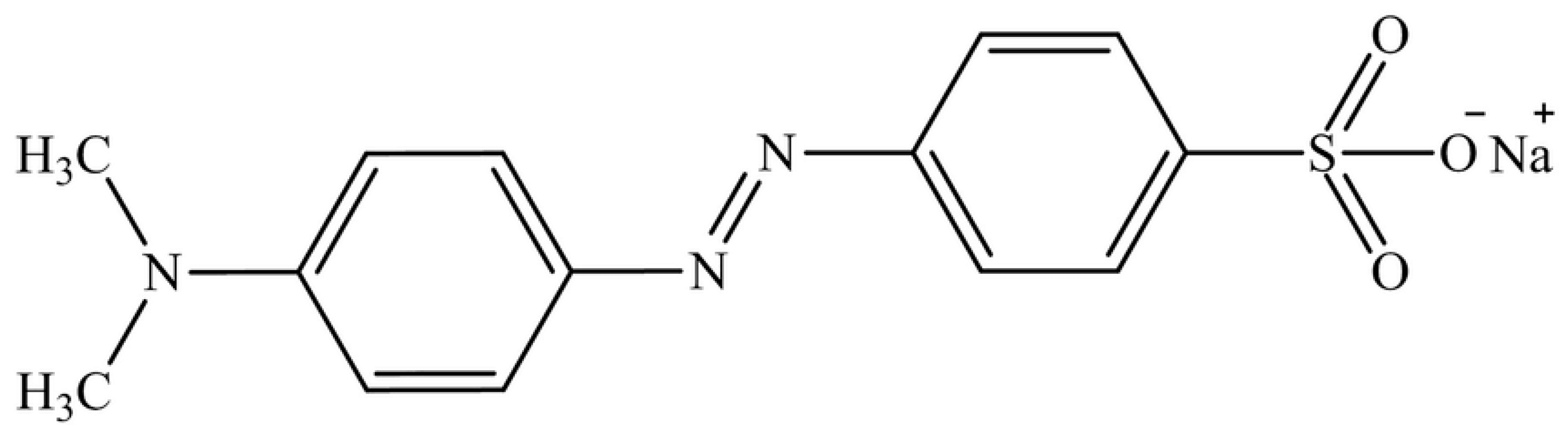
Novel ZIF-67@Bentonite (ZIF-67@BNT) Nanocomposite for Aqueous Methyl Orange Removal
Abstract
Featured Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
2.2. Synthesis of ZIF-67 and ZIF-67@BNT
2.3. Response Surface Methodology (RSM)
2.4. Batch Adsorption Experiment
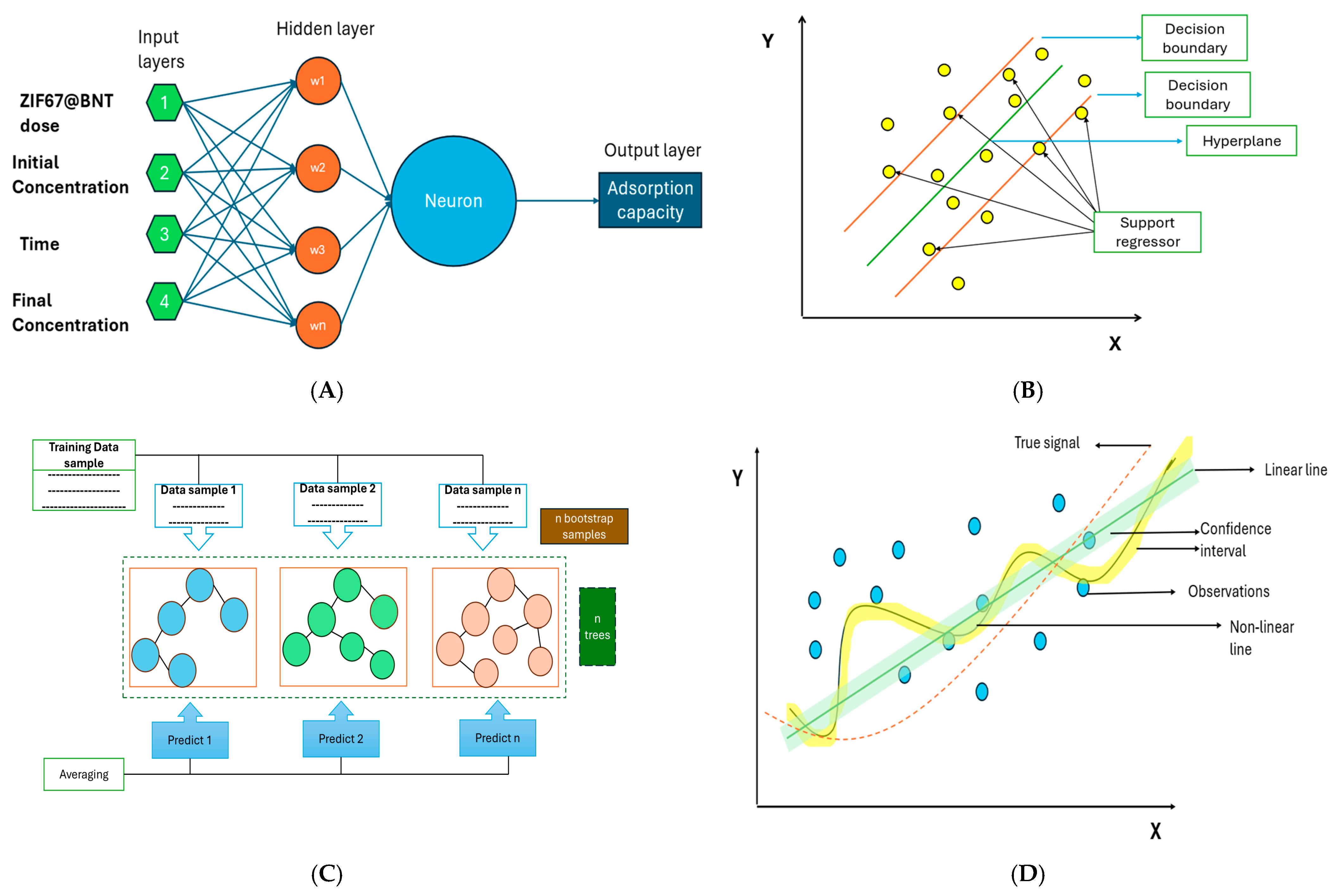
2.5. Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) Modeling
2.5.1. Artificial Neural Network
2.5.2. Support Vector Regression
2.5.3. Random Forest
2.5.4. Gaussian Process
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. ZIF-67@BNT Characterization
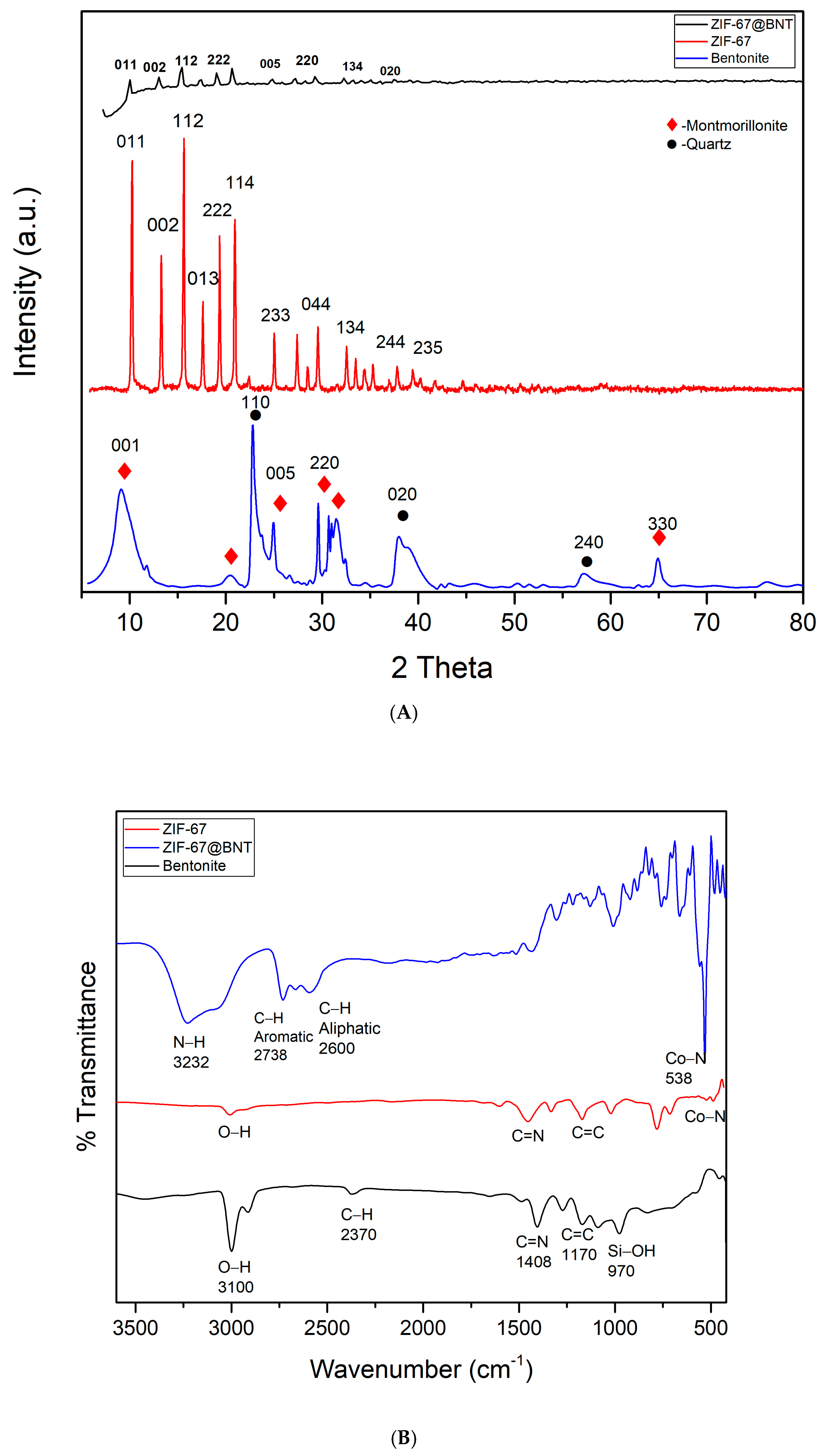
3.1.1. X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
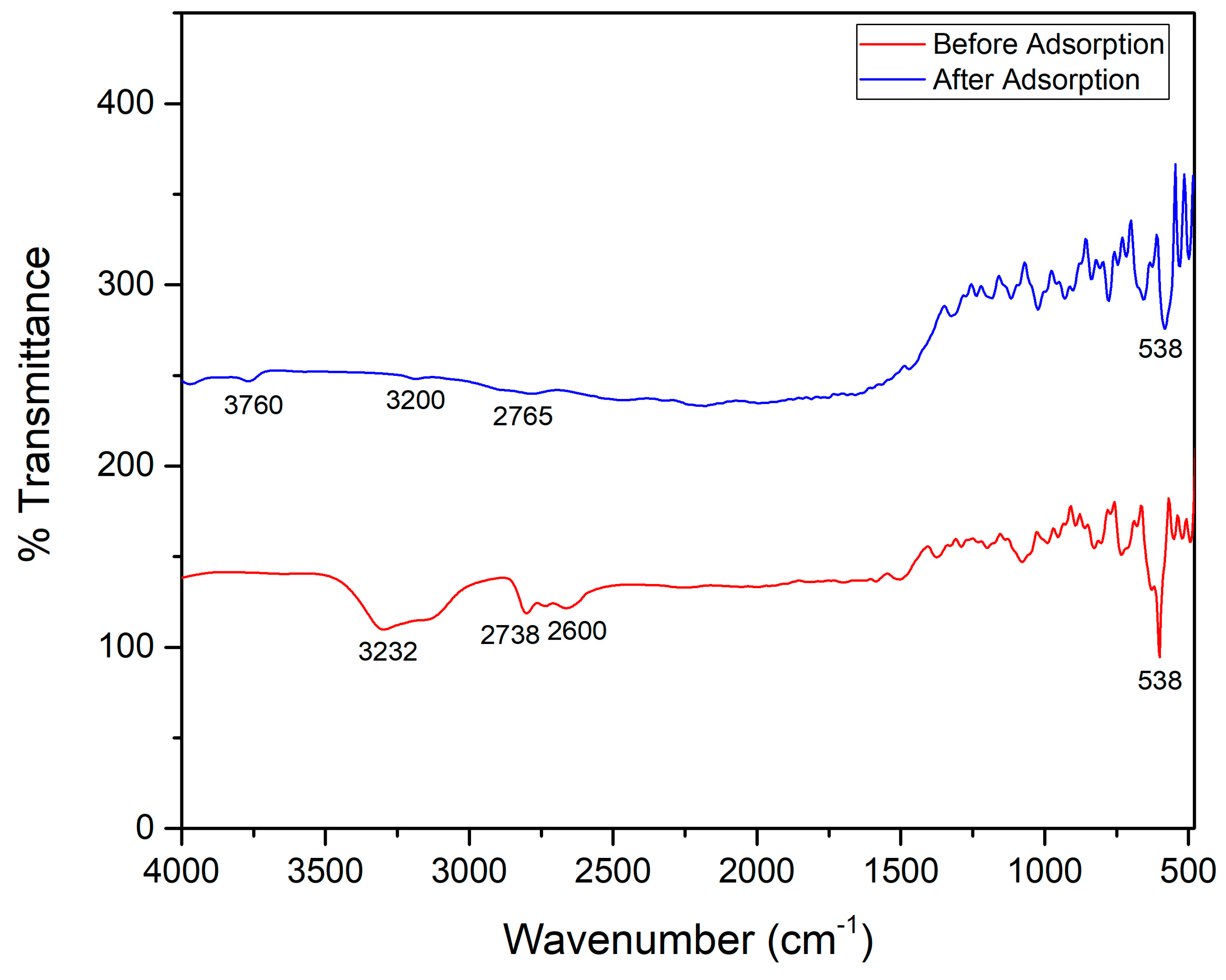
3.1.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy Analysis
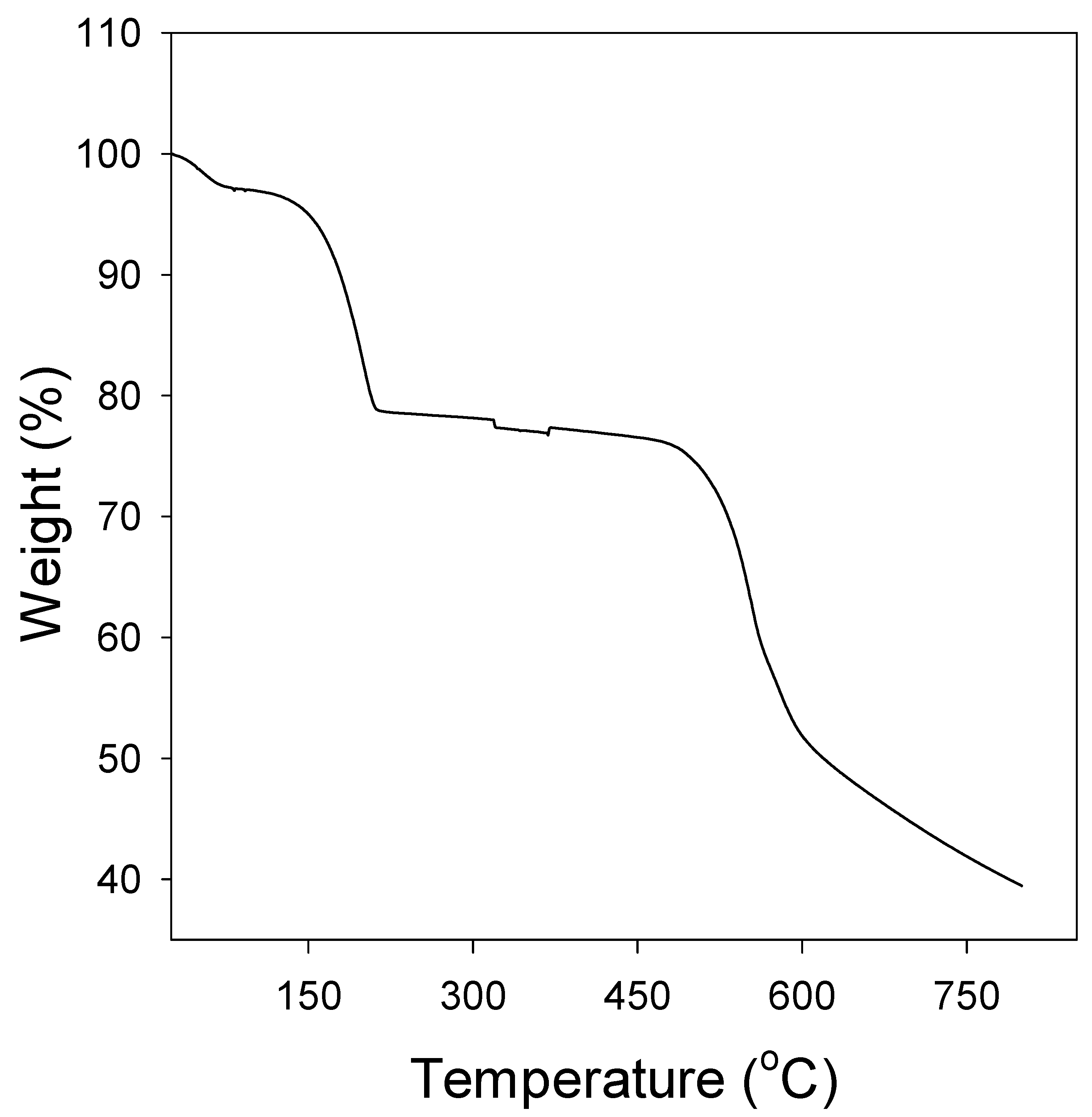
3.1.3. Thermogravimetric Analysis
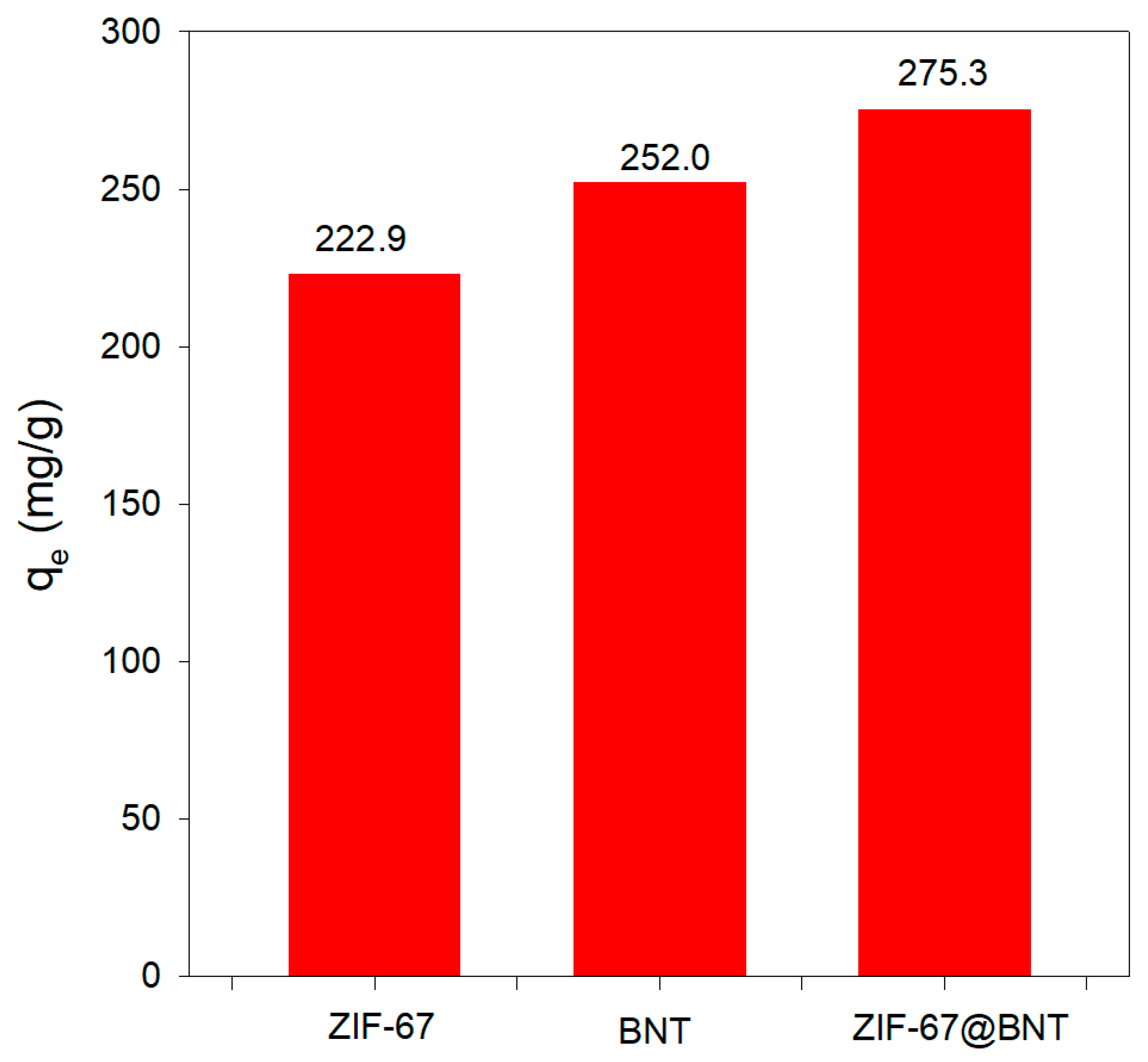
3.2. Benchmarking the Performance of the ZIF-67@BNT Nanocomposite with Its Constituents
3.3. Analysis of Methyl Orange Adsorption Using ZIF-67@BNT
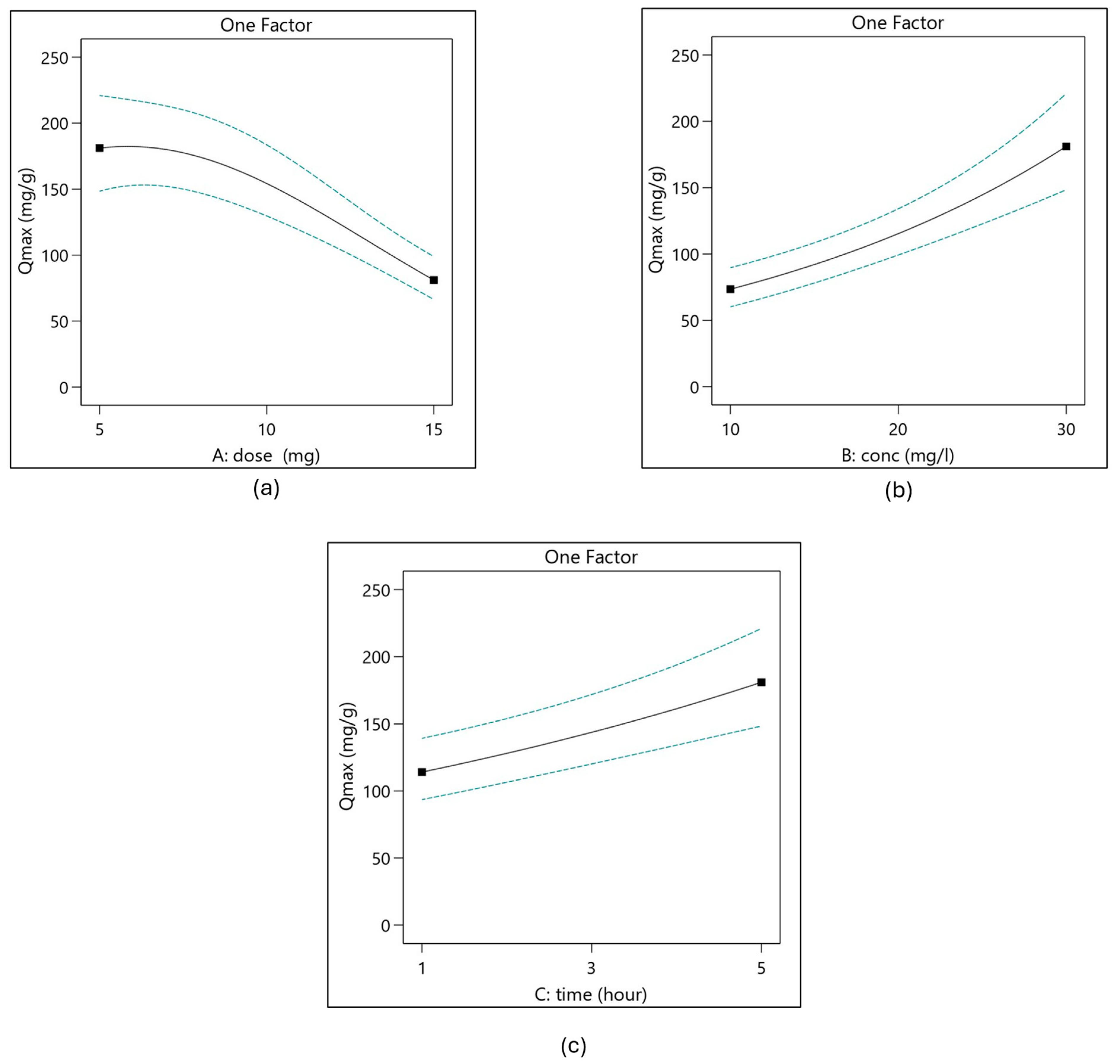
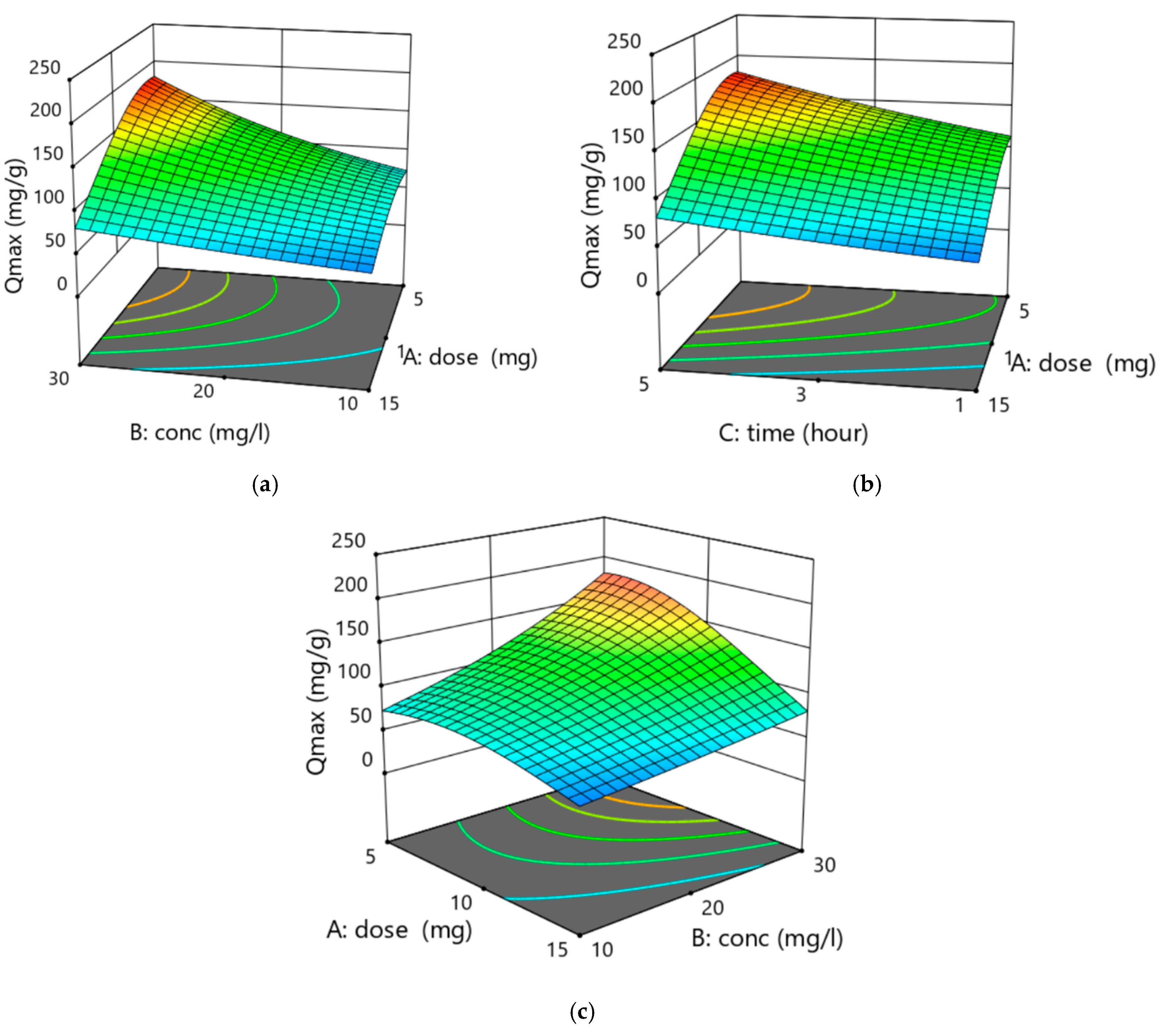
3.3.1. Experimental Design and Analysis of Variance
3.3.2. Examine the Effect of Process Parameters Using ANOVA
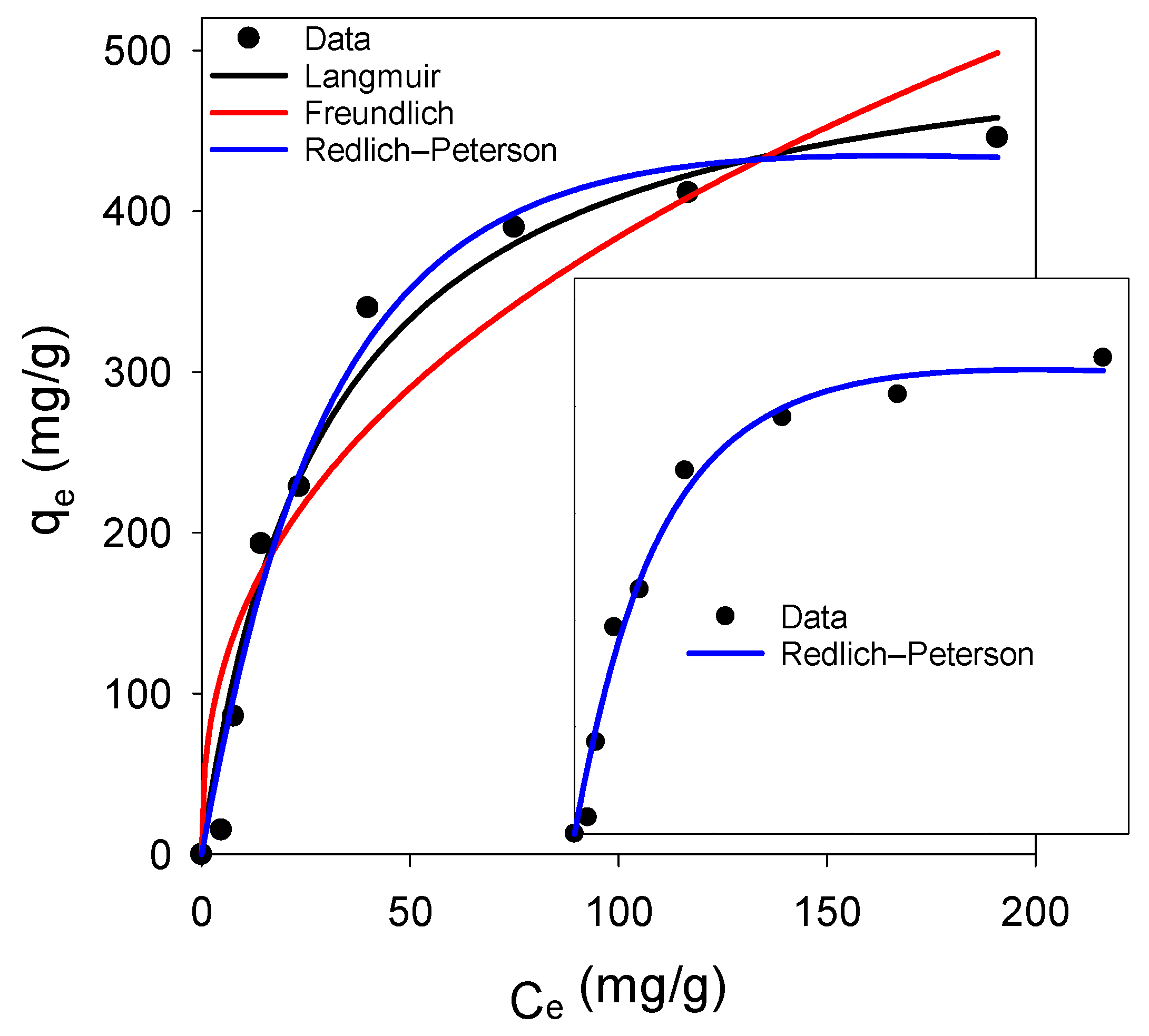
3.3.3. Adsorption Kinetics and Isotherm Analysis
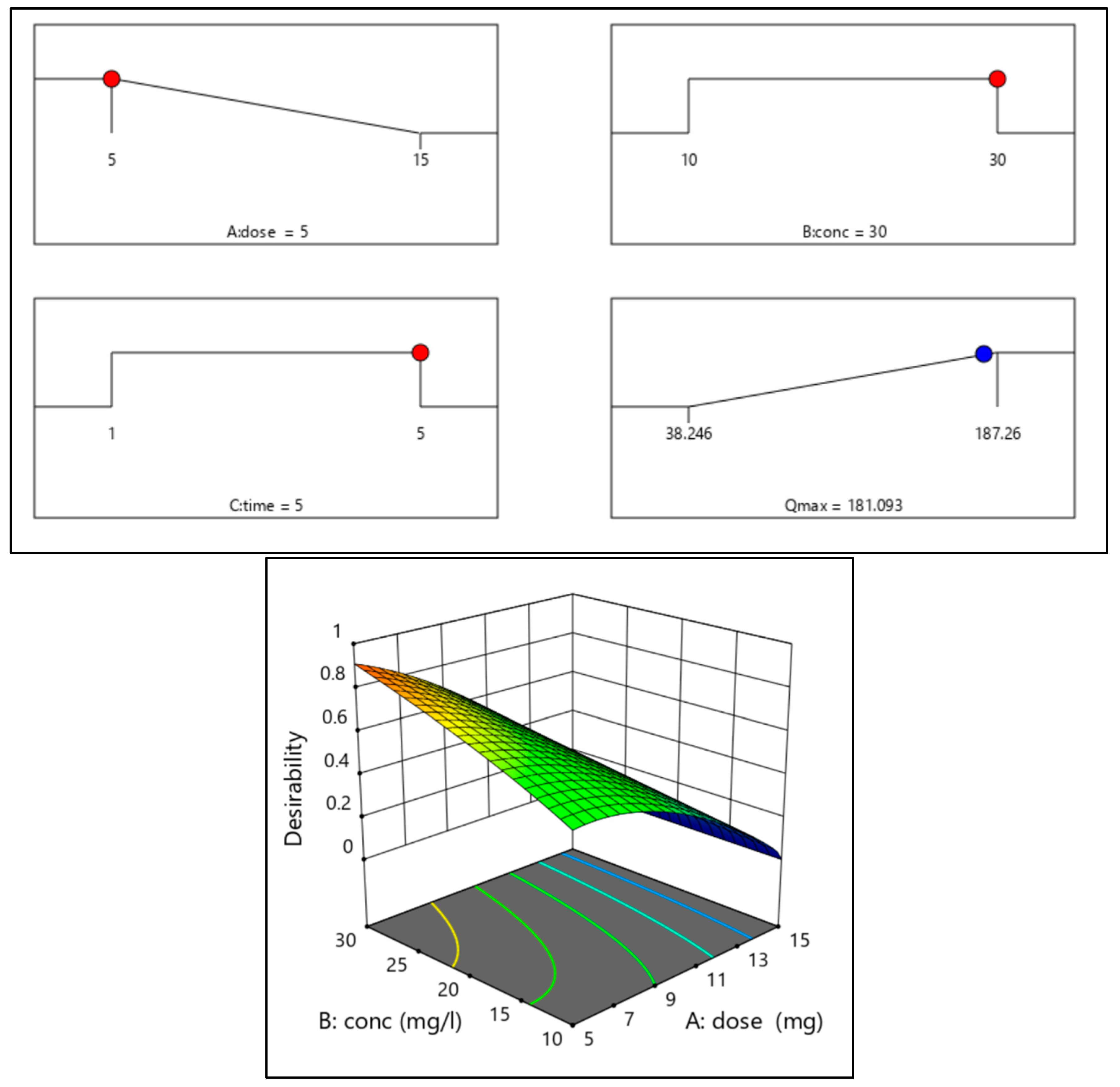
3.3.4. Post-Analysis of MO Adsorption on ZIF-67@BNT Nanocomposite
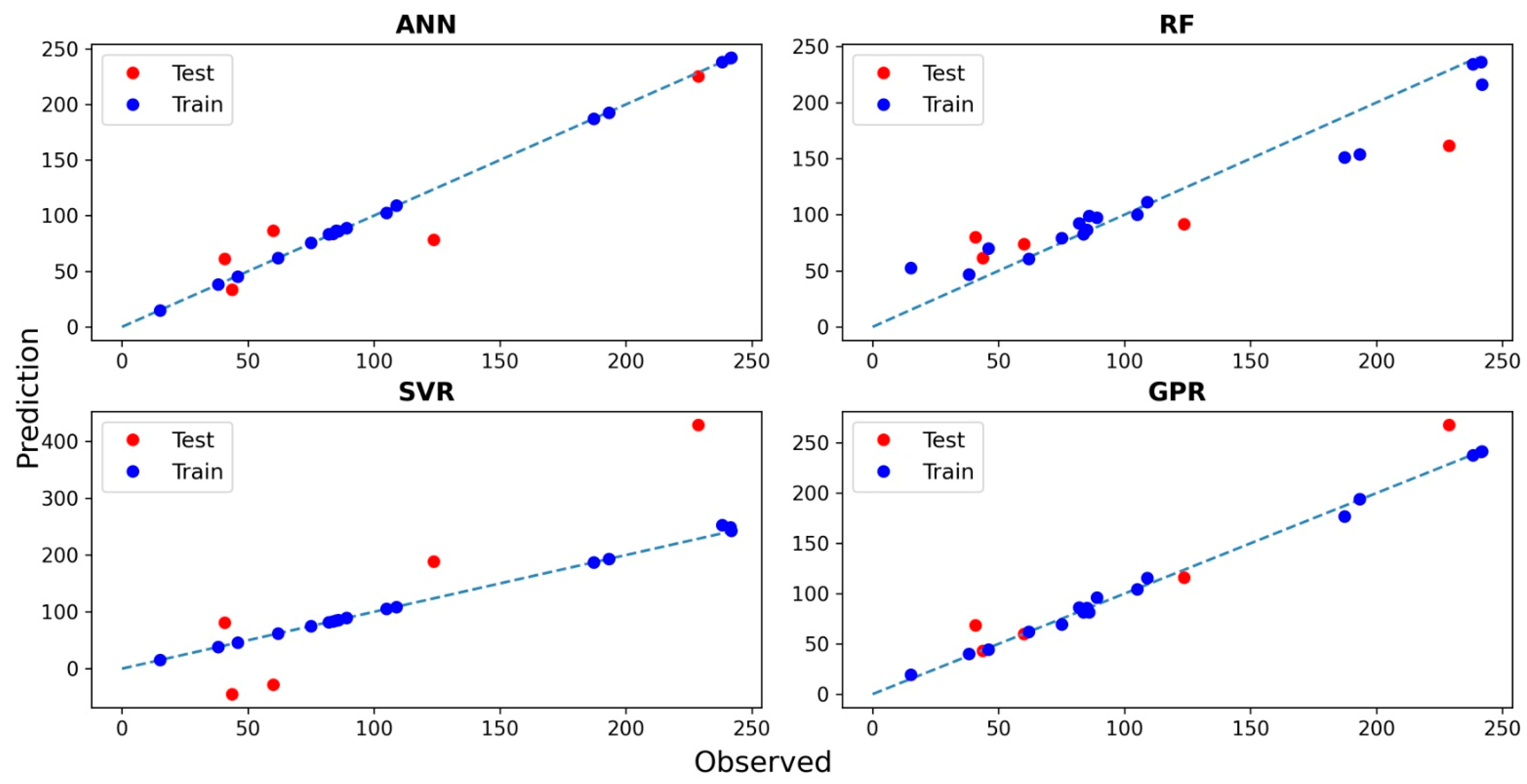
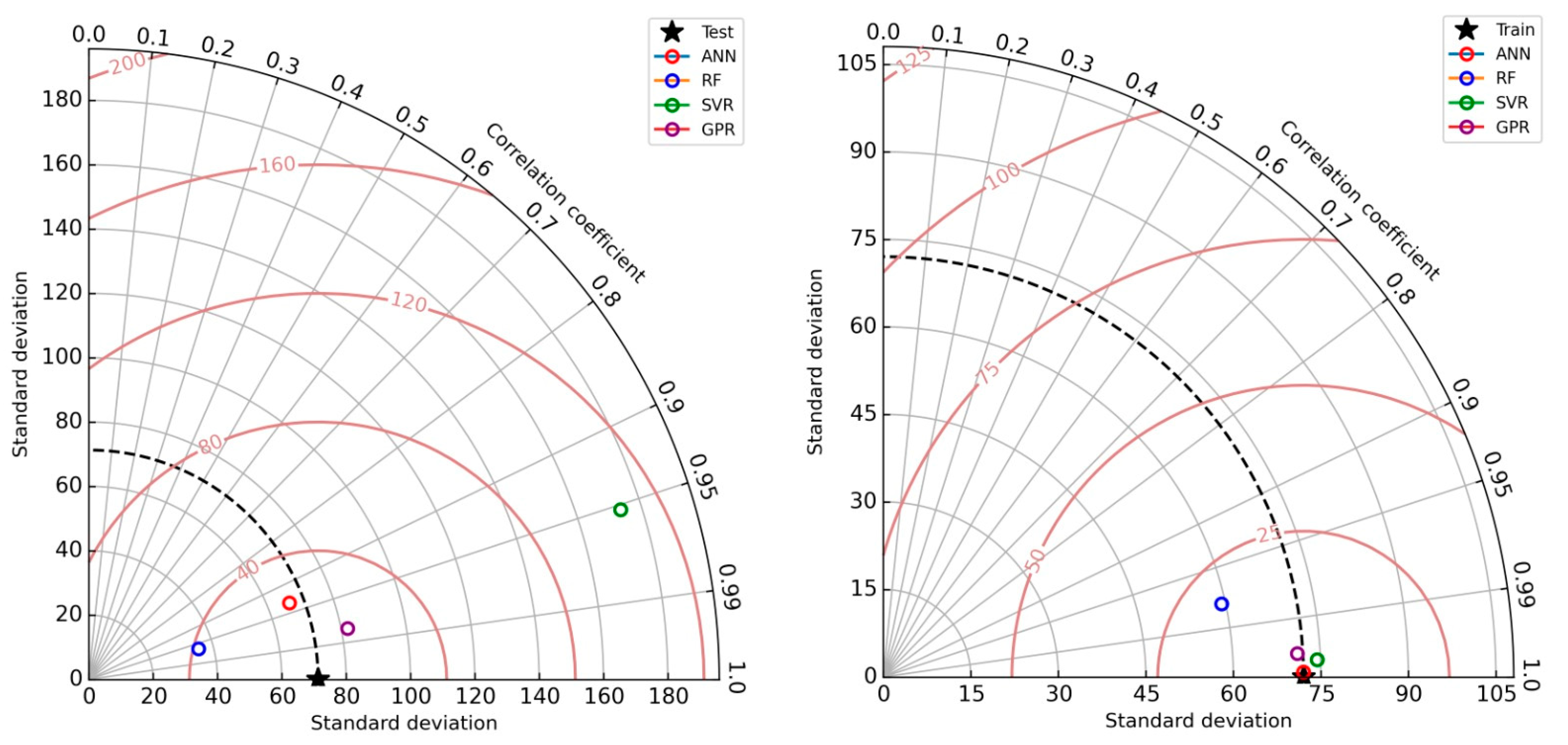
3.4. Predicting MO Adsorption Capacity with Machine Learning Techniques
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aniagor, C.O.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Ighalo, J.O.; Oba, S.N. Adsorption of doxycycline from aqueous media: A review. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Liu, J.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, B.; Ho, W. Hierarchical porous Ni/Co-LDH hollow dodecahedron with excellent adsorption property for Congo red and Cr(VI) ions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 478, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbagh, M.; Hussaini, M.; Ismail, U.; Ahmed, H.R.; Al-Suwaiyan, M.; Vohra, M. Novel nafion-palygorskite composite for Pb/Lead treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 22, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Vohra, M.S.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: Progress of adsorbents development and their effectiveness. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.I.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Novel CTAB functionalized graphene oxide for selenium removal: Adsorption results and ANN & RSM modeling. Emergent Mater. 2023, 7, 547–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaggout, F.R.; El-Ashgar, N.M.; Zourab, S.M.; El-Nahhal, I.M.; Motaweh, H. Encapsulation of methyl orange pH-indicator into a sol-gel matrix. Mater. Lett. 2005, 59, 2928–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, K.; Khan, S.U.; Washeem, M.; Khan, S.U. Energy efficient removal of COD from landfill leachate wastewater using electrocoagulation: Parametric optimization using RSM. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 3625–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anil, K.; Surenjan, A. Green synthesis, characterisation, and performance evaluation of ZnO/TiO2 nanocomposite for cationic and anionic dye removal from aqueous solutions under solar irradiation. Water Pr. Technol. 2024, 19, 824–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaji, C.; Rifi, S.K.; Digua, K.; Madinzi, A.; Chatoui, M.; Driouich, A.; Ettaloui, Z.; Kurniawan, T.A.; Anouzla, A.; Souabi, S. Optimization of the coagulation-flocculation process using response surface methodology for wastewater pretreatment generated by vegetable oil refineries: A path towards environmental sustainability. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2024, 22, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nowaiser, W.K.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Synthesis and application of novel GO@ZIF-7 nanocomposite for the removal of lead from aqueous solutions. Emergent Mater. 2023, 7, 1043–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Ullah, S.; Shahid, M.U.; Hossain, I.; Najam, T.; Ismail, M.A.; Rehman, A.U.; Karim, R.; Shah, S.S.A. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIF-8 & ZIF-67): Synthesis and application for wastewater treatment. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 356, 129828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, G.; Liu, D.; Zhang, J. The application of ZIF-67 and its derivatives: Adsorption, separation, electrochemistry and catalysts. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 6, 1887–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.J.; Ampiaw, R.E.; Lee, W. Adsorptive removal of dyes from wastewater using a metal-organic framework: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 284, 131314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganiyu, S.A.; Suleiman, M.A.; Al-Amrani, W.A.; Usman, A.K.; Onaizi, S.A. Adsorptive removal of organic pollutants from contaminated waters using zeolitic imidazolate framework Composites: A comprehensive and Up-to-date review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 318, 123765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Khan, N.A.; Cheng, C.; Shah, S.S.A.; Najam, T.; Arshad, M.; Sharif, A.; Akhtar, S.; Rehman, A.U. Surface induced growth of ZIF-67 at Co-layered double hydroxide: Removal of methylene blue and methyl orange from water. Appl. Clay Sci. 2020, 190, 105564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrudin, N.N.; Nawi, M.A.; Jawad, A.H.; Sabar, S. Adsorption Characteristics and Mechanistic Study of Immobilized Chitosan-Montmorillonite Composite for Methyl Orange removal. J. Polym. Environ. 2020, 28, 1901–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barakan, S.; Aghazadeh, V. The advantages of clay mineral modification methods for enhancing adsorption efficiency in wastewater treatment: A review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 28, 2572–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ewis, D.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Benamor, A.; El-Naas, M.H. Adsorption of organic water pollutants by clays and clay minerals composites: A comprehensive review. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 229, 106686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Ajmal, S.; Hussain, T.; Rahman, M.U. Clay-based materials for enhanced water treatment: Adsorption mechanisms, challenges, and future directions. J. Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appl. Sci. 2023, 1, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Novel MgCuAl-layered triple hydroxide for aqueous selenite and selenate treatment. Emergent Mater 2024, 7, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazir, M.A.; Najam, T.; Zarin, K.; Shahzad, K.; Javed, M.S.; Jamshaid, M.; Bashir, M.A.; Shah, S.S.A.; Rehman, A.U. Enhanced adsorption removal of methyl orange from water by porous bimetallic Ni/Co MOF composite: A systematic study of adsorption kinetics. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 4841–4856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, N.T.T.; Thien, T.V.; Du, P.D.; Chau, V.T.T.; Mau, T.X.; Khieu, D.Q. Adsorptive removal of Congo red from aqueous solution using zeolitic imidazolate framework-67. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakar, N.; Isloor, A.M.; Padaki, M.; Ismail, A.F. Fabrication of TiO2@ZIF-67 metal organic framework composite incorporated PVDF membranes for the removal of hazardous reactive black 5 and Congo red dyes from contaminated water. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Xiao, Z. Synthesis of novel Ag@ZIF-67 rhombic dodecahedron for enhanced adsorptive removal of antibiotic and organic dye. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 328, 115323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, P.; Chen, H.; Zhou, Y. Adsorption performance of one- and two-component anionic dyes using core-shell ZIF-8@ZIF-67. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 315, 123538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighat, G.A.; Sadeghi, S.; Saghi, M.H.; Ghadiri, S.K.; Anastopoulos, I.; Giannakoudakis, D.A.; Colmenares, J.C.; Shams, M. Zeolitic imidazolate frameworks (ZIFs) of various morphologies against eriochrome black-T (EBT): Optimizing the key physicochemical features by process modeling. J. Solid State Chem. 2022, 315, 125391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Jain, S.; Nehra, M.; Dilbaghi, N.; Marrazza, G.; Kim, K.H. Green synthesis of metal–organic frameworks: A state-of-the-art review of potential environmental and medical applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 420, 213407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Kong, L.; Ruan, Y.; Diao, Z.; Shih, K.; Su, M.; Hou, L.; Chen, D. Green and facile synthesis of cobalt-based metal–organic frameworks for the efficient removal of Congo red from aqueous solution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 578, 500–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, R.; Ren, S.; Zhou, H.; Wu, Q.; Zhen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Fang, S. Magnetic beads embedded in poly (sodium-p-styrenesulfonate) and ZIF-67: Removal of nitrophenol from water. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 265, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Xiao, Z. Hierarchical mesoporous ZIF-67@LDH for efficient adsorption of aqueous Methyl Orange and Alizarine Red S. Powder Technol. 2020, 377, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiee, A.; Nasab, S.G.; Teimouri, A. Synthesis and characterization of pistachio shell/nanodiopside nanocomposite and its application for removal of Crystal Violet dye from aqueous solutions using central composite design. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2019, 100, 1624–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Ibrahim, A.I.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Synthesis and application of MgCuAl-layered triple hydroxide/carboxylated carbon nanotubes/bentonite nanocomposite for the effective removal of lead from contaminated water. Results Eng. 2024, 24, 102991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marahel, F.; Goodajdar, B.M.; Niknam, L.; Faridnia, M.; Pournamdari, E.; Doost, S.M. Ultrasonic assisted adsorption of methylene blue dye and neural network model for adsorption of methylene blue dye by synthesised Mn-doped PbS nanoparticles. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2021, 103, 3059–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kooh, M.R.R.; Thotagamuge, R.; Chau, Y.F.C.; Mahadi, A.H.; Lim, C.M. Machine learning approaches to predict adsorption capacity of Azolla pinnata in the removal of methylene blue. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2022, 132, 104134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Hussaini, M.; Vohra, M.S. H2S and SO2 toxic gases removal using date palm-tree branches based activated carbon: Experimental findings and machine learning (ML) modeling. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCulloch, W.S.; Pitts, W. A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull. Math. Biophys. 1943, 5, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Crystal violet removal using ZIF-60: Batch adsorption studies, mechanistic & machine learning modeling. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 33, 103456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigzadeh, B.; Bahrami, M.; Amiri, M.J.; Mahmoudi, M.R. A new approach in adsorption modeling using random forest regression, Bayesian multiple linear regression, and multiple linear regression: 2,4-D adsorption by a green adsorbent. Water Sci. Technol. 2020, 82, 1586–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, U.M.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Aqueous Pb(II) Removal Using ZIF-60: Adsorption Studies, Response Surface Methodology and Machine Learning Predictions. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, M.A.; Althobaiti, M.M.; Al-Wesabi, F.N.; Alabdan, R.; Mahgoub, H.; Hilal, A.M.; Motwakel, A.; Al Duhayyim, M. Gaussian Process Regression and Machine Learning Methods for Carbon-Based Material Adsorption. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2022, 2022, 3901608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, K.G.; Gupta, S.S. Adsorption of a few heavy metals on natural and modified kaolinite and montmorillonite: A review. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 140, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Gao, X.; Gong, C.; Wang, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Gurzadyan, G.G.; Sun, L. Metal–organic frameworks (ZIF-67) as efficient cocatalysts for photocatalytic reduction of CO2: The role of the morphology effect. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4768–4775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhou, K.; Feng, Y.; Yao, J. Morphology Control of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework by Addition of Amino Acid l-Histidine. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 1080–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamdouh, N.; Farghali, A.A.; El Rouby, W.M.A.; Abdelwahab, A. Effect of ZIF-67-derived Co3O4 on the activity of CNTs/NiCo2O4 nanocomposite for methanol oxidation reaction. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 93, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeerken, A.; Lin, J.; Wang, X.; Luo, Y.; Ma, H. Fabrication of novel porous ZIF-67/PES composite microspheres and the efficient adsorption of triphenylmethane dyes from water. CrystEngComm 2023, 25, 1076–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narimbi, J.; Balakrishnan, S.; Perova, T.S.; Dee, G.; Swiegers, G.F.; Gun’ko, Y.K. XRD and Spectroscopic Investigations of ZIF—Microchannel Glass Plates Composites. Materials 2023, 16, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wi, W.; Nowicki, P.; Bujdák, J. Controversial Issues Related to Dye Adsorption on Clay Minerals: A Critical Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 6951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Song, X.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, J.; Pei, J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67 for shape stabilization and enhanced thermal stability of paraffin-based phase change materials. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 9962–9967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Vohra, M.S. Selenocyanate removal using combined system of TiO2 photocatalysis and Fe(III)/SiO2 adsorption {UV-TiO2/[Fe(III)/SiO2]}: Complex destruction and simultaneous selenium species adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 500, 156525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cravillon, J.; Münzer, S.; Lohmeier, S.J.; Feldhoff, A.; Huber, K.; Wiebcke, M. Rapid room-temperature synthesis and characterization of nanocrystals of a prototypical zeolitic imidazolate framework. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 1410–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Qian, X.; Rui, X.; Liu, H.; Yadian, B.; Zhou, K.; Wei, J.; Yan, Q.; Feng, X.; Long, Y.; et al. Zeolitic imidazolate framework 67-derived high symmetric porous Co3O4 hollow dodecahedra with highly enhanced lithium storage capability. Small 2014, 10, 1932–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madejová, J. FTIR techniques in clay mineral studies. Vib. Spectrosc. 2003, 31, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigatti, M.F.; Galan, E.; Theng, B.K.G. Chapter 2 Structures and Mineralogy of Clay Minerals. Dev. Clay Sci. 2006, 1, 19–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.N.; Sharma, N.; Kumar, L. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide (GO) by Modified Hummers Method and Its Thermal Reduction to Obtain Reduced Graphene Oxide (rGO) *. Graphene 2017, 6, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, W.; Gao, X.; Ji, G.; Xing, Y.; Du, C.; Liu, Z. Fabrication of a magnetic nanocomposite photocatalysts Fe3O4@ZIF- 67 for degradation of dyes in water under visible light irradiation. J. Solid State Chem. 2017, 255, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Ren, S.; Zhao, Q.; Lu, R.; Hang, C.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, H. Selective separation of methyl orange from water using magnetic ZIF-67 composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 333, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Lu, R.; Ren, S.S.; Chen, C.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X. Three dimensional reduced graphene oxide/ZIF-67 aerogel: Effective removal cationic and anionic dyes from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 348, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarker, T.; Tahmid, I.; Sarker, R.K.; Dey, S.C.; Islam, M.T.; Sarker, M. ZIF-67-based materials as adsorbent for liquid phase adsorption-a review. Polyhedron 2024, 260, 117069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussaini, M.; Vohra, M. LDH-TiO2 Composite for Selenocyanate (SeCN−) Photocatalytic Degradation: Characterization, Treatment Efficiency, Reaction Intermediates and Modeling. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balarak, D.; Zafariyan, M.; Igwegbe, C.A.; Onyechi, K.K.; Ighalo, J.O. Adsorption of Acid Blue 92 Dye from Aqueous Solutions by Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes: Isothermal, Kinetic, and Thermodynamic Studies. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 869–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghdoust, S.; Arabkhani, P.; Ghaderi, S.; Ghaedi, M.; Asfaram, A. Rapid microwave-assisted synthesis of a magnetic biochar@ZIF-67: An efficient nanocomposite-based adsorbent for the dye-contaminated water cleanup. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 9257–9270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattanapan, S.; Srikram, J.; Kongsune, P. Adsorption of Methyl Orange on Coffee grounds Activated Carbon. Energy Procedia 2017, 138, 949–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Liu, S.Q. Photocatalytic Oxidation of Ammonia via an Activated Carbon-Nickel Ferrite Hybrid Catalyst under Visible Light Irradiation. Acta Phys. Chim. Sin. 2014, 30, 1697–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlNaimat, S.; Ismail, U.M.; Ibrahim, A.I.; Muse, A.; Faheem, K.; Mustafa, M.; Vohra, M.S.; Onaizi, S.A. Machine learning modeling and statistical optimization of dye removal from contaminated water using CTAB-functionalized graphene oxide. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Mona, S.; Sharma, P. Greenly synthesised novel microporous ZnO/GO for adsorption of methyl orange and malachite green. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2024, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Semenchenko, L.; Lim, W.T.; Rivas, M.F.B.; Varela-Guerrero, V.; Jeong, H.K. Facile synthesis of Cd-substituted zeolitic-imidazolate framework Cd-ZIF-8 and mixed-metal CdZn-ZIF-8. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 264, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption isotherm models: Classification; physical meaning, application and solving method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayawei, N.; Ebelegi, A.N.; Wankasi, D. Modelling and Interpretation of Adsorption Isotherms. J. Chem. 2017, 2017, 3039817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Huang, X.; Tang, Z.; Huang, Q.; Niu, F.; Wang, X. Polymer-based nanocomposites for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 3562–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, A.; Santamaría, L.; Korili, S.; Vicente, M.; Barbosa, L.; de Souza, S.; Marçal, L.; de Faria, E.; Ciuffi, K. A review of organic-inorganic hybrid clay based adsorbents for contaminants removal: Synthesis, perspectives and applications. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 105808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Miao, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, H.; Bai, S.; Liu, W. Facile synthesis of an ultrathin ZIF-67 layer on the surface of Sn/Ti co-doped hematite for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 8848–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wang, W.; Zhao, Y.; Bai, H.; Wen, T.; Kang, S.; Song, G.; Song, S.; Komarneni, S. Removal of heavy metals and dyes by clay-based adsorbents: From natural clays to 1D and 2D nano-composites. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 420, 127574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaffino, C. Exploiting the Potentiality of Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering (sers) for the Identification of Natural Dyes in Ancient Textiles: From Hyphenated Techniques to In-Situ Analysis. Ph.D. Thesis, Università Degli Studi di Milano, Milano, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-M.; Ying, R.-J.; Han, C.-X.; Hu, Q.-T.; Xu, H.-M.; Li, J.-H.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, W. Adsorptive removal of organic dyes from aqueous solution by a Zr-based metal-organic framework: Effects of Ce(III) doping. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 3913–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R. Mechanism and Application of Metal-Organic Framework in Wastewater Treatment. Highlights Sci. Eng. Technol. 2022, 6, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Wang, Y.; He, P.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G. Recent Advances in Metal–Organic Framework (MOF)-Based Composites for Organic Effluent Remediation. Materials 2024, 17, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Factors | Levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| A | Adsorbent dose (mg) | 5 | 10 | 15 |
| B | Methyl orange (mg/L) | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| C | Time (hours) | 1 | 3 | 5 |
| Run | A: Adsorbent Dose (mg) | B: Methyl Orange (mg/L) | C: Time (Hours) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 15 | 30 | 5 | 82 |
| 2 | 5 | 20 | 3 | 89 |
| 3 | 15 | 30 | 1 | 46 |
| 4 | 10 | 20 | 5 | 105 |
| 5 | 10 | 10 | 3 | 62 |
| 6 | 5 | 10 | 5 | 84 |
| 7 | 10 | 20 | 3 | 85 |
| 8 | 5 | 30 | 1 | 109 |
| 9 | 10 | 20 | 1 | 75 |
| 10 | 5 | 30 | 5 | 187 |
| 11 | 15 | 10 | 5 | 44 |
| 12 | 5 | 10 | 1 | 41 |
| 13 | 10 | 30 | 3 | 124 |
| 14 | 15 | 10 | 1 | 38 |
| 15 | 15 | 20 | 3 | 60 |
| Source | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom (df) | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 2.71 | 5 | 0.5424 | 36.79 | <0.0001 | Significant |
| A: Adsorbent dose | 0.7823 | 1 | 0.7823 | 53.06 | <0.0001 | |
| B: Methyl Orange | 1.08 | 1 | 1.08 | 73.49 | <0.0001 | |
| C: Time | 0.5330 | 1 | 0.5330 | 36.15 | <0.000 | |
| AB | 0.1187 | 1 | 0.1187 | 8.05 | 0.0002 | |
| A2 | 0.1942 | 1 | 0.1942 | 13.17 | 0.0195 | |
| Residual | 0.1327 | 9 | 0.0147 | 0.0055 | ||
| Core Total | 2.84 | 14 |
| Adsorbent | Initial Concentration | Adsorbent Dose | Initial pH | Temperature | Time | Adsorption Capacity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni@ZIF-67 | 40 | 20 | 6 | Room | 180 | 33.17 | [21] |
| Ag@ZIF-67 | 200 | 20 | 6 | 30 | 180 | 994.6 | [24] |
| ZIF-67@LDH | 20 | 6 | 30 | 500 | 663.4 | [30] | |
| CGAC | 300 | 50 | 3 | 40 | 90 | 658 | [62] |
| AC/NiFe2O4 | 100 | 300 | 3 | 30 | 180 | 182.82 | [63] |
| CS-MT Composite | 40 | 320 | 6.3 | 30 | 60 | 154.4 | [17] |
| CTAB@GO | 300 | 50 | 4 | Room | 1440 | 1301.5 | [64] |
| ZnO/GO Nanocomposite | 40 | 20 | 4 | 60 | 50 | 296.73 | [65] |
| Cd-ZIF-8 Composite | 200 | 50 | 5 | 25 | 120 | 425.8 | [66] |
| This Study | 30 | 5 | - | Room | 300 | 187 | - |
| Models | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-First Order | Pseudo-Second Order | Avrami | |||||||
| qe (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg/g) | k2 (g/mg.min) | R2 | qe (mg/g) | ka (min−1) | n | R2 |
| 338 | 0.0216 | 0.8837 | 360.7 | 9.464 × 10−5 | 0.9585 | 386.8 | 0.0013 | 0.401 | 0.9949 |
| Models | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm | Freundlich Adsorption Isotherm | Redlich–Peterson Adsorption Isotherm | |||||||
| qmax (mg/g) | KL (L/mg) | R2 | n | KF | R2 | KR (L/g) | aR (L/mg) | g | R2 |
| 528.7 | 0.034 | 0.9746 | 2.48 | 59.8 | 0.9024 | 14.06 | 0.0081 | 1.23 | 0.9823 |
| Index | Adsorbent Dose (mg) | Methyl Orange (mg/L) | Time (Hours) | Adsorption Capacity (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Count | 22 | 22 | 22 | 22 |
| Mean | 8.40 | 26.81 | 9.68 | 112.49 |
| Median | 5 | 20 | 5 | 85.41 |
| Mode | 5 | 10 | 24 | - |
| Minimum | 5 | 5 | 1 | 15.18 |
| Maximum | 15 | 100 | 24 | 241.80 |
| Range | 10 | 95 | 23 | 226.61 |
| Standard deviation | 4.19 | 22.60 | 10.10 | 73.91 |
| Sample variance | 17.58 | 510.82 | 102.13 | 5463.98 |
| Testing | Training | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algorithm | R2 | RMSE | MAE | R2 | RMSE | MAE |
| ANN | 0.872 | 25.582 | 21.143 | 0.999 | 0.833 | 0.553 |
| Random forest | 0.927 | 38.835 | 33.888 | 0.955 | 18.822 | 13.374 |
| Support vector regression | 0.907 | 110.956 | 96.385 | 0.998 | 3.997 | 1.476 |
| Gaussian process regression | 0.962 | 21.687 | 14.989 | 0.996 | 4.179 | 3.051 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faheem, K.; Onaizi, S.A.; Vohra, M.S. Novel ZIF-67@Bentonite (ZIF-67@BNT) Nanocomposite for Aqueous Methyl Orange Removal. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073562
Faheem K, Onaizi SA, Vohra MS. Novel ZIF-67@Bentonite (ZIF-67@BNT) Nanocomposite for Aqueous Methyl Orange Removal. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(7):3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073562
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaheem, Kashif, Sagheer A. Onaizi, and Muhammad S. Vohra. 2025. "Novel ZIF-67@Bentonite (ZIF-67@BNT) Nanocomposite for Aqueous Methyl Orange Removal" Applied Sciences 15, no. 7: 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073562
APA StyleFaheem, K., Onaizi, S. A., & Vohra, M. S. (2025). Novel ZIF-67@Bentonite (ZIF-67@BNT) Nanocomposite for Aqueous Methyl Orange Removal. Applied Sciences, 15(7), 3562. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15073562







