New Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for Lactic Acid Extraction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. DES Preparation
2.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR)
2.3. Thermal Properties
2.4. Density and Viscosity Measurements
2.5. Extraction and Stripping of LA
2.6. Lactic Acid Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
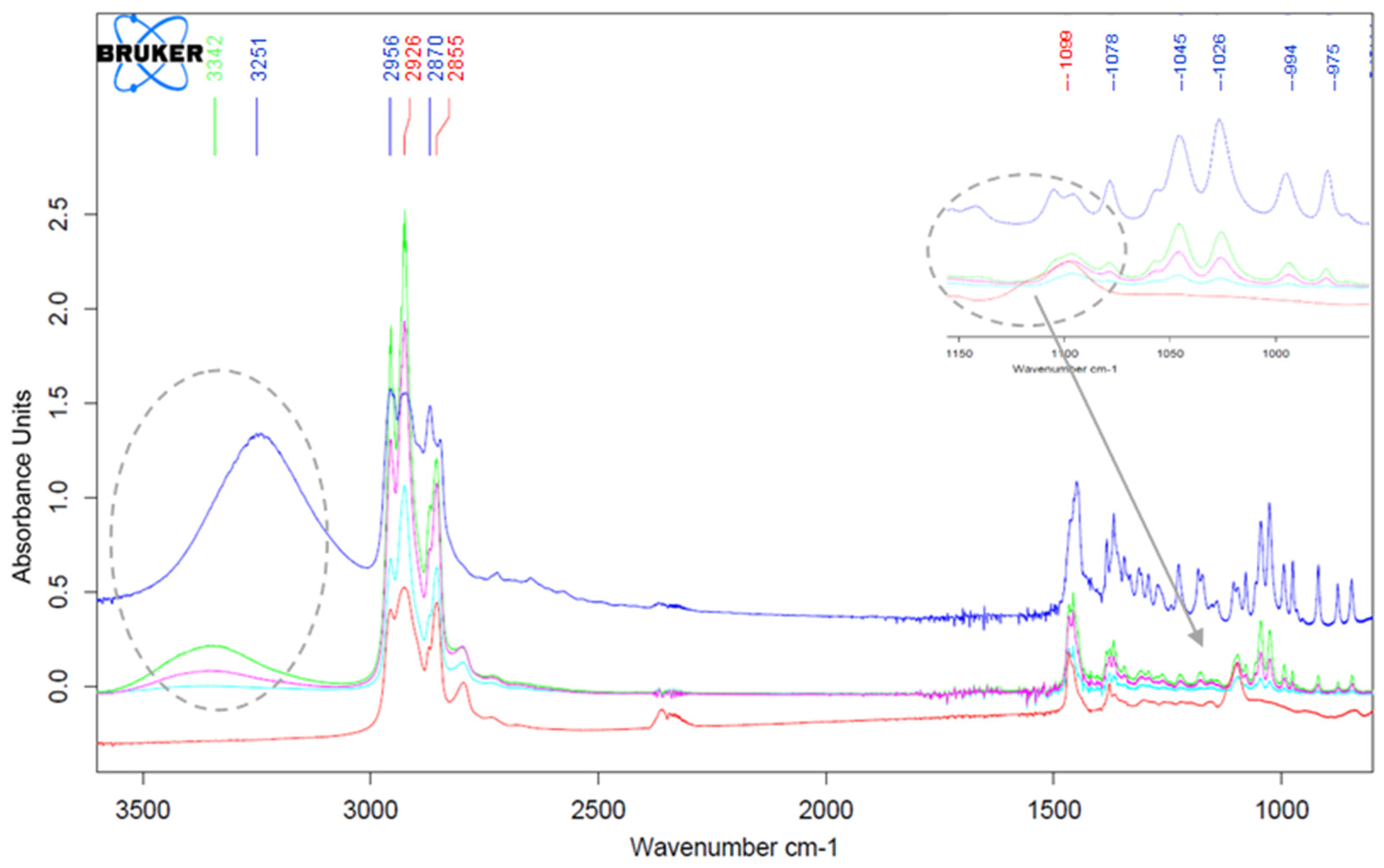
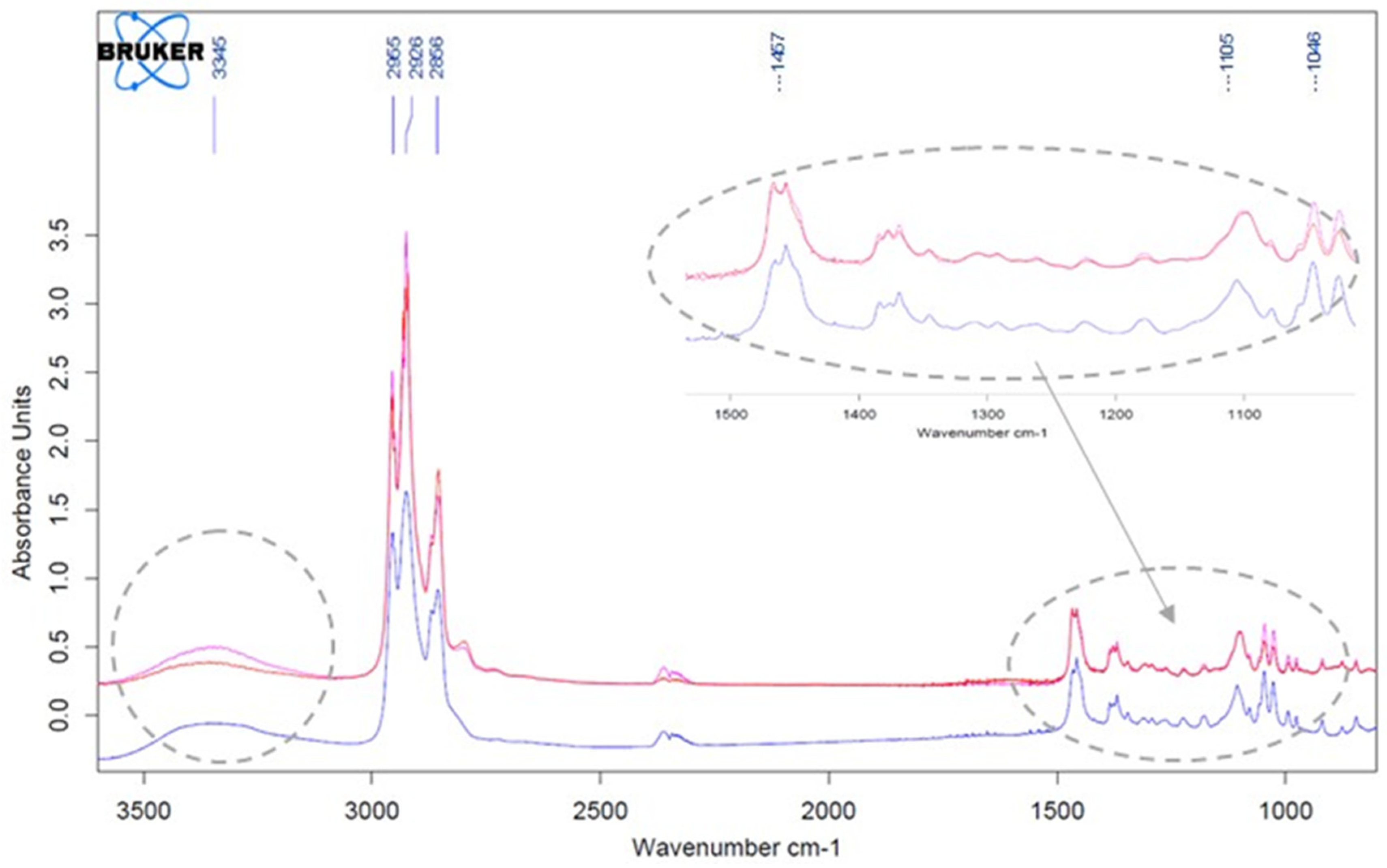
3.1. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectrophotometry (FTIR)
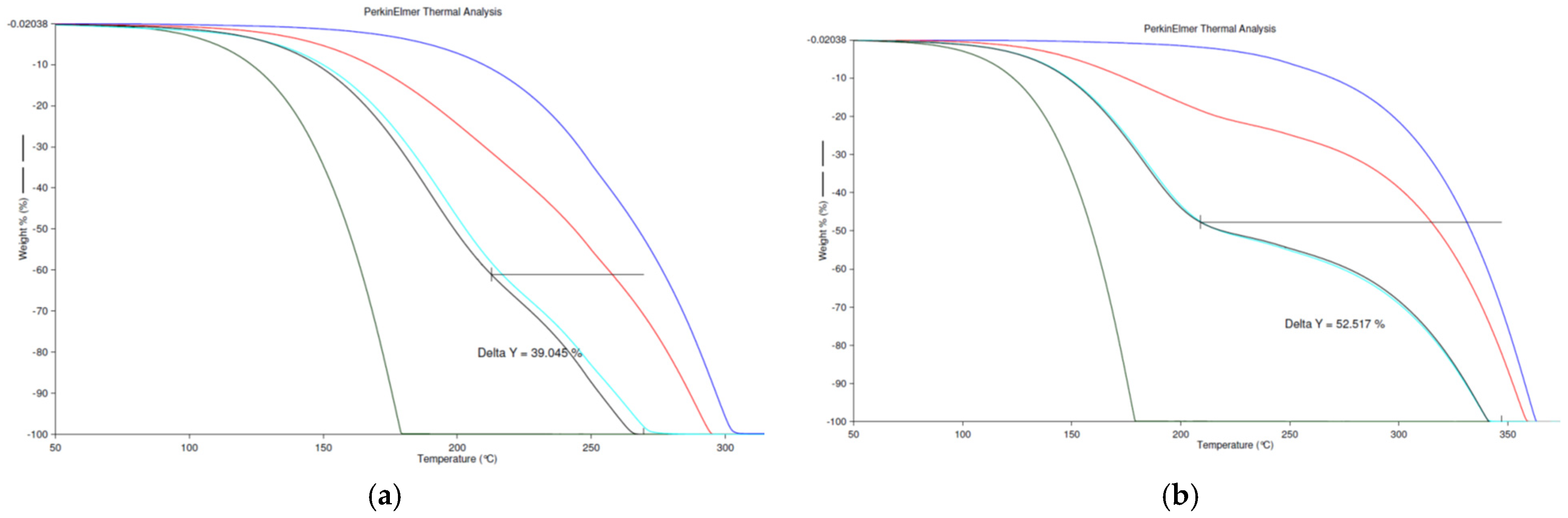
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
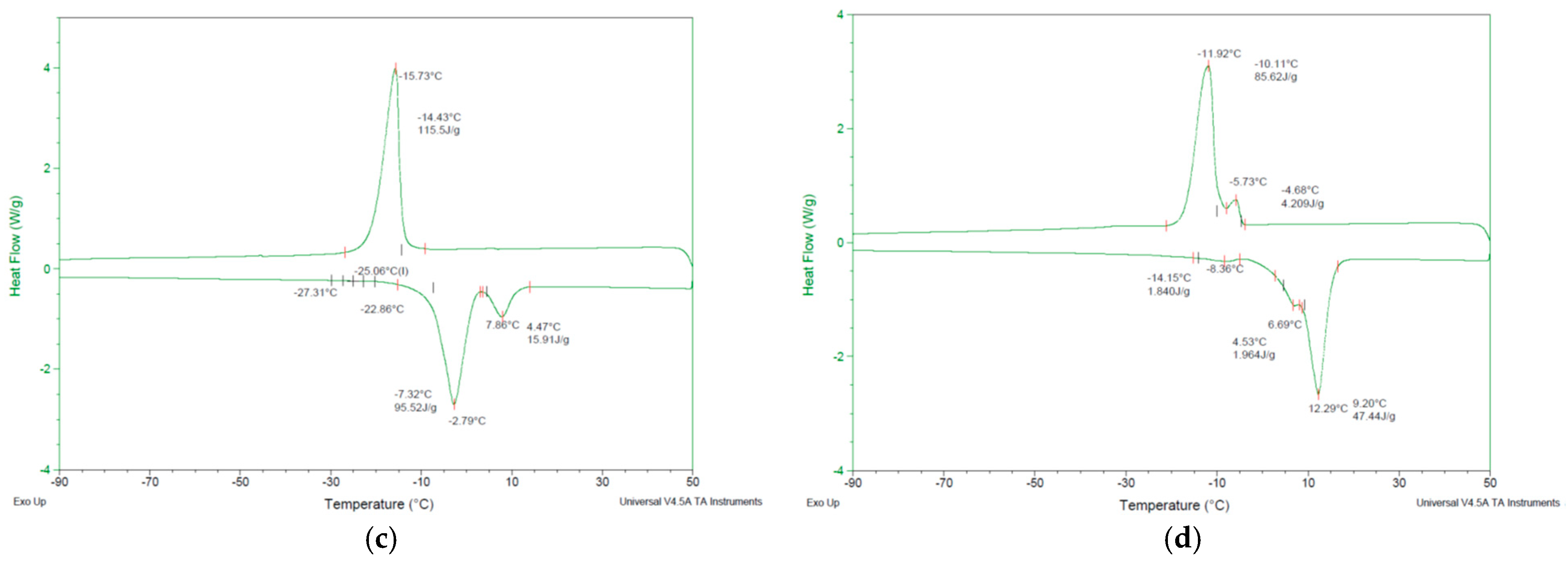
3.3. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
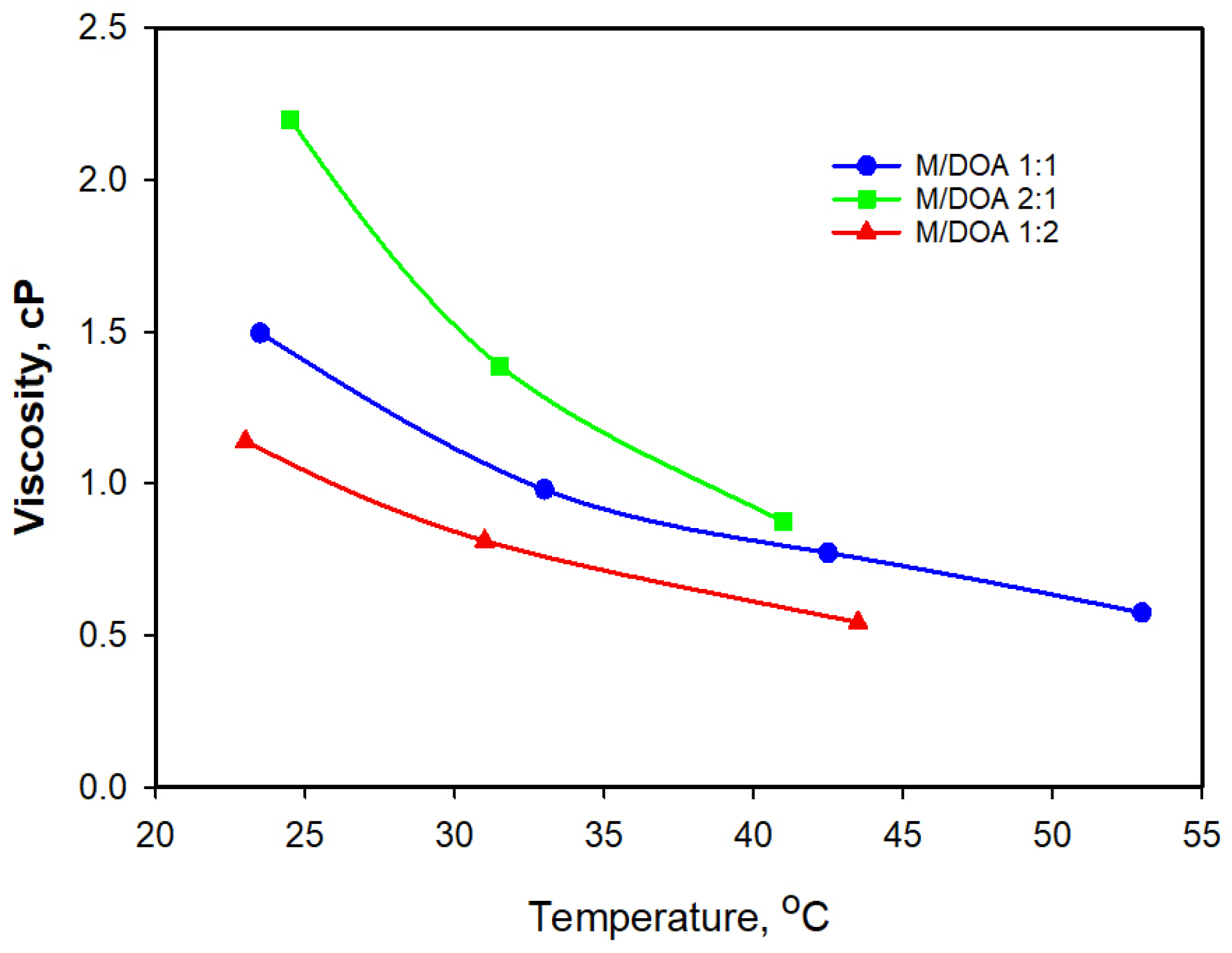
3.4. Density and Viscosity Measurements
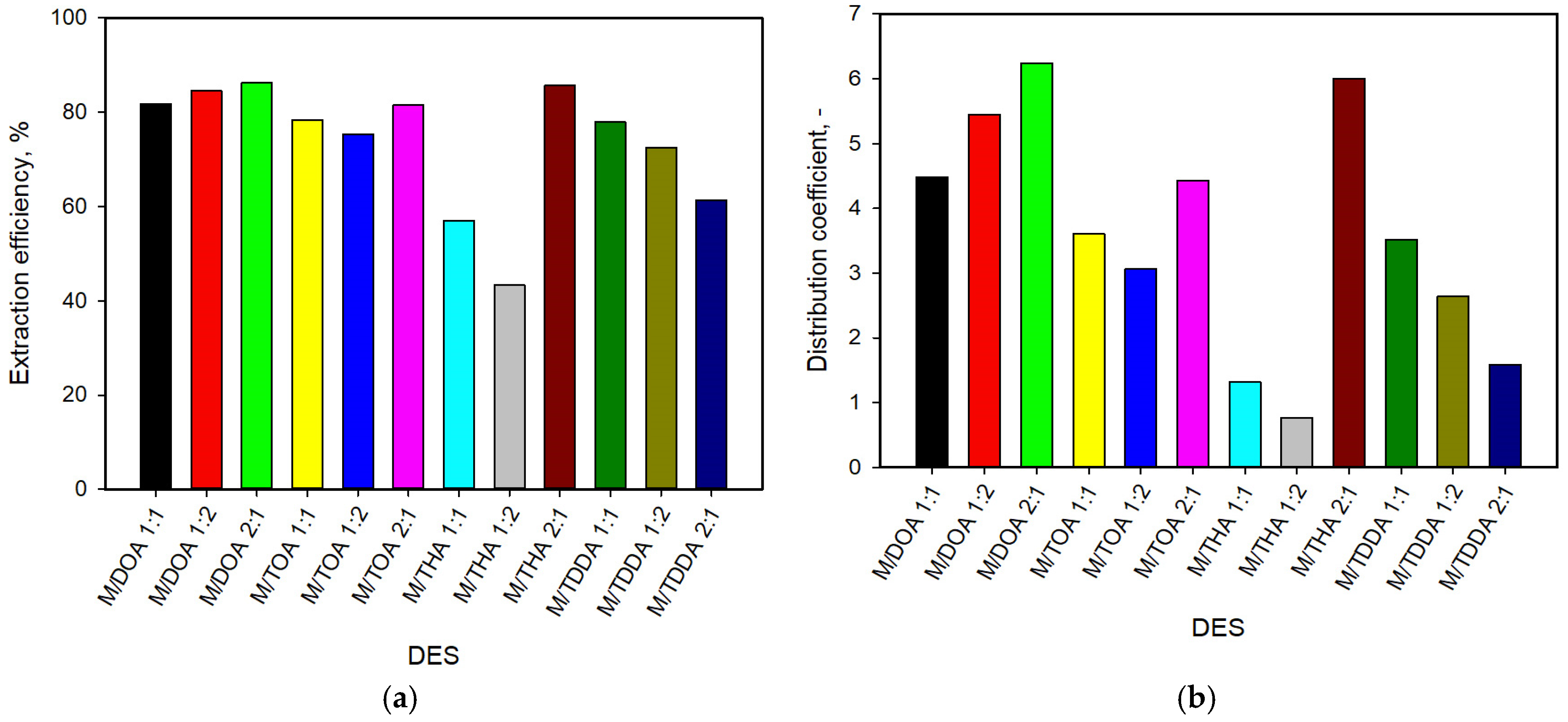
3.5. Extraction and Stripping of Lactic Acid
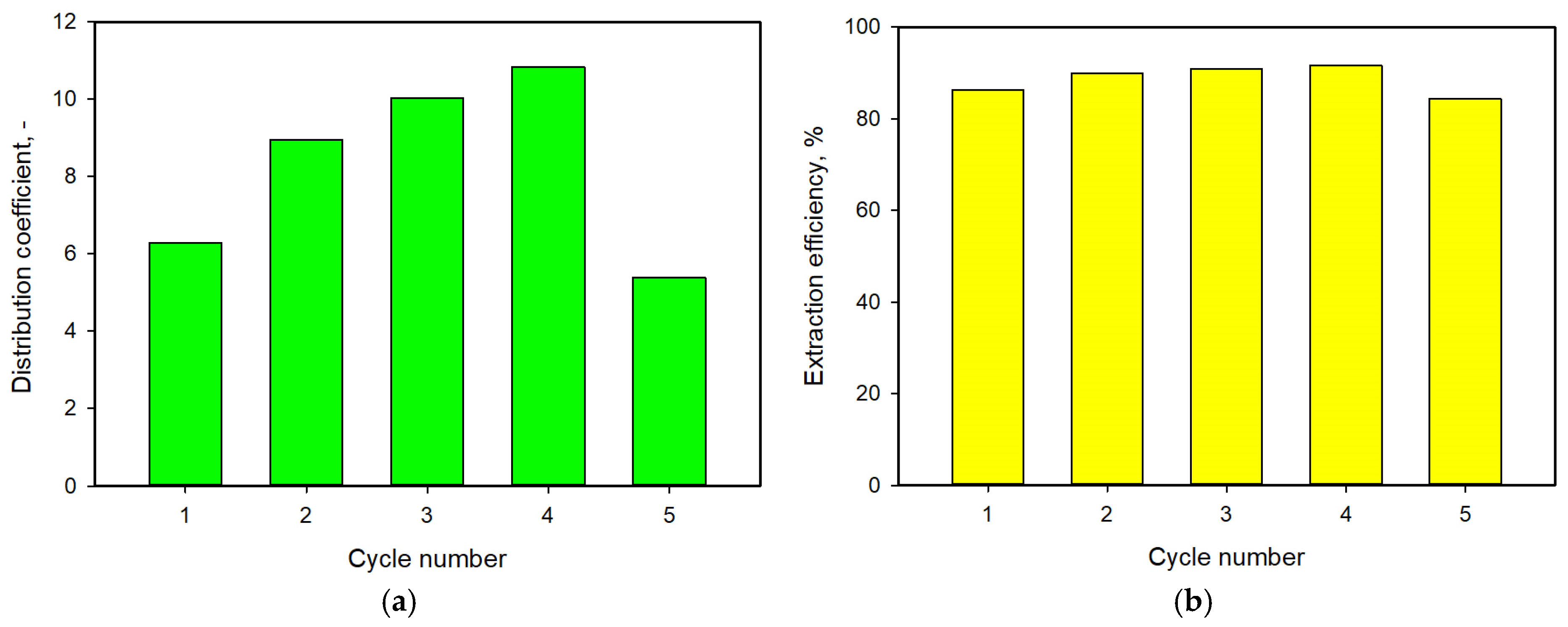
3.6. Consecutive Extraction of Lactic Acid with M/DOA 1:2 DES
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Frieling, K.P. Schuegerl Recovery of Lactic Acid from Aqueous Model Solutions and Fermentation Broths. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 685–696. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandri, M.; Schneider, R.; Venus, J. Membrane Technologies for Lactic Acid Separation from Fermentation Broths Derived from Renewable Resources. Membranes 2018, 8, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.D.; Lee, M.Y.; Hwang, Y.S.; Cho, Y.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, H.B. Separation and Purification of Lactic Acid from Fermentation Broth Using Membrane-Integrated Separation Processes. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 8301–8310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, N.A.S.; Lim, S.J.; Maskat, M.Y.; Mutalib, S.A.; Zaini, N.A.M. Lactic Acid Separation and Recovery from Fermentation Broth by Ion-Exchange Resin: A Review. Bioresour. Bioprocess. 2021, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tönjes, S.; Uitterhaegen, E.; De Winter, K.; Soetaert, W. Reactive Extraction Technologies for Organic Acids in Industrial Fermentation Processes—A Review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 356, 129881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beg, D.; Kumar, A.; Shende, D.; Wasewar, K. Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Lactic Acid Using Non-Toxic Solvents. Chem. Data Collect. 2022, 38, 100823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teke, G.M.; Gakingo, G.K.; Pott, R.W.M. The Liquid-Liquid Extractive Fermentation of L–Lactic Acid in a Novel Semi-Partition Bioreactor (SPB). J. Biotechnol. 2022, 360, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinov’eva, I.V.; Zakhodyaeva, Y.A.; Voshkin, A.A. Extraction of Lactic Acid Using the Polyethylene Glycol–Sodium Sulfate–Water System. Theor. Found. Chem. Eng. 2021, 55, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyuchoukov, G.; Yankov, D. Lactic Acid Extraction by Means of Long Chain Tertiary Amines: A Comparative Theoretical and Experimental Study. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Thakur, A. Reactive Extraction of Lactic Acid Using Environmentally Benign Green Solvents and Synergistic Mixture of Extractants. Sci. Iran. 2019, 26, 3456–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayazit, Ş.S.; Uslu, H.; İnci, İ. Comparison of the Efficiencies of Amine Extractants on Lactic Acid with Different Organic Solvents. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2011, 56, 750–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Munro, H.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Preparation of Novel, Moisture-Stable, Lewis-Acidic Ionic Liquids Containing Quaternary Ammonium Salts with Functional Side Chains. Chem. Commun. 2001, 19, 2010–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, A.P.; Capper, G.; Davies, D.L.; Rasheed, R.K.; Tambyrajah, V. Novel Solvent Properties of Choline Chloride/Urea mixtures. Chem. Commun. 2003, 39, 70–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, M.A.R.; Pinho, S.P.; Coutinho, J.A.P. Insights into the Nature of Eutectic and Deep Eutectic Mixtures. J. Solut. Chem. 2019, 48, 962–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, E.L.; Abbott, A.P.; Ryder, K.S. Deep Eutectic Solvents (DESs) and Their Applications. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 11060–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zainal-Abidin, M.H.; Hayyan, M.; Hayyan, A.; Jayakumar, N.S. New Horizons in the Extraction of Bioactive Compounds Using Deep Eutectic Solvents: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 979, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Guo, X.; Xu, T.; Fan, L.; Zhou, X.; Wu, S. Ionic Deep Eutectic Solvents for the Extraction and Separation of Natural Products. J. Chromatogr. A 2019, 1598, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyniukova, A.; Holuša, J.; Musiolek, D.; Sedlakova-Kadukova, J.; Płotka-Wasylka, J.; Andruch, V. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Separation and Determination of Bioactive Compounds in Medicinal Plants. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 172, 114047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruesgas-Ramón, M.; Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Durand, E. Application of Deep Eutectic Solvents (DES) for Phenolic Compounds Extraction: Overview, Challenges, and Opportunities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Y.; Witkamp, G.-J.; Verpoorte, R.; Choi, Y.H. Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents as a New Extraction Media for Phenolic Metabolites in Carthamus tinctorius L. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 6272–6278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, C.; Gallo, V.; Della Posta, S.; Dugo, L.; Mazzeo, L.; Cocchi, M.; Piemonte, V.; De Gara, L. Choline Chloride–Lactic Acid-Based NADES As an Extraction Medium in a Response Surface Methodology-Optimized Method for the Extraction of Phenolic Compounds from Hazelnut Skin. Molecules 2021, 26, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, F.B.; Nemli, E.; Bekdeşer, B.; Çelik, S.E.; Lalikoglu, M.; Aşçı, Y.S.; Capanoglu, E.; Bener, M.; Apak, R. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Valuable Phenolics from Sunflower Pomace with Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents and Food Applications of the Extracts. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 411, 125699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görüşük, E.M.; Lalikoglu, M.; Aşçı, Y.S.; Bener, M.; Bekdeşer, B.; Apak, R. Novel Tributyl Phosphate-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent: Application in Microwave Assisted Extraction of Carotenoids. Food Chem. 2024, 459, 140418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Cheng, H.; Song, Z.; Ji, L.; Chen, L.; Qi, Z. Selection of Deep Eutectic Solvents for Extractive Deterpenation of Lemon Essential Oil. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 350, 118524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, D.; Wang, B.; Li, D. Ultrasound-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvents Extraction of Podophyllotoxins from Juniperus Sabina L: Optimization, Enrichment, and Anti-Drug Resistant Bacteria Activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 221, 119408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañadas, R.; González-Miquel, M.; González, E.J.; Díaz, I.; Rodríguez, M. Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents for Extraction of Natural Phenolic Antioxidants from Winery Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2021, 254, 117590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalikoglu, M. Intensification of Formic Acid from Dilute Aqueous Solutions Using Menthol Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2022, 99, 100303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, S.; Kurtulbaş, E. An Advanced Approach for the Recovery of Acetic Acid from Its Aqueous Media: Deep Eutectic Liquids versus Ionic Liquids. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2022, 12, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baş, Y.; Lalikoglu, M.; Uthan, A.; Kordon, E.; Anur, A.; Aşçı, Y.S. Realization for Rapid Extraction of Citric Acid from Aqueous Solutions Using Deep Eutectic Solvents. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 411, 125699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Zamora, C.; González-Sálamo, J.; Hernández-Sánchez, C.; Hernández-Borges, J. Menthol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent Dispersive Liquid–Liquid Microextraction: A Simple and Quick Approach for the Analysis of Phthalic Acid Esters from Water and Beverage Samples. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 8783–8794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmelmayer, P.; Steiner, L.; Weber, H.; Kienberger, M. Thymol-Menthol-Based Deep Eutectic Solvent as a Modifier in Reactive Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Carboxylic Acids from Pretreated Sweet Sorghum Silage Press Juice. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 310, 123060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demmelmayer, P.; Foo, J.W.; Wiesler, D.; Rudelstorfer, G.; Kienberger, M. Reactive Liquid-Liquid Extraction of Lactic Acid from Microfiltered Sweet Sorghum Silage Press Juice in an Agitated Extraction Column Using a Hydrophobic Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent as Modifier. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 458, 142463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, K.; Datta, D. Recovery of Nicotinic Acid (Niacin) Using Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: Ultrasonication Facilitated Extraction. Chem. Data Collect. 2022, 41, 100934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulia, K.; Adam, D.; Zahrina, I.; Krisanti, E. Green Extraction of Palmitic Acid from Palm Oil Using Betaine-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvents. Int. J. Technol. 2018, 9, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulia, K.; Masanari, E.; Zahrina, I.; Susanto, B.; Krisanti, E.A. Optimization of Palmitic Acid Extraction from Palm Oil with Betaine-Based Natural Deep Eutectic Solvent Using Response Surface Methodology. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2175, 020041. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Fang, H.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X. Extraction Performance Evaluation of Amide-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents for Carboxylic Acid: Molecular Dynamics Simulations and a Mini-Pilot Study. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 304, 122360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveiro, E.; González, B.; Domínguez, Á. Extraction of Adipic, Levulinic and Succinic Acids from Water Using TOPO-Based Deep Eutectic Solvents. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020, 241, 116692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Ma, W.; Zhao, J.; Yu, J.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X. In-Situ Formation of Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents to Separate Lactic Acid: Lactam as Hydrogen Bond Acceptor and Lactic Acid as Hydrogen Bond Donor. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 353, 128511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Han, X.; Huang, X.; Zhao, J.; Ren, Q.; Luo, H. Menthol-Based Eutectic Mixtures: Novel Potential Temporary Consolidants for Archaeological Excavation Applications. J. Cult. Herit. 2019, 39, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, K.; Shimoaka, T.; Akai, N.; Katsumoto, Y. Relationship between the Broad OH Stretching Band of Methanol and Hydrogen-Bonding Patterns in the Liquid Phase. J. Phys. Chem. A 2008, 112, 7342–7348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Trindle, C.; Knee, J.L. Communication: Frequency Shifts of an Intramolecular Hydrogen Bond as a Measure of Intermolecular Hydrogen Bond Strengths. J. Chem. Phys. 2012, 137, 091101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, B.D.; Florindo, C.; Iff, L.C.; Coelho, M.A.Z.; Marrucho, I.M. Menthol-Based Eutectic Mixtures: Hydrophobic Low Viscosity Solvents. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 2469–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroso, I.M.; Craveiro, R.; Rocha, Â.; Dionísio, M.; Barreiros, S.; Reis, R.L.; Paiva, A.; Duarte, A.R.C. Design of Controlled Release Systems for THEDES—Therapeutic Deep Eutectic Solvents, Using Supercritical Fluid Technology. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 492, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, R.; Banerjee, T. Liquid–Liquid Extraction of Lower Alcohols Using Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvent: Experiments and COSMO-SAC Predictions. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 3371–3381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chemical BooK, Dioctylamine (1120-48-5). Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ProductMSDSDetailCB7389427_EN.htm (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Chemical BooK, Tridodecylamine (102-87-4). Available online: https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_US_CB5727311.aspx (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Yamashita, H.; Hirakura, Y.; Yuda, M.; Terada, K. Coformer Screening Using Thermal Analysis Based on Binary Phase Diagrams. Pharm. Res. 2014, 31, 1946–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toprakçı, İ.; Pekel, A.G.; Kurtulbaş, E.; Şahin, S. Special Designed Menthol-Based Deep Eutectic Liquid for the Removal of Herbicide 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic Acid through Reactive Liquid–Liquid Extraction. Chem. Pap. 2020, 74, 3995–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Su, B.; Wei, Q.; Ren, X. Selective Separation of Lactic, Malic, and Tartaric Acids Based on the Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents of Terpenes and Amides. Green. Chem. 2021, 23, 5866–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Osch, D.J.G.P.; Zubeir, L.F.; Van Den Bruinhorst, A.; Rocha, M.A.A.; Kroon, M.C. Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as Water-Immiscible Extractants. Green. Chem. 2015, 17, 4518–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aşçı, Y.S.; Lalikoglu, M. Development of New Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents Based on Trioctylphosphine Oxide for Reactive Extraction of Carboxylic Acids. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 1356–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Name | Abbreviation | Supplier | Purity |
|---|---|---|---|
| L (+) Lactic acid | LA | Acros Organics, Oslo, Norway | ≥90% |
| Crystalline L-(+) Lactic acid | LA | Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | ≥98% |
| L-Menthol | M | Sigma-Aldrich, Burlington, MA, USA | ≥99% |
| Dioctyl amine | DOA | Fluka, Buchs, Switzerland | ≥97% |
| Trihexyl amine | THA | Janssen Chemica, Beerse, Belgium | ≥95% |
| Trioctyl amine | TOA | Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA | ≥95% |
| Tridodecyl amine | TDDA | Merck, Rahway, NJ, USA | ≥95% |
| Mixture Components | Molar Ratio |
|---|---|
| M/DOA | 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 |
| M/TOA | 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 |
| M/THA | 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 |
| M/TDDA | 1:1, 1:2, 2:1 |
| Pure Compound | T °C | DES | Tdeg (°C) | First Step Decomposition Degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| L-Menthol | 175 | M/DOA 1:1 | 280 | - |
| DOA | 305 | M/DOA 1:2 | 290 | - |
| TOA | 365 | M/TOA 1:2 | 360 | 26.5% |
| THA | 465 | M/THA 1:1 | 275 | - |
| TDDA | 470 | M/THA 1:2 | 290 | - |
| M/TDDA 1:1 | 460 | 30% | ||
| M/TDDA 1:2 | 460 | 18% |
| Eutectic Mixtures (Ratio) | First Step Tdeg (°C) | Decomposition Degree (%) | Second Step Tdeg (°C) | Decomposition Degree (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M/DOA 1:2 ex | - | - | 275 | 100 |
| M/DOA 1:2 re-ex | - | - | 275 | 100 |
| M/TOA 1:1 ex | 220 | 50 | 340 | 50 |
| M/TOA 1:1 re-ex | 220 | 50 | 340 | 50 |
| M/THA 1:1 ex | - | - | 275 | 100 |
| M/THA 1:1 re-ex | - | - | 275 | 100 |
| M/TDDA 1:2 ex | 230 | 41 | 450 | 59 |
| DES | Ratio | First Stripping, % | First and Second Stripping, % |
|---|---|---|---|
| M/DOA | 2:1 | 95 | 97 |
| M/THA | 1:2 | 86 | 86 |
| M/THA | 2:1 | 94 | 95 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ivanova, D.; Apostolov, A.; Tuleshkov, P.; Novakov, C.; Yankov, D. New Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for Lactic Acid Extraction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073564
Ivanova D, Apostolov A, Tuleshkov P, Novakov C, Yankov D. New Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for Lactic Acid Extraction. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073564
Chicago/Turabian StyleIvanova, Denitsa, Apostol Apostolov, Pencho Tuleshkov, Christo Novakov, and Dragomir Yankov. 2025. "New Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for Lactic Acid Extraction" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073564
APA StyleIvanova, D., Apostolov, A., Tuleshkov, P., Novakov, C., & Yankov, D. (2025). New Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Deep Eutectic Solvents as a Tool for Lactic Acid Extraction. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3564. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073564






