Behavioral and Cognitive Electrophysiological Differences in the Executive Functions of Taiwanese Basketball Players as a Function of Playing Position
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
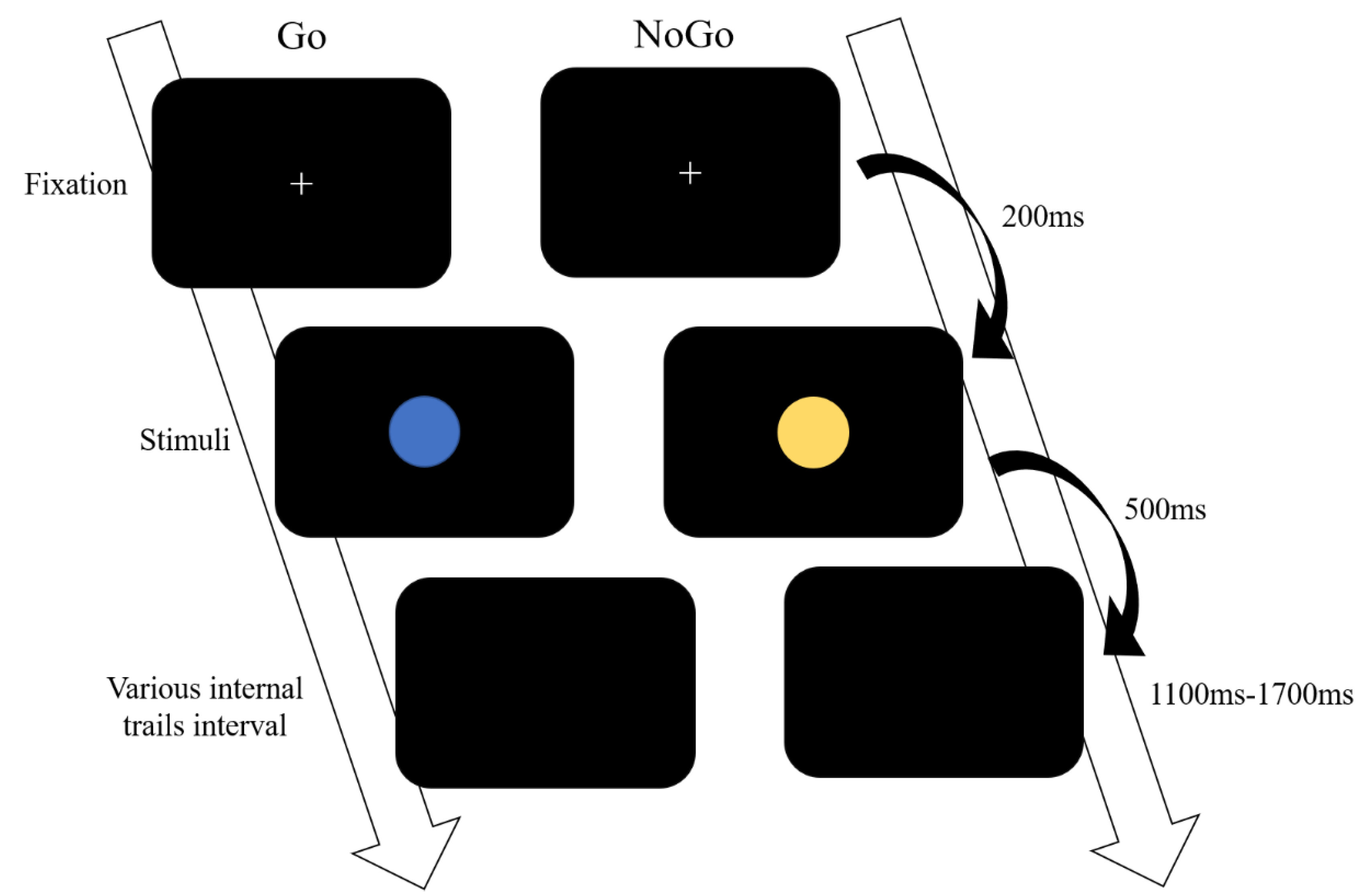
2.3. Go/NoGo Paradigm
2.4. Cardiorespiratory Fitness Estimation
2.5. Electrophysiological Recording and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
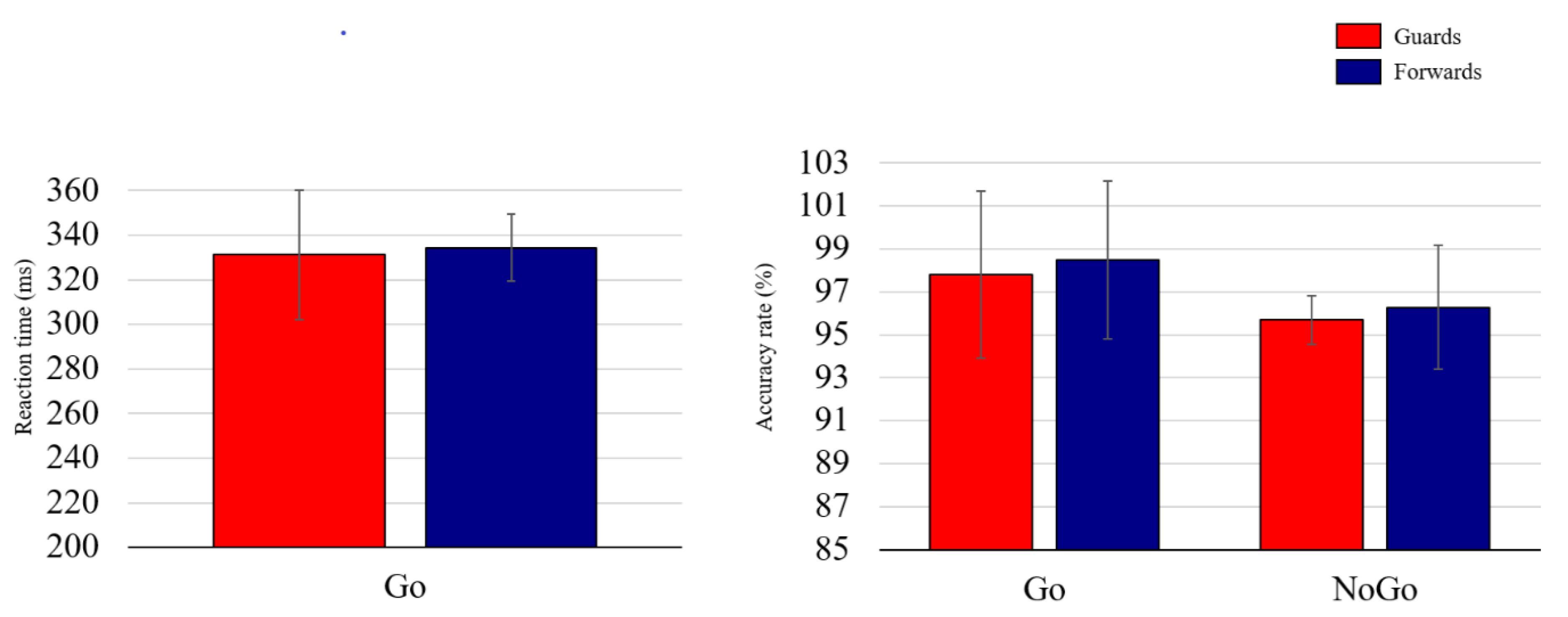
3.2. Behavioral Performance
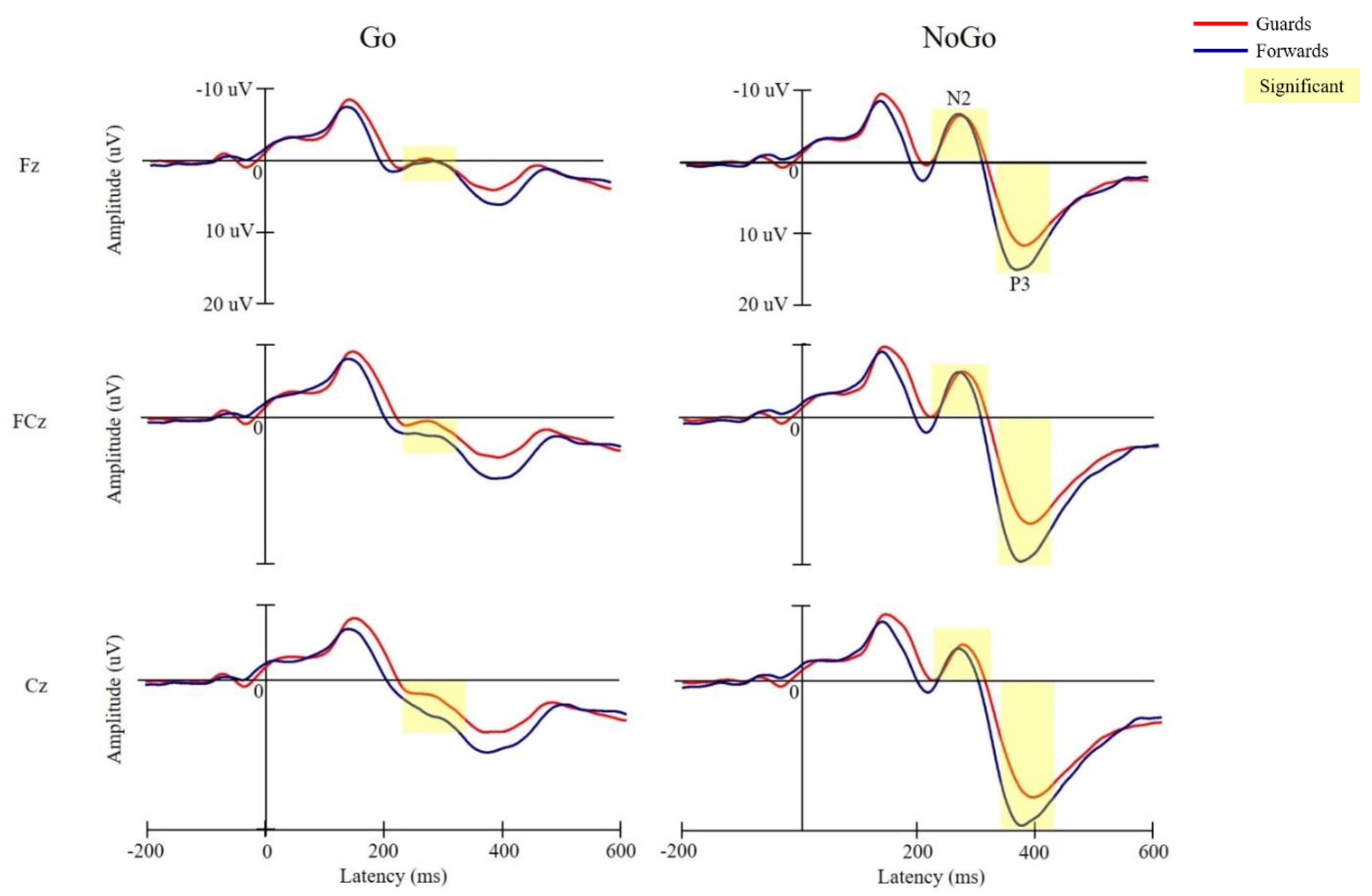
3.3. Electrophysiological Performance
3.3.1. N2 Latency
3.3.2. N2 Amplitude
3.3.3. P3 Latency
3.3.4. P3 Amplitude
4. Discussion
4.1. Behavioral Indices
4.2. Electrophysiological Performance
4.3. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tsai, C.L.; Chen, F.C.; Pan, C.Y.; Wang, C.H.; Huang, T.H.; Chen, T.C. Impact of acute aerobic exercise and cardiorespiratory fitness on visuospatial attention performance and serum BDNF levels. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2014, 41, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.L.; Wang, W.L. Exercise-mode-related changes in task-switching performance in the elderly. Front. Behavi. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isoglu-Alkac, U.; Ermutlu, M.N.; Eskikutr, G.; Yücesir, L.; Temel, S.D.; Temel, T. Dancers and fastball sports athletes have different spatial visual attention styles. Cogn. Neurodyn. 2018, 12, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.M.; Ward, P.; Smeeton, N.; Ward, J. Task specificity, role, and anticipation skill in soccer. Res. Q. Exerc. Sport. 2008, 79, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.L.; Wang, C.H.; Pan, C.Y.; Chen, F.C.; Huang, S.Y.; Tseng, Y.T. The effects of different exercise types on visuospatial attention in the elderly. Psychol. Sport. Exerc. 2016, 26, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.L.; Pan, C.Y.; Chen, F.C.; Tseng, Y.T. Open-and closed-skill exercise interventions produce different neurocognitive effects on executive functions in the elderly: A 6-month randomized, controlled trial. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Russo, F.; Bultrini, A.; Brunelli, S.; Delussu, A.S.; Polidori, L.; Taddei, F.; Traballesi, M.; Spinelli, D. Benefits of sports participation for executive function in disabled athletes. J. Neurotrauma 2010, 27, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestberg, T.; Gustafson, R.; Marurex, L.; Ingvar, M.; Petrovic, P. Executive functions predict the success of top-soccer players. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e34731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamand, A. Executive function. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 2013, 64, 135–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montuori, S.; D’Aurizio, G.; Foti, F.; Liparoti, M.; Lardone, A.; Pesoil, M.; Sorrentino, G.; Mandolesi, L.; Curcio, G.; Sorrentino, P. Executive functioning profiles in elite volleyball athletes: Preliminary results by a sport-specific task switching protocol. Hum. Mov. Sci. 2019, 63, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianco, V.; Di Russo, F.; Perri, R.L.; Berchicci, M. Different proactive and reactive action control in fencers’ and boxers’ brain. Neuroscience 2017, 343, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, M. Visual attention: The past 25 years. Vis. Res. 2011, 51, 1484–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.L.; Chang, Y.K.; Hung, T.M.; Tseng, Y.T.; Chen, T.C. The neurophysiological performance of visuospatial working memory in children with developmental coordination disorder. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2012, 54, 1114–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donkers, F.C.; Van Boxtel, G.J. The N2 in go/no-go tasks reflects conflict monitoring not response inhibition. Brain Cogn. 2004, 56, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, R.; Liu, X.; Zhao, G.; Zheng, Y.; Gong, M.; Zhang, J. The impairing effects of mental fatigue on response inhibition: An ERP study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuis, S.; Yeung, N.; Van Den Wildenberg, W.; Ridderinkhof, K.R. Electrophysiological correlates of anterior cingulate function in a go/no-go task: Effects of response conflict and trial type frequency. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 2003, 3, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.L.; Johnstone, S.J.; Barry, R.J. Movement-related potentials in the Go/NoGo task: The P3 reflects both cognitive and motor inhibition. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drinkwater, E.J.; Pyne, D.B.; McKenna, M.J. Design and interpretation of anthropometric and fitness testing of basketball players. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trninić, S.; Dizdar, D. System of the performance evaluation criteria weighted per positions in the basketball game. Coll. Antropol. 2000, 24, 217–234. [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher, N.; Schmidt, M.; Wellmann, K.; Braumann, K. General perceptual-cognitive abilities: Age and position in soccer. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestberg, T.; Reinebo, G.; Marurex, L.; Ingvar, M.; Petrovic, P. Core executive functions are associated with success in young elite soccer players. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wylie, S.A.; Bashore, T.R.; Van Wouwe, N.C.; Mason, E.J.; John, K.D.; Neimat, J.S.; Ally, B.A. Exposing an “Intangible” cognitive skill among collegiate football players: Enhanced interference control. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köklü, Y.; Alemdaroğlu, U.; Koçak, F.; Erol, A.; Fındıkoğlu, G. Comparison of chosen physical fitness characteristics of Turkish professional basketball players by division and playing position. J. Hum. Kinet. 2011, 30, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlan, A.T.; Tucker, P.S.; Dalbo, V.J. A comparison of linear speed, closed-skill agility, and open-skill agility qualities between backcourt and frontcourt adult semiprofessional male basketball players. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2014, 28, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheppard, J.M.; Young, W.B. Agility literature review: Classifications, training and testing. J. Sports Sci. 2006, 24, 919–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puente, C.; Abián-Vicén, J.; Areces, F.; López, R.; Del Coso, J. Physical and physiological demands of experienced male basketball players during a competitive game. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2017, 31, 956–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cid-Fernández, S.; Lindín, M.; Diaz, F. Effects of amnestic mild cognitive impairment on N2 and P3 Go/NoGo ERP components. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 38, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Russo, F.; Taddei, F.; Aprile, T.; Spinelli, D. Neural correlates of fast stimulus discrimination and response selection in top-level fencers. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 408, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruin, K.; Wijers, A.; Van Staveren, A. Response priming in a go/nogo task: Do we have to explain the go/nogo N2 effect in terms of response activation instead of inhibition? Clin. Neurophysiol. 2001, 112, 1660–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, A. On the utility of P3 amplitude as a measure of processing capacity. Psychophysiology 2001, 38, 557–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderman, B.L.; Olson, R.L.; Brush, C.J. Using event-related potentials to study the effects of chronic exercise on cognitive function. Int. J. Sport Exerc. Psychol. 2019, 17, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, G.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, X. Impulse inhibition in people with Internet addiction disorder: Electrophysiological evidence from a Go/NoGo study. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 485, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubia, K.; Hyde, Z.; Halari, R.; Giampietro, V.; Smith, A. Effects of age and sex on developmental neural networks of visual–spatial attention allocation. Neuroimage 2010, 51, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emilija, S.; Nenad, S.; Aaron, T.S.; Vincent, J.D.; Daniel, M.B.; Zoran, M. The activity demands and physiological responses encountered during basketball match-play: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 111–135. [Google Scholar]
- Folstein, M.F.; Folstein, S.E.; McHugh, P.R. “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J. Psychiatr. Res. 1975, 12, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Brown, G.K. BDI-II, 2nd ed.; The Psychological Corporation: San Antonio, TX, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.L.; Huang, T.H.; Tsai, M.C. Neurocognitive performances of visuospatial attention and the correlations with metabolic and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with obesity. Exp. Physiol. 2017, 102, 1683–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, C.L.; Pan, C.Y.; Cen, F.C.; Huang, T.H.; Tsai, M.C.; Chuang, C.Y. Differences in neurocognitive performance and metabolic and inflammatory indices in male adults with obesity as a function of regular exercise. Exp. Physiol. 2019, 104, 1650–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krustrup, P.; Mohr, M.; Amstrup, T.; Rysgaard, T.; Johansen, J.; Steensberg, A.; Pedersen, P.K.; Bangsbo, J. The yo-yo intermittent recovery test: Physiological response, reliability, and validity. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2003, 35, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bangsbo, J.; Iaia, F.M.; Krustrup, P. The Yo-Yo intermittent recovery test. Sports Med. 2008, 38, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, P.D.; Stoerig, P.; Falkenstein, M. ERP—Correlates of response selection in a response conflict paradigm. Brain Res. 2008, 1189, 127–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amenedo, E.; Dıaz, F. Aging-related changes in processing of non-target and target stimuli during an auditory oddball task. Biol. Psychol. 1998, 48, 235–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piispala, J.; Kallio, M.; Bloigu, R.; Jansson-Verkasalo, E. Delayed N2 response in Go condition in a visual Go/Nogo ERP study in children who stutter. J. Fluen. Disord. 2016, 48, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maimón, A.Q.; Courel-Ibáñez, J.; Ruíz, F.J.R. The basketball pass: A systematic review. J. Hum. Kinet. 2020, 71, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, E.; Cárdenas, D.; Saiz de Baranda, P.; Palao, J.M. Analysis of the final actions used in basketball during formative years according to player’s. J. Hum. Mov. Stud. 2006, 50, 427–431. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.L.; Pan, C.Y.; Chen, F.C.; Wang, C.H.; Chou, F.Y. Effects of acute aerobic exercise on a task-switching protocol and brain-derived neurotrophic factor concentrations in young adults with different levels of cardiorespiratory fitness. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 836–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, B.; Goldman, M. Optimal strategy in basketball. In Handbook of Statistical Methods and Analyses in Sports; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2017; pp. 245–260. [Google Scholar]
- Sindik, J. Performance indicators of the top basketball players: Relations with several variables. Coll. Antropol. 2015, 39, 617–624. [Google Scholar]
| Guards (n = 27) | Forwards (n = 19) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 20.74 ± 1.10 | 20.26 ± 1.24 | 0.175 |
| Handiness (R(L)) | 24 (3) | 16 (3) | 0.643 |
| Education (years) | 14.44 ± 1.37 | 14.00 ± 0.94 | 0.199 |
| Height (cm) * | 178.59 ± 5.87 | 190.74 ± 4.65 | <0.001 |
| Weight (kg) * | 73.54 ± 7.79 | 86.74 ± 7.33 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.04 ± 1.98 | 23.80 ± 1.61 | 0.173 |
| MMSE | 28.74 ± 1.13 | 28.33 ± 1.45 | 0.318 |
| BDI-II | 6.89 ± 6.03 | 9.00 ± 5.95 | 0.282 |
| BE (years) | 7.22 ± 3.27 | 6.32 ± 2.65 | 0.324 |
| TF (times/week) | 8.48 ± 2.38 | 7.53 ± 2.72 | 0.212 |
| TP (hr/time) | 2.60 ± 0.46 | 2.50 ± 0.50 | 0.480 |
| VO2 max (ml/kg/min) | 46.87 ± 3.27 | 47.79 ± 3.84 | 0.949 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, Y.-K.; Pan, C.-Y.; Chen, F.-C.; Tseng, Y.-T.; Tsai, C.-L. Behavioral and Cognitive Electrophysiological Differences in the Executive Functions of Taiwanese Basketball Players as a Function of Playing Position. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060387
Chiu Y-K, Pan C-Y, Chen F-C, Tseng Y-T, Tsai C-L. Behavioral and Cognitive Electrophysiological Differences in the Executive Functions of Taiwanese Basketball Players as a Function of Playing Position. Brain Sciences. 2020; 10(6):387. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060387
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, Yi-Kang, Chien-Yu Pan, Fu-Chen Chen, Yu-Ting Tseng, and Chia-Liang Tsai. 2020. "Behavioral and Cognitive Electrophysiological Differences in the Executive Functions of Taiwanese Basketball Players as a Function of Playing Position" Brain Sciences 10, no. 6: 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060387
APA StyleChiu, Y.-K., Pan, C.-Y., Chen, F.-C., Tseng, Y.-T., & Tsai, C.-L. (2020). Behavioral and Cognitive Electrophysiological Differences in the Executive Functions of Taiwanese Basketball Players as a Function of Playing Position. Brain Sciences, 10(6), 387. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10060387







