.; Kang, L.; Ma, Y.; Fu, L.; Jia, L.; Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Hou, L.; Wang, L.; et al. Clinical Evidence of Exercise Benefits for Stroke. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1000, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.-H.; Paik, N.-J. Mobile Game-based Virtual Reality Program for Upper Extremity Stroke Rehabilitation. J. Vis. Exp. 2018, e56241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhoun, H.Y.; Tan, B.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, C.; Yu, L. Task-based mirror therapy enhances the upper limb motor function in subacute stroke patients: A randomized control trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 56, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueye, T.; Dedkova, M.; Rogalewicz, V.; Grunerova-Lippertova, M.; Angerova, Y. Early post-stroke rehabilitation for upper limb motor function using virtual reality and exoskeleton: Equally efficient in older patients. Neurol. Neurochir. Polska 2021, 55, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehem, S.; Gilliaux, M.; Stoquart, G.; Detrembleur, C.; Jacquemin, G.; Palumbo, S.; Frederick, A.; Lejeune, T. Effectiveness of upper-limb robotic-assisted therapy in the early rehabilitation phase after stroke: A single-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 62, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiper, P.; Szczudlik, A.; Agostini, M.; Opara, J.; Nowobilski, R.; Ventura, L.; Tonin, P.; Turolla, A. Virtual Reality for Upper Limb Rehabilitation in Subacute and Chronic Stroke: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 834–842.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, F.; Miccinilli, S.; Pellegrino, G.; Zollo, L.; Simonetti, D.; Bressi, F.; Florio, L.; Ranieri, F.; Falato, E.; Di Santo, A.; et al. Transcutaneous Vagus Nerve Stimulation Combined with Robotic Rehabilitation Improves Upper Limb Function after Stroke. Neural Plast. 2017, 2017, 7876507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yue, Z.; Wang, J. Robotics in Lower-Limb Rehabilitation after Stroke. Behav. Neurol. 2017, 2017, 3731802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, P.; Horgan, F.; Blake, C.; Ehrensberger, M.; Simpson, D.; Monaghan, K. Mirror therapy for improving lower limb motor function and mobility after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gait Posture 2018, 63, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scrivener, K.; Dorsch, S.; McCluskey, A.; Schurr, K.; Graham, P.L.; Cao, Z.; Shepherd, R.; Tyson, S. Bobath therapy is inferior to task-specific training and not superior to other interventions in improving lower limb activities after stroke: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2020, 66, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharififar, S.; Shuster, J.J.; Bishop, M.D. Adding electrical stimulation during standard rehabilitation after stroke to improve motor function. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Q. Virtual reality for limb motor function, balance, gait, cognition and daily function of stroke patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Adv. Nurs. 2021, 77, 3255–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Son, H.; Yeo, B. The effects of lower extremity cross-training on gait and balance in stroke patients: A double-blinded randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 57, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noveletto, F.; Soares, A.V.; Eichinger, F.L.F.; Domenech, S.C.; Hounsell, M.D.S.; Filho, P.B. Biomedical Serious Game System for Lower Limb Motor Rehabilitation of Hemiparetic Stroke Patients. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2020, 28, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Z.; Sui, M.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zheng, X.; Cai, C.; Jin, D. Effectiveness of Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation on Lower Limbs of Patients With Hemiplegia After Chronic Stroke: A Systematic Review. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 99, 1011–1022.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aprilea, I.; Iacovelli, C.; Goffredo, M.; Cruciani, A.; Galli, M.; Simbolotti, C.; Pecchioli, C.; Padua, L.; Galafate, D.; Pournajaf, S.; et al. Efficacy of end-effector Robot-Assisted Gait Training in subacute stroke patients: Clinical and gait outcomes from a pilot bi-centre study. Neurorehabilitation 2019, 45, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Fernández, A.; Lobo-Prat, J.; Font-Llagunes, J.M. Systematic review on wearable lower-limb exoskeletons for gait training in neuromuscular impairments. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Kern, M.; Fowkes, E.; Afzal, T.; Contreras-Vidal, J.-L.; Francisco, G.E.; Chang, S.-H. Effects of an exoskeleton-assisted gait training on post-stroke lower-limb muscle coordination. J. Neural Eng. 2021, 18, 046039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefeber, N.; De Buyzer, S.; Dassen, N.; De Keersmaecker, E.; Kerckhofs, E.; Swinnen, E. Energy consumption and cost during walking with different modalities of assistance after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Disabil. Rehabil. 2019, 42, 1650–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wei, J.; Huang, X.; Duan, Q.; Zhang, T. Effects of a Brain-Computer Interface-Operated Lower Limb Rehabilitation Robot on Motor Function Recovery in Patients with Stroke. J. Health Eng. 2021, 2021, 4710044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, D.Y.; Chun, M.H.; Kim, S.W.; Jeon, H.R.; Hwang, C.H.; Choi, J.K.; Bae, S. Effects of robot-(Morning Walk®) assisted gait training for patients after stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2018, 33, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Shimizu, I.; Hiroi, Y.; Kawaki, M.; Sato, D.; Nagasawa, M. Feasibility and efficacy of high-speed gait training with a voluntary driven exoskeleton robot for gait and balance dysfunction in patients with chronic stroke. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2015, 38, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Nunen, M.P.M.; Gerrits, K.H.L.; Konijnenbelt, M.; Janssen, T.; De Haan, A. Recovery of walking ability using a robotic device in subacute stroke patients: A randomized controlled study. Disabil. Rehabil. Assist. Technol. 2013, 10, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, L.; Park, I.J.; Kim, E.J.; Park, M.S.; You, S.H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Ko, H.-Y.; Shin, Y.-I. Effects of Innovative WALKBOT Robotic-Assisted Locomotor Training on Balance and Gait Recovery in Hemiparetic Stroke: A Prospective, Randomized, Experimenter Blinded Case Control Study With a Four-Week Follow-Up. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2015, 23, 636–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Shin, J.-H.; Yang, S.P.; Shin, M.A.; Lee, S.H. Robot-assisted gait training for balance and lower extremity function in patients with infratentorial stroke: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wall, A.; Borg, J.; Vreede, K.; Palmcrantz, S. A randomized controlled study incorporating an electromechanical gait machine, the Hybrid Assistive Limb, in gait training of patients with severe limitations in walking in the subacute phase after stroke. PloS ONE 2020, 15, e0229707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, N.R.; Joo, M.C.; Kim, S.; Kim, M.-S. Robot-assisted gait training effectively improved lateropulsion in subacute stroke patients: A single-blinded randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2019, 54, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeung, L.-F.; Lau, C.C.Y.; Lai, C.W.K.; Soo, Y.O.Y.; Chan, M.-L.; Tong, R.K.Y. Effects of wearable ankle robotics for stair and over-ground training on sub-acute stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, Y.; Park, J.; Lee, H.; Nam, K.; Choi, M.; Yu, C.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, X.; Lee, J.; Kwon, B. Effects of electromechanically assisted gait trainer with Exowalk® in patients with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 52, jrm00097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidler, J.; Nichols, D.; Pelliccio, M.; Brady, K.; Campbell, D.D.; Kahn, J.H.; Hornby, T.G. Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating the Effectiveness of the Lokomat in Subacute Stroke. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2008, 23, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westlake, K.P.; Patten, C. Pilot study of Lokomat versus manual-assisted treadmill training for locomotor recovery post-stroke. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2009, 6, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, D.-H.; Shin, W.-S. Effects of robot-assisted gait training on spatiotemporal gait parameters and balance in patients with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled pilot trial. Neurorehabilitation 2016, 38, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Yang, Z.; Lei, L.; Chaoming, N.; Ming, W. Robot-Assisted Gait Training Plan for Patients in Poststroke Recovery Period: A Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 5820304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, T.; Kanata, Y.; Uegaki, R.; Yamaguchi, T.; Morisaki, K.; Nakano, S.; Domen, K. Effects of gait exercise assist robot (GEAR) on subjects with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled pilot trial. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2020, 29, 104886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alingh, J.F.; Fleerkotte, B.M.; Groen, B.E.; Rietman, J.S.; Weerdesteyn, V.; van Asseldonk, E.H.F.; Geurts, A.C.H.; Buurke, J.H. Effect of assist-as-needed robotic gait training on the gait pattern post stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, A.; Stone, K.; Martinelli, L.; Fryer, S.; Smith, G.; Lambrick, D.; Stoner, L.; Jobson, S.; Faulkner, J. Effect of combined home-based, overground robotic-assisted gait training and usual physiotherapy on clinical functional outcomes in people with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Rehabil. 2020, 35, 882–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, C.J.; Chun, M.H.M.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.Y.P. Effects of robot (SUBAR)-assisted gait training in patients with chronic stroke. Medicine 2021, 100, e27974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chung, Y. The effects of robot-assisted gait training using virtual reality and auditory stimulation on balance and gait abilities in persons with stroke. Neurorehabilitation 2018, 43, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos, M.B.; De Oliveira, C.B.; Dos Santos, A.; Pires, C.G.; Dylewski, V.; Arida, R.M. A Comparative Study of Conventional Physiotherapy versus Robot-Assisted Gait Training Associated to Physiotherapy in Individuals with Ataxia after Stroke. Behav. Neurol. 2018, 2018, 2892065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafaoglu, R.; Erhan, B.; Yeldan, I.; Hüseyinsinoğlu, B.E.; Gündüz, B.; Özdinçler, A.R. The effects of body weight-supported treadmill training on static and dynamic balance in stroke patients: A pilot, single-blind, randomized trial. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 64, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfi, M.; Valè, N.; Dimitrova, E.; Zanolin, M.E.; Mattiuz, N.; Battistuzzi, E.; Beccari, M.; Geroin, C.; Picelli, A.; Waldner, A.; et al. Robot-Assisted Stair Climbing Training on Postural Control and Sensory Integration Processes in Chronic Post-stroke Patients: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gschwind, Y.J.; Kressig, R.W.; Lacroix, A.; Muehlbauer, T.; Pfenninger, B.; Granacher, U. A best practice fall prevention exercise program to improve balance, strength/power, and psychosocial health in older adults: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. BMC Geriatr. 2013, 13, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downs, S.; Marquez, J.; Chiarelli, P. The Berg Balance Scale has high intra- and inter-rater reliability but absolute reliability varies across the scale: A systematic review. J. Physiother. 2013, 59, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, S.; Miyata, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Takeda, R.; Iwamoto, H. The minimal clinically important difference in Berg Balance Scale scores among patients with early subacute stroke: A multicenter, retrospective, observational study. Top. Stroke Rehabil. 2021, 29, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.-X.; Ge, L.; Wang, C.C.; Ma, Q.-S.; Liao, Y.-T.; Huang, P.-P.; Wang, G.-D.; Xie, Q.-L.; Rask, M. Robot-assisted therapy for balance function rehabilitation after stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Nurs. Stud. 2019, 95, 7–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolucci, S.; DI Vita, A.; Massicci, R.; Traballesi, M.; Bureca, I.; Matano, A.; Iosa, M.; Guariglia, C. Impact of participation on rehabilitation results: A multivariate study. Eur. J. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 48, 455–466. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, W.H.; Yun-Hee, K. Robot-assisted Therapy in Stroke Rehabilitation. J. Stroke 2013, 15, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz Martínez, A.; Muñoz, J.; Palacios, F. The muscle inhibitory period by transcranial magnetic stimulation. Study in stroke patients. Electromyogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. 1998, 38, 189–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lorusso, M.; Tramontano, M.; Casciello, M.; Pece, A.; Smania, N.; Morone, G.; Tamburella, F. Efficacy of Overground Robotic Gait Training on Balance in Stroke Survivors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.X.; Yao, J.; Zirek, Y.; Reijnierse, E.M.; Maier, A.B. Muscle mass, strength, and physical performance predicting activities of daily living: A meta-analysis. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 11, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressi, F.; Bravi, M.; Campagnola, B.; Bruno, D.; Marzolla, A.; Santacaterina, F.; Miccinilli, S.; Sterzi, S. Robotic treatment of the upper limb in chronic stroke and cerebral neuroplasticity: A systematic review. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2020, 34 (Suppl. S3), 11–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.; Saini, M.; Kumar, N.; Srivastava, M.V.P.; Mehndiratta, A. Evidence of neuroplasticity with robotic hand exoskeleton for post-stroke rehabilitation: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2021, 18, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Park, G.; Shin, J.-H.; You, J.H. Neuroplastic effects of end-effector robotic gait training for hemiparetic stroke: A randomised controlled trial. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, J.; Roig, M.; Eng, J.J.; MacKay-Lyons, M.; Fung, J.; Ploughman, M.; Bailey, D.M.; Sweet, S.N.; Giacomantonio, N.; Thiel, A.; et al. High-Intensity Interval Training After Stroke: An Opportunity to Promote Functional Recovery, Cardiovascular Health, and Neuroplasticity. Neurorehabilit. Neural Repair 2018, 32, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahayu, U.B.; Wibowo, S.; Setyopranoto, I.; Romli, M.H. Effectiveness of physiotherapy interventions in brain plasticity, balance and functional ability in stroke survivors: A randomized controlled trial. Neurorehabilitation 2020, 47, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil Seo, H.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, S.H.; Yi, Y.; Kim, K.D.; Oh, B.-M. Robotic-assisted gait training combined with transcranial direct current stimulation in chronic stroke patients: A pilot double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Restor. Neurol. Neurosci. 2017, 35, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, K.; Stephenson, M.; Lockwood, C. The economic cost of robotic rehabilitation for adult stroke patients. JBI Évid. Synth. 2019, 17, 520–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Otaka, Y.; Kumagai, M.; Sugasawa, M.; Mori, N.; Kondo, K. Effects of Balance Exercise Assist Robot training for patients with hemiparetic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2022, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, J.H.; Seong, H.Y.; Ko, S.-H.; Jo, W.-R.; Sohn, H.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Son, J.H.; Seo, H.-Y.; Son, Y.-R.; Mun, S.-J.; et al. Effects of trunk stabilization training robot on postural control and gait in patients with chronic stroke: A randomized controlled trial. Int. J. Rehabil. Res. 2020, 43, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Luca, A.; Squeri, V.; Barone, L.M.; Mansin, H.V.; Ricci, S.; Pisu, I.; Cassiano, C.; Capra, C.; Lentino, C.; De Michieli, L.; et al. Dynamic Stability and Trunk Control Improvements Following Robotic Balance and Core Stability Training in Chronic Stroke Survivors: A Pilot Study. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, S.; Facciorusso, S.; Cinone, N.; Armiento, R.; Picelli, A.; Avvantaggiato, C.; Ciritella, C.; Fiore, P.; Santamato, A. Effectiveness of robotic balance training on postural instability in patients with mild Parkinson’s disease: A pilot, single blind, randomized controlled trial. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| BBS | TUG | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable Studied | β | 95% CI | p-Value | β | 95% CI | p-Value |
| Treatment duration (in weeks) | 0.222 | (−0.512; 0.957) | 0.5529 | −1.019 | (−1.827; −0.210) | 0.0135 * |
| Weekly sessions | 1.074 | (−0.626; 2.775) | 0.2157 | −1.333 | (−3.197; 0.530) | 0.1608 |
| Single-session duration | 0.051 | (−0.043; 0.145) | 0.2854 | 0.040 | (−0.041; 0.121) | 0.9726 |
| Devices: Lokomat® vs. others | 0.873 | (−2.572; 4.317) | 0.6196 | −3.566 | (−7.629; 0.498) | 0.0854 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loro, A.; Borg, M.B.; Battaglia, M.; Amico, A.P.; Antenucci, R.; Benanti, P.; Bertoni, M.; Bissolotti, L.; Boldrini, P.; Bonaiuti, D.; et al. Balance Rehabilitation through Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010092
Loro A, Borg MB, Battaglia M, Amico AP, Antenucci R, Benanti P, Bertoni M, Bissolotti L, Boldrini P, Bonaiuti D, et al. Balance Rehabilitation through Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoro, Alberto, Margherita Beatrice Borg, Marco Battaglia, Angelo Paolo Amico, Roberto Antenucci, Paolo Benanti, Michele Bertoni, Luciano Bissolotti, Paolo Boldrini, Donatella Bonaiuti, and et al. 2023. "Balance Rehabilitation through Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010092
APA StyleLoro, A., Borg, M. B., Battaglia, M., Amico, A. P., Antenucci, R., Benanti, P., Bertoni, M., Bissolotti, L., Boldrini, P., Bonaiuti, D., Bowman, T., Capecci, M., Castelli, E., Cavalli, L., Cinone, N., Cosenza, L., Di Censo, R., Di Stefano, G., Draicchio, F., ... Baricich, A. (2023). Balance Rehabilitation through Robot-Assisted Gait Training in Post-Stroke Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010092













