Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-based Adaptive Actor-Critic
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- it introduces an original nonlinear state-feedback neural network-based controller for ORM tracking, tuned with VRFT, serving as initialization for the AAC learning controller that further improves the ORM tracking and accelerates convergence to the optimal controller. This leads to the novel VRFT-AAC combination;
- the case study proves implementation of the novel mixed control learning approach for ORM tracking. The MIMO validation scenario also demonstrates good decoupling ability of learned controllers, even under constraints and nonlinearities. Comparisons with a model-free batch fitted Q-learning scheme and with a model-based batch-fitted Q-learning approach are also offered. Statistical characterization case studies in different learning settings are given.
- theoretical analysis ensures that the AAC learning scheme preserves the CS stability throughout the updates and converges to the optimal control.
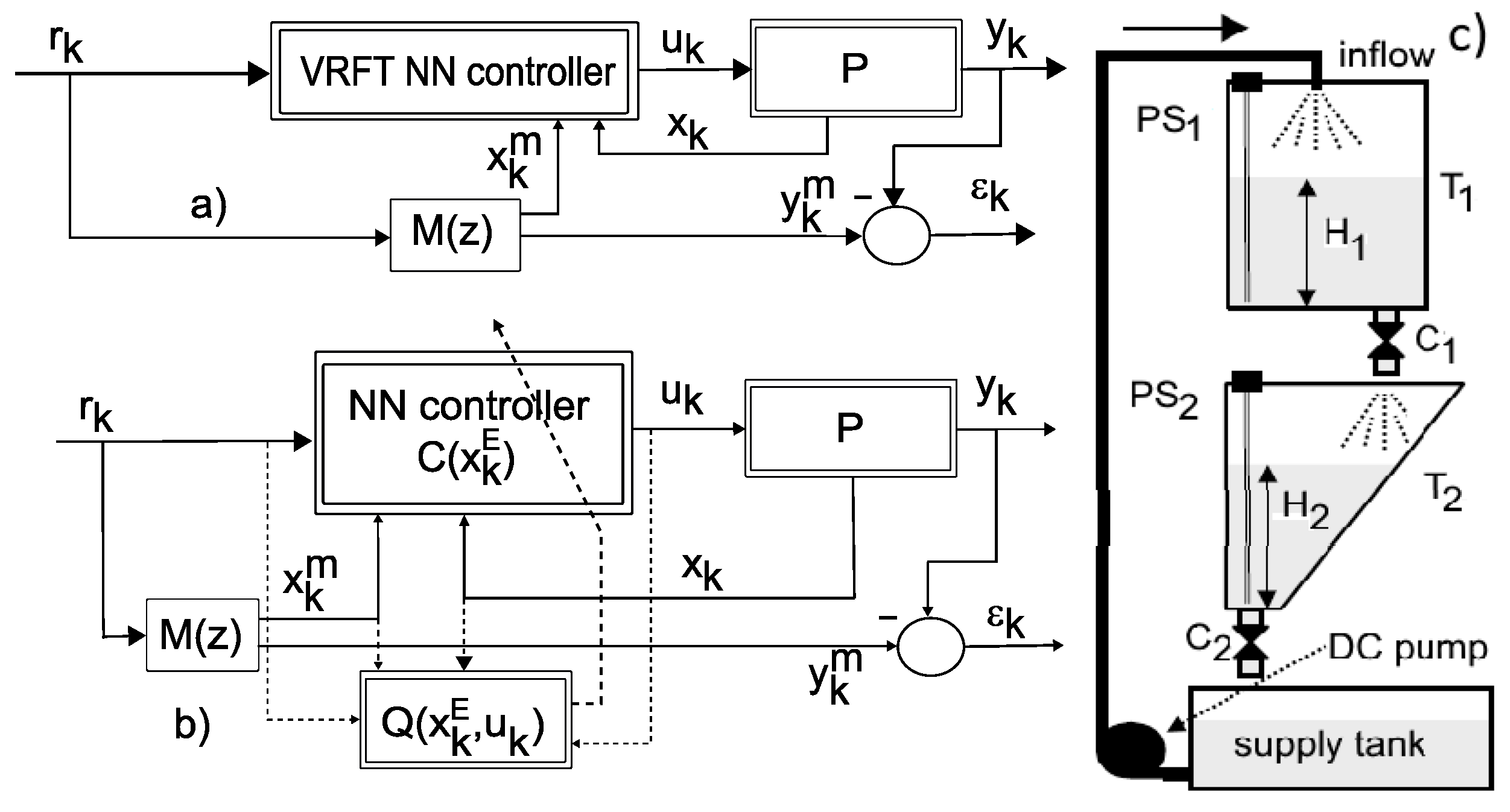
2. Output Model Reference Control for Unknown Systems
3. Nonlinear State-Feedback VRFT for Approximate ORM Tracking Control Using Neural Networks
4. Adaptive Actor-Critic Learning for ORM Tracking Control
4.1. Adaptive Actor-Critic Design
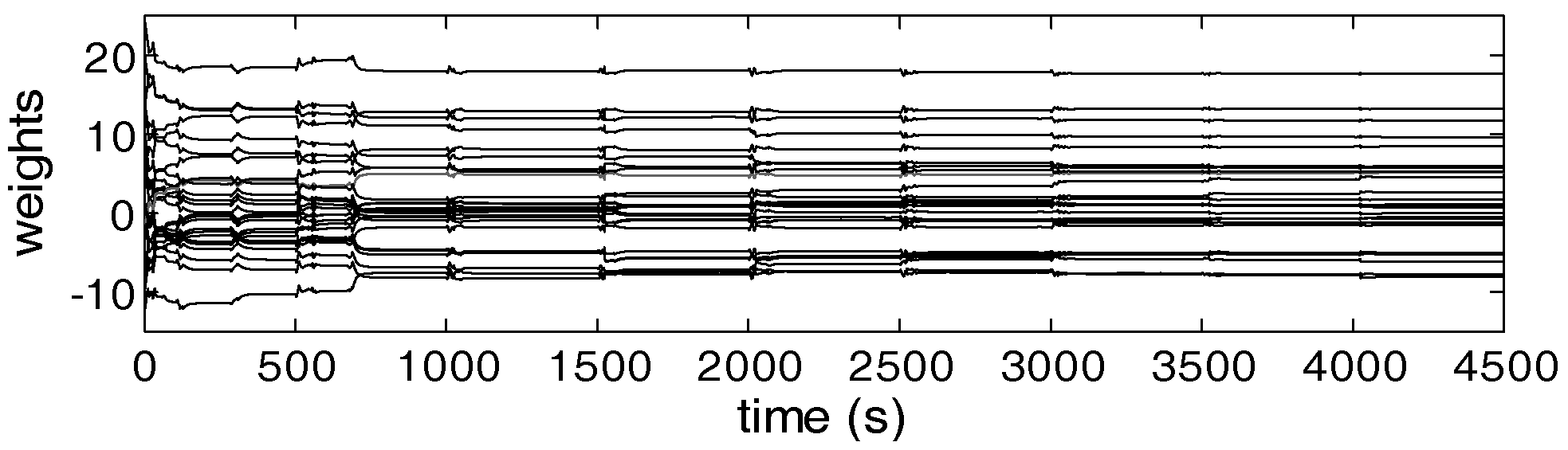
4.2. AAC Using Neural Networks As Approximators
4.3. Convergence of the AAC Learning Scheme with NNs
4.4. Summary of the Mixed VRFT-AAC Design Approach
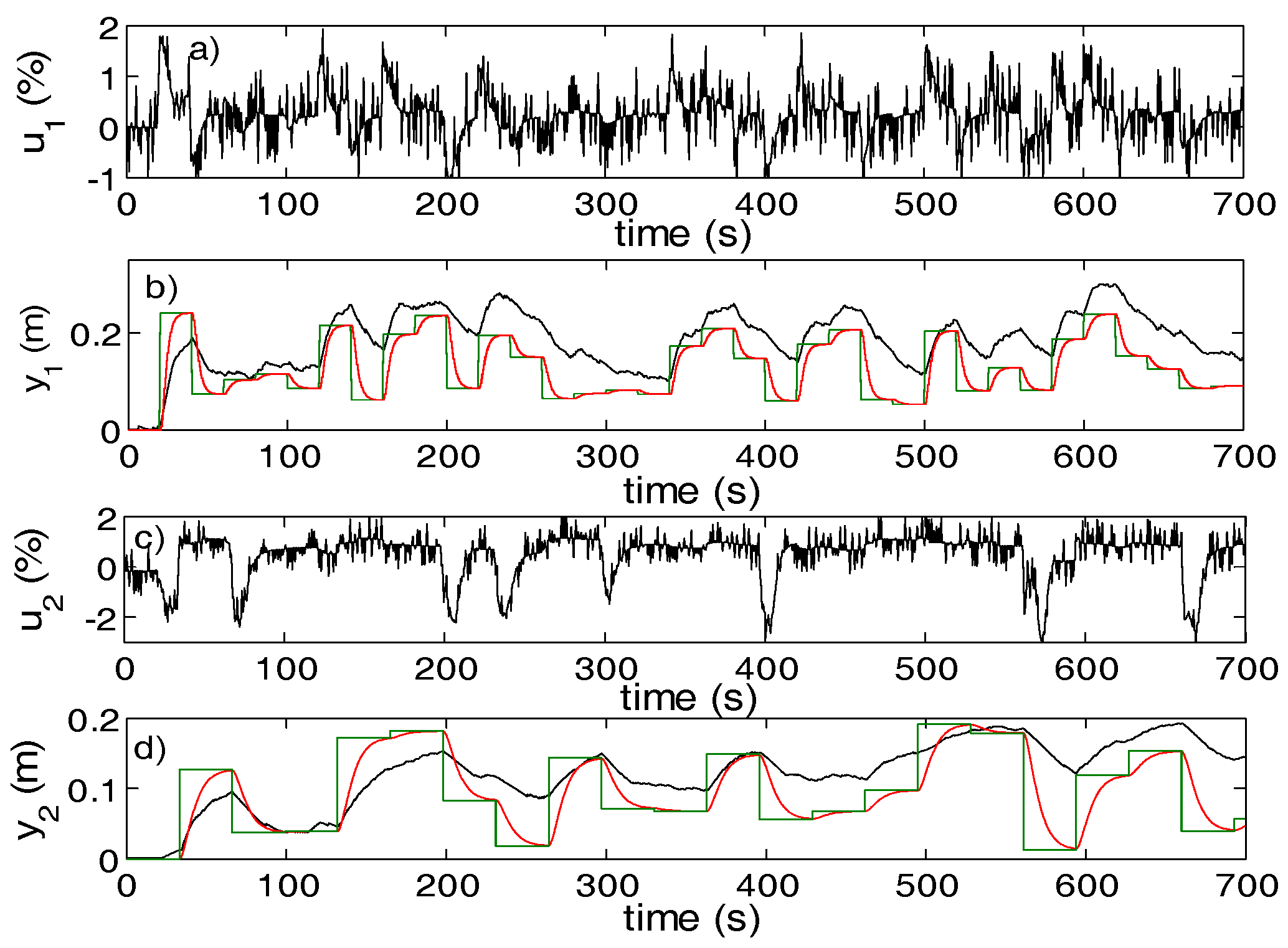
5. Validation Case Study
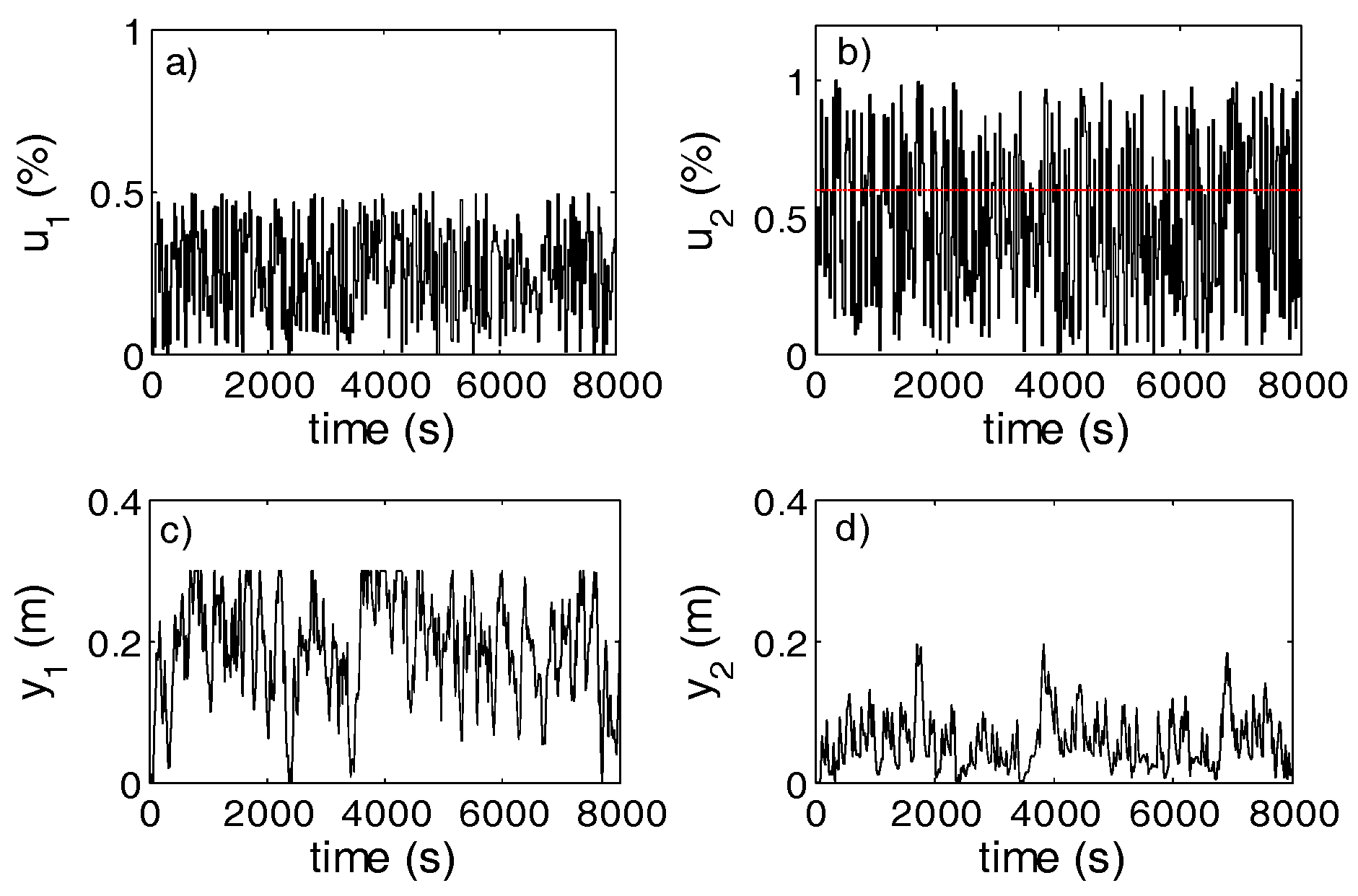
5.1. AAC Design for a MIMO Vertical Tank System
5.2. Statistical Investigations of the AAC Control Performance
5.3. Comments on the AAC Learning Performance
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- Hou, Z.-S.; Wang, Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective. Inf. Sci. 2013, 235, 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fliess, M.; Join, C. Model-free control. Int. J. Control 2013, 86, 2228–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Z.-S.; Jin, S. Data-driven model-free adaptive control for a class of MIMO nonlinear discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 2173–2188. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Campi, M.C.; Lecchini, A.; Savaresi, S.M. Virtual reference feedback tuning: A direct method for the design of feedback controllers. Automatica 2002, 38, 1337–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjalmarsson, H. Iterative feedback tuning—An overview. Int. J. Adapt. Control Signal Process. 2002, 16, 373–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spall, J.C.; Cristion, J.A. Model-free control of nonlinear stochastic systems with discrete-time measurements. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 1998, 43, 1198–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, M.; Karimi, A.; Longchamp, R. Iterative learning control based on stochastic approximation. In Proceedings of the 17th IFAC World Congress, Seoul, Korea, 6–11 July 2008; pp. 1478–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Petriu, E.M. Optimal behaviour prediction using a primitive-based data-driven model-free iterative learning control approach. Comp. Ind. 2015, 74, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hou, Z.; Feng, Y.; Chi, R. Data-driven approximate value iteration with optimality error bound analysis. Automatica 2017, 78, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Petriu, E.M.; Preitl, S. Iterative data-driven tuning of controllers for nonlinear systems with constraints. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6360–6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Z.-H.; Liu, G.-P.; Zhou, D.; Sun, D. Data-based predictive control for networked nonlinear systems with network-induced delay and packet dropout. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 1249–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-driven model-free slip control of anti-lock braking systems using reinforcement Q-learning. Neurocomputing 2018, 275, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Wang, T.; Yin, S.; Gao, H. Data-Based Optimal Control for Networked Double-Layer Industrial Processes. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4179–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Hou, Z.-S.; Jin, S.; Huang, B. An improved data-driven point-to-point ILC using additional on-line control inputs with experimental verification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2017, 49, 687–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, G.-H. Model-free adaptive control design for nonlinear discrete-time processes with reinforcement learning techniques. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2018, 49, 2298–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, R.; Huang, B.; Hou, Z.; Jin, S. Data-driven high-order terminal iterative learning control with a faster convergence speed. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 2018, 28, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, J.-C.; Ge, G.-P. Data-based approach for feedback–feedforward controller design using closed-loop plant data. ISA Trans. 2018, 80, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Werbos, P.J. Approximate dynamic programming for real-time control and neural modeling. In Handbook of Intelligent Control: Neural, Fuzzy, and Adaptive Approaches; White, D.A., Sofge, D.A., Eds.; Van Nostrand Reinhold: New York, NY, USA, 1992; pp. 493–525. [Google Scholar]
- Bertsekas, D.P.; Tsitsiklis, J.N. Neuro-Dynamic Programming; Athena Scientific: Belmont, MA, USA, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Watkins, C.; Dayan, P. Q-learning. Mach. Learn. 1991, 8, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, D. Adaptive dynamic programming: An introduction. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2009, 4, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, F.; Vrabie, D.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control: Using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Syst. Mag. 2012, 32, 76–105. [Google Scholar]
- Prokhorov, D.V.; Wunsch, D.C. Adaptive critic designs. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1997, 8, 997–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Lewis, F.; Liu, D.; Song, R.; Lin, H. Discrete-time local value iteration adaptive dynamic programming: Convergence analysis. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 2018, 48, 875–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, A. Revisiting approximate dynamic programming and its convergence. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2014, 44, 2733–2743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, C.; Ni, Z.; Sun, C.; He, H. Data-driven tracking control with adaptive dynamic programming for a class of continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2017, 47, 1460–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venayagamoorthy, G.K.; Harley, R.G.; Wunsch, D.C. Comparison of heuristic dynamic programming and dual heuristic programming adaptive critics for neurocontrol of a turbogenerator. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2002, 13, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; He, H.; Zhong, Z.; Prokhorov, D.V. Model-free dual heuristic dynamic programming. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari, A. Optimal triggering of networked control systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2018, 29, 3011–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, H.; Gao, Z.; Su, H. Online adaptive policy iteration based fault-tolerant control algorithm for continuous-time nonlinear tracking systems with actuator failures. J. Frankl. Inst. 2018, 355, 6947–6968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcouglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, F.L.; Vamvoudakis, K.G. Reinforcement learning for partially observable dynamic processes: Adaptive dynamic programming using measured output data. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2011, 41, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, D. Data-based controllability and observability analysis of linear discrete-time systems. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 2011, 22, 2388–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruelens, F.; Claessens, B.J.; Vandael, S.; de Schutter, B.; Babuška, R.; Belmans, R. Residential demand response of thermostatically controlled loads using batch reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 2149–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Javaherian, H.; Kovalenko, O.; Huang, T. Adaptive critic learning techniques for engine torque and air-fuel ratio control. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2008, 38, 988–993. [Google Scholar]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Petriu, E.M. Model-free primitive-based iterative learning control approach to trajectory tracking of MIMO systems with experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 26, 2925–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campestrini, L.; Eckhard, D.; Bazanella, A.S.; Gevers, M. Data-driven model reference control design by prediction error identification. J. Frankl. Inst. 2017, 354, 2628–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campestrini, L.; Eckhard, D.; Gevers, M.; Bazanella, A. Virtual reference feedback tuning for non-minimum phase plants. Automatica 2011, 47, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formentin, S.; Savaresi, S.M.; Del Re, L. Non-iterative direct data-driven controller tuning for multivariable systems: Theory and application. IET Control Theory Appl. 2012, 6, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, P.; Liu, D.; Wang, D.; Ma, H. Data-driven controller design for general MIMO nonlinear systems via virtual reference feedback tuning and neural networks. Neurocomputing 2016, 171, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campi, M.C.; Savaresi, S.M. Direct nonlinear control design: The virtual reference feedback tuning (VRFT) approach. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control 2006, 51, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esparza, A.; Sala, A.; Albertos, P. Neural networks in virtual reference tuning. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2011, 24, 983–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Three-level hierarchical model-free learning approach to trajectory tracking control. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2016, 55, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C. Model-free control performance improvement using virtual reference feedback tuning and reinforcement Q-learning. Int. J. Syst. Sci. 2017, 48, 1071–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busoniu, L.; Ernst, D.; de Schutter, B.; Babuska, R. Approximate reinforcement learning: An overview. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Symposium on Adaptive Dynamic Programming and Reinforcement Learning, Paris, France, 11–15 April 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Inteco Ltd. Multitank System, User’s Manual; Inteco Ltd.: Krakow, Poland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hagan, M.T.; Menhaj, M.B. Training feed-forward networks with the Marquardt algorithm. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. 1994, 5, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Liu, J.; Sang, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Q. Fast neural network training on FPGA using quasi-Newton optimisation method. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2018, 26, 1575–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livieris, I.E. Improving the classification efficiency of an ANN utilizing a new training methodology. Informatics 2019, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, M.F. A scaled conjugate gradient algorithm for fast supervised learning. Neural Netw. 1993, 6, 525–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livieris, I.E.; Pintelas, P. A new conjugate gradient algorithm for training neural networks based on a modified secant equation. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 221, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-driven MIMO model-free reference tracking control with nonlinear state-feedback and fractional order controllers. Appl. Soft Comput. 2018, 73, 992–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Roman, R.-C. Data-driven model reference control of MIMO vertical tank systems with model-free VRFT and Q-Learning. ISA Trans. 2018, 73, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, H.; Ni, Z.; Fu, J. A three-network architecture for on-line learning and optimization based on adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing 2012, 78, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Wang, B.; Liu, D. A supervised actor-critic approach for adaptive cruise control. Soft Comput. 2013, 17, 2089–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E.; Petriu, E.M.; Preitl, S.; Dragos, C.-A. Data-driven reference trajectory tracking algorithm and experimental validation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2013, 9, 2327–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-based two-degree-of-freedom iterative control approach to constrained non-linear systems. IET Control Theory Appl. 2015, 9, 1000–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Jagannathan, S. Reinforcement learning controller design for affine nonlinear discrete-time systems using online approximators. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. B Cybern. 2012, 42, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Scenario | Avg. | Min. | Success Rate | Avg. Episodes | Std. Episodes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full Tuning | Perturbed | |||||
| yes | yes | 0.48 | 0.46 | 88% | 25 | 4.9 |
| yes | no | 0.76 | 0.45 | 53% | 43 | 6.3 |
| no | yes | 0.64 | 0.59 | 100% | 16 | 3.2 |
| no | no | 0.526 | 0.50 | 100% | 10 | 2.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radac, M.-B.; Precup, R.-E. Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-based Adaptive Actor-Critic. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091807
Radac M-B, Precup R-E. Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-based Adaptive Actor-Critic. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(9):1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091807
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadac, Mircea-Bogdan, and Radu-Emil Precup. 2019. "Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-based Adaptive Actor-Critic" Applied Sciences 9, no. 9: 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091807
APA StyleRadac, M.-B., & Precup, R.-E. (2019). Data-Driven Model-Free Tracking Reinforcement Learning Control with VRFT-based Adaptive Actor-Critic. Applied Sciences, 9(9), 1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9091807






