Viper Venom and Synthetic Peptides: Emerging Active Ingredients in Anti-Ageing Cosmeceuticals
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Peptides—From Snake Venom to the Cosmetic Industry
| Signal | Carrier | Neurotransmitter Inhibitor | Enzyme Inhibitor | Obtained from the Digestion of Structural Proteins |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of Action | ||||
| Stimulates the production of matrix proteins (collagen and elastin) and cell growth, among other cellular metabolic functions | Facilitates the transport of important substances or trace elements inside the cell, such as copper and magnesium | Prevents the release of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction by cleaving the SNARE protein “SNAP-25”, which inhibits signal transduction pathways | Prevents the degradation of collagen and other proteins by inhibiting the activity of the respective enzymes and interfering with the breakdown processes | Improves water-holding capacity, hydration and elasticity of the skin |
| Peptide (INCI name) | ||||
| Acetyl tetrapeptide-9 [37] Acetyl tetrapeptide-11 [38] Cyclotetrapeptide-24 Aminocyclohexane Carboxylate [39] Hexapeptide-10 [40] Hexapeptide-11 [41] Hexapeptide-14 [42] Acetyl sh-Heptapeptide-1 [43] Oligopeptide-68 [44] Nicotiana benthamiana Hexapeptide-40 SH-Oligopeptide-1 [45] Nicotiana benthamiana Hexapeptide-40 SH-Polypeptide-5 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana Hexapeptide-40 SH-Polypeptide-7 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana SH-Polypeptide-45 [30] Tripeptide-3/5 [33] Tripeptide-32 [46] Nicotiana benthamiana SH-Polypeptide-7 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana Hexapeptide-40S H-Polypeptide-9 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana SH-Oligopeptide-2 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana Hexapeptide-40 SH-Polypeptide 2 [30] Nicotiana benthamiana SH-Polypeptide-15 [30] Pentapeptide-34 [28] Palmitoyl pentapeptide-4 [47] Pamlitoyl tripeptide-38 [48] Palmitoyl Tripeptide-1 [49] Palmitoyl tetrapeptide-7/3 [30] Palmitoyl hexapeptide-12 [50] Trifluoroacetyl-tripeptide-2 [51] Tripeptide-10 Citrulline [52] Tripeptide-41 [53] | Copper Tripeptide-1 [54] Manganese tripeptide 1 [55] Diaminopropionoyl Tripeptide-33 [56] Tripeptide-9 Citrulline [57] | Tripeptide-3 [58] Pentapeptide-3 [55] Acetyl Tripeptide-30 Citrulline and Pentapeptide-18 [59] Pentapeptide-18 [27] Acetyl hexapeptide-8 [60] Acetyl Dipeptide-1 Cetyl Ester [61] Acetyl Tetrapeptide-5 [62] Acetyl Octapeptide-3 [63] Acetyl hexapeptide-3 [64] | Silk fibroin peptides [65] Rice peptides [66] Soybean peptides [67] | Keratin-based peptides [68] |
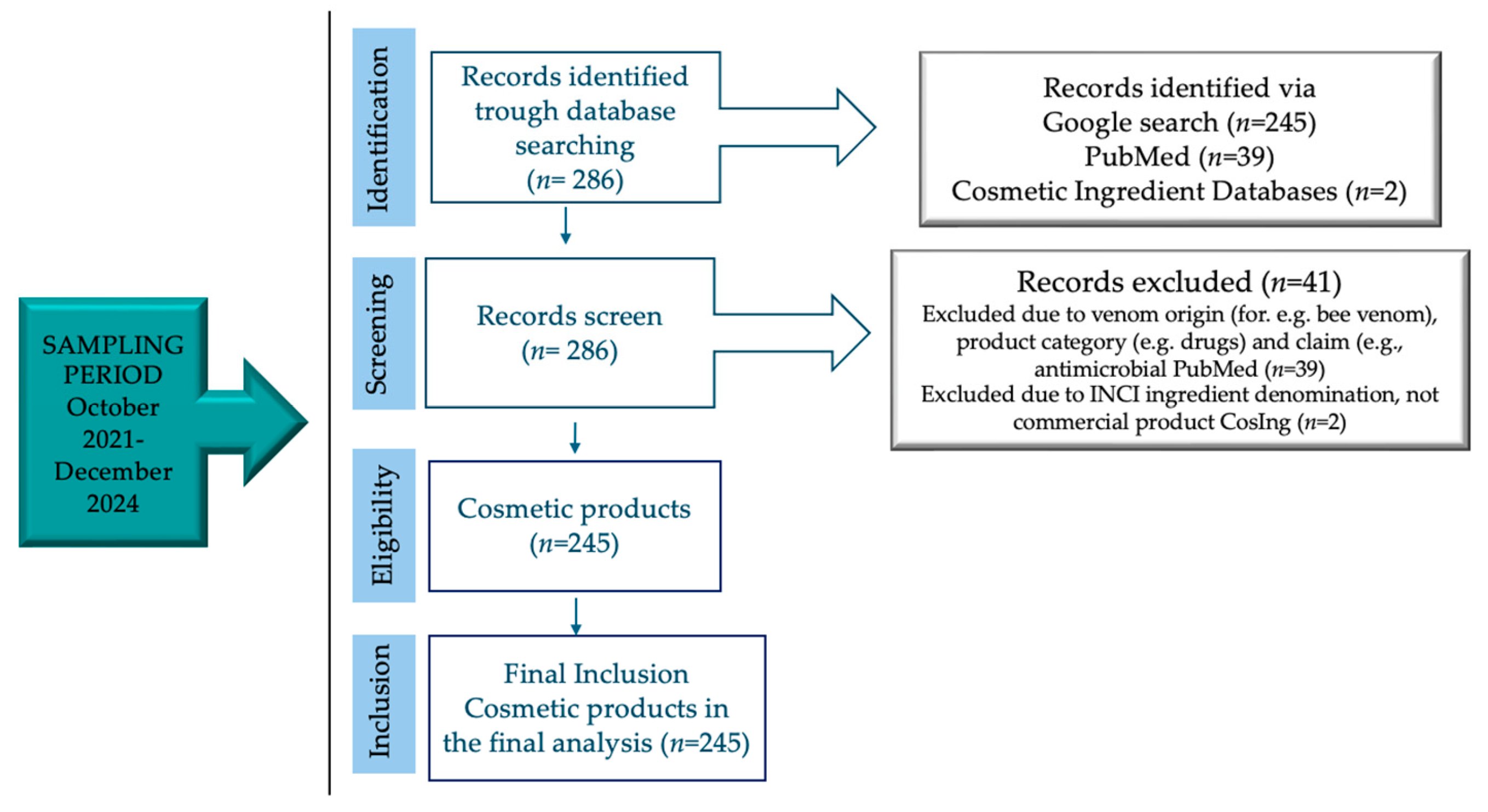
3. Materials and Methods
4. Results and Discussion
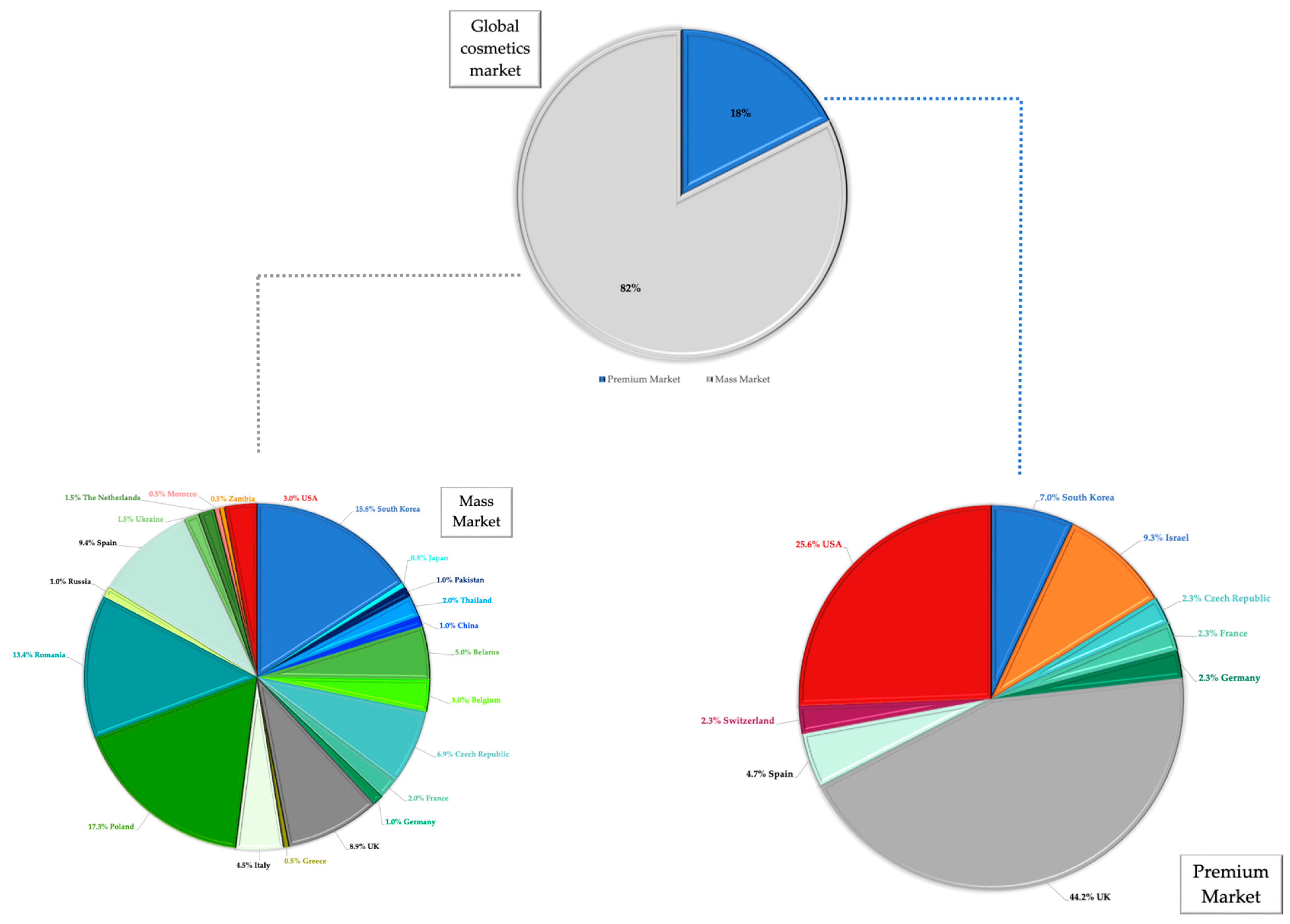
4.1. Consideration on the Global Cosmetics Market
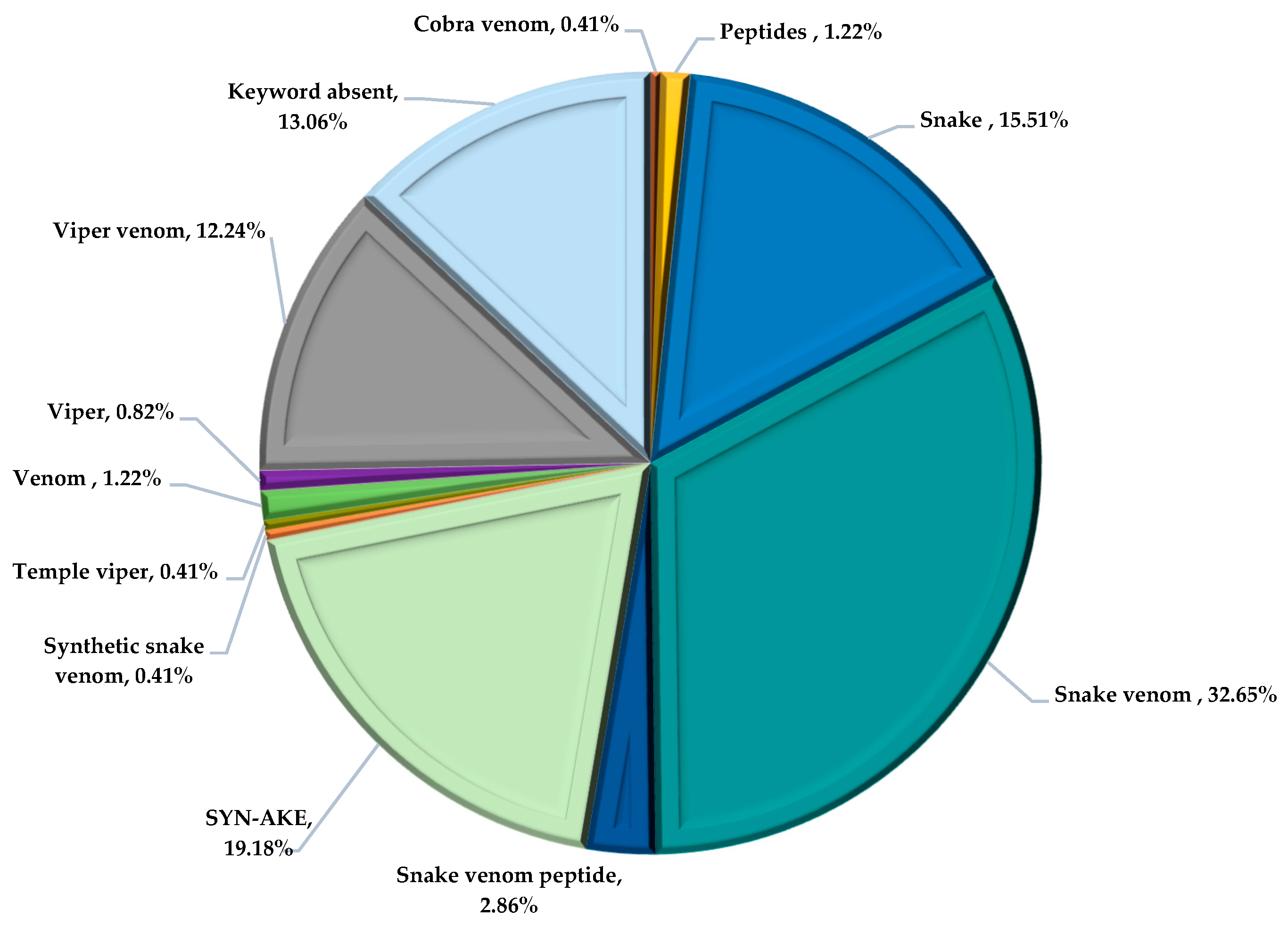
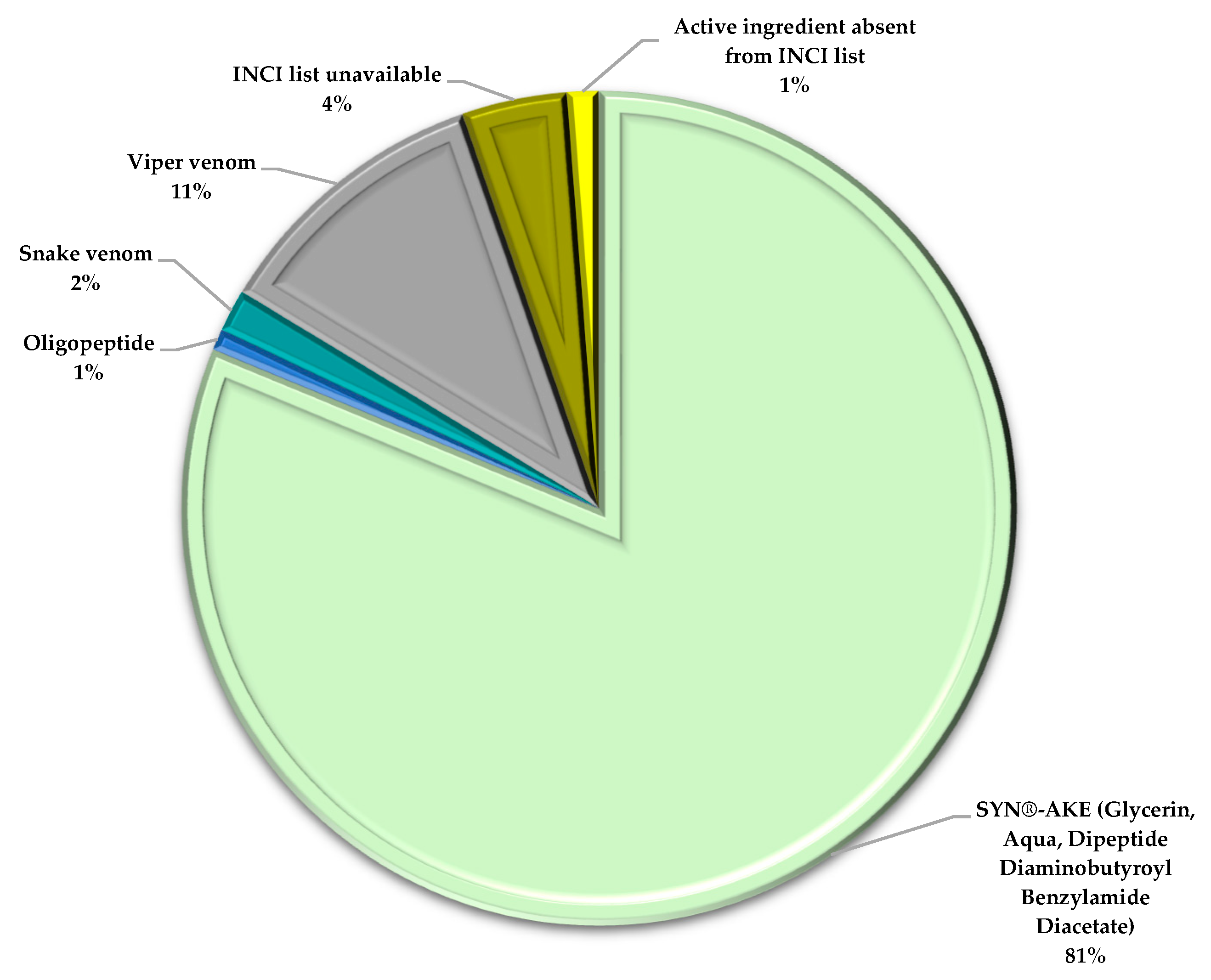
4.2. Active Ingredient
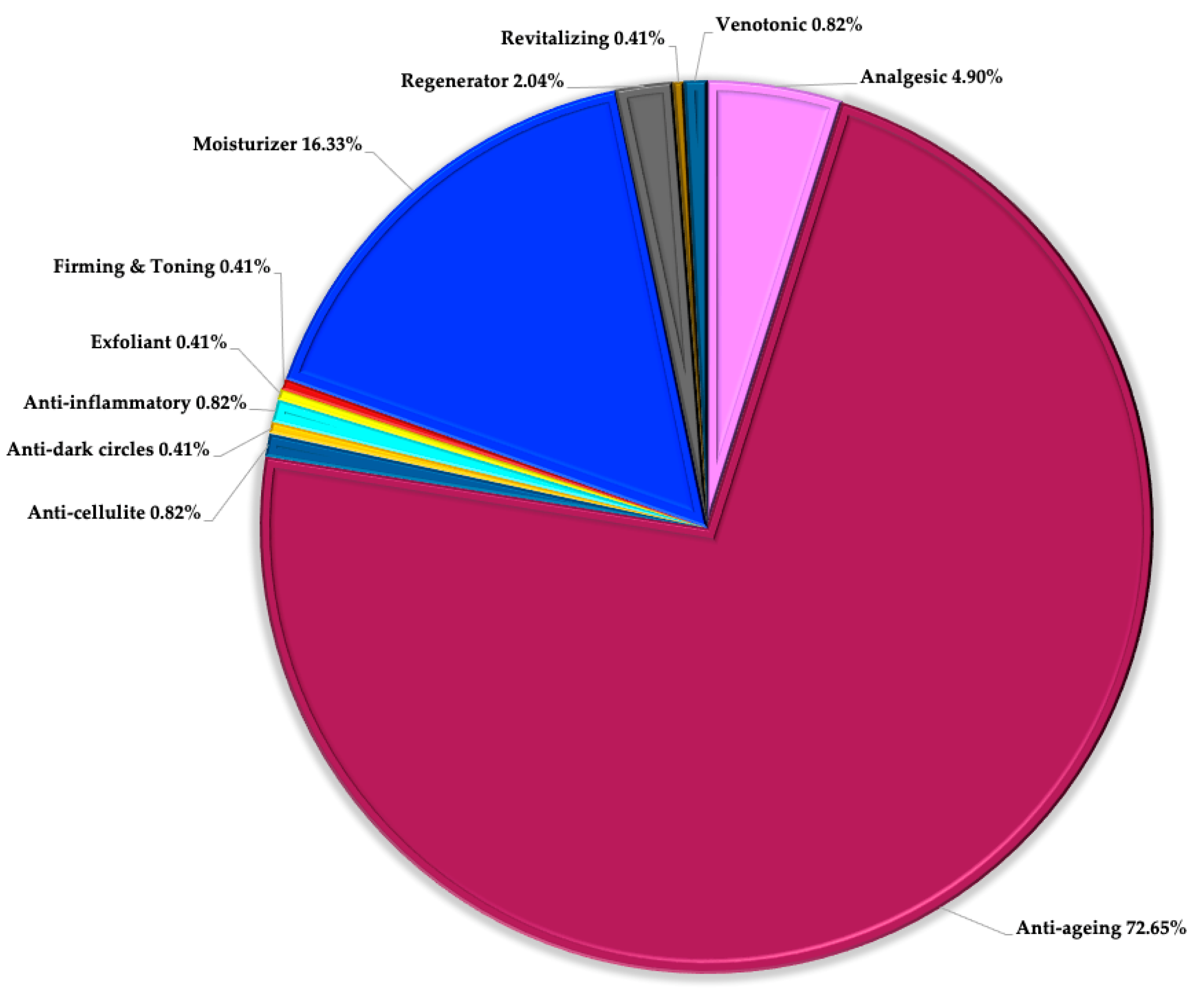
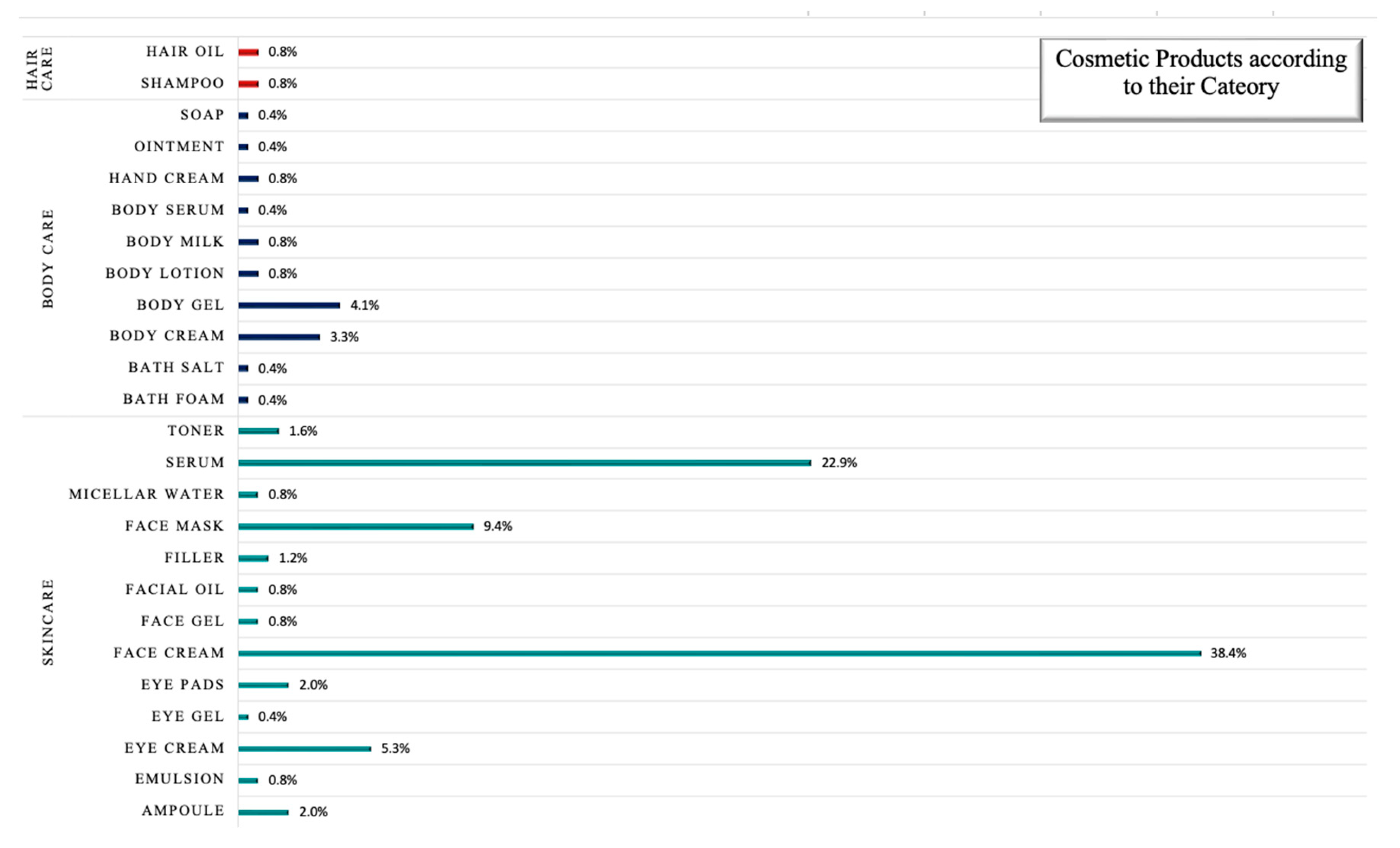
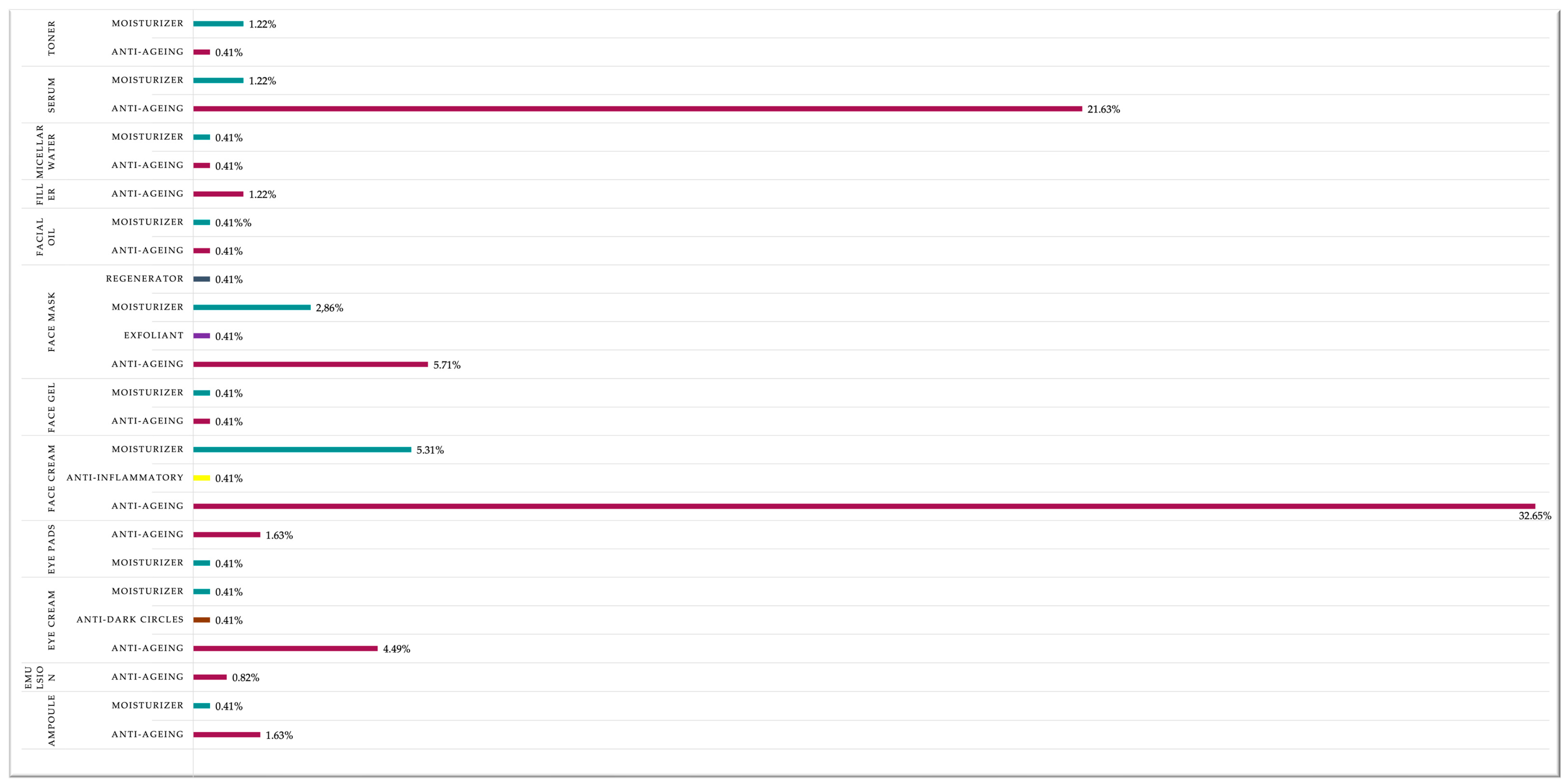
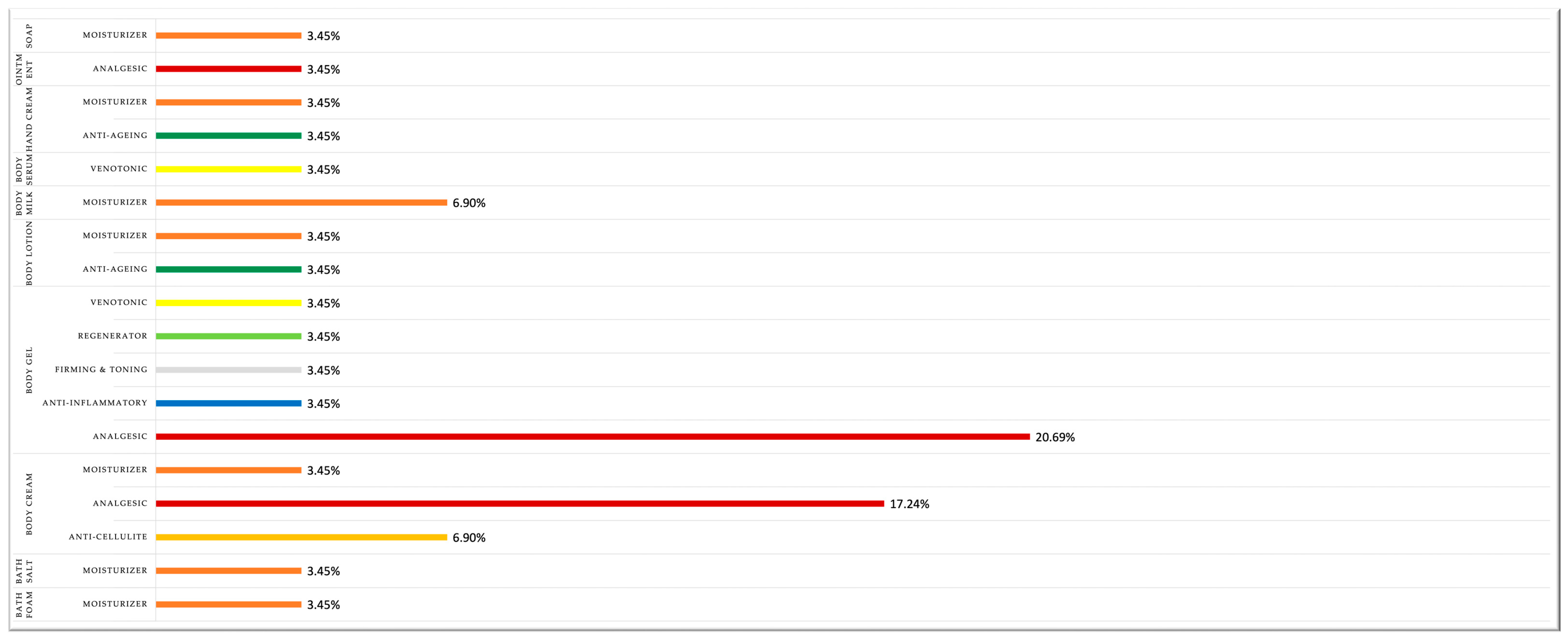
4.3. Cosmetic Product Category and Claimed Effects
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munawar, A.; Ali, S.A.; Akrem, A.; Betzel, C. Snake Venom Peptides: Tools of Biodiscovery. Toxins 2018, 10, 474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fry, B.G.; Roelants, K.; Champagne, D.E.; Scheib, H.; Tyndall, J.D.A.; King, G.F.; Nevalainen, T.J.; Norman, J.A.; Lewis, R.J.; Norton, R.S.; et al. The Toxicogenomic Multiverse: Convergent Recruitment of Proteins into Animal Venoms. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 2009, 10, 483–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utkin, Y.N. Animal Venom Studies: Current Benefits and Future Developments. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vonk, F.J.; Harrison, R.A.; Fry, B.G. Complex Cocktails: The Evolutionary Novelty of Venoms. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2013, 28, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fry, B.G.; Casewell, N.R.; Wüster, W.; Vidal, N.; Young, B.; Jackson, T.N.W. The Structural and Functional Diversification of the Toxicofera Reptile Venom System. Toxicon 2012, 60, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Laustsen, A.H.; Sunagar, K. Causes and Consequences of Snake Venom Variation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.A.; Mikail, M.A.; Zamakshshari, N.; Abdullah, A.S.H. Natural Anti-Aging Skincare: Role and Potential. Biogerontology 2020, 21, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aziz, T.M.A.; Soares, A.G.; Stockand, J.D. Snake Venoms in Drug Discovery: Valuable Therapeutic Tools for Life Saving. Toxins 2019, 11, 564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, C.R.; Arrahman, A.; Xie, C.; Casewell, N.R.; Lewis, R.J.; Kool, J.; Cardoso, F.C. Multifunctional Toxins in Snake Venoms and Therapeutic Implications: From Pain to Hemorrhage and Necrosis. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Still, K.B.M.; Slagboom, J.; Kidwai, S.; Xie, C.; Zhao, Y.; Eisses, B.; Jiang, Z.; Vonk, F.J.; Somsen, G.W.; Casewell, N.R.; et al. Development of High-Throughput Screening Assays for Profiling Snake Venom Phospholipase A2 Activity after Chromatographic Fractionation. Toxicon 2020, 184, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, P.G.; Ramírez, D.; Alzate-Morales, J.; Caballero, J.; Kaas, Q.; González, W. Computational Studies of Snake Venom Toxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirakabad, F.S.T.; Khoramgah, M.S.; Kamyar, K.F.; Tabarzad, M.; Ranjbari, J. Peptide Dendrimers as Valuable Biomaterials in Medical Sciences. Life Sci. 2019, 233, 116754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preciado, L.M.; Pereañez, J.A. Low Molecular Mass Natural and Synthetic Inhibitors of Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. Toxin Rev. 2018, 37, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottrall, J.L.; Madaras, F.; Biven, C.D.; Venning, M.G.; Mirtschin, P.J. Proteolytic Activity of Elapid and Viperid Snake Venoms and Its Implication to Digestion. J. Venom. Res. 2010, 1, 18–28. [Google Scholar]
- Markland, F.S.; Swenson, S. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases. Toxicon 2013, 62, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Koh, C.Y. Snake Venom Three-Finger Toxins and Their Potential in Drug Development Targeting Cardiovascular Diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, M.-C.; Hsieh, W.H.; Smith, L.A.; Lee, C.Y. Effects on Waglerin-1 on Neuromuscular on Neuromuscular Transmission of mouse nerve-muscle preparations. Toxicon 1995, 33, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molles, B.E.; Rezai, P.; Kline, E.F.; McArdle, J.J.; Sine, S.M.; Taylor, P. Identification of Residues at the α and ε Subunit Interfaces Mediating Species Selectivity of Waglerin-1 for Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 5433–5440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasheverov, I.E.; Utkin, Y.N.; Tsetlin, V.I. Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Peptides Acting on Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2430–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaev, A.N.; Okhmanovich, K.A.; Osipov, V.N. A Shortened, Protecting Group Free, Synthesis of the Anti-Wrinkle Venom Analogue Syn-Ake® Exploiting an Optimized Hofmann-Type Rearrangement. Tetrahedron Lett. 2014, 55, 5745–5747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Falla, T.J. Cosmeceuticals and Peptides. Clin. Dermatol. 2009, 27, 485–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moisa, D.G.; Gligor, F.G.; Rus, L.L.; Morgovan, C.; Frum, A.; Juncan, A.M. Snake Venom—An Emerging Challenge in Cosmetology. In Proceedings of the Naunyn—Schmiedebergs Archives of Pharmacology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2022; p. s72. [Google Scholar]
- SYN®-COLL. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/en/businesses/perfumery-beauty/beauty-care/products/syn-coll.html (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- SYN®-AKE. Available online: https://www.dsm-firmenich.com/en/businesses/perfumery-beauty/beauty-care/products/syn-ake.html (accessed on 19 September 2022).
- Errante, F.; Ledwoń, P.; Latajka, R.; Rovero, P.; Papini, A.M. Cosmeceutical Peptides in the Framework of Sustainable Wellness Economy. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 572923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalska, H.; Czajkowska, K.; Cichowska, J.; Lenart, A. What’s New in Biopotential of Fruit and Vegetable by-Products Applied in the Food Processing Industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 67, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schagen, S.K. Topical Peptide Treatments with Effective Anti-Aging Results. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, T.N.; Moraes, C.A.P. Bioactive Peptides: Applications and Relevance for Cosmeceuticals. Cosmetics 2018, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolopoulos, V.; Bojarska, J.; Chai, T.T.; Elnagdy, S.; Kaczmarek, K.; Matsoukas, J.; New, R.; Parang, K.; Lopez, O.P.; Parhiz, H.; et al. A Global Review on Short Peptides: Frontiers and Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.S.; Almeida, I.F.; Magalhães, M.C.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M. Trending Anti-Aging Peptides. Cosmetics 2020, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negahdaripour, M.; Owji, H.; Eslami, M.; Zamani, M.; Vakili, B.; Sabetian, S.; Nezafat, N.; Ghasemi, Y. Selected Application of Peptide Molecules as Pharmaceutical Agents and in Cosmeceuticals. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 1275–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorouhi, F.; Maibach, H.I. Role of Topical Peptides in Preventing or Treating Aged Skin. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pai, V.; Bhandari, P.; Shukla, P. Topical Peptides as Cosmeceuticals. Indian. J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2017, 83, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resende, D.I.S.P.; Ferreira, M.S.; Sousa-Lobo, J.M.; Sousa, E.; Almeida, I.F. Usage of Synthetic Peptides in Cosmetics for Sensitive Skin. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husein el Hadmed, H.; Castillo, R.F. Cosmeceuticals: Peptides, Proteins, and Growth Factors. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vialox PentaPeptide-3. Available online: https://www.dermmalls.com/pages/vialox-pentapeptide-3 (accessed on 19 September 2021).
- Acetyl Tetrapeptide-9. Available online: https://inci.guide/peptides/acetyl-tetrapeptide-9 (accessed on 24 March 2025).
- Acetyl Tetrapeptide-11. Available online: https://inci.guide/peptides/acetyl-tetrapeptide-11 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Cyclotetrapeptide-24 Aminocyclohexane Carboxylate. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Cyclotetrapeptide-24-aminocyclohexane-carboxylate (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Hexapeptide-10. Available online: https://www.motifbiotech.com/products/Hexapeptide-10.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Hexapeptide-11. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.com/hexapeptide-11.html?srsltid=AfmBOoofesSvZirfdWuraO-XSH6nxXrxsBHZ-J_r3qpNfAbEd4fRHdMA (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Hexapeptide-14. Available online: https://cosmileeurope.eu/inci/detail/6395/hexapeptide-14/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Acetyl Sh-Heptapeptide-1. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.com/acetyl-sh-heptapeptide-1.html?srsltid=AfmBOoqphWYegQfRAXKW_r8vGGnRlbqtkl8VkbeT4zru5JDqTp7AG9Hx (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Oligopeptide-68. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.eu/oligopeptide-68.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Nicotiana Benthamiana Hexapeptide-40 SH-Oligopeptide-1. Available online: https://incidecoder.com/ingredients/nicotiana-benthamiana-hexapeptide-40-sh-oligopeptide-1 (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tripeptie-32. Available online: https://cosmileeurope.eu/inci/detail/16542/tripeptide-32/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Palmitoyl Pentapeptide-4. Available online: https://www.creative-peptides.com/article/palmitoyl-pentapeptide-4-146.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Palmitoyl Tripeptide-38. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.com/palmitoyl-tripeptide-38.html?srsltid=AfmBOoo1Tc8ZeCkzld9v4SWiASoojANDqqEyLh6N3jDa2UEFzXBeNTyQ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Veiga, E.; Ferreira, L.; Correia, M.; Pires, P.C.; Hameed, H.; Araújo, A.R.T.S.; Cefali, L.C.; Mazzola, P.G.; Hamishehkar, H.; Veiga, F.; et al. Anti-Aging Peptides for Advanced Skincare: Focus on Nanodelivery Systems. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2023, 89, 105087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmitoyl Hexapeptide-12. Available online: https://www.creative-peptides.com/article/palmitoyl-hexapeptide-12-a-natural-powerful-antiager-145.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Trifluoroacetyl Tripeptide-2. Available online: https://www.creative-peptides.com/article/function-of-trifluoroacetyl-tripeptide-2-in-human-skin-140.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tripeptide-10 Citrulline. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.com/tripeptide-10-citrulline.html?srsltid=AfmBOoqs3KPJTCwKI1qca1CQ9LBXh_KoDTnqywHNJk6Nr41LonNc1ett (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tripeptide-41. Available online: https://cosmileeurope.eu/inci/detail/18956/tripeptide-41/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Liu, T.; Hu, L.; Lu, B.; Bo, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhan, J.; Pei, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, Z.; Guo, C.; et al. A Novel Delivery Vehicle for Copper Peptides. New J. Chem. 2022, 47, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pintea, A.; Manea, A.; Pintea, C.; Vlad, R.A.; Bîrsan, M.; Antonoaea, P.; Rédai, E.M.; Ciurba, A. Peptides: Emerging Candidates for the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Senescence: A Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaminopropionoyl Tripeptide-33. Available online: https://cosmileeurope.eu/inci/detail/4286/diaminopropionoyl-tripeptide-33/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tripeptide-9 Citrulline. Available online: https://cosmileeurope.eu/inci/detail/16559/tripeptide-9-citrulline/ (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Tripeptide-3. Available online: https://www.creative-peptides.com/article/effects-of-tripeptide-3-in-skin-138.html (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, N.; Liang, L.; Li, M.; Nie, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhou, Q.; Shu, P. Evaluation of the Anti-Aging Potential of Acetyl Tripeptide-30 Citrulline in Cosmetics. Int. J. Pharm. 2024, 663, 124557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raikou, V.; Kalogria, E.; Varvaresou, A.; Tsirivas, E.; Panderi, I. Quantitation of Acetyl Hexapeptide-8 in Cosmetics by Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Photo Diode Array Detection. Separations 2021, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acetyl Dipeptide-1 Cetyl Ester. Available online: https://www.medchemexpress.com/acetyl-dipeptide-1-cetyl-ester.html?srsltid=AfmBOoqweYgHIYUFu6GAktzBMVxlSU_shezCxu-mG2lcjuYk5ETnCqer (accessed on 25 March 2025).
- Waszkielewicz, A.M.; Mirosław, K. Peptides and Their Mechanisms of Action in the Skin. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 11495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, Y.; Seo, C.; Choi, S.; Oh, S.; Min, J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.D.; Jeong, D.H.; et al. Method Development for Acetyl Octapeptide-3 Analysis by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadini, K.A.; Mercurio, D.G.; Campos, P.M.B.G.M. Acetyl Hexapeptide-3 in a Cosmetic Formulation Acts on Skin Mechanical Properties—Clinical Study. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Gao, X.; Yin, Y.; Wang, J.; Dong, K.; Shi, D.; Wu, X.; Guo, C. Silk Fibroin Peptide Self-Assembled Nanofibers Delivered Naringenin to Alleviate Cisplatin-Induced Acute Kidney Injury by Inhibiting MtDNA-CGAS-STING Pathway. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2023, 177, 113844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, S.; Pooja, K.; Pal, G.K. Exploration of Rice Protein Hydrolysates and Peptides with Special Reference to Antioxidant Potential: Computational Derived Approaches for Bio-Activity Determination. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 80, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanos, C.; Matsuoka, Y.; Maruyama, N. Soybean Proteins/Peptides: A Review on Their Importance, Biosynthesis, Vacuolar Sorting, and Accumulation in Seeds. Peptides 2021, 143, 170598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiselvi, V.; Deena Praveena, K.; Ayyadurai, N.; Madhan, B.; Kamini, N.R.; Ganesan, P. Keratin-Derived Small Peptides Support the Growth of Endothelial and Fibroblast Cells and Activate Angiogenic Signaling. Biochem. Eng. J. 2025, 215, 109595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, C.-P.; Tang, C.S.; Wei, K.K. Supply Chain Analysis: A Handbook on the Interaction of Information, System and Optimization; Springer Science+Bussiness Media: New York, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kapferer, J.-N.; Bastien, V. The challenges of luxury branding. In The Luxury Strategy: Break the Rules of Marketing to Build Luxury Brands; Kogan Page: London, UK, 2009; pp. 473–491. [Google Scholar]
- Juncan, A.M.; Moisă, D.G.; Santini, A.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.L.; Vonica-țincu, A.L.; Loghin, F. Advantages of Hyaluronic Acid and Its Combination with Other Bioactive Ingredients in Cosmeceuticals. Molecules 2021, 26, 4429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmetics Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report by Product (Skin Care, Hair Care, Makeup, Fragrance), by End-User (Men, Women), by Distribution Channel, by Region, and Segment Forecasts, 2023–2030. Available online: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/cosmetics-market (accessed on 2 April 2023).
- Revenue of the Beauty & Personal Care Market Worldwide by Country in 2021. Available online: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/758635/revenue-of-the-cosmetics-and-personal-care-market-worldwide-by-country (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Nirthanan, S. Snake Three-Finger α-Neurotoxins and Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors: Molecules, Mechanisms and Medicine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 181, 114168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SYN®-AKE. Available online: https://www.ulprospector.com/en/eu/PersonalCare/Detail/472/302760/SYN-AKE (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Altay Benetti, A.; Tarbox, T.; Benetti, C. Current Insights into the Formulation and Delivery of Therapeutic and Cosmeceutical Agents for Aging Skin. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI). Available online: https://www.cirs-reach.com/Cosmetic_Inventory/International_Nomenclature_of_Cosmetic_Ingredients_INCI.html (accessed on 1 April 2023).
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Structural Characteristics of the Aging Skin: A Review. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2007, 26, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.L.; Loghin, F. Development and Evaluation of a Novel Anti-Ageing Cream Based on Hyaluronic Acid and Other Innovative Cosmetic Actives. Polymers 2023, 15, 4134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Hong, Y.; Kim, M. Structural and Functional Changes and Possible Molecular Mechanisms in Aged Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, J.R.; E Silva, S.A.M.; Holsback, V.S.S.; Leonardi, G.R. Skin Occlusive Performance: Sustainable Alternatives for Petrolatum in Skincare Formulations. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 4775–4780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodén, M. Treatments Improving Skin Barrier Function. Curr. Probl. Dermatol. 2016, 49, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juncan, A.M.; Morgovan, C.; Rus, L.L. Selection and Application of Synthetic versus Natural Emollients in the Formulation of Skin Care Products. Rev. Chim. 2019, 70, 2764–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.Y.; Um, J.Y.; Chung, B.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Park, J.S.; Kim, J.C.; Park, C.W.; Kim, H.O. Moisturizer in Patients with Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Medicina 2022, 58, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moisă, D.G.; Juncan, A.M.; Rus, L.-L.; Vonica-Țincu, A.L.; Cormoș, G.; Gligor, F.G. Viper Venom and Synthetic Peptides: Emerging Active Ingredients in Anti-Ageing Cosmeceuticals. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084501
Moisă DG, Juncan AM, Rus L-L, Vonica-Țincu AL, Cormoș G, Gligor FG. Viper Venom and Synthetic Peptides: Emerging Active Ingredients in Anti-Ageing Cosmeceuticals. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(8):4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084501
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoisă, Dana Georgiana, Anca Maria Juncan, Luca-Liviu Rus, Andreea Loredana Vonica-Țincu, Gabriela Cormoș, and Felicia Gabriela Gligor. 2025. "Viper Venom and Synthetic Peptides: Emerging Active Ingredients in Anti-Ageing Cosmeceuticals" Applied Sciences 15, no. 8: 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084501
APA StyleMoisă, D. G., Juncan, A. M., Rus, L.-L., Vonica-Țincu, A. L., Cormoș, G., & Gligor, F. G. (2025). Viper Venom and Synthetic Peptides: Emerging Active Ingredients in Anti-Ageing Cosmeceuticals. Applied Sciences, 15(8), 4501. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15084501








