Gaze Estimation Based on a Multi-Stream Adaptive Feature Fusion Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A novel MSMI-Net is proposed, which extracts high-dimensional eye features and low-dimensional facial features through a multi-stream design. The first stream focuses on eye feature extraction, while the second stream utilizes a shallow convolutional network to extract eye-face features. Both streams work collaboratively to optimize gaze direction estimation.
- In the feature fusion stream, a Joint Convolutional Block Attention Module (JointCBAM) is introduced to efficiently integrate binocular and facial features. Furthermore, to adequately account for the weight distribution of eye and facial features during fusion, an AWAM is designed. This mechanism dynamically optimizes feature weight distribution during training, increasing the proportion of effective features and further enhancing gaze estimation accuracy.
- Experiments on three benchmark datasets, MPIIFaceGaze, EYEDIAP, and Gaze360, demonstrate that MSMI-Net achieves state-of-the-art performance in gaze estimation. Ablation studies further validate the effectiveness of our contributions.
2. Related Work
2.1. Model-Based Gaze Estimation
2.2. Appearance-Based Gaze Estimation
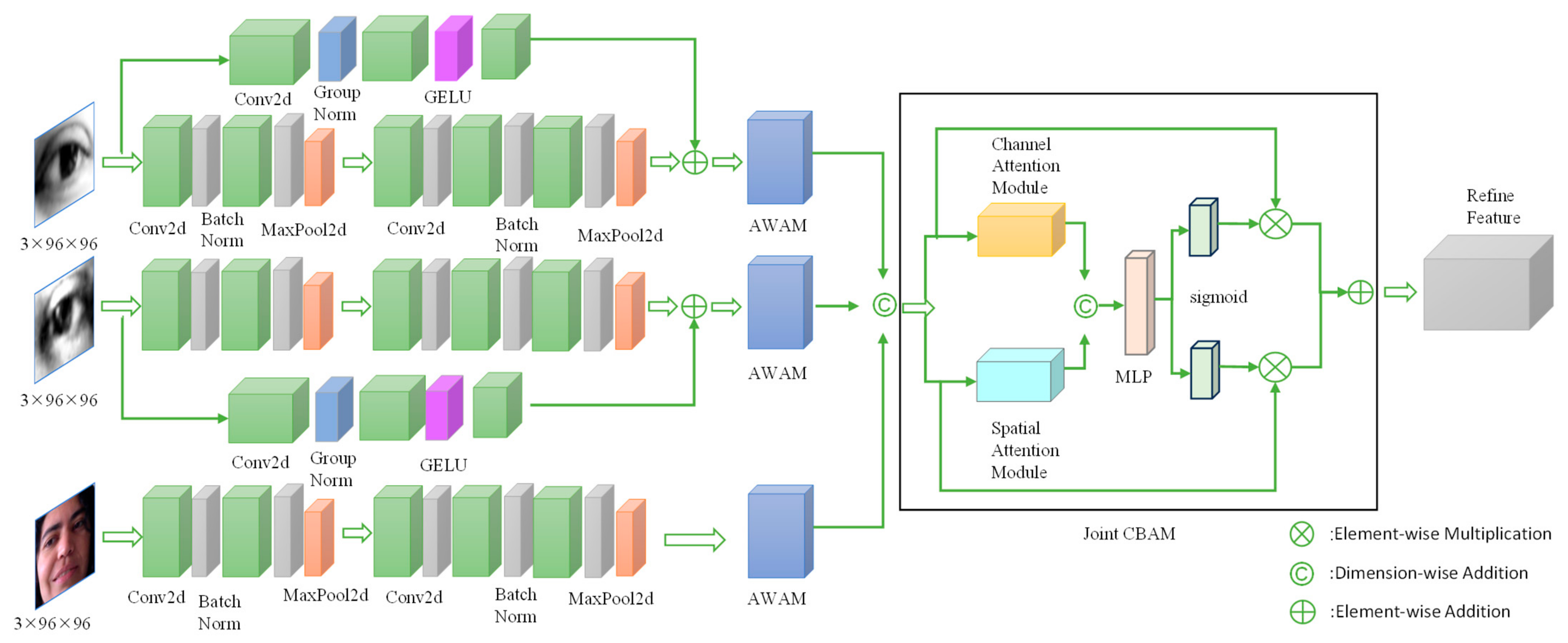
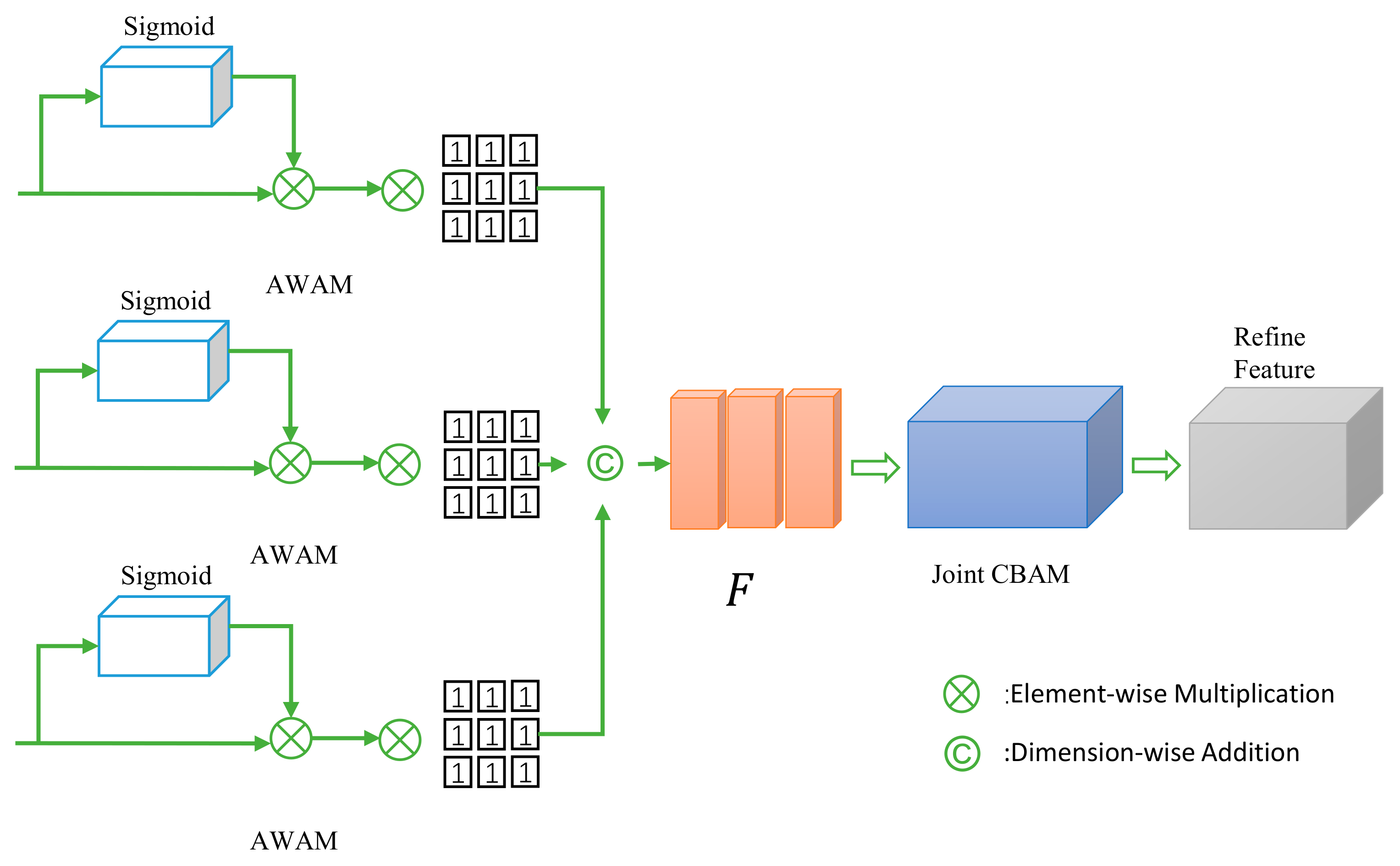
3. Proposed Method
3.1. Network Overview
3.2. Eye Image Stream
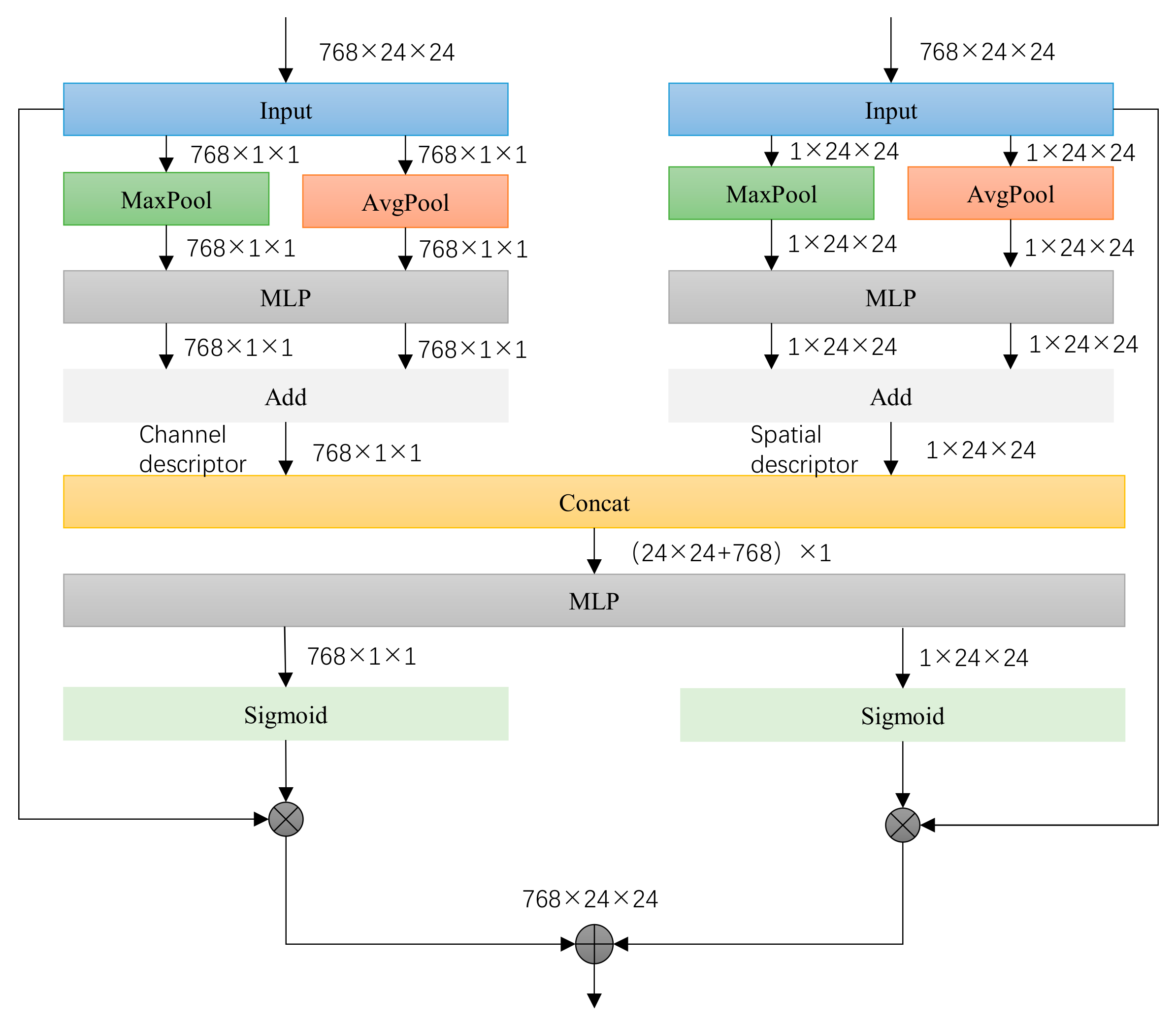
3.3. Fusion Stream
3.4. Gaze Result Evaluation
4. Experiments
4.1. Settings
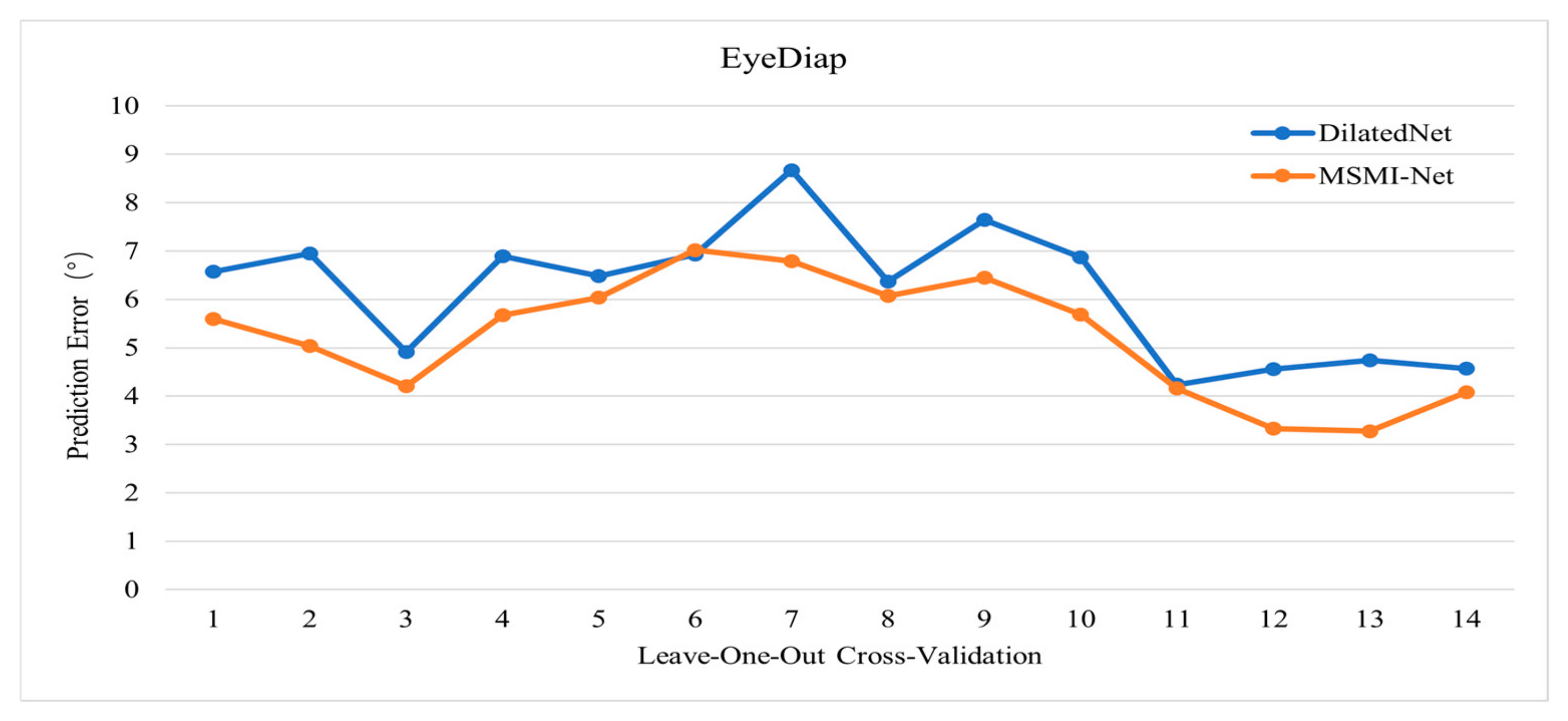
4.2. Performance
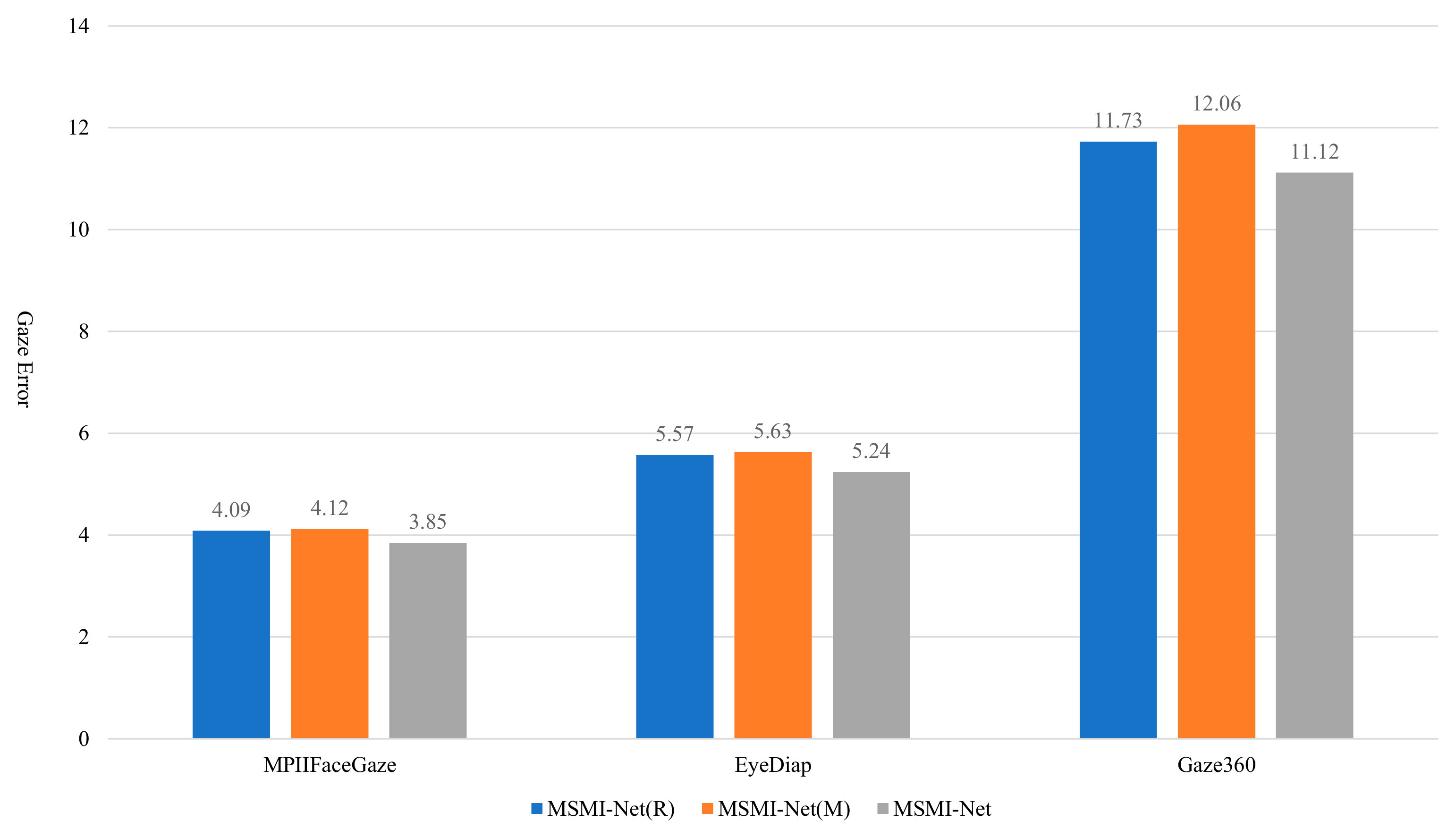
4.3. Ablation Study
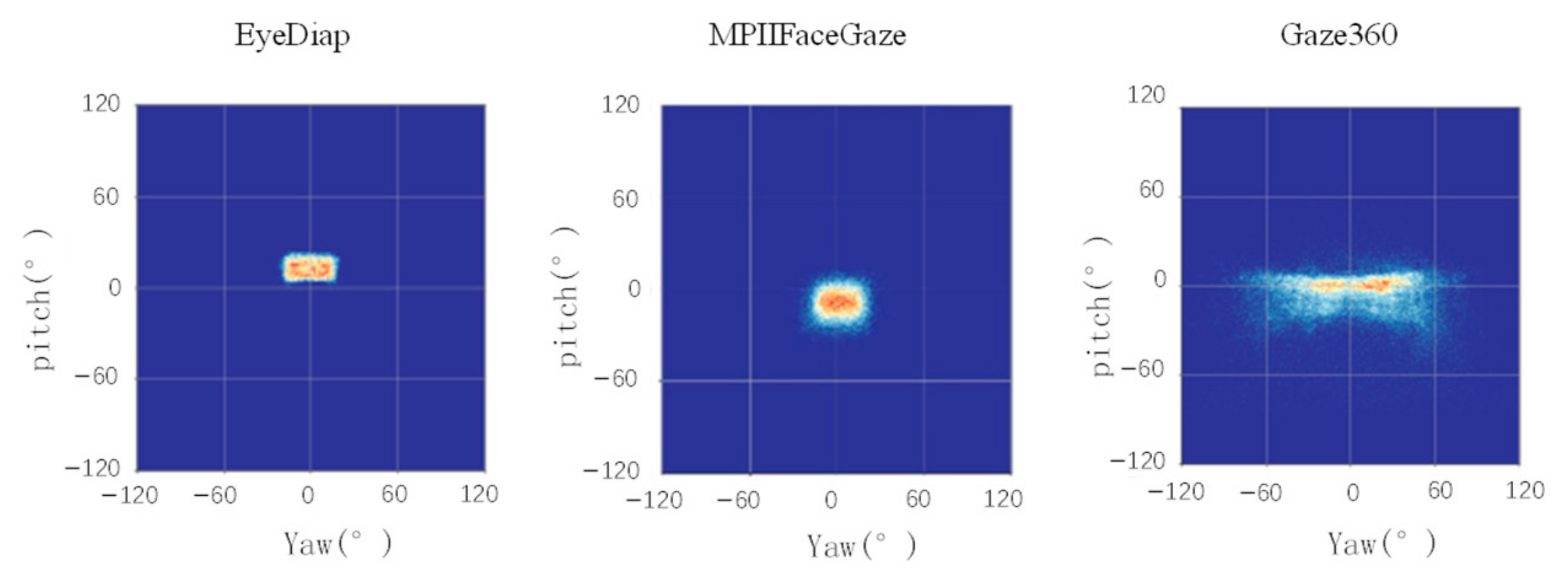
4.4. Results Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajanna, V.; Hammond, T. A gaze-assisted multimodal approach to rich and accessible human-computer interaction. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1803.04713. [Google Scholar]
- Andrist, S.; Tan, X.Z.; Gleicher, M.; Mutlu, B. Conversational gaze aversion for humanlike robots. In Proceedings of the 2014 ACM/IEEE International Conference on Human-Robot Interaction, Bielefeld, Germany, 3–6 March 2014; pp. 25–32. [Google Scholar]
- Clay, V.; König, P.; Koenig, S. Eye tracking in virtual reality. J. Eye Mov. Res. 2019, 12, 10–16910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patney, A.; Kim, J.; Salvi, M.; Kaplanyan, A.; Wyman, C.; Benty, N.; Lefohn, A.; Luebke, D. Perceptually-based foveated virtual reality. In Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2016 Emerging Technologies, Anaheim, CA, USA, 24–28 July 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chatelain, P.; Sharma, H.; Drukker, L.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Noble, J.A. Evaluation of gaze tracking calibration for longitudinal biomedical imaging studies. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2018, 50, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rayner, K. Eye movements in reading and information processing: 20 years of research. Psychol. Bull. 1998, 124, 372. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S.; Vora, S.; Yuen, K.; Trivedi, M.M. Dynamics of driver’s gaze: Explorations in behavior modeling and maneuver prediction. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2018, 3, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Z.; Ji, Q. Eye gaze tracking under natural head movements. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR’05), San Diego, CA, USA, 20–26 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 918–923. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Ji, Q. Real time eye gaze tracking with 3d deformable eye-face model. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 1003–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, H.; Jindal, S.; Manduchi, R. Rethinking model-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the ACM on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–11 August 2022; Volume 5, pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, F.; Okabe, T.; Sugano, Y.; Sato, Y. Learning gaze biases with head motion for head pose-free gaze estimation. Image Vis. Comput. 2014, 32, 169–179. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Lam, H.K.; Han, J.; Ouyang, G.; Li, X.; Liu, H. Appearance-based gaze estimation for ASD diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022, 52, 6504–6517. [Google Scholar]
- Elfares, M.; Hu, Z.; Reisert, P.; Bulling, A.; Küsters, R. Federated learning for appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the Gaze Meets Machine Learning Workshop, PMLR, New Orleans, LA, USA, 16 December 2023; pp. 20–36. [Google Scholar]
- Elfares, M.; Reisert, P.; Hu, Z.; Tang, W.; Küsters, R.; Bulling, A. PrivatEyes: Appearance-based Gaze Estimation Using Federated Secure Multi-Party Computation. In Proceedings of the ACM on Human-Computer Interaction, O‘ahu, HI, USA, 11–16 May 2024; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.; Ji, Q. 3D gaze estimation without explicit personal calibration. Pattern Recognit. 2018, 79, 216–227. [Google Scholar]
- Sugano, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sato, Y. Learning-by-synthesis for appearance-based 3d gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 1821–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Kendall, A.; Gal, Y. What uncertainties do we need in bayesian deep learning for computer vision? Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugano, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sato, Y. Generalizing eye tracking with bayesian adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 11907–11916. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. Appearance-based gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 4511–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F.; Zhang, X. Appearance-based gaze estimation via evaluation-guided asymmetric regression. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 100–115. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Lu, F. Gaze estimation using transformer. In Proceedings of the 2022 26th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Montreal, QC, Canada, 21–25 August 2022; pp. 3341–3347. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, F.; Yang, W.; Wang, G.; Su, N. Agent-guided gaze estimation network by two-eye asymmetry exploration. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 27–30 October 2024; pp. 2320–2326. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, Z.; Lv, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Chen, J. Frequency-spatial interaction network for gaze estimation. Displays 2025, 86, 102878. [Google Scholar]
- Valenti, R.; Sebe, N.; Gevers, T. Combining head pose and eye location information for gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2011, 21, 802–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, A.; Nitschke, C. Point of gaze estimation through corneal surface reflection in an active illumination environment. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2012: 12th European Conference on Computer Vision, Florence, Italy, 7–13 October 2012, Proceedings, Part II 12; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012; pp. 159–172. [Google Scholar]
- Sei, M.; Utsumi, A.; Yamazoe, H.; Lee, J. Model-based deep gaze estimation using incrementally updated face-shape parame-ters. In Proceedings of the 2023 Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Tubingen, Germany, 30 May–2 June 2023; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, G.Z.; Guo, Y. EasyGaze3D: Towards effective and flexible 3D gaze estimation from a single RGB camera. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), Detroit, MI, USA, 1–5 October 2023; pp. 6537–6543. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, K.; Li, Y.; Guo, Z.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y. Model-Based 3D Gaze Estimation Using a TOF Camera. Sensors 2024, 24, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baluja, S.; Pomerleau, D. Non-intrusive gaze tracking using artificial neural networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 1993, 6, 153–156. [Google Scholar]
- Sugano, Y.; Matsushita, Y.; Sato, Y. Appearance-based gaze estimation using visual saliency. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2012, 35, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krafka, K.; Khosla, A.; Kellnhofer, P.; Kannan, H.; Bhandarkar, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Eye tracking for everyone. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2176–2184. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y.; Fritz, M.; Bulling, A. Mpiigaze: Real-world dataset and deep appearance-based gaze estimation. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 41, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Huang, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Lu, F. A coarse-to-fine adaptive network for appearance-based gaze estimation. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Singapore, 7–12 February 2020; Volume 34, pp. 10623–10630. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Fang, F.; Hou, G.; Li, Z.; Niu, R. Appearance-based gaze estimation with feature fusion of multi-level information elements. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2023, 10, 1080–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ververas, E.; Gkagkos, P.; Deng, J.; Doukas, M.C.; Guo, J.; Zafeiriou, S. 3DGazeNet: Generalizing 3D Gaze Estimation with Weak-Supervision from Synthetic Views. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Milan, Italy, 29 September–4 October 2024; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 387–404. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, C.Y.; Feichtenhofer, C.; Darrell, T. A convnet for the 2020s. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2022; pp. 11976–11986. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Funes Mora, K.A.; Monay, F.; Odobez, J.M. Eyediap: A database for the development and evaluation of gaze estimation algorithms from rgb and rgb-d cameras. In Proceedings of the Symposium on Eye Tracking Research and Applications, Safety Harbor, FL, USA, 26–28 March 2014; pp. 255–258. [Google Scholar]
- Kellnhofer, P.; Recasens, A.; Stent, S.; Matusik, W.; Torralba, A. Gaze360: Physically unconstrained gaze estimation in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6912–6921. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Shi, B.E. Appearance-based gaze estimation using dilated-convolutions. In Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 309–324. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Wang, H.; Bao, Y.; Lu, F. Appearance-based gaze estimation with deep learning: A review and benchmark. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2024, 46, 7509–7528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Lu, F. Adaptive feature fusion network for gaze tracking in mobile tablets. In Proceedings of the 2020 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), Milan, Italy, 10–15 January 2021; pp. 9936–9943. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, G.; Shi, J.; Xu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Du, Y.; Zhen, X.; Liu, H. Gaze estimation by attention-induced hierarchical variational auto-encoder. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2023, 54, 2592–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, Z.; Hungler, P.; Etemad, A. Multistream gaze estimation with anatomical eye region isolation by synthetic to real transfer learning. IEEE Trans. Artif. Intell. 2024, 5, 4232–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, T.; Chang, H.J.; Demiris, Y. Rt-gene: Real-time eye gaze estimation in natural environments. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 334–352. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Oh, J.O.; Chang, H.J.; Na, J.H.; Tae, M.; Zhang, Z.; Choi, S.I. Gazecaps: Gaze estimation with self-attention-routed capsules. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 18–22 June 2023; pp. 2669–2677. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, J.; Zhang, X.; Sugano, Y. UniGaze: Towards Universal Gaze Estimation via Large-scale Pre-Training. arXiv 2025, arXiv:2502.02307. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Lee, S.H. GazeSymCAT: A Symmetric Cross-Attention Transformer for Robust Gaze Estimation under Extreme Head Poses and Gaze Variations. J. Comput. Des. Eng. 2025, 12, qwaf017. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, D.; El-Sharkawy, M. Thin mobilenet: An enhanced mobilenet architecture. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 10th Annual Ubiquitous Computing, Electronics & Mobile Communication Conference (UEMCON), New York, NY, USA, 10–12 October 2019; pp. 0280–0285. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
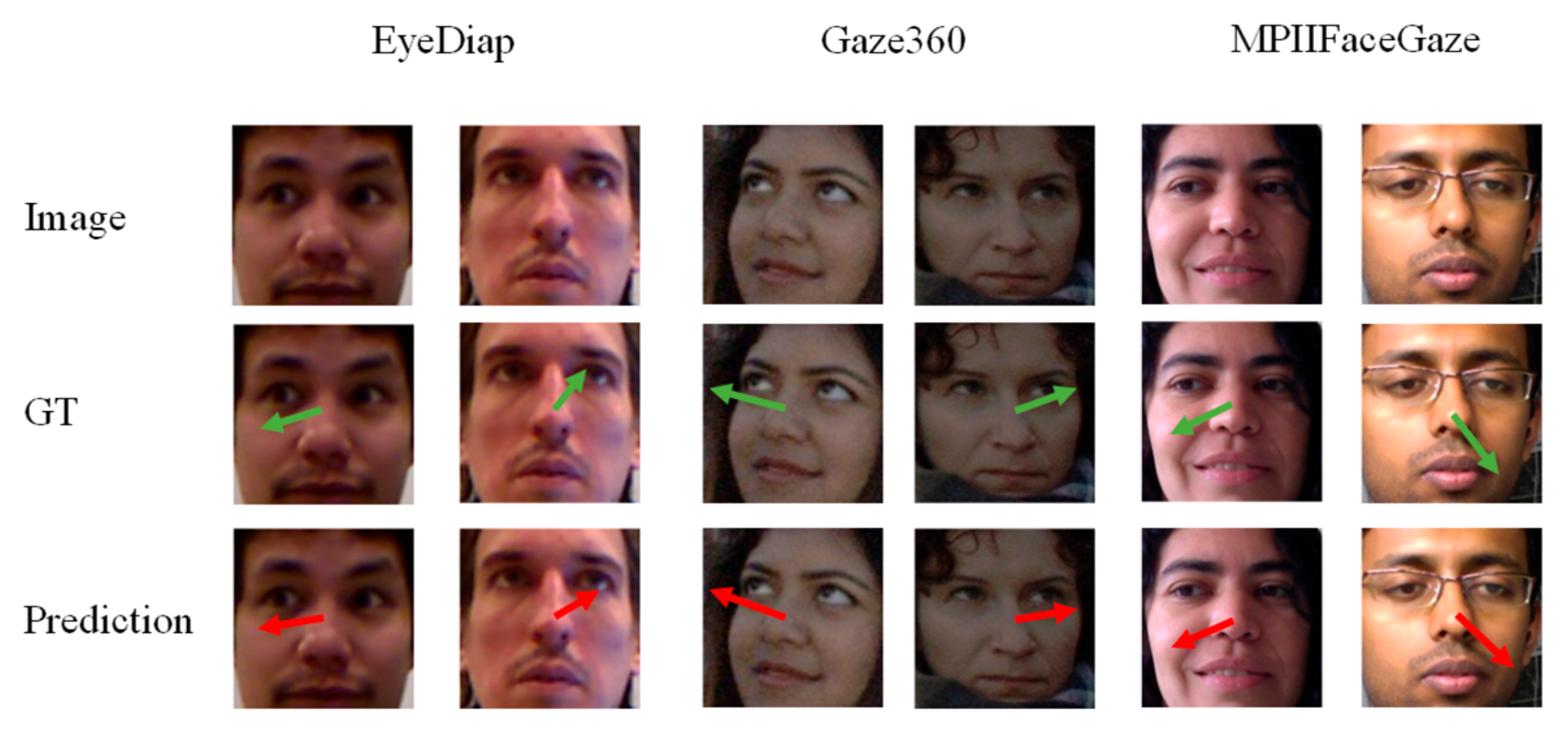




| Model | MPIIFaceGaze | EyeDiap | Gaze360 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AFF-Net | 4.34 | 6.41 | - |
| Dilated-Net | 4.44 | 6.17 | 13.73 |
| CA-Net | 4.27 | 5.27 | 11.20 |
| RT-GENE | 4.66 | 6.02 | 12.26 |
| FullFace | 4.93 | 6.53 | 14.90 |
| ARE-Net | 5.00 | 6.1 | - |
| MSGazeNet | 4.64 | 5.86 | - |
| VGE-Net | 3.90 | 6.6 | - |
| GazeCaps | 4.06 | 5.10 | 10.04 |
| UniGaze-H | 4.51 | 5.88 | 12.37 |
| GazeSymCAT | 4.11 | 5.13 | - |
| MSMI-Net | 3.85 | 5.24 | 11.12 |
| Model | MPIIFaceGaze |
|---|---|
| Without Fusion-Stream | 5.09 |
| Without Eye-Stream | 4.32 |
| MSMI-Net | 3.85 |
| Model | MPIIFaceGaze |
|---|---|
| Without JointCBAM | 4.67 |
| Without AWAM | 4.43 |
| MSMI-Net | 3.85 |
| Model | MPIIFaceGaze |
|---|---|
| MSMI-SE | 4.19 |
| MSMI-CBAM | 3.97 |
| MSMI-Net | 3.85 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Tong, E.; Zhang, K.; Cheng, N.; Lai, Z.; Pan, Z. Gaze Estimation Based on a Multi-Stream Adaptive Feature Fusion Network. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073684
Li C, Tong E, Zhang K, Cheng N, Lai Z, Pan Z. Gaze Estimation Based on a Multi-Stream Adaptive Feature Fusion Network. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073684
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Changli, Enrui Tong, Kao Zhang, Nenglun Cheng, Zhongyuan Lai, and Zhigeng Pan. 2025. "Gaze Estimation Based on a Multi-Stream Adaptive Feature Fusion Network" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073684
APA StyleLi, C., Tong, E., Zhang, K., Cheng, N., Lai, Z., & Pan, Z. (2025). Gaze Estimation Based on a Multi-Stream Adaptive Feature Fusion Network. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3684. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073684







