Experimental Investigation of Acoustic Signal Characteristics of Blockages in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipelines Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methodology
2.1. Theoretical Background
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Test Conditions and Data Analysis
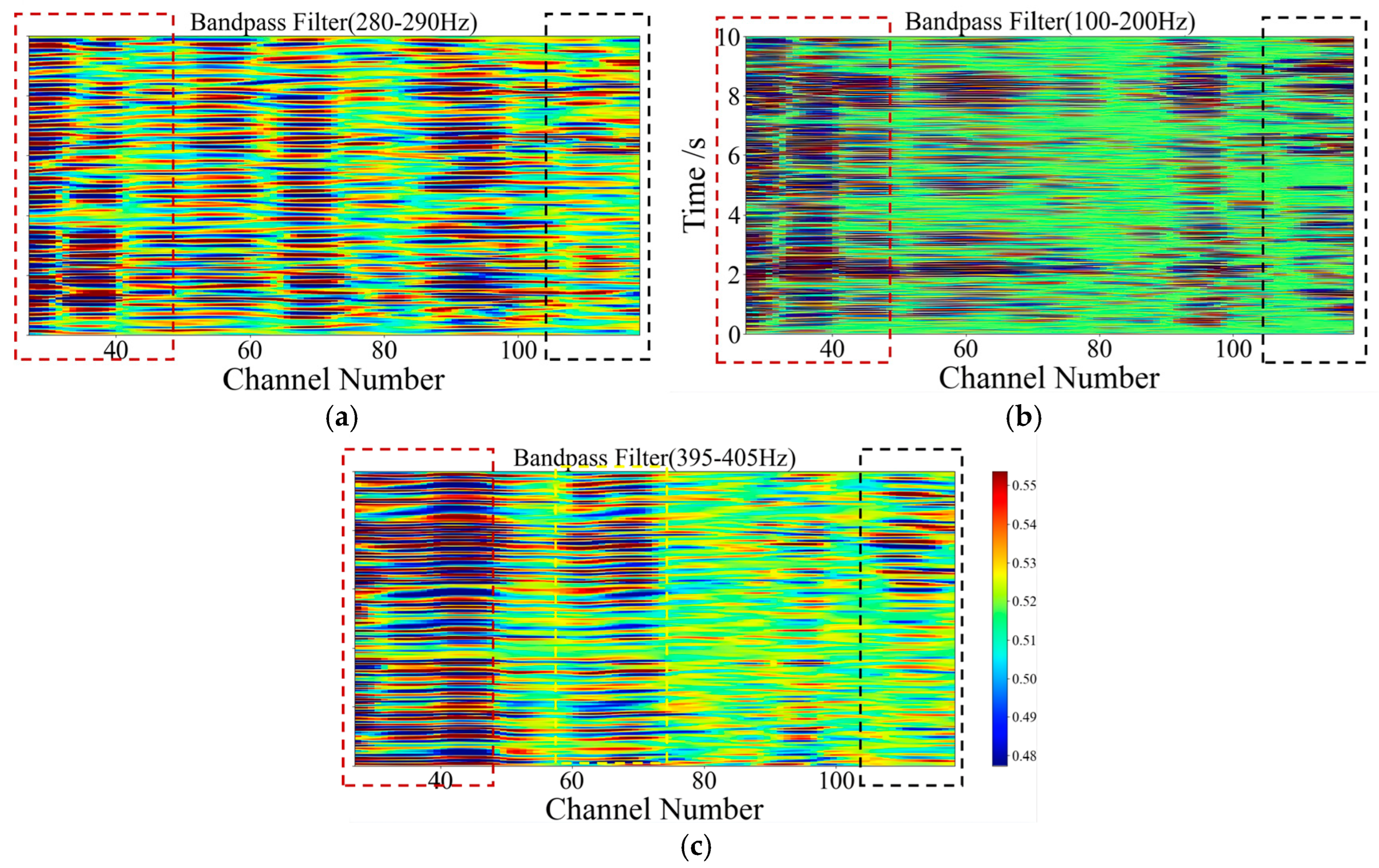
3. Signal Characteristics for Blockage Identification
3.1. Time-Domain Characteristics
3.2. Frequency-Domain Characteristics
- (1)
- The inlet (channels 106–118) and outlet (channels 28–50) regions exhibit persistent or intermittent high-intensity signals across all bands due to flow entry and exit effects.
- (2)
- In the 100–200 Hz and 280–290 Hz bands, high-intensity signals are not unique to the blockage region; they also appear in other unobstructed sections (e.g., channels 50–60, 90–100), making these bands unreliable for blockage localization.
- (3)
- The 395–405 Hz band served as the core frequency band for the blockage region under the 50% blockage condition. Within this band, only the blockage region (channels 70–75) exhibited strong, temporally continuous high-amplitude signals, showing a distinct energy difference compared to unobstructed regions. This clear contrast in acoustic intensity allows for reliable discrimination between blocked and unblocked channel areas.
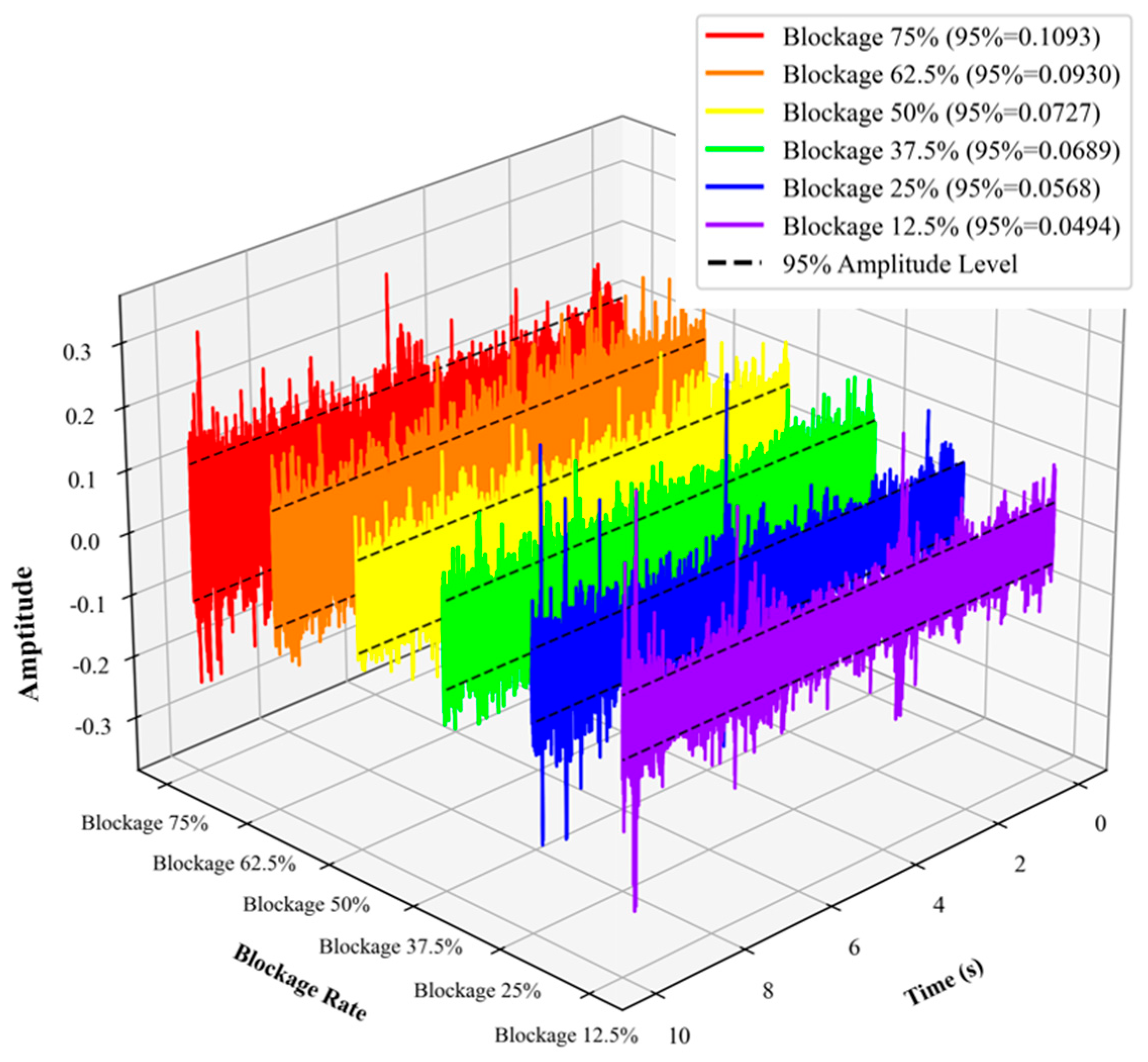
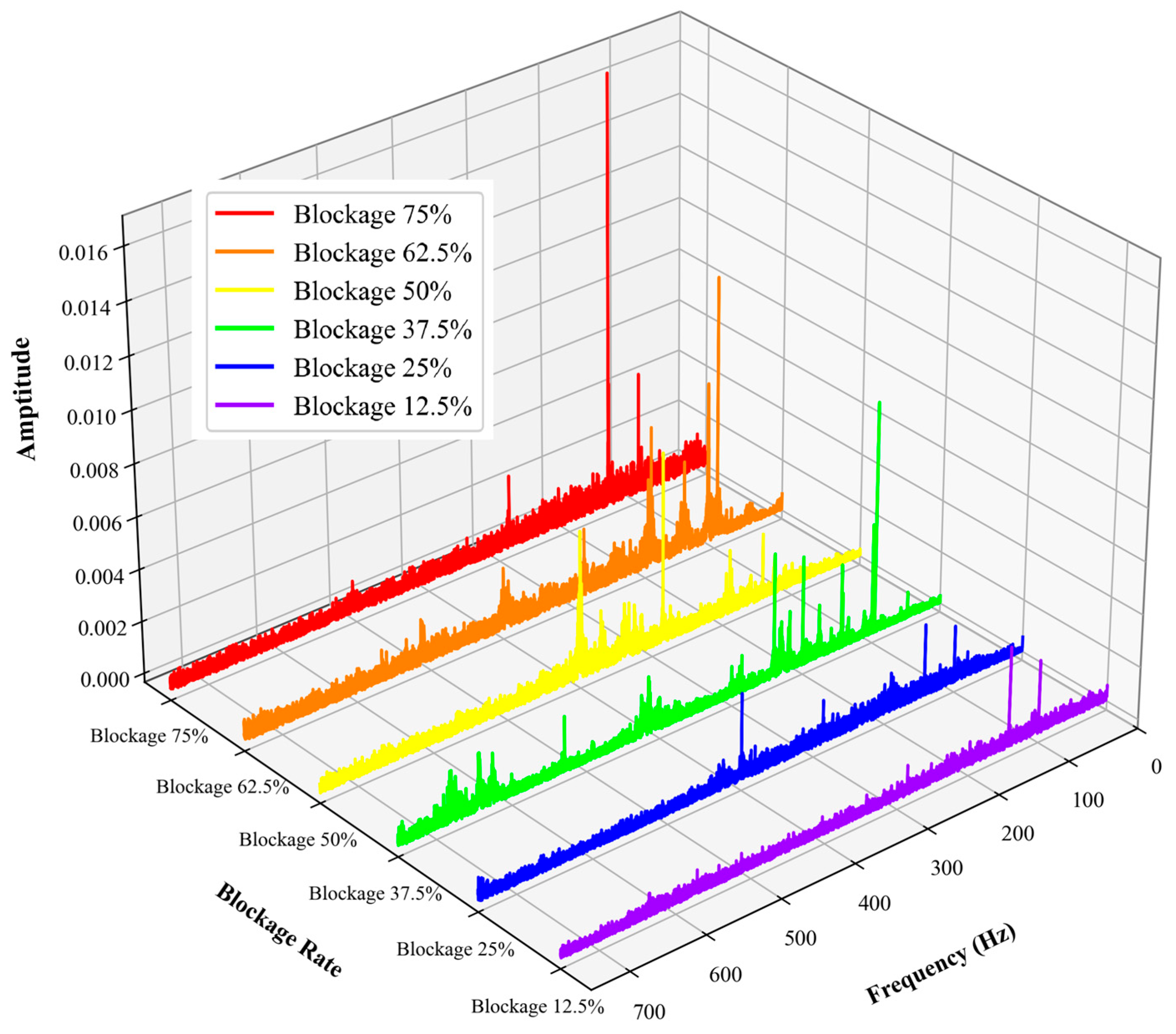
4. Signal Characteristics for Blockage Severity Assessment
4.1. Time-Domain Characteristics
4.2. Frequency-Domain Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.S.; Yu, S.F.; Zhou, K.; Liu, X.B.; Zhang, Y.L. Blockage Inspection Technology and Its Adaptability for Drainage System in Highway Tunnels. Guangdong Highw. Commun. 2024, 50, 72–77. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.J.; Du, K.; Chen, X.; Xiao, R.H. Preliminary Study on Inspection and Assessment Technologies for Tunnel Drainage Systems. Tunn. Rail Transit 2019, S1, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.L. Influencing Factors of Crystalline Blockage in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipes and Prevention Countermeasures. Master’s Thesis, Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, Xi’an, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.H.; Zhong, W.J.; Wang, H.; Song, H.X.; Liu, X.B. Study on Treatment of Crystallization Blockage in Drainage Systems of Highway Tunnel. Guangdong Highw. Commun. 2023, 49, 61–66. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.Q.; Jiang, Y.J.; Liu, S.G.; Zeng, C.Y.; Xiao, R.H. Cleaning Technology of Central Drainage Pipe of Operating Highway Tunnel Based on High Pressure Cleaning Technology. Tunn. Constr. 2021, 41, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport. JTG H12-2015; Technical Code of Maintenance for Highway Tunnel. People’s Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Cheng, C.J.; Wang, M. Automated detection of sewer pipe defects in closed-circuit television images using deep learning techniques. Autom. Constr. 2018, 95, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.F.; Feng, Z.; Huang, G.Y.; Li, Y. A clustering method for underground drainage pipeline blockage identification based on acoustic features. J. Yunnan Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2018, 40, 665–675. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.; Zhu, Z.; Xing, L.W. Residual stress measurement of high-grade steel pipeline via ultrasonic method and verification by small hole method. Oil Gas Storage Transp. 2021, 40, 533–538. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, M.; Gu, L.; Xie, S.; Liu, F.; Lu, H. Performance Improvement of Dual-Pulse Heterodyne Distributed Acoustic Sensor for Sound Detection. Sensors 2020, 20, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liu, W.; Yao, G.F.; Pang, Y.D.; Wu, J.; Xu, D.; Wu, S.; Huang, J.B.; Xu, C.R. Equivalent Self-Noise Suppression of DAS System Integrated with Multi-Core Fiber Based on Phase Matching Scheme. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.G.; Cao, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lu, H.L. Binary-Tree Structure for Extended Range-Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juarez, J.C.; Taylor, H.F. Field Test of a Distributed Fiber-Optic Intrusion Sensor System for Long Perimeters. Appl. Opt. 2007, 46, 1968–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellmauthaler, A.; LeBlanc, M.; Bush, J.; Willis, M.E.; Maida, J.L.; Wilson, G.A. Real-Time DAS VSP Acquisition and Processing on Single- and Multi-Mode Fibers. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 14847–14852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlo, S.; Malcovati, P.; Norgia, M.; Pesatori, A.; Svelto, C.; Pniov, A.; Zhimov, A.; Nesterov, E.; Karassik, V. Runways Ground Monitoring System by Phase-Sensitive Optical-Fiber OTDR. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Inertial Sensors and Systems (INERTIAL), Kauai, HI, USA, 27–30 March 2017; pp. 523–529. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Q.W.; Chen, D.; Li, H.; Liang, W.B.; He, Z.Y. Monitoring Pipeline Leakage Using Fiber-Optic Distributed Acoustic Sensor. Acta Optica Sinica 2019, 39, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, L. Current Status and Future of Research and Applications for Distributed Fiber Optic Sensing Technology. Acta Optica Sinica 2024, 44, 11–73. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, N.Z.; Guo, G.C. Study on optical fiber sensor for detection and positioning of oil pipeline ice-blocking. Transducer Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 29, 30–32. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.D.; Fan, C.Z.; Li, H. Nonintrusive Distributed Flow Rate Sensing System Based on Flow-Induced Vibrations Detection. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.C.; Zhang, D.; Luo, Q. Leakage Identification and Localization Method for Gas Pipeline Based on Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2025, 62, 111–117. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, F. Application of Pipeline Leakage Detection Based on Distributed Fiber Optic Acoustic Sensing Technology. Water Purif. Technol. 2024, 43, 154–159. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S. Research on Pipeline Leakage Monitoring Technology Based on Distributed Acoustic Sensing Fiber. Master’s Thesis, Dalian University of Technology, Dalian, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, L.; Zhang, D.D.; Liu, C.Y. Research on the Influencing Factors of Blockage Identification in Filling Pipeline based on DAS Sensing. Study Opt. Commun. 2024, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.Y.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, C.Y. Experimental Study on Plugging Identification of Filling Pipeline based on FBG Monitoring. Study Opt. Commun. 2025, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.D. Research on Monitoring Technology of Pipeline Flow Rate and Leakage Based on Optical Fiber Distributed Acoustic Sensor. Master’s Thesis, Huazhong University of Science & Technology, Wuhan, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ashry, I.; Mao, Y.; Wang, B.W.; Hveding, F.; Bukhamsin, A.Y.; Ng, T.K.; Ooi, B.S. A Review of Distributed Fiber-optic Sensing in the Oil and Gas Industry. J. Light. Technol. 2021, 40, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemes, A.; Zhao, J.; Jacono, D.L. The interaction between flow-induced vibration mechanisms of a square cylinder with varying angles of attack. J. Fluid Mech. 2012, 710, 102–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
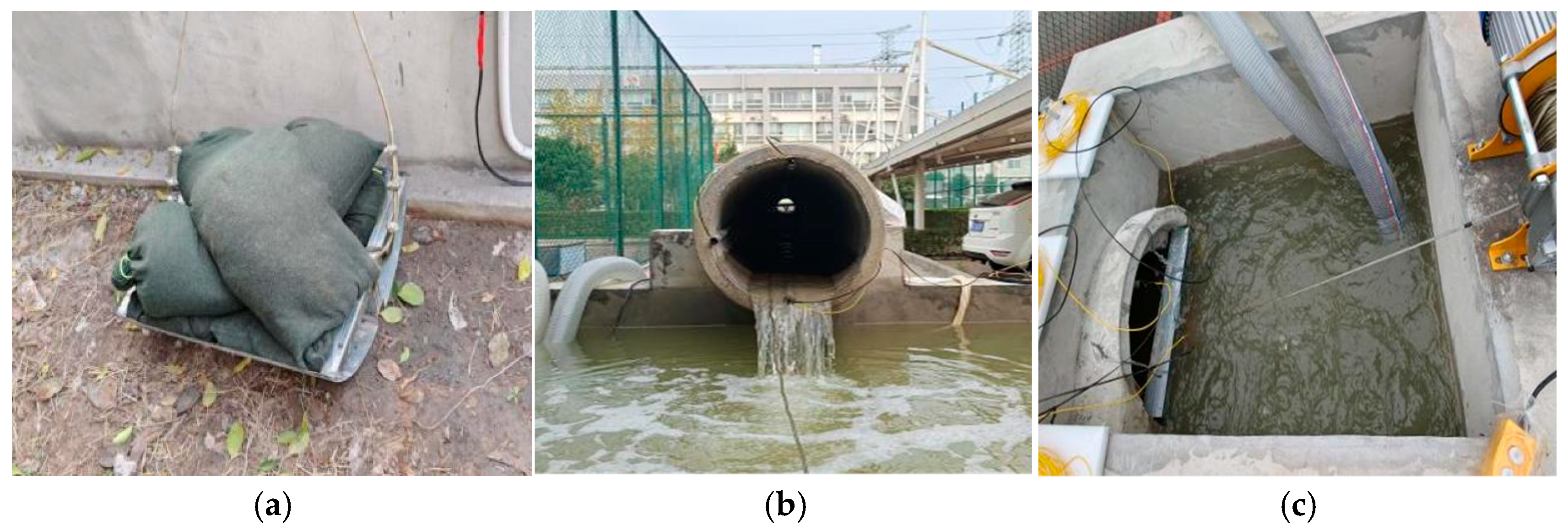





| Component | Model/Material | Key Parameters | Quantity/Length | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drainage Pipeline | Concrete, DN500 | Diameter: 0.5 m | 6 × 3 m | Assembled from six 3 m segments |
| Reservoir Tank | Brick construction | 3.5 m × 3.5 m × 1 m | 1 | Water source for circulation |
| Buffer Tank | Brick construction | 1 m × 1 m × 1 m | 1 | Stabilizes inflow to pipeline |
| Circulation Pipes | PVC Reinforced Hose | Diameter: 10 cm | 2 × 20 m | Connects pumps and tanks |
| Water Pump | QDX50-7-1.5 | Flow rate: 50 m3/h | 1 | Provides circulating flow |
| Support Piers | Brick construction | 0.5 m × 0.2 m × 0.5 m | Several | Supports the pipeline |
| Obstruction Tray | Steel | Diameter: 0.5 m | 1 | Semi-circular, matches pipe ID |
| DAS Interrogator | HIF-DAS V2 | – | 1 | Acquires and demodulates fiber signal |
| Sensing Fiber | G.657A Butterfly-shaped skin-line optical fiber | 7 mm | 20 m | Deployed along the interior top of the pipeline |
| Pipeline Section | Optical Fiber Start (Outlet) | Midpoint (Pipeline Center) | Optical Fiber End (Inlet) | Channel Acquisition Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Pipe | 28 (18 m) | 73 (9 m) | 118 (0 m) | 28~118 (0–18 m) |
 (the direction of laser propagation) (the direction of laser propagation) | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Wan, F.; Li, S.; Shen, H.; Zhang, N.; Xie, W.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, X. Experimental Investigation of Acoustic Signal Characteristics of Blockages in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipelines Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010491
Wan F, Li S, Shen H, Zhang N, Xie W, Yan Y, Zhang X. Experimental Investigation of Acoustic Signal Characteristics of Blockages in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipelines Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010491
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Fei, Shuai Li, Hongfei Shen, Nian Zhang, Wenjun Xie, Yuchen Yan, and Xuan Zhang. 2026. "Experimental Investigation of Acoustic Signal Characteristics of Blockages in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipelines Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010491
APA StyleWan, F., Li, S., Shen, H., Zhang, N., Xie, W., Yan, Y., & Zhang, X. (2026). Experimental Investigation of Acoustic Signal Characteristics of Blockages in Highway Tunnel Drainage Pipelines Using Distributed Acoustic Sensing. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 491. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010491






