Co-Gasification of Bio-Oil and Black Liquor as Renewable Gasification Feedstocks
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
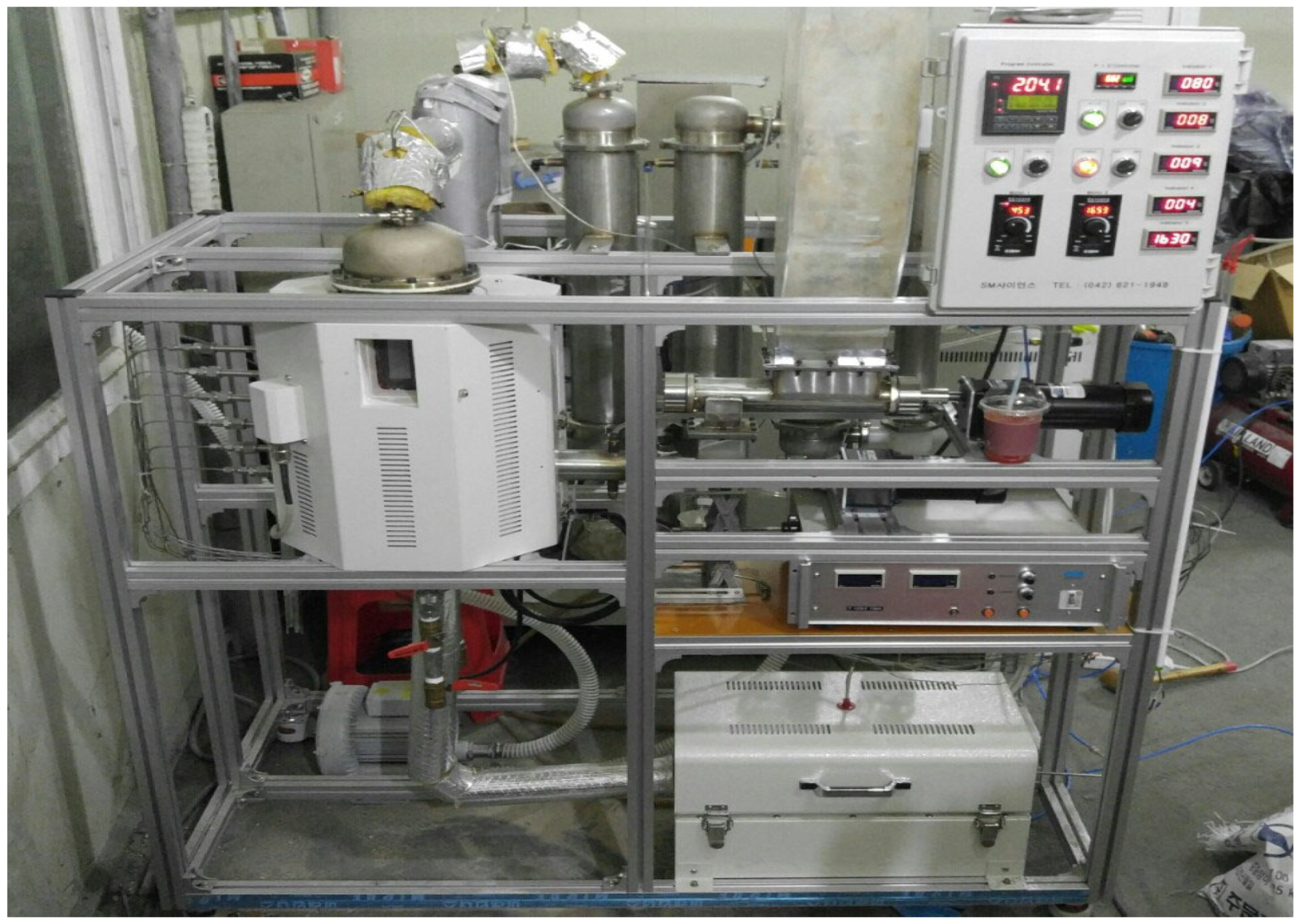
2.2. Experimental Apparatus and Method
2.3. Chemical Reaction Mechanism in the Gasifier
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Bio-Oil Produced by Fast Pyrolysis
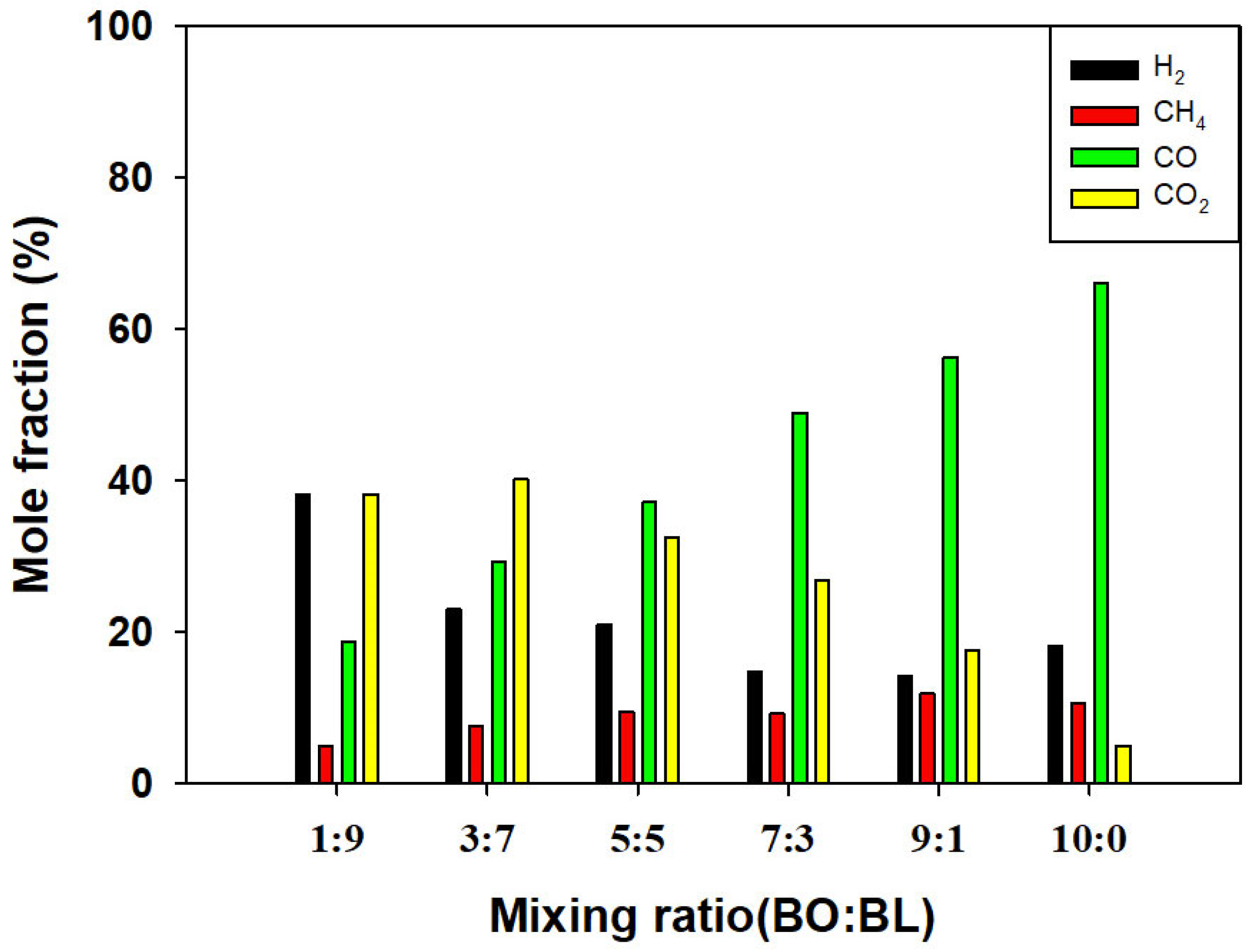
3.2. Characteristics of the Co-Gasification Syngas Products
3.3. Evaluation of Gasification Efficiency
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CCR | Carbon conversion ratio |
| CGE | Cold gas efficiency |
| DME | Dimethyl ether |
| ER | Equivalence ratio |
| LHV | Lower heating value |
| SMR | Steam methane reforming |
| WGS | Water–gas shift |
References
- Chen, T.; Wu, C.; Liu, R. Steam reforming of bio-oil from rice husks fast pyrolysis for hydrogen production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 9236–9240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.L.; Zhu, Y.H.; Zhu, M.Q.; Kang, K.; Sun, R.C. A review of gasification of bio-oil for gas production. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2019, 3, 1600–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buelvas, A.; Quintero-Coronel, D.A.; Vanegas, O.; Ortegon, K.; Bula, A.; Mesa, J.; González-Quiroga, A. Gasification of solid biomass or fast pyrolysis bio-oil: Comparative energy and exergy analyses using AspenPlus®. Eng. Rep. 2024, 6, e12825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G. Techno-economic analysis of advanced biofuel production based on bio-oil gasification. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 191, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekbom, T.; Lindblom, M.; Berglin, N.; Ahlvik, P. Technical and Commercial Feasibility Study of Black Liquor Gasification with Methanol/DME Production as Motor Fuels for Automotive Uses—BLGMF; Final Report; Nykomb Synergetics AB: Stockholm, Sweden, 2003; Available online: https://dspace.tul.cz/server/api/core/bitstreams/d150c6e3-7383-40fb-b8dc-56d2a9040827/content (accessed on 1 December 2025).
- Naqvi, M.; Yan, J.; Dahlquist, E. Black liquor gasification integrated in pulp and paper mills: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8001–8015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, Y.; Furusjö, E.; Kirtania, K.; Gebart, R.; Granberg, F. A study of black liquor and pyrolysis oil co-gasification in pilot scale. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2018, 8, 113–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-Oller, A.; Furusjö, E.; Umeki, K. ‘Fuel conversion characteristics of black liquor and pyrolysis oil mixtures: Efficient gasification with inherent catalyst’ ScienceDirect. Biomass Bioenergy 2015, 79, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, P. Biomass Gasification and Pyrolysis: Practical Design and Theory; Elsevier: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, P.; Xiong, Z.; Chang, J.; Wu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, J. An Experimental Study on Biomass Air–Steam Gasification in a Fluidized Bed. Bioresour. Technol. 2004, 95, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gil, J.; Aznar, M.P.; Caballero, M.A.; Francés, E.; Corella, J. Biomass Gasification in Fluidized Bed at Pilot Scale with Steam–Oxygen Mixtures. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1999, 38, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Kim, H. The Reduction and Control of Tar during Biomass Gasification: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 397–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.C.; Lee, B.K.; Yoo, H.S.; Choi, H.S. Influence of Operating Conditions for Fast Pyrolysis and Pyrolysis Oil Production in a Conical Spouted-Bed Reactor. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2019, 42, 2493–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D5373; Standard Test Methods for Instrumental Determination of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen in Laboratory Samples of Coal. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2021.
- ASTM D3172; Standard Practice for Proximate Analysis of Coal and Coke. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- ASTM D4809; Standard Test Method for Heat of Combustion of Liquid Hydrocarbon Fuels by Bomb Calorimeter (Precision Method). ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Park, H.C.; Yun, D.W.; Choi, M.K.; Choi, H.S. Study on biomass fast pyrolysis kinetics in an isothermal spouted-bed thermogravimetric analyzer and its application to CFD. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 168, 105777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KS I ISO 6976; Natural Gas—Calculation of Calorific Values, Density, Relative Density and Wobbe Indices from Composition. Korean Agency for Technology and Standards: Eumseong, Republic of Korea, 2021.
- Reed, T. Biomass Gasification: Principles and Technology; Noyes Data Corporation: Park Ridge, NJ, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kinoshita, C. Kinetic Model of Biomass Gasification. Sol. Energy 1993, 51, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcazar-Ruiz, A.; Ortiz, M.L.; Dorado, F.; Sanchez-Silva, L. Gasification versus fast pyrolysis bio-oil production: A life cycle assessment. J. Clean Prod. 2022, 336, 130373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.G.; Choi, M.K.; Choi, D.H.; Choi, H.S. Quality improvement and tar reduction of syngas produced by bio-oil gasification. Energy 2021, 236, 121473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.J.; Ramaswamy, S. Thermodynamic Analysis of Black Liquor Steam Gasification. BioResources 2011, 6, 3210–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bach-Oller, A.; Kirtania, K.; Furusjö, E.; Umeki, K. Co-gasification of black liquor and pyrolysis oil at high temperature: Part 1. Fate of alkali elements. Fuel 2017, 202, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandara, J.C.; Eikeland, M.S.; Moldestad, B.M.E. Analysis of the effect of steam-to-biomass ratio in fluidized bed gasification with multiphase particle-in-cell CFD simulation. In Proceedings of the 58th SIMS, Reykjavik, Iceland, 25–27 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, D.; Wang, Q.; Xie, G.; Ye, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Ye, C. Effect of air equivalence ratio on the characteristics of biomass partial gasification for syngas and biochar co-production in the fluidized bed. Renew. Energy 2024, 222, 119881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Proximate analysis (wt.%) | |
| Moisture | 3.19 |
| Volatiles | 78.58 |
| Ash | 17.09 |
| Fixed carbon | 1.15 |
| Elemental analysis (wt.%) a | |
| C | 47.12 |
| H | 6 |
| O b | 46.77 |
| N | 0.11 |
| S | - |
| Higher heating value (MJ/kg) c | 16.48 |
| Properties | Bio | Black | (BO:BL) | (BO:BL) | (BO:BL) | (BO:BL) | (BO:BL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil | Liquor | 1:9 | 3:7 | 5:5 | 7:3 | 9:1 | ||
| Moisture content (wt.%) | 33.14 | 81.96 | 59.56 | 56.69 | 53.91 | 50.96 | 44.25 | |
| Volatile (wt.%) | 62.17 | 11.90 | 37.61 | 40.20 | 43.31 | 46.17 | 52.77 | |
| Fixed carbon (wt.%) | 4.11 | 0.56 | 0.83 | 1.39 | 1.78 | 2.09 | 2.51 | |
| Ash (wt.%) | 0.59 | 5.57 | 2.01 | 1.72 | 0.99 | 0.77 | 0.47 | |
| Element (wt.%) | C | 49.86 | 36.81 | 39.88 | 41.31 | 45.35 | 55.29 | 55.29 |
| H | 6.28 | 5.57 | 6.00 | 6.38 | 6.42 | 6.49 | 6.49 | |
| O | 43.28 | 57.11 | 53.67 | 51.75 | 47.65 | 37.64 | 37.64 | |
| N | 0.58 | 0.51 | 0.45 | 0.56 | 0.58 | 0.58 | 0.58 | |
| S | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | |
| Conditions | Value |
|---|---|
| Reactor type | MSB-TGA (Diameter: 57 mm, Height: 68 mm, Gas inlet diameter: 13 mm) |
| Sample | Bio-oil + Black liquor |
| Pyrolysis oil input (g/h) | 1 |
| Reaction temperature (°C) | 800 |
| BO:BL ratio | 1:9, 3;7, 5:5, 7:3, 9:1 |
| Equivalence ratio | 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 |
| Oxidant | Nitrogen + Oxygen |
| Reaction Type | Chemical Reaction |
|---|---|
| Carbon reactions | |
| R1 | C + CO2 ↔ 2CO, +172 kJ/mol |
| R2 | C + H2O ↔ CO + H2, +131 kJ/mol |
| R3 | C + 2H2 ↔ CH4, −74.8 kJ/mol |
| R4 | C + 0.5O2 → CO, −11 kJ/mol |
| Oxidation reactions | |
| R5 | C + O2 → CO2, −394 kJ/mol |
| R6 | CO + 0.5O2 → CO2, −284 kJ/mol |
| R7 | CH4 + 2O2 ↔ CO2 + 2H2O, −803 kJ/mol |
| R8 | H2 + 0.5O2 → H2O, −242 kJ/mol |
| Water–gas shift reactions | |
| R9 | CO + H2O ↔ CO2 + H2, −41.2 kJ/mol |
| Methanation reactions | |
| R10 | 2CO + 2H2 → CH4 + CO, −247 kJ/mol |
| R11 | CO + 3H2 ↔ CH4 + H2O, −206 kJ/mol |
| R14 | CO2 + 4H2 → CH4 + 2H2O, −165 kJ/mol |
| Methane steam reforming reactions | |
| R12 | CH4 + H2O ↔ CO +3H2, +206 kJ/mol |
| R13 | CH4 + 0.5O2 → CO + 2H2, −36 kJ/mol |
| Reaction Type | Chemical Reaction |
|---|---|
| Boudouard reactions | |
| R14 | C(s) + CO2 ↔ 2CO, +172 kJ/mol |
| Water gas primary reactions | |
| R15 | C(s) + H2O ↔ CO + H2, +131 kJ/mol |
| Methanation reactions | |
| R16 | C(s) + 2H2 → CH4, −75 kJ/mol |
| Water–gas shift reactions | |
| R17 | CO + H2O ↔ CO2 +H2, −41 kJ/mol |
| Methane steam reforming reactions | |
| R18 | CH4 + H2O ↔ CO +3H2, +206 kJ/mol |
| Carbonate reduction reaction | |
| R19 | Na2CO3 + 2C ↔ 2Na(g) + 3CO |
| Reaction Temperature | 400 °C | 450 °C | 500 °C | 550 °C | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Char | Yield (wt.%) | 29.6 | 24.4 | 21.3 | 17.2 |
| HHV (MJ/kg) | 29.0 | 30.2 | 31.0 | 31.6 | |
| Energy yield (%) | 52.1 | 44.7 | 40.1 | 33.0 | |
| Bio-oil | Yield (wt.%) | 44.2 | 50.8 | 52.5 | 43.9 |
| HHV (MJ/kg) | 17.2 | 18.1 | 18.4 | 18.0 | |
| Energy yield (%) | 46.2 | 55.6 | 58.7 | 48.0 | |
| Average energy yield (%) | 49.1 | 50.2 | 49.4 | 40.5 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Hwang, J.G.; Hong, S.W.; Choi, M.K.; Choi, H.S. Co-Gasification of Bio-Oil and Black Liquor as Renewable Gasification Feedstocks. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010359
Hwang JG, Hong SW, Choi MK, Choi HS. Co-Gasification of Bio-Oil and Black Liquor as Renewable Gasification Feedstocks. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):359. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010359
Chicago/Turabian StyleHwang, Jae Gyu, Seong Wan Hong, Myung Kyu Choi, and Hang Seok Choi. 2026. "Co-Gasification of Bio-Oil and Black Liquor as Renewable Gasification Feedstocks" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010359
APA StyleHwang, J. G., Hong, S. W., Choi, M. K., & Choi, H. S. (2026). Co-Gasification of Bio-Oil and Black Liquor as Renewable Gasification Feedstocks. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 359. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010359





