Numerical Analysis of the Effect of the Rock Particle Size on the Macroscopic Mechanical Properties Under Uniaxial Compression and Shearing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Effect of the Average Particle Size on the Model’s Macroscopic Mechanical Behavior
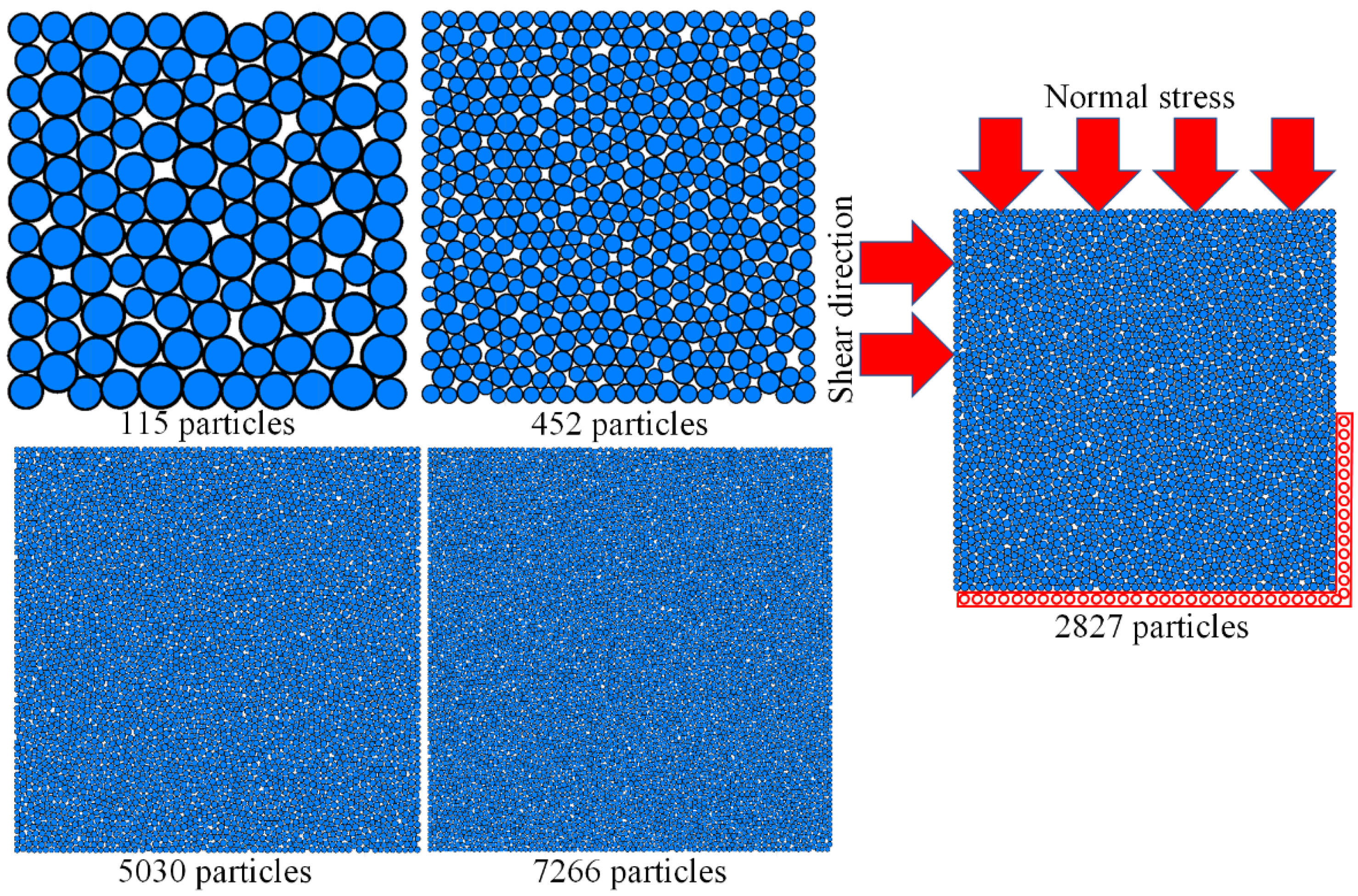
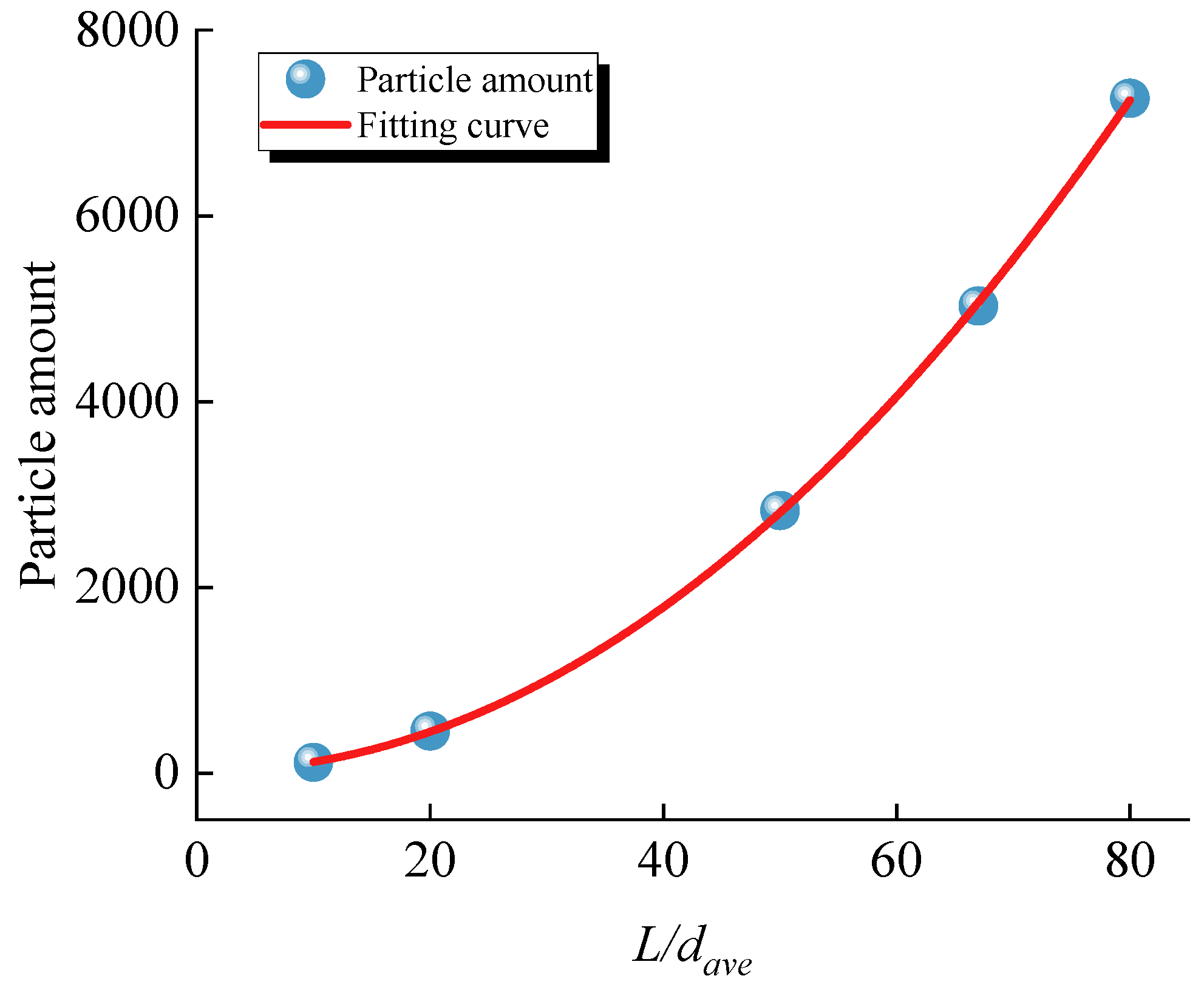
2.1. Effect of the Average Particle Size on the Model’s Mechanical Behavior
2.2. Effect of the Average Particle Size on the Compressive Strength
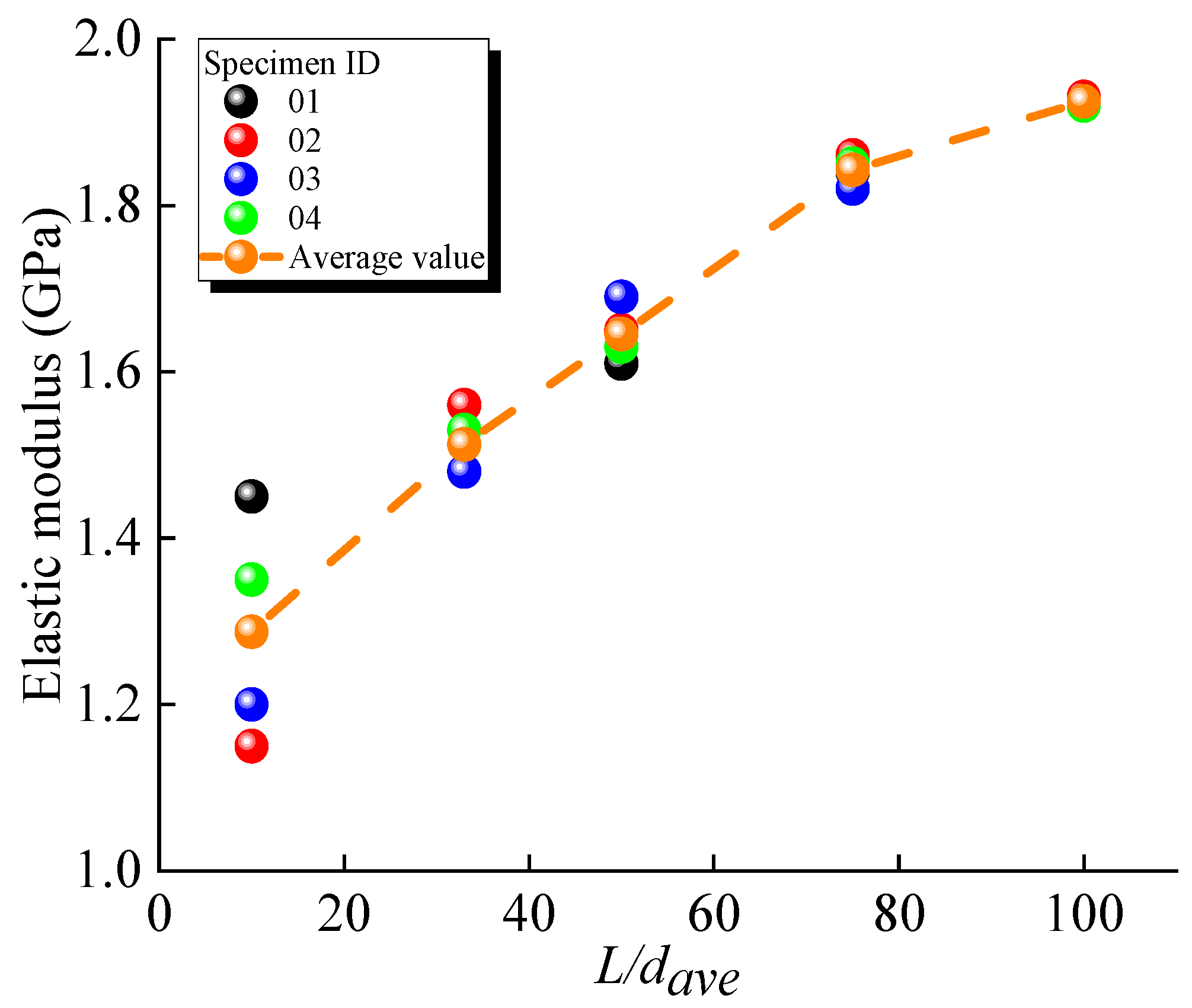
2.3. Effect of the Average Particle Size on the Elastic Modulus
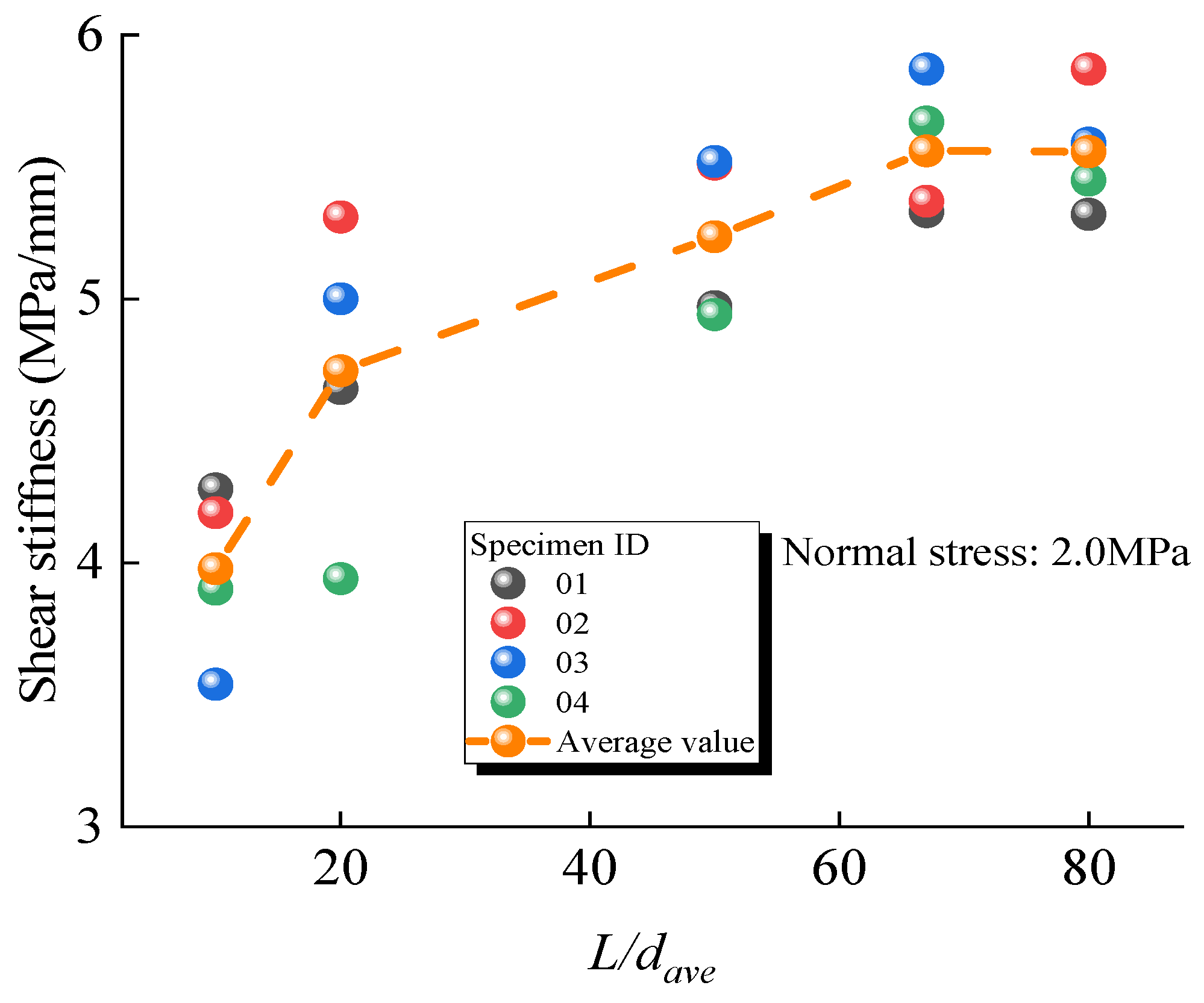
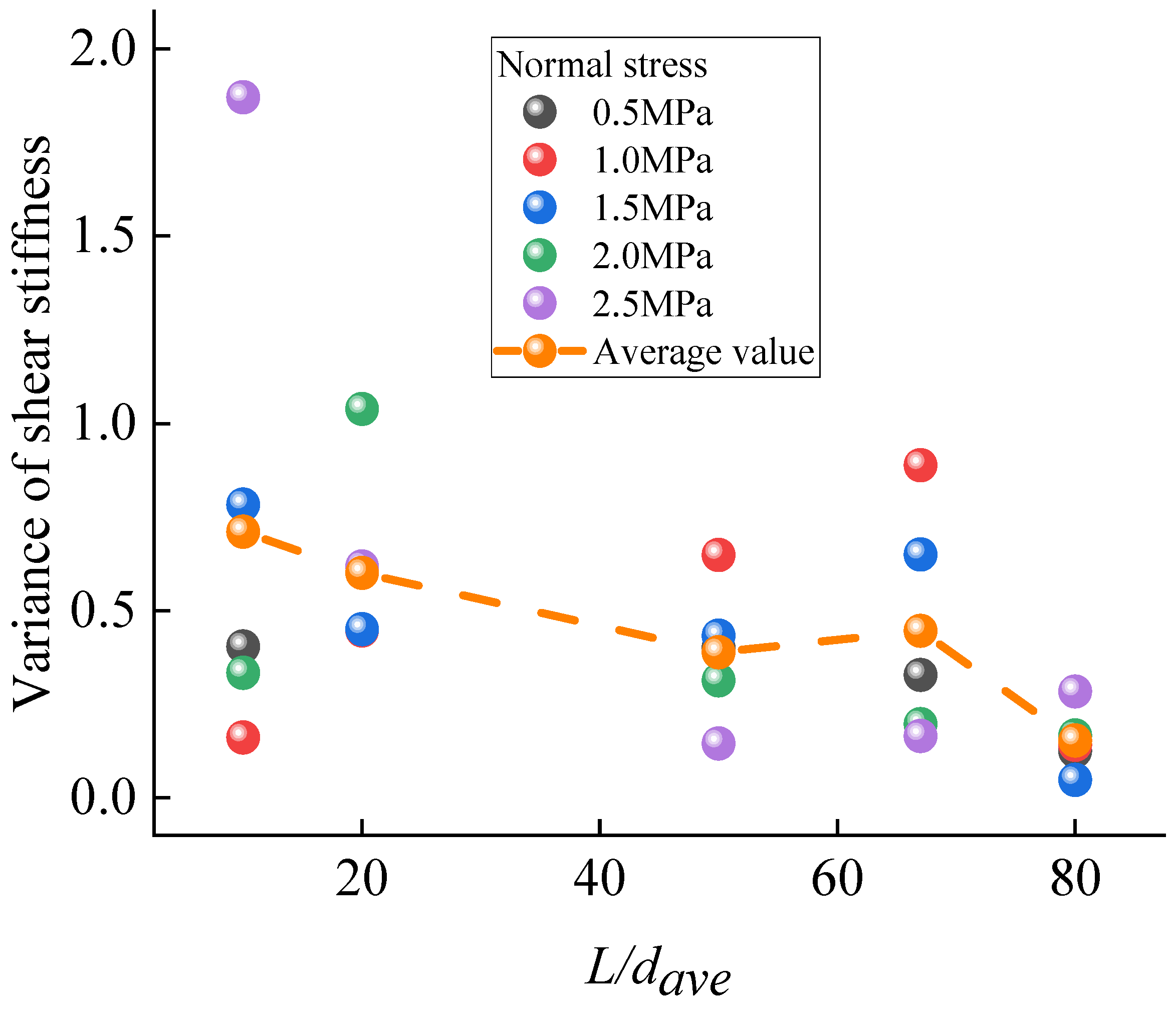
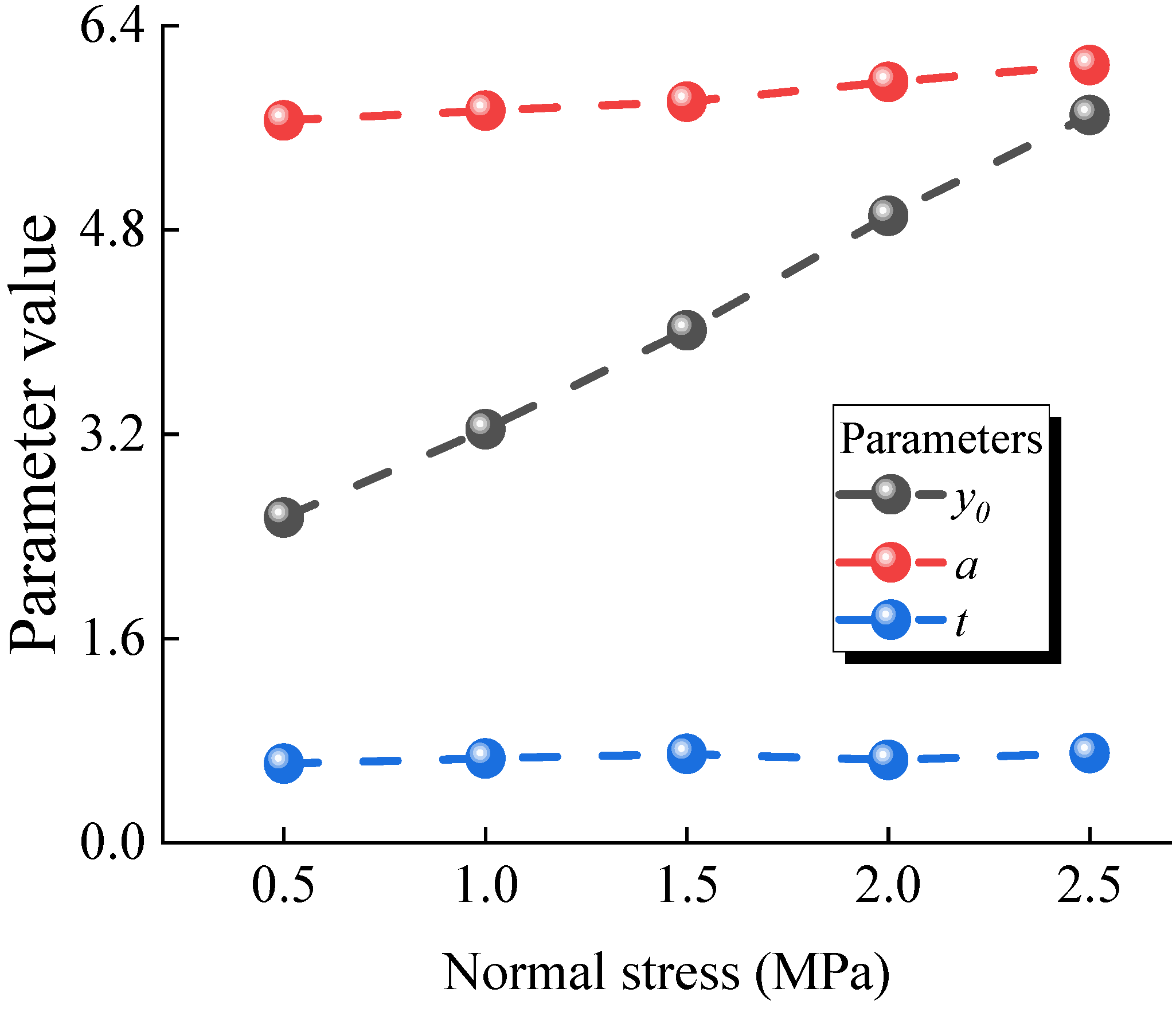
2.4. Effect of the Average Particle Size on the Model’s Shear Mechanical Behavior
2.5. Discussion
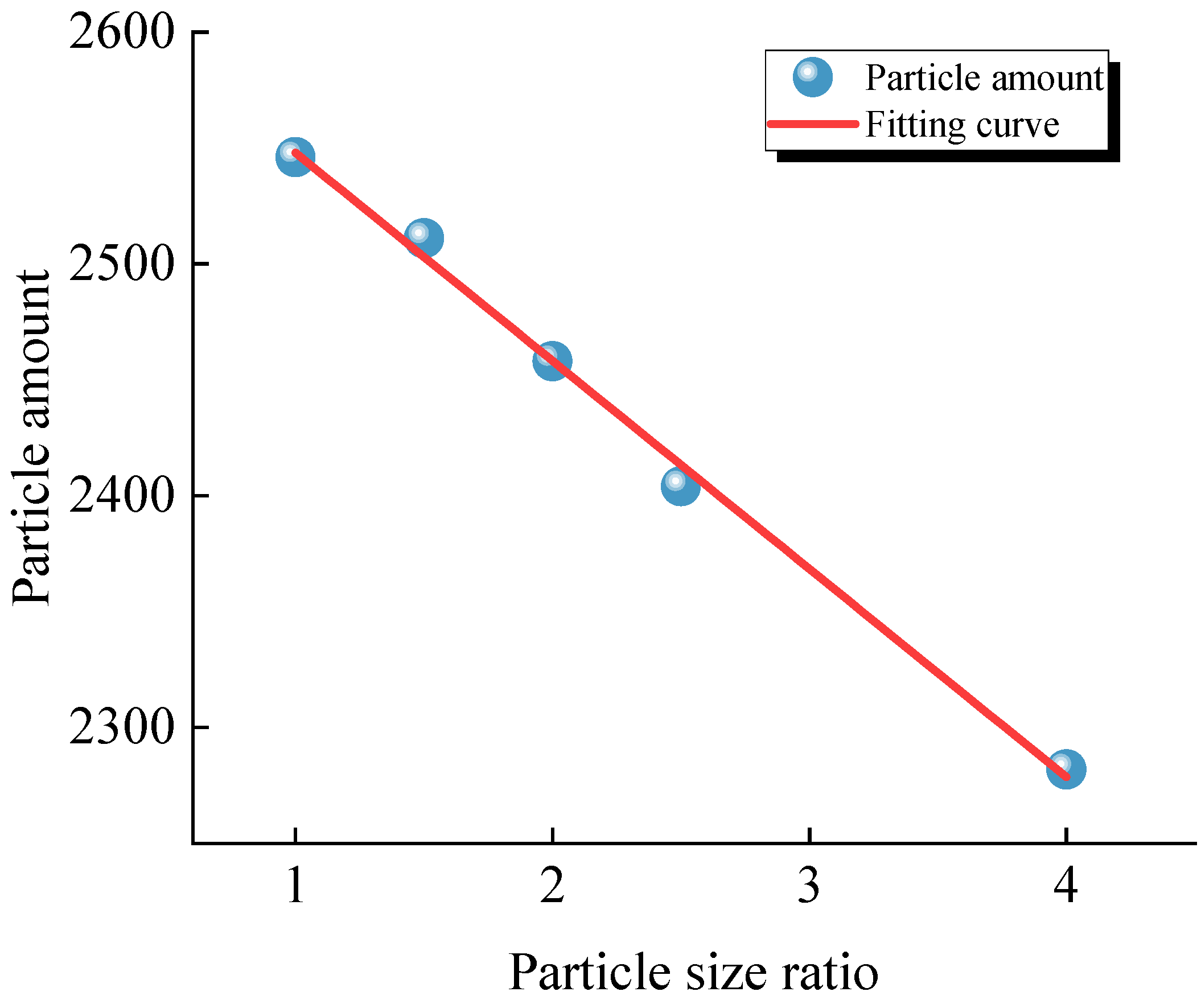
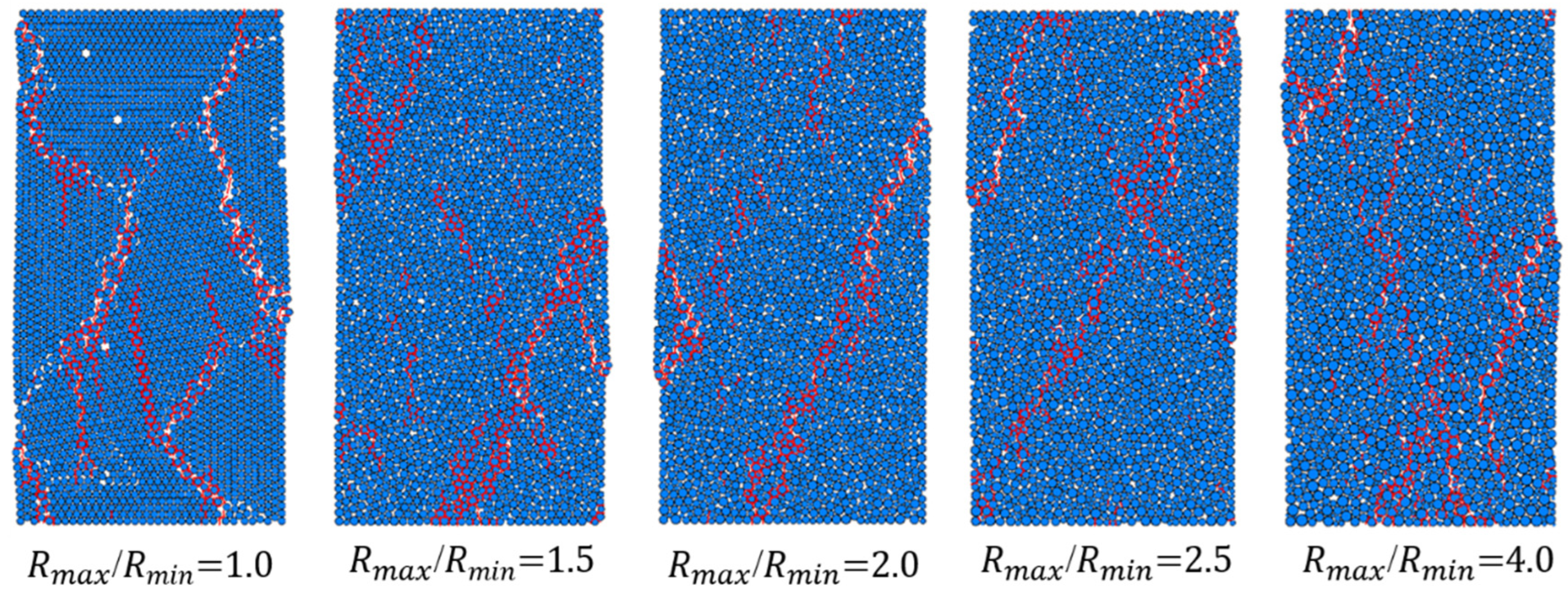
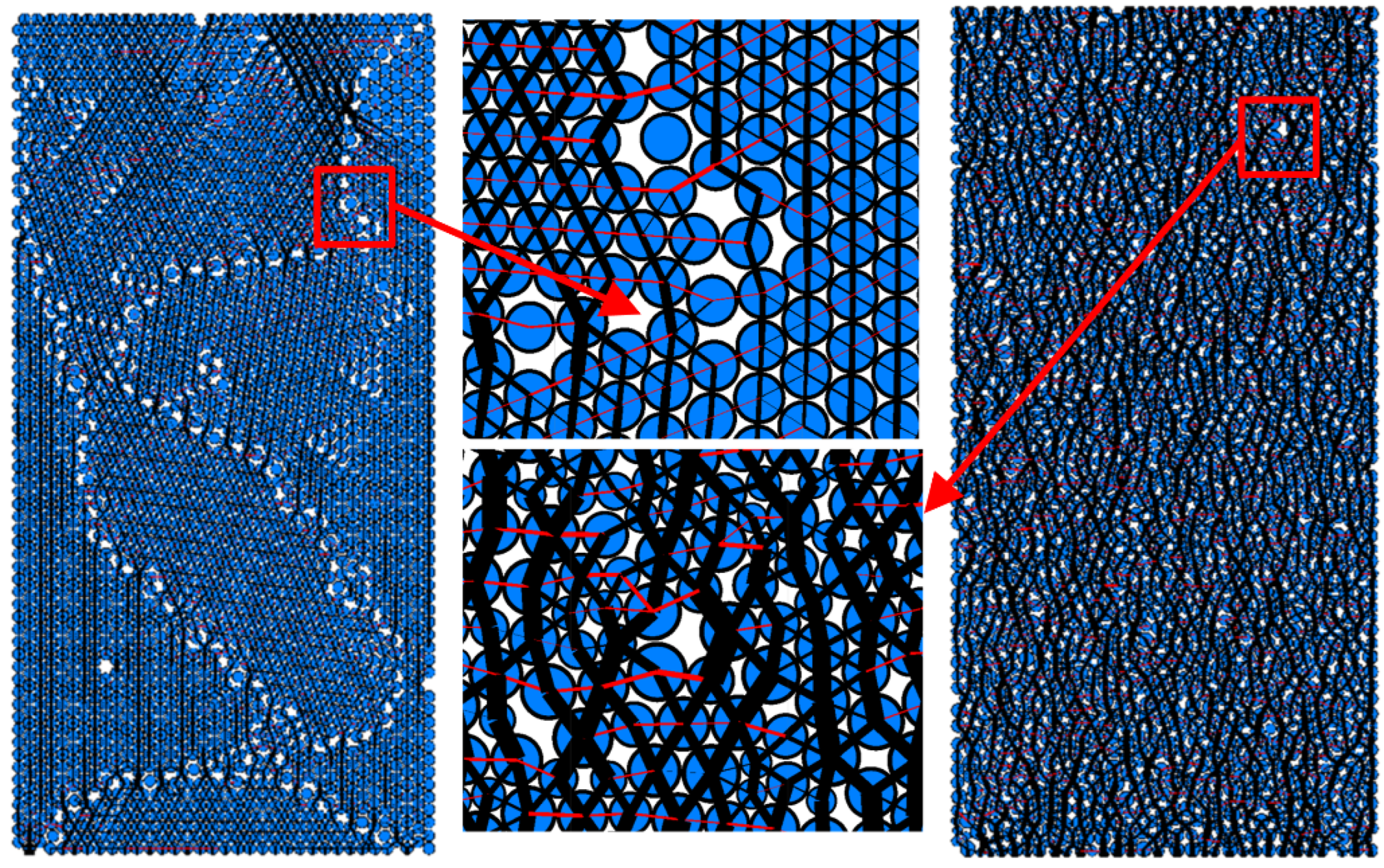
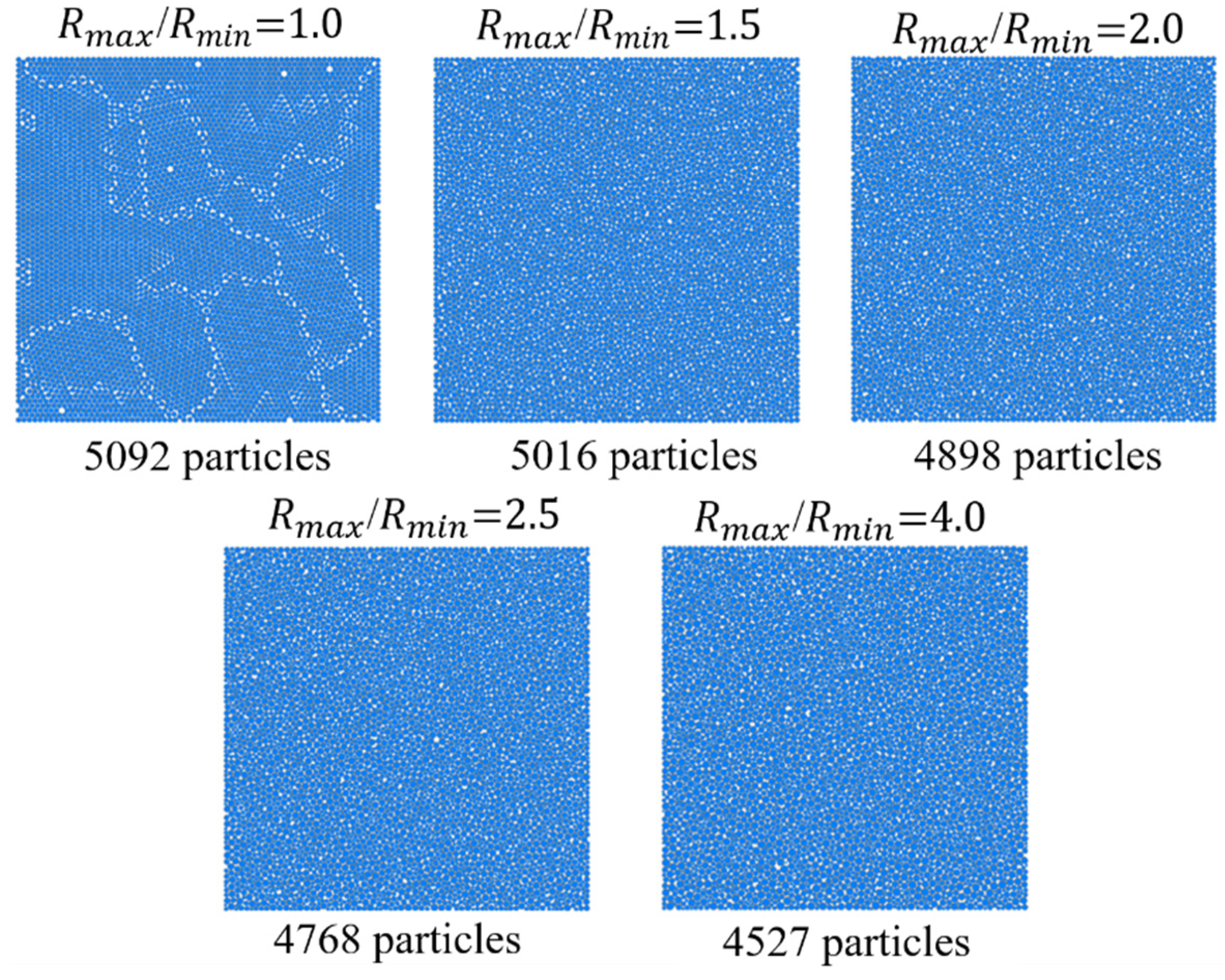
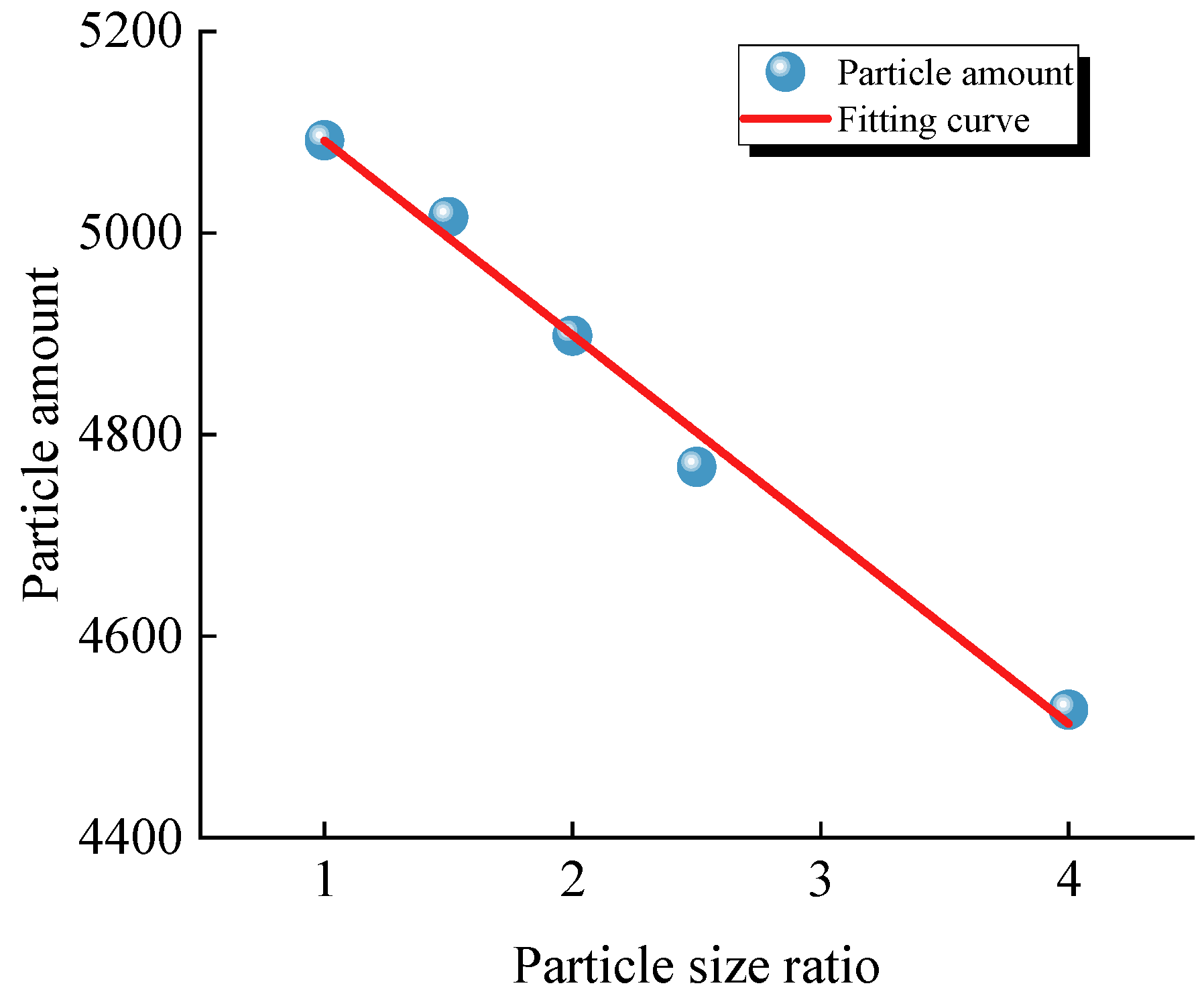
3. Effect of the Particle Size Ratio on the Macroscopic Mechanical Behavior
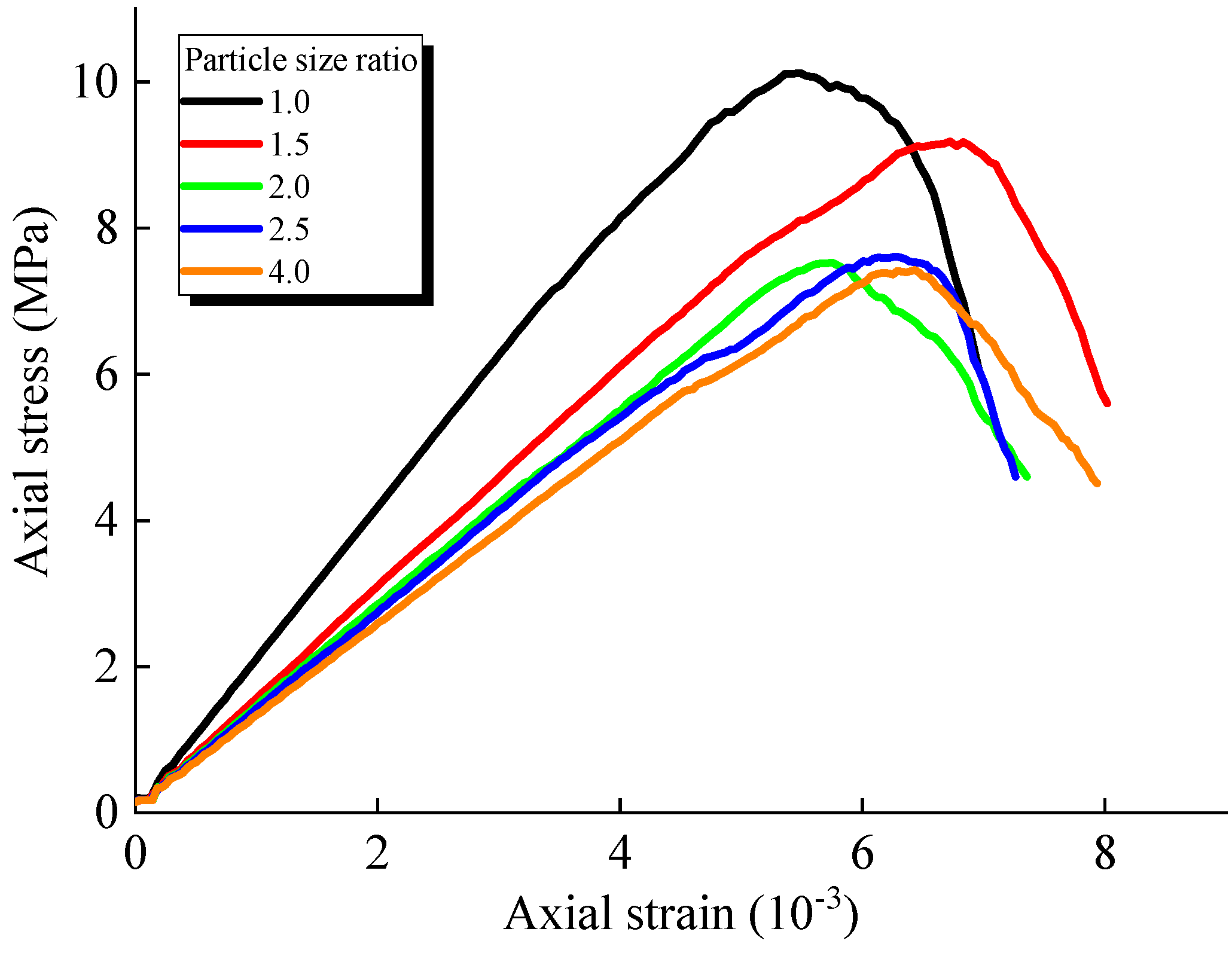
3.1. Effect of the Particle Size Ratio on the Models’ Uniaxial Compression Mechanical Behavior
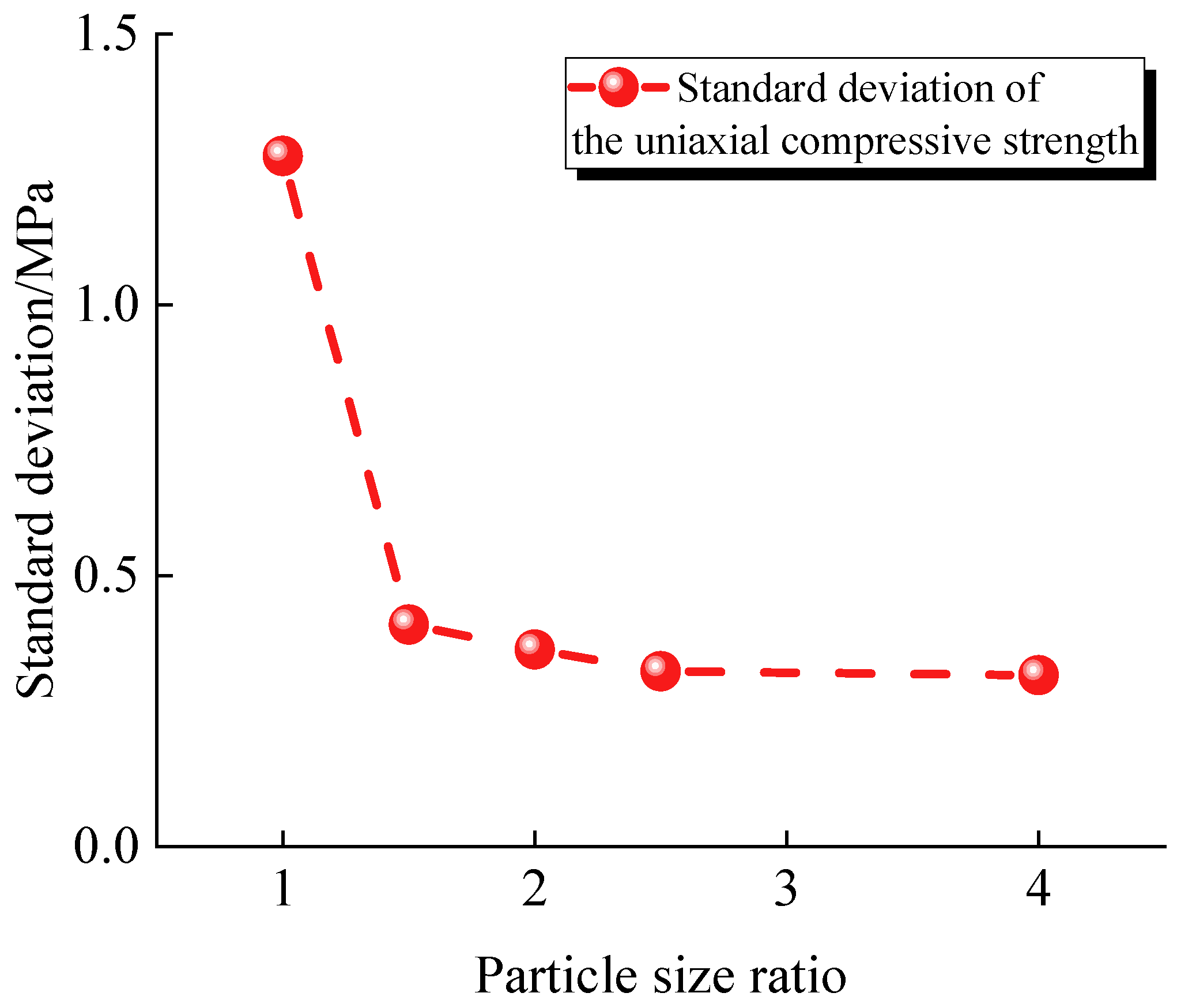
3.2. Effect of the Particle Size Ratio on the Uniaxial Compressive Strength
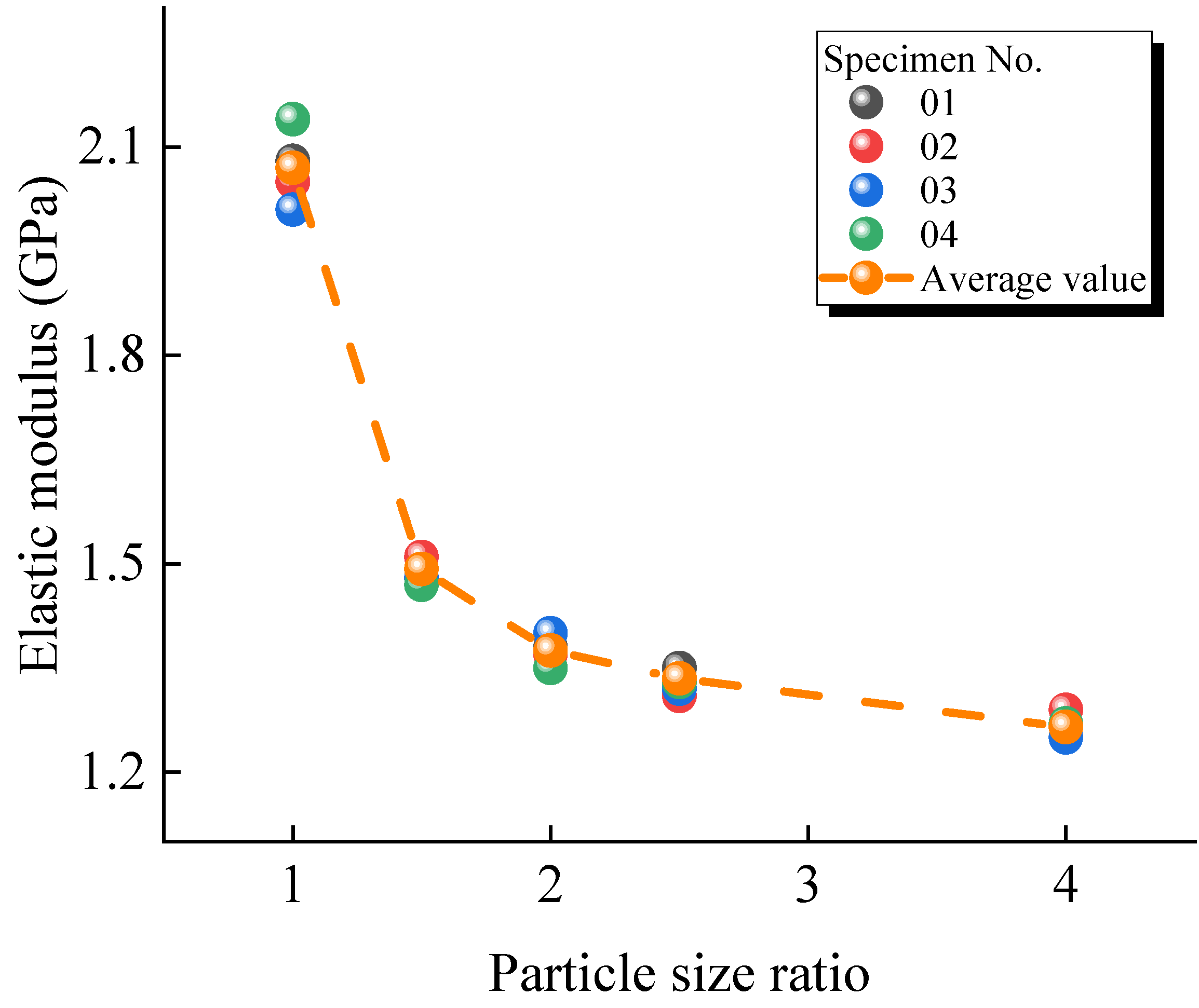
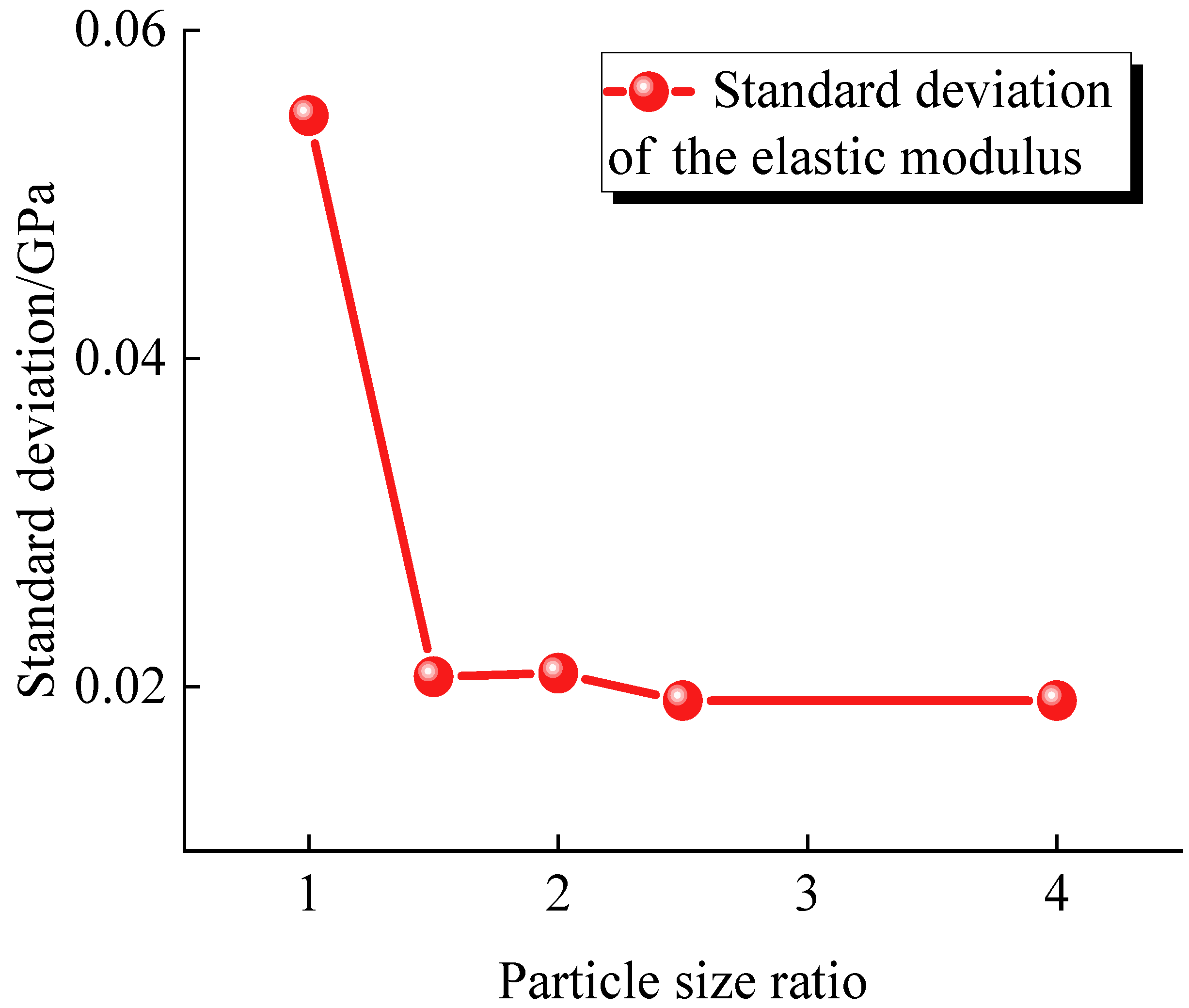
3.3. Effect of the Particle Size Ratio on the Elastic Modulus
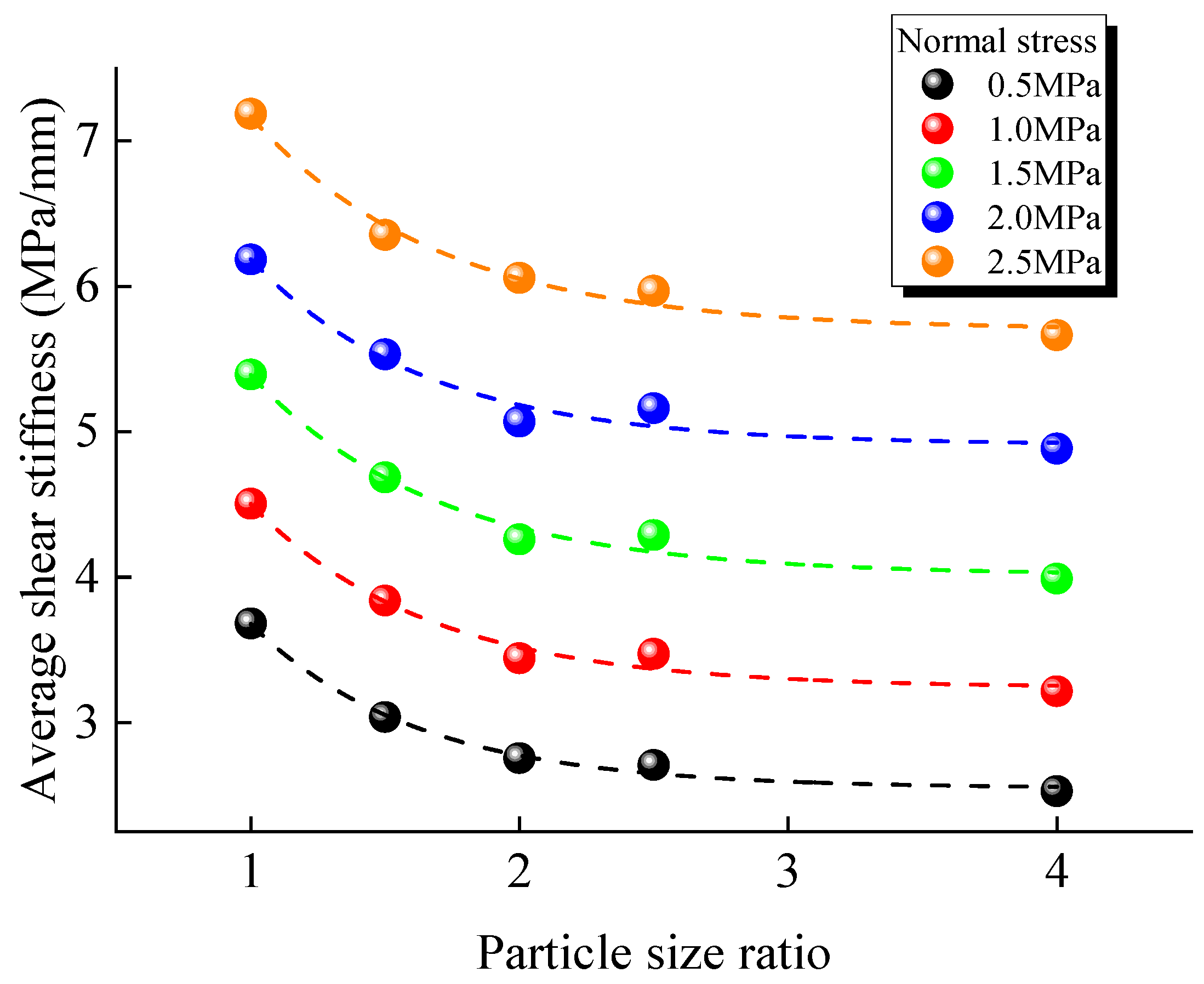
3.4. Effect of the Particle Size Ratio on the Models’ Shear Mechanical Behavior
3.5. Discussion
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Effect of the particle size on the mechanical properties—The results demonstrate that decreasing the particle size (increasing L/dave) leads to a denser packing of particles within the model, thereby enhancing the mechanical properties. Specifically, the uniaxial compressive strength increases by 62.7% and the elastic modulus increases by 49.6% as L/dave increases from 10 to 100. The shear stiffness also increases by approximately 40% as L/dave increases from 10 to 80.
- (2)
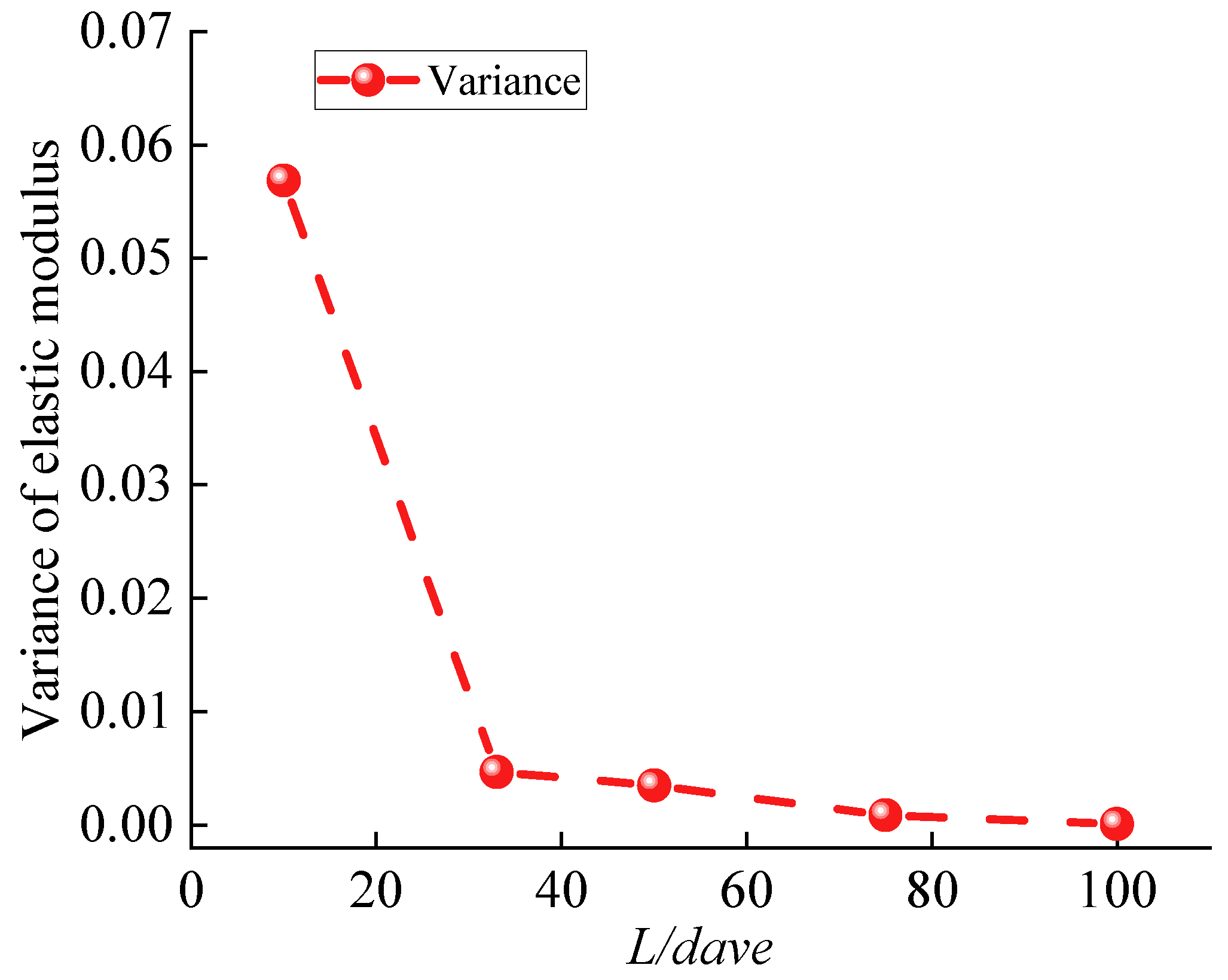
- Reduction in the dispersion of mechanical properties—The dispersion of the compressive strength, elastic modulus, and shear stiffness decreases significantly with increasing L/dave. When L/dave increases from 10 to 100, the dispersion of compressive strength decreases by 88.51%, the dispersion of the elastic modulus decreases by 99.82%, and the dispersion of shear stiffness decreases by 71.87%. This indicates that smaller particle sizes result in more uniform and reliable numerical simulation results. Setting L/dave greater than 50 is recommended to ensure the reliability of the numerical simulations.
- (3)
- Effect of the particle size ratio on the mechanical properties—Increasing the particle size ratio enhances the particle gradation but reduces the uniaxial compressive strength and elastic modulus. When the particle size ratio increases from 1.0 to 4.0, the uniaxial compressive strength decreases by 29.10% and the elastic modulus decreases by 38.89%. However, the dispersion of mechanical properties is significantly reduced when the particle size ratio is greater than 1.5. This suggests that a particle size ratio greater than 1.5 should be used to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the numerical simulations.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khosravi, M.; Tabasi, S.; Hossam Eldien, H.; Motahari, M.R.; Alizadeh, S.M. Evaluation and prediction of the rock static and dynamic parameters. J. Appl. Geophys. 2022, 199, 104581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, G.; Gaines, S. Evaluation of stress path and load rate effects on rock strength using compression testing data for Stanstead Granite. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2023, 169, 105455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lyu, C.; Lu, G.; Shi, X.; Li, H.; Liang, C.; Deng, C. Evaluating a new method for direct testing of rock tensile strength. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2022, 160, 105258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakov, A.V.; Pryazhnikov, M.I.; Suleymana, Y.N.; Meshkova, V.D.; Guzei, D.V. Experimental study of nanoparticle size and material effect on the oil wettability characteristics of various rock types. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 327, 114906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Ren, S.; Xu, H.; Luo, S.; Tao, Z.; Zhu, C. Experimental study on the shear performance of quasi-NPR steel bolted rock joints. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 15, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, J.; Shi, Z.; Chen, J.; Lin, H. Fatigue characteristics and fracture behaviour of sandstone under discontinuous multilevel constant-amplitude fatigue disturbance. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2022, 274, 108773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lin, H.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Mechanical behavior of rock-like specimen containing hole-joint combined flaw under uniaxial loading: Findings from DIC and AE monitoring. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 3426–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decký, M.; Remišová, E.; Mečár, M.; Bartuška, L.; Lizbetin, J.; Drevený, I. In situ Determination of Load Bearing Capacity of Soils on the Airfields. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 15, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bandis, S.; Lumsden, A.; Barton, N. Experimental studies of scale effects on the shear behaviour of rock joints. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. Geomech. Abstr. 1981, 18, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barton, N.; Choubey, V. The shear strength of rock joints in theory and practice. Rock Mech. 1977, 10, 1–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, R.; Qin, J.B.; Huang, M.; Du, S.G.; Liu, J.; Hu, G.J. An Innovative Sampling Method for Determining the Scale Effect of Rock Joints. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2018, 52, 935–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardin, N.; Feng, Q.; Stephansson, O. Application of a new in situ 3D laser scanner to study the scale effect on the rock joint surface roughness. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2004, 41, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fardin, N.; Stephansson, O.; Jing, L. The scale dependence of rock joint surface roughness. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2001, 38, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishaan Lilienthal, G.; Zhong, Y.; Makhnenko, R.Y. Fracture process zone in crystalline rock: Effect of specimen size and shape. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2023, 128, 104118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sheng, B.; Xie, S.; Cao, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, H. Crack propagation and scale effect of random fractured rock under compression-shear loading. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 5164–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Sun, J.; Lai, Y.; Wei, C.; Hou, J.; Bai, S.; Huang, X.; Liu, H.; Xiong, K.; Cheng, S. Study on size effect of jointed rock mass and influencing factors of the REV size based on the SRM method. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 127, 104613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhimi, A.; Alavi Gharahbagh, E. Discrete element analysis of the effect of pore size and pore distribution on the mechanical behavior of rock. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Tan, C.; Nie, Z.; Ma, W.; Chen, D.; Sun, Q. Multi-dimensional size effects and representative elements for non-persistent fractured rock masses: A perspective of geometric parameter distribution. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2023, 15, 2339–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sangsefidi, M.; Akbardoost, J.; Zhaleh, A.R. Assessment of mode I fracture of rock-type sharp V-notched samples considering the size effect. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2021, 116, 103136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; An, D.; Yu, B. Experimental study on development characteristics and size effect of rock fracture process zone. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 241, 107377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, P.; Ashrafi, M.J.; Fakhimi, A. Physical and numerical evaluation of effect of specimen size on dynamic tensile strength of rock. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 142, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, L.; Ding, X. Study of scale effect on intact rock strength using particle flow modeling. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 2011, 48, 1320–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahaaddini, M.; Hagan, P.C.; Mitra, R.; Hebblewhite, B.K. Scale effect on the shear behaviour of rock joints based on a numerical study. Eng. Geol. 2014, 181, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, W.; He, D. Influence of structural plane microscopic parameters on direct shear strength. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2018, 2018, 9178140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.-h.; Yao, R.; Lin, H.; Lin, Q.-b.; Meng, Q.; Li, T. Shear behaviour of 3D nonpersistent jointed rock-like specimens: Experiment and numerical simulation. Comput. Geotech. 2022, 148, 104858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, R.-h.; Yao, R.; Hu, T.; Wang, C.; Li, K.; Meng, J. Failure and mechanical behavior of transversely isotropic rock under compression-shear tests: Laboratory testing and numerical simulation. Eng. Fract. Mech. 2021, 241, 107389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Cao, P.; Liu, Y.; Cao, R.; Li, J. Mechanical behaviour of a jointed rock mass with a circular hole under compression-shear loading: Experimental and numerical studies. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2021, 114, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Li, Q.; Yu, B.; Huang, C.; Gao, Z. Mechanical behavior and failure characteristics of rock with double holes. Structures 2023, 54, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Dou, L.; Zhang, S.; Cui, X.; Xing, Q.; Li, J. Numerical study of the influence of grain size and heterogeneity on thermal cracking and damage of granite. Geoenergy Sci. Eng. 2024, 233, 212507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Wong, L.N.Y.; Teh, C.I. Influence of grain size on strength of polymineralic crystalline rock: New insights from DEM grain-based modeling. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 13, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Qi, Z. Effect of Model Scale and Particle Size Distribution on PFC3D Simulation Results. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2014, 47, 2139–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi, P.; Fakhimi, A. Bonded particle modeling of grain size effect on tensile and compressive strengths of rock under static and dynamic loading. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 104013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Bayona, F.; Johansson, F.; Mas-Ivars, D.; Sánchez-Juncal, A.; Bolin, A. Using PFC2D to simulate the shear behaviour of joints in hard crystalline rock. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2022, 81, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Ou, K. Shear Mechanical Properties of Rock Joints Under Non-Uniform Load Based on DEM. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, H.; Ding, X.; Xie, S. Scale effect of shear mechanical properties of non-penetrating horizontal rock-like joints. Environ. Earth Sci. 2021, 80, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
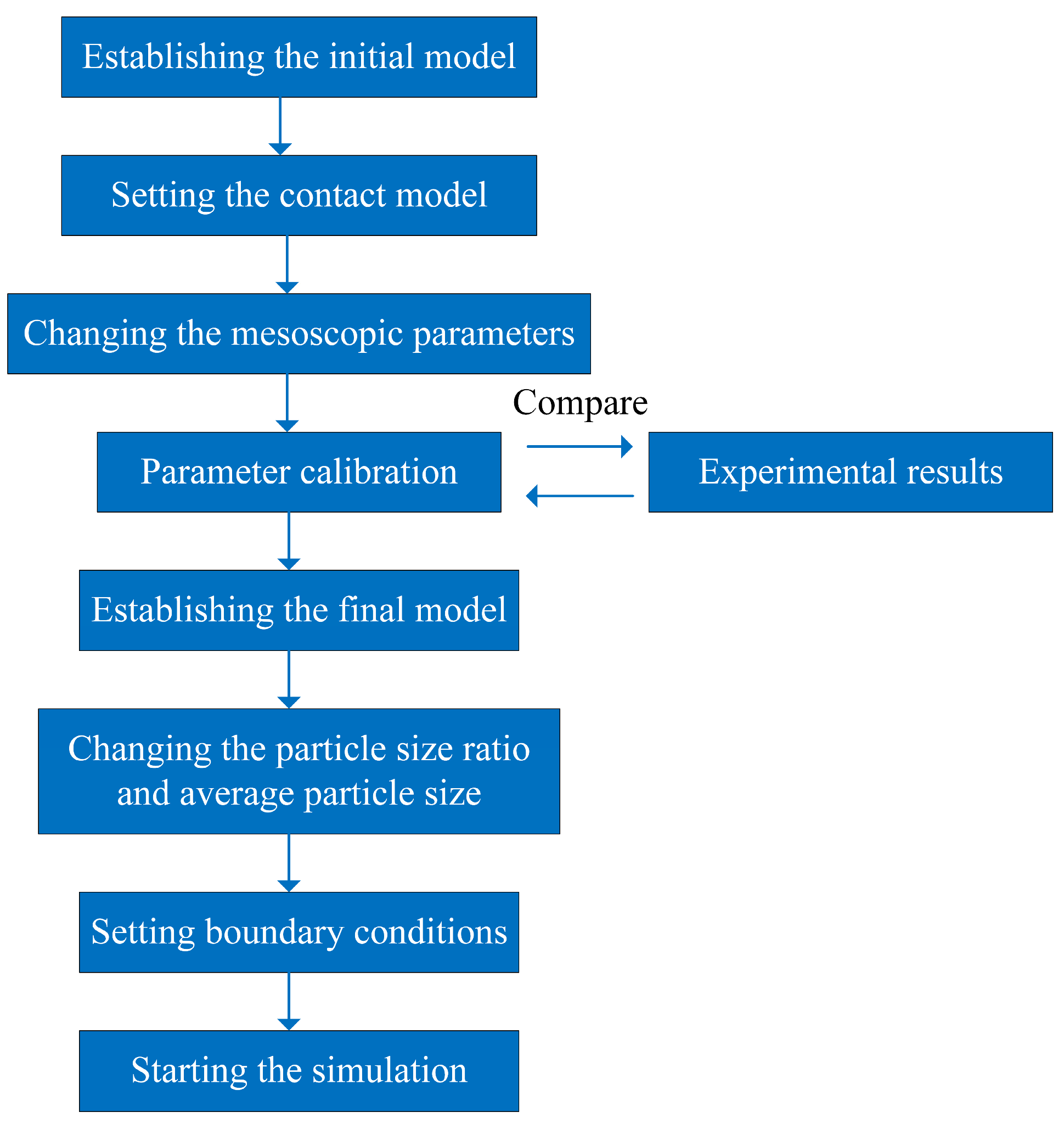
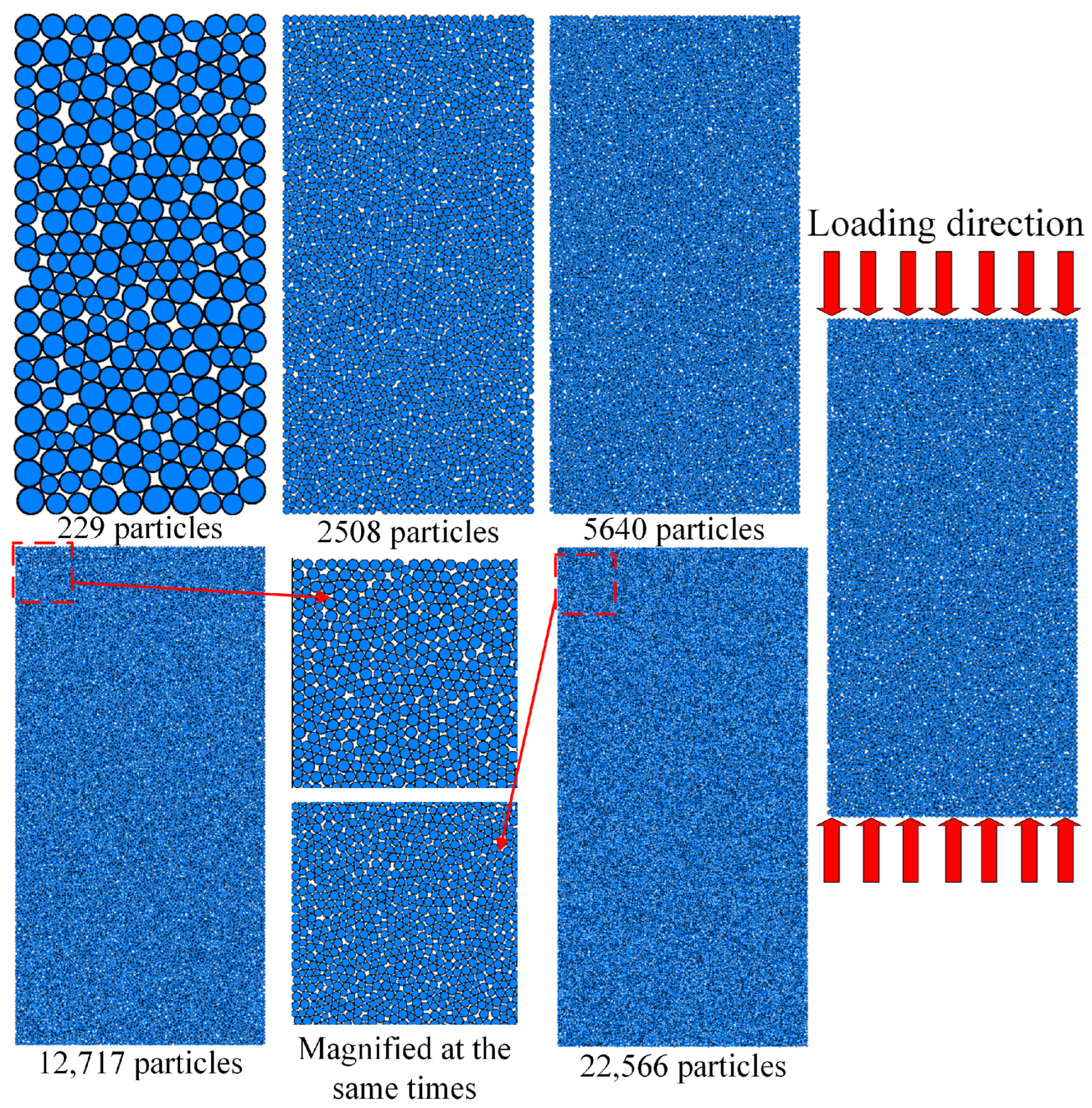

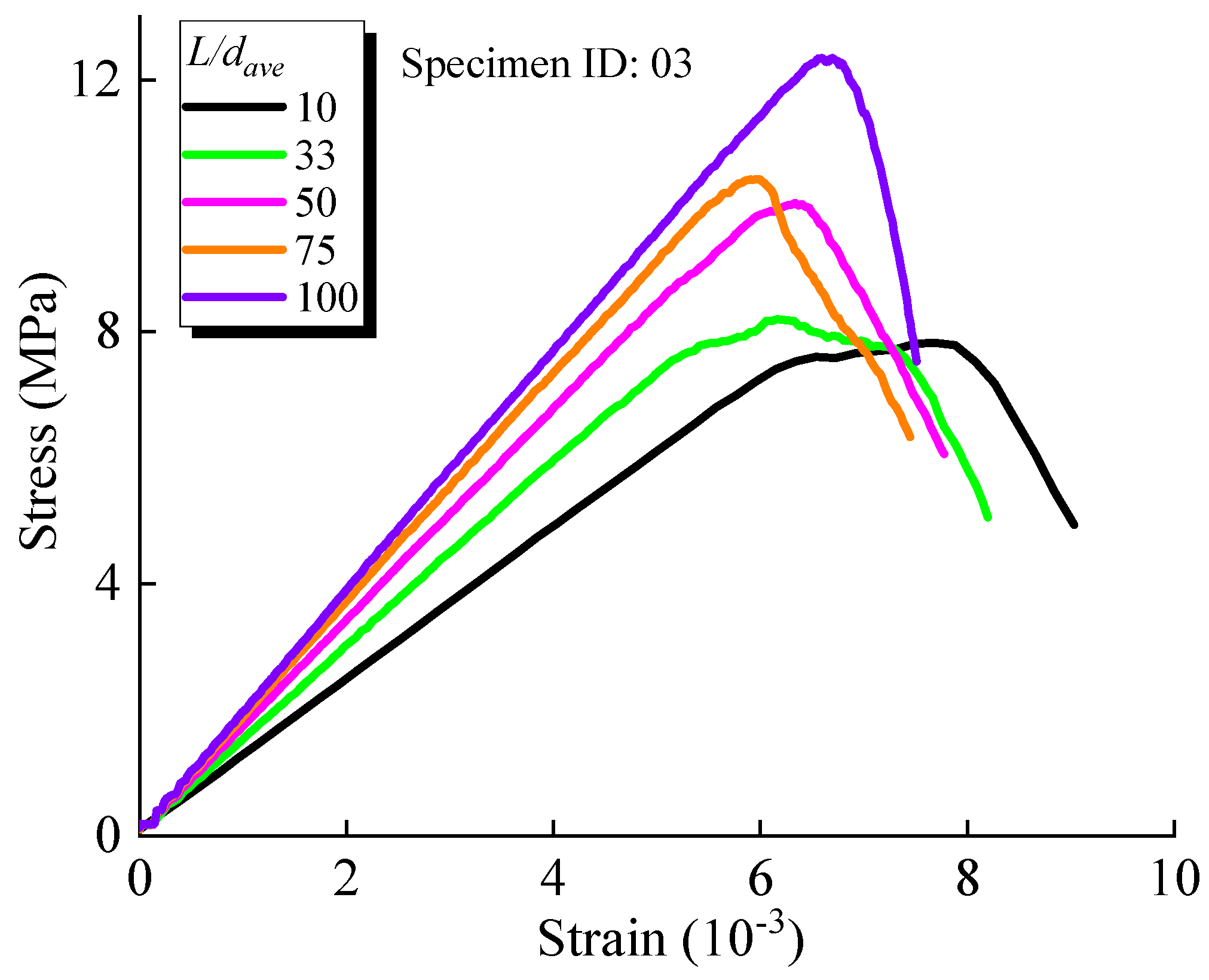

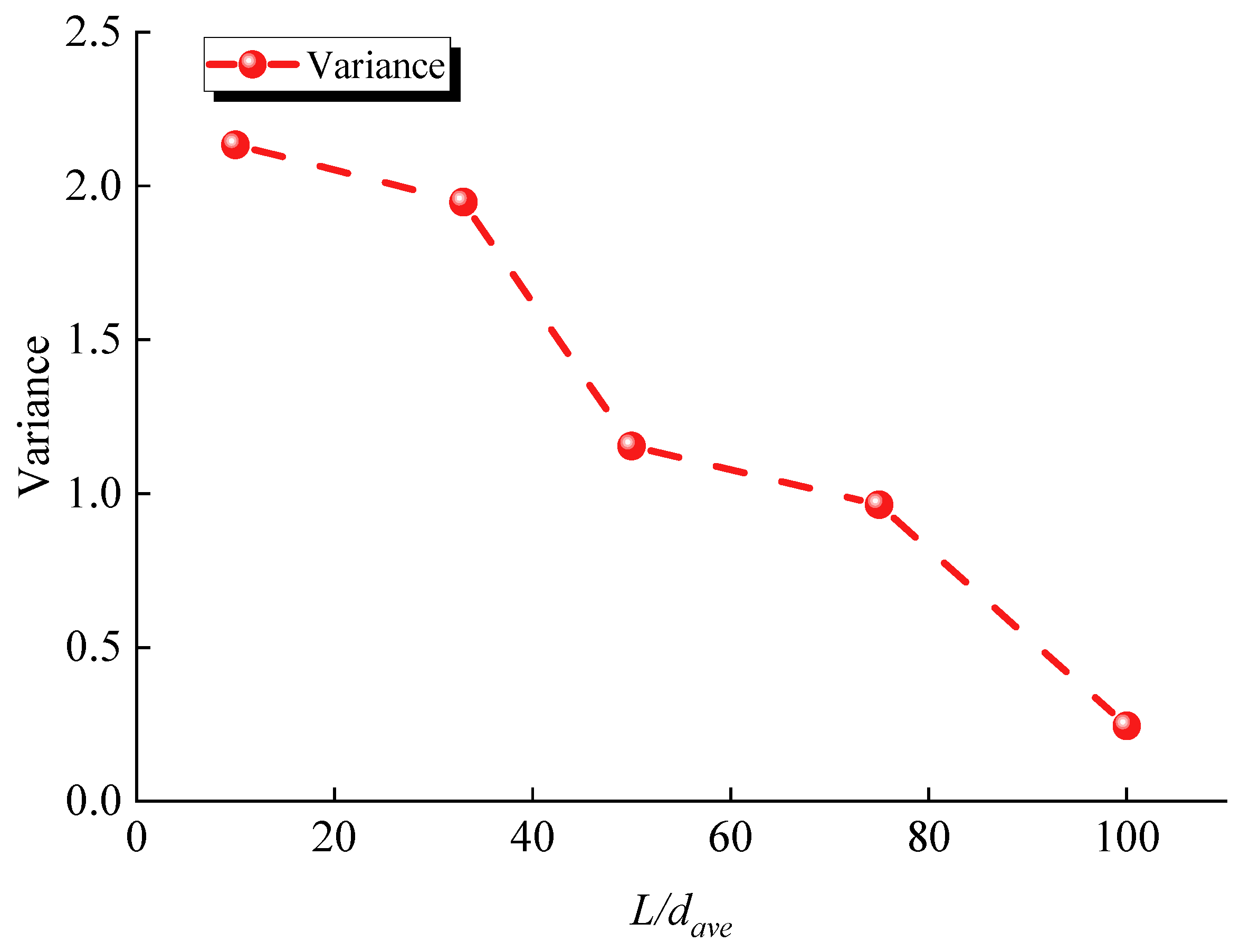


| Parameter Type | Mesoscopic Parameters | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Particles’ basic parameters | Particle density (kg/m3) | 2020 |
| Porosity | 0.1 | |
| Particle radius ratio | 1.5 | |
| Contact modulus (GPa) | 1.95 | |
| Stiffness ratio | 1.5 | |
| Friction coefficient | 5.5 | |
| Parallel bonding parameters | Parallel bonding modulus (MPa) | 30 |
| Parallel bonding stiffness ratio | 3.0 | |
| Parallel bonding normal strength (MPa) | 1.6 | |
| Parallel bonding cohesion (MPa) | 1.68 | |
| Parallel bonding internal friction angle (°) | 55.3 |
| Specimen ID | Particle Size Range () (mm) | |
|---|---|---|
| 01, 02, 03, 04 | 2.0~3.0 | 10 |
| 0.6~0.9 | 33 | |
| 0.4~0.6 | 50 | |
| 0.267~0.4 | 75 | |
| 0.2~0.3 | 100 |
| L/dave | Compressive Strength Range (MPa) | Percentage of the Range of Average Strength |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 1.99 | 26.5% |
| 33 | 1.72 | 19.3% |
| 50 | 1.51 | 15.1% |
| 75 | 1.23 | 10.9% |
| 100 | 0.55 | 4.5% |
| L/dave | Elastic Modulus Range (GPa) | Percentage of the Range of the Average Elastic Modulus |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.30 | 23.3% |
| 33 | 0.08 | 5.3% |
| 50 | 0.08 | 4.9% |
| 75 | 0.04 | 2.2% |
| 100 | 0.01 | 0.5% |
| Specimen ID | ) (mm) | L/dave | Normal Stress (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01, 02, 03, 04 | 4.0~6.0 | 10 | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 |
| 2.0~3.0 | 20 | ||
| 0.8~1.2 | 50 | ||
| 0.6~0.9 | 67 | ||
| 0.5~0.75 | 80 |
| L/dave | Normal Stress | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 MPa | 1.0 MPa | 1.5 MPa | 2.0 MPa | 2.5 MPa | |
| 10 | 2.52 | 2.89 | 3.14 | 3.98 | 4.35 |
| 20 | 2.70 | 3.31 | 4.01 | 4.73 | 5.49 |
| 50 | 2.86 | 3.67 | 4.42 | 5.24 | 6.05 |
| 67 | 3.01 | 3.79 | 4.63 | 5.56 | 6.34 |
| 80 | 3.32 | 3.90 | 4.65 | 5.56 | 6.44 |
| Increasing ratio | 31.75% | 34.95% | 48.09% | 39.70% | 48.05% |
| Specimen ID | Particle Size Range () (mm) | Particle Size Ratio Rmas/Rmin |
|---|---|---|
| 01, 02, 03, 04 | 0.75~0.75 | 1.0 |
| 0.6~0.9 | 1.5 | |
| 0.5~1.0 | 2.0 | |
| 0.429~1.0725 | 2.5 | |
| 0.3~1.2 | 4.0 |
| Specimen ID | Particle Size Range (mm) | Normal Stress (MPa) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 01, 02, 03, 04 | 0.75~0.75 | 1.0 | 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 2.5 |
| 0.6~0.9 | 1.5 | ||
| 0.5~1.0 | 2.0 | ||
| 0.429~1.0725 | 2.5 | ||
| 0.3~1.2 | 4.0 |
| Normal Stress | 0.5 MPa | 1.0 MPa | 1.5 MPa | 2.0 MPa | 2.5 MPa | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | ||||||
| 2.55 | 3.24 | 4.02 | 4.91 | 5.70 | ||
| 5.66 | 5.74 | 5.81 | 5.96 | 6.09 | ||
| 0.62 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.65 | 0.70 | ||
| (COD) | 0.994 | 0.983 | 0.982 | 0.971 | 0.987 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Li, S.; Feng, X.; Li, Z.; Ding, X.; Lin, H. Numerical Analysis of the Effect of the Rock Particle Size on the Macroscopic Mechanical Properties Under Uniaxial Compression and Shearing. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094882
Yang C, Li S, Feng X, Li Z, Ding X, Lin H. Numerical Analysis of the Effect of the Rock Particle Size on the Macroscopic Mechanical Properties Under Uniaxial Compression and Shearing. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094882
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chaoyi, Su Li, Xinglong Feng, Zhengrong Li, Xuran Ding, and Hang Lin. 2025. "Numerical Analysis of the Effect of the Rock Particle Size on the Macroscopic Mechanical Properties Under Uniaxial Compression and Shearing" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094882
APA StyleYang, C., Li, S., Feng, X., Li, Z., Ding, X., & Lin, H. (2025). Numerical Analysis of the Effect of the Rock Particle Size on the Macroscopic Mechanical Properties Under Uniaxial Compression and Shearing. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4882. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094882







