Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Image Acquisition and Cortical Feature-Based Structural Network
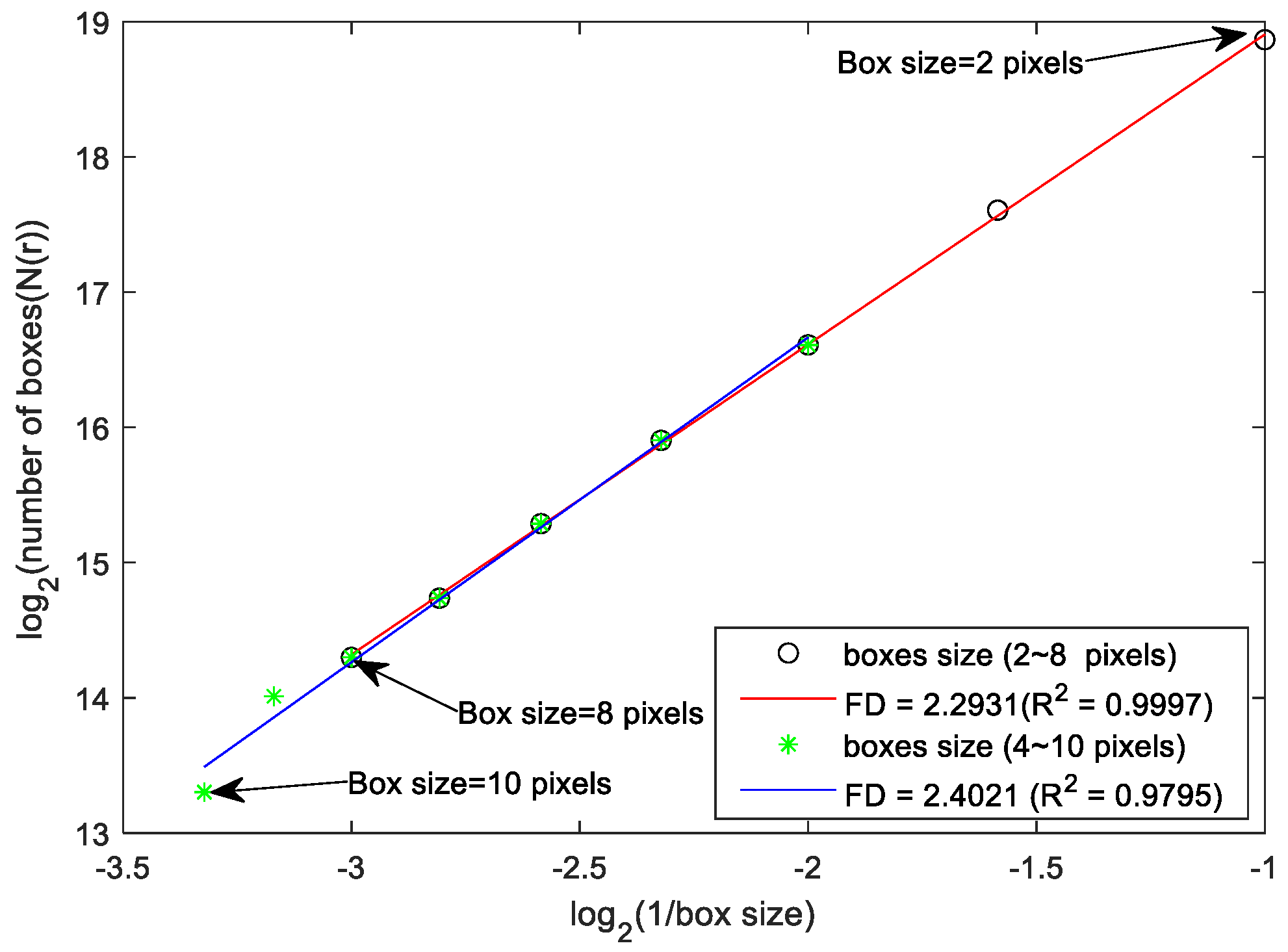
2.3. FD Analysis and Brain Structural Network
2.4. Network Property Analysis of Intra-Modular and Inter-Modular Connectivity
2.4.1. Intra-Modular Connectivity Analysis
2.4.2. Inter-Modular Connectivity Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients with MCI Exhibit Significant Lateralized FD Changes Mainly in Temporal Lobe Regions
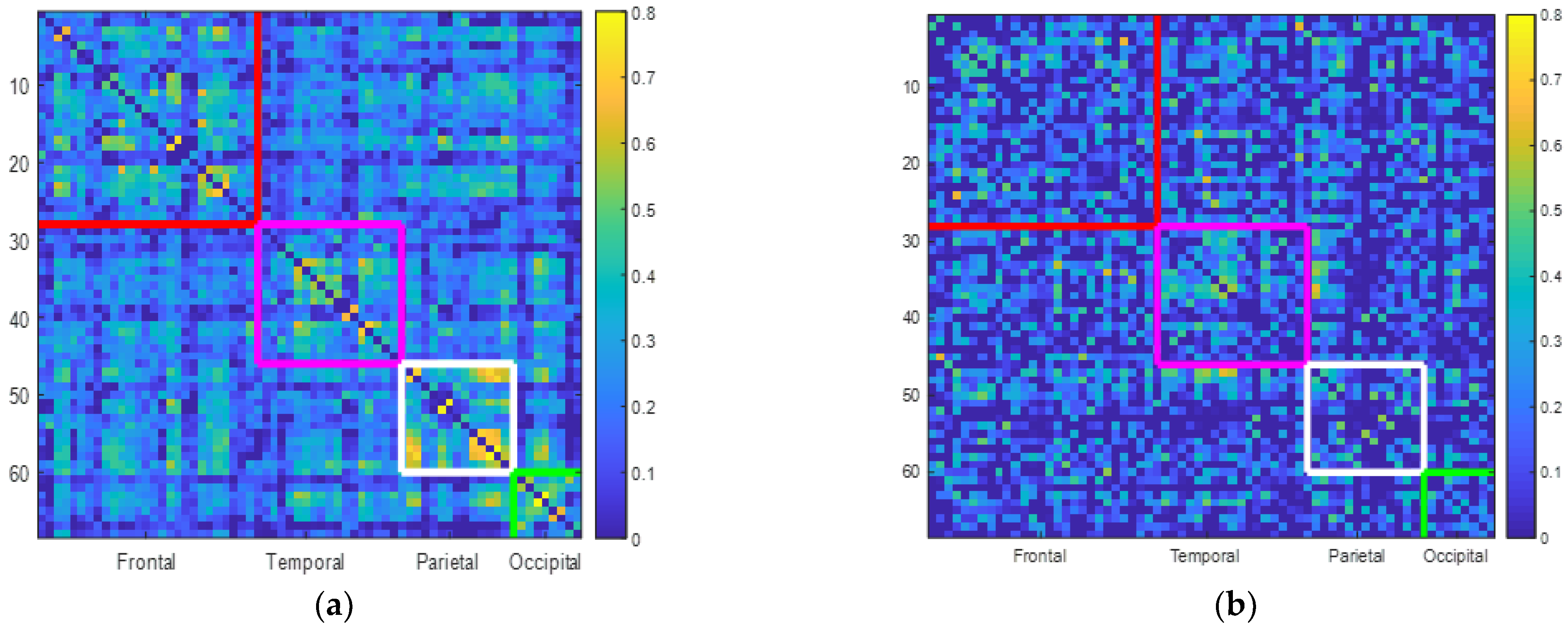
3.2. Patients with MCI Exhibit Lower Correlation Rates within and between Lobes
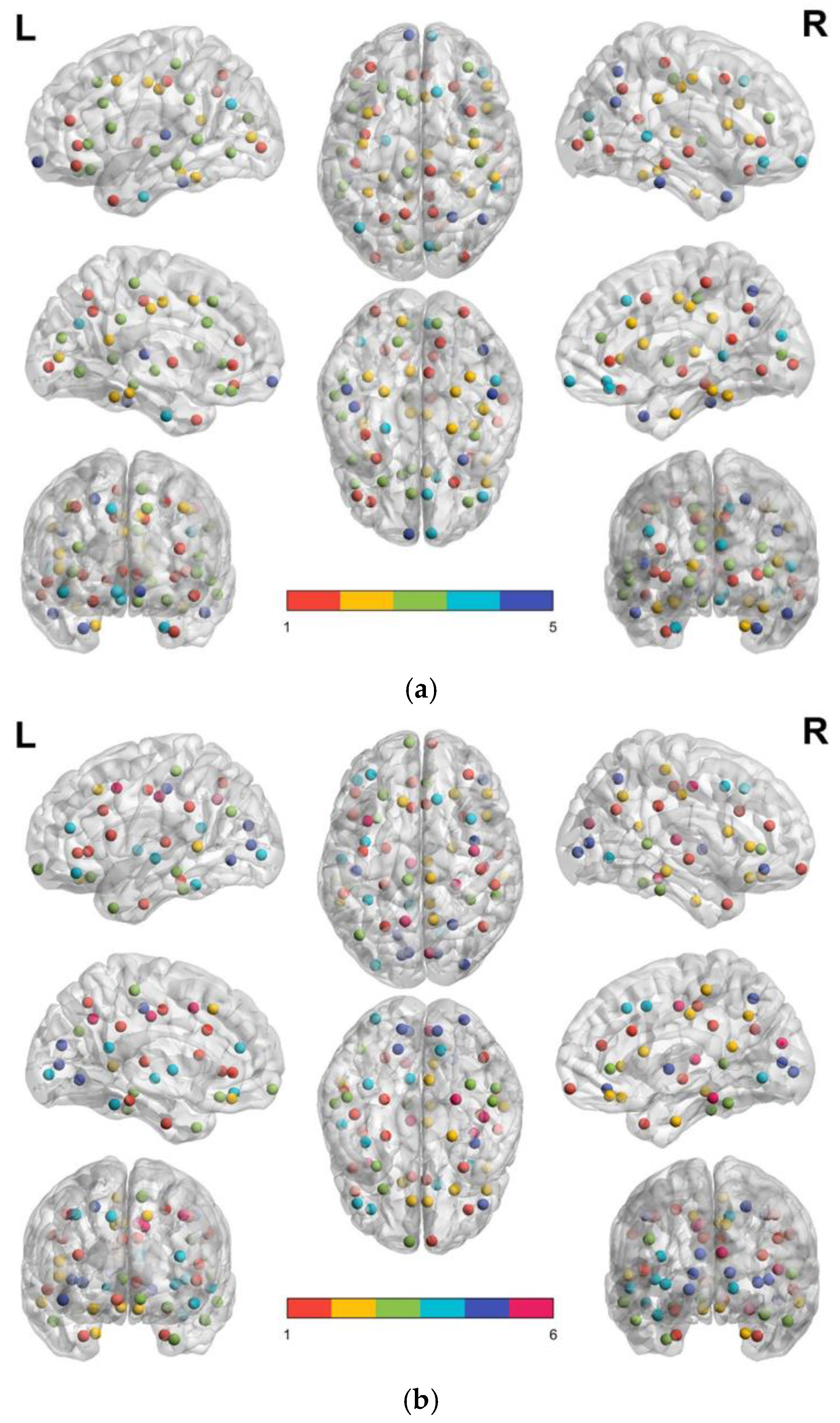
3.3. Patients with MCI Reveal Smaller Modular Size and Less Node Integration in Their Brain Structural Network
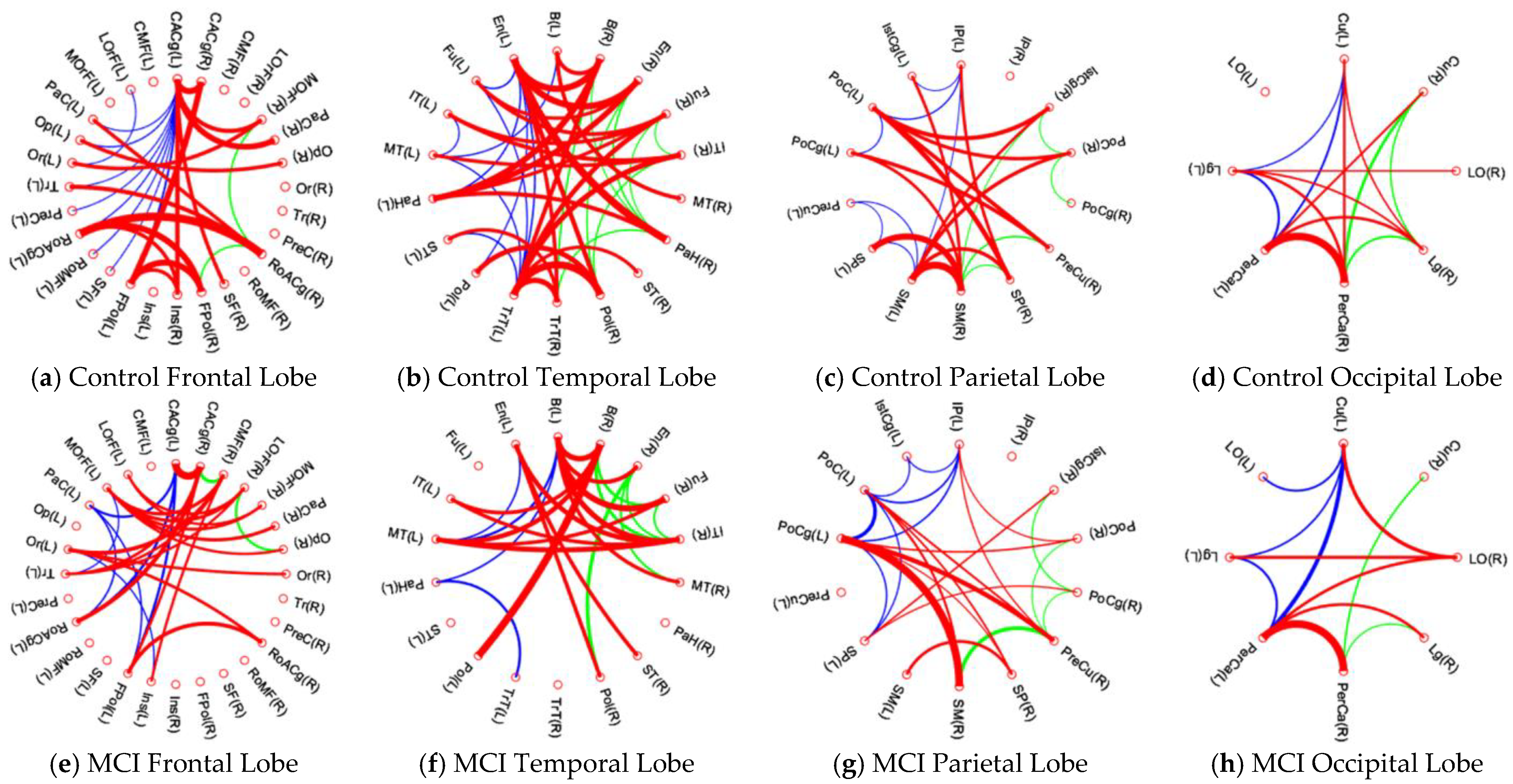
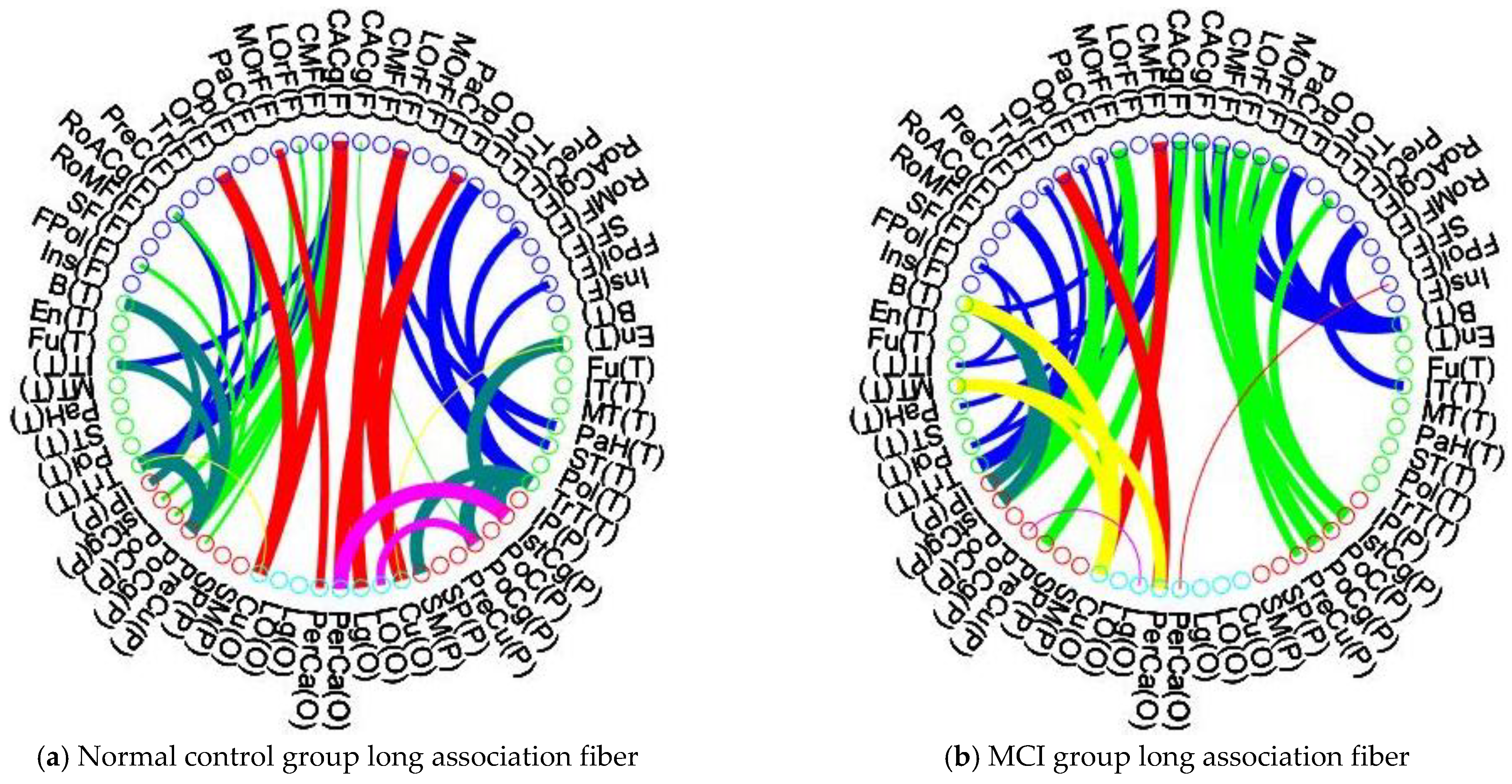
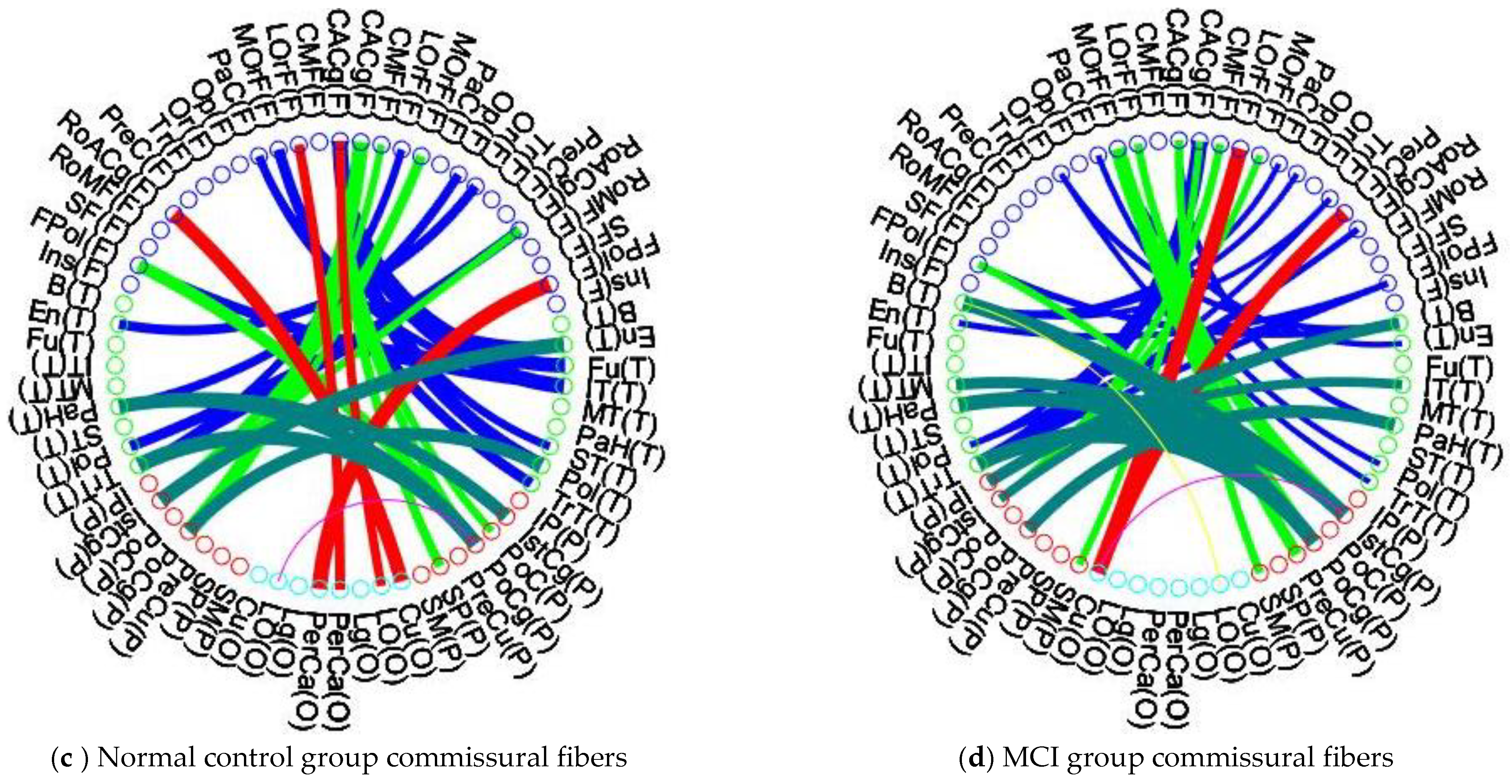
3.4. Patients with MCI Reveal Significant Alteration of Intra-Lobular and Inter-Lobular Connectivity in Their Brain Structural Network
4. Discussion
4.1. FD Analyis Reveals Better Ability for Detecting of Cerebral Changes in MCI Patients
4.2. Patients with MCI Show Shrinkage of Modular Size and Less Functional Lobe Integration in Their Brain Structural Network
4.3. Intra-Lobular and Inter-Lobular Connectivity Decrease in the Brain Structural Network of Patients with MCI
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vega, J.N.; Newhouse, P.A. Mild cognitive impairment: Diagnosis, longitudinal course, and emerging treatments. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2014, 16, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaei-Jafari, H.; Shaw, M.E.; Cherbuin, N. Cerebral atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 1, 487–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, R.; Knopman, D.S. Classification and epidemiology of MCI. Clin. Geriatr. Med. 2013, 29, 753–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild Cognitive Impairment. Continuum (Minneap. Minn.) 2016, 22, 404–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Chertkow, H.; Lerch, J.P.; Evans, A.C.; Dorr, A.E.; Kabani, N.J. Spatial patterns of cortical thinning in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2006, 129, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desikan, R.S.; Fischl, B.; Cabral, H.J.; Kemper, T.L.; Guttmann, C.R.G.; Blacker, D.; Hyman, B.T.; Albert, M.S.; Killiany, R.J. MRI measures of temporoparietal regions show differential rates of atrophy during prodromal AD. Neurology 2008, 71, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.; Gharapetian, L.; Mcevoy, L.; Fennema-Notestine, C.; Hagler, D.; Holland, D.; Dale, A. Relationship between regional atrophy rates and cognitive decline in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluimer, J.D.; van der Flier, W.M.; Karas, G.B.; van Schijndel, R.; Barnes, J.; Boyes, R.G.; Cover, K.S.; Olabarriaga, S.D.; Fox, N.C.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Accelerating regional atrophy rates in the progression from normal aging to Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. Radiol. 2009, 19, 2826–2833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B. How long is the coast of Britain? Statistical self-similarity and fractional dimension. Science 1967, 156, 636–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban, F.J.; Sepulcre, J.; de Miras, J.R.; Navas, J.; de Mendizábal, N.V.; Goñi, J.; Villoslada, P. Fractal dimension analysis of grey matter in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 282, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.D.; Brown, B.; Hwang, M.; Jeon, T.; George, A.T. Fractal dimension analysis of the cortical ribbon in mild Alz-heimer’s disease. NeuroImage 2010, 53, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Shyu, K.K.; Jao, C.W.; Wang, Z.Y.; Soong, B.W.; Wu, H.M.; Wang, P.S. Fractal dimension analysis for quantifying cerebellar morphological change of multiple system atrophy of the cerebellar type (MSA-C). NeuroImage 2010, 49, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.F.; Zhang, X.H.; Zou, T.X.; Huang, N.X.; Chen, H.J. Reduced Cortical Complexity in Cirrhotic Patients with Minimal Hepatic Encephalopathy. Neural Plast. 2020, 2020, 7364649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collantoni, E.; Madan, C.R.; Meneguzzo, P.; Chiappini, I.; Tenconi, E.; Manara, R.; Favaro, A. Cortical Complexity in Anorexia Nervosa: A Fractal Dimension Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheelakumari, R.; Rajagopalan, V.; Chandran, A.; Varghese, T.; Zhang, L.; Yue, G.H.; Mathuranath, P.S.; Kesavadas, C. Quantitative analysis of grey matter degeneration in FTD patients using fractal dimension analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1221–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sporns, O.; Chialvo, D.R.; Kaiser, M.; Hilgetag, C.C. Organization, development and function of complex brain networks. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2004, 8, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortunato, S.; Barthelemy, M. Resolution limit in community detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeley, W.W. Selective functional, regional, and neuronal vulnerability in frontotemporal dementia. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2008, 21, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Dagher, A.; Chen, Z.; Charil, A.; Zijdenbos, A.; Worsley, K.; Evans, A. Impaired small-world efficiency in structural cortical networks in multiple sclerosis associated with white matter lesion load. Brain 2009, 132, 3366–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supekar, K.; Menon, V.; Rubin, D.; Musen, M.; Greicius, M.D. Network analysis of intrinsic functional brain connectivity in Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2008, 4, e1000100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.J.; He, Y.; Rosa-Neto, P.; Germann, J.; Evans, A.C. Revealing modular architecture of human brain structural networks by using cortical thickness from MRI. Cereb. Cortex 2008, 18, 2374–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.G.; Wang, D.; Liu, K.; Weng, J.; Guan, Y.; Chan, K.C.C.; Chu, W.C.W.; Shi, L. Brain Structure Network Analysis in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanabria-Diaz, G.; Melie-García, L.; Iturria-Medina, Y.; Alemán-Gómez, Y.; Hernández-González, G.; Valdés-Urrutia, L.; Valdés-Sosa, P. Surface area and cortical thickness descriptors reveal different attributes of the structural human brain networks. Neuroimage 2010, 50, 1497–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jao, C.W.; Soong, B.W.; Wang, T.Y.; Wu, H.M.; Lu, C.F.; Wang, P.S.; Wu, Y.T. Intra-and Inter-Modular Connectivity Alterations in the Brain Structural Network of Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3. Entropy 2019, 21, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desikan, R.S.; Ségonne, F.; Fischl, B.; Quinn, B.T.; Dickerson, B.C.; Blacker, D.; Albert, M.S. An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 968–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.C. Mild cognitive impairment as a diagnostic entity. J. Intern. Med. 2004, 256, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional Cartography of Complex Metabolic Networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, S.; Delampady, M. False discovery rates and multiple testing. Resonance 2013, 18, 1095–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.; Preacher, K.J. On Effect Size. Psychol. Methods 2012, 17, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullmore, E.T.; Suckling, J.; Overmeyer, S.; Rabe-Hesketh, S.; Taylor, E.; Brammer, M.J. Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 1999, 18, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.; Wang, J.; He, Y. Brain Net Viewer: A network visualization tool for human brain connectomics. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68910. [Google Scholar]
- Leonardo, P.; Chiara, M.; Anna, P.; Antonio, G.; Nicola, D.S.; Mario, M.; Domenico, I.; Emilia, S.; Stefano, D. Fractal dimension of cerebral white matter: A consistent feature for prediction of the cognitive performance in patients with small vessel disease and mild cognitive impairment. NeuroImage Clin. 2019, 24, 101990. [Google Scholar]
- Nicastro, N.; Malpetti, M.; Cope, T.E.; Bevan-Jones, W.R.; Mak, E.; Passamonti, L.; Rowe, J.B.; O’Brien, J.T. Cortical Complexity Analyses and Their Cognitive Correlate in Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 76, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, P.J.; Scheltens, P.; Verhey, F.R.J.; Schmand, B.; Launer, L.J.; Jolles, J.; Jonker, C. Medial temporal lobe atrophy and memory dysfunction as predictors for dementia in subjects with mild cognitive impairment. J. Neurol. 1999, 246, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korf, E.S.C.; Wahlund, L.O.; Visser, P.J.; Scheltens, P. Medial temporal lobe atrophy on MRI predicts dementia in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 2004, 63, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jack, C.R.J.; Petersen, R.C.; Xu, Y.C.; O’Brien, P.C.; Smith, G.E.; Ivnik, R.J.; Boeve, B.F.; Waring, S.C.; Tangalos, E.G.; Kokmen, E. Prediction of AD with MRI-based hippocampal volume in mild cognitive impairment. Neurology 1999, 52, 1397–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Qing, Z.; Lu, J.; Obeso, I.; Zhang, B.; Li, Y. Altered sulcogyral patterns of orbitofrontal cortex in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2020, 302, 111108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, G.C.; Tewarie, P.; Vidaurre, D.; Liuzzi, L.; Woolrich, M.W.; Brookes, M.J. Dynamics of large-scale electrophysiological networks: A technical review. Neuroimage 2017, 180, 559–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišić, B.; Betzel, R.F.; De Reus, M.A.; Van Den Heuvel, M.P.; Berman, M.G.; McIntosh, A.R.; Sporns, O. Network-level structure-function relationships in human neocortex. Cereb. Cortex 2016, 26, 3285–3296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.; Tewarie, P.; Hillebrand, A.; Douw, L.; van Dijk, B.W.; Stufflebeam, S.M.; Van Mieghem, P. A Mapping Between Structural and Functional Brain Networks. Brain Connect. 2016, 6, 298–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, D.A.; Cohen, A.; Power, J.D.; Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Church, J.; Miezin, F.M.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. Functional Brain Networks Develop from a “Local to Distributed” Organization. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2009, 5, e1000381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosenbach, N.U.F.; Fair, D.A.; Miezin, F.M.; Cohen, A.L.; Wenger, K.K.; Dosenbach, R.A.T.; Fox, M.D.; Snyder, A.Z.; Vincent, J.L.; Raichle, M.E.; et al. Distinct brain networks for adaptive and stable task control in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11073–11078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dosenbach, N.U.; Visscher, K.M.; Palmer, E.D.; Miezin, F.M.; Wenger, K.K.; Kang, H.C.; Burgund, E.D.; Grimes, A.L.; Schlaggar, B.L.; Petersen, S.E. A core system for the implementation of task sets. Neuron 2006, 50, 799–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooley, S.A.; Cabeen, R.P.; Laidlaw, D.H.; Conturo, T.E.; Lane, E.M.; Heaps, J.M.; Bolzenius, J.D.; Baker, L.M.; Salminen, L.E.; Scott, S.E.; et al. Posterior brain white matter abnormalities in older adults with probable mild cognitive impairment. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2015, 37, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, H.Y.; Xie, C.M.; Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.J.; Teng, G.J.; Li, S.J. Modular reorganization of brain resting state networks and its independent validation in Alzheimer’s disease patients. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, M.; Liu, K.; Li, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Yin, X.; Lai, Y.; Fang, J.; Tong, H.; et al. Alterations of Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 12, 615048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buldú, J.M.; Bajo, R.; Maestú, F.; Castellanos, N.; Leyva, I.; Gil, P.; Sendiña-Nadal, I.; Almendral, J.A.; Nevado, A.; del-Pozo, F.; et al. Reorganization of functional networks in mild cognitive impairment. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Hsu, J.-L.; Lin, K.-J.; Liu, H.-L.; Wey, S.-P.; Hsiao, I.-T.; Weiner, M.; Aisen, P.; Petersen, R.; Jack, C.R.; et al. Characteristic patterns of inter- and intra-hemispheric metabolic connectivity in patients with stable and progressive mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| MCI (n = 30) | CP (n = 30) | p Values | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yearsAge, years | 70 ± 5.2 | 69 ± 3.7 | 0.57 |
| Sex, female/male | 16/14 | 15/15 | 0.8003 |
| Dominant hand, right/ left | 30/0 | 30/0 | |
| Education, years | 11.3 ± 3.6 | 11.4 ± 3.4 | 0.558 |
| MMSE | 24.76 ± 3.22 | 28.86 ± 0.74 | <0.001 |
| CDR global | 0.5 | 0 | |
| CDR Memory | 0.5 | 0 |
| Frontal | ROI | Abbreviation | Temporal | ROI | Abbreviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1,2 | Caudal anterior cingulate | CACg | 37,38 | Medial temporal | MT |
| 3,4 | Caudal middle frontal | CMF | 39,40 | Para hippocampal | PaH |
| 5,6 | Lateral orbital frontal | LOrF | 41,42 | Superior temporal | ST |
| 7,8 | Medial orbital frontal | MOrF | 43,44 | Temporal pole | TPol |
| 9,10 | Paracentral | PaC | 45,46 | Transverse temporal | TrT |
| 11,12 | Parsopercularis | Op | Parietal | ||
| 13,14 | Parsorbitalis | Or | 47,48 | Inferior parietal | IP |
| 15,16 | Parstriangularis | Tr | 49,50 | Isthmus cingulate | IstCg |
| 17,18 | Precentral | PreC | 51,52 | Postcentral | PoC |
| 19,20 | Rostral anterior cingulate | RoACg | 53,54 | Posterior cingulate | PoCg |
| 21,22 | Rostral middle frontal | RoMF | 55,56 | Precuneus | PreCu |
| 23,24 | Superior frontal | SF | 57,58 | Superior parietal | SP |
| 25,26 | Frontal pole | FPol | 59,60 | Supra marginal | SM |
| 27,28 | Insula | Ins | Occipital | ||
| Temporal | 61,62 | Cuneus | Cu | ||
| 29,30 | Bankssts | B | 63,64 | Lateral occipital | LO |
| 31,32 | Entorhinal | En | 65,66 | Lingual | Lg |
| 33,34 | Fusiform | Fu | 67,68 | Pericaicarine | PerCa |
| 35,36 | Inferior temporal | IT |
| Lobe | Control | MCI | p-Value | Effect Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal (L) | 2.2324 ± 0.0161 | 2.2319 ± 0.0224 | 0.9149 | 0.0128 |
| Frontal (R) | 2.2393 ± 0.0144 | 2.2331 ± 0.0213 | 0.1858 | 0.1681 |
| Temporal (L) | 2.2108 ± 0.0108 | 2.1908 ± 0.0200 | <0.001 * | 0.5283 |
| Temporal (R) | 2.1985 ± 0.0146 | 2.1849 ± 0.0189 | 0.0025 * | 0.3735 |
| Parietal (L) | 2.2902 ± 0.0183 | 2.2844 ± 0.0158 | 0.1922 | 0.1672 |
| Parietal (R) | 2.2990 ± 0.0184 | 2.2822 ± 0.0209 | 0.0015 * | 0.3924 |
| Occipital (L) | 2.2146 ± 0.0301 | 2.2084 ± 0.0299 | 0.4262 | 0.1028 |
| Occipital (R) | 2.2247 ± 0.0334 | 2.2159 ± 0.0240 | 0.2469 | 0.1498 |
| Left Hemisphere | Controls | MCI | p-Value | Effect Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frontal (L) | Paracentral | 2.1765 ± 0.0523 | 2.1546 ± 0.0443 | 0.0268 | 0.22 |
| Rostral middle frontal | 2.4095 ± 0.0178 | 2.4009 ± 0.0247 | 0.0353 | 0.20 | |
| Frontal (R) | Caudal anterior cingulate | 2.1322 ± 0.0554 | 2.1037 ± 0.0497 | 0.0196 | 0.26 |
| Caudal middle frontal | 2.2911 ± 0.0448 | 2.2766 ± 0.0335 | 0.0363 | 0.18 | |
| Medial orbital frontal | 2.2473 ± 0.0359 | 2.2235 ± 0.0776 | 0.0342 | 0.19 | |
| Paracentral | 2.2118 ± 0.0361 | 2.1724 ± 0.0378 | 0.0003 | 0.47 | |
| Superior frontal | 2.4082 ± 0.0169 | 2.3988 ± 0.0166 | 0.0189 | 0.27 | |
| Temporal (L) | Medial Temporal | 2.3148 ± 0.0274 | 2.2970 ± 0.0334 | 0.0245 | 0.28 |
| Fusiform | 2.2993 ± 0.0271 | 2.2853 ± 0.0248 | 0.0183 | 0.26 | |
| Inferior temporal | 2.3358 ± 0.020 | 2.3223 ± 0.0294 | 0.0182 | 0.26 | |
| Transverse Temporal | 2.0486 ± 0.0498 | 2.0229 ± 0.0595 | 0.0248 | 0.23 | |
| Entorhinal | 2.1278 ± 0.0415 | 2.0766 ± 0.0518 | 0.0004 | 0.47 | |
| Temporal pole | 2.1937 ± 0.0352 | 2.1734 ± 0.0445 | 0.0213 | 0.25 | |
| Temporal (R) | Bankssts | 2.1815 ± 0.0385 | 2.1622 ± 0.0562 | 0.0352 | 0.20 |
| Fusiform | 2.2994 ± 0.0268 | 2.2816 ± 0.0341 | 0.0195 | 0.28 | |
| Para hippocampal | 2.0464 ± 0.0590 | 2.0165 ± 0.050 | 0.0200 | 0.26 | |
| Transverse Temporal | 1.9913 ± 0.0621 | 1.9542 ± 0.0654 | 0.0216 | 0.28 | |
| Superior temporal | 2.3435 ± 0.0351 | 2.333 ± 0.0281 | 0.0438 | 0.16 | |
| Parietal (L) | Postcentral | 2.2919 ± 0.02879 | 2.2807 ± 0.0267 | 0.0368 | 0.20 |
| Supra marginal | 2.3867 ± 0.0271 | 2.3737 ± 0.0263 | 0.0242 | 0.28 | |
| Parietal (R) | Inferior parietal | 2.4292 ± 0.020 | 2.4181 ± 0.0171 | 0.0275 | 0.27 |
| Superior parietal | 2.3581 ± 0.0221 | 2.3424 ± 0.0193 | 0.0076 | 0.35 | |
| Postcentral | 2.2829 ± 0.02169 | 2.2624 ± 0.0279 | 0.0047 | 0.38 | |
| Poster cingulate | 2.2097 ± 0.0602 | 2.1864 ± 0.0652 | 0.0362 | 0.18 | |
| Supra marginal | 2.3886 ± 0.02437 | 2.3574 ± 0.0329 | 0.0342 | 0.47 | |
| Occipital (R) | Lateral occipital | 2.3713 ± 0.0256 | 2.3619 ± 0.0261 | 0.0357 | 0.18 |
| lingual | 2.2721 ± 0.0257 | 2.2528 ± 0.0373 | 0.0288 | 0.29 |
| (a) | Modules of FD-based brain structural network in the control group |
| Module 1 (19) | Frontal: parsorbitalis, roatral anterior cingulate, rostral middle frontal, insula, Temporal: temporal pole, Parietal:postcentral, precuneus, superior parietal, Occipital: lateral occipital |
| Frontal: rostral anterior cingulate, caudal middle frontal, lateral orbital frontal, paracentral Temporal: middle temporal, superior temporal Parietal: isthmus cingulate, precuneus Occipital: lateral occipital, lingual | |
| Module 2 (17) | Frontal: caudal middle frontal, precentral, Temporal: fusiform, parahippocampal, Parietal: isthmus cingulate, posterior cingulate, Occipital: pericalcarine |
| Frontal: precentral, caudal anterior cingulate, parsopercularis, parstriangularis, Temporal: entorhinal, fusiform, parahippocampal, transverse temporal Parietal: posteror cingulate, supra marginal | |
| Module 3 (17) | Frontal: caudal anterior cingulate, lateral orbital frontal, medial orbital frontal, paracentral, parsopercularis, parstriangularis, superior frontal, Temporal: bankssts, middle temporal, superior temporal, Parietal: supra marginal, Occipital: cuneus, lingual |
| Frontal: rostral middle frontal, insula, Parietal: postcentral Occipital: pericalcarine | |
| Module 4 (8) | Temporal: entorhinal, Parietal: inferior parietal |
| Frontal: medial orbito frontal, parsorbitalis, superior frontal, frontal pole Temporal: bankssts, Occipital: cuneus | |
| Module 5 (7) | Frontal: frontal pole, Temporal: inferior temporal, transverse temporal |
| Temporal: inferior temporal, temporal pole, Parietal: superior parietal, inferior parietal | |
| (b) | Modules of FD-based brain structural network in the MCI group |
| Module 1 (18) | Frontal: caudal anterior cingulate, parsopercularis, parstriangularis, rostral anterior frontal, Temporal: entorhinal, para hippocampal, transverse temporal, Parietal: precentral, superior parietal, supra marginal |
| Frontal: caudal anterior cingulate, rostral middle frontal, frontal pole, Temporal: superior temporal, temporal pole, Parietal: inferior parietal, postcentral, supra marginal | |
| Module 2 (13) | Frontal: medial orbital frontal, superior frontal, Temporal: bankssts, entorhinal |
| Frontal: lateral orbital frontal, medial orbital frontal, paracentral, parsopercularis, parstriangularis, Temporal: middle temporal, Parietal: isthmus cingulate, posterior cingulate, precuneus | |
| Module 3 (11) | Frontal: lateral orbital frontal, paracentral, frontal pole, Temporal: inferior temporal, middle temporal, temporal pole, Parietal: inferior parietal |
| Frontal: rostral anterior frontal, Temporal: bankssts, fusiform, inferior temporal | |
| Module 4 (10) | Frontal: parsorbitalis, rostral middle frontal, insula Temporal: fusiform, superior temporal Parietal: isthmus cingulate, Occipital: lateral occipital |
| Frontal: caudal middle frontal, superior frontal, Occipital: lingual | |
| Module 5 (9) | Parietal: postcentral, Occipital: cuneus, lingual, pericalcarine |
| Frontal: parsorbitalis, insula, Parietal: superior parietal, Occipital: lateral occipital, pericalcarine | |
| Module 6 (7) | Frontal: caudal middle frontal, Parietal: posterior cingulate, precuneus |
| Frontal: precentral, Temporal: para hippocampal, transverse temporal, Occipital: cuneus |
| Lobe | Frontal | Temporal | Parietal | Occipital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemisphere | L/R/B | L/R/B | L/R/B | L/R/B |
| Controls | 9/2/15 | 9/8/24 | 7/5/13 | 3/3/8 |
| MCIs | 6/2/18 | 4/6/14 | 7/4/12 | 4/2/5 |
| Group | Frontal | Temporal | Parietal | Occipital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | 0.3686 | 0.4239 | 0.3378 | 0.4642 |
| MCIs | 0.3157 * | 0.3542 * | 0.2747 * | 0.4125 * |
| Ratio (MCI/Control) | 85.6% | 83.5% | 81.3% | 88.8% |
| Group | Frontal | Temporal | Parietal | Occipital |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Controls | 0.6345 | 0.633 | 0.6265 | 0.6341 |
| MCIs | 0.5440 * | 0.5558 * | 0.4772 * | 0.4293 ** |
| Ratio (EM/Control) | 85.7% | 87.8% | 76.2% | 67.7% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lau, C.I.; Yeh, J.-H.; Tsai, Y.-F.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Wu, Y.-T.; Jao, C.-W. Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010093
Lau CI, Yeh J-H, Tsai Y-F, Hsiao C-Y, Wu Y-T, Jao C-W. Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis. Brain Sciences. 2023; 13(1):93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010093
Chicago/Turabian StyleLau, Chi Ieong, Jiann-Horng Yeh, Yuh-Feng Tsai, Chen-Yu Hsiao, Yu-Te Wu, and Chi-Wen Jao. 2023. "Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis" Brain Sciences 13, no. 1: 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010093
APA StyleLau, C. I., Yeh, J.-H., Tsai, Y.-F., Hsiao, C.-Y., Wu, Y.-T., & Jao, C.-W. (2023). Decreased Brain Structural Network Connectivity in Patients with Mild Cognitive Impairment: A Novel Fractal Dimension Analysis. Brain Sciences, 13(1), 93. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci13010093






