Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
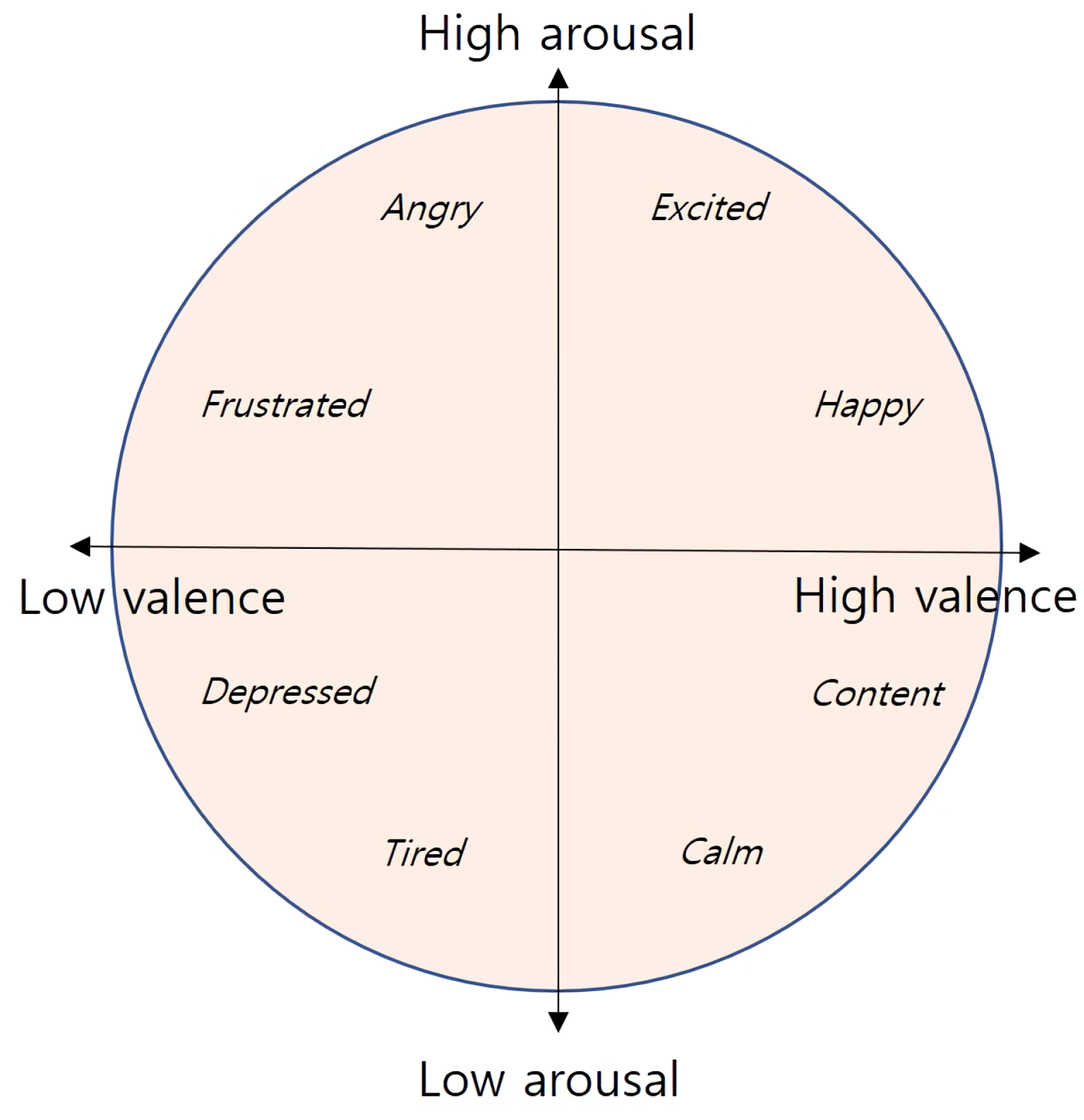
2.1. Arousal Valence Emotion Model
- Distinguish emotions as discrete labels, e.g., joy, sad, anger, happy, fear, etc. Although this method is conceptually simple, it is problematic when representing blended emotions that cannot be classified as a single case; and it cannot define the degree of emotion state, e.g., how glad you are.
- Use multiple dimensions to label emotions. However, this means each dimension is an emotional indicator, hence creating not a single scale but several continuous scales.
2.2. Hand-Crafted Features for Emotion Recognition
3. Short-Term Emotion Recognition with Single-Pulse PPG Signal
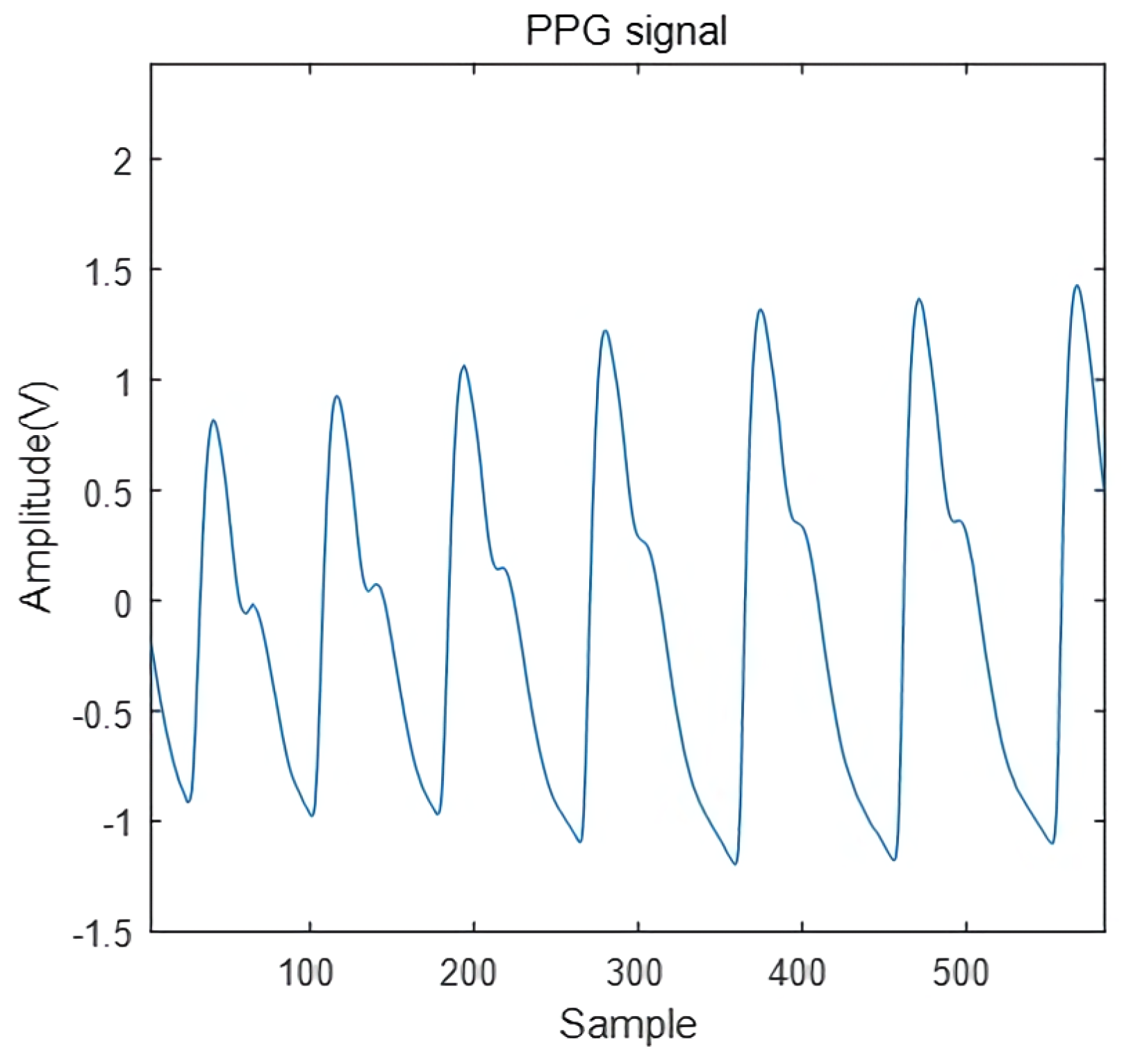
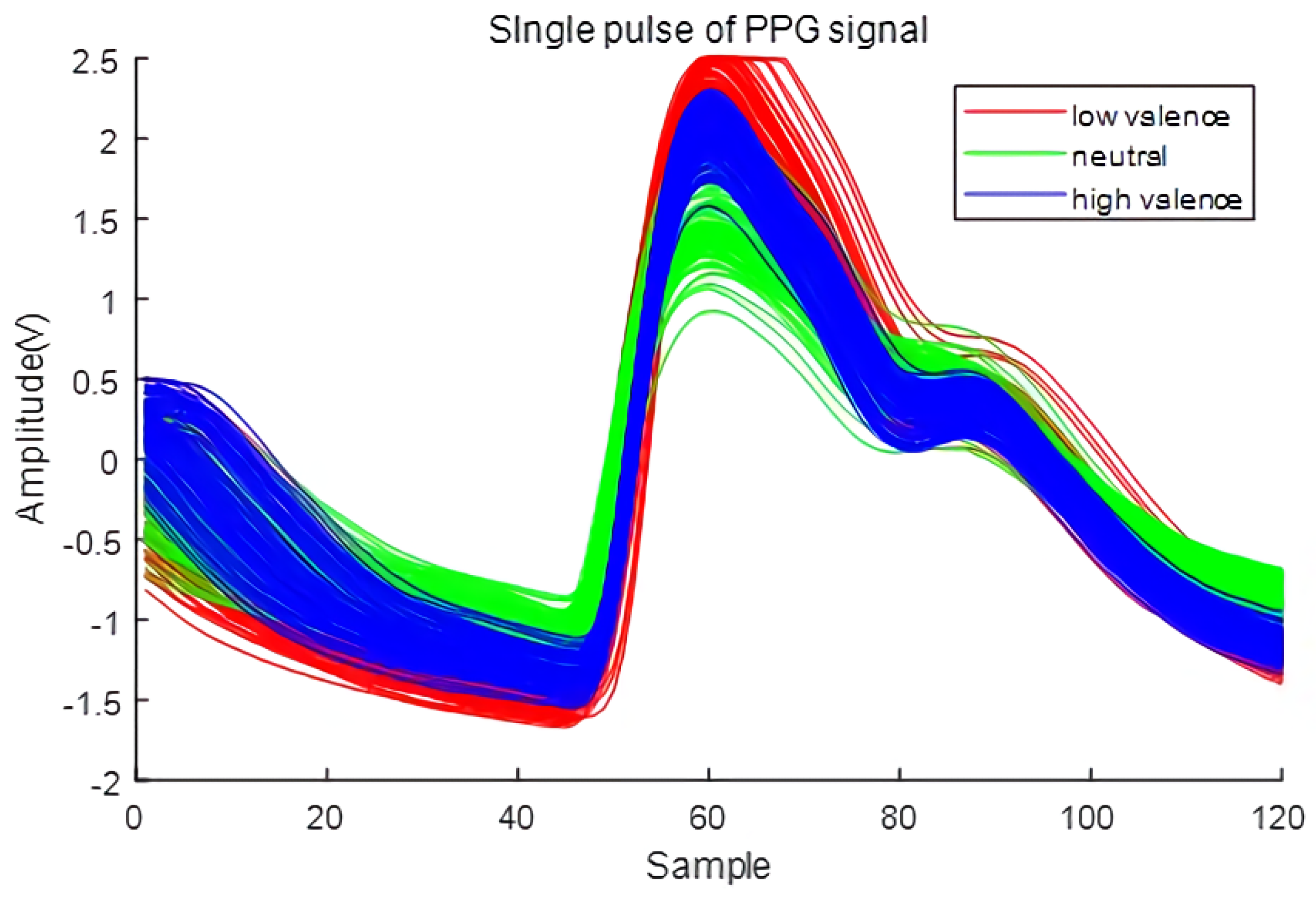
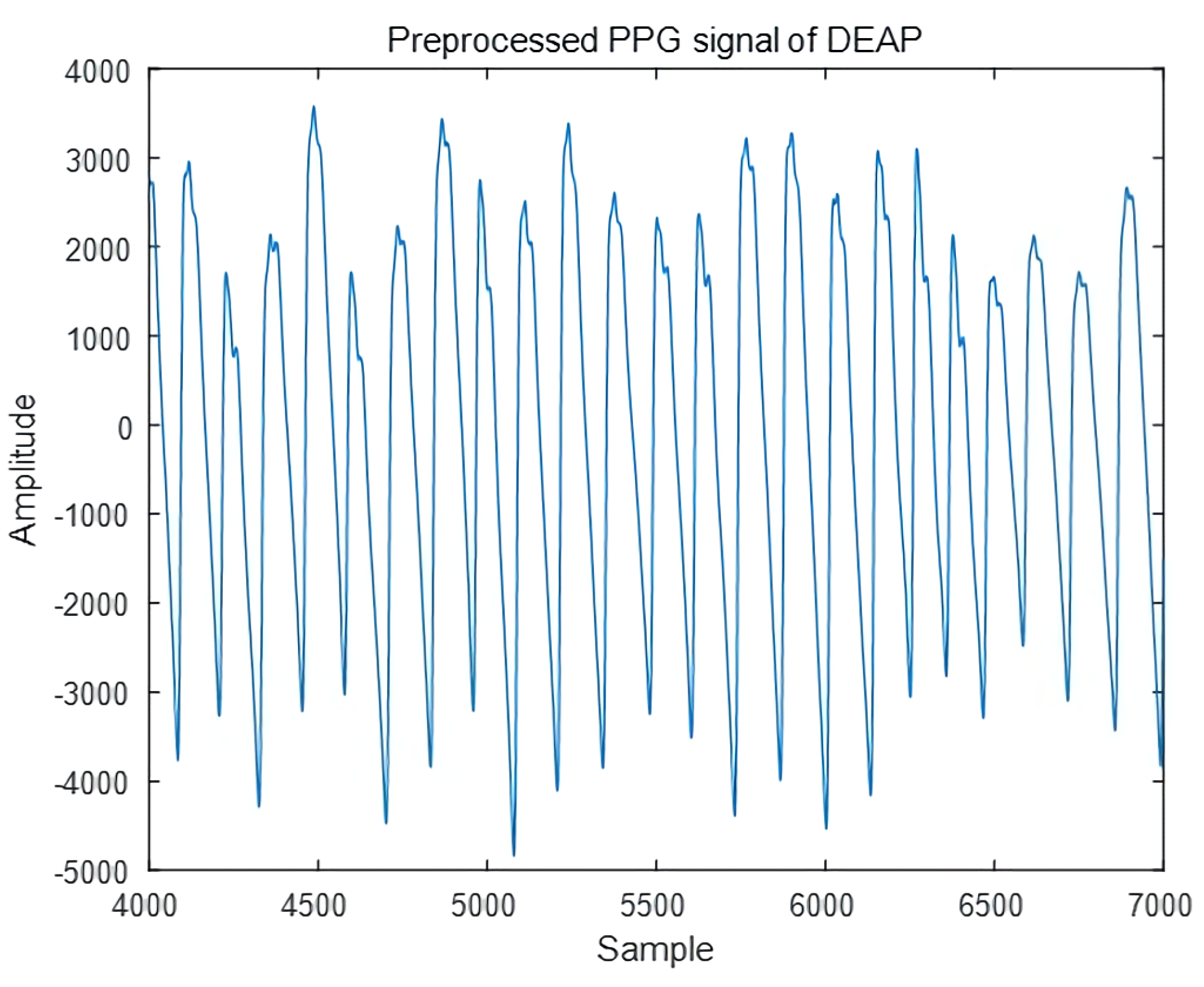
3.1. Single-Pulse Analysis of PPG Signal for Emotion Recognition
3.2. Feature Extractor Using Single-Pulse PPG Signal
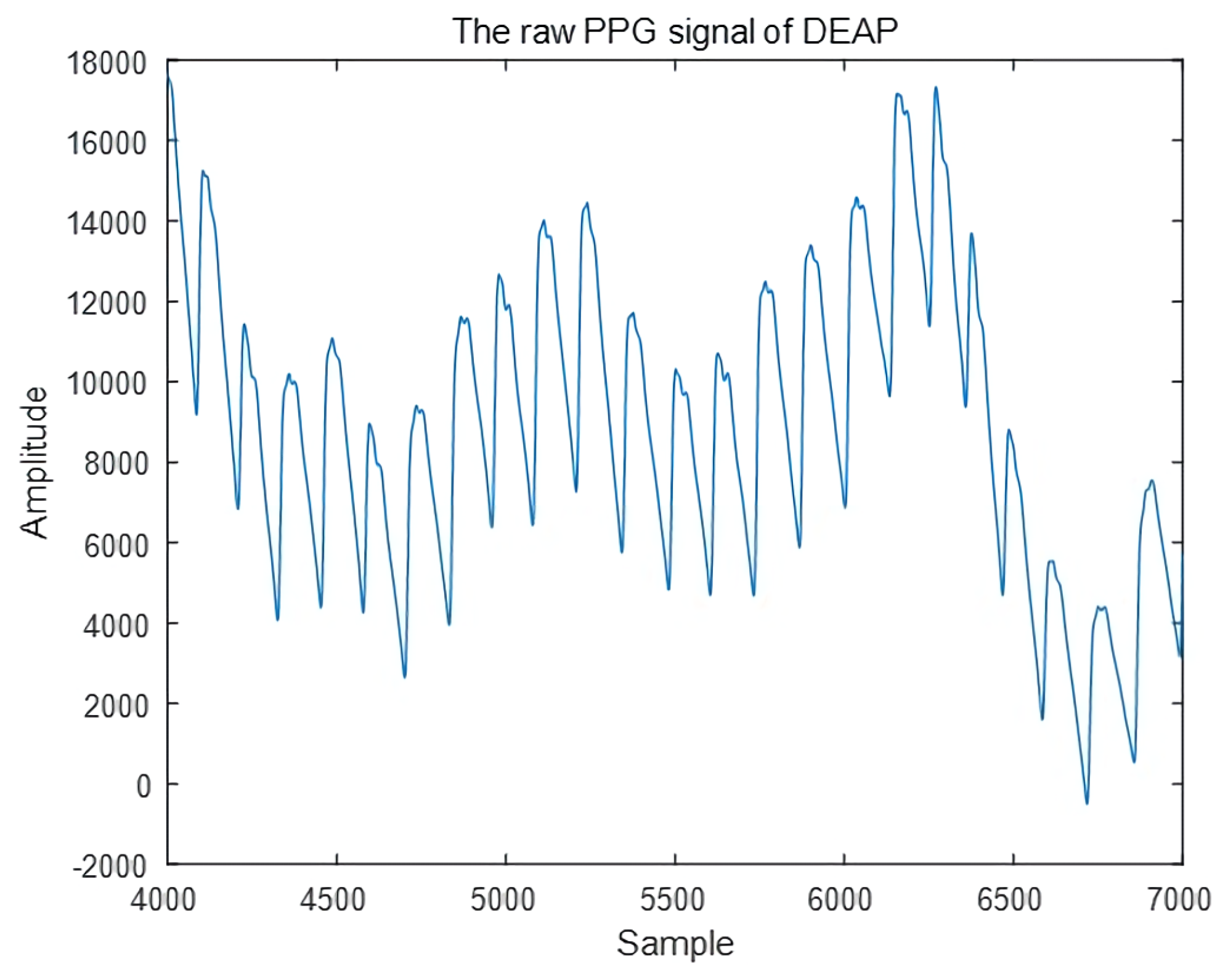
3.2.1. Dividing PPG Signals as Single Pulse
3.2.2. Personal Normalization
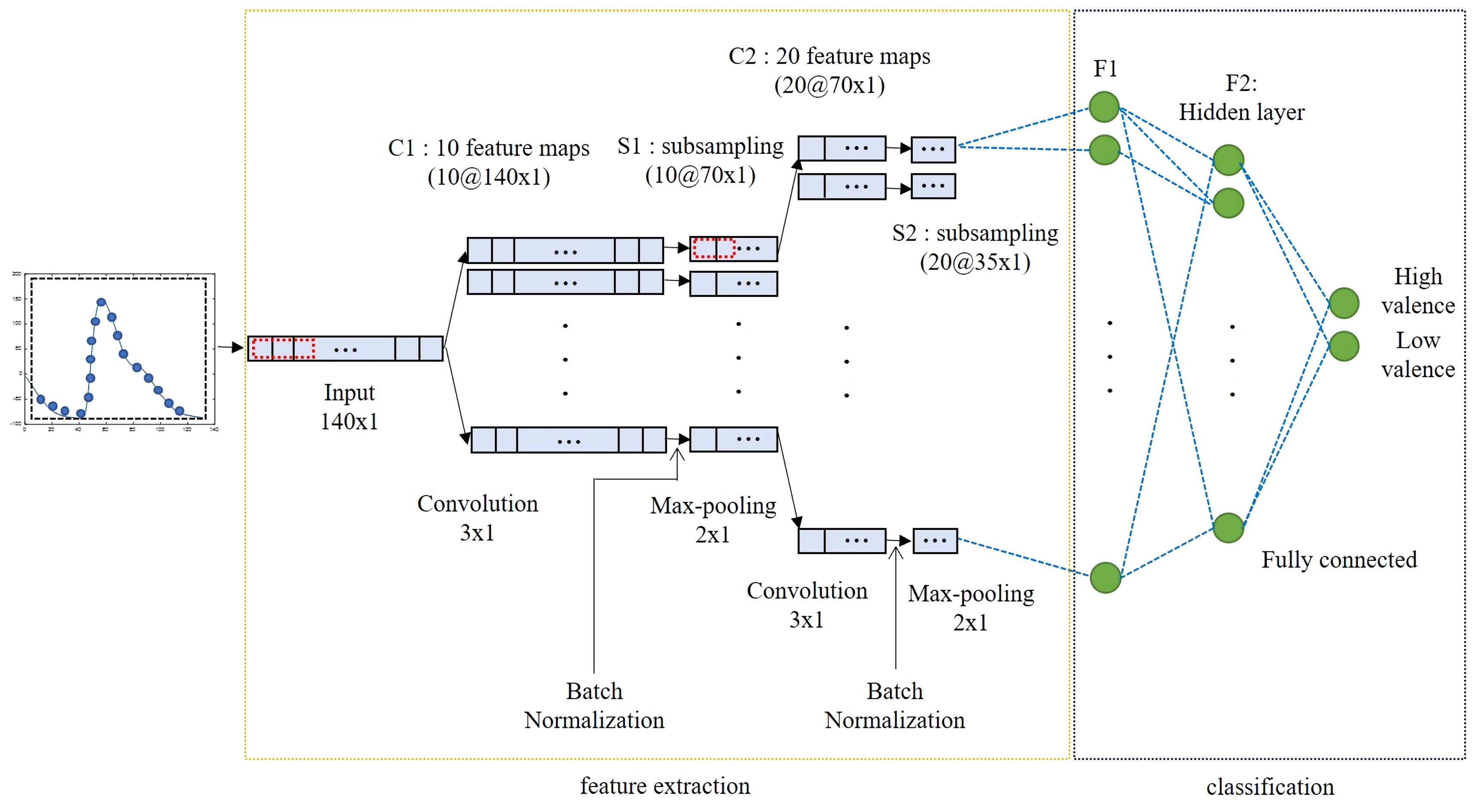
3.2.3. 1D-Convolutional Neural Network
4. Experiment
4.1. DEAP Dataset
4.2. Experimental Setting
4.3. Experimental Result
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hönig, F.; Batliner, A.; Nöth, E. Real-time recognition of the affective user state with physiological signals. In Proceedings of the Doctoral Consortium, Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Lisbon, Portugal, 12–14 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Cowie, R.; Douglas-Cowie, E.; Tsapatsoulis, N.; Votsis, G.; Kollias, S.; Fellenz, W.; Taylor, J.G. Emotion recognition in human-computer interaction. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2001, 18, 32–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Zhou, Y.; Xia, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Q. Progressive Filtering Approach for Early Human Action Recognition. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2018, 16, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Kim, M.; Kim, Y.; Hong, N.; Ryu, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, S. Soft robot review. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2017, 15, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busso, C.; Deng, Z.; Yildirim, S.; Bulut, M.; Lee, C.M.; Kazemzadeh, A.; Lee, S.; Neumann, U.; Narayanan, S. Analysis of emotion recognition using facial expressions, speech and multimodal information. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Multimodal Interfaces, State College, PA, USA, 13–15 October 2004; pp. 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, T.; Xia, Z.; Dong, J.; Zhao, Q. A Sociable Human-robot Interaction Scheme Based on Body Emotion Analysis. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2019, 17, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassili, J.N. Emotion recognition: The role of facial movement and the relative importance of upper and lower areas of the face. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1979, 37, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ayadi, M.; Kamel, M.S.; Karray, F. Survey on speech emotion recognition: Features, classification schemes, and databases. Pattern Recognit. 2011, 44, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.P.; Wang, C.H.; Jung, T.P.; Wu, T.L.; Jeng, S.K.; Duann, J.R.; Chen, J.H. EEG-based emotion recognition in music listening. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 57, 1798–1806. [Google Scholar]
- Wagner, J.; Kim, J.; André, E. From physiological signals to emotions: Implementing and comparing selected methods for feature extraction and classification. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 6 July 2005; pp. 940–943. [Google Scholar]
- Jerritta, S.; Murugappan, M.; Nagarajan, R.; Wan, K. Physiological signals based human emotion recognition: A review. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE 7th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Penang, Malaysia, 4–6 March 2011; pp. 410–415. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Sourina, O.; Nguyen, M.K. Real-time EEG-based emotion recognition and its applications. In Transactions on Computational Science XII; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2011; pp. 256–277. [Google Scholar]
- Nakasone, A.; Prendinger, H.; Ishizuka, M. Emotion recognition from electromyography and skin conductance. In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Biosignal Interpretation, Tokyo, Japan, 6–8 September 2005; pp. 219–222. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xu, C.; Feng, Z. Analysis of physiological for emotion recognition with the IRS model. Neurocomputing 2016, 178, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; André, E. Emotion recognition based on physiological changes in music listening. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2008, 30, 2067–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giakoumis, D.; Tzovaras, D.; Moustakas, K.; Hassapis, G. Automatic recognition of boredom in video games using novel biosignal moment-based features. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2011, 2, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Nie, D.; Lu, B.L. Emotional state classification from EEG data using machine learning approach. Neurocomputing 2014, 129, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenke, R.; Peer, A.; Buss, M. Feature extraction and selection for emotion recognition from EEG. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2014, 5, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mert, A.; Akan, A. Emotion recognition from EEG signals by using multivariate empirical mode decomposition. Pattern Anal. Appl. 2018, 21, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirayucharoensak, S.; Pan-Ngum, S.; Israsena, P. EEG-based emotion recognition using deep learning network with principal component based covariate shift adaptation. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 627892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, H.P.; Bengio, Y.; Yannakakis, G.N. Learning deep physiological models of affect. IEEE Comput. Intell. Mag. 2013, 8, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhagry, S.; Fahmy, A.A.; El-Khoribi, R.A. Emotion Recognition based on EEG using LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Emotion 2017, 8, 355–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Emotion Recognition from Multi-Channel EEG through Parallel Convolutional Recurrent Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Rakshit, R.; Reddy, V.R.; Deshpande, P. Emotion detection and recognition using HRV features derived from photoplethysmogram signals. In Proceedings of the 2nd Workshop on Emotion Representations and Modelling for Companion Systems, Tokyo, Japan, 16 November 2016; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Lazarus, R.S.; Speisman, J.C.; Mordkoff, A.M. The relationship between autonomic indicators of psychological stress: Heart rate and skin conductance. Psychosom. Med. 1963, 25, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, G.; Seo, S.; Hong, S.; Kim, H. Emotion extraction based on multi bio-signal using back-propagation neural network. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 4925–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.W.; Huang, Y.S.; Lin, C.H.; Chien, J.C.; Haraikawa, K.; Shieh, J.S. Heart rate variability signal features for emotion recognition by using principal component analysis and support vectors machine. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 16th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Bioengineering (BIBE), Taichung, Taiwan, 31 October–2 November 2016; pp. 274–277. [Google Scholar]
- Goshvarpour, A.; Goshvarpour, A. Poincaré’s section analysis for PPG-based automatic emotion recognition. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2018, 114, 400–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.A. A circumplex model of affect. J. Personal. Soc. Psychol. 1980, 39, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; Alam, M.G.R.; Uddin, M.Z.; Huda, S.; Almogren, A.; Fortino, G. Human emotion recognition using deep belief network architecture. Inf. Fusion 2019, 51, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Peng, Y.; Lu, B.L. EEG-based emotion classification using deep belief networks. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME), Chengdu, China, 14–18 July 2014; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Chen, X.; Zhan, Q.; Yang, T.; Xia, S. Respiration-based emotion recognition with deep learning. Comput. Ind. 2017, 92, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koelstra, S.; Muhl, C.; Soleymani, M.; Lee, J.S.; Yazdani, A.; Ebrahimi, T.; Pun, T.; Nijholt, A.; Patras, I. Deap: A database for emotion analysis; using physiological signals. IEEE Trans. Affect. Comput. 2012, 3, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, H.P. Advancing Affect Modeling via Preference Learning and Unsupervised Feature Extraction; Center for Computer Cames Research, IT University of Copenhagen: Copenhagen, Denmark, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang, X.; Rozgic, V.; Crystal, M. Compact unsupervised eeg response representation for emotion recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE-EMBS International Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics (BHI), Valencia, Spain, 1–4 June 2014; pp. 736–739. [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Valencia, C.A.; Daza-Santacoloma, G.; Orozco-Gutiérrez, A.A. Electric propagation modeling of Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) using the finite element method (FEM). In Proceedings of the 2014 XIX Symposium on Image, Signal Processing and Artificial Vision, Armenia, Colombia, 17–19 September 2014; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Plataniotis, K.N. EEG-based affect states classification using deep belief networks. In Proceedings of the 2016 Digital Media Industry & Academic Forum (DMIAF), Santorini, Greece, 4–6 July 2016; pp. 148–153. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zheng, W.L.; Lu, B.L. Emotion recognition using multimodal deep learning. In International Conference on Neural Information Processing; Springer: Kyoto, Japan, 2016; pp. 521–529. [Google Scholar]
- Chao, H.; Dong, L.; Liu, Y.; Lu, B. Emotion Recognition from Multiband EEG Signals Using CapsNet. Sensors 2019, 19, 2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Method | Bio-Signal | Classification Accuracy | Recognition Term | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Valence | Arousal | |||
| CNN (Martinez et al., 2013) [34] | BVP, SC | 63.3 | 69.1 | 30 s |
| SVM (Zhuang et al., 2014) [35] | EEG | 70.9 | 67.1 | 60 s |
| Hidden Markov models (Torres et al., 2014) [36] | RSP, GSR, EEG, TEMP | 58.8 | 75.0 | 60 s |
| Deep belief networks (Xu et al., 2016) [37] | EEG | 66.9 | 69.8 | 30 s |
| Multimodal deep learning (Liu et al., 2016) [38] | EOG, EEG | 85.2 | 80.5 | 63 s |
| Deep sparse auto-encoders (Zhang et al., 2017) [32] | RSP | 73.06 | 80.78 | 20 s |
| Multivariate empirical mode decomposition (Mert et al., 2018) [19] | EEG | 72.87 | 75.00 | 60 s |
| Multiband feature matrix and CapsNet (Chao et al., 2019) [39] | EEG | 66.73 | 68.28 | 3 s |
| Proposed 1D CNN | PPG | 75.3 | 76.2 | 1.1 s |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, M.S.; Lee, Y.K.; Pae, D.S.; Lim, M.T.; Kim, D.W.; Kang, T.K. Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163355
Lee MS, Lee YK, Pae DS, Lim MT, Kim DW, Kang TK. Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2019; 9(16):3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163355
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Min Seop, Yun Kyu Lee, Dong Sung Pae, Myo Taeg Lim, Dong Won Kim, and Tae Koo Kang. 2019. "Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network" Applied Sciences 9, no. 16: 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163355
APA StyleLee, M. S., Lee, Y. K., Pae, D. S., Lim, M. T., Kim, D. W., & Kang, T. K. (2019). Fast Emotion Recognition Based on Single Pulse PPG Signal with Convolutional Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 9(16), 3355. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9163355







