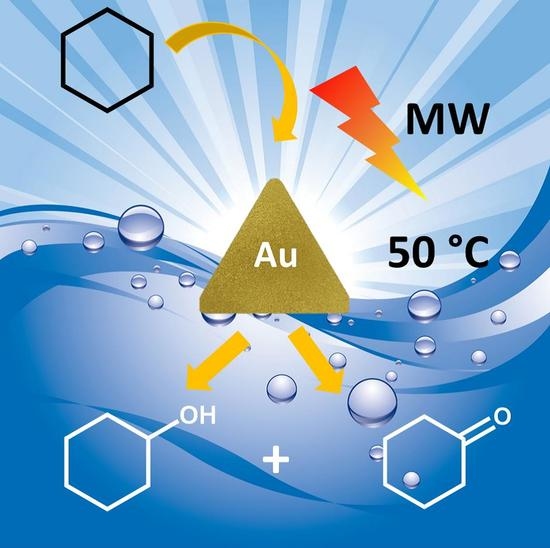
Gold Nanotriangles as Selective Catalysts for Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Production
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
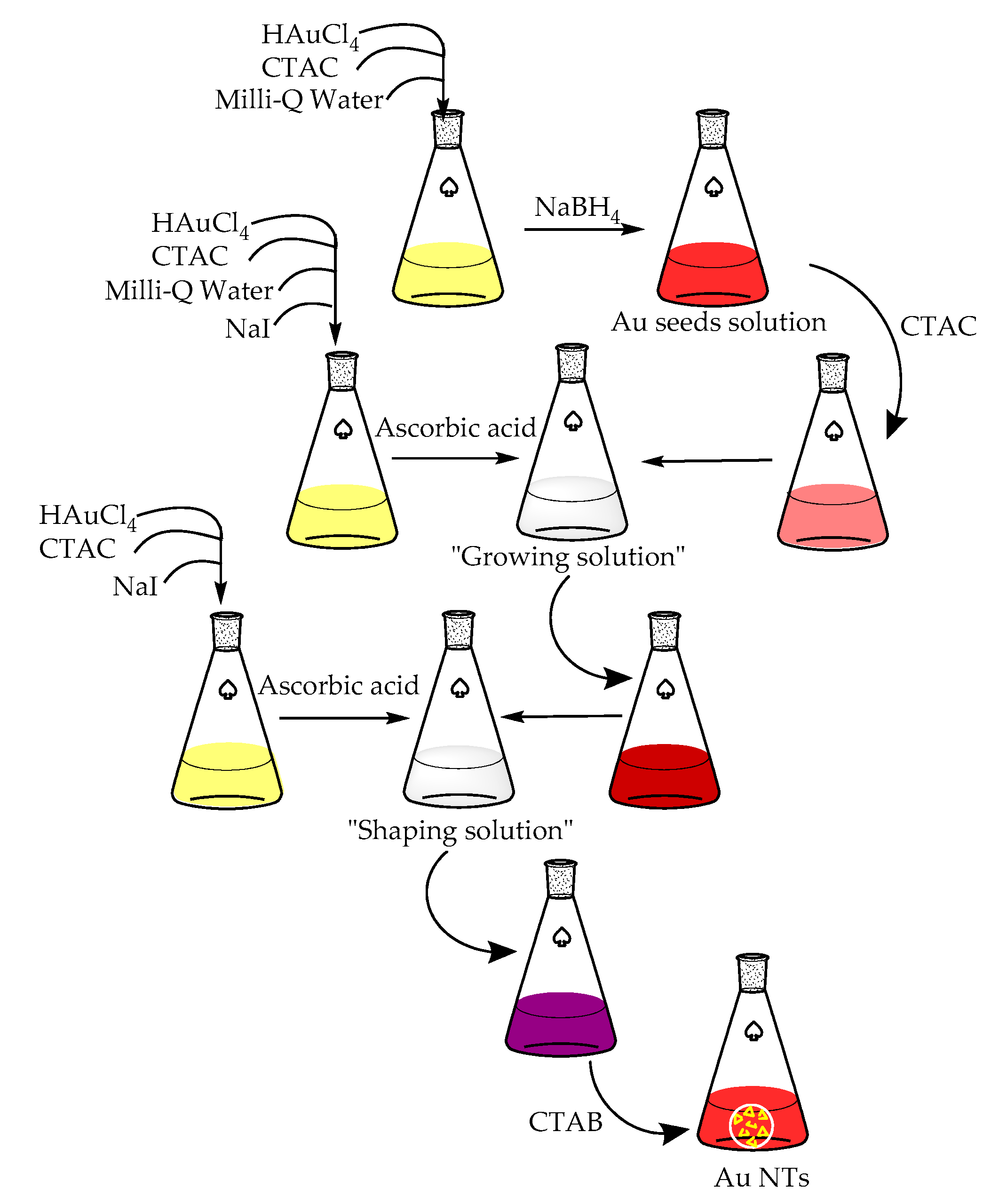
2. Materials and Methods
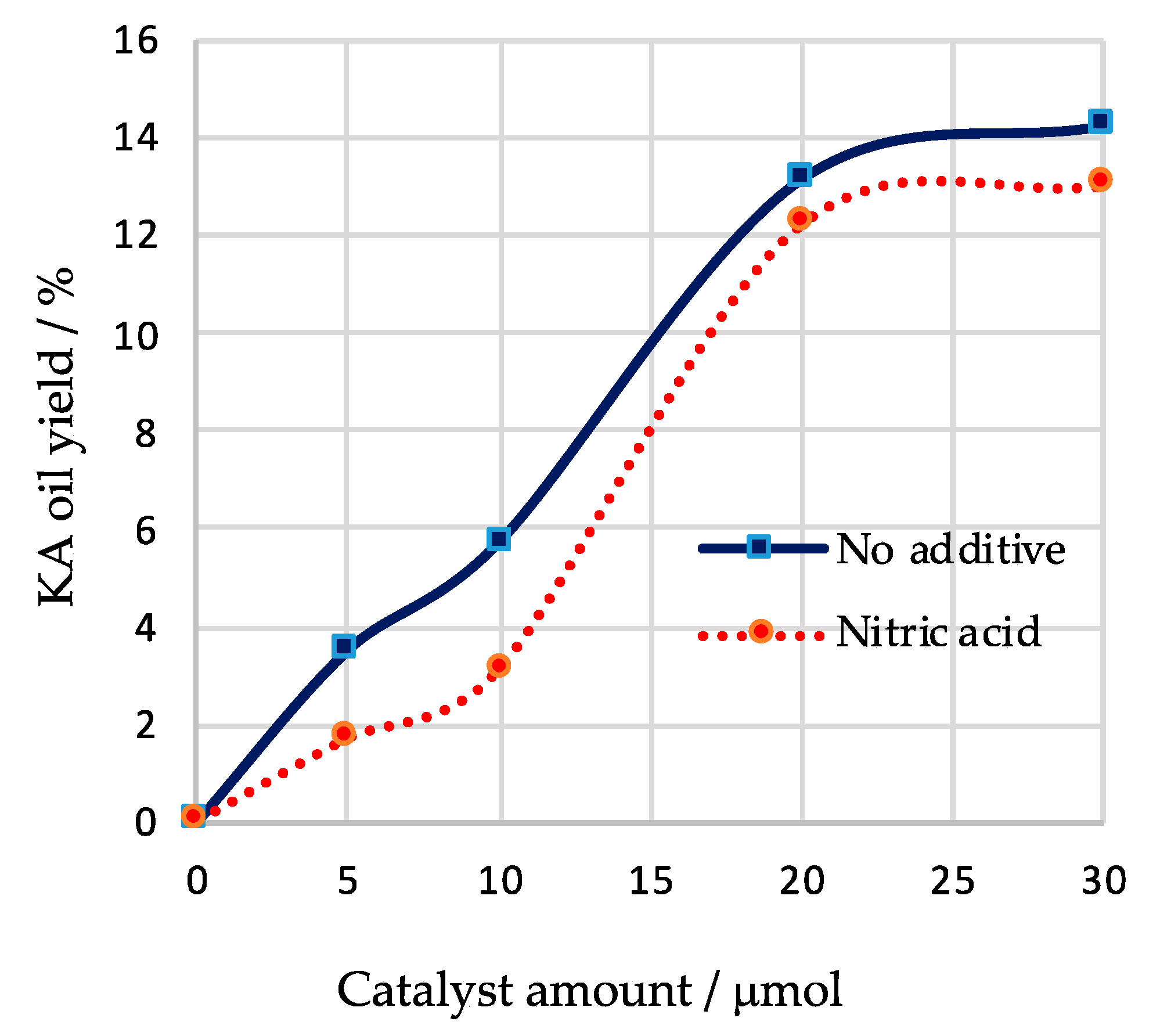
3. Results
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carneiro, J.T.; Savenije, T.J.; Moulijn, J.A.; Mul, G. The effect of Au on TiO2 catalyzed selective photocatalytic oxidation of cyclohexane. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011, 217, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereijgers, B.P.C.; Weckhuysen, B.M. An attempt to selectively oxidize methane over supported gold catalysts. J. Catal. 2010, 270, 16–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, A.; Koeckritz, A.; Kalevaru, V.N.; Bagabas, A.; Martin, A. Significant formation of adipic acid by direct oxidation of cyclohexane using supported nano-gold catalysts. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 1330–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, M.; Liu, X.; Murphy, D.M.; Whiston, K.; Hutchings, G.J. Cyclohexane oxidation using Au/MgO: An investigation of the reaction mechanism. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2012, 14, 16279–16285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Conte, M.; Sankar, M.; He, Q.; Murphy, D.M.; Morgan, D.; Jenkins, R.L.; Knight, D.; Whiston, K.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Liquid phase oxidation of cyclohexane using bimetallic Au-Pd/MgO catalysts. Appl. Catal. 2015, 504, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Wang, J.; Rocha, B.G.M.; Maldonado-Hódar, F.J.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Supported gold nanoparticles as reusable catalysts for oxidation reactions of industrial significance. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Gold nanoparticles deposited on surface modified carbon xerogels as reusable catalysts for cyclohexane C-H activation towards CO and water. Molecules 2017, 22, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Figueiredo, J.L.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Gold nanoparticles deposited on surface modified carbon materials as reusable catalysts for hydrocarboxylation of cyclohexane. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 547, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carabineiro, S.A.C.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Avalos-Borja, M.; Buijnsters, J.G.; Pombeiro, A.J.L.; Figueiredo, J.L. Gold nanoparticles supported on carbon materials for cyclohexane oxidation with hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Catal. 2013, 467, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.J.; Landon, P.; Enache, D.; Carley, A.F.; Roberts, M.W.; Hutchings, G.J. Selective conversion of cyclohexane to cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone using a gold catalyst under mild conditions. Catal. Lett. 2005, 101, 175–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, G.J.; Carrettin, S.; Landon, P.; Edwards, J.K.; Enache, D.; Knight, D.W.; Xu, Y.-J.; Carley, A.F. New approaches to designing selective oxidation catalysts: Au/C a versatile catalyst. Top. Catal. 2006, 38, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayani, V.J.; Mayani, S.V.; Kim, S.W. Palladium, Gold, and Gold–Palladium Nanoparticle-Supported Carbon Materials for Cyclohexane Oxidation. Chem. Eng. Commun. 2015, 203, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.G.; Li, G.; Liu, L.P.; Liu, H.O. Au nanoparticles supported on Cr-based metal-organic framework as bimetallic catalyst for selective oxidation of cyclohexane to cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol. Catal. Commun. 2012, 27, 200–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Singh, R.; Pala, R.G.S.; Sivakumar, S. Sinter-resistant gold nanoparticles encapsulated by zeolite nanoshell for oxidation of cyclohexane. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 8015–8020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhu, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Cai, Z.; Shen, Y.; He, C. In Fundamental of Chemical Engineering; Cao, Z., Sun, L., Cao, X.Q., He, Y.H., Eds.; TransTec Publications Inc.: Zurich, Switzerland, 2011; Volume 233–235, pp. 254–259. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.-X.; He, C.-H.; Zhu, M.-Q.; Fang, S. A highly active Au/Al2O3 catalyst for cyclohexane oxidation using molecular oxygen. Catal. Lett. 2007, 114, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini-Monfared, H.; Meyer, H.; Janiak, C. Dioxygen oxidation of 1-phenylethanol with gold nanoparticles and N-hydroxyphthalimide in ionic liquid. J. Mol. Catal. 2013, 372, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvers, B. Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 6th ed.; Ullmann, F., Hawkins, S., Schula, G., Gerhartz, W., Russey, W.E., Elvers, B., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 41–49. [Google Scholar]
- Adipic acid (ADPA): 2016 World Market Outlook and Forecast up to 2020; Merchant Research and Consulting: Birmingham, UK, 2016.
- Kulikova, V.S.; Shestakov, A.F. Functionalization of alkanes by gold nanoparticles stabilized by 1-dodecanethiol in organic media. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 1, 507–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.G.; Xia, Y.N. Shape-Controlled Synthesis of Gold and Silver Nanoparticles. Science 2002, 298, 2176–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priecel, P.; Salami, H.A.; Padilla, R.H.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A. Anisotropic gold nanoparticles: Preparation and applications in catalysis. Chin. J. Catal. 2016, 37, 1619–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarabelli, L.; Coronado-Puchau, M.; Giner-Casares, J.J.; Langer, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Monodisperse gold nanotriangles: Size control, large-scale self-assembly, and performance in surface-enhanced Raman scattering. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 5833–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weissermel, K.; Arpe, H.J. Industrial Organic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Weissermel, K., Arpe, H.J., Eds.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 1993; ISBN 3-527-26995-9. [Google Scholar]
- Shul’pin, G.B.; Nizova, G.V. Formation of alkyl peroxides in oxidation of alkanes by H2O2 catalyzed by transition metal complexes. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1992, 48, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shul’pin, G.B.; Matthes, M.G.; Romakh, V.B.; Barbosa, M.I.F.; Aoyagi, J.L.T.; Mandelli, D. Oxidations by the system ‘hydrogen peroxide-[Mn2L2O3][PF6]2 (L=1,4,7-trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane)-carboxylic acid’. Part 10: Co-catalytic effect of different carboxylic acids in the oxidation of cyclohexane, cyclohexanol, and acetone. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 2143–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Water-soluble C-scorpionate complexes: Catalytic and biological applications. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 2236–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbatini, A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Drew, M.G.B.; Pettinari, C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Microwave-assisted and solvent-free peroxidative oxidation of 1-phenylethanol to acetophenone with a Cu(II)-TEMPO catalytic system. Cat. Com. 2014, 48, 4048–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutradhar, M.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Guedes da Silva, M.F.C.; Liu, C.-M.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Trinuclear Cu(II) structural isomers: Coordination, magnetism, electrochemistry and catalytic activity toward oxidation of alkanes. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 3959–3969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmudov, K.T.; Kopylovich, M.N.; Sabbatini, A.; Drew, M.G.B.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pettinari, C.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Cooperative metal-ligand assisted E/Z isomerisation and cyano-groups activation at CuII and CoII complexes of arylhydrazones of active methylene nitriles. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9946–9958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timokhin, I.; Pettinari, C.; Marchetti, F.; Pettinari, R.; Condello, F.; Galli, S.; Alegria, E.C.B.A.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Novel coordination polymers with (pyrazolato)-based tectons: Catalytic activity in the peroxidative oxidation of alcohols and cyclohexane. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 2303–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopylovich, M.N.; Mahmudov, K.T.; Silva, M.F.C.G.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Kuznetsov, M.L.; Silva, T.F.S.; Fraústo da Silva, J.J.R.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Trends in properties of para-substituted 3-(phenylhydrazo)pentane-2,4-diones. J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2011, 24, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäckwall, J.-E. (Ed.) Modern Oxidation Methods; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 6th ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2016; Volume 11, pp. 41–49.
- Martins, L.M.D.R.S.; Pombeiro, A.J.L. Tris(pyrazol-1yl)methane metal complexes for catalytic mild oxidative functionalizations of alkanes, alkenes and ketones. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 265, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

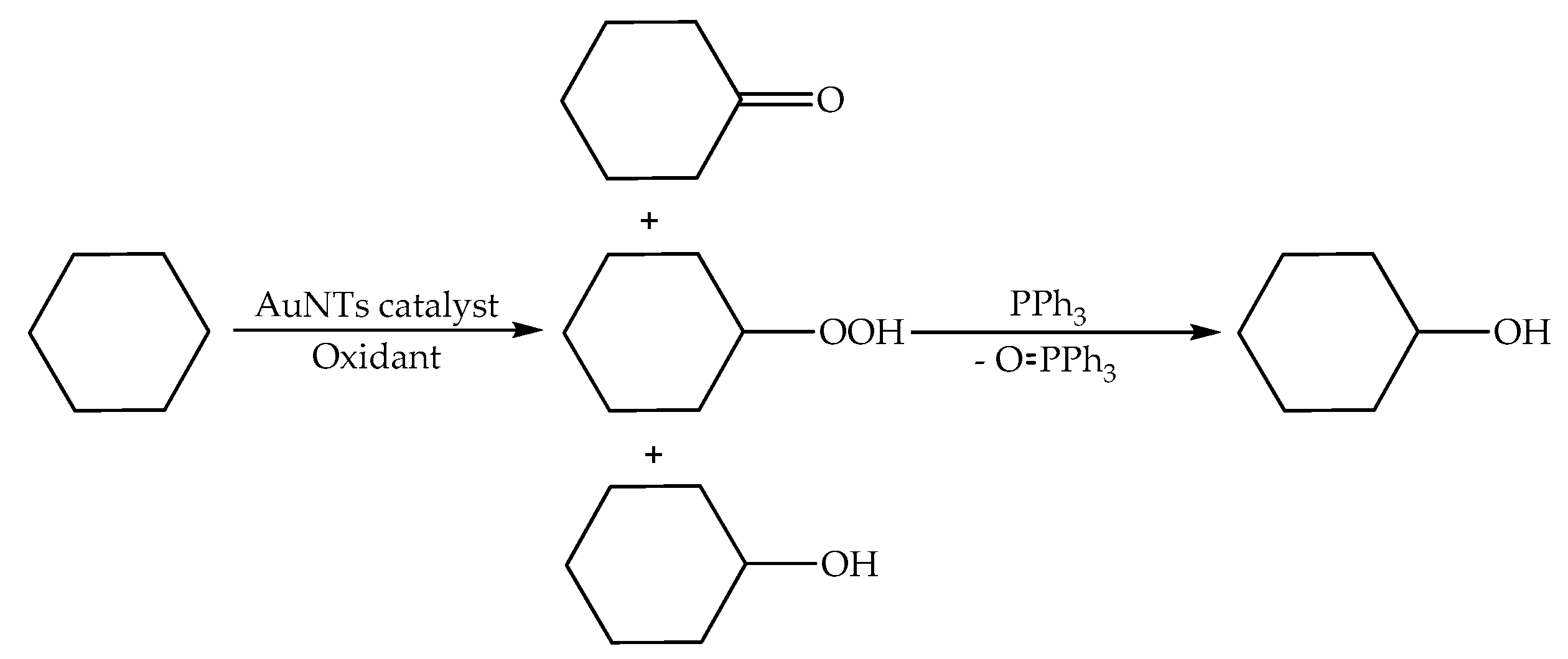
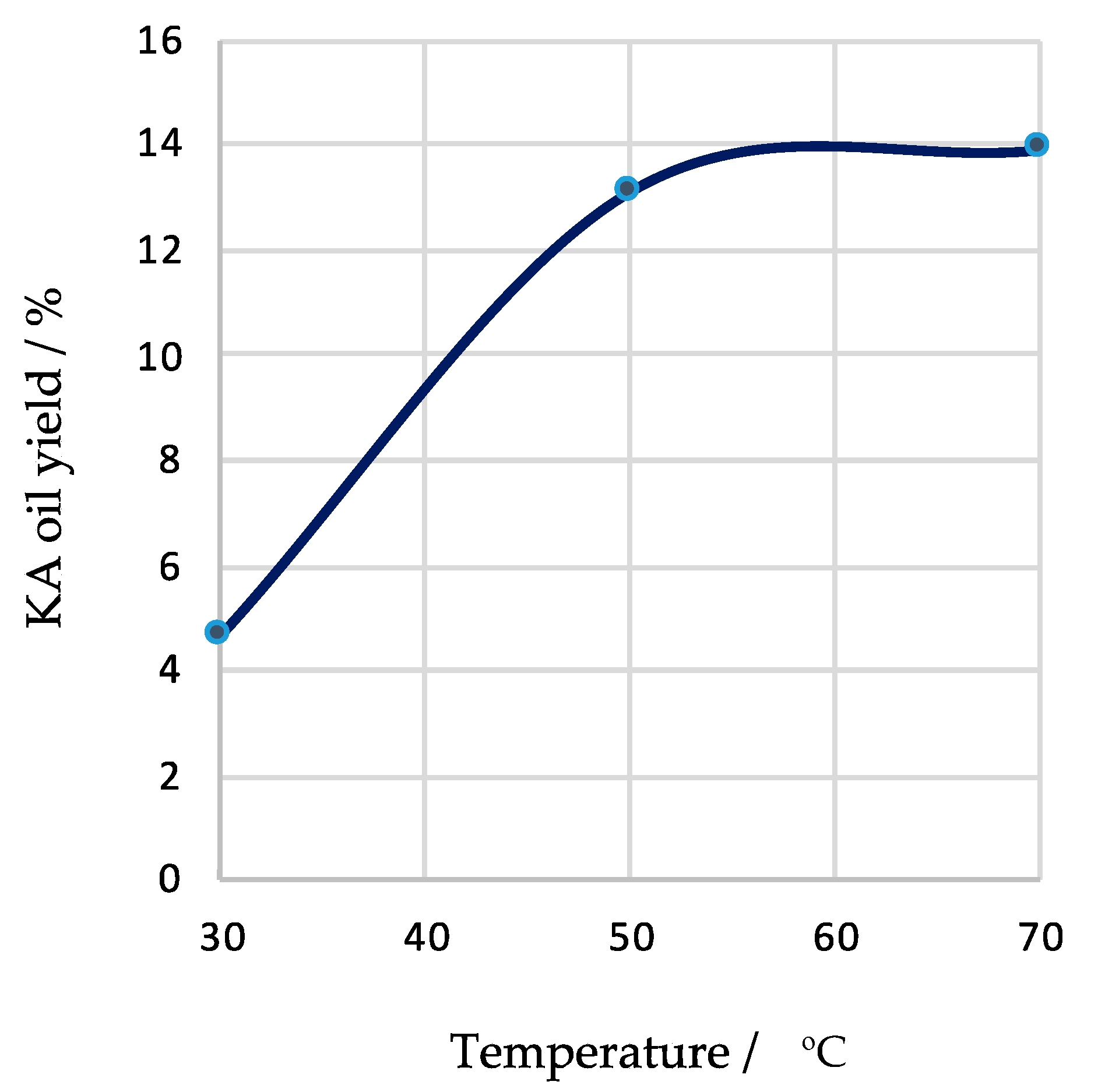
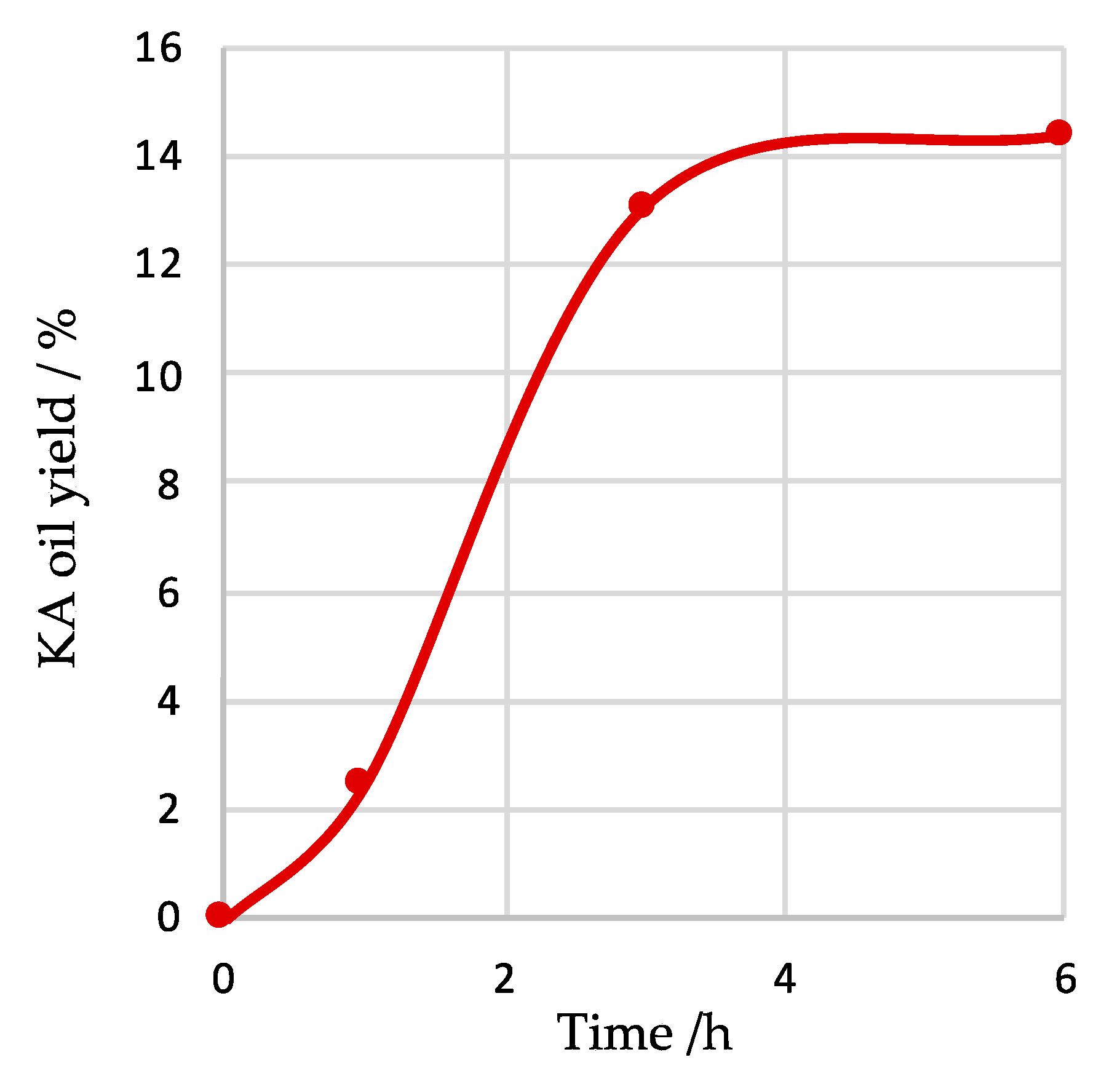



| Entry | Catalyst Amount/µmol | T/°C | Time/h | Additive | Conversion/% b | Yield/% c | Selectivity/% d | Total TON e | Total TOF/h−1 f | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CyO (K) | CyOH (A) | Total | |||||||||
| 1 | 5 | 50 | 3 | --- | 3.9 | 3.5 | --- | 3.5 | 90 | 35 | 12 |
| 2 | 10 | 50 | 3 | --- | 6.3 | 5.7 | --- | 5.7 | 90 | 29 | 10 |
| 3 | 20 | 50 | 3 | --- | 13.9 | 13.1 | --- | 13.1 | 94 | 33 | 11 |
| 4 | 30 | 50 | 3 | --- | 14.2 | 14.2 | --- | 14.2 | 100 | 24 | 8 |
| 5 | 5 | 50 | 3 | HNO3 | 1.9 | 1.7 | --- | 1.7 | 89 | 17 | 6 |
| 6 | 10 | 50 | 3 | HNO3 | 3.4 | 3.1 | --- | 3.1 | 91 | 16 | 5 |
| 7 | 20 | 50 | 3 | HNO3 | 12.8 | 10.3 | 1.9 | 12.2 | 95 | 31 | 10 |
| 8 | 20 | 50 | 3 | H2SO4 | 3.5 | 3.3 | --- | 3.3 | 94 | 8 | 3 |
| 9 | 20 | 30 | 3 | --- | 5.4 | 4.7 | --- | 4.7 | 87 | 12 | 4 |
| 10 | 20 | 70 | 3 | --- | 14.2 | 12.3 | 1.6 | 13.9 | 98 | 35 | 12 |
| 11 | 20 | 50 | 1 | --- | 2.6 | 2.5 | --- | 2.5 | 96 | 6 | 6 |
| 12 | 20 | 50 | 6 | --- | 14.9 | 11.3 | 3.1 | 14.4 | 97 | 36 | 6 |
| 13 | --- | 50 | 3 | --- | 1.5 | 1.2 | --- | 1.2 | 80 | --- | --- |
| 14 g | 20 | 50 | 3 | --- | 6.9 | 6.7 | --- | 6.7 | 97 | 17 | 6 |
| 15 g | 20 | 50 | 3 | HNO3 | 6.2 | 5.9 | --- | 5.9 | 95 | 15 | 5 |
| 16 h | 20 | 50 | 3 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
| Catalyst Amount/µmol | Au NTs Surface/Volume Ratio/×10−4 nm−1 μmol−1 |
|---|---|
| 5 | 50 |
| 10 | 25 |
| 20 | 13 |
| 30 | 8 |
| MW-Reaction Conditions | Pressure/atm |
|---|---|
| Control (without catalyst) | 1.3 |
| TBHP | 5.3 |
| H2O2 | 5.6 |
| air | 1.0 |
| Entry | Catalyst Amount/µmol | Additive | Yield/% b | Total TON c | Conversion/% | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CyO (K) | CyOH (A) | Total | |||||
| 1 | 5 | --- | 0.2 | --- | 0.2 | 2 | 0.5 |
| 2 | 10 | --- | 0.3 | --- | 0.3 | 2 | 0.6 |
| 3 | 20 | --- | 0.5 | --- | 0.5 | 1 | 0.9 |
| 4 | 30 | --- | 2.0 | --- | 2.0 | 3 | 2 |
| 5 | 5 | HNO3 | 0.6 | --- | 0.6 | 6 | 0.8 |
| 6 d | 20 | --- | 0.2 | --- | 0.2 | 1 | 0.3 |
| 7 d | 20 | HNO3 | 0.3 | --- | 0.3 | 1 | 0.3 |
| 8 e | 20 | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matias, I.A.S.; Ribeiro, A.P.C.; Oliveira-Silva, R.P.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Martins, L.M.D.R.S. Gold Nanotriangles as Selective Catalysts for Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Production. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122655
Matias IAS, Ribeiro APC, Oliveira-Silva RP, Prazeres DMF, Martins LMDRS. Gold Nanotriangles as Selective Catalysts for Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Production. Applied Sciences. 2018; 8(12):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122655
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatias, Inês A. S., A. P. C. Ribeiro, Rui P. Oliveira-Silva, Duarte M. F. Prazeres, and Luísa M. D. R. S. Martins. 2018. "Gold Nanotriangles as Selective Catalysts for Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Production" Applied Sciences 8, no. 12: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122655
APA StyleMatias, I. A. S., Ribeiro, A. P. C., Oliveira-Silva, R. P., Prazeres, D. M. F., & Martins, L. M. D. R. S. (2018). Gold Nanotriangles as Selective Catalysts for Cyclohexanol and Cyclohexanone Production. Applied Sciences, 8(12), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8122655