The Impact of the S-Adenosylmethionine Analogue Sinefungin on Viral Life Cycles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells, Viruses, and Compounds
2.2. The Cytotoxicity Assay
2.3. The Plaque Reduction Assay in Infected Monolayers
2.4. The Virus Yield Reduction Assay
2.5. Molecular Validation
2.6. The Statistical Analysis
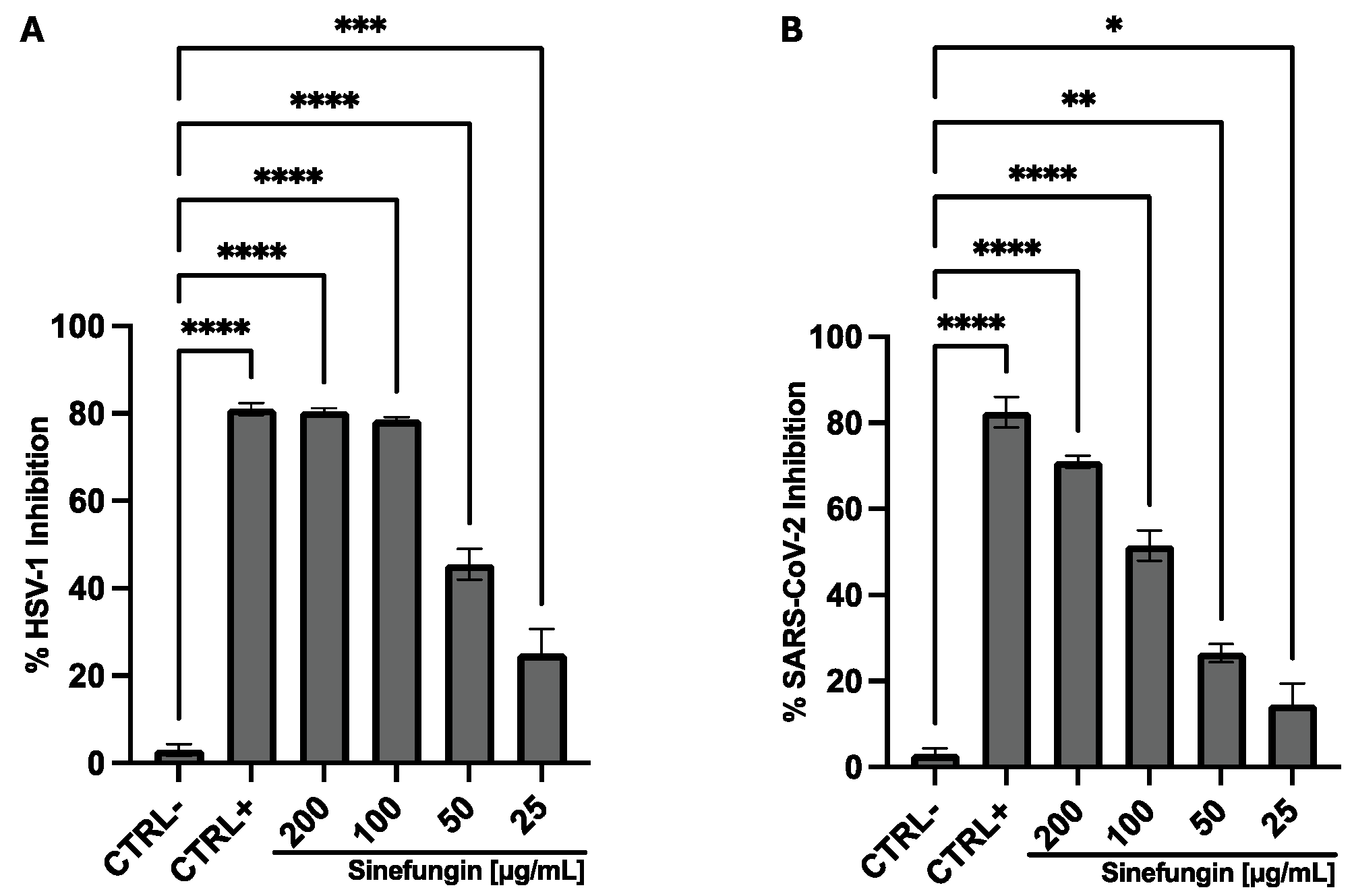
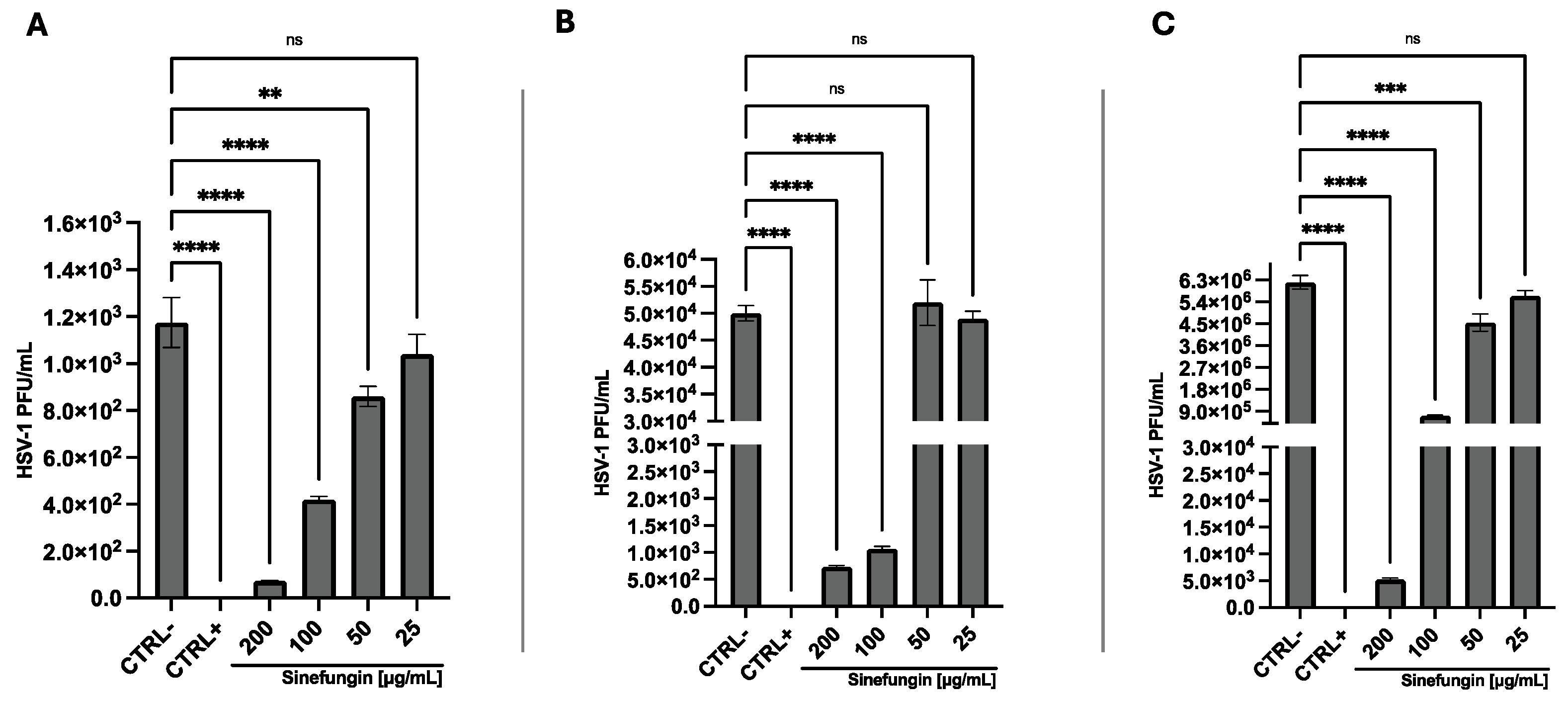
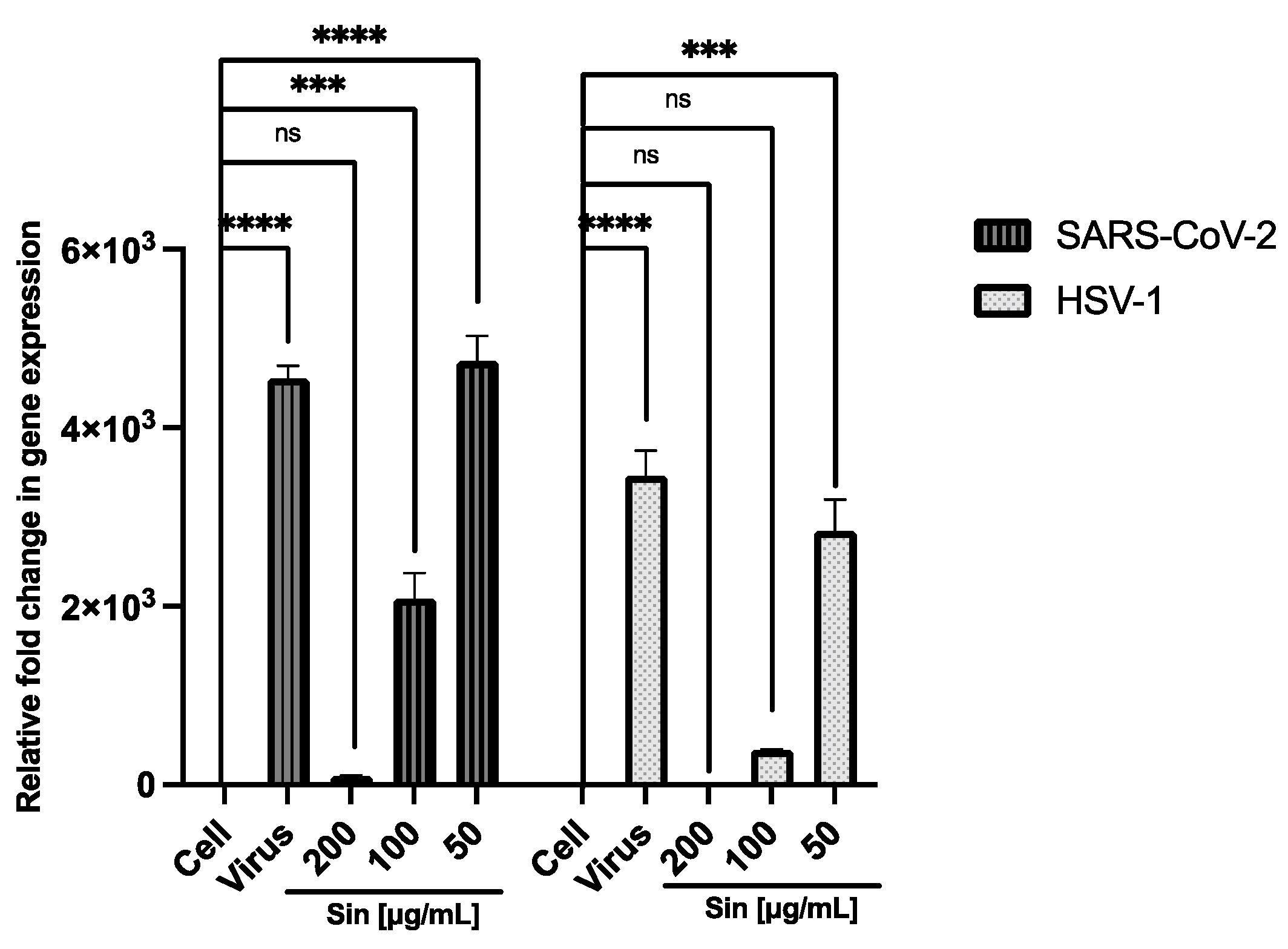
3. Results
3.1. Cell Viability
3.2. Antiviral Activity
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oladipo, E.K.; Olufemi, S.E.; Adediran, D.A.; Adejumo, I.O.; Jimah, E.M.; Oloke, J.K.; Udekwu, C.C.; Ogunwobi, O.O. Epigenetic Modifications in Solid Tumor Metastasis in People of African Ancestry. Front. Oncol. 2024, 14, 1325614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franci, G.; Miceli, M.; Altucci, L. Targeting Epigenetic Networks with Polypharmacology: A New Avenue to Tackle Cancer. Epigenomics 2010, 2, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.G.; Gelb, A.M.; Nussbaum, M.; Haveson, S.; Ghali, V. Primary Smooth Muscle Tumors of Venous Origin. Ann. Surg. 1982, 196, 720–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Mohapatra, T. Epigenetic Modifications in Genome Help Remembering the Stress Tolerance Strategy Adopted by the Plant. Front. Biosci. 2024, 29, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casadesús, J.; Sánchez-Romero, M.A. DNA Methylation in Prokaryotes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1389, 21–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balakrishnan, L.; Milavetz, B. Epigenetic Regulation of Viral Biological Processes. Viruses 2017, 9, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Rana, T.M. Regulation of Antiviral Innate Immunity by Chemical Modification of Viral RNA. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2022, 13, e1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, H.; Li, M.; Li, P.; Ji, S. Virus-Induced Host Genomic Remodeling Dysregulates Gene Expression, Triggering Tumorigenesis. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2024, 14, 1359766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, R.; Xie, Z. The Roles of DNA Methylation on the Promotor of the Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) Gene and the Genome in Patients with EBV-Associated Diseases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 106, 4413–4426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaro-Filho, S.M.; Pereira Chaves, C.B.; Felix, S.P.; Basto, D.L.; de Almeida, L.M.; Moreira, M.A.M. HPV DNA Methylation at the Early Promoter and E1/E2 Integrity: A Comparison between HPV16, HPV18 and HPV45 in Cervical Cancer. Papillomavirus Res. 2018, 5, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folliero, V.; Dell’Annunziata, F.; Chianese, A.; Morone, M.V.; Mensitieri, F.; Di Spirito, F.; Mollo, A.; Amato, M.; Galdiero, M.; Dal Piaz, F.; et al. Epigenetic and Genetic Keys to Fight HPV-Related Cancers. Cancers 2023, 15, 5583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markiewicz, L.; Drazkowska, K.; Sikorski, P.J. Tricks and Threats of RNA Viruses—Towards Understanding the Fate of Viral RNA. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 669–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, D.G.; Kennedy, E.M.; Dumm, R.E.; Bogerd, H.P.; Tsai, K.; Heaton, N.S.; Cullen, B.R. Epitranscriptomic Enhancement of Influenza A Virus Gene Expression and Replication. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 377–386.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Sun, F.-J.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, L.-R.; Xie, L.-L.; Xia, P.-Y. Enhancement of Biofilm Formation by Subinhibitory Concentrations of Macrolides in icaADBC-Positive and -Negative Clinical Isolates of Staphylococcus Epidermidis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 2707–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Guo, X.; Zhao, B.; Jiang, J. Emerging Role of N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification in Regulation of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Virus-Host Interactions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 173, 116231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Mitra Basu, S.; De, A.; Mallick, A.; Das, S.; Rath, S. Concurrent Microbial Keratitis and Nasolacrimal Duct Obstruction: Concordance, Etiopathogenesis, and Outcome. Cornea 2019, 38, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuroda, Y.; Yamagata, H.; Nemoto, M.; Inagaki, K.; Tamura, T.; Maeda, K. Antiviral Effect of Sinefungin on in Vitro Growth of Feline Herpesvirus Type 1. J. Antibiot. 2019, 72, 981–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, C.S.; Borchardt, R.T.; Stone, H.O. Sinefungin, a Potent Inhibitor of Virion mRNA(Guanine-7-)-Methyltransferase, mRNA(Nucleoside-2′-)-Methyltransferase, and Viral Multiplication. J. Biol. Chem. 1978, 253, 4075–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mody, P.H.; Pathak, S.; Hanson, L.K.; Spencer, J.V. Herpes Simplex Virus: A Versatile Tool for Insights Into Evolution, Gene Delivery, and Tumor Immunotherapy. Virology 2020, 11, 1178122X20913274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabidi, N.Z.; Liew, H.L.; Farouk, I.A.; Puniyamurti, A.; Yip, A.J.W.; Wijesinghe, V.N.; Low, Z.Y.; Tang, J.W.; Chow, V.T.K.; Lal, S.K. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Variants: Implications on Immune Escape, Vaccination, Therapeutic and Diagnostic Strategies. Viruses 2023, 15, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Annunziata, F.; Mosidze, E.; Folliero, V.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Lopardo, V.; Pagliano, P.; Porta, G.D.; Galdiero, M.; Bakuridze, A.D.; Franci, G. Eco-Friendly Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles from Peel and Juice C. Limon and Their Antiviral Efficacy against HSV-1 and SARS-CoV-2. Virus Res. 2024, 349, 199455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell’Annunziata, F.; Sellitto, C.; Franci, G.; Marcotullio, M.C.; Piovan, A.; Della Marca, R.; Folliero, V.; Galdiero, M.; Filippelli, A.; Conti, V.; et al. Antiviral Activity of Ficus Rubiginosa Leaf Extracts against HSV-1, HCoV-229E and PV-1. Viruses 2022, 14, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Qiao, X.; Fang, Y.; Guo, R.; Bai, P.; Liu, S.; Li, T.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, S.; Na, Z.; et al. Epigenetics-Targeted Drugs: Current Paradigms and Future Challenges. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nehme, Z.; Pasquereau, S.; Herbein, G. Control of Viral Infections by Epigenetic-Targeted Therapy. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, R.; Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Weng, J.; Tan, H.; Guo, T.; Wang, M.; Xie, J. The Epigenetic Modification of DNA Methylation in Neurological Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1401962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafaati, M.; Zandi, M.; Priyanka; Choudhary, O.P. Impact of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Re-Emerging Viruses. Travel Med. Infect. Dis. 2023, 52, 102535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruggieri, A.; Helm, M.; Chatel-Chaix, L. An Epigenetic “Extreme Makeover”: The Methylation of Flaviviral RNA (and Beyond). RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 696–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milavetz, B.I.; Balakrishnan, L. Viral Epigenetics. In Cancer Epigenetics; Verma, M., Ed.; Methods in Molecular Biology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1238, pp. 569–596. ISBN 978-1-4939-1803-4. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, A.; Ganguly, A.; Kumar, A.; Srivastava, N.; Pathak, R. Harnessing Epigenetics: Innovative Approaches in Diagnosing and Combating Viral Acute Respiratory Infections. Pathogens 2025, 14, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, A.; Ludwig, S. Host-Targeted Antivirals against SARS-CoV-2 in Clinical Development—Prospect or Disappointment? Antivir. Res. 2025, 235, 106101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Chavarria, A.; Sanders, K.N.; Ghalei, H.; Khoshnevis, S. Sinefungin, a Natural Nucleoside Analog of S-Adenosyl Methionine, Impairs the Pathogenicity of Candida albicans. NPJ Antimicrob. Resist. 2024, 2, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobrovs, R.; Kanepe, I.; Narvaiss, N.; Patetko, L.; Kalnins, G.; Sisovs, M.; Bula, A.L.; Grinberga, S.; Boroduskis, M.; Ramata-Stunda, A.; et al. Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 and Nsp16 Methyltransferase Inhibitors by High-Throughput Virtual Screening. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Chorba, J.S.; Whelan, S.P.J. Vesicular Stomatitis Viruses Resistant to the Methylase Inhibitor Sinefungin Upregulate RNA Synthesis and Reveal Mutations That Affect mRNA Cap Methylation. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4104–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Zhou, D.; Xu, C.; Song, X.; Wang, X.; Qin, C.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhu, M. Screening of RNA Methyltransferase NSP16 Inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus and Study of Related Mechanisms. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2025, 17, 1237–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Sinefungin | |
|---|---|
| Chemical structure | 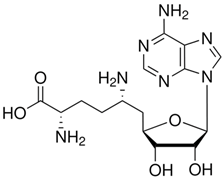 |
| Molecular formula | C15H23N7O5 |
| Molecular weight | 381.39 g/mol |
| Appearance | Colorless |
| Density | 1.2 g/cm3 |
| Purity | 95% (HPLC) |
| Solubility in water | 20 mg/mL |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dell’Annunziata, F.; Capuano, N.; De Prisco, M.; Rufolo, S.; Folliero, V.; Franci, G. The Impact of the S-Adenosylmethionine Analogue Sinefungin on Viral Life Cycles. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094942
Dell’Annunziata F, Capuano N, De Prisco M, Rufolo S, Folliero V, Franci G. The Impact of the S-Adenosylmethionine Analogue Sinefungin on Viral Life Cycles. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094942
Chicago/Turabian StyleDell’Annunziata, Federica, Nicoletta Capuano, Mariagrazia De Prisco, Sandra Rufolo, Veronica Folliero, and Gianluigi Franci. 2025. "The Impact of the S-Adenosylmethionine Analogue Sinefungin on Viral Life Cycles" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094942
APA StyleDell’Annunziata, F., Capuano, N., De Prisco, M., Rufolo, S., Folliero, V., & Franci, G. (2025). The Impact of the S-Adenosylmethionine Analogue Sinefungin on Viral Life Cycles. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4942. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094942








