Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activities of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on Aspergillus flavus
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Microorganisms
2.2. Measurement of the Antifungal Activities of the Test Compounds
2.3. Aflatoxin Measurement Using High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
2.4. Isolation of Total RNA and Gene Expression Analysis by RT-qPCR
3. Results
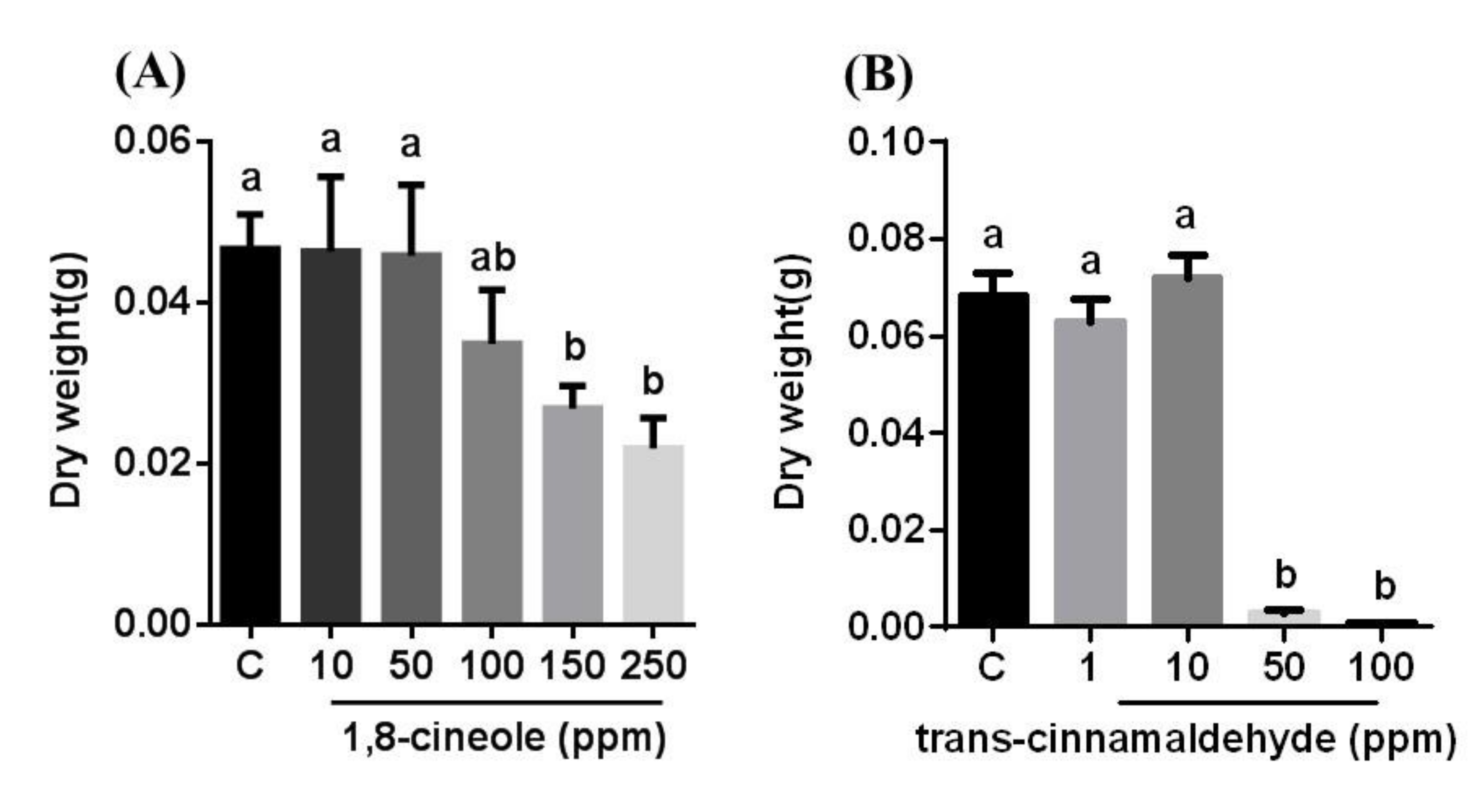
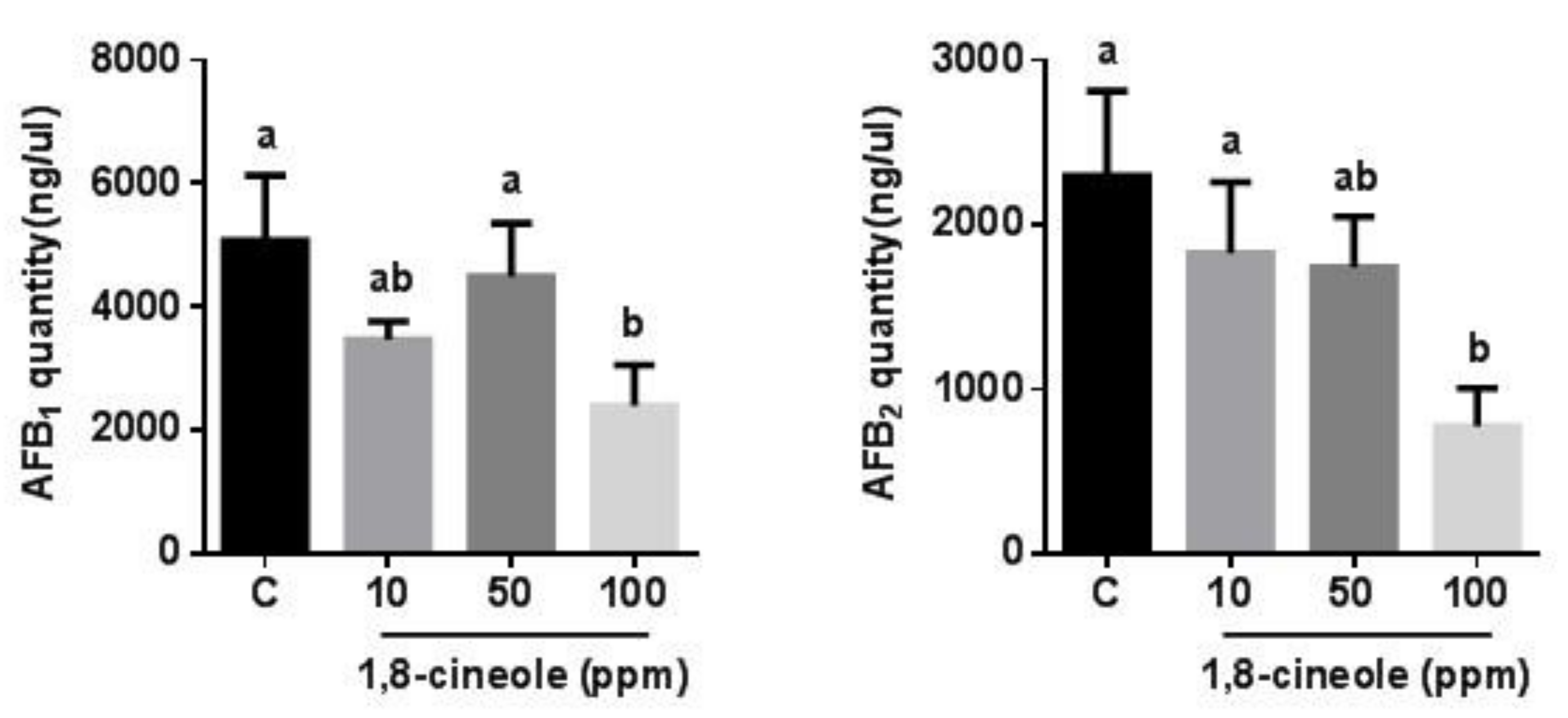
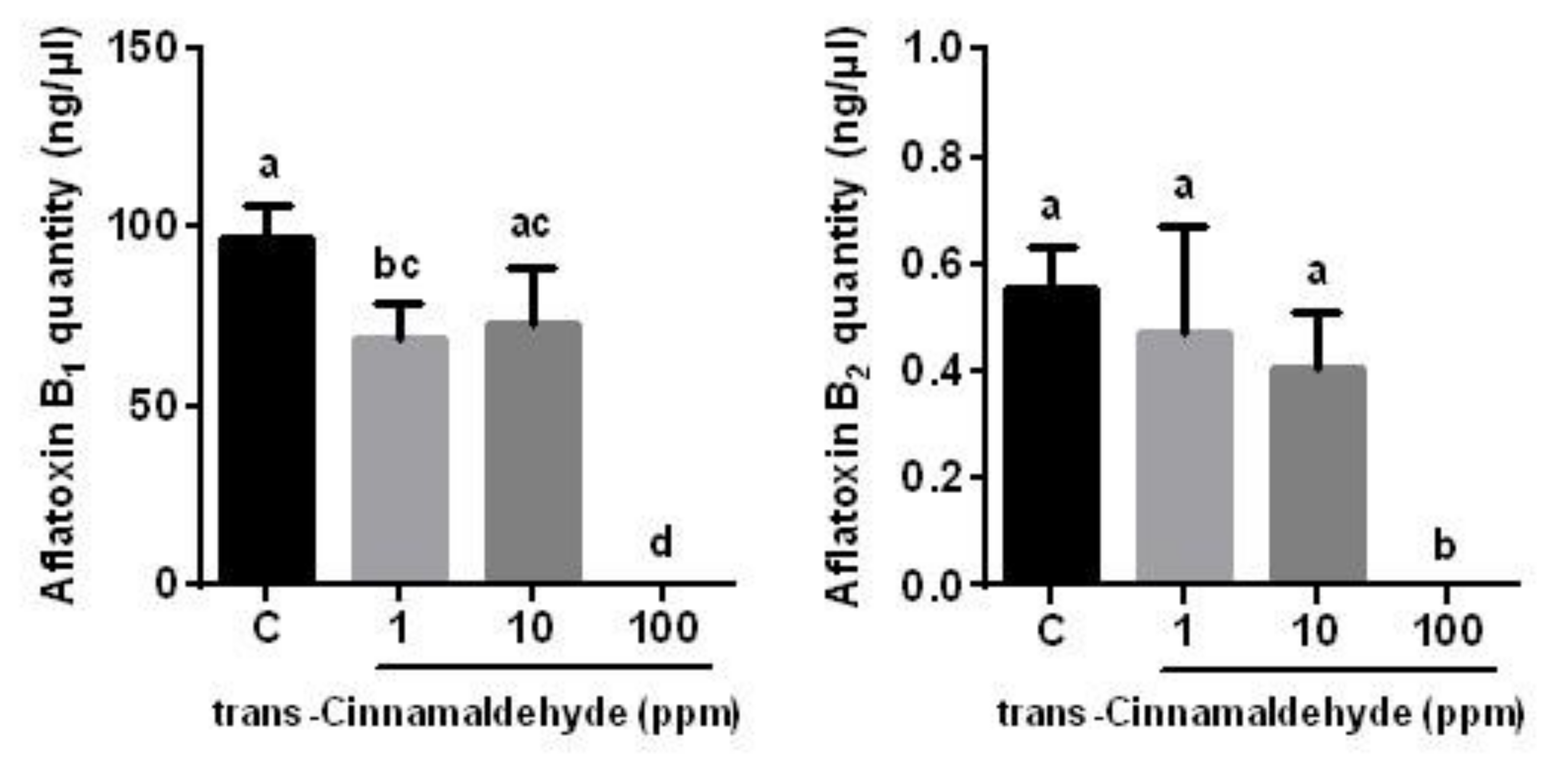
3.1. Effects of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on A. flavus Growth and Aflatoxin Production
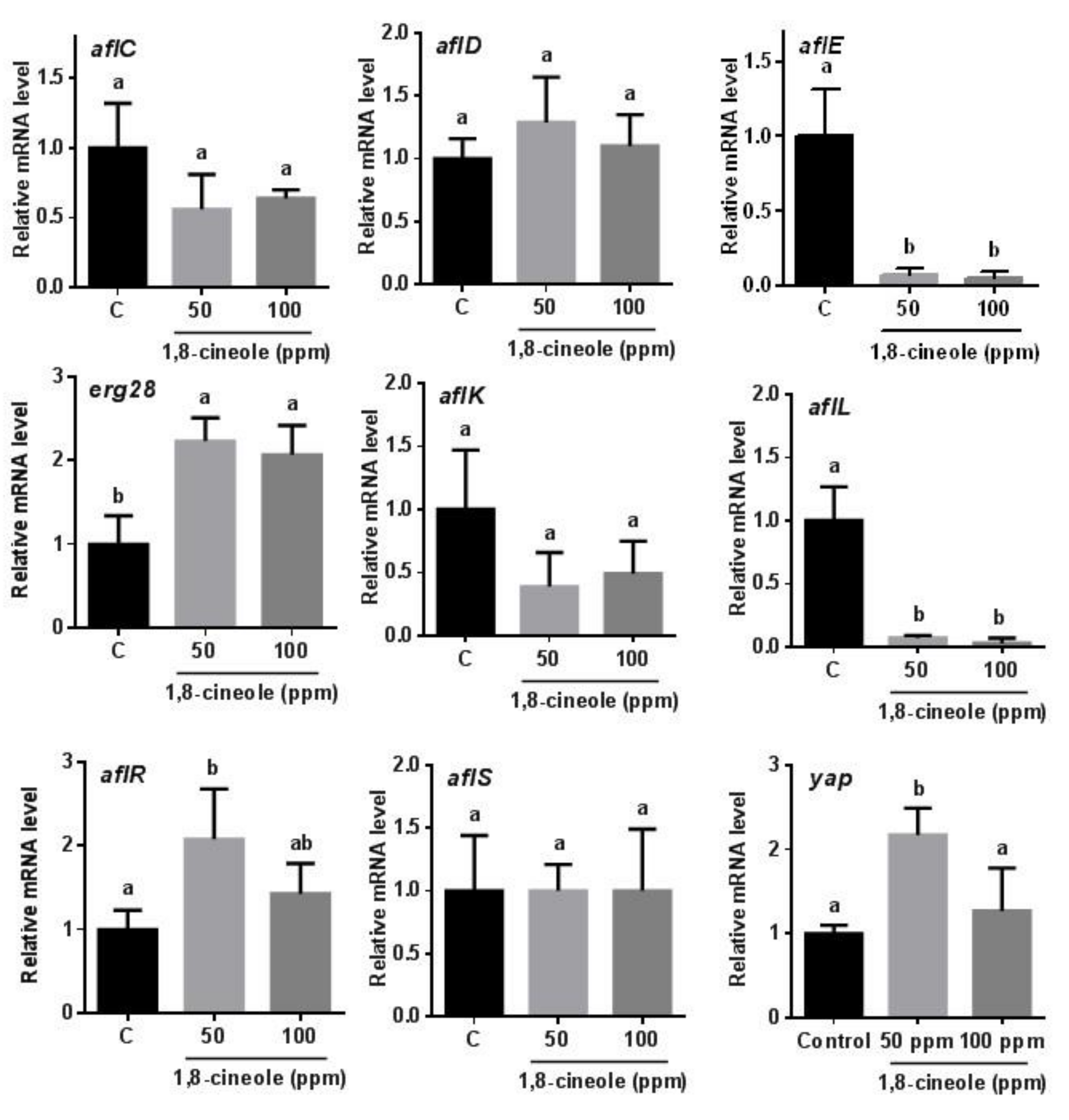
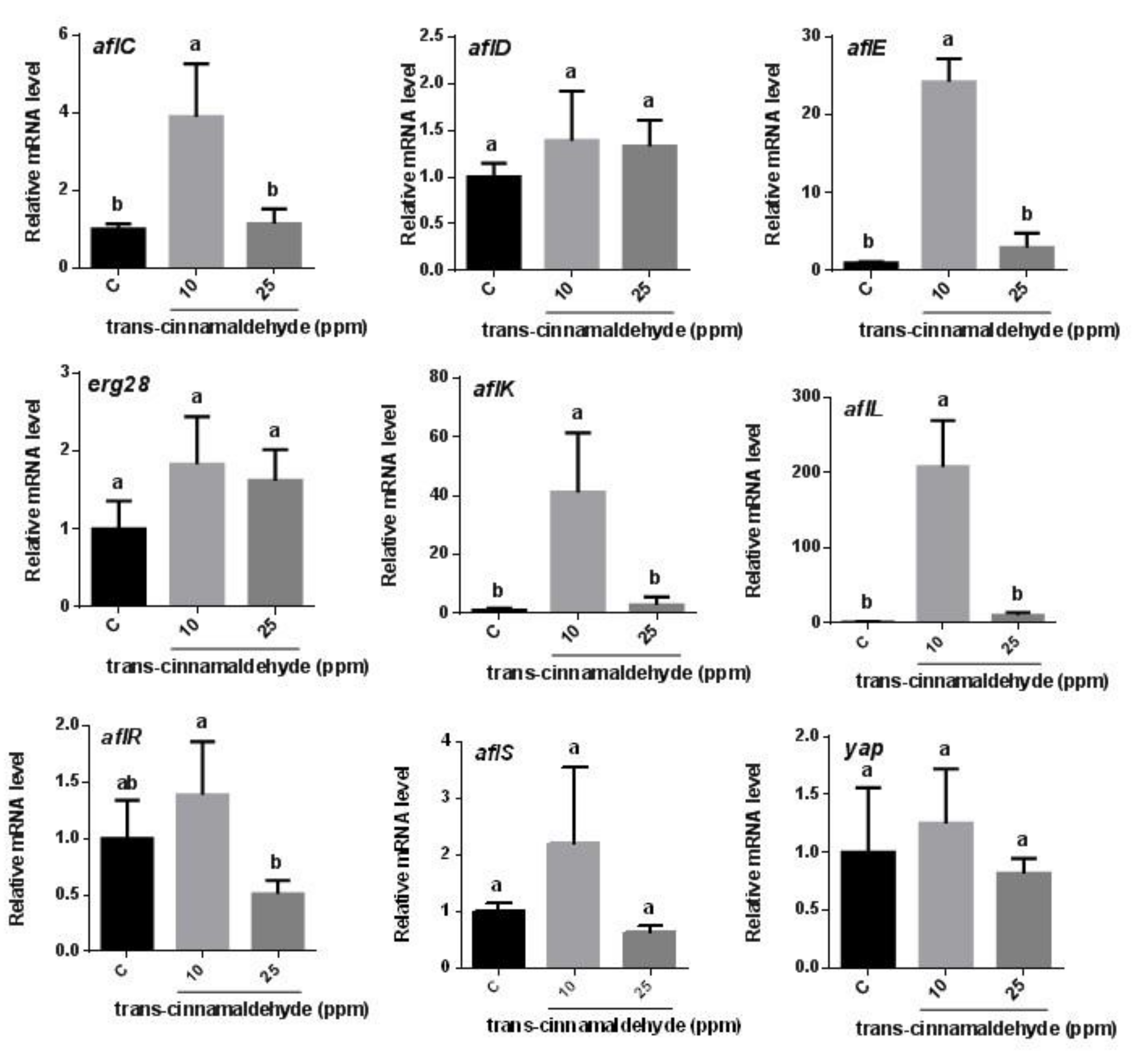
3.2. RT-qPCR Analysis of the Expression of Genes Involved in Aflatoxin Biosynthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lee, H.K.; Lee, S. Toxicities of active constituent isolated from Thymus vulgaris flowers and its structural derivatives against Tribolium castaneum (Herbst). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2016, 59, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.E.; Kim, J.M.; Lee, N.H.; Yang, J.E.; Lee, H.S. Acaricidal and insecticidal activities of essential oils against a stored–food mite and stored-grain insects. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 174–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, Y.J.; Lee, S.G.; Lee, H.S. Acaricidal and insecticidal activities of essential oils of Cinnamomum zeylanicum barks cultivated from France and India against Dermatophagoides spp., Tyrophagus putrescentiae and Ricania sp. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enan, E. Insecticidal activity of essential oils: Octopaminergic sites of action. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2001, 130, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.S.; Lee, B.H.; Kim, T.W.; Ren, Y.L.; Lee, S.E. Proteomic evaluation of adults of rhyzopertha dominica resistant to phosphine. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2008, 25, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paster, N.; Menasherov, M.; Ravid, U.; Juven, B. Antifungal activity of oregano and thyme essential oils applied as fumigants against fungi attacking stored grain. J. Food Prot. 1995, 58, 81–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, H.; Han, Q.; Lai, X.; Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Yuan, J.; et al. Efficacy and mechanism of cinnamon essential oil on inhibition of Colletotrichum acutatum isolated from ‘Hongyang’ kiwifruit. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalagatur, N.K.; Nirmal Ghosh, O.S.; Sundararaj, N.; Mudili, V. Antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles encapsulated with Cymbopogon martinii essential oil on plant pathogenic fungi Fusarium graminearum. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.; Lee, B.H.; Moon, Y.S.; Kim, K.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, S.E. Antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic effects of a fumigant, ethanedinitrile, on Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hassan, Y.I.; Lepp, D.; Shao, S.; Zhou, T. Strategies and methodologies for developing detoxification systems to mitigate mycotoxins. Toxins 2017, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bluma, R.; Amaiden, M.R.; Etcheverry, M. Screening of argentine plant extracts: impact on growth parameters and aflatoxin B1 accumulation by Aspergillus section Flavi. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 122, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateo, E.M.; Gómez, J.V.; Domínquez, I.; Gimeno-Adelantado, J.V.; Mateo-Castro, R.; Gavara, R.; Jiménez, M. Impact of bioactive packaging systems based on EVOH films and essential oils in the control of aflatoxigenic fungi and aflatoxin production in maize. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 254, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, R.; Singh, P.; Prakash, B.; Dubey, N.K. Antifungal, aflatoxin inhibition and antioxidant activity of Callistemon lanceolatus (Sm.) sweet essential oil and its major component 1,8-cineole against fungal isolates from chickpea seeds. Food Control 2012, 25, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Xing, F.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Hua, H.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Inhibitory effect of cinnamaldehyde, citral, and eugenol on aflatoxin biosynthetic gene expression and aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis in Aspergillus flavus. J. Food Sci. 2015, 80, M2917–M2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.S.; Choi, W.S.; Park, E.S.; Bae, I.K.; Choi, S.D.; Paek, O.; Kim, S.H.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, S.E. Antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic methylenedioxy-containing compounds and piperine-like synthetic compounds. Toxins 2016, 8, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Mahoney, N.; Campbell, B.C. Inhibition of aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis by piperlongumine isolated from Piper longum L. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2002, 12, 679–682. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, X.; Huang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Lin, X. An improvement of the 2ˆ(-delta delta CT) method for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction data analysis. Biostat. Bioinform. Biomath. 2013, 3, 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Zhang, L.; Liu, M.; Su, Y.T.; Xie, W.M.; Zhang, N.Y.; Dai, J.F.; Wang, Y.; Rajput, S.A.; Qi, D.S.; et al. Individual and combined occurrence of mycotoxins in feed ingredients and complete feeds in China. Toxins 2018, 10, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tola, M.; Kebede, B. Occurrence, importance and control of mycotoxins: A review. Cogent Food Agric. 2016, 2, 1191103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, Y.S.; Kim, L.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, S.E. 4-Hydroxy-7-methyl-3-phenylcoumarin suppress aflatoxin biosynthesis via downregulation of aflK expressing versicolorin B synthase in Aspergillus flavus. Molecules 2017, 22, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.S.; Kim, H.M.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, S.E. Organic acids suppress aflatoxin production via lowering expression of aflatoxin biosynthesis-related genes in Aspergillus flavus. Food Control 2018, 88, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghanpour-Farashah, A.; Taheri, P. Antifungal and antiaflatoxigenic effects of Mentha longifolia essential oil against Aspergillus flavus. Int. J. New Technol. Res. 2016, 2, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J. Current understanding on aflatoxin biosynthesis and future perspective in reducing aflatoxin contamination. Toxins 2012, 4, 1024–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Q.; Shang, B.; Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; Liu, Y. Cinnamaldehyde inhibits fungal growth and aflatoxin B1 biosynthesis by modulating the oxidative stress response of Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1355–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.-M.; Kwon, H.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-E. Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activities of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on Aspergillus flavus. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091655
Kim H-M, Kwon H, Kim K, Lee S-E. Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activities of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on Aspergillus flavus. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(9):1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091655
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hyeong-Mi, Hyunwoo Kwon, Kyeongsoon Kim, and Sung-Eun Lee. 2018. "Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activities of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on Aspergillus flavus" Applied Sciences 8, no. 9: 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091655
APA StyleKim, H.-M., Kwon, H., Kim, K., & Lee, S.-E. (2018). Antifungal and Antiaflatoxigenic Activities of 1,8-Cineole and t-Cinnamaldehyde on Aspergillus flavus. Applied Sciences, 8(9), 1655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8091655




