Temperature Prediction of Wet Clutch Friction Pair Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Finite Element-Based Temperature Prediction Model for Wet Clutch Friction Pair
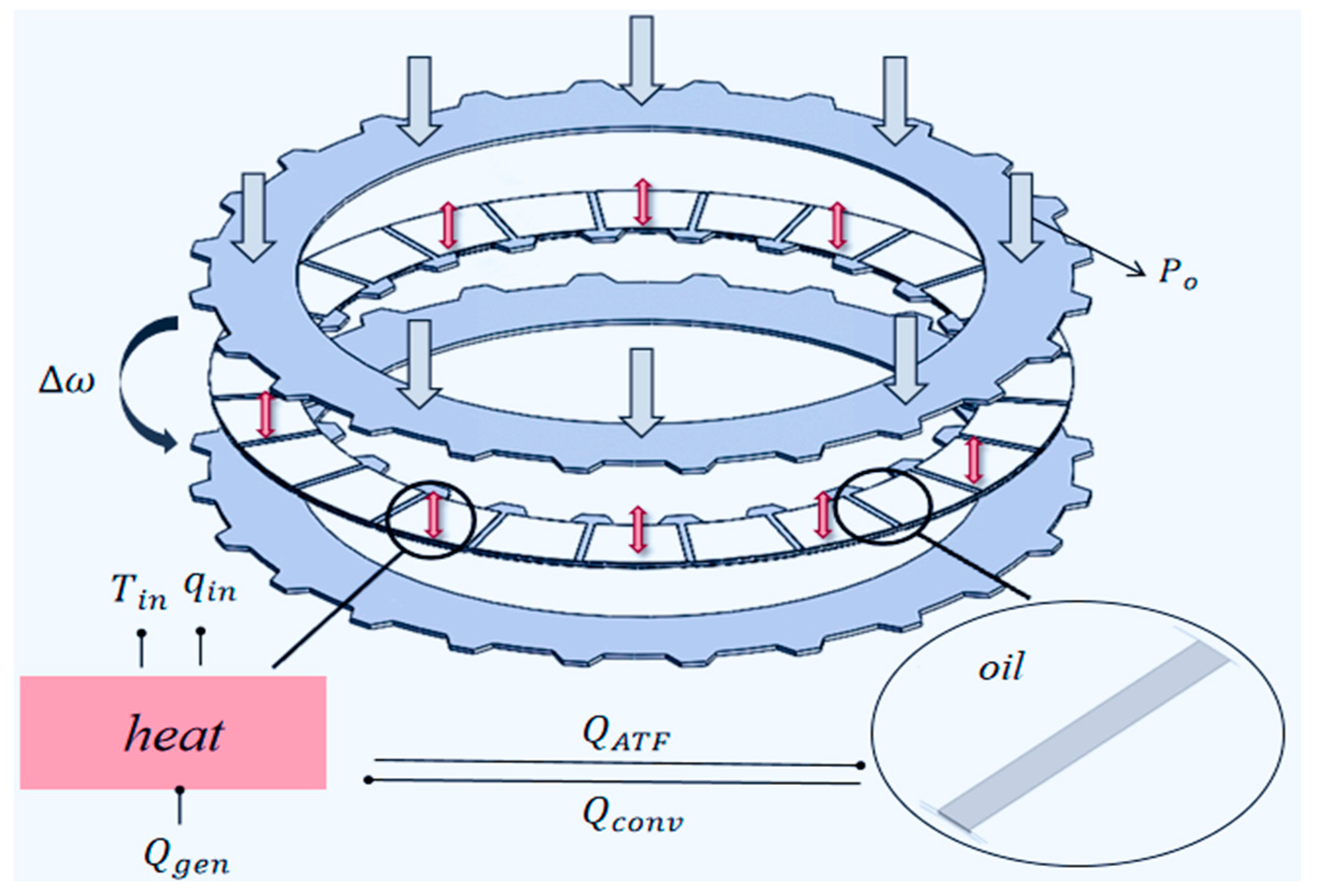
2.1. Theoretical Analysis of Heat-Fluid-Solid Coupling
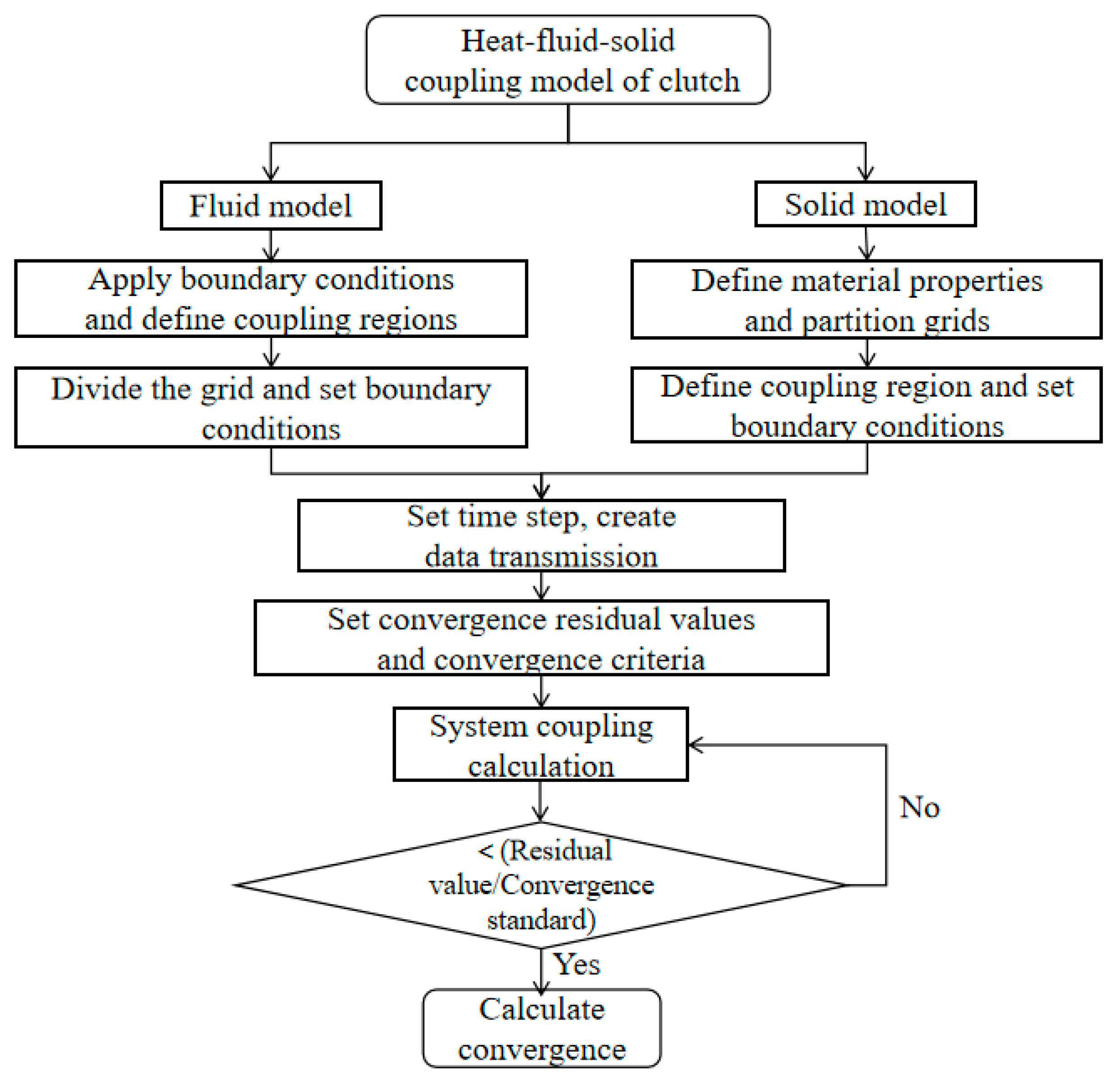
2.2. Development of the Heat-Fluid-Solid Coupled Finite Element Model for the Clutch
2.3. Calculation of the Heat-Fluid-Solid Coupled Finite Element Model
2.4. Analysis of Temperature Field Distribution Characteristics
2.5. Operating Condition Parameter Influence Analysis
3. Temperature Prediction Model Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network
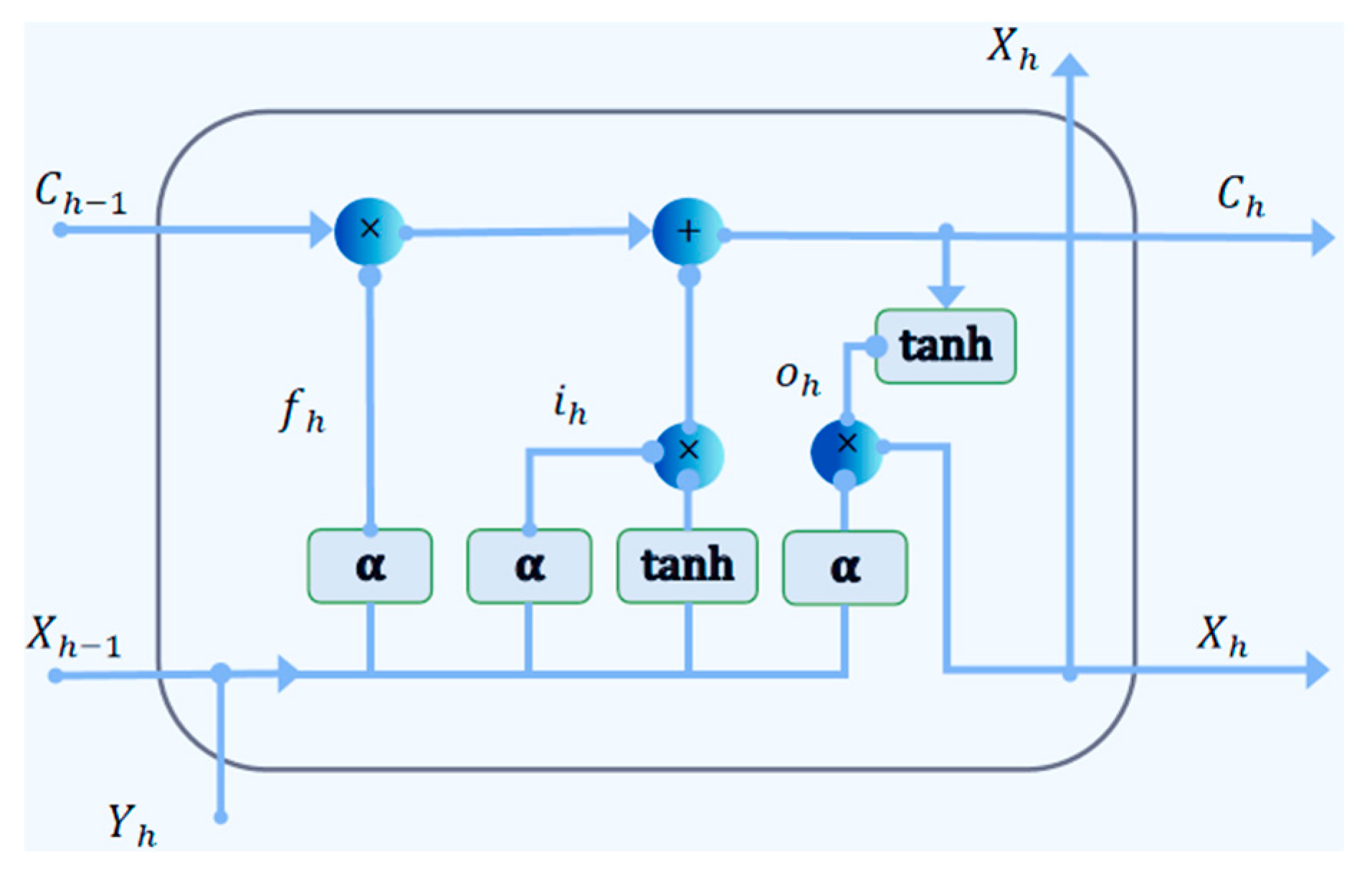
3.1. LSTM Neural Network
3.2. Acquisition and Processing of Temperature Data
3.3. Construction of the Optuna-LSTM Temperature Prediction Model
3.4. Training the Optuna-LSTM Temperature Prediction Model
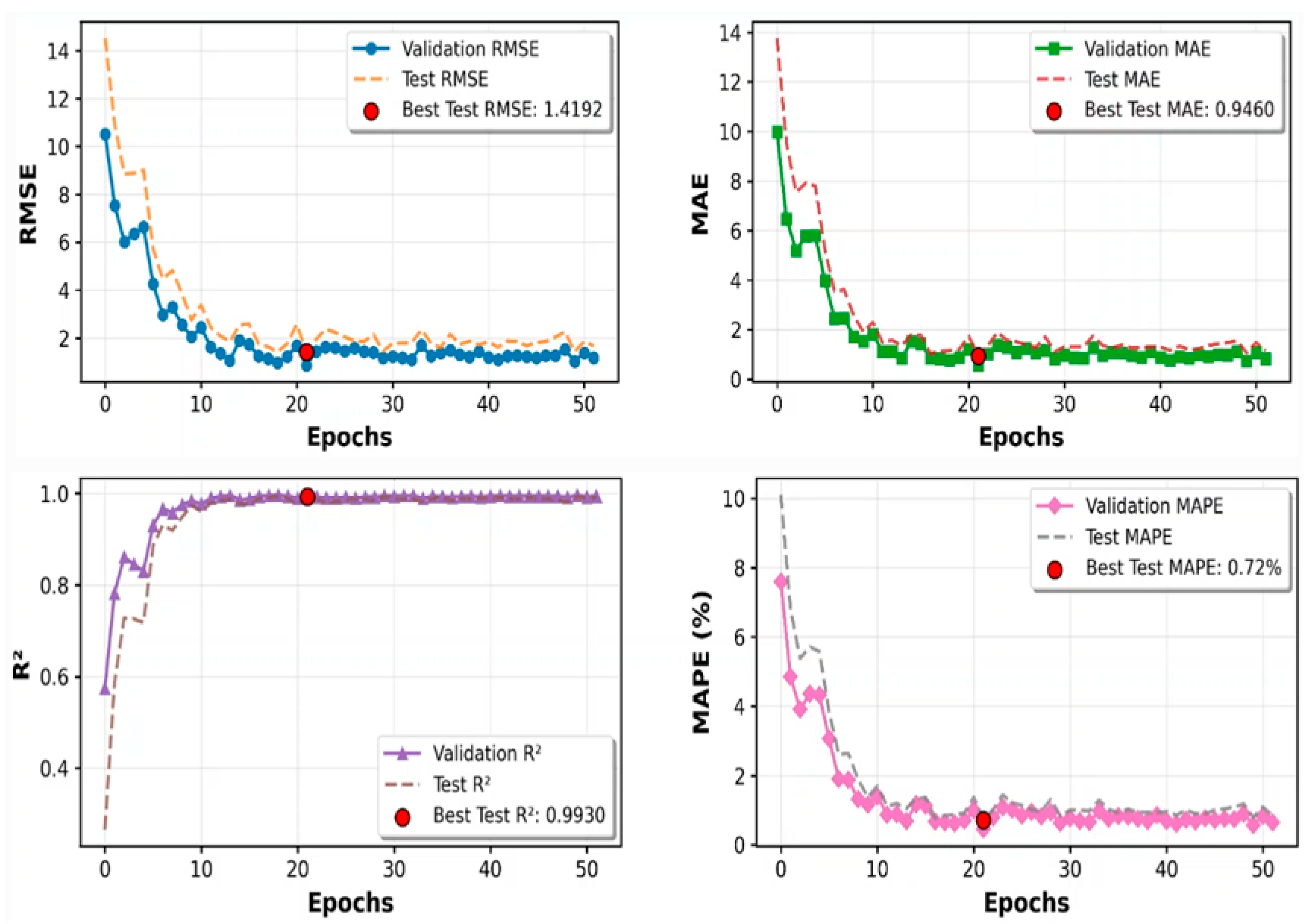
3.5. Analysis of Temperature Prediction Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- The finite element model of wet clutch based on heat-fluid-solid coupling effect is established to solve the problem that the traditional thermal model is insufficient to characterize the nonlinear change of temperature.
- (2)
- The Optuna-LSTM temperature prediction model is constructed through the cooperative operation of the early shutdown strategy combined with the Optun framework.
- (3)
- According to the error function and prediction performance of the Optuna-LSTM model, it is indicated that the Optuna-LSTM model can achieve accurate and efficient temperature prediction.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wei, Y.; Bao, H.; Li, Q.; Huang, Z. Thermal-fluid coupling analysis of aviation wet friction clutch with wavy separation spring. Ind. Lubr. Tribol. 2025, 77, 370–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Wu, Y.; Ji, H.; Liu, Y. Dynamic axial and radial temperature prediction of multi-plate frictional wet clutches in vehicle transmissions with the thermal resistance network method. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 3239–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Fan, G.; Qi, Z.; Song, A.; Zhang, G.; Min, X. Prediction of the surface temperature of AMT clutch-disc based on projection pursuit regression. In Proceedings of the World Automation Congress 2012, Puerto Vallarta, Mexico, 24–28 June 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Groetsch, D.; Voelkel, K.; Pflaum, H.; Stahl, K. Real-time temperature calculation and temperature prediction of wet multi-plate clutches. Forsch. Ingenieurwesen 2021, 85, 923–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Khonsari, M.M.; McCarthy, D.M.C.; Lundin, J. On the Wear prediction of the paper-based friction material in a wet clutch. Wear 2015, 334, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yi, Y.B.; Bao, K. Prediction of thermally induced postbuckling of clutch disks using the finite element method. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 235, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Ma, B.; Chen, M.; Li, H.; Liu, J.; Li, M. Investigation on the failure mechanism and safety mechanical-thermal boundary of a multi-disc clutch. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 103, 319–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Jin, W.; Zhang, Z.; Lv, X.; Zhang, T. Analysis on effects of material parameters on thermoelastic instability of separate plate in wet clutch. J. Tribol. 2024, 146, 034103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peta, K.; Kubiak, K.J.; Sfravara, F.; Brown, C.A. Dynamic wettability of complex fractal isotropic surfaces—Multiscale correlations. Tribol. Int. 2026, 214, 111145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, Y.; Wan, L. A proposed torque calculation model for multi-plate clutch considering boundary lubrication conditions and heat transfer. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2020, 157, 119732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Yan, H. Thermal-fluid-solid coupling simulation and oil groove structure optimization of wet friction clutch for high-speed helicopter. Machines 2023, 11, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, J.; Jang, S. Temperature analysis of wet clutch surfaces during clutch engagement processes based on friction pad patterns. Int. J. Automot. Technol. 2020, 21, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lan, C.; Gong, Y. Clutch Pressure Plate Temperature Prediction Based on Bi-LSTM and Migration Learning. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, T.; Xu, X.; Xu, J.; Zhang, Y. The drag characteristics prediction of multi-plate frictional wet clutches in vehicle transmissions. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2023, 37, 3249–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pointner-Gabriel, L.; Voelkel, K.; Pflaum, H.; Stahl, K. A methodology for data-driven modeling and prediction of the drag losses of wet clutches. Forsch. Ingenieurwesen 2023, 87, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altenburg, S.; Schuchter, F.; Bause, K.; Albers, A. Nutzung von KI-Methoden für die Kupplungsentwicklung in automobilen Antriebssträngen = Use of AI methods for clutch development in automotive drivetrains. Forsch. Ingenieurwesen/Eng. Res. 2023, 87, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Garg, A.; Gao, L. Enhancing real-time degradation prediction of lithium-ion battery: A digital twin framework with CNN-LSTM-attention model. Energy 2023, 286, 129681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheisari, M.; Shafi, J.; Kosari, S.; Amanabadi, S.; Mehdizadeh, S.; Fernandez Campusano, C.; Barzan Abdalla, H. Development of improved deep learning models for multi-step ahead forecasting of daily river water temperature. Eng. Appl. Comput. Fluid Mech. 2025, 19, 2450477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Wang, S.; Cao, W.; Hai, N.; Fernandez, C. Enhanced transformer encoder long short-term memory hybrid neural network for multiple temperature state of charge estimation of lithium-ion batteries. J. Power Sources 2025, 632, 236411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, S.; Dai, B.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, F.; Yang, W.; Li, Y. Enhancing Road Surface Temperature Prediction: A Novel Approach Integrating Transfer Learning with Long Short-Term Memory Neural Networks. J. Transp. Eng. Part B Pavements 2025, 151, 04024063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, L.; Wei, L.; Qiang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Zhan, P. Dynamic performance prediction and experimental analysis of wet clutch actuator considering thermal flow characteristics. Flow Meas. Instrum. 2024, 97, 102592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ma, B.; Stanciulescu, I.; Li, H.; Wang, L. Experimental investigation of friction disc temperature field under cooling fluid. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2020, 235, 3377–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Cui, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation on the thermal-fluid-solid multi-physical field coupling characteristics of wet friction pairs considering cavitation effect. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2024, 260, 124955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, L.; Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Chen, R. The simulation analysis of fluid internal characteristics of wet clutch during the engaging process. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation (ICMA), Takamatsu, Japan, 6–9 August 2017; pp. 2045–2050. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, B.; Qin, D.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Q. Research on temperature rise of wet clutch based on multi-field coupling. In Proceedings of the International Design Engineering Technical Conferences and Computers and Information in Engineering Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2019; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 59308, p. V010T11A001. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H. Constructing Attention-LSTM-VAE Power Load Model Based on Multiple Features. Adv. Math. Phys. 2024, 2024, 1041791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, S.; Li, L. A novel variant of LSTM stock prediction method incorporating attention mechanism. Mathematics 2024, 12, 945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Tao, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, J.; Li, T.; Shan, F.; Zheng, W. Estimation of Maize Water Requirements Based on the Low-Cost Image Acquisition Methods and the Meteorological Parameters. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanifi, S.; Cammarono, A.; Zare-Behtash, H. Advanced hyperparameter optimization of deep learning models for wind power prediction. Renew. Energy 2023, 221, 119700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Density /kg/m3 | Young’s Modulus /GPa | Poisson’s Ratio | Coefficient of Thermal Expansion/K−1 | Thermal Conductivity /W/(m·K) | Specific Heat Capacity/J/(Kg·K) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Paper-based material | 748 | 1.1 | 0.05 | 1 × 10−5 | 4.8 | 1618 |
| Steel | 7880 | 210 | 0.275 | 1.16 × 10−5 | 49 | 452 |
| Density /Kg/m3 | Specific Heat Capacity /J/(Kg⋅K) | Thermal Conductivity/W/(m·K) | Viscosity /Kg/(m·s) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 879 | 1880 | 0.146 | 0.02576 |
| Hidden Layer | Number of Nodes | Learning Rate | Optimizer | Activation Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 0.001 | Adam | Relu |
| Total Prediction Time/s | Samples Processed/ Time Steps: 50 | Through Put Samples/s | Average Latency/ ms/Sample |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 32 | 0.001 | Adam |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Yang, Y.; Su, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, A. Temperature Prediction of Wet Clutch Friction Pair Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network. Appl. Sci. 2026, 16, 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010362
Yang Y, Su C, Wang Z, Zhou C, Zhang A. Temperature Prediction of Wet Clutch Friction Pair Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network. Applied Sciences. 2026; 16(1):362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010362
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Yuqi, Chengyun Su, Zhifei Wang, Chao Zhou, and Aolong Zhang. 2026. "Temperature Prediction of Wet Clutch Friction Pair Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network" Applied Sciences 16, no. 1: 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010362
APA StyleYang, Y., Su, C., Wang, Z., Zhou, C., & Zhang, A. (2026). Temperature Prediction of Wet Clutch Friction Pair Based on Optuna-LSTM Neural Network. Applied Sciences, 16(1), 362. https://doi.org/10.3390/app16010362






