A Comprehensive Analysis of Radiological Parameters in Historical City Soil: The Case of Mardin, Turkiye
Abstract
1. Introduction
| Sources | Dose Ranges | World Averages |
|---|---|---|
| Inhalation (Rn-222) | 0.20–10.00 | 1.26 |
| Cosmic Rays | 0.30–1.00 | 0.39 |
| Terrestrial Gamma Rays | 0.30–1.00 | 0.48 |
| Ingestion (K-40) | 0.20–1.00 | 0.29 |
| Total | 1.00–13.00 | 2.40 |

2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation and Measurements of Gamma Spectrometry
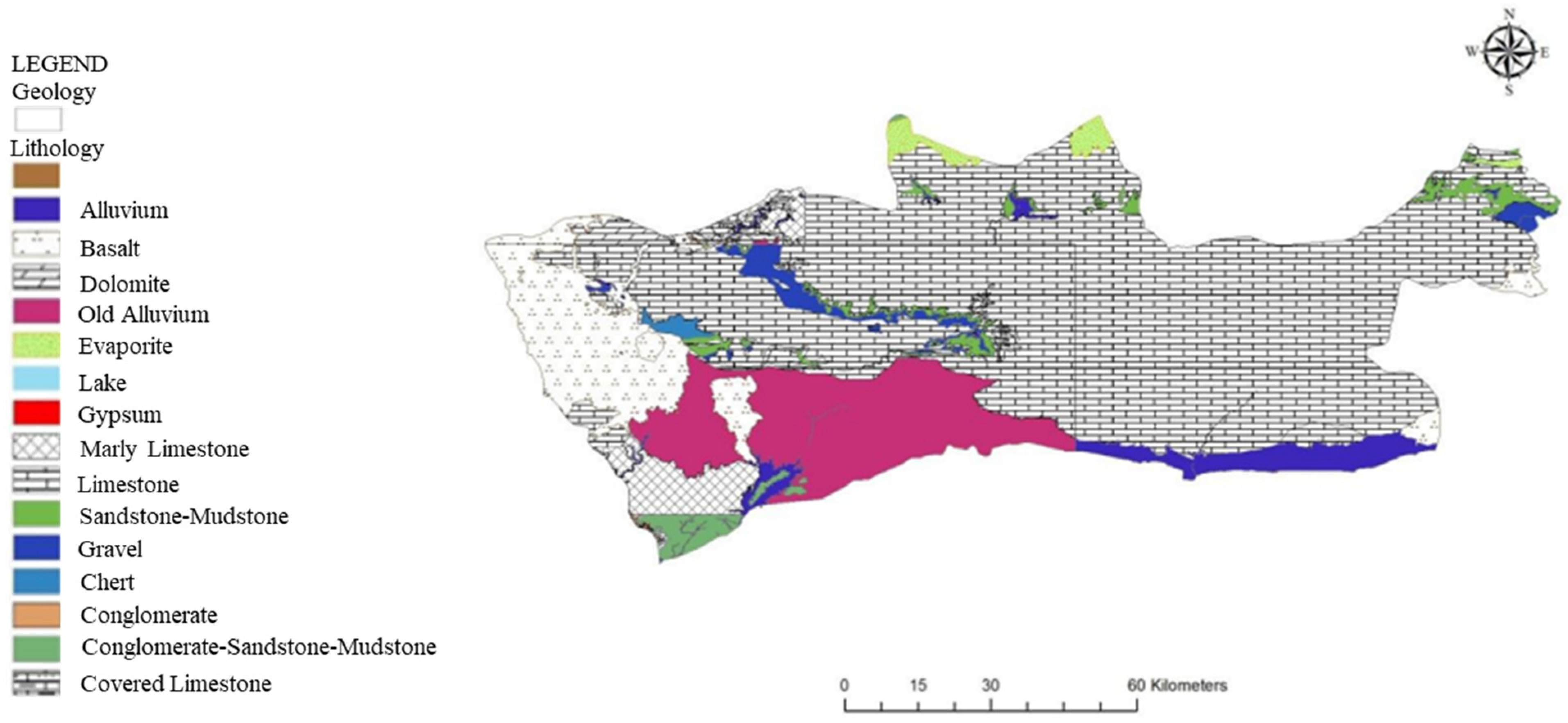
2.2. Geology
2.3. Radiological Hazard Determination
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- United National Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, UNSCEAR 2000 Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, Volume I: Sources; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ojovan, M.I.; Lee, W.E.; Kalmykov, S.N. Chapter 5—Background Radiation. In An Introduction to Nuclear Waste Immobilisation, 3rd ed.; Ojovan, M.I., Lee, W.E., Kalmykov, S.N., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United National Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation (UNSCEAR). Sources and Effects of Ionizing Radiation, United Nations Scientific Committee on the Effects of Atomic Radiation, UNSCEAR 2008 Report to the General Assembly with Scientific Annexes, Volume I: Sources; United Nations: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.-C.; Zeng, F.-C.; Lin, C.-C.; Yeh, Y.-L.; Huang, W.-H. Assessment of Soil Radioactivity Associated with Risk and Correlation with Soil Properties near Maanshan Nuclear Power Plant, Taiwan. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 9239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khawlay, A.H.; Khan, A.R.; Pathan, J.M. Radiological and health hazards resulting from radioactivity and elemental composition of some soil samples. Pol. J. Med. Phys. Eng. 2020, 26, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, V.; Rani, A.; Mehra, R.; Ramola, C. Assesment of Natural Radioactivity Levels and Associated Dose Rate in Soil Samples from Northern Rajasthan, India. J. Rad. Prot. Dosim. 2013, 158, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, J.; Singh, H.; Singh, S.; Bajwa, B.S.; Sonkawade, R.G. Comparative study of natural radioactivity levels in soil samples from the Upper Siwaliks and Punjab, India usinggamma-ray spectrometry. J. Environ. Radio-Act. 2009, 100, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohakwere-Eze, M.C.; Nafiu, M.; Singh, S.K.; Kabiru, M.; Simon, J. Assessment of Natural Radioactivity and Radiation Hazard in Soil and Rock Samples from Mining Sites within North-Eastern Nigeria. Phys. Access 2024, 4, 74–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidane, Y.B.; Deressu, T.T.; Belete, G.D. Evaluation of Natural Radioactivity Level in Surface Soil from Bambasi District in Benishangul Gumuz Region, Ethiopia. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2024, 2024, 6633673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yameogo, Z.; Nabayaogo, D.; Kabore, O.; Bangou, C.; Zebo, I.; Zoungrana, M. Measurements of natural radioactivity and exposure rates in soil samples from Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso. J. Mater. Environ. Sci. 2022, 13, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Jasaitis, D.; Vigilija Klima, V.; Pečiulienė, M.; Vasiliauskienė, V.; Konstantinova, M. Comparative Assessment of Radiation Background Due to Natural and Artificial Radionuclides in Soil in Specific Areas on the Territories of State of Washington (USA) and Lithuania. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2020, 231, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joel, E.; Omeje, M.; Olawole, O.; Adeyemi, G.; Akinpelu, A.; Embong, Z.; Saeed, M. In-situ assessment of natural terrestrial-radioactivity from Uranium-238 (238U), Thorium-232 (232Th) and Potassium-40 (40K) in coastal urban-environment and its possible health implications. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamislioglu, M.; Eke, C.; Kocak, I.; Buyuk, B.; Ozaydin Ozkara, R.; Temiz, U. Investigation of natural and artificial radioactivity levels in travertines of the Cappadocia region in Turkey. Environ. Geochem. Health 2024, 46, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uğur, F.A.; Turhan, Ş.; Gören, E.; Gezer, F.; Yeğingil, Z.; Şahan, H.; Şahan, M.; Tel, E.; Karahan, G. A survey of distribution of terrestrial radionuclides in surface soil samples in and around Osmaniye province, Turkey. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2013, 154, 483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurnaz, A.; Küçükömeroğlu, B.; Keser, R.; Okumuşoglu, N.T.; Korkmaz, F.; Karahan, G.; Çevik, U. Determination of radioactivity levels and hazards of soil and sediment samples in Fırtına Valley (Rize. Türkiye). Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2007, 65, 1281–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cengiz, G.B.; Reşitoğlu, S. Determination of natural radioactivity levels in Kars city center, Turkey. J. Nucl. Sci. 2014, 1, 32. [Google Scholar]
- Maden, N.; Akaryalı, E.; Gücer, M.A. Excess lifetime cancer risk due to natural radioactivity in Gümüşhane Province, NE Turkey. Turk. J. Earth Sci. 2020, 29, 347–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otansev, P.; Karahan, G.; Kam, E.; Barut, I.; Taskin, H. Assessment of natural radioactivity concentrations and gamma dose rate levels in Kayseri, Turkey. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 2012, 148, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canbazoğlu, C.; Turhan, Ş.; Bakkal, S.; Uğur, F.A.; Gören, E. Analysis of gamma emitting radionuclides (terrestrial and anthropogenic) in soil samples from Kilis province in south Anatolia, Turkey. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2013, 62, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yumun, Z.; Bayrak, K.; Aksoy, H.; Aysel, U. A Study of Background Radioactivity Level For Edirne, Turkey. J. Eng. Technol. Appl. Sci. 2018, 3, 135–139. [Google Scholar]
- TUIK. Turkish Statistical Institute. 2023. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Kategori/GetKategori?p=Nufus-ve-Demografi-109 (accessed on 18 January 2025).
- Available online: https://mardin.ktb.gov.tr/TR-56480/genel-bilgiler.html (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Google Earth, Pro; Google LLC: Mountain View, CA, USA, 2025.
- TAEK (Turkey Atomic Energy Agency); Türkiye Çevresel Radyoaktivite Atlası” (in Turkish) (Turkiye Environmental Radioactivity Atlas); Oğuz, F.; Yücel, B.; Arıkan, İ.H. (Eds.) Ankara. 2013. Available online: https://kurumsalarsiv.tenmak.gov.tr/bitstreams/0dff3979-776a-4cd3-89a7-fd2d217e620b/download (accessed on 10 January 2025).
- AFAD. 2019 Report: Disaster and Emergency Management Authority of Turkey. Available online: https://webdosya.csb.gov.tr/db/mardin/duyurular/imar-planina--8230-84966-20240122160302.pdf (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Dzaugis, M.E.; Spivack, A.J.; Dunlea, A.G.; Murray, R.W.; and D’Hondt, S. Radiolytic Hydrogen Production in the Subseafloor Basaltic Aquifer. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seow, S.Q.; Mohan Viswanathan, P.; Dodge-Wan, D. Distribution of natural radioactivity in different geological formations and their environmental risk assessment in Malaysia. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 43292–43308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.H.; Chen, Z.M.; Chen, T.C.; Yeh, Y.L. Assessing Radiological Risks of Natural Radionuclides on Sustainable Campus Environment. Sustainability 2025, 17, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escareño-Juarez, E.; Fernández-Saavedra, R.; Gómez-Mancebo, M.B.; Barrado, A.I.; Cardona, A.I.; Rucandio, I. Radioactivity Levels and Heavy Metal Concentration in Mining Areas in Zacatecas, Mexico. Toxics 2024, 12, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, N.; Cumali, B.O.; Aysal, N.; Kajjumba, G.W.; Nemlioglu, S. Radiological hazard assessment of natural radioactivity in Avcilar region, Turkey: A case of Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa Avcilar Campus. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2022, 33, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguelem, E.J.M.; Ndontchueng, M.M.; Motapon, O.; Darko, E.O.; Simo, A. Determination of 226 Ra, 232 Th, 40 K and 235 U in soil samples from bauxite core deposits in western Cameroon. Radioprotection 2016, 51, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aközcan, S. Natural and artificial radioactivity levels and hazards of soils in the Kücük Menderes Basin, Turkey. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 4611–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowole, O. Determination of radiological hazard associated with the use of Imayan River sediment as building material. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 2015, 19, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Santis, M.; Di Gianantonio, E.; Straface, G.; Cavaliere, A.F.; Caruso, A.; Schiavon, F.; Berletti, R.; Clementi, M. Ionizing radiations in pregnancy and teratogenesis: A review of literature. Reprod. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, N.; Karakelle, B.; Temelli, U.E.; Nemlioglu, S. Natural radioactivity and hazard level assessment of cements and cement raw materials. In Recycling and Reuse Approaches for Better Sustainability, Environmental Science and Engineering; Balkaya, N., Guneysu, S., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altun, M.; Sezgin, N.; Nemlioglu, S.; Karakelle, B.; Can, N.; Temelli, U.E. Natural radioactivity and hazard-level assessment of Portland cements in Turkey. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2017, 314, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| (2) | |
| (3) | |
| (4) | |
| (5) | |
| (6) | |
| (7) | |
| ARa, AK, and ATh are the specific activities of Ra-226, K-40, and Th-232 | |
| DR is the absorbed dose rate in the air (nGy h−1) | |
| DL is expectancy of life (estimated as 70 years), and RF is the risk factor provided as 0.05 Sv−1 (fatal cancer risk per Sievert) |
| Province | Num. of Samples | Ra-226 (Bq·kg−1) | Th-232 (Bq·kg−1) | K-40 (Bq·kg−1) | Cs-137 (Bq·kg−1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mardin | 23 | 33.66 | 29.37 | 385.63 | 20.52 | [24] |
| Adıyaman | 32 | 23.98 | 29.09 | 402.20 | 6.58 | |
| Batman | 12 | 30.17 | 30.58 | 471.17 | 14.05 | |
| Diyarbakır | 27 | 23.45 | 19.76 | 368.70 | 16.02 | |
| Gaziantep | 23 | 26.29 | 24.78 | 225.22 | 6.29 | |
| Kilis | 19 | 18.80 | 17.60 | 222.09 | 11.11 | |
| Siirt | 19 | 28.50 | 30.16 | 497.41 | 10.22 | |
| Şanlıurfa | 24 | 27.58 | 29.82 | 330.13 | 11.12 | |
| Şırnak | 24 | 32.45 | 26.46 | 339.33 | 18.57 | |
| Turkiye (mean) | 1913 | 27.56 | 32.65 | 439.93 | 12.03 | [24] |
| World (median) | N/A | 35.00 | 30.00 | 400.00 | N/A | [1] |
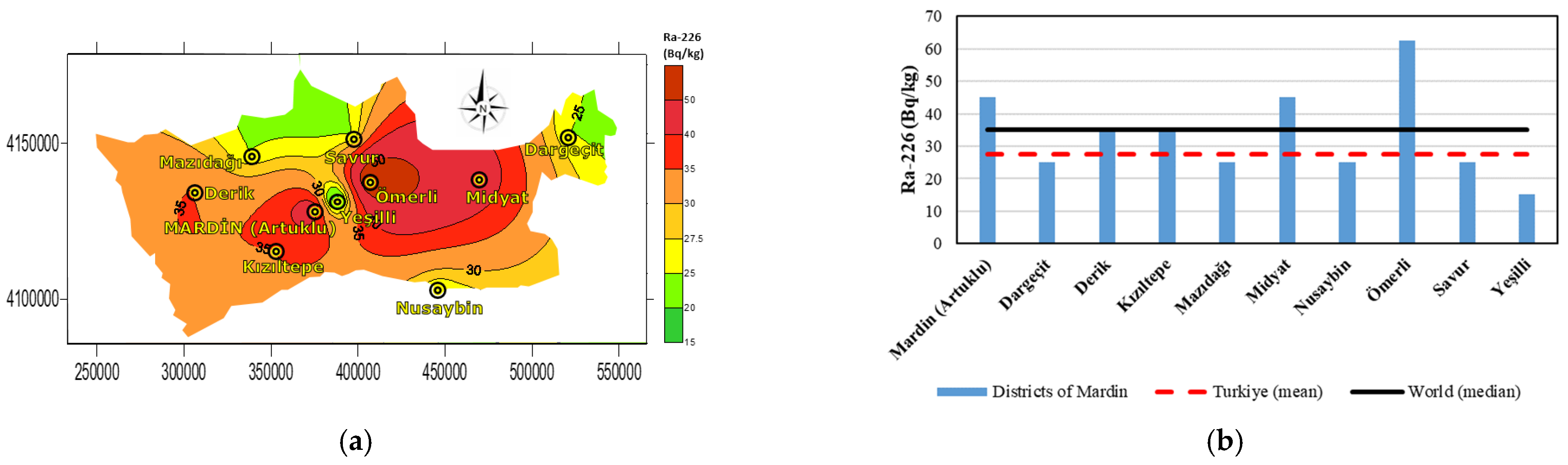
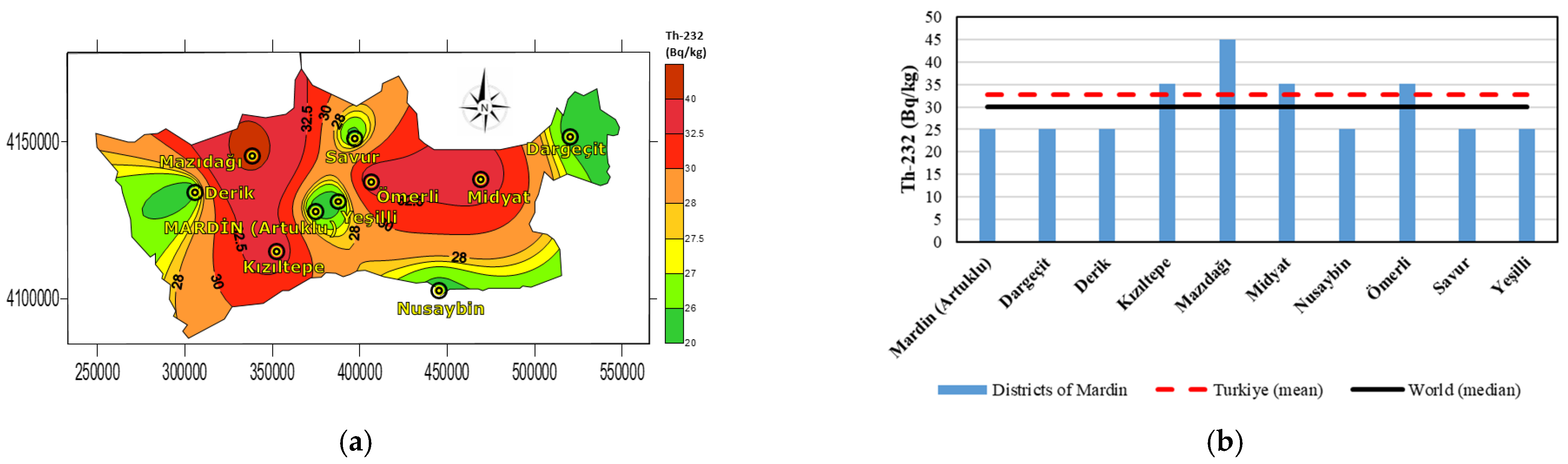
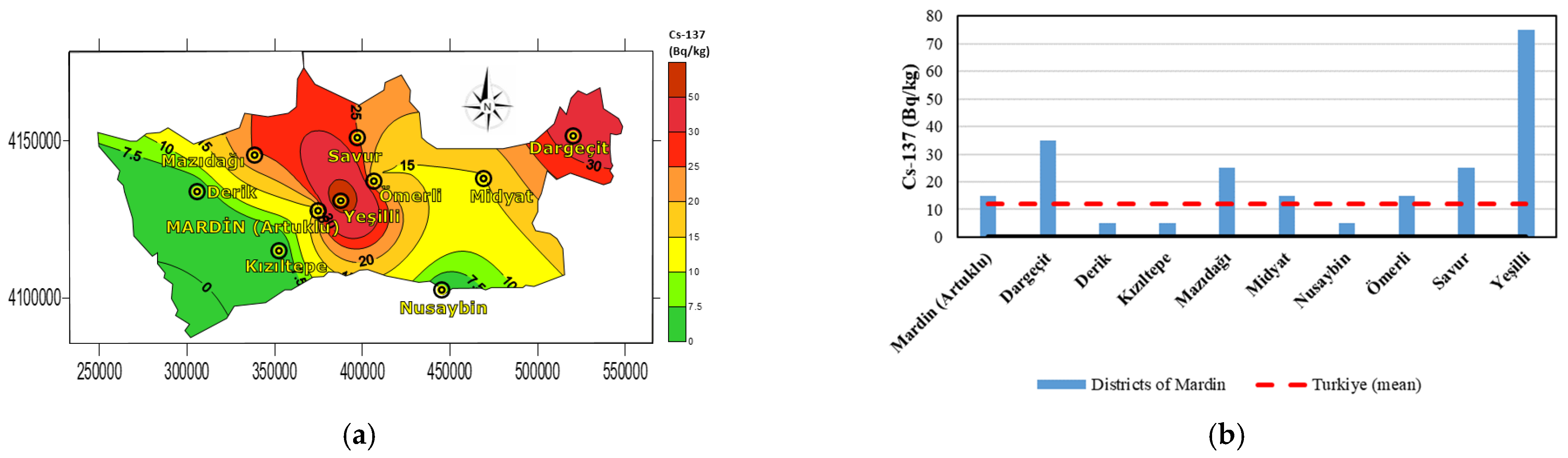
| Districts | Coordinates | Ra-226 (Bq·kg−1) | Th-232 (Bq·kg−1) | K-40 (Bq·kg−1) | Cs-137 (Bq·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mardin (Artuklu) | 37.31290° N, 40.73411° E | 45.05 | 25.05 | 450.05 | 15.05 |
| Dargeçit | 37.54618° N, 41.72038° E | 25.05 | 25.05 | 350.05 | 35.05 |
| Derik | 37.36466° N, 40.26794° E | 35.05 | 25.05 | 350.05 | 5.00 |
| Kızıltepe | 37.19138° N, 40.58595° E | 35.05 | 35.05 | 450.05 | 5.00 |
| Mazıdağı | 37.47737° N, 40.48674° E | 25.05 | 45.05 | 450.05 | 25.05 |
| Midyat | 37.41515° N, 41.37343° E | 45.05 | 35.05 | 450.05 | 15.05 |
| Nusaybin | 37.06964° N, 41.21400° E | 25.05 | 25.05 | 250.05 | 5.00 |
| Ömerli | 37.40311° N, 40.95482° E | 62.55 | 35.05 | 450.05 | 15.05 |
| Savur | 37.53393° N, 40.88709° E | 25.05 | 25.05 | 350.05 | 25.05 |
| Yeşilli | 37.33961° N, 40.82302° E | 15.05 | 25.05 | 350.05 | 75.05 |
| Max | - | 62.55 | 45.05 | 450.05 | 75.05 |
| Min | - | 15.05 | 25.05 | 250.05 | 5.00 |
| Mean | - | 33.66 | 29.37 | 385.63 | 20.52 |
| Turkiye (mean) * | - | 27.56 | 32.65 | 439.93 | 12.03 |
| UNSCEAR ** | - | 35.00 | 30.00 | 400.00 | N/A |
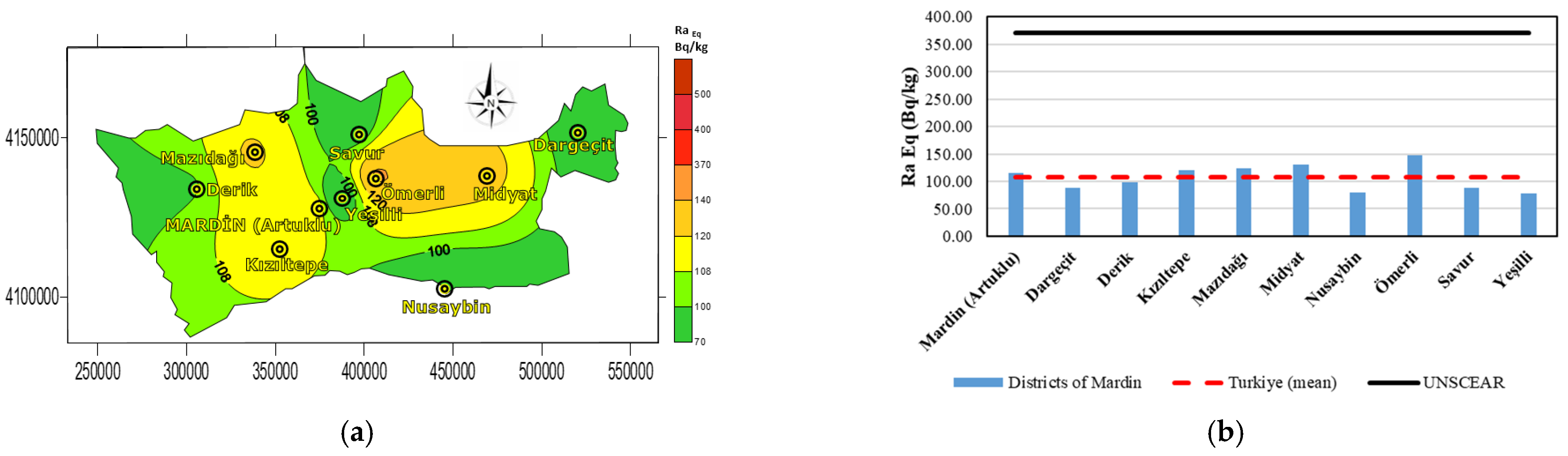
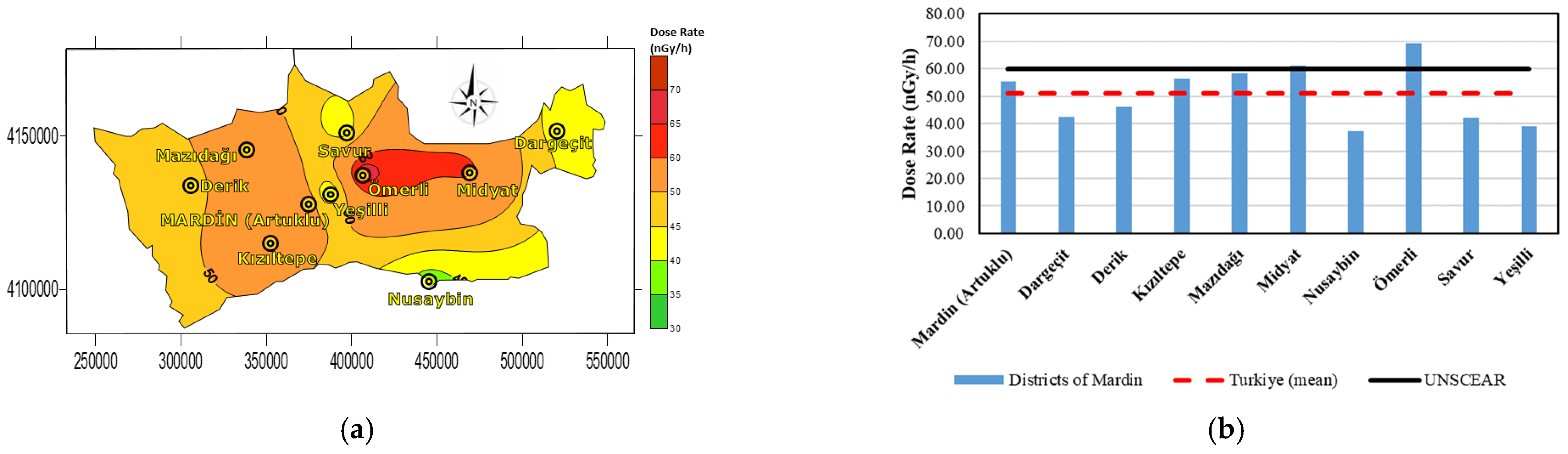
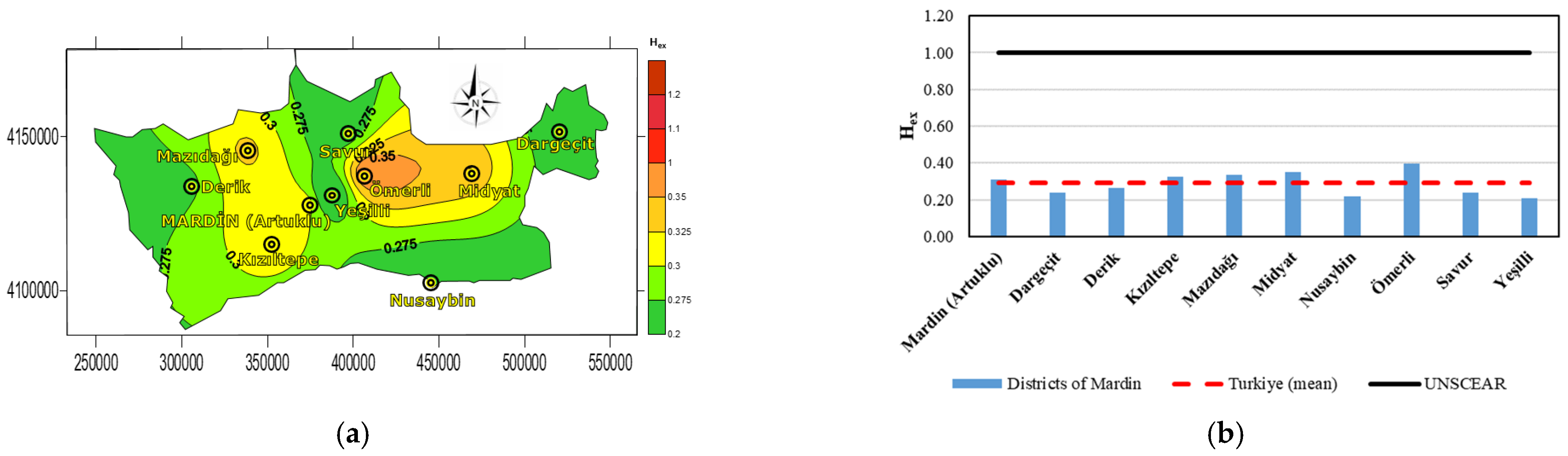
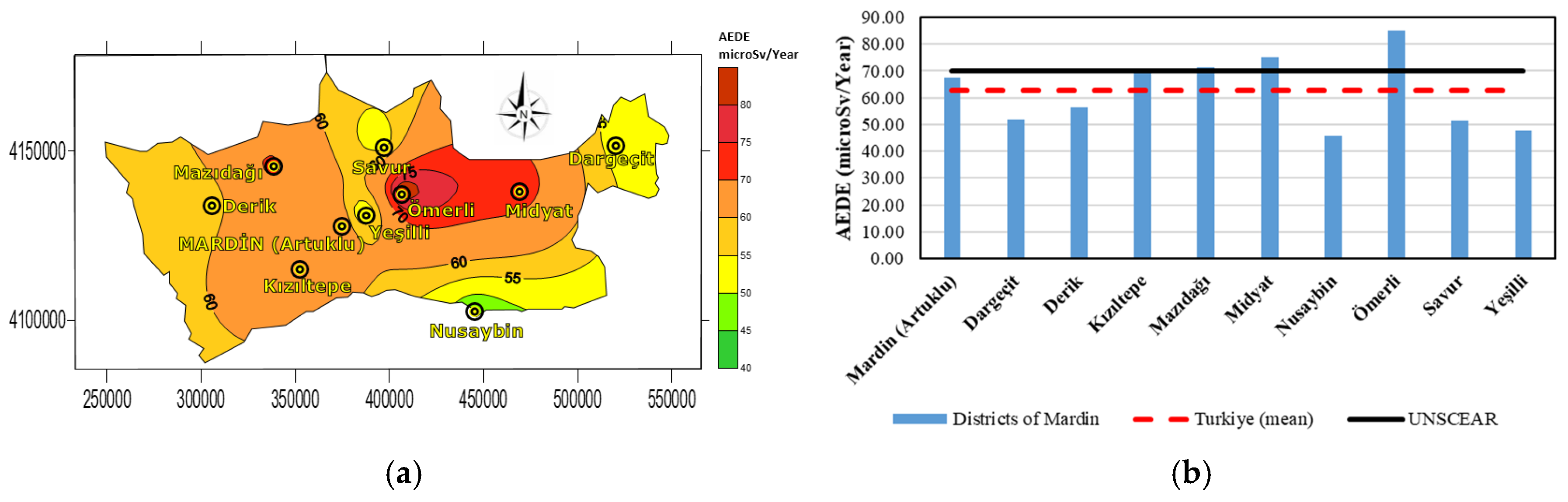
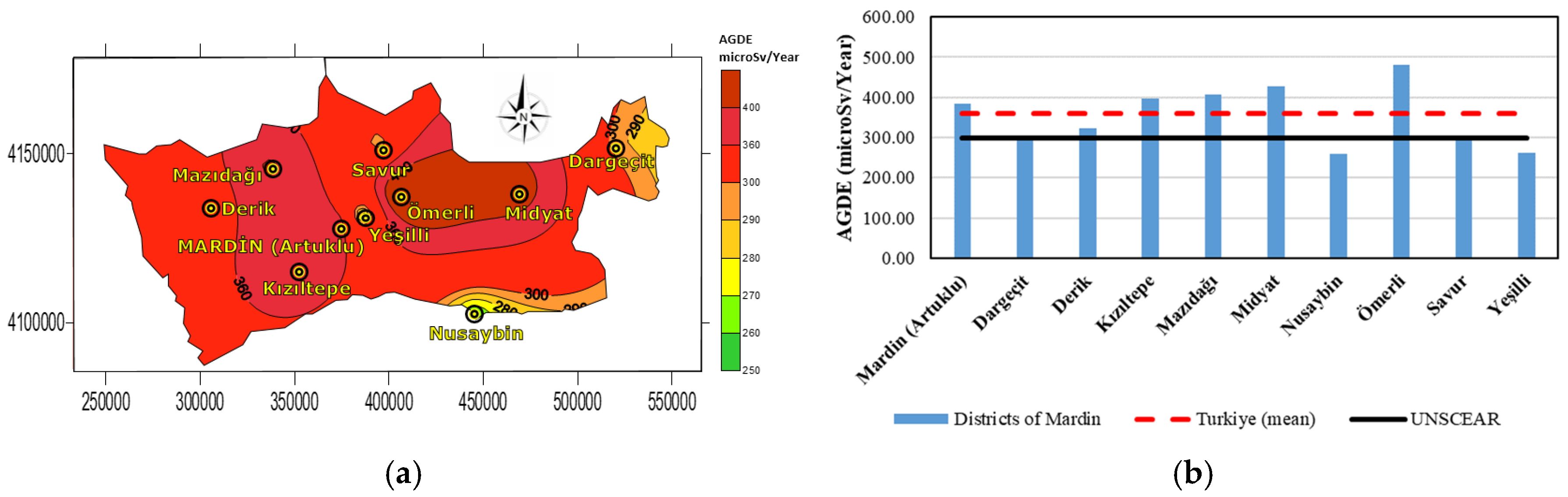
| Districts | Raeq (Bq·kg−1) | DR (nGy/h) | Hex | AEDE (microSv/Year) | AGDE (microSv/Year) | ELCR |
| Mardin (Artuklu) | 115.52 | 55.16 | 0.31 | 67.65 | 385.22 | 0.00023 |
| Dargeçit | 87.82 | 42.35 | 0.23 | 51.94 | 292.02 | 0.00018 |
| Derik | 97.82 | 46.07 | 0.26 | 56.50 | 322.92 | 0.00019 |
| Kızıltepe | 119.82 | 56.28 | 0.32 | 69.02 | 396.12 | 0.00024 |
| Mazıdağı | 124.12 | 58.30 | 0.33 | 71.50 | 407.02 | 0.00025 |
| Midyat | 129.82 | 61.20 | 0.35 | 75.05 | 427.02 | 0.00026 |
| Nusaybin | 80.12 | 37.28 | 0.21 | 45.72 | 260.62 | 0.00016 |
| Ömerli | 147.32 | 69.28 | 0.39 | 84.97 | 481.10 | 0.00029 |
| Savur | 87.82 | 42.05 | 0.23 | 51.57 | 292.02 | 0.00018 |
| Yeşilli | 77.82 | 38.93 | 0.21 | 47.74 | 261.12 | 0.00016 |
| Max | 147.32 | 69.28 | 0.39 | 84.97 | 481.1 | 0.00029 |
| Min | 77.82 | 37.28 | 0.21 | 45.72 | 260.62 | 0.00016 |
| Mean | 105.35 | 49.98 | 0.28 | 61.3 | 347.86 | 0.00021 |
| Turkiye (mean) * | 108.12 | 51.15 | 0.29 | 62.74 | 359.77 | 0.00021 |
| UNSCEAR ** | 370 | 60 | <1 | 70 | 300 | 0.00029 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çetin, E.; Sezgin, N.; Nemlioglu, S. A Comprehensive Analysis of Radiological Parameters in Historical City Soil: The Case of Mardin, Turkiye. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094792
Çetin E, Sezgin N, Nemlioglu S. A Comprehensive Analysis of Radiological Parameters in Historical City Soil: The Case of Mardin, Turkiye. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(9):4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094792
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇetin, Ender, Naim Sezgin, and Semih Nemlioglu. 2025. "A Comprehensive Analysis of Radiological Parameters in Historical City Soil: The Case of Mardin, Turkiye" Applied Sciences 15, no. 9: 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094792
APA StyleÇetin, E., Sezgin, N., & Nemlioglu, S. (2025). A Comprehensive Analysis of Radiological Parameters in Historical City Soil: The Case of Mardin, Turkiye. Applied Sciences, 15(9), 4792. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15094792







