Abstract
Polyethylene imine (PEI) is a synthetic water-soluble and nitrogen-rich polymer with an ethylene amine repeating unit. It exists in a linear or branched forms and finds applications in various areas. PEI is often chemically modified by crosslinking reactions using molecular and polymeric crosslinkers (e.g., trichlorotriazine, epichlorohydrin, ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether, poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether, etc.) to increase its stability and reduce its water solubility. PEI (pristine/crosslinked) has a strong affinity for metal cations (e.g., Cu2+, Au3+, Pb2+, etc.), where the nitrogen atoms interact with the metal ions, and hence is suitable to remove metals from water with high efficiency. A thin film of crosslinked PEI on substrates can be prepared and finds diverse applications such as in removing metals and dyes, and biofouling prevention in the marine environment. The copper ion, as an example, can be stored (adsorbed) in a thin film of crosslinked PEI on a carbon cloth substrate, which can be released to water by passing an electric current through the film or with an acid treatment. It has also been reported that crosslinked PEI and composite materials can be used for the adsorption of dyes and gases such as CO2 and SO2 from the environment. The performance of pristine/composite/crosslinked PEI in gas, metal ion, and dye adsorption is affected by several factors. The focus of this review is to discuss the different reactions used to crosslink PEI and review the properties of the crosslinked materials and their applications. Studies have shown that the properties of the crosslinked PEI and hence its success in capturing metal ions, dyes, and CO2 is dependent not only on the type of crosslinker but also on the degree of crosslinking.
1. Introduction
Heavy metals are common pollutants in the environment that present a major threat to public health, even at trace levels. Heavy metals enter the environment from different sources, which include metal plating, pickling, pigment industries, tanneries, municipal landfills, and wastewater treatment facilities []. Some of the heavy metals are needed by animals and plants; however, even these biologically essential metals become toxic and pose a health risk if they are found in the environment beyond a certain acceptable level. While copper is found in biological molecules such as in chlorophyll, enzymes, etc., and hence is essential for proper functioning of biological processes [], it is also known for its toxicity when it is found above a certain limit. The presence of excess copper can inactivate enzymes and form copper–protein aggregates that disturb the normal functioning of biological processes in the organism [,]. Studies also show that when the concentration of copper is above 1.3 mg L−1 in drinking water, it can cause kidney failure and other ailments, which clearly signifies the importance of monitoring copper levels in the environment and taking appropriate actions to mitigate their impacts []. Many approaches have been studied and developed to remove heavy metals from the environment to minimize impacts, which include flocculation, membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, and adsorption precipitation methods [,,]. Among them, ion exchange and adsorption are attractive options due to their simple operation and potential recovery and reuse of the metals and the adsorbents [,]. One of the most widely researched area in the field of sensing and removal of heavy metals from the environment is the use of polymeric materials. In this regard, polyethylene imine (PEI)/composite-based materials are interesting and have been widely investigated.
Structurally, PEI exists in both linear and branched forms; can have primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups; and can be synthesized with various molecular weights [] (Figure 1). PEI is a water-soluble polyamine known for its high adhesion and adsorption properties. It contains polar amino groups, allowing for strong electrostatic interactions with ions and making it effective at absorbing dyes and toxic anions []. The stability of PEI in water is increased by either binding the material onto insoluble support materials and/or by chemically crosslinking the polymer using reagents like glutaraldehyde and epichlorohydrin (ECH) [,]. For example, glutaraldehyde is extensively used in the crosslinking of PEI to create a mechanically and chemically robust material. The large number of amine groups on crosslinked PEI makes it an ideal polymeric ligand for complexing numerous heavy metal ions []. Crosslinked PEI coatings, for instance, were found to efficiently adsorb copper ions from water under acidic conditions [,]. In another study, the highest copper adsorption was achieved using PEI cryogels crosslinked with diglycidyl ethers in alkaline media []. Some previous studies have shown the adsorption of copper from 2 to 200 ppb concentrations in seawater [,]. More importantly, the adsorbed metal ions can be released by chemical treatment, allowing the regeneration and reuse of the crosslinked material [,], and making PEI an interesting polymer for industrial uses such as waste water treatment [].
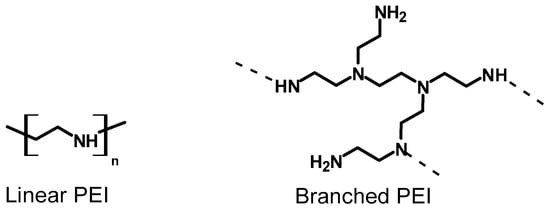
Figure 1.
Types of polyethylene imine (PEI) architectures.
PEI and modifications/composites have also been used in other fields, including biomedical applications. PEI exhibits pH-dependent properties due to the protonation of its amino groups, which makes it suitable for controlled drug release systems and pH-responsive drug delivery []. Its high cationic charge density and its interaction with negatively charged molecules or surfaces makes it useful in applications such as gene delivery and flocculation processes []. The cellulose paper industry, detergents, adhesives, water treatment agents, sensors, carbon dioxide capture, batteries, and cosmetics are some of the other areas where PEI and its composites have been used in the past [,,,].
The use of non-crosslinked PEI (polychelatogen) for removing pollutants such as dyes and heavy metals has also been investigated in a system called polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration (PEUF). PEI interacts with pollutants by complexation, hydrogen bonding, and other electrostatic interactions []. A flat membrane filter with high permeability in a “dead end“ operating mode is used to filter out the PEI–pollutant complex. The PEI is finally recovered by decomposition [,]. Clearly, PEUF is an alternative way where pristine PEI is used to capture heavy metals from water samples. However, while the preparation of crosslinked PEI has an additional crosslinking reaction step, the low solubility of the crosslinked material in water will allow its use as an adsorbent and in the recovery of the material by a filtration step without the need to use high pressures for separation. Moreover, crosslinking increases the stability of PEI and hence it avoids/minimizes the chance of low-molecular-weight organic fragments entering the environment during filtration. Studies also show that the crosslinked PEI is more selective toward copper than it is toward zinc, which can be used to separate the two ions efficiently. In the presence of equimolar copper and zinc in water samples, crosslinked PEI adsorbed copper selectively while a trace amount of zinc got adsorbed. On the other hand, in non-crosslinked PEI, a larger amount of zinc is adsorbed [].
The present review starts by critically discussing the various crosslinking reactions of PEI and possible reaction mechanisms reported in the literature. In addition to presenting the reactions, this review discusses the properties of the resulting crosslinked materials. Then, this review discusses the applications of crosslinked PEI, such as in heavy metal adsorption, and its release with an acid treatment and electrochemical processes. The preparation of a thin coating (by spin and spray coating techniques) and subsequent crosslinking reactions are also presented. The thin film properties, adsorption, and electrochemically triggered release of copper are discussed with a great emphasis, as they are deemed to have importance in anti-fouling systems in the marine environment without impacting the environment with a high level of copper. The roles of crosslinked PEI in CO2, dye, and aldehyde adsorption are also briefly discussed. This review has also surveyed the adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherms of heavy metals and dyes onto crosslinked PEI.
2. Crosslinking of PEI and Reaction Mechanisms
The chemical crosslinking of polymers involves covalently bonding of one part of a polymer chain to another polymer chain. Often, small molecular crosslinkers are used to join the polymer chins. Crosslinking reactions enhance the stability and mechanical strength of the polymer material and change the physical state of the material to make it suitable for practical applications. PEI, being a nitrogen-rich organic polymer, is known to be effectively crosslinked using small molecular crosslinkers to give a three-dimensional network that can retain its structure during adsorption processes. The traditionally used chemical crosslinkers include glutaraldehyde, glyoxal, dichloroethane, ECH, triglycidyl trimethylolpropane ether, etc. (Figure 2), and follow various crosslinking reaction mechanisms. However, in general terms, the reaction take place between the lone pair of electron-possessing nitrogen atoms of PEI and the electrophilic centers found in the molecular/polymeric crosslinkers.
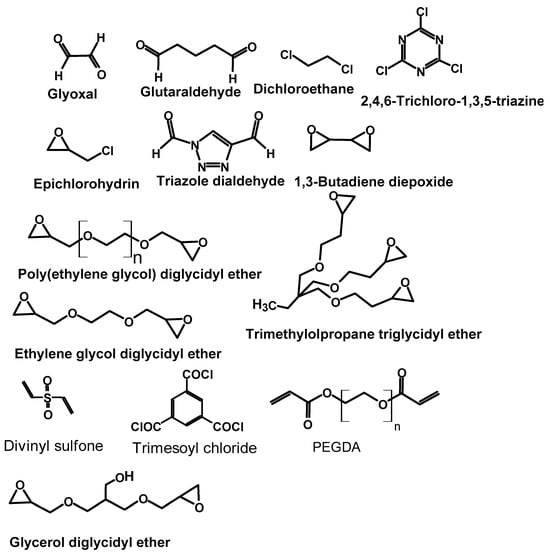
Figure 2.
Molecular, oligomer, and polymeric crosslinkers used to crosslink polyethylene imine.
The crosslinking of PEI with dialdehyde-containing molecules such as glyoxal and glutaraldehyde has been reported by different research groups and is known to yield a highly stable material. The crosslinking reaction can be achieved easily by mixing PEI and the crosslinker and stirring at room temperature to yield a yellowish/orangish powder []. The crosslinking reaction can also be carried out by dipping a PEI-coated surface in a crosslinker solution []. The reaction is expected to take place between the nitrogen of the polymer with the electron-deficient carbonyl group of the crosslinkers.
Studies of the mechanisms of the reaction between glutaraldehyde and PEI have revealed that the reaction involves more than one type of mechanism. The first possible pathway reported is Schiff base formation, where a C=N double bond is formed between the two reacting functional groups (Scheme 1) [,,]. Schiff base formation has been confirmed from an IR study where C=N stretching was detected at 1650 cm−1, while the appearance of sharp peaks at 2937 and 2850 cm−1 were assigned to a C-H bending mode, and a low-frequency mode of C-H bending appeared at 1453 cm−1.
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of crosslinked polyethylene imine with glutaraldehyde as the crosslinker [].
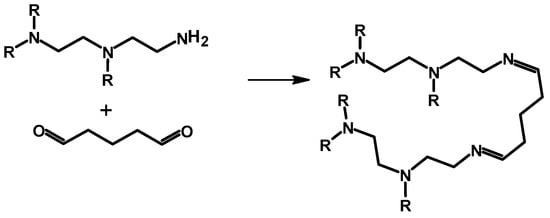
The introduction of polar groups such as OH, COOH, and C=O on the surface of inert materials will assist in adhesion and the preparation of stable polar coatings. The material to be coated on the modified surface is then applied using coating techniques such as spraying, vapor deposition, printing, dipping, and other known film-making techniques []. Gutowski et al. [] studied an alternative coating method whereby an oxidized surface was treated with 1:1 mixture by weight of PEI and glutaraldehyde at a total solid content of 1% in water that was suitable for effective adhesion enhancement. Complete crosslinking occurs when the water is evaporated to leave a polymerized red/orange solid that is no longer soluble in water. The proposed mechanism for the crosslinking reaction involves aldol condensation polymerization of the glutaraldehyde crosslinker with a dehydration reaction producing an ethylenic double bond and a carbonyl group in conjugation with the carbonyl group attached to the backbone of the glutaraldehyde polymer. The presence of the basic amino group in PEI catalyzes the polymerization reaction of glutaraldehyde. The carbonyl group of the polymerized glutaraldehyde and the amine of the PEI undergo a Schiff base reaction to form a conjugated imine bond (Scheme 2) in the subsequent reaction step [,]. To better understand the nature of the crosslinked material, the individual reactants (PEI and glutaraldehyde) before crosslinking and the mixture of PEI–glutaraldehyde, Gutowski et al. used 13C NMR spectroscopy. The NMR spectrum of glutaraldehyde in water is more complex with peaks appearing from 0 to above 200 pm. Strong 13C NMR peaks have been observed at around 100 ppm and in the region below 50 ppm. The complex NMR spectrum is attributed to the tendency of glutaraldehyde to form a mixture of isomers, such as cyclic hemiacetals, when it is in water []. The 13C NMR spectrum of the branched PEI, on the other hand, gave eight sharp peaks, where seven of them appeared in the aliphatic region. A 13C NMR study of the crosslinked material (after the PEI and glutaraldehyde were kept together for some time) was also conducted by the research group. In the spectrum, peaks associated with glutaraldehyde disappeared and a broadening of peaks were observed, which were both attributed to the formation of a rigid polymer network. The presence of an imine bond in the crosslinked material was also proposed, as a new peak at 174 ppm appeared while the peak at 205 ppm disappeared [].

Scheme 2.
Proposed crosslinking mechanism of polyethylene imine with glutaraldehyde [].
It is known that reactive amino functional group-containing molecules or polymers react with aldehydes and acids. Jeon et al. prepared crosslinked PEI for a CO2 adsorption study []. The crosslinkers used in the study were a glyoxal solution (GOX, 40 wt% in H2O) and oxalic acid (OA). The authors observed an increase in the viscosity of the material with time, indicating the occurrence of a crosslinking reaction. The reaction was performed in methanol by dissolving 1 g of PEI (MW = 1200 g/mol) and mixing it with the crosslinker (glyoxal/oxalic acid) dissolved in 1 mL of methanol. After heating the mixture for 6 h at 60 °C, the solvent was evaporated, and the material left was cured by heating to 80 °C for 6 h under stirring and finally heating at 100 °C for 6 h under vacuum to remove water and other low-molecular-weight adsorbed molecules. The materials prepared were named 2.5GOX-PEI and 2.5OA-PEI, where the numbers refer to the molar ratio of the crosslinker to nitrogen atoms in PEI. Like the previous study reported by Jung et al. [], 13C NMR was used to study the crosslinking reaction mechanism and propose the structure of the crosslinked PEIs. The structure of the pristine PEI showed 13C peaks all below 60 ppm (aliphatic region), which is a clear indicator of the aliphatic carbon atoms (methylene groups), and the structure proposed for PEI is shown in Figure 1. The 2.5GOX-PEI and 2.5OA-PEI materials also gave distinct and sharp peaks, unlike the broadened peaks reported when ECH and 1,3-butadiene diepoxide (BDDE) crosslinkers are used. Moreover, weak peaks were observed around 165 ppm for 2.5GOX-PEI, while the 2.5OA-PEI material gave a peak at 165 and another peak above 170 ppm. The peak appearing at around 165 ppm for 2.5GOX-PEI is assigned to the carbon atom of carbonyl group of an amide structure [], which was interpreted as the crosslinking reaction with glyoxal proceeds via amide bond formation instead of the imine bond formation. Moreover, the ratio of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines found in the crosslinked materials were calculated based on the 13C NMR spectrum. A slight increase in the tertiary amine content that was found in 2.5GOX-PEI (31.9%) as compared to PEI (29.1%) was interpreted as the preferred reaction of glyoxal with the secondary amine and hence supporting the proposed amide bond formation in the crosslinking reaction. However, the tertiary amine content showed a decrease in the 2.5OA-PEI material compared to PEI and 2.5GOX-PEI. The inconsistency in the ratio of the tertiary amine to secondary to primary amines in 2.5OA-PEI could also arise from quaternary ammonium cation and carboxylate anion formation, which potentially underestimates the tertiary amine concentration in the structure. The proposed structures of the glyoxal- and oxalic acid-crosslinked materials are shown in Figure 3.
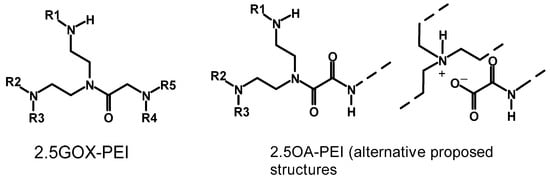
Figure 3.
Proposed crosslinking products of polyethylene imine with glutaraldehyde [].
The adsorption capacity of a composite of crosslinked materials/MSU-F for CO2 were measured and both showed lower adsorption capacities in comparison with a standard material represented by the code MSU-F/50PEI. The lowest weight gain after the capture of CO2 was observed for MSU-F/2.5GOX-50PEI, which was thought to be due to the lower concentration of primary amines in the glyoxal-crosslinked material.
There are various coordinating molecules and polymers for Cu2+ and Cu+ ions, of which imidazole- and triazole-based molecules are well-known ligands. Tris[(benzyltriazolyl)methyl]amine (TBTA) is one of these ligands widely used in reactions that involve Cu+ [,]. With the aim of tuning the affinity of crosslinked PEI to a specific oxidation state of copper (Cu+ or Cu2+), a triazole-based crosslinker (a triazole dialdehyde (TA)) and (benzyl)triazole carbaldehyde (BTA) were synthesized by Movahedi et al. to crosslink PEI []. The two crosslinkers were used in the presence/absence of glutaraldehyde. Imine bond formation is the mechanism proposed for the crosslinking reaction. The crosslinked materials were also treated with a reducing agent (Na(BH(OAC)3) to reduce the imine bond (Schiff base) to an amine bond (single bond). The reduction step aims at improving the stability of the crosslinked material toward hydrolysis reaction []. The structures of TA and BTA and the reactions are shown in Scheme 3.
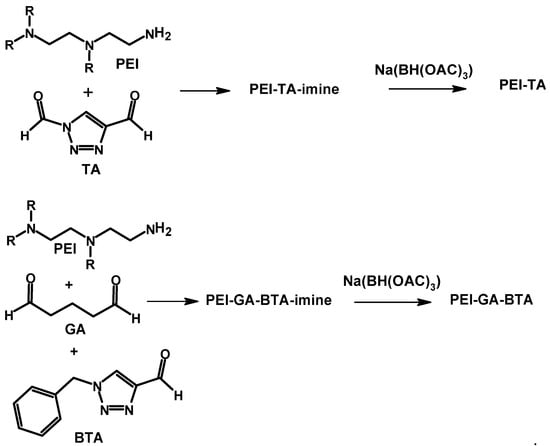
Scheme 3.
Crosslinking reaction of polyethylene imine with triazole-containing molecules and subsequent reduction of the imine bond [].
The materials prepared were analyzed using multiple techniques. The elemental analysis technique was used to determine the elemental composition of the materials. In this case, the authors measured the nitrogen content of the materials. The result indicated the presence of 12.6 wt%, 20.3 wt%, and 15.5 wt% N in PEI-GA, PEI-TA, and PEI-GA-BTA, respectively, consistent with the structures of TA and BTA and their contributions to the total nitrogen content of the final crosslinked materials. The IR spectra of the three materials were found to be similar and support imine bond formation, as peaks corresponding to C-N and C=N stretches were observed in the three materials. The Cu2+ adsorption capacity was found to be 8.1 wt% (PEI-GA), 12.2 wt% (PEI-TA), and 3.5 wt% (PEI-GA-BTA), and the adsorption capacities dwindled after the reduction of the imine bond with the reducing agent. The higher adsorption capacity of PEI-TA compared to the others is believed to be due to the formation of a porous structure (SEM study) and due to the presence of the additional copper-binding triazole ring in the structure. The materials prepared have also shown a higher selectivity for Cu2+ over Zn2+ in an adsorption experiment performed with a water sample containing both ions. The triazole-based crosslinked materials have also shown a strong affinity for Cu+, showing the potential of the material to be used as an antifouling coating []. It is noted that Cu+-containing compounds are potent against the growth of biological organisms on marine surfaces.
PEI is also crosslinked with other type of small molecules that possess an electrophilic carbon bonded to an electron-withdrawing elements such as chlorine. Such crosslinkers include dichloroethane, epichlorohydrin [], trichlorotriazine, and epoxy-containing crosslinkers ((such as glycerol diglycidyl ether [], ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether [], and 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether []) (Figure 2).
Carbon dioxide emission to the atmosphere from the excessive use of fossil fuels has remained a concern for the global community due to its greenhouse effect and causing the global temperature to rise. Researchers have designed different strategies to capture CO2 from its source [], of which one of them is the absorption CO2 using aqueous amines, such as monoethanolamine (MEA), diethanolamine (DEA), and piperazine (PZ) [,], where the CO2 reacts with the adsorbing amine. This method, however, is known to form corrosive fumes and the regeneration process is energy-demanding. As alternative to the use of aqueous amines, amine-impregnated solid adsorbents were studied for capturing CO2 from plants. However, with this method, the formation of urea during the regeneration process and leaching of the amine molecules are some of the issues observed []. With the objective of overcoming the abovementioned issues associated with aqueous amines, crosslinked materials are used as amine-based adsorbents. Jung et al. evaluated an epoxide crosslinker (BDDE and ECH) (Figure 2) as a crosslinker for PEI on silica to enhance the physical and chemical stability of PEI-impregnated adsorbents []. To understand the extent of crosslinking and to propose the structures of the resulting crosslinked materials, 13C NMR was employed. The 13C NMR spectra of the BDDE- and ECH-crosslinked PEI showed distinct and sharp peaks in the aliphatic region (appearing below 60 ppm). The peak positions also have a similar chemical shift position. Both materials have also given weak signals at around 70 and 71 ppm attributed to the OH-containing carbon atoms. The ratios of the primary, secondary, and tertiary amines in the crosslinked materials were also calculated. The result showed that the pristine PEI (before crosslinking) showed 36.6%, 34.5% and 29.1% of primary amines, secondary amines, and tertiary amines, respectively. The BDDE-crosslinked material, on the other hand, showed 33.5% primary amines, 36.2% secondary amines, and 30.3% tertiary amines. A total of 34.1% primary amines, 35.8% secondary amines, and 30.1% tertiary amines were found in ECH-crosslinked PEI. The ratio of the primary, secondary, and tertiary amines in the three materials clearly show the degree of the crosslinking reactions. In more detail, the primary amine concentration in the pristine PEI is higher than in the two crosslinked materials. The secondary amine and tertiary amine concentrations have increased in both cases, which indicates the crosslinking of the materials. A higher conversion rate of primary amines to secondary amines (8.6%) compared to a lower conversion of secondary amines to tertiary amines (3.3%) was observed in the BDDE-crosslinked material. The corresponding values for the ECH-crosslinked material were 6.8% (conversion of primary amines to secondary amines) and 2.8% (conversion rate of secondary amines to tertiary amines). These conversion values indicate that both crosslinkers react with primary amines better than they do with secondary amines. When the two crosslinkers are compared, BDDE is more reactive with primary amines than ECH.
It is noted that the chemical shift of the carbons in pristine PEI were assigned as follows. The carbon that has a tertiary amine at the α-position and a primary amine at the β-position has the highest chemical shift in the spectrum (at >55 ppm). The next carbon with a chemical shift to a lower ppm is the one that has a tertiary amine at the α-position and a secondary amine at the β-position (~53 ppm). The last carbon, which appears up field (~35 ppm) in the spectrum, was assigned to the carbon in PEI that has a primary amine at the α-position and a tertiary amine at the β-position. Such an analysis was applied to the 13C NMR spectra of the crosslinked materials, and the structures were proposed, as shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4.
Proposed structures of crosslinked and pristine polyethylene imine [].
The adsorption capacity of the materials for CO2 was investigated, and it was found that BDDE was higher than the ECH-crosslinked material. It was suggested this difference is due to the number of hydroxyl groups found in the sorbents, which considerably affected the CO2 adsorption. This can be taken yet as another example that reveals that the property of the final material will depend on the nature of the crosslinker. Hence, a careful choice of the crosslinker and reaction conditions has a paramount importance in governing the structure of the material and its efficiency in absorbing target analytes.
Scheme 4 shows the crosslinking reaction of PEI with ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (EGDE). The reaction is between the amine of the PEI and the reactive three-membered epoxy ring in a nucleophilic attack, which opens the ring of the epoxide to form a hydroxyl group-containing product. The crosslinked polymer was prepared in a facile reaction that involves a reverse suspension polymerization reaction []. The EGDE crosslinker was first dissolved in a desired amount of toluene and the water-soluble PEI and a non-ionic surfactant and emulsifier (Span 80) were dropped into the organic phase and the reaction mixture was heated at 45 °C for 4 h to produce the crosslinked material. The beads produced were rinsed with methanol and pure H2O before being dried at 50 °C overnight. The prepared material was characterized by multiple techniques to understand its morphology and elemental composition. The SEM study revealed the polymer to have a regular sphere shape, and the surface was found to be relatively smooth. An IR study of both the monomers and the final crosslinked polymer was conducted. The result showed the disappearance of a peak at 911 cm−1 associated with the epoxy ring, which indicated the occurrence of the reaction. Moreover, the band at 1654 cm−1, which is associated with N-H deformation, weakened, which supports a crosslinking reaction. The crosslinked polymer was found to have 69.4%, 14.5%, and 16.1% atomic percentages of O, N, and C, respectively, from an XPS wide-scan spectrum study. The amounts of primary amines, secondary amines, and tertiary amines were calculated to be 29.6%, 45.9%, and 24.6%, respectively. The result shows that the crosslinked material is potentially suitable for Au3+ adsorption, for which the material was prepared. In fact, the crosslinked polymer gave a high sorption capacity and high selectivity for Au3+ due to its high density of amine and hydroxyl groups on the surface, which is discussed in a later section in more detail.
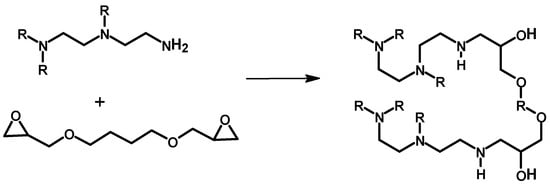
Scheme 4.
Crosslinking reaction of polyethylene imine with EGDE [].
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE, Mn = 500 g/mol) and 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether were used as crosslinkers of PEI at low temperature (below 0 °C) (an ice templating technique), as has been described by Narayan et al. (Scheme 5) [] and Chatterjee et al. []. The process of the crosslinking reaction involved the mixing of the PEI and the crosslinker, vortexing, and subsequently freezing the mixture in liquid nitrogen or a dry ice–acetone bath to yield PEI 196 and PEI 78, respectively [], or freezing the mixture at −15 °C []. PEI 196 and PEI 78 are discussed hereafter. The frozen materials were then thawed at room temperature, and the samples were collected carefully from the vial. A SEM study of both materials (PEI 196 and PEI 78) revealed the formation of porous crosslinked materials. The degree of crosslinking was estimated from an XPS study by looking at the ratio of the C-O to C-N bonds in the crosslinked materials. A lower C-O to C-N bond ratio will imply less crosslinking, as the oxygen will come from the crosslinker. The result showed PEI 196 to have a lower C-O to C-N bond ratio and hence a lower degree of crosslinking [], which is expected due to the very low reaction temperature (−196 °C). The better crosslinking reaction of PEI 78 has also resulted a lower percentage of primary and secondary amines in the final material as compared to its counterpart (PEI 196). The materials prepared were used to investigate the adsorption capacity of CO2 and the impact of material exposure to SO2 on the adsorbed CO2. The highly porous crosslinked material showed a high efficiency in CO2 capture, with PEI 196 showing better performance, which could be due to the presence of higher concentrations of primary and secondary amines, among other factors. More discussion on the adsorption of CO2 and effect of SO2 is available in Section 3.4.
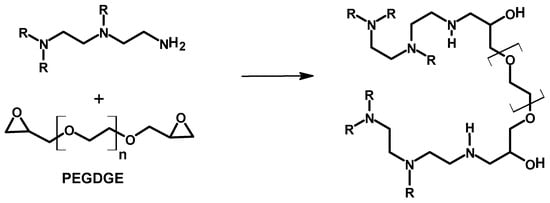
Scheme 5.
Partial structure of poly(ethylene glycol)diglycidyl ether-crosslinked polyethylene imine [].
Similar to the crosslinking reaction discussed at −78 and −196 °C (ice templating method), Sahiner et al. crosslinked PEI with glycerol diglycidyl ether (GDE) in excess water at −18 °C [], which resulted a porous structure. The material was used for the direct removal of organic dyes (discussed in Section 3.3).
The crosslinking reaction involves epoxide ring opening and the formation of secondary amines, tertiary amines, and esters, as discussed by Narayanan et al. [] and Yoo et al. [] and shown in Scheme 6.
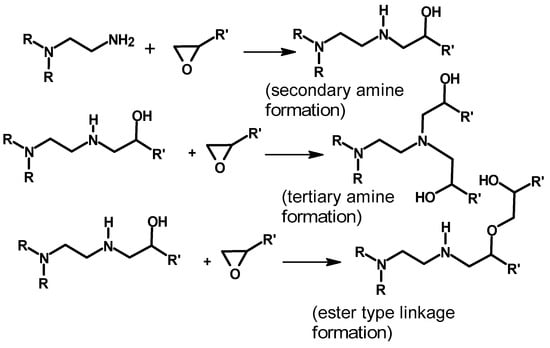
Scheme 6.
SN2 ring opening of the epoxide between polyethylene imine and poly(ethylene glycol)diglycidyl ether-crosslinked polyethylene imine [,].
Naga et al. reported the crosslinking of PEI with PEGDGE (n = 9 and n = 23) (PEGDGE-400 and PEGDGE-1000) to yield a PEI-PEGDE gel in a reaction referred to be a ring opening addition reaction [,]. The reaction was conducted in DMSO (30 wt% of the monomers) as a solvent in the presence of PPh3 as a catalyst at 90 °C or just in water without the use of the PPh3 catalyst at room temperature to yield the gels. The materials were characterized with different techniques. In the IR study, the characteristic peaks of the epoxy ring at 800 cm−1 and amine group at 1500 and 1600 cm−1 disappeared, indicating the progression of the crosslinking reactions under the reaction conditions used. The gel formation times of PEGDGE-400 and PEGDGE-1000 were monitored using a viscometer at room temperature, revealing a shorter time for PEGDE400 as compared to its counterpart crosslinked material.
The synthesis of gels and porous polymers was achieved by an aza-Michael addition reaction of PEI with polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) in DMSO, EtOH, or H2O, and reaction is shown in Scheme 7 []. Different molecular weight PEGDA samples were used (PEGDA200, PEGDA400, PEGDA600, and PEGDA1000).
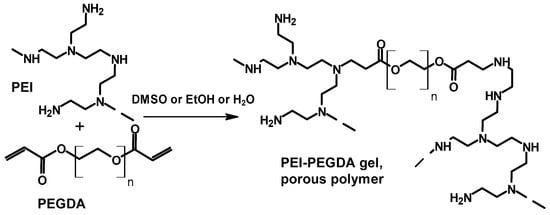
Scheme 7.
Synthesis of gels and porous polymers by an aza-Michael addition reaction of PEI with polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA) [].
The crosslinked gel prepared in water was not gelling, probably due to the hydrolytic degradation of the ester functional group. However, the reaction in DMSO gave a gel. Interestingly, gel formation in ethanol was found to depend on the molecular weight of the cross linker (PEGDA). It was found that relatively higher molecular weight crosslinkers gave a gel, while for a lower molecular weight crosslinker (PEGDA200), gel formation was found to depend on the reaction conditions. One can infer from this that not only the solvent type used will affect the crosslinking reaction but also the molecular weight of the crosslinker should be kept in the picture to fully understand the process. Like before, in this case, IR spectroscopy was also used to monitor the extent of the crosslinking reaction. In the PEI-PEDA400 reaction system in 30 wt% in DMSO, the IR peaks at 700 cm−1 (from acrylate), 1500 cm−1, and 1600 cm−1 (from amine) almost vanished, indicating the occurrence of the reaction between the amine and the crosslinker. The mechanical properties and the speed of gel formation have been also studied. PEI-PEDA obtained in EtOH with 20 wt% monomers were also tested for its solvent absorption capacity. The polymer absorbed solvents (hexane, ethanol, acetone, toluene, water, DMSO, DCM, and chloroform) and gained 100–350% in volume based on the original size.
A crosslinking reaction of PEI is also possible using crosslinkers that have a leaving group, such as an sp3 C-Br bond. The crosslinking reaction proceeds via an amine alkylation reaction between the alkyl bromide of the crosslinker and the amine groups of the branched PEI, with bromine being substituted with amine functional group of the amine. Hamdy et al. used bromoalkyl phenyl attached to a triazene core unit as a crosslinker (2,4,6-tris-(4-bromomethyl-3-fluoro-phenyl)-1,3,5-triazine (4BMFPT)) for PEI, as shown in Scheme 8, for CO2 selective capture at ambient temperature []. Different materials with different mixing ratios of the crosslinker to PEI were synthesized. The materials prepared were characterized with IR, elemental analysis, and SEM, and the materials were tested for their performance in CO2 capture. It is important to note that the direct capture of CO2 from air is not facile, as a material with a high selectivity and strong reactivity with CO2 is required []. Hence, careful control of the reaction conditions to ensure the presence of amine functionalities is necessary to achieve a high CO2 adsorption capacity and fast kinetics. The crosslinking reaction of PEI with 4BMFPT was performed by stirring at 82 °C for three nights, and the solid was washed with a multitude of solvents. The product was also washed with KOH to remove the HBr formed during the reaction. The dried materials showed colors ranging from pale yellow to darker to deep orange, depending on the feed ratio of the monomers. The final materials were also found to have a course to spongy texture, depending on the feed ratio of the monomers. The PEI-4BMFPT crosslinked material resulted in spherical particles. The adsorption kinetics of the crosslinked material were found to be fast and reached a CO2 adsorption of 2.31 mmol g−1 under 1 atm, 90% CO2/Ar at 30 °C.
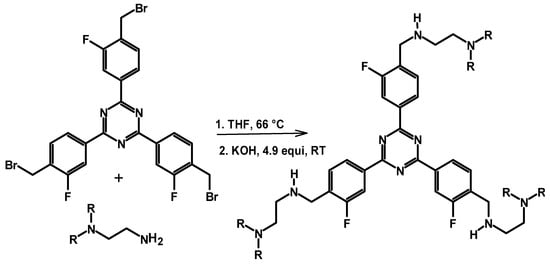
Scheme 8.
Crosslinking of PEI with triazine moiety-containing molecules with a good leaving group [,].
A trichloro-substituted triazine crosslinker (2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine, TCT) was used to crosslink PEI by Hu et al. to prepare a material for the efficient recovery of gold from waste water, and the reaction is shown in Scheme 9 []. The reaction is a nucleophilic aromatic substitution reaction carried out at 70 °C with molar ratios from 10:1 to 2:1 (PEI to TCT ratio). The reactions yielded pale-yellow precipitates with a 35–85% yield. The 13C NMR peaks associated with PEI in the aliphatic region were broad, featureless bands in the crosslinked material, which are indications of the formation of a rigid material. This is in contrast to the sharp peaks seen in the 13C spectrum of the pristine PEI, supporting the occurrence of reaction between the crosslinker and PEI. A relatively sharp peak appearing at 165 ppm corresponds to the aromatic carbons of TCT, indicating that the substitution reaction between PEI and TCT occurred. In the IR study, the C-Cl stretching/bending vibrations associated with the TCT crosslinker (at 1267 and 850 cm−1) disappeared from the spectrum of the crosslinked material, supporting the expected Cl substitution by the amine. Details about its use for Au3+ adsorption are discussed in Section 3.1.
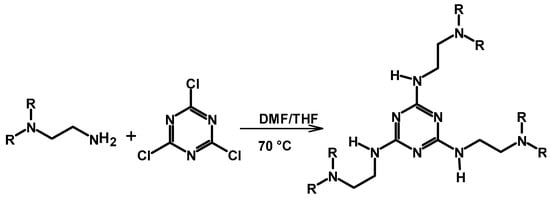
Scheme 9.
Crosslinking of PEI with triazine moiety-containing molecules with a good leaving group [,].
The crosslinking of PEI using ECH to reduce its water solubility and engineer the material’s properties was also studied in the past, and the crosslinked polymer was used for the removal of metal ions and dyes [,,]. Saad et al. prepared crosslinked PEI using ECH in the presence of a NaOH solution at 50–70 °C, which formed a gel like material in few minutes. In this case, the mechanism involves both nucleophilic substitution of the chlorine from ECH and ring opening of the three-membered ring (Scheme 10) []. The metal adsorption characteristic is briefly discussed in Section 3.1 below.
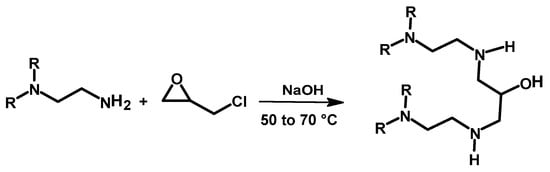
Scheme 10.
Crosslinking reaction of polyethylene imine with ECH [].
Xu et al. crosslinked PEI with ECH in a process called sedimentation polymerization [,] for CO2 adsorption. In this case, PEI and ECH were kept together at room temperature for 20 min. The mixture was injected through a column of canola oil using a syringe to form a sediment in the form of droplets. The column where the sediment was collected was kept in a water bath at 80 °C. The process resulted in crosslinked beads of PEI with a high surface area and thermal stability; so, the issues with solvent loss encountered with conventional amines were avoided. The crosslinking reaction mechanism and subsequent CO2 capture via a proposed carbamate formation are shown in Scheme 11. Interestingly, the material was regenerated via microwave heating for a batch experiment. The sedimentation polymerization gave beads with a low poly dispersity and with sizes in the range of 1200–1400 mm, as revealed by an SEM study. In the IR study, several peaks were observed from 1000 cm−1 to 3330 cm−1, corresponding to -OH stretching, -NH stretching, -CH stretching, -OH bending, -CH2 bending, and C-N stretching. The amount of the ECH crosslinker was varied to yield materials with a different degree of crosslinking, which was studied using IR spectroscopy. A decrease in the intensity of N-H and C-N stretching at 3268 cm−1 and 1103 cm−1, respectively, with the use of a higher amount of the crosslinker was attributed to a decrease in the amount of 1o and/or 2o amines in the crosslinked material. The thermogravimetric analysis demonstrated that the PEI HBs remained thermally stable at least up to 230 °C, which would be helpful for the regeneration of the crosslinked material for the batch adsorption of CO2. A fast thermal degradation of the crosslinked material occurred at temperature above 250 °C. CO2 adsorption details are discussed in Section 3.4.
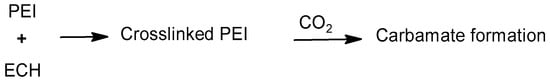
Scheme 11.
Crosslinking of polyethylene imine with ECH and proposed CO2 capture mechanism [].
In summary, the chemical crosslinking of PEI involves using crosslinking agents such as ECH and glutaraldehyde to form covalent bonds between PEI chains. The type of crosslinker, its concentration, and the reaction conditions provide different properties to the succeeding material, such as swellability, mechanical strength, and adsorption capacity. For instance, an increase in the degree of crosslinking will impact the available amine concentration and hence affect the overall properties of the material. The chemical structure of the crosslinked materials varies depending on the crosslinker used, resulting in materials having different functional groups that can form different interactions with different elements and molecules.
Undoubtedly, the crosslinking reactions discussed above play significant roles in altering the final materials’ properties. The reactions form a strong covalent bond, for example, in a nucleophilic substitution reaction and hence the reactions are irreversible. Recently, the idea of preparing crosslinked polymers using dynamic covalent crosslinkers that provide the materials unique properties, such as reversibility, reprocessability, self-healing, and the ability to respond to analytes, has found huge attention. For example, the synthesis and characterization of a hydrogel that responds to different stimuli have been reported [,]. In this regard, the use of crosslinker for PEI that provides a stable crosslinked material while reversibility is achieved when needed is interesting and deserves wider investigation in the future []. One such crosslinker for PEI is glutaraldehyde, which form an imine bond. It is known that the imine functionality is reversible and recyclable via a hydrolysis reaction []. Other dynamic covalent crosslinkers for PEI should be further studied in the future.
3. Applications of Crosslinked PEI
3.1. Adsorption of Heavy Metal Ions and Adsorption Models
The crosslinking of PEI/or biomass-modified PEI using an appropriate crosslinker is necessary to reduce the water solubility of PEI and hence to make it useful for an adsorption experiment with heavy metals [,]. Chen et al. prepared a magnetic gel material (PEI/Fe3O4) consisting of a biomass (corncob) modified by glutaraldehyde-crosslinked PEI for the adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ from aqueous solutions []. The materials prepared were characterized by different techniques, such as FTIR, SEM, and so on. The maximum adsorption of Cu2+ and Pb2+ was measured under different conditions: contact time, initial concentration, amount of the adsorbent, pH, and temperature. A fast adsorption in the first 1 h was recorded, while the following 1 h was slow and the adsorption reached a saturation point after 2 h. The decrease in the adsorption rate in the second 1 h is attributed to the decrease in the concentration gradient between the ions found at the surface of the adsorbent and the ions in solution and or due to ion–ion repulsion. The adsorption experimental data collected were fitted using the Langmuir (Equation (1)) and Freundlich (Equation (2)) isothermal adsorption models [] and the adsorption turned out to be better fitted by the Langmuir equation.
qe is the adsorbed amount at equilibrium in mg g−1, ce is the adsorbate’s equilibrium concentration in mg L−1, q0 is the maximum amount of monolayer adsorption in mg g−1, and KL is the Langmuir adsorption constant. A plot between ce/qe versus ce generates a straight line with a slope of 1/q0 and a y-intercept equal to 1/KLq0.
Similarly, b and n in Equation (2) are the Freundlich adsorption equilibrium constants.
A plot of ln qe versus ln ce produces a straight line with a slope equal to 1/n and a y-intercept of ln b.
The Langmuir isothermal adsorption model best fits the adsorption data for both ions, as revealed from a slightly higher value of the R2 (a statical value) as compared to the Freundlich isothermal adsorption model. One of the bases of the Langmuir adsorption model is the presence of a chemical adsorption on the surface of the adsorbent []. A Langmuir adsorption model of the ions in the PEI-CC@Fe3O4 implies that it is mainly chemical adsorption []. When it comes to the adsorption kinetics, a pseudo-second order model was found to best fit the experimental data, giving an R2 value of >0.99 for both Cu2+ and Pd2+. A pseudo-first order gave a slightly lower R2 value in relative terms to the previous model. The adsorption thermodynamics have also been studied for both ions at 308 K, and ΔG values were measured. Moreover, the mechanisms of interaction of both ions with the adsorbing material with the analytes were proposed. The interaction involves the nitrogen of the amine and the OH of the carbohydrate (corn) and forms four bonds around the ions [].
Glutaraldehyde-crosslinked PEI (PEI-GA) was used to adsorb Au3+ and Pd2+ in a wide pH range of 1 to 9 and at 25 °C, giving an adsorption amount of 2575 and 497 mg g−1, respectively []. Au3+ was adsorbed completely within 10 min for 8.3 mg L−1 and 20 min was needed for complete adsorption of Pd2+ from 9.7 mg L−1 concentrations in a water sample. In total, 2 h and 9 h adsorption equilibrium times were required for 523.9 mg L−1 Au3+ and for 565.6 mg L−1 Pd2+, respectively. The adsorption isotherm in this study was best described using the Sips model (Equation (3)), where βs is a model exponent and αs and ks are model constants in L mg−1 and L g−1, respectively. The Sips equation combines the Freundlich and Langmuir isotherms, and the model has been developed after recognizing the issue of a continual rise in the adsorbed quantity with an increase in concentration in the Freundlich equation []. The authors have also noted that the PEI-GA crosslinked material also exhibits high selectivity and repeatability toward Au3+ and Pd2+, with the adsorption mechanism involving chelation coordination and electrostatic interactions for both ions.
A water-insoluble epichlorohydrin-crosslinked PEI resin has also been prepared and used for trace metal and metalloid removal from mining and industrial wastewaters, and its suitability for complex various divalent metal cations were explored []. The synthesis and characteristics of the polymer are discussed in Section 2 (Scheme 10). The complexation order for metal ions studied was Cr > Zn > Fe > Ni > Mn > Pb. Among the metal cations in this study, chromium was found to have a high affinity toward the crosslinked polymer, while SeO32− and AsO2− were found to be poorly adsorbed. The study found adsorption percentages of Cr 97%, Ni 82%, Mn 79%, Pb 63%, and Zn 96%. The desorption of the ions was successfully achieved using HNO3 and the recovered polymer was reused for another batch of adsorption, where significant efficiency was recorded.
The chemical modification of PEI and subsequent crosslinking for various applications were also investigated. For example, a sulfonated crosslinked PEI was prepared by reacting the crosslinked polymer with 3-chloropropanesulfonyl chloride and heating under reflux overnight. The material was found to exhibit a high efficiency to remove Hg, with the percentage reaching up to 87% in synthetic solutions, with high selectivity even in the presence of competing ions such as Mn, Ni, Fe, Pb, Zn, and Cr. The mechanism of removal was proposed as a mercury ion binds to the functional groups present in the polymer, mainly the sulfate groups. The experimental adsorption data were fitted to adsorption isotherms, of which the Freundlich isotherm (Equation (2)) was found to fit best. The adsorption kinetics of mercury in the adsorbent is best fits a pseudo-second-order model (Equation (4)), which means that adsorption occurred via chemisorption []. Moreover, the crosslinked material can be regenerated by HNO3 treatment and hence is reusable for another batch of adsorption.
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (DGE-PEG), 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether (DGE-1,4-BD), and glutaric aldehyde (GA) were used as PEI crosslinkers to prepare cryogels. The crosslinkers were added to PEI in different molar ratios (1:1 and 1:2 molar ratios) and the reactions were performed at 23 °C (room temperature) and another batch at −20 °C. The crosslinked polymers were washed and dried in an oven before usage in adsorption studies. The degree of crosslinking was calculated from elemental studies, with GA giving a higher degree of crosslinking compared to the other crosslinkers (DGE-PEG and DGE-1,4-BD). The pH of the solution in GA crosslinking should be kept between 4.5 to 4.7, as a higher pH value increases the crosslinking extent. The materials used were Hg2+ as [HgCl4]2− complex and Cu2+ metal ions for sorption with DGE-PEG and DGE-1,4-BD, showing a high absorption efficiency. Moreover, generally, the crosslinked materials at lower temperature gave a higher absorption capacity of the ions than the ones prepared at room temperature, which could probably be due to the difference in the available amine groups of the crosslinked materials. Generally, more than a 98% Hg2+ removal efficiency was recorded from chloride solutions of Hg2+ []. The mechanism of interaction of the crosslinked materials with the Hg2+ proposed was an electrostatic interaction between an ammonium chloride salt found on the crosslinker with that of Hgcl4−, giving R3NH+HgCl3− [].
Selenium is a micronutrient with a permissible level of 0.05 mg L−1 in the environment. Higher concentrations of selenium in the environment, however, are toxic to aquatic life, which is a concern worldwide. There are several methods that have been studied to remove selenium from the environment, which include both physical and chemical methods. Sulfonated crosslinked PEI was used to remove particularly SeO32− from mining wastewater []. The sulfonic acid group is attached on the PEI by heating a mixture of crosslinked PEI and 3-chloropropanesulfonyl chloride in tetrahydrofuran at 70 °C. It is reported that the sulfonated crosslinked PEI showed a removal efficiency of 80 and 81% at pH 3 and pH 8, respectively []. Importantly, the authors demonstrated that the material is reusable for a second batch experiment after desorbing the selenite using an acid solution. The regenerated PEI showed a 72% removal efficiency of SeO32−.
PEI (MW = 10,000, 99%) was heated with 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine (TCT) at 70 °C with molar ratios from 10:1 to 2:1 in DMF to give a pale-yellow precipitate in a 35–85% of reaction yield (Scheme 9) []. The crosslinked polymers were characterized using spectroscopic techniques such as solid-state NMR and FTIR. The solid material was used to adsorb Au3+ from an aqueous solution, which showed an adsorption efficiency that reached up to 95.6% within 10 s, and an adsorption capacity of 1073.0 mg g−1 was recorded. This is a fast adsorption process. Moreover, the ion selectivity of the triazine-crosslinked polymer was also evaluated in a sample that consisted of Cu2+, Cd2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+ ions in addition to Au3+. The study showed that 97.9% of the Au3+ was selectively adsorbed in the presence of the competitive metal cations, showing the high affinity of the crosslinked material for gold. The adsorption efficiency of the crosslinked material for Cd2+, Cu2+, Ni2+, and Pb2+ was measured to be 1.79%, 3.06%, 1.52%, and 1.97%, respectively. Such excellent adsorption performance is mainly attributed to the complexation and mechanical stability of triazine-crosslinked PEI adsorbent. The regeneration of the adsorbent material was achieved using an HCl solution containing thiourea, which resulted in the release of 100% of adsorbed Au3+ within a minute and up to 10 times, signifying that the crosslinked polymer is reusable. The regenerated polymer was again used in five consecutive adsorption experiments without showing performance degradation. To test whether the adsorption of gold was dominated by physical or chemical adsorption mechanisms, the adsorption experimental data were fitted in two classical kinetic models: pseudo-first-order (Equation (5)) (diffusion of the adsorbate) and pseudo-second-order (Equation (4)) (chemisorption). A larger correlation for the pseudo-second-order model indicates that the Au3+ adsorption on the crosslinked polymer is more likely a chemisorption process, which might involve chelation and ion exchange [].
Au3+ was also recovered from a water solution using EGDE-crosslinked PEI as an adsorbent (Scheme 4) in a reverse suspension reaction. To a solution of EGDE in toluene, a water solution of PEI and span surfactant was added dropwise. The crosslinking reaction was achieved easily at 45 °C for 4 h, and further washing and drying gave a solid adsorbent. The maximum uptake amount of Au3+ was up to 944 mg g−1 from a gold-containing water sample. However, the adsorption capacity for gold slightly decreased to 887 mg g−1 in the presence of competitive ions, which is the case in gold-containing waste water. The little effect of the presence of competitive ions of gold adsorption is explained in terms of electrostatic attraction between the adsorbent and the analytes. Gold, under acidic conditions, exists in the form of AuCl4− (negatively charged), which is expected to form an electrostatic attraction with the positively charged adsorbent (protonation of the nitrogen of PEI is expected under acidic conditions). On the other hand, the metal cations will have repulsion with the positively charged adsorbent, which explains why the uptake of the positively charged metal ions was remarkably suppressed. Moreover, the polymer removed 88.7% of gold from water. The Langmuir and Freundlich equations were used to fit the experimental adsorption of Au(III) on the crosslinked polymer, but the Langmuir model (Equation (1)) [] was found to best describe the adsorption on the polymer studied. The pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic equations were applied to fit the sorption kinetic data. The pseudo-second-order equation described the kinetic sorption procedure on the polymer, as evidenced by the high R2 value (0.998). Gold is assumed to have been removed by an electrostatic interaction and or chelation and is shown in Figure 5.
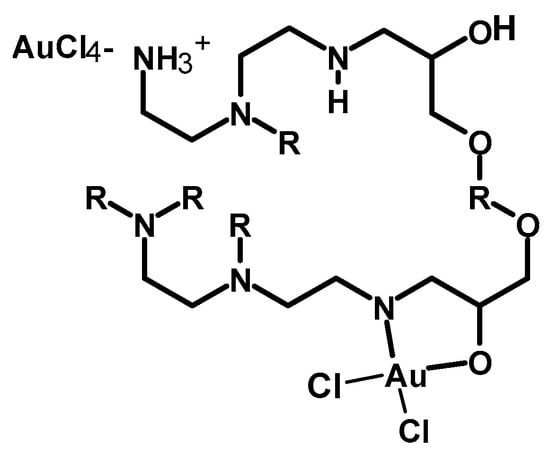
Figure 5.
Proposed gold chelation and electrostatic interaction with the crosslinked material [].
A glutaraldehyde-crosslinked PEI-coated polysulfone/Escherichia coli bacterial biomass composite fiber (PEI-PSBF) was used as an adsorbent for Pd2+ from acidic solutions []. The fiber was prepared by passing a DMF-dissolved polysulfone and E. coli biomass through a spinneret with a 0.1 mm diameter into deionized water. The extruded materials were collected, washed, and then lyophilized using a freeze dryer to yield the composite material (PSBF) []. The PSBF was the mixed with a 2.3% PEI solution and crosslinked by adding the desired amount of the crosslinker. The deionized water-washed material was dried using a freeze drier (TFD Series, Ilshinbiobase, Korea). The crosslinked PEI-coated PSBF was used to take up Pd2+ and the adsorption capacity was found to be seven times higher and to have faster sorption kinetics in comparison with the adsorbent that was not coated with PEI (PSBF only). The kinetic data were well described by the pseudo-second-order kinetic model. The study revealed fast adsorption kinetics for Pd2+, with an adsorption efficiency of 216.9 mg g−1 (from Langmuir model) of the analyte with adsorption reaching at equilibrium in 240 min. On the other hand, the theoretical sorption capacities were studied (adsorption isotherms). In this case, the Freundlich model was best for PSBF while Langmuir model was best for the PEI-PSBF adsorbent. The adsorbent was recovered by releasing the Pd2+ using a 0.1 M HCl/0.01 M thiourea solution mixture, with a desorption efficiency of the mixture of approximately 97.4%, and it was noted that the material can be reused for adsorption for up to five batches of adsorption and desorption processes.
PEI in a Ca2+-alginate hydrogel matrix was crosslinked with glutaraldehyde to effectively adsorb and recover gold from acidic solutions []. Alginate, an anionic polysaccharide, forms stable hydrogels with divalent metal ions, including Ca2+. The crosslinked material was achieved by the extrusion of a mixture of PEI and alginate onto a mixture of CaCl2 and glutaraldehyde [,]. Solid formation was accompanied by ionotropic gelation and a crosslinking reaction. The two other materials prepared and tested for gold uptake consisted of PEI, alginate, and CaCl2 (without crosslinking), and pristine (consisting only alginate and CaCl2). The materials were washed and solid products were obtained by freeze drying. The adsorbent capacities of the three materials for gold were tested. While the glutaraldehyde-crosslinked material showed an adsorption capacity of 2300 mg g−1, the non-crosslinked material showed an adsorption capacity of 1400 mg g−1 for gold. The pristine material consisting of alginate and CaCl2 showed poor gold adsorption (4.81 mg g−1). The desorption of gold was achieved using thiourea/HCl, and its best combination resulted in the leaching out of 97% of the gold from the adsorbent. The gold binding mechanisms were studied and elucidated with the aid of XRD and XPS as involving sequential electrostatic interaction and reduction by the amine, hydroxyl, and aldehyde groups.
PEI was crosslinked with glutaraldehyde and glyoxal in the presence of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) in a typical beaker reaction at room temperature to yield an orangish-reddish crosslinked material (Figure 6). The resulting material was a jelly before it was put into an oven for drying. The crosslinked material was mixed with a copper ion-spiked water solution and stirred at room temperature to evaluate the copper binding capacity of the adsorbent material. The bulk crosslinked material was found to be efficient at removing copper ions from water within a short period of time. The study showed that the copper adsorption of the material was up to 350 mg g−1 for the crosslinked polymer, which has HPMC as an additive, and leached out later. However, the two other crosslinked polymers—one without HPMC but crosslinked with glutaraldehyde and the second materials crosslinked with glyoxal—showed a lower copper adsorption capacity. The adsorption of Cu2+ on the crosslinked PEI is best described by a pseudo-second-order kinetic model (Equation (4)), as revealed by the high R2 value of a linear plot plot of t/qt versus t. The material is also reusable for repeated adsorption batches after the release of adsorbed copper ions in 2% HNO3 [].

Figure 6.
Photo of the crosslinked polyethylene imine material (texture dried and before drying) [].
Zho et al. used PEI to crosslink cellulose nanocrystals for effective use as adsorbent of rare earth elements (REEs) from water and recovery of the REEs. Apart from the role of PEI in crosslinking the cellulose nanocrystals, it will also act as a coordination cite and hence bind the REEs in an aqueous solution. The use of PEI as a crosslinker avoids the use of toxic crosslinkers as well. The crosslinked material prepared gave adsorption capacities of 0.611, 0.670, and 0.719 mmol g−1 for La3+, Eu3+, and Er3+, respectively, with the primary and secondary amines playing roles in the binding process. Rare earth elements have similar chemical properties and hence are difficult to separate when they are found together in a sample. However, this PEI-crosslinked cellulose adsorbent showed a binding preference toward Er3+ compared to La3+ and Eu3+, which makes the crosslinked material interesting for a real application [].
The synthesis of porous crosslinked PEI was found to be interesting to increase the adsorption capacity and the adsorption kinetics of heavy metal cations. In this regard, PEI-coated diatomaceous earth (DE) was crosslinked with glutaraldehyde, with the DE serving as bio-template. The template was removed in subsequent steps to yield a porous structure. The synthesis of the adsorbent involved the dispersion of washed DE into a solution containing PEI in 0.5 mol L−1 NaCl to yield a 10 wt% (DE plus PEI) dispersion. The solid dispersion was collected after centrifugation and crosslinked with a glutaraldehyde solution (0.5 wt%). The particles were collected and washed and subjected to etching with alkaline KOH to remove the bio-template (DE) and hence resulted a porous crosslinked PEI []. The size of 80% of the particles, as measured with 2000 (Malvern Instruments Ltd., U.K.), was found to be below 100 μm, while the particles were within the range of 2–150 μm. Interestingly, the copper ion uptake capacity of the etched GA-PEI resin was determined to be >8 times greater than non-etched GA-PEI-DE particles, revealing the importance of etching, which led to a more porous structure. The porous PEI material was also tested for its selectivity for ions and found to be more selective for copper ions compared to commercial resins (Purolite S930 Plus and Lewatit TP 220) [], indicating the potential of the crosslinked material for binding copper ions in a water sample. The adsorption of copper was found to be very fast, with the adsorption reaching a capacity of 77% in 15 min and adsorption was completed within 1 h. The adsorption isotherms of etched GA-PEI-DE and Purolite S930 (commercial resin) were best described by the Langmuir model.
In another work, aerogels were prepared by blending PEI with different materials such as chitosan [] and alginate [] for Cr6+ adsorption. Li et al. prepared a cellulose/PEI nanofibril aerogel for Cu2+ and Pb2+ adsorption. The maximum adsorption capacities were calculated to be 357.44 mg g−1 and 175.44 mg g−1 for Cu2+ and Pb2+, respectively []. Su et al. prepared an aerogel by blending PEI/montmorillonite/sodium alginate/carboxylated chitosan and Ca2+. The aerogel had high physical stability due to the various intermolecular forces existing between the blended materials. The material showed an adsorption ability toward Cu2+ in aqueous solution. The 2.5 wt% PEI-containing material showed a maximum adsorption capacity of 203.99 mg g−1 []. The material was also reusable, showing a 51.4% Cu2+ removal efficiency after 10 cycles of adsorption and desorption studies. Wang et al. prepared a three-dimensional porous aerogel from a chitosan-modified PEI crosslinked with ECH. The material was used to remove Cr6+ from the environment and showed a maximum adsorption capacity of 445.29 mg g−1 []. The adsorption kinetics and isotherm experimental data were fitted using adsorption models. A pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Langmuir isotherm model were found to explain the experimental data. Moreover, the material has a high adsorption capacity after more than 10 adsorption and desorption cycles, demonstrating the stability and recyclability of the polymer. Table 1 shows a summary of PEI-based crosslinked materials and their performance in metal adsorption from aqueous solutions. Looking at the materials discussed in this review, the reactions conditions and the types of crosslinkers play significant roles. Among the widely used crosslinkers, glutaraldehyde is at the forefront due to its fast reaction with PEI and due to its high tendency to crosslink PEI. As indicated in Table 1 (and discussed earlier), the glutaraldehyde-crosslinked material (in the presence of an additive or not) showed excellent adsorption capacities for different metal cations, such as Cu2+, Pd2+, and Au3+, in water. For example, a gold adsorption of 2300 mg g−1 was reported by Bediako et al. [] using a PEI/Ca2+-alginate hydrogel crosslinked with glutaraldehyde. Copper and lead adsorption reached up to 459 and 497 mg g−1 in a glutaraldehyde-crosslinked PEI/Fe3O4/corncob composite and PEI only material, respectively. However, poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether-, 1,4-butanediol diglycidyl ether-, and EGDE-crosslinked materials have also given respectable adsorption values for Hg2+, Cu2+, and Au3+, as summarized in this review. In particular, materials that have chelating cites such as NH2 and OH groups work well as adsorbents for metal ions and other pollutants. Equally important is the desorption efficiency and the reusability of the crosslinked materials. While most of the materials discussed can be regenerated by chemical treatments, a 2,4,6-trichloro-1,3,5-triazine (TCT)-crosslinked PEI material reported by Hu et al. [] is among the substances with the fastest regeneration kinetics (1 min) and an almost 100% regeneration efficiency. The material worked fine for up to 10 adsorption and desorption cycles.

Table 1.
PEI-based materials, crosslinkers, and applications in metal removal from aqueous solutions.
3.2. Adsorption of Heavy Metals on a PEI Coating and Release
The deposition of films on substrates has been used in different research areas and material productions. Some of these film-making techniques, such as spin coating, spray coating and doctor blading, have widely been known in organic photovoltaic research and material production [,,]. The use of spin coating and spray coating methods in PEI film making has also been reported in the literature. A glutaraldehyde (GA)-mediated covalent layer-by-layer (LbL) assembly technique was reported to yield a layer with a thickness on the nanometer scale for MnCO3 adsorption []. Spin coating was used to make a thin film of PEI on a silicon wafer substrate, which was subsequently crosslinked by immersing the coated substrate in a glutaraldehyde solution to give a coating thickness of 7.9 nm, as determined by ellipsometry [,]. The crosslinked PEI coating was then immersed in water with a known concentration of Cu2+ that ranged from 2 to 200 ppb for a Cu2+ uptake experiment. The result has shown that the coating accumulates as much as 13, 8, and 5 wt% copper from 200, 20, and 2 ppb in artificial seawater, respectively. The selectivity of the coating was also tested by immersing it in a water sample that contained 12 ions, including Cu2+. Even though Zn2+ gets adsorbed quickly, Cu2+ is seen to displace the adsorbed Zn2+ over time and hence copper eventually accumulates preferably in the crosslinked PEI material. The demonstrated selective adsorption of copper at low concentrations from artificial seawater can have an application in water purification by sensing and extraction of copper ions from seawater [].
In another study, nano-thin coatings of glutaraldehyde (GA)-crosslinked PEI/mesoporous diatomaceous earth particles were prepared for the selective and effective adsorption of copper from seawater. The composite material could remove Cu at 200 ppb from artificial seawater in the presence of other competing metal ions. The selectivity of the crosslinked polymer for copper was compared with that of the non-crosslinked PEI. While a trace amount of Zn was detected in the crosslinked polymer, about 30% of zinc relative to the amount of the adsorbed copper was found in the non-crosslinked PEI. The regeneration of the material for subsequent adsorption was also demonstrated by treating the coating with an acid [].
Biological organisms such as bacteria, diatoms, and microalgae accumulate quickly on marine infrastructures if left unprotected for some time. Such growth of organisms on surfaces is known as fouling. A ship, for example, would consume 40% more fuel after 6 months due to additional hull drag from fouling if no antifouling (AF) paint is used on the body of the ship []. Copper compounds are traditionally used in the marine environment to control biological growth. For instance, Cu-based paints such as copper pyrithione (CuPT) and Cu2O are used on ships and other marine environment infrastructures for fighting potential fouling []. However, the use of copper-based paints will likely increase the copper concentration in the marine water via the gradual leaching of copper from the paint, which has become a threat to the life of sea inhabitants. Copper concentrations that exceed 3.1 ppb (the U.S. federal standard) affect various life stages of marine organisms, including mussels, oysters, scallops, sea urchins, and crustaceans []. While the use of copper is necessary to avoid/minimize the impact of fouling, it should be performed in such a way that the impact of copper to the marine environment is avoided. This is possible through the controlled release and adsorption of Cu from the paint. In this regard, a study was conducted on Cu2+ uptake in a PEI coating and its electrochemically initiated release on a need basis (Scheme 12). In the work, a thin film of PEI/HPMC was deposited on a conducting carbon cloth substrate using a spray coating technique. The coating was then crosslinked by immersing the coated material in a dilute glutaraldehyde solution. The HPMC additive is sparingly soluble in water, which leaches out from the coating upon keeping it in water to yield a porous structure. Copper ions were adsorbed on the coating by dipping the crosslinked-PEI-coated carbon cloth in an artificially prepared copper solution. Once copper adsorption was completed, the release of the stored Cu2+ was investigated by electrochemical means by applying different current densities to the coating. The amounts of Cu2+ released were measured to be 4.1, 11.8, and 19.9 mg cm−2 L−1 for 1, 2, and 5 mA cm−2 of applied current, respectively. However, 20.6 mg cm−2 L−1 of copper was measured at an applied current of 15 mA cm−2, which is almost similar to the amount of copper collected from 5 mA cm−2 of applied current. The release of the adsorbed copper was also achieved by an acid treatment (2% HNO3), resulting in the release of 12.5 mg cm−2 L−1 copper within 20 min and 18.1 mg cm−2 L−1 after 24 h, which is slightly lower than the chronopotentiometric release at 5 mA cm−2. The regenerated coatings were also reusable for the subsequent adsorption of copper ions. Scheme 12 shows the preparation of the crosslinked PEI coating, uptake of copper ions, and release of Cu2+ [].
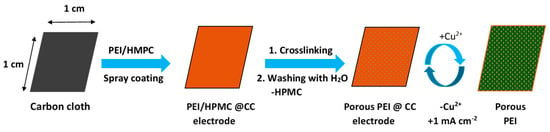
Scheme 12.
Preparation of the porous PEI@CC electrode and working principle of the reversible copper uptake and electrochemical release, simplified on a segment of a carbon cloth (CC) fiber (figure adapted from ref. []).
In conclusion, the use of a thin coating of crosslinked PEI on a conducting carbon cloth/other substrate to adsorb and release ions in a controlled way has been reported in the literature. The idea of the electrochemical-triggered release of ions such as copper stems from the need to control the amount of copper that goes into the environment from antifouling coatings of marine infrastructure. Further work will be needed to transfer the proof-of-concept work into practical applications. The coated films will also find applications in water purification and the concentration of trace metals from the environment. The use of coatings for the adsorption and release of other metal ions can also be investigated.
3.3. Crosslinked PEI for Dye Adsorption and the Separation of Organic Acids and Aldehydes
Polar dyes, such as reactive dyes, acid dyes, and direct dyes, are widely manufactured and used in various industries, including textile and paper []. Apart from the aesthetic issues that dyes can cause, the release of dyes into water bodies can have a significant impact on aquatic life by hindering light penetration and hence disrupting the aquatic ecosystems []. This is a series concern worldwide that needs to be addressed. The presence of some dyes as low as <100 mg L−1 in drinking water has adverse effects on human health, causing respiratory infections, hepatitis, vomiting, stomach aches, and even death [,].
To address this problem, researchers have been exploring various methods for the removal of polar dyes from water using adsorbents such as chitosan and other bio-sorbents []. One promising approach involves the use of polymers as adsorbents. PEI is an effective material for dye adsorption due to its high density of amine groups, which can interact with various dyes through electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. For example, Takagishi et al. crosslinked PEI with dichloroethane, glyoxal, or glutaraldehyde to yield a water-insoluble polymer and used it to adsorb methyl orange and its other homologues. The glutaraldehyde-crosslinked material showed a markedly increased binding affinity toward the dyes due to a higher degree of crosslinking compared to the other crosslinkers tested in the study []. You et al. prepared an ECH-crosslinked composite of chitosan/PEI/Fe3O4 using a facile one-pot synthesis approach where a mixture of FeCl3·6H2O, FeCl2·4H2O and chitosan was heated in a water–acetic acid mixed solvent at 90 °C under an inert gas atmosphere. The mixture was treated with aqueous ammonia, followed by the addition of PEI and the crosslinker. The final product was obtained after washing and freeze drying. The adsorption capacity of the prepared magnetic adsorbent toward Congo red (CoR) in aqueous solutions was investigated []. The chitosan/PEI/Fe3O4 composite showed an enhanced removing capacity (1876 mg g−1 at 40 °C) for CoR from aqueous solutions with an over 99.3% CoR removal efficiency. In a temperature-dependent adsorption experiment, the adsorbent performed at a relatively higher temperature (40 °C). The experimental adsorption kinetic data were better fitted by a pseudo-second-order model. Liu et al. incorporated crosslinked PEI onto a nylon microfiltration membrane. The membrane soaked in PEI was treated with trimesoyl chloride (1,3,5-benzenetricarbonyl trichloride) for an interfacial amide bond forming reaction (crosslinking reaction) to take place between the amine-rich PEI and the crosslinker. This composite membrane demonstrated strong dye adsorption capabilities. For example, the adsorption capacity for Sunset Yellow (SY) was measured to be 0.7 mg cm−2. The nylon-crosslinked PEI composite showed an absorption capacity of 600 mg g−1 for SY dye [].
Glycerol diglycidyl ether (GDE) crosslinked PEI at −18 °C in a cryopolymerization technique to yield a porous material (pore size > 100 μm) to adsorb dyes having charged groups. The PEI cryogel modified with [PF6]− was used to adsorb bovine serum albumin (BSA), giving an adsorption capacity of 47.8 ± 5.7 mg g−1. The material prepared was also successful at removing methyl orange (MO) and eosin Y (EY), with removal efficiencies reaching 98.5 and 98.6%, respectively, from an aqueous solution. The crosslinked material was also used as a column packing material to separate methylene blue (MB) successfully from a mixture of MO and EY [].
Song et al. prepared water-insoluble PEI/polyacrylonitrile nanofibrous films by crosslinking with ECH. The maximum adsorption of the material for MO reached 636.94 mg g−1 []. The material has also demonstrated its reusability by maintaining a 75% MO adsorption capacity after four cycles of adsorption and desorption experiments. PEI has also been used as a crosslinker for a cellulose-based aerogel adsorbent consisting of cellulose acetoacetate and β-cyclodextrin for removing harmful dyes from water. The adsorption capacity of the material was tested toward MO and was found to reach up to 1013.11 mg g−1 at 25 °C [].
3-Aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) was grafted on multiwall carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) by refluxing the two materials together and mixed with PEI and crosslinked with ECH to yield the crosslinked material (Scheme 13). The material produced was used to remove Reactive Yellow from water and found to have a 2.8 times higher adsorption capacity than that of MWCNT only, showing the superiority of the composite material for the adsorption of Reactive Yellow. The kinetic studies showed the removal of 99% of the dye molecules (50–100 mg L−1) in less than 15 min, demonstrating the effectiveness of the adsorbent to rapidly eliminate reactive dyes from aqueous solutions [].
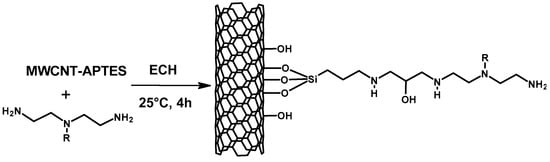
Scheme 13.
Reaction pathway for the preparation of PEI/APTES-MWCNTs (adapted from ref. []).
Lignocellulose biomass materials are important sources of value-added organic acids and aldehydes, such as furfural, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, vanillin, and so on, by hydrolysis reactions []. Obtaining these compounds in pure form has been a long-standing challenge, and extraction, chromatography, and adsorption methods have been studied. Yang et al. [] studied glutaraldehyde-crosslinked PEI to selectively separate the lignocellulose-derived organic acids and aldehydes without significantly adsorbing sugars. The study was performed on single, binary, and multiple solutes to understand the effects of solutes on the selectivity and adsorption capacity of the adsorbent. The adsorption efficacy of aldehydes over organic acids was achieved by adding inexpensive neutral salts as a composite material. An acid–base reaction is expected to take place between the amine functional group of PEI with an acidic functional group-possessing organic acid to form a salt in the interaction. The presence of other salts does not favor the adsorption of organic acids. An aldehyde functional organic compound, on the other hand, can be absorbed on PEI via a nucleophilic addition/elimination reaction between the aldehyde and the amine functional groups []. The recovery of the adsorbed molecules was achieved using a 1 mole/L HCl solution. Overall, a crosslinked-PEI-based adsorbent in the form of a powder, nanofibers, membrane or aerogel is well qualified to serve as a potential candidate for dye, organic acid and aldehyde removal from samples. Table 2 shows a summary of PEI-based crosslinked materials and their applications in dye adsorption from the environment.

Table 2.
PEI-based materials and their applications in removing dyes from samples.
3.4. Pristine and Crosslinked PEI in CO2 Adsorption
Extensive scientific proof indicates that the world has seen an increase in CO2 emissions from fossil fuel, which have caused the global temperature to rise. In the fight against global warming, reducing the production and emission of CO2 to the environment has been the focus of researchers. In this quest, the development and use of CO2 capture systems are worth mentioning. Nitrogen-rich solid adsorbents are widely used to capture CO2. To enhance CO2 absorption, researchers have explored modified PEI as a viable approach. PEI, when chemically modified, demonstrates an improved capability to capture and bind CO2, thereby offering a promising method for mitigating CO2 impacts.
PEI was crosslinked with ECH in a one-step reaction to yield PEI hydrogel beads (PEI HBs) with an increased surface area. The material showed increased performance in capturing CO2 compared to that of liquid PEI. Moreover, the crosslinked polymer showed excellent thermal stability and issues with solvent loss were avoided []. It is noted that a dry crosslinked PEI has very little tendency to capture CO2 due to the closed structure and hence low diffusibility of the CO2 gas. However, with the addition of water, the CO2 uptake showed an improvement, with uptake reaching to 60.2 mg g−1 at a 70% water weight ratio. The improvement of the CO2 capture capacity of the material with the addition of water was attributed to the swelling of the crosslinked material and hence allowing the CO2 gas to diffuse through the material, and the presence of water might have allowed the tertiary amines to play a role in capturing the CO2 gas []. The formation of carbamic acid and bicarbonate was detected in IR study in the wet crosslinked PEI, which is a proof of the capture of CO2 gas. Microwave heating in a method called “temperature swing” (the CO2-loaded crosslinked PEI is heated with a microwave followed by addition of water and then cooling) regenerated the used crosslinked PEI successfully. Heating the sample in a convection oven at 165 °C for 45 min has also achieved the desorption of the CO2. The material was recycled for about 10 times and the adsorption capacity of the material remained stable, indicating the material’s recyclability. PEI crosslinked with triglycidyl trimethylolpropane ether (TTE) also showed a CO2 uptake efficiency of approximately 50 mg g−1 of sorbent [].
PEI dispersed in mesoporous silica and mesoporous silica (without PEI) were compared for their CO2 adsorption capacities from a mixture of gases consisting of CO2, N2, O2, CO, H2O, and NOx (a flue gas) generated from a natural gas-fired boiler. The PEI-loaded mesoporous silica showed a higher adsorption capacity and higher selectivity for CO2 than ordinary sorbents. The mesoporous silica alone (MCM-41) (without PEI) was found to have an adsorption capacity of 8.6 mg g−1, while the PEI-containing silica (MCM-41-PEI-50) showed a CO2 adsorption capacity of 112 mg g−1, clearly showing the positive role of PEI. The lower adsorption capacity of the silica (without PEI) was due to a weak chemical interaction between the adsorbent and CO2 []. Pure PEI has shown an adsorption capacity of 109 mg/g, as reported in another study []. In another study, a PEI-loaded porous mesoporous molecular sieve (SBA-15) was used for CO2 sorption in a temperature- and time-dependent study []. An adsorption study at higher temperature (75 °C) improved the adsorption of CO2, which could be due to the flexibility of the adsorbent material and better diffusibility of the CO2 gas. Linear and branched PEI were crosslinked with divinyl sulfone to yield rigid and insoluble structures that were studied for CO2 gas adsorption. The best performance was an adsorption capacity of 4.34 mmol g−1 at 1 bar of CO2 from the linear microgel, which is an environmentally friendly gel that functions as a well-performing dry CO2 adsorbent []. Xu et al. modified a molecular sieve (MCM-41) using PEI to prepare a MCM-41-PEI adsorbent for CO2. It was found that PEI loading of 50% (by mass) in MCM-41-PEI showed the highest CO2 adsorption capacity of 246 mg g−1 (based on PEI), 30 times higher than that of MCM-41 and 2.3 times higher compared to pristine PEI (109 mg g−1) []. According to Sun et al., PEI mixed with ethanolamine (MEA) and impregnated with FNG-II silica (FS) adsorbents were good CO2 adsorbents from a simulated biogas. A composite material made up of FS, 10% PEI, and 10% MEA exhibited an attractive CO2 adsorption capacity of ca. 64.68 mg g−1, which was increased by 81 % in comparison to FS-20% PEI. The material has also shown a higher thermal stability [].
A commercial polymethacrylate resin with a bead size of 0.44 mm diameter was impregnated with PEI and used to adsorb CO2 from a biogas []. The surface area (m2/g) and pore volume (m3/g) of the resulting material were measured at different loadings of PEI. The surface area dropped from 587 m2/g (without PEI) to 14 m2/g (with 50% of PEI). Similarly the pore volume decreased from 1.45 cm3/g to 0.26 cm3/g. Interestingly, both parameters got smaller with an increase in the loading of PEI, with the smallest value recorded being with 50% of PEI loading. The decreases in the parameters indicate the successful loading of the branched PEI into the support pores, reducing the average pore volume of the sorbent with increasing amine loading. The CO2 gas is expected to undergo an acid–base reaction with the basic amino group of the PEI during the adsorption process. The CO2 adsorption capacity of the untreated polymethacrylate was found to be negligible, while the highest was 2.7 mmol/g for 30PEI-HP2MGL. An IR analysis has shown that the adsorption of CO2 on the adsorbent is due to the formation of zwitterion intermediate between the CO2 and the basic amine group of the PEI and finally due to the formation of ammonium–carbamate ion pairs (Scheme 14).
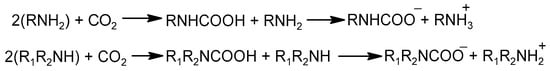
Scheme 14.
Reaction mechanism for the adsorption of CO2 [].
An ice templating method was developed to prepare self-supported crosslinked branched PEI materials for CO2 adsorption from simulated flue gas []. The ice templating method requires a thorough mixing of the PEI with the crosslinker (poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether) in vortex mixer (500 rpm) for 5 sec followed by keeping the mixture in a freezer (−10 °C) for two days or putting the vial containing the mixture in liquid nitrogen for instant freezing. The frozen materials are then thawed at room temperature and the sample is collected and washed. The schematic synthesis of the self-supported PEI adsorbent is shown in Scheme 15. The process yields a porous structure of a crosslinked PEI. The sorbent capacity of the prepared materials was measured to be from 0.32 to 2.81 mol CO2/kg. At 65% relative humidity, the adsorption capacity was even measured to be higher (5.5 mol CO2/kg). The material has also shown fast adsorption kinetics, reaching 80% of its maximum capacity in only 18 min. The prepared adsorbent also presents stable recyclability over 50 dry adsorption–desorption cycles with only a minor loss of CO2 capacity (4%). The synthesis of the material is also claimed to be economically feasible and it can likely be easily molded into any shape. Therefore, the material is considered a promising new material for post-combustion CO2 capture.

Scheme 15.
Schematic of the synthesis of the self-supported polyethylene imine adsorbent (adapted from ref. []).
The CO2 adsorption efficiency and effect of the presence of SO2 on the adsorption capacity of two self-supported crosslinked PEIs named PEI 196 and PEI 78 were studied. The two materials were prepared at low temperatures (−196 and −78 °C) []. The pore diameter and wall thickness of the crosslinked were measured using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (Zeiss Ultra60 FE). The pore length, pore width, and pore wall thickness were measured to be 19.6, 6.3, and 6.1 μm, respectively, for PEI 78. On the other hand, the corresponding values for PEI 196 were 27.3, 5.2, and 3.0 μm, respectively. In the study of the materials with elemental analysis and XPS, PEI 196 showed a lower degree of crosslinking and hence had more primary and secondary amines compared to the other material obtained at a relatively higher reaction temperature (−78 °C). PEI 196 was found to be impacted in its CO2 adsorption capacity, showing a 32% drop when SO2 was present []. The reaction of SO2 with an OH functional group of the crosslinked polymer is shown in Scheme 16. A similar reaction is sought to take place with primary amines of the crosslinked PEI polymers.
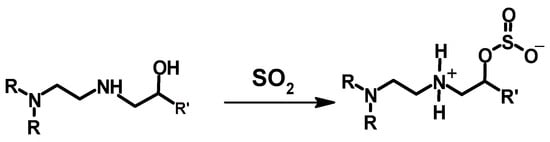
Scheme 16.
Segment of crosslinked PEI and proposed interaction with SO2 [].
Porous PEI with and without Al2O3 powder additive were crosslinked poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether at low temperature (−196 °C). The Al2O3-containing material gave a narrow pore size distribution and thinner pore walls compared to the material without Al2O3 in the morphology study. PEI only showed a pore length of 5–10 μm and a pore wall thickness of 4–6 μm. On the other hand, the materials with 10%, 20%, 40% Al2O3-containing PEI showed a rather smaller pore length and narrow pore thicknesses, with values in the range of 0–5 μm for pore length and 2–4 μm for pore wall thickness, giving these materials a higher CO2 uptake efficiency. Out of the three prepared samples containing different loads of Al2O3, the 6.5 wt% Al2O3-containing material showed the highest CO2 uptake (1.23 mmol/g of sorbent) [].
A solid fiber sorbent produced from an N,N-diglycidyl-4-glycidyloxyaniline-crosslinked PEI (0.35/1 wt. ratio) captures 0.37 mmol of CO2 per g of fiber and 0.67 (post combustion) mmol CO2 per g of fiber. A nonoptimized prototype hollow fiber assembled into a ten-fiber module was manufactured and exhibited a stable 0.2 mmol CO2 g-fiber−1 capture during direct air capture cycling [].
The capture of CO2 using amine-containing materials such as PEI and tetraethylenepentamine (TEPA) is known to proceed through the formation of a stable carbamate. It is also important to consider how facile is the desorption of CO2 and regeneration of the amine adsorbent. For a low-cost application, a material that could be regenerated at low temperature is preferable. In this regard, a systematic study using different amines was conducted, of which an isopropyl amino group-containing material was found to exhibit the highest CO2 capacity for low-temperature regeneration [].
PEI in its different forms (pristine, crosslinked, and dispersed in a support material) is among the materials widely studied for CO2 capture. The materials’ success in capturing CO2 selectively depends on various factors, such as the type of crosslinker used, the reaction conditions, the temperature where the adsorption is performed, and so on. For example, a comparison of two materials prepared at a very low temperature (−196 °C and −78 °C) is reported in the literature. The material prepared at −196 °C was found to have a higher loading of primary amines and hence was better at capturing CO2 gas. The presence of water also affects the performance of the material in reacting with CO2. A study has showed that a crosslinked PEI gel performs better in the presence of water compared to the dry analogue. Some materials could be rigid in structure and might not allow the diffusion of CO2 gas. In such cases, a higher temperature has improved the adsorption capacity of the material due to the improvement in the flexibility (improved porosity) of the material at higher temperature. In another study, a comparison of BDDE and ECH as crosslinkers revealed that BDDE gave better CO2 capture due to a higher amount of hydroxyl groups in the final product. These examples are testament of the fact that the type of crosslinkers and the reaction conditions are key parameters in the development of materials useful for CO2 capture. Overall, amine-containing materials such as PEI are among the most studied and are promising materials for CO2 capture.
4. Conclusions
Crosslinked PEI and its composites have proven to be versatile materials used in multiple areas. The crosslinking reaction and other modifications of PEI are achieved via chemical and physical methods to make the material suitable for the specific applications. The crosslinking process enhances PEI’s stability and adsorption capacity, which are crucial for environmental and industrial applications. PEI is effective at adsorbing heavy metals. Crosslinked PEI has an enhanced adsorption capabilities for metals like Cu2⁺, Pb2⁺, Au3+, and Pd2+. The adsorption capacities of the crosslinked PEI for metals can be tuned through the use of appropriate crosslinking reactions, as well as the manipulation of the reactions conditions. As described in the literature, the porosity of the resulting material will have a crucial role in improving the metal capturing tendency. In this regard, researchers have used templates for the synthesis of the materials whereby the templates are removed by storing the material in appropriate solvent (and or by treating with chemicals) and the template leaches out with the objective of improving porosity. The concentrations of the primary, secondary, and tertiary amines have also paramount importance in the behavior of the final product. Moreover, the basic amino groups in PEI enables it to interact with dyes such as methyl orange, Congo red, and various other organic molecules through electrostatic interactions, hydrogen bonding, and van der Waals forces. The strong interactions with these organic molecules make PEI a potential alternative for removing dyes from contaminated water. Crosslinked PEI is also used in the separation of value-added organic acids and aldehydes, such as furfural, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, vanillin, and so on, from a lignocellulose mixture of compounds. The fact that PEI is used to separate a particular organic compound that possess the necessary functional group from a mixture is interesting and can potentially have applications in a range of research areas, such as in organic synthesis and natural product chemistry, where the separation of compounds is part and parcel of the research. Reports have also revealed that crosslinked PEI has enormous potential in capturing CO2 from the environment. In addition to the adsorption of various pollutants, the adsorbates are also easily released using acid treatment, electrochemical processes, and other chemical treatments. The regeneration of the material without apparent degradation makes crosslinked PEI reusable and hence cost effective. Overall, due to the facile nature of the crosslinking reactions, modifications and its recyclability, PEI is a low-cost alternative for various adsorption applications. This review has attempted to bring together the major crosslinking reaction techniques reported in the literature. The mechanisms of the reactions and the characteristics of the final materials are discussed. For commercial applications, material recyclability is important for price affordability. The different ways reported to regenerate and reuse crosslinked PEI are discussed in detail. One technique discussed is by passing an electric current to alter the pH of the water and hence to facilitate the desorption of metal ions from a film of crosslinked adsorbent. The application of the materials in removing pollutants such as metal cations, CO2, and dyes and the adsorption models are discussed.
5. Future Directions
The type of crosslinker and the reaction conditions affect the subsequent material properties, which in turn determine the adsorption capacity of the crosslinked PEI/composites for metal cations, dyes, and CO2 and other pollutants. In this regard, several crosslinkers for PEI have been developed and used to crosslink PEI under different reaction conditions, resulting in different functional groups in the crosslinked material. However, there are not many comparative studies of performances of the materials prepared with different types of crosslinkers but under similar adsorption conditions. We believe that such comparative experimental studies will help us to better understand the adsorption mechanisms and the actions of different functional groups in the crosslinked material. Density functional theory (DFT) calculation can be used as a tool to predict materials’ properties and the adsorption tendency of the materials toward different types of pollutants. A comprehensive study that includes both theoretical and experimental components will help us to understand materials’ properties well. which will pave the way toward developing state-of-the-art materials for future commercialization. The stability and cost of crosslinked materials are other key aspects for commercial applications that need focus in the future. PEI comes from commercial sources with different architectures and molecular weights. In our review, we have identified that the literature is not clear on the effects of the architecture and molecular weight on the ensuing properties of the crosslinked materials, which need more work in the future.
Moreover, our review article is based on materials prepared in small scale and tested at a laboratory level. Such studies may not necessarily reflect the performance of the materials when they are used at a larger scale. Such studies are lacking in the current literature, which we recommend researchers to work on in the future. Also, the deposition of PEI on a substrate and subsequent crosslinking have also been briefly reported in the literature. However, there are only few reports of PEI-based thin films and deposition techniques in the literature, which we believe future studies can focus on for future large-scale production. The use of such thin films in the adsorption of different types of metals should be studied. The impact of the presence of SO2 on CO2 adsorption efficiency is reported in the literature. The influence of the presence of other gases (including the presence of trapped water in the adsorbent) in CO2 capture fefficiency has already been investigated. The study has shown that the presence of water together with a solid crosslinked PEI improves the performance of the material to capture CO2. However, more comprehensive studies are needed in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.G. and M.R.A.; formal analysis, A.C., A.A.S., S.P., M.R.A. and D.G. investigation, A.C., A.A.S., S.P., M.R.A. and D.G.; data curation, A.C., A.A.S., S.P., M.R.A. and D.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.C., A.A.S. and D.G.; writing—review and editing, A.C., A.A.S., S.P., M.R.A. and D.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge the University of the South Pacific, Suva, Fiji. M. R. A. thanks the Australian Government through the Australian Research Council’s Discovery Projects funding scheme (project DP210101243).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fischer, R.J.; Pang, D.; Beatty, S.T.; Rosenberg, E. Silica-polyamine composite materials for heavy metal ion removal, recovery, and recycling. II. Metal ion separations from mine wastewater and soft metal ion extraction efficiency. Sep. Sci. Technol. 1999, 34, 3125–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Festa, R.A.; Thiele, D.J. Copper: An essential metal in biology. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R877–R883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niyogi, S.; Wood, C.M. Biotic ligand model, a flexible tool for developing site-specific water quality guidelines for metals. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6177–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viarengo, A.; Pertica, M.; Mancinelli, G.; Burlando, B.; Canesi, L.; Orunesu, M. In vivo effects of copper on the calcium homeostasis mechanisms of mussel gill cell plasma membranes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C Pharmacol. Toxicol. Endocrinol. 1996, 113, 421–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.D.; Watson, M.A.; Brown, J.; Jefcoat, I.A. Peanut hull pellets as a single use sorbent for the capture of Cu(II) from wastewater. Waste Manag. 2002, 22, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edebali, S.; Pehlivan, E. Evaluation of chelate and cation exchange resins to remove copper ions. Powder Technol. 2016, 301, 520–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khulbe, K.C.; Matsuura, T. Removal of heavy metals and pollutants by membrane adsorption techniques. Appl. Water Sci. 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Guo, J. Removal of chromium from wastewater by membrane filtration, chemical precipitation, ion exchange, adsorption electrocoagulation, electrochemical reduction, electrodialysis, electrodeionization, photocatalysis and nanotechnology: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2020, 18, 2055–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, Z.-B.; Zhang, Z.-J.; Ma, S.; Tang, C.-M.; Xu, J.-Q. Preparation and application of polyethyleneimine-modified corncob magnetic gel for removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions from aqueous solution. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 1950–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassileva, P.; Uzunov, I.; Popova, T.; Voykova, D.; Avramova, I.; Mehandjiev, D. Biochars as a solution for silver removal and antimicrobial activity in aqueous systems. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landa, M.; Kotera, M.; Remy, J.-S.; Badi, N. Preparation of poly(ethylene imine) derivatives with precisely controlled molecular weight. Eur. Polym. J. 2016, 84, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, F.-F.; Lu, G.-X.; Zhou, L.-Y.; Yang, Q.-B. Preparation of PEI nanofiber membrane based on in situ and solution crosslinking technology and their adsorption properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 48279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movahedi, A.; Lundin, A.; Kann, N.; Nydén, M.; Moth-Poulsen, K. Cu(i) stabilizing crosslinked polyethyleneimine. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 18327–18336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Pan, B.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Lv, L.; Zhang, W. Immobilization of polyethylenimine nanoclusters onto a cation exchange resin through self-crosslinking for selective Cu(II) removal. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayalew, Z.M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, X. Synthesis and application of polyethyleneimine (PEI)-based composite/nanocomposite material for heavy metals removal from wastewater: A critical review. JHM Adv. 2022, 8, 100158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, J.B.; Larsson, M.; Kaur, S.; Nosrati, A.; Nydén, M. Glutaraldehyde-crosslinking for improved copper absorption selectivity and chemical stability of polyethyleneimine coatings. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privar, Y.; Malakhova, I.; Pestov, A.; Fedorets, A.; Azarova, Y.; Schwarz, S.; Bratskaya, S. Polyethyleneimine cryogels for metal ions sorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 334, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, J.B.; Larsson, M.; Coad, B.R.; Skinner, W.M.; Nydén, M. Polyethyleneimine for copper absorption: Kinetics, selectivity and efficiency in artificial seawater. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 25063–25066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindén, J.B.; Larsson, M.; Kaur, S.; Skinner, W.M.; Miklavcic, S.J.; Nann, T.; Kempson, I.M.; Nydén, M. Polyethyleneimine for copper absorption II: Kinetics, selectivity and efficiency from seawater. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 51883–51890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Wu, A.; Luan, S. Synthesis and investigation of the imprinting efficiency of ion imprinted nanoparticles for recognizing copper. PCCP 2014, 16, 16158–16165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, D.M.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Tutu, H. Development and application of cross-linked polyethylenimine for trace metal and metalloid removal from mining and industrial wastewaters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 93, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimesh, S. Polyethylenimine as a promising vector for targeted siRNA delivery. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, H.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, M.S.; Khang, G.; Lee, I.W.; Lee, H.B. Polyethyleneimine-mediated gene delivery into human adipose derived stem cells. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 2415–2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Du, H.; Mullins, R.H.; Kommalapati, R.R. Polyethylenimine applications in carbon dioxide capture and separation: From theoretical study to experimental work. Energy Technol. 2017, 5, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Qu, F.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. A facile, sensitive, and rapid spectrophotometric method for copper(II) ion detection in aqueous media using polyethyleneimine. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1680–S1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.E.; Lou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sahiner, N.; Sandoval, N.R.; Shantz, D.F.; Grayson, S.M. Comparison of Cross-linked branched and linear poly(ethylene imine) microgel microstructures and their impact in antimicrobial behavior, copper chelation, and carbon dioxide capture. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2020, 2, 826–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qu, G.; Xie, L.; Tang, S.; Lei, H.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, Y.-F. Efficient removal of antibiotics from wastewater by chitosan/polyethyleneimine/Ti3C2 MXene composite hydrogels: Synthesis, adsorption, kinetics and mechanisms. Colloids Surf. A 2024, 702, 135111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyarce, E.; Roa, K.; Boulett, A.; Sotelo, S.; Cantero-López, P.; Sánchez, J.; Rivas, B.L. Removal of dyes by polymer-enhanced ultrafiltration: An overview. Polymers 2021, 13, 3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cojocaru, C.; Zakrzewska-Trznadel, G.; Jaworska, A. Removal of cobalt ions from aqueous solutions by polymer assisted ultrafiltration using experimental design approach. part 1: Optimization of complexation conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korus, I. Separation of heavy metal ions from multi-component solutions using ultrafiltration enhanced with complexing polymer. Desalination Water Treat. 2023, 314, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, A.Y.; Prasad, S.; Pan, X.; Andersson, M.R.; Gedefaw, D. Glutaraldehyde and glyoxal crosslinked polyethylenimine for copper ion adsorption from water. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202104318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmas, S.; Gedefaw, D.A.; Larsson, M.; Ying, Y.; Cavallaro, A.; Andersson, G.G.; Nydén, M.; Andersson, M.R. Porous PEI coating for copper ion storage and its controlled electrochemical release. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2020, 4, 1900123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, W.S.; Li, S.; Filippou, C.; Hoobin, P.; Petinakis, S. Interface/interphase engineering of polymers for adhesion enhancement: Part II. Theoretical and technological aspects of surface-engineered interphase-interface systems for adhesion enhancement. J. Adhes. 2003, 79, 483–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, W.S.; Bilyk, A.; Li, S.; Espiritu, M.; Burgar, I. The influence of structure of the interface and interphase on paint adhesion. Compos. Interfaces 2005, 12, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whipple, E.B.; Ruta, M. Structure of aqueous glutaraldehyde. J. Org. Chem. 1974, 39, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Jung, H.; Jo, D.H.; Kim, S.H. Development of crosslinked PEI solid adsorbents for CO2 capture. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2287–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Jeon, S.; Jo, D.H.; Huh, J.; Kim, S.H. Effect of crosslinking on the CO2 adsorption of polyethyleneimine-impregnated sorbents. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 307, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.R.; Hilgraf, R.; Sharpless, K.B.; Fokin, V.V. Polytriazoles as Copper(I)-Stabilizing Ligands in Catalysis. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 2853–2855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson Trojer, M.; Movahedi, A.; Blanck, H.; Nydén, M. Imidazole and triazole coordination chemistry for antifouling coatings. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 946739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Magid, A.F.; Carson, K.G.; Harris, B.D.; Maryanoff, C.A.; Shah, R.D. Reductive Amination of Aldehydes and Ketones with Sodium Triacetoxyborohydride. Studies on Direct and Indirect Reductive Amination Procedures1. J. Org. Chem. 1996, 61, 3849–3862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaiari, N.S.; Alzahrani, F.M.; Katubi, K.M.; Amari, A.; Rebah, F.B.; Tahoon, M.A. Polyethylenimine-modified magnetic chitosan for the uptake of arsenic from water. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubilay, S.; Demirci, S.; Can, M.; Aktas, N.; Sahiner, N. Dichromate and arsenate anion removal by PEI microgel, cryogel, and bulkgel. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 104799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, L.; Wang, W.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Adsorptive recovery of Au(III) from aqueous solution using crosslinked polyethyleneimine resins. Chemosphere 2020, 241, 125122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rochelle, G.T. Amine scrubbing for CO2 capture. Science 2009, 325, 1652–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishnoi, S.; Rochelle, G.T. Absorption of carbon dioxide into aqueous piperazine: Reaction kinetics, mass transfer and solubility. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2000, 55, 5531–5543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Jiang, J.; Yan, F.; Tian, S.; Chen, X. The influence of polyethyleneimine type and molecular weight on the CO2 capture performance of PEI-nano silica adsorbents. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Lively, R.P.; Jones, C.W. Effect of SO2 on the CO2 capture performance of self-supported branched poly(ethyleneimine) scaffolds. Energy Fuel. 2023, 37, 5257–5269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Sen Gupta, S.; Kumaraswamy, G. Omniphilic Polymeric Sponges by Ice Templating. Chem. Mater. 2016, 28, 1823–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahiner, N.; Demirci, S. Poly ionic liquid cryogel of polyethyleneimine: Synthesis, characterization, and testing in absorption studies. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 43478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.-J.; Narayanan, P.; Jones, C.W. Self-supported branched poly(ethyleneimine) materials for CO2 adsorption from simulated flue gas. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 19513–19521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naga, N.; Sato, M.; Mori, K.; Nageh, H.; Nakano, T. Synthesis of network polymers by means of addition reactions of multifunctional-amine and poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether or diacrylate compounds. Polymers 2020, 12, 2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehlers, J.-E.; Rondan, N.G.; Huynh, L.K.; Pham, H.; Marks, M.; Truong, T.N. Theoretical study on mechanisms of the epoxy−amine curing reaction. Macromolecules 2007, 40, 4370–4377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdy, L.B.; Gougsa, A.; Chow, W.Y.; Russell, J.E.; García-Díez, E.; Kulakova, V.; Garcia, S.; Barron, A.R.; Taddei, M.; Andreoli, E. Overcoming mass transfer limitations in cross-linked polyethyleneimine-based adsorbents to enable selective CO2 capture at ambient temperature. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3174–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-E.; Chang, J.-S.; Lee, K.-W. Carbon Dioxide Utilization for Global Sustainability: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Carbon Dioxide Utilization, Seoul, Korea, October 12–16, 2003; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004; Volume 153. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, B.; Yang, M.; Huang, H.; Song, Z.; Tao, P.; Wu, Y.; Tang, K.; Chen, X.; Yang, C. Triazine-crosslinked polyethyleneimine for efficient adsorption and recovery of gold from wastewater. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Wang, H.; Xu, J.; Du, X.; Cheng, X.; Du, Z.; Wang, H. Fabrication of MXene/PEI functionalized sodium alginate aerogel and its excellent adsorption behavior for Cr(VI) and congo red from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratskaya, S.; Privar, Y.; Ustinov, A.; Azarova, Y.; Pestov, A. Recovery of Au(III), Pt(IV), and Pd(II) using pyridylethyl-containing polymers: Chitosan derivatives vs synthetic polymers. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 10377–10385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pejcic, B.; Heath, C.; Wood, C.D. Carbon capture with polyethylenimine hydrogel beads (PEI HBs). J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 21468–21474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckenstein, E.; Hong, L. Sedimentation polymerization. Polymer 1995, 36, 2857–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Tavakoli, S.; Parvathaneni, R.P.; Nawale, G.N.; Oommen, O.P.; Hilborn, J.; Varghese, O.P. Dynamic covalent crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels and nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 6399–6412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, L.; Van Zee, N.J.; Nicolaÿ, R. Dually Crosslinked Polymer Networks Incorporating Dynamic Covalent Bonds. Polymers 2021, 13, 396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.Y.; Kamarulzaman, S.; Rasyiddin, R.; Sim, S.Y.X.; Seah, G.E.K.K.; Gan, A.W.; Li, Z.; Png, Z.M.; Goh, S.S. Dynamic crosslinking of thermoplastics via perfluorophenyl nitrene C–H insertion to form recyclable thermosets. Chem 2025, 102479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Luo, X.; Su, T.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, Z.; Ji, H. PEI modified magnetic porous cassava residue microspheres for adsorbing Cd(II) from aqueous solution. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 159, 110741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalam, S.; Abu-Khamsin, S.A.; Kamal, M.S.; Patil, S. Surfactant adsorption isotherms: A review. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 32342–32348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Zhang, K.; Tang, K. Highly efficient and fast adsorption of Au(III) and Pd(II) by crosslinked polyethyleneimine-glutaraldehyde. AIChE J. 2023, 69, e17950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, D.M.G.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Tutu, H. Sulfonated cross-linked polyethylenimine for selective removal of mercury from aqueous solutions. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 94, 1916–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.; Mitsuhashi, M.; Tanibe, H.; Yoshida, H. Adsorption of metal ions on polyaminated highly porous chitosan chelating resin. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 1993, 32, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saad, D.M.G.; Cukrowska, E.M.; Tutu, H. Modified cross-linked polyethylenimine for the removal of selenite from mining wastewaters. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2013, 95, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, C.-W.; Kang, S.B.; Kim, S.; Yun, Y.-S.; Won, S.W. Reusable polyethylenimine-coated polysulfone/bacterial biomass composite fiber biosorbent for recovery of Pd(II) from acidic solutions. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 302, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.W.; Kim, S.; Kotte, P.; Lim, A.; Yun, Y.-S. Cationic polymer-immobilized polysulfone-based fibers as high performance sorbents for Pt(IV) recovery from acidic solutions. JHM Adv. 2013, 263, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bediako, J.K.; Lin, S.; Sarkar, A.K.; Zhao, Y.; Choi, J.-W.; Song, M.-H.; Wei, W.; Reddy, D.H.K.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Benignly-fabricated crosslinked polyethylenimine/calcium-alginate fibers as high-performance adsorbents for effective recovery of gold. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 252, 119389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Du, Q.; Liu, T.; Sun, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Xia, Y.; Xia, L. Methylene blue adsorption on graphene oxide/calcium alginate composites. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Singh, S.K.; Bajpai, J.; Bajpai, A.K.; Shrivastava, R.B. Iron crosslinked alginate as novel nanosorbents for removal of arsenic ions and bacteriological contamination from water. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Repo, E.; Song, Y.; Yin, D.; Hammouda, S.B.; Chen, L.; Kalliola, S.; Tang, J.; Tam, K.C.; Sillanpää, M. Polyethylenimine-cross-linked cellulose nanocrystals for highly efficient recovery of rare earth elements from water and a mechanism study. Green Chem. 2017, 19, 4816–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Kempson, I.; Xu, H.; Nydén, M.; Larsson, M. Bio-template assisted synthesis of porous glutaraldehyde-polyethyleneimine particulate resin for selective copper ion binding and recovery. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 12043–12052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Tian, Y.; Kong, L.; Zhang, J.; Zuo, W.; Li, Y.; Cai, G. A novel 3D superelastic polyethyleneimine functionalized chitosan aerogels for selective removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous solution: Performance and mechanisms. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 425, 131722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; An, Q.; Xiao, Z.; Zheng, W.; Zhai, S. Flexible core-shell/bead-like alginate@PEI with exceptional adsorption capacity, recycling performance toward batch and column sorption of Cr(VI). Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 313, 475–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zuo, K.; Wu, W.; Xu, Z.; Yi, Y.; Jing, Y.; Dai, H.; Fang, G. Shape memory aerogels from nanocellulose and polyethyleneimine as a novel adsorbent for removal of Cu(II) and Pb(II). Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 196, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Qiu, W.; Deng, T.; Zheng, X.; Wang, H.; Wen, P. Fabrication of physically multi-crosslinked sodium alginate/carboxylated-chitosan/montmorillonite-base aerogel modified by polyethyleneimine for the efficient adsorption of organic dye and Cu(II) contaminants. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 330, 125321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzid, H.; Prosa, M.; Bolognesi, M.; Chehata, N.; Gedefaw, D.; Albonetti, C.; Andersson, M.R.; Muccini, M.; Bouazizi, A.; Seri, M. Impact of environmentally friendly processing solvents on the properties of blade-coated polymer solar cells. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2019, 57, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjuggren, J.M.; Sharma, A.; Gedefaw, D.; Elmas, S.; Pan, C.; Kirk, B.; Zhao, X.; Andersson, G.; Andersson, M.R. Facile synthesis of an efficient and robust cathode interface material for polymer solar cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 7130–7139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolognesi, M.; Gedefaw, D.; Cavazzini, M.; Catellani, M.; Andersson, M.R.; Muccini, M.; Kozma, E.; Seri, M. Side chain modification on PDI-spirobifluorene-based molecular acceptors and its impact on organic solar cell performances. New. J. Chem. 2018, 42, 18633–18640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, W.; Gao, C.; Möhwald, H. Poly(ethyleneimine) microcapsules: Glutaraldehyde-mediated assembly and the influence of molecular weight on their properties. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2008, 19, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, M.P.; Bendick, J.A.; Holm, E.R.; Hertel, W.M. Economic impact of biofouling on a naval surface ship. Biofouling 2011, 27, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciriminna, R.; Bright, F.V.; Pagliaro, M. Ecofriendly antifouling marine coatings. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, R.T.; Damon, M.; Johnson, L.T.; Gonzalez, J.A. Conceptual issues in designing a policy to phase out metal-based antifouling paints on recreational boats in San Diego Bay. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greluk, M.; Hubicki, Z. Efficient removal of Acid Orange 7 dye from water using the strongly basic anion exchange resin Amberlite IRA-958. Desalination 2011, 278, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Adhikary, S.; Bhattacharya, S.; Roy, D.; Chatterjee, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Banerjee, D.; Ganguly, A.; Nanda, S.; Rajak, P. Contamination of textile dyes in aquatic environment: Adverse impacts on aquatic ecosystem and human health, and its management using bioremediation. J. Environ. Manage. 2024, 353, 120103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lellis, B.; Fávaro-Polonio, C.Z.; Pamphile, J.A.; Polonio, J.C. Effects of textile dyes on health and the environment and bioremediation potential of living organisms. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradi, O.; Sharma, G. Emerging novel polymeric adsorbents for removing dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive review and comparison with other adsorbents. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwala, R.; Mulky, L. Adsorption of dyes from wastewater: A comprehensive review. ChemBioEng Rev. 2023, 10, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagishi, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Hayashi, A.; Kuroki, N. Interaction of crosslinked polyethylenimine with a homologous series of methyl orange derivatives in aqueous solution. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Chem. Ed. 1983, 21, 2311–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, L.; Huang, C.; Lu, F.; Wang, A.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q. Facile synthesis of high performance porous magnetic chitosan-polyethylenimine polymer composite for Congo red removal. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 1620–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Cheng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, L. Interfacially crosslinked composite porous membranes for ultrafast removal of anionic dyes from water through permeating adsorption. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 337, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, S.; Qi, H. A novel crosslinking strategy on functional cellulose-based aerogel for effective and selective removal of dye. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 463, 142404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Won, S.W. Polyethylenimine-crosslinked 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane-grafted multiwall carbon nanotubes for efficient adsorption of reactive yellow 2 from water. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chundawat, S.P.S.; Beckham, G.T.; Himmel, M.E.; Dale, B.E. Deconstruction of lignocellulosic biomass to fuels and chemicals. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2011, 2, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Runge, T. Cross-linked polyethylenimine for selective adsorption and effective recovery of lignocellulose-derived organic acids and aldehydes. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, P.D.; Kenig, E.Y. CO2-Alkanolamine reaction kinetics: A review of recent studies. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2007, 30, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Myers, M.B.; Versteeg, F.G.; Pejcic, B.; Heath, C.; Wood, C.D. Direct air capture (DAC) of CO2 using polyethylenimine (PEI) “snow”: A scalable strategy. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 7151–7154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Adsorption separation of carbon dioxide from flue gas of natural gas-fired boiler by a novel nanoporous “molecular basket” adsorbent. Fuel Process. Technol. 2005, 86, 1457–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Andresen, J.M.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Novel Polyethylenimine-Modified Mesoporous Molecular Sieve of MCM-41 Type as High-Capacity Adsorbent for CO2 Capture. Energy Fuels 2002, 16, 1463–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Schwartz, V.; Clark, J.C.; Ma, X.; Overbury, S.H.; Xu, X.; Song, C. Infrared study of CO2 sorption over “molecular basket” sorbent consisting of polyethylenimine-modified mesoporous molecular sieve. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 7260–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Andrésen, J.M.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Preparation and characterization of novel CO2 “molecular basket” adsorbents based on polymer-modified mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2003, 62, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; Yang, H.; Liu, J. Enhanced adsorption of carbon dioxide from simulated biogas on PEI/MEA-functionalized silica. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, O.; Joseph, B.; Kuhn, J.N. CO2 separation from biogas using PEI-modified crosslinked polymethacrylate resin sorbent. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 103, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.; Guntupalli, P.; Lively, R.P.; Jones, C.W. Alumina incorporation in self-supported poly(ethylenimine) sorbents for direct air capture. Chem Bio Eng. 2024, 1, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilfong, W.C.; Wang, Q.; Ji, T.; Baker, J.S.; Shi, F.; Yi, S.; Gray, M.L. Directly spun epoxy-crosslinked polyethylenimine fiber sorbents for direct air capture and postcombustion capture of CO2. Energy Technol. 2022, 10, 2200356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numaguchi, R.; Fujiki, J.; Yamada, H.; Firoz; Chowdhury, A.; Kida, K.; Goto, K.; Okumura, T.; Yoshizawa, K.; Yogo, K. Development of post-combustion CO2 capture system using amine-impregnated solid sorbent. Energy Procedia 2017, 114, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).