Abstract
Active volcanic calderas often experience significant ground deformation, characterized by uplift and subsidence, typically with a radial or elliptical pattern centered on the caldera. However, the detection of small second-order anomalies within the main deformation pattern can provide critical insight into impending eruptions and/or hazardous structural and volcano-tectonic features. In this study, we present a simple but novel method for detecting and interpreting second-order deformation anomalies at Campi Flegrei caldera by filtering the primary, radial deformation signal observed during volcanic unrest phases. For this purpose, we used a procedure based on the polynomial fit of vertical displacement data, assuming that they depend only on the distance from the deformation center. By subtracting the best fitting radial deformation from the observed vertical displacement, we generated an anomaly map that highlights sectors with unexpected deformation patterns. We applied the proposed procedure to analyze the ground deformation at the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) that occurred from 2016 to 2021, by using MT-InSAR data from Sentinel-1. Coeval GPS datasets were also used for cross-checking the obtained results. The results of this analysis show a pronounced NE-SW alignment that separates sectors with different uplift trends. It highlights a primary volcano-tectonic structure potentially linked to high seismic hazard. This method, after further investigation, can provide a valuable tool for improving hazard assessment and understanding the structural dynamics of calderas during unrest phases, with implications for improving preparedness in densely populated volcanic regions.
1. Introduction
Calderas are sub-circular depressions that form during the partial emptying of magma reservoirs associated with large eruptions [1]. A number of calderas are marked by the uplift (resurgence) of their sunken floor, resulting from magma accumulation at depth and accompanied by minor eruptions. Caldera resurgence, with radial or elliptical shape, represents the largest and most peculiar type of volcanic ground deformation, with amounts ranging from centimeters to a thousand meters and a duration of up to several thousand years [1]. The processes driving caldera uplift generally relate resurgence to the input of new magma, which is often stimulated by the pressure drop that follows a caldera-forming eruption [2,3,4]. However, part of the caldera resurgence can be related to the increase in the pressure of the geothermal system, as a consequence of the heating due to magmatic gas inflow [5,6,7].
Unrest episodes may be indicative of short-term inflation events that give rise to caldera resurgence [8]. Most volcanic eruptions are preceded and accompanied by a period of unrest. This is defined as a change from the normal state or usual behavior of a volcano. Large calderas may show episodes of unrest that commonly occur for years, decades or centuries, with or without a following eruption [9,10,11].
The potential hazards associated with unrest also include volcano-tectonic seismicity, ground uplift and horizontal deformation, hydrothermal explosions or gas emissions, fault and fracture opening, increased degassing, and landslides [9,12]. Such events may result in significant physical damage to buildings, critical infrastructure (i.e., electricity, telecommunications, and water and sewerage networks), roads and railways, and harbor functionality [13,14]. These damages may also result in significant economic loss through business interruption, tourism income drop, decreases in property values, and increases in insurance premiums [12,14,15,16].
Ground deformation during unrest phases is characterized by high uplift and/or subsidence rates, related to inflation and deflation of the caldera floor due to magmatic and/or hydrothermal processes. It is usually characterized by marked radial or elliptical symmetry (first-order ground deformation), which rapidly decreases with distance from the caldera center. The general, symmetrical pattern of ground deformation is indicative of the main source activated, which can be magmatic or hydrothermal [7]. However, mostly hidden by the main field, ground deformations are also affected by structural discontinuities or secondary inflation sources, i.e., faults and/or smaller pressure sources including rising magma dykes, etc. Investigation of the smaller, second-order anomalies of unrest-related ground deformation is generally neglected, possibly leading to deficiencies in hazard analysis of the unrest phenomena and hiding the identification of possible pathways for magma rising, eventually leading to an eruption.
In this paper, we propose a simple procedure for filtering the first-order ground deformation radial signal, i.e., the one produced by the main volcanic source, in an active volcanic caldera during unrest phases by using Sentinel-1 Synthetic Aperture Radar Multi-Temporal Interferometry (MT-InSAR) data. Such filtering, almost eliminating the effect of the main volcanic source, allows us to highlight second-order ground deformations or local anomalies that characterize the complex volcano-tectonic evolution of a caldera during unrest. The early detection of local trends in ground deformation within or around the caldera can provide useful elements for monitoring main fault and fracture openings, the main volcano-tectonic structural features, and the most likely areas of possible vent opening.
The proposed procedure was developed during the study of the unrest phase affecting the Campi Flegrei caldera, Italy, as this caldera is considered one of the highest volcanic risk areas in the world [17]. Actually, a phase of unrest is ongoing, characterized by an uplift of 139 cm from November 2005 to June 2024 at the RITE GNSS station located at the Pozzuoli historical center, with average velocity rates of 20 +/− 3 mm/month since April 2024 [18]. Seismic activity increased progressively during the unrest, both in frequency and in maximum magnitude [7], to reach a maximum magnitude of Md = 4.4, for a seismic event that occurred on 20 May 2024 [18]. The Campi Flegrei caldera had already experienced significant uplift and seismicity in the periods 1970–1972 and 1982–1984 [7,13], but hazard assessments in this region have been rather concentrated solely on the eruption hazard rather than on all the possible phenomena linked to unrest [12]. The ongoing unrest has been explained by several volcanological models, which can be classified in two main categories: magma rising at shallow depths, in the form of pressurized sills (e.g., [19,20,21,22]), and an increase in pressure in shallow aquifers due to heating by gases rising from the main magma chamber (e.g., [7,23]) located at 7-8 km in depth [24]. All of these papers try to explain the main, mostly symmetrical, ground deformation field.
Only recently, a few scientific articles have begun to use different approaches to analyzing spatial and temporal second-order anomalies in the ground deformation field at Campi Flegrei caldera. Giudicepietro et al. [25] analyzed Sentinel-1 and COSMO-SkyMed Multi-Temporal DInSAR measurements and GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) data to reveal and investigate a geodetic anomaly that has been observed since 2021 in the Mt. Olibano–Accademia area, locally deviating from the typical bell-shaped deformation pattern recognized at Campi Flegrei. Scotto di Uccio et al. [26] mapped the last decade of seismicity, providing high-precision location of earthquakes and revealing the presently activated fault zones of the inner caldera; they showed an overall quasi-elliptical distribution of seismicity in the caldera and outlined complex seismogenic structures at a smaller scale, one of which is located at the edge of the Solfatara crater. Tramelli et al. [27] evaluated the 3D distribution of the b value, which represents the scaling parameter of the Gutenberg-Richter relation, revealing a correlation with the structure and the porosity of the hydrothermal system involved in the unrest phenomena in the Campi Flegrei volcanic area. Finally, Amoruso and Crescentini [20] analyzed ground displacements from ERS-ENVISAT and Sentinel-1A SAR images to investigate the 1993–2000 subsidence and 2015–2022 uplift by applying an empirical orthogonal function analysis to the displacement time series for detailing deformation linked to local fluid migration in the Solfatara area.
All of these papers aimed to find detailed information on secondary volcano-tectonic sources and structures at early stages of development, which are useful in better forecasting eruptive and/or seismic hazards. Our paper presents a simple but robust procedure, developed using Campi Flegrei ground uplift data, to recover such critical information by subtracting the main deformation pattern, which is likely due to the main volcanic source, and considering the second-order anomalies of the ground deformation field.
2. Study Area
The 12-km-diameter, active Campi Flegrei caldera (Figure 1) is located in southern Italy, west of Naples town, and it is characterized by volcanic activity that started between the late Middle and the early Upper Pleistocene prior to 80 ka BP [28,29]. Campi Flegrei has been considered a nested caldera e.g., [30], generated by two collapses occurring at 40 ka BP (Campanian Ignimbrite: [31,32]) and 15 ka BP (Neapolitan Yellow Tuff eruption: [28,33,34,35] (Figure 1). However, De Natale et al. [36,37] and Rolandi et al. [38] have recently shown that Campanian Ignimbrite eruption occurred North of the Campi Flegrei caldera and did not cause any caldera collapse. Therefore, the Campi Flegrei caldera would have been generated by the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff (NYT) eruption [38,39].
The post 15 ka evolution of the NYT caldera was marked by the development of a resurgent dome in the inner part of the caldera (Figure 1), including the proximal sector of the Pozzuoli Bay, characterized by an uplift of about 100 m [11,40,41]. The dome resurgence resulted in the emersion of marine deposits forming the so-called La Starza terrace (Figure 1), which is presently exposed up to ∼30 m above sea level [42].
The post-collapse volcanic activity was characterized by over 70 events (Figure 1) concentrated in three main epochs (15 to ~9.5 ka BP; 8.6–8.2 ka BP; 4.4 and 3.8 ka BP) [43,44,45,46,47]. The Agnano–Monte Spina eruption (4.4 ka BP [48,49]) was the most powerful explosive event among all the post-caldera eruptions. The last epoch was followed by a prolonged period of volcanic quiescence that persists today, interrupted only by the Monte Nuovo eruption in 1538 AD, a small phreato-magmatic one with VEI=2 [50,51,52].
The geology of the study area is mainly characterized by volcanic units, made up of pyroclastic deposits, tuffs and ignimbrites, and by recent alluvial, colluvial, slope, and coastal deposits (Figure 1). The main volcano tectonic structure is formed by the structural rims forming the NYT caldera and more recent volcanic vents [42,53,54,55,56,57], as clearly recognized on land by morphological scarps (Quarto, Pianura, Soccavo, Posillipo, etc.) and in the Pozzuoli Bay offshore by the presence of a ring-fault system [41,42,58,59]. N–S trending fault segments, including the Bacoli and Baia faults and the Monte Nuovo fault, delimit the western inner border of the caldera; several E-W-, NW-SE-, and NE-SW- trending fault segments are present within the central resurgent area and the eastern caldera border (Figure 1). The observed crosscutting relationships indicate that the recent E-W and N-S structures overprint the NE-SW and NW-SE lineaments, which are inherited regional trends linked to the Pleistocene extensional tectonics [40,56,60,61].
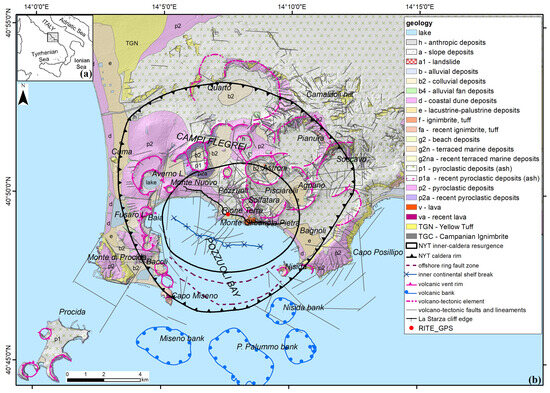
Figure 1.
Geological map of the Campi Flegrei caldera (b) with study area location (a). References for the map elements: geological units [41], NYT caldera rim and inner-caldera resurgence [37,38], volcanic and morphological elements ([42] and reference therein), volcano-tectonic faults and lineaments [57].
Ground Deformation in Historical Times
During the last 2100 years, the central sector of the Campi Flegrei caldera has undergone alternating phases of subsidence and uplift in the range of about 20 m, with maximum values centered in the Pozzuoli town central area, associated with fumarolic and hydrothermal processes, that are locally referred to as ‘bradyseism’ (e.g., [62,63]).
A long subsidence phase (about 18 m) continued at least since the Roman Republic Age (II-III centuries BC) to the Middle Age around the XV century, probably interrupted by an uplift during the V-VIII centuries. A strong uplift (reaching about 16 m) occurred for almost a century before the Monte Nuovo eruption (1538 AD) [54,64,65].
The quiescence after the 1538 phreato-magmatic eruption has been characterized by a progressive subsidence of more than 8 m in the central sector of the caldera area, lasting until 1950. Since that date, a new period of intermittent uplift has begun, with unrest episodes occurring in 1950–1951, 1969–1972, 1982–1984, during which the ground uplift at the port of Pozzuoli town reached about 4 m with respect to the ground level before 1950 (Figure 2). After the end of 1984, the ground subsided about 0.94 m, until the end of 2005. Since the last months of 2005, ground uplift started again and is still in progress (Figure 2); total uplift for the ongoing unrest has reached 1.39 m at the end of June 2024 [18]. The origin of this inflation–deflation process of the caldera (Figure 2) is still under debate and may be related to the magma intrusion, pressurization–depressurization of the hydrothermal system, or both [20,21,22,54,66,67,68,69].
The ground uplift of the 1950–1951 was not accompanied by felt seismicity, and during the period 1969–1972, the seismicity was of very low magnitude, up to about M = 2.1. During the period 1983–1984, on the contrary, seismicity was very frequent (about 16,000 earthquakes were recorded by the analogue seismic network of the time) and with significant magnitude (Mmax = 4.0) [43,70,71]; a total maximum ground uplift of 1.8 m was recorded (Figure 3) near the town center of Pozzuoli [72]. Seismic activity was characterized as Md = 4.0 during an event on 4 April 1983 and as Md = 3.8 on 8 December 1984, resulting in substantial damage to buildings and the evacuation of over 40,000 residents from the central town of Pozzuoli. Seismicity here is very shallow (in the first 3 km of the crust) so that even earthquakes of magnitude 4 or lower can be very damaging for the closest buildings in this very densely urbanized area.
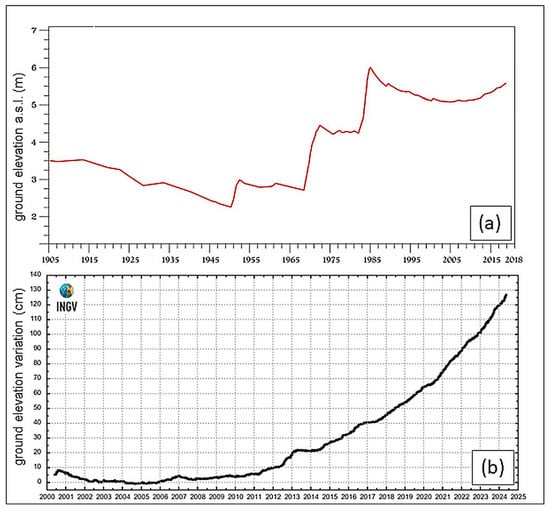
Figure 2.
Ground deformation trend, located in the maximum deformation area close to the “Rione Terra” district in the Pozzuoli city center: (a) levelling measurements from 1905 to 2017 at the altimetric benchmark 25A [71,73]; (b) GNNS measurements at the RITE station from June 2000 to June 2024 [18]. The location of the RITE station is shown in Figure 1; the RITE station is located in the same site as benchmark 25A.
A subsidence of about 1 m occurred during 1985–2005. In the last two decades, the central portion of Campi Flegrei caldera has experienced ground uplift of about 1.4 m and an increase in magnitude and extent of seismicity, especially since 2021 [18,74].
During the ongoing unrest, although the average uplift rate (70 mm/yr from June 2024 to 2025) is much lower than those in the ‘70s and 80s’ (about 440 mm/yr in 1969–1972 and 590 mm/yr in 1982–1985 [71]) (Figure 2), seismicity reached the highest magnitude ever recorded before, during an earthquake of M = 4.2 which occurred on 27 September 2023 and a strongest magnitude of M = 4.4 which occurred on 20 May 2024. The progressive increase in earthquake frequency and maximum magnitude had already been clearly forecasted [7,75] due to the progressive increase in underground pressure, which has also generated a progressive increase in the ground level.
The pattern of ground deformation during the recent unrest episodes displays maximum values at Pozzuoli harbor and is characterized by a rapid radial decay of the deformation that reaches a minimum at a distance of 6 km from the center [76,77,78]. The decay seems homogenous at large scale, and its geometry does not change over time. No accurate data are available on the ground deformation of the sea floor in Pozzuoli Bay, even if deformation, as seen in geophysical data [41], has also involved the side of the caldera that is submerged in the sea.
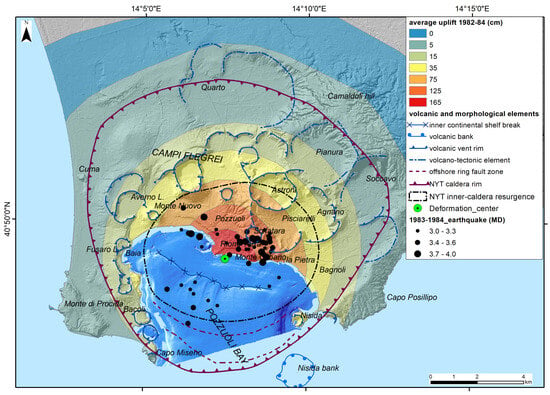
Figure 3.
Epicenters of earthquakes [79] compared with the ground deformation and cumulative uplift during the 1982–1984 bradyseismic crisis [80,81]. Volcanic and morphological elements by Sacchi et al. [42]; the DEM of the sea floor in Pozzuoli Bay is by Somma et al. [82].
3. Methods
3.1. Satellite Radar Interferometric Dataset
Monitoring of ground deformation at Campi Flegrei volcanic caldera (Figure 2) has been carried out through ground-based topographic leveling networks since 1905 [71]. Since the 2000s, this classic geodetic system has been integrated with a permanent Global Positioning System (GPS) monitoring network on land [83,84].
In the last decade, MT-InSAR has become a powerful technique for measuring slow ground deformation movements occurring in a range of dynamic processes, including volcanism and volcano-tectonics processes [85,86,87]. The MT-InSAR technique provides very accurate, unidimensional, millimetric measurements of ground movements along the line of sight (LOS), which is the straight line between the radar sensor and the target [88,89]. Due to its capability to accurately monitor slow deformation processes, the use of MT-InSAR in monitoring ground deformation has been widely applied in areas of volcanic risk [90,91], as for example at Ischia and La Palma volcanic islands [92,93].
Several differential inteferometric SAR techniques have already been used for analyzing the spatial distribution of recent ground deformation in Campi Flegrei volcanic area, exploiting the C-band sensors onboard ERS (from 1992 to 2001), ENVISAT (from 2002 to 2010), and RADARSAT (from 2003 to 2007) satellites in several papers [78,87,94,95].
In this paper, vertical ground deformation movements (VGDMs) were assessed during the Jan. 2016–Dec. 2021 interval by analyzing European Ground Motion Service (EGMS) data in vertical and horizontal polarizations available for the Campi Flegrei area. The EGMS is implemented by the European Space Agency processing Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) images of Sentinel-1 satellites’ constellation [96,97] to provide Advanced Differential Interferometric SAR (A-DInSAR) data over the main part of the European territory since 2015 (https://land.copernicus.eu/en/products/european-ground-motion-service, accessed on 28 Novembre 2024). This service processes average velocities and deformation time series, derived by both persistent scatterer [98] and distributed scatterer [99,100] techniques. The EGMS provides data at full resolution (20 by 5 m) in the locally referenced satellite LOS (the basic product) or the globally referenced GNNS (the calibrated product) and, finally, two Orho datasets by combining DInSAR displacement calibrated data of ascending and descending orbits resampled to a 100 m grid. One of the layers is a purely vertical displacement (EGMS Ortho Vertical), while the other is a purely east-west horizontal displacement (EGMS Ortho East/West) in a final resolution of 100 by 100 m. These datasets (Table 1) were downloaded and imported into a Geographic Information System (GIS) by using ArcGIS Pro software, version 2.3.1, produced by ESRI (https://www.esri.com/en-us/arcgis/products/arcgis-pro/overview, accessed on 28 Novembre 2024) to identify the places with active ground deformation process in the Campi Flegrei area.

Table 1.
Characteristics of ortho EGMS datasets (EGMS).
3.2. Ortho Vertical Dataset Processing for Best Fitting Axial–Symmetric Model
The Ortho Vertical dataset is formed by 23,970 points, characterized by values of total vertical deformation during 2016–2021 ranging from −82.2 to +547.2 mm with a mean of +21.77 mm with a standard deviation of 69.77 due to the wide range of data values that are not clustered around the mean value. The measurement uncertainties in annual velocity can be estimated by the RMSE (root mean square error) values, having a mean value of 1.18 mm (ranging from 0.4 to 8) with a standard deviation of 0.88.
The Ortho Vertical dataset was implemented by calculating—using ArcGisPRO 2.3.1. software—the distance r to the caldera’s center of maximum deformation for each point, as defined by several authors [20,84,101,102]. Values of r lower than 500 m have not been considered for the calculation of the polynomial curves, considering that many sectors within this distance to the deformation center fall within the sea, and few uplift values are available.
Our goal was to subtract the axial–symmetrical part from the ground deformation, so we searched for the axial–symmetric function that gave the best fit to the vertical deformation data. Since there is not a scientific consensus about a given model for source of the actual unrest, as explained before, we tested several functions, as well as the most used volcanological models. Among several models tested, we report here the fit with the simple function which has the most similar shape to the data, as well as the most commonly used model to fit ground deformation within volcanoes. They are the Gaussian function and the Mogi model, respectively [103]. The analysis and computation procedures involved the use of both Microsoft Excel (ver. 2502 for Microsoft 365 MSO) and R (ver. 4.2.0) software.
The Gaussian function, in our case, takes the following form:
where h(r) is the vertical displacement at a distance r from the point of maximum displacement h(0), and σ is a parameter (in the original formulation, the standard deviation) which determines the decay of the curve.
The Mogi [103] formula, which represents the effect of a point source of pressure increase and has been, for many decades, the most used model to fit and interpret ground deformation data at volcanoes, has the following form:
where K is a constant, depending on the source volume, overpressure, and medium rigidity; d is the source depth; and r is the distance from the point of maximum displacement.
Each one of the two functions has two unknown parameters: they are h(0) and σ for the Gaussian function and K and d for the Mogi model. A least squares solution can easily be found for each one of these functions using a numerical search procedure in the two-variable space. The resulting best fitting Gaussian curve has the following parameters: h(0) = 0.550 m, σ = 2.0. The resulting best fitting Mogi model has the following parameters: K = 4009.5 m3, d = 2700 m.
Figure 4 shows the best fitting Gaussian curves obtained by varying the parameters. It is evident that the Gaussian shape is not very similar to the data decay as a function of distance. In particular, even the best fitting curve, obtained for σ = 2.0, almost systematically overestimates the uplift at a short distance, while it underestimates uplift above 4500 m of distance. Nor varying the shape parameters can give a better fit to the observed data.
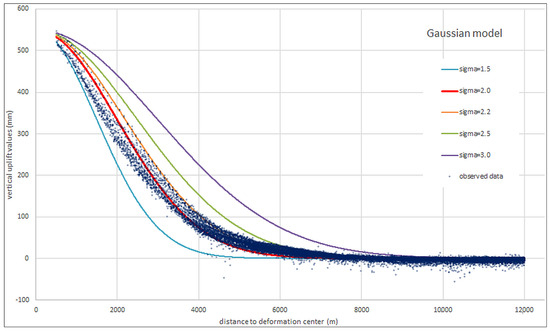
Figure 4.
Best fitting Gaussian models for different sigma values.
Considering the Mogi model results (Figure 5), we show the best fitting models obtained by varying the parameter d; also in this case, we see that even the best fitting model, for d = 2700 m, systematically underestimates the uplift at distances lower than about 3500 m and overestimates uplift at higher distances.
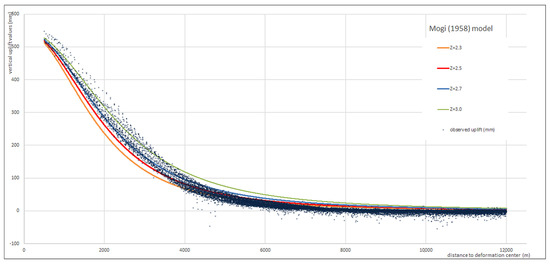
Figure 5.
Best fitting Mogi models for different Z values (Z = d/1000).
The statistic we used to evaluate the goodness of fit is R2, the ‘coefficient of determination’, defined as R2 = 1 − SSres/SStot, where SSres is the sum of squared residuals between the theoretical model and the data, and SStot is the sum of the squared differences from the average data value. It is worth noting that the closer to 1 the R2 value is, the better the model fits to the data. The R2 parameters for the two models, which indicate the goodness of fit, are R2 = 0.9724 for the Gaussian function and R2 = 0.9543 for the Mogi model, respectively.
It is clear that simple functions with two parameters, or even the most used model for volcanic pressure sources, are not able to give a very good fit to the axial–symmetrical shape of the data. So, we proceed to test a completely general axial–symmetric function, which is represented by a polynomial of a suitable degree.
We have to stress that we searched for an axial–symmetric function giving the best possible fit to the data. The analysis and computation procedures involved the use of R software. The distances to the deformation center (denoted as r), which were calculated using ArcGIS Pro, were imported into R along with the vertical uplift values (z) that were measured by satellites at each specific target point. Then, a series of polynomial curves describing theoretical radial ground deformation with a progressively higher accuracy were generated by using the imported dataset of r and z values (Table 2). These polynomials were derived up to the 20th degree; in Figure 6, we show only curves up to 6th degree due to almost fully overlapping for curves of degrees higher than 6. Coefficients for polynomial curves are shown in Table 3.

Table 2.
R2 and RMSE values for calculated polynomial curves.
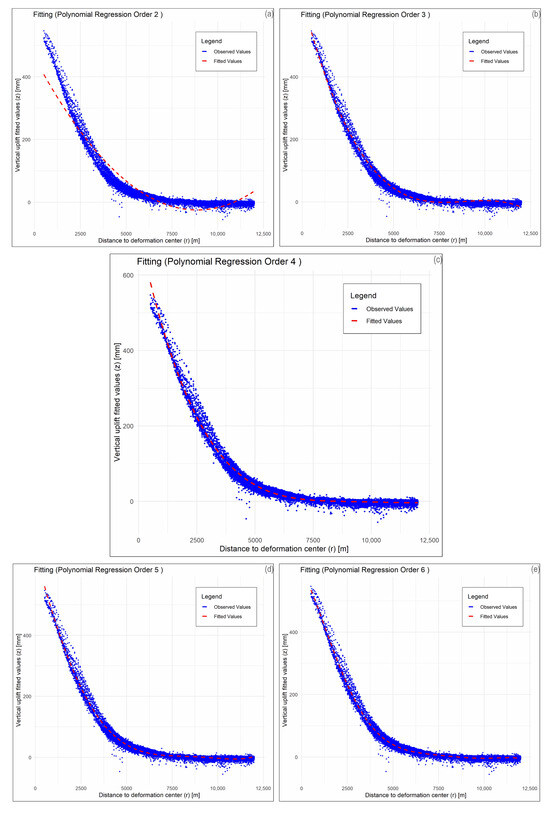
Figure 6.
Polynomial curves of increasing degree (from two to six) fitting the obtained set of data describing the “distance to the center/cumulative uplift”. Upon increasing the degree of the polynomial regression curve, the RMSE values became lower and the adjusted R2 stabilized (Table 2). Equations are shown in Table 3. Explanation of polynomial curves: (a) 2nd degree; (b) 3rd degree; (c) 4th degree; (d) 5th degree; (e) 6th degree.

Table 3.
Coefficients for polynomial curves of the 2nd to 6th degree.
The curve of the 2nd degree shows a significant geometric discrepancy from the data (Figure 6a), while the 3rd degree curve shows some mismatches for distances greater than 5 km (Figure 6b); the 4th, 5th and 6th degree curves show only minor differences for distances greater than 7–8 km (Figure 6c–e). We also computed best fitting parameters, i.e., adjusted R2 (coefficient of determination) and RMSE values, for polynomial functions from the 2nd to 20th order (Table 2). We observed that the adjusted R2 and RMSE value become quite stable at the fourth degree and that very small improvements are obtained by considering higher degrees. The selection of the best polynomial degree was made by considering the RMSE and by choosing the minimum order over which the improvement in the RMSE can be neglected, i.e., one order of magnitude lower than the intrinsic data error. Thus, we chose the fourth degree to best fit the vertical uplift.
On the basis of the above-described considerations, the predicted uplift values for each point were calculated based on the best fitting fourth-degree, as shown in Equation (3):
where
y = 7.463E-14x4 − 2.963E-09x3 + 4.391E-05x2 − 2.892x + 715.4
- x = r (distance to the deformation center);
- y = z (vertical uplift value in the EGMS ortho-vertical dataset).
3.3. Calculation of Vertical Ground Deformation Residuals
The obtained predicted values were imported back into the GIS project for further spatial analysis. A comparison was made between the predicted uplift values and the actual satellite-measured uplift values for each point. The residuals were measured as the differences between the expected (predicted) values and the observed (measured) values of z. Negative values of the residuals mean that the measured values are greater than the expected values of vertical ground deformation, while positive values of the residuals mean that the measured values are lower than the expected values. The calculated residuals were then mapped to visualize the spatial distribution of discrepancies between the measured and predicted uplift values that show second-order ground deformation vertical patterns.
The spatial representation of these residuals provides valuable insights into the deformation patterns and allows for a better understanding of the areas experiencing significant differences in uplift or subsidence with reference to a simple radial circular model. By identifying these discrepancies, it is possible to refine models and improve the accuracy of future predictions.
3.4. Residuals’ Analysis and Comparison with Seismic and Volcano-Tectonic Datasets
In order to analyze possible correlations between obtained deformation residuals with seismic activity and volcano-tectonic dynamics, the available earthquake and fault datasets were considered. The seismic dataset was obtained from the Italian Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV) online databases. We considered only seismic events with magnitude greater than 3.0 that have occurred since 1983 in the Campi Flegrei area and its surroundings (Figure 3 and Figure 7). These earthquakes were clustered during the periods of 1983–1984 and 2017–2024, corresponding to the most relevant bradyseismic crises.
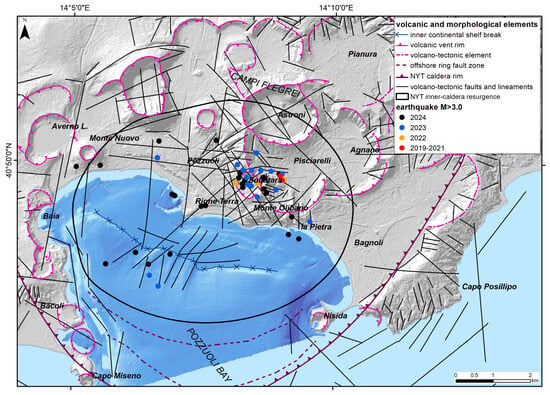
Figure 7.
Location of epicenters of the earthquakes Md > 3.0 that occurred from 2019 to July 2024. Seismic events according to INGV databases (see text for references).
In detail, we collected data referring to all seismic events that occurred since 1985 within the study area of Campi Flegrei from two sources:
- (a)
- The INGV national earthquake list, available at https://terremoti.ingv.it/en (accessed on 28 Novembre 2024);
- (b)
- The INGV Osservatorio Vesuviano regional earthquake list, specifically referring to the Campi Flegrei volcanic area for years 1983–1984 and 2005–2024 [79], available at https://terremoti.ov.ingv.it/gossip/flegrei/years.html (accessed on 28 Novembre 2024).
The datasets of volcanic (caldera boundaries, crater rims, and volcanic banks) and morphological elements (Figure 1) are derived from Sacchi et al. [41,42] and Steinmann et al. [59,60], volcano-tectonic faults and lineaments are from Natale et al. [104,105], and offshore faults are from Natale et al. [57,106].
3.5. Cross-Checking with Coeval GPS Datasets
To confirm our findings and perform a cross-validation of our results with a completely independent dataset, we repeated the same analysis carried out with the EGMS Ortho Vertical Sentinel-1 dataset by using the GPS measurements available for the study area. Data were obtained from the INGV Osservatorio Vesuviano GPS network [82]. In detail, we used the vertical displacement data for twenty-one GPS stations located in the Campi Flegrei area (Figure 8), selecting the measurements from January 2015 to December 2021 [107,108]. For each GPS point, the distance to the deformation center and the 2016–2021 cumulative vertical uplift value were calculated. A value of 3 mm was declared by De Martino et al. (2022) [107] for the uncertainty of the vertical deformation in 2016–2021, as measured by the GPS. Then, a series of polynomial curves describing theoretical radial ground deformation with a progressively higher accuracy were generated by using the imported values for each point.
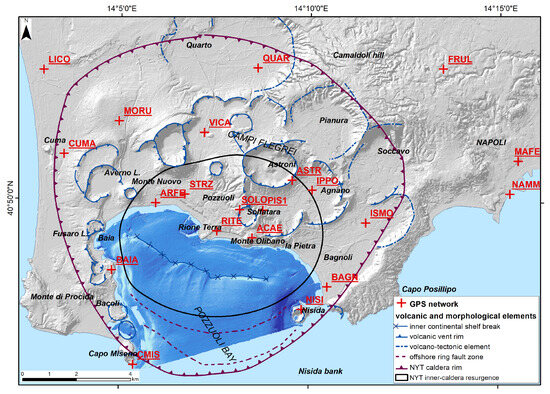
Figure 8.
Location of the GPS station of the INGV network; GPS location by De Martino et al. [84].
As for interferometric data, we chose the best fitting polynomial curve considering adjusted R2 values, which again resulted in the fourth degree (4), characterized by an adjusted R2 = 0.9935; it was then used for calculating the expected uplift according to a model of radial deformation. The predicted uplift values for each point were calculated based on the following equation:
where
y = −4E-14x4 − 2E-13x3 + 2E-05x2 - 0.2105x + 675.49
- x = distance to the deformation center;
- y = vertical uplift value in the vertical GPS dataset.
Then, the two datasets (vertical GPS and Ortho Vertical Sentinel-1) were compared, showing a very high correlation, as described in the Results section.
4. Results
4.1. Trends in Vertical and Horizontal Ground Deformation
The trends in vertical and horizontal ground deformation occurring on land in 2016–2021 are shown in the EGMS Ortho Vertical and EGMS Ortho East/West datasets (Figure 9 and Figure 10). The ground deformation patterns referring to the 2016–2021 period show that the eastern sector of Campi Flegrei is characterized by eastward horizontal movements, whereas the western sector is characterized by westward horizontal movements with maximum values in the caldera central area of about 2 km to the west and east outside Pozzuoli (Figure 9). As we are considering only the E-W component of horizontal movements, the velocity values strongly decreased along the N-S linear axis crossing through the center of the caldera deformation, which is located near Pozzuoli city center. Along this axis, the N-S component of the horizontal movements is very high, and the E-W component is almost null due to the radial geometry of ground deformation. For this reason, considering the SAR acquisition geometry, the spatial pattern of horizontal velocity looks larger in the E to W direction.
The central area with negligible east–west displacement is characterized by maximum uplift rates (Figure 9 and Figure 10). The vertical ground deformation of Campi Flegrei during 2016–2021 period is mainly spatially symmetrical with a radial pattern (Figure 10), with annual velocity varying from + 90 mm/yr in the central sector to zero in an annular strip between 6 and 7 km away from the center of deformation. The areas external to the caldera rim, beyond 7–8 km from the center (Figure 10), are also characterized by small subsidence rates (−1 to −3 mm/year) that may only locally show lower rates of up to −14 mm/yr due to local subsidence due to underground cavities or landslide processes. The ground uplift is confined within a circle of about 7 km in diameter, roughly corresponding to the caldera rim, and is further amplified in the resurgent block [54,77,109] due to the control of the ring faults, bounding both the caldera and the resurgent block, over the ground deformation.
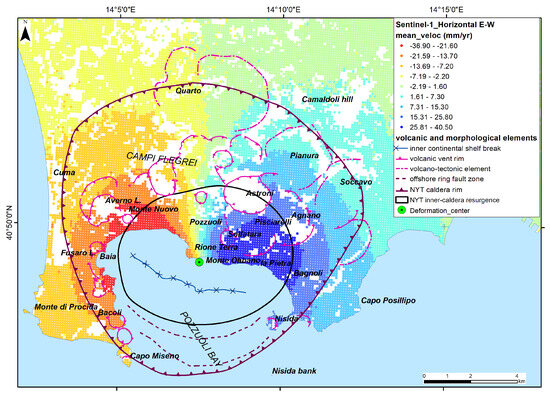
Figure 9.
E-W horizontal component of ground deformation at Campi Flegrei during 2015–2021 derived from the EGMS Ortho East/West dataset [110]. Class limits were obtained using the Natural Break (Jerkins) method.
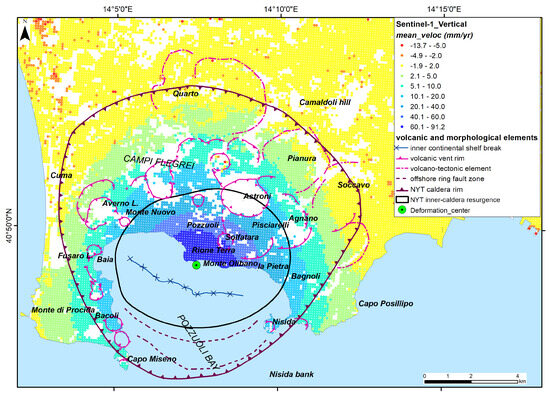
Figure 10.
Vertical component of ground deformation at Campi Flegrei during 2015–2021 derived from the ortho-vertical EGMS dataset [110].
4.2. Vertical Ground Deformation Shape
The best fit curve for the vertical displacement component, obtained with the methodology described in Section 3, is shown in Figure 6c. It represents the theoretical radial and symmetric geometry of ongoing ground deformation along the vertical component and can be used to predict the best fit expected value at a given distance from the deformation center for each point within the caldera.
The radial vertical deformation that occurred in the 2016–2021 period is characterized by a bell shape with a maximum in the center and values approaching zero radially moving away. The uplift values decline rapidly between 0.5 and 4.0 km of distance, then the reduction rate progressively slows up to about 6.0 km of distance; finally, the uplift becomes very low up to 8–9 km from the center. This curve is not linked to one of the volcano-tectonic interpretative models discussed in literature and briefly described in Section 1 but represents the best fit geometric representation of the average spatial trend of the first-order vertical ground deformation.
4.3. Differences Between Predicted and Observed Vertical Ground Displacements
The maps of the differences between the expected best fit values at a given distance from the deformation center calculated with polynomial curves of different grades—i.e., third (Figure 11), fourth (Figure 12), fifth (Figure 13) and sixth (Figure 14)—and the observed (measured) values of vertical ground deformation allow us to visualize the spatial distribution of the residuals, i.e., the differences between the predicted and measured uplift values in SAR target points. The obtained dataset is made up of 15,900 points with values of differences between predicted and observed vertical ground deformation (i.e., residuals) ranging from about −100 mm to about +70 mm in six years.
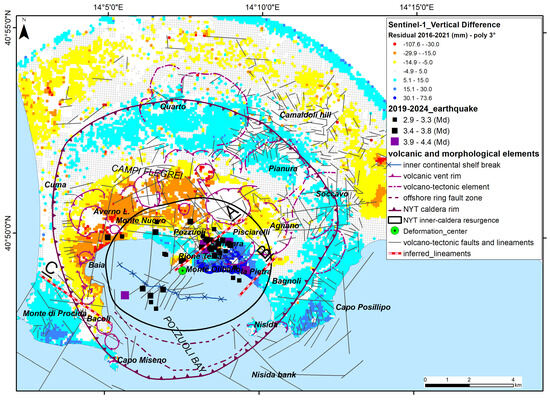
Figure 11.
Vertical ground deformation anomalies obtained by using a third-order polynomial curve compared with volcano-tectonic elements and seismic events.
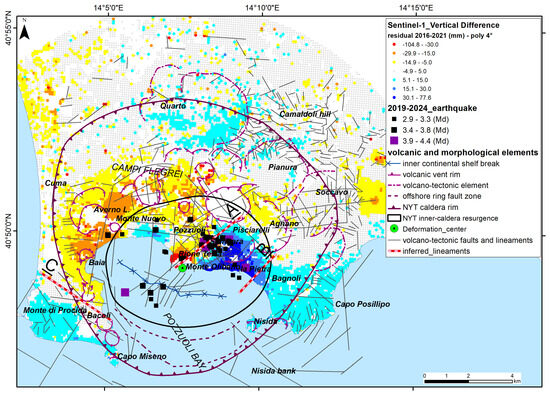
Figure 12.
Vertical ground deformation anomalies obtained by using a fourth-order polynomial curve compared with volcano-tectonic elements and seismic events.
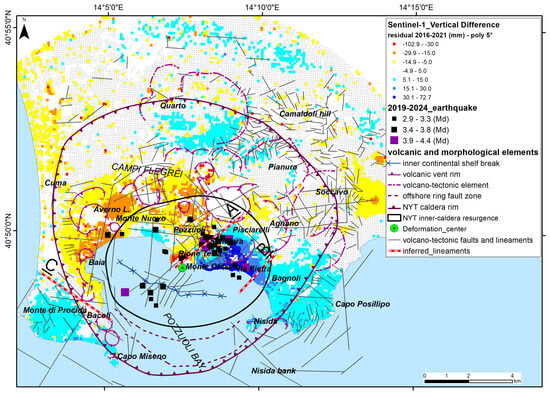
Figure 13.
Vertical ground deformation anomalies obtained by using a fifth-order polynomial curve compared with volcano-tectonic elements and seismic events.
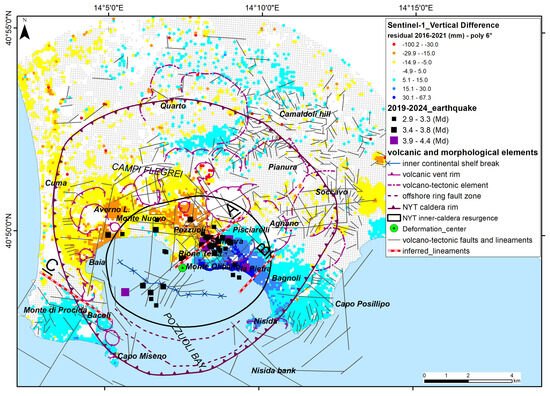
Figure 14.
Vertical ground deformation anomalies obtained by using a sixth-order polynomial curve compared with volcano-tectonic elements and seismic events.
In these maps (Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14), areas where the observed uplift is significantly higher than the predicted values are characterized by negative values (lower than −15 mm) and are mapped in yellow to red. Conversely, areas where the observed uplift is lower than what was predicted by the polynomial models have positive values (higher than +15 mm) and are shaded in light to dark blue. The spatial representation of these differences provides relevant insights into the second-order patterns of deformation and allows for a better understanding of the areas experiencing significant differences in uplift or subsidence.
It is important to observe how the residual deformation values vary in the maps obtained using the different polynomial curves (Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14). The second-degree curve was not used for the map because of the very high values of RMSE (Table 2 and Figure 6a). The map related to the third-degree polynomial curve (Figure 11), despite the low values of adjusted R2 and RMSE (Table 2), shows anomalous concentric bands of residuals due to an oscillation in the tail of the retrieved polynomial function (Figure 6b) at distances of greater than 4–5 km from the center of deformation.
The concentric bands are no longer visible in the map in Figure 12, relating to the fourth-order polynomial curve, and the distribution of residuals becomes stable and remains constant even in the maps relating to the fifth-order (Figure 13) and sixth-order (Figure 14) polynomial curves, with only minor differences in the peripheral areas of the caldera. The values of adjusted R2 and RMSE (Table 2) are stable for these curves.
Within the caldera area, two main anomalies are always well mapped (Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14); (i) a large area of negative values is located between Baia to the west and Pozzuoli city center to the east, and (ii) a sector with high positive values is located between Monte di Procida, Monte Olibano, la Pietra, and Bagnoli. These sectors with differences in uplift are separated by some lineaments, described as follows.
- A well-marked SW-NE-oriented line (A) goes from the caldera deformation center to Pisciarelli and Agnano and separates sectors characterized by about 60–75 mm of difference in vertical ground deformation.
- An ill-defined SSW-NNE-oriented line (B) between Bagnoli and La Pietra separates sectors characterized by +15 mm to +45 mm of uplift anomaly (about 30 mm of difference in total).
- A well-marked WNW-ESE-oriented line (C) goes from Baia to Fusaro Lake and separates sectors characterized by −15 mm to +15 mm of uplift anomaly (about 30 mm of difference in total).
Considering the best fitting fourth-order curve results, the area with the highest anomaly in vertical uplift (up to 75 mm) is analyzed in Figure 15. The north-western sector (Rione Terra, Pozzuoli, Astroni), characterized by negative values (i.e., an observed uplift higher than the predicted values), is separated by the south-eastern sector (Monte Olibano, Solfatara and Bagnoli), with high positive values (i.e., an observed uplift lower than the predicted values) in a SW-NE-oriented complex strip, wherein several earthquakes are also localized. Lineament A falls within a sector crossed by several SW-NE, N-S, and NW-SE faults, and the differential uplift seems to be controlled by the SW-NE fault set. This lineament crosses the Solfatara crater and the Pisciarelli fumarole system and separates Rione Terra from the Monte Olibano hills. A clear spatial correlation is visible among the 2019–2024 earthquake epicenters and uplift anomalies along lineament A between Pozzuoli and Bagnoli. Lineament B does not correspond to any mapped fault and is parallel to the local orientation of the caldera rim.
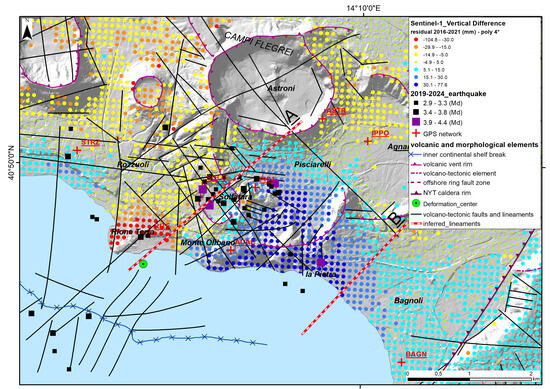
Figure 15.
Details of the main area of anomaly between Pozzuoli and Bagnoli using the best fitting fourth-grade polynomial curve.
In Figure 16, the westernmost sector of the caldera is shown, where lineament C seems to be crossed by N-S, E-W, and NW-SE faults. An anomaly of around 30 mm in vertical uplift is present along the lineament crossing the NYT caldera rim. The earthquake epicenters near the lineament C are located in the sea, along faults located in the bay bottom.
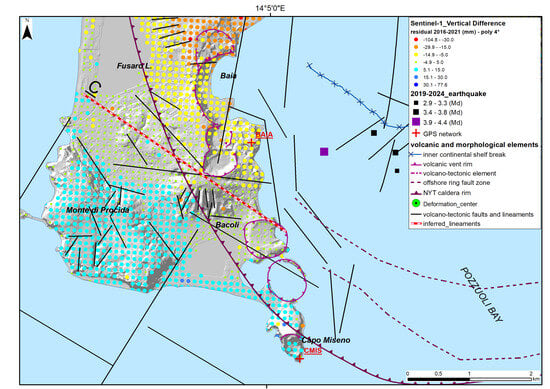
Figure 16.
Details of the main area of anomaly between Monte di Procida and Baia using the best fitting fourth-grade polynomial curve.
4.4. Comparison Between Sentinel-1 and GPS Datasets
In order to perform a reliability check and cross-validate the results obtained with the proposed methodology applied to MT-InSAR Sentinel-1 data, we analyzed the available GPS dataset for the study area by considering the results in terms of vertical ground deformation measured in the same time interval (i.e., 2016–2021) with the two different technologies. The results obtained by GPS data and Sentinel-1 data were correlated by a regression analysis. Because the two datasets differ greatly in their numbers of data (n = 21 for GPS and n = 15,900 for Sentinel-1), we selected the 21 data within Sentinel-1 that are located in the nearest position (within a radius of 58 m) of GPS stations for comparison. In this way, we obtained a dataset of 21 control points located near the GPS stations (Figure 8) and characterized by both GPS and Sentinel-1 measurements of vertical ground deformation during the same time interval.
The results of the correlation analysis for measurements in these control points indicate a strong correlation with very similar data. The linear regression of the couple of values (GPS and Sentinel-1 measurements) for each point (Figure 17) gave very high values of correlation, with an R2 value of 0.9926.
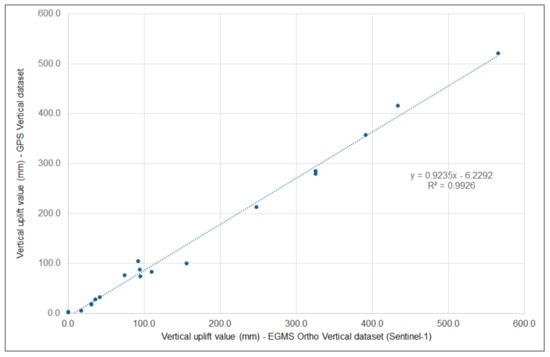
Figure 17.
Linear correlation between GPS (x axis) and Sentinel-1 (y axis) data for each point.
5. Discussion
Our work carefully investigated the detailed features of the vertical ground displacement pattern at Campi Flegrei and its relationship with the main structural and seismotectonic features of the area. What is very clearly observed during uplift and subsidence episodes in this area, in fact, is the remarkably constant shape of the ground displacements (Figure 18), which appear radially symmetrical to a large extent. Furthermore, seismicity also appears remarkably concentrated within a limited area and mainly clustered in a few clearly evident sectors [7] (Figure 7).
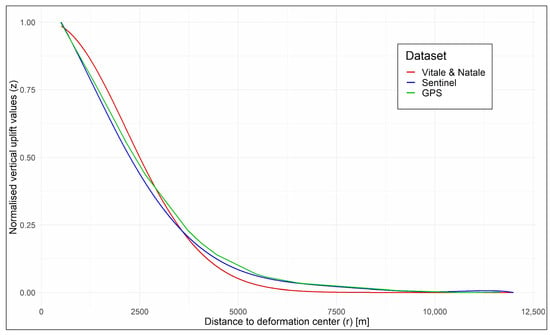
Figure 18.
Plot of normalized vertical ground deformation values (N) vs. distance to the caldera deformation center (R). Comparison between the curve by Vitale and Natale [102], which was derived by levelling measurements between 1905 and 1992, 2000–2019 GPS data, and 2016–2021 GPS data [106,107] used for cross-validation, and our curve, which was derived from Sentinel-1 ortho-vertical DInSAR 2016-2021 data [109].
In order to obtain relevant information on the ground deformation shape, we compared recent normalized deformation patterns (Figure 18)—referring to uplift data from 2016 to 2021 obtained from both Sentinel-1 ortho-vertical DInSAR data and coeval GPS data—with those of the last 120 years, which were derived by levelling measurements between 1905 and 1992 and 2000–2019 GNNS data on uplift and subsidence gathered in different unrest periods [102]. Figure 18 shows a similar shape for the three plotted datasets. It is evident that unrest episodes at Campi Flegrei caldera, occurred in the last 120 years during both inflation and deflation episodes, involve similar ground deformation patterns, with a radial symmetry around a constant deformation center. The GPS curve shows slightly higher values than the Sentinel-1 curve at distances of 1 to 6 km. Minor differences can be observed at distances lower than 3000 m, where the curve by Vitale & Natale [102] shows values slightly higher than the 2016–2021 curves, and between 3000 and 9000 m., where the curve shows values slightly lower than the Sentinel and GPS curves.
Our results confirm that the overall first-order geometry of the vertical ground deformation pattern at Campi Flegrei is radial, ‘bell-shaped’, and very concentrated in a small area [7,13,37,67], which likely corresponds to the resurgent block inside the caldera [54] (Figure 10). The vertical deformation we inferred in the analyzed period (2016–2021) is an uplift, but it has been observed from MT-InSAR, precision levelling, and GPS measurements during the period 1905–2019 that the subsidence in the area is also perfectly specular to the uplift [69,111,112,113]. As shown by De Natale and Pingue [76] and De Natale et al. [77], the very constant shape of deformation pattern both for uplift and for subsidence as well as the large amount of deformation can be well explained by the presence of a central resurgent area bordered by ring faults. Such a structure is likely to be represented by the central resurgent block recently clearly evidenced by Rolandi et al. [54] and already hypothesized and supported by the combined observations of seismicity and ring faults at sea by Sacchi et al. [41,42]. The main radially symmetrical pattern has been explained by different authors in terms of the main volcanic source, which could almost equally be direct magma pressure caused by sill intrusions [21,22] or an increase in pressure in the geothermal system caused by hot gas rising from the main magma chamber [7,23,114].
However, our work identifies, for the first time, some peculiar deviations (anomalies in uplift) from such a ‘bell-shaped’ pattern, which can be interpreted in terms of structural heterogeneities in the area. The main radial pattern of vertical deformation data was parametrized by a polynomial function of the fourth order.
A careful analysis was carried out regarding the order of the polynomial to be used to describe the first-order deformation geometry. Based on the following considerations, the fourth-order polynomial was deemed the best fitting. The map of residuals obtained using the third-order polynomial, although it already gives good results in terms of RMSE and adjusted R2 (Table 2), shows some relevant boundary effects in the peripheral sectors of the caldera (Figure 10), due to some oscillation in the tail of the curve of the third-order polynomial function (Figure 6b). Such boundary effects are no longer present when using the fourth-order polynomial (Figure 6c and Figure 12). The results obtained with fifth- and sixth-order polynomials (Figure 6d,e, Figure 13 and Figure 14) are comparable to those of the fourth-order polynomial, so there is no need to use these higher orders. Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13 and Figure 14 show that the results of the deformation residuals (second-order anomalies) are very stable in the central sector of the caldera and do not depend on the polynomial function assumed. The different polynomial orders applied to the dataset highlight the complexity of the deformation field and the necessity of balancing between model accuracy and physical interpretation. The fourth-degree polynomial was selected as the best compromise between model complexity and fitting accuracy, since the RMSE and adjusted R2 values become stable from this order onwards. Higher-degree polynomials only marginally improve model performance but may introduce unnecessary overfitting effects.
The deviations from the best fitting curve are significantly non-random (Figure 12). The most prominent lineament is the sharp change between negative and positive anomalies, separated by a roughly NE-SW line slightly east of the Rione Terra and crossing Solfatara crater (Figure 15). This line closely resembles the tectonic lineation connecting La Pietra to the western Agnano plain-bounding faults [26,110,111], and most of the seismicity, particularly the largest magnitude earthquakes, appears located along or very close to this line. The clustering of seismicity along the separation line between negative and positive anomalies strongly suggests this is a major structural feature, as does the observed deviation of the deformation pattern from a purely radial one, which is somewhat related to co-seismic displacements. We recall that very shallow seismicity, typical of Campi Flegrei earthquakes, can produce measurable co-seismic displacements from some mm to some cm, even with magnitudes as low as 4. The example of the 2017 Casamicciola (Ischia Island) M = 4.0 earthquake is worth noting; it caused more than 4 cm of subsidence in the hanging wall. The depth of the Casamicciola earthquake was about 2 km, a depth very similar to the Campi Flegrei earthquakes [18,55,115,116].
The detected alignment A in Figure 15, which sharply separates positive and negative vertical deformation anomalies, is then likely to correspond to a main seismic fault zone, which can cause the largest-magnitude earthquakes in the area.
It is interesting to note that earthquakes that occurred before 2020 (Figure 7), when the total uplift was lower (65 cm since 2005; Figure 2b) than today, were much more concentrated around this structure. This agrees with the hypothesis that this could be the main seismogenic structure in the area and that other structural features located more distant from the center of uplift have been progressively activated by a progressive enlargement of the critical stress threshold, which is associated with an increase in ground uplift [117,118,119]). Such a main structural feature in the area possibly also represents the most likely zone for possible vent opening in a future eruptive scenario (phreatic and/or magmatic). In particular, the small area included among Rione Terra, Solfatara-Pisciarelli, and La Pietra appears to be the most anomalous one, characterized by the sharp change in the sign of the residual displacement and by the most prominent anomalies, indicating a local relative subsidence.
Some recent papers (i.e., [26]) have identified some of the main faults and volcano-tectonic structures of the area from precise earthquake locations; however, as we have shown in this paper, displacement anomalies from MT-InSAR data analyses can be even more powerful indicators of structural features.
Giudicepietro et al. [25] also found an anomaly in the temporal evolution of ground deformation in a small part (the Mt. Olibano area) of the anomalous area we identify here. It is important to stress, however, that Giudicepietro et al. [25] is aimed to detect differences in the time evolution trends of ground displacements in different areas, whereas our paper detects differences in the spatial trends of ground deformation by identifying the second-order asymmetric behavior among different areas, which are abruptly separated by a marked and constant structural lineation. In fact, the former authors found that the anomalous deformation in the Mt. Olibano area only occurred in the 2021–2023 period, whereas we put into evidence a ‘spatial’ and persistent (since 2015 until 2020, at least) anomalous deformation in a larger area.
Regarding the limitations of our study, it is well known that the uncertainty in GPS and Sentinel-1 measurements is very low (about 3.0 mm and 1.2 mm on average, respectively) and therefore does not significantly affect the results in terms of differences between expected and observed vertical deformations. Thus, the main result of the paper, i.e., a second-order deviation from the radial symmetry of a large area, sharply separated from the other one by a rather straight lineation, appears to be robust. What are obviously still open to discussion are the details of its interpretation within a volcanological and seismotectonic framework. The temporal evolution anomaly evidenced during the period 2021–2023 [25], a period characterized by high seismicity, could be mainly due to the effect of co-seismic deformations generated by several earthquakes with a magnitude of between 3 and 4. Our finding of the sharp lineation separating the two differently deforming areas, along which most of seismicity clusters, can be interpreted as a dominant tectonic structure of the area. This result, going well beyond previous observations, also adds significance to the observations of Giudicepietro et al. [25].
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we have presented a simple method for detecting second-order deformation anomalies by filtering the primary radial deformation signal observed during phases of unrest at Campi Flegrei caldera. The procedure is based on the polynomial fit of the vertical displacement data, assuming they only depend on the distance from the deformation center and on the computation of the differences between theoretical radial vertical displacements and observed ones. This approach emphasizes the study’s main objective: highlighting second-order deformation anomalies without introducing excessive model complexity. The use of polynomial fitting, particularly the fourth-order curve, ensures that the main axial–symmetric pattern is preserved and successfully subtracted from the global field, so that the residuals indicate smaller-scale, geologically meaningful deviations. In this way, we can generate an anomaly map that highlights sectors with peculiar deformation patterns during unrest.
We identified, using a polynomial function of the sole distance from the maximum deformation center, the best coefficients to fit the ground displacement pattern derived from the MT-InSAR Sentinel-1 vertical dataset referring to the 2016–2021 period. In addition to polynomial fitting, we fitted our data using a Gaussian curve and the Mogi model. As can be seen (Figure 4 and Figure 5), however, the best fit obtained with such models yielded lower R2 values and were less effective in describing the observed deformation pattern, as both of them are in fact unable to simulate the observed shape over the whole range of distance. The polynomial fitting approach resulted in the most suitable method for our study, as it was able to provide, with few coefficients, an almost perfect fit to the axial–symmetrical part of the ground uplift, which likely represents the effect of the main volcanological source, whatever it is.
We confirmed that the first-order geometry of vertical displacement is radially symmetric; we also tested the best fitting function obtained from MT-InSAR data against the one obtained from coeval GPS data. We obtained very similar functions with the two different data sets, thus confirming the robustness of the procedure. Finally, we explored the obtained second-order anomalies.
There are many models in the literature for the main volcanic source of deformation [7,21,22,23,24,113], and all of these models predict an axial–symmetric ground deformation. We used the most general axial–symmetrical function, built as a polynomial, for obtaining the best fit to the observed data. By subtracting such a best fitting axial–symmetric field, we succeeded in showing the very clear second-order features of the ground deformation field, hidden by the main field. Such features appear to be very well correlated with the most seismically active lineaments, thus corroborating their interpretation in terms of relevant volcano-tectonic structures.
The resulting anomalies are non-random and show well-defined differential behavior between two contiguous areas: one with significant positive residuals, another with negative ones. The separation between the two areas is remarkably linear, with most of the largest earthquakes occurring in a cluster around this line. We then interpreted such discontinuity as a main structural feature of the area.
The obtained results show that seismic structures that have not yet been fully activated can be recognized in the early stages of ground deformation from differential ground displacement anomalies, if appropriately filtered and analyzed. The spatial distribution of earthquakes occurring since 2022 confirms the clustering of most of the largest-magnitude events around this structural feature, as detected from the analysis of deformations measured in 2015–2021, thus proving the robustness of the results obtained by such analyses. It is important to note that the most seismically active zones, which in this case also encompass the most hydrothermally active ones, such as the Solfatara crater, are also the most likely to feature vent opening in cases of eruption. By identifying these ground deformation anomalies, it is possible to identify the most seismically active structures and the most likely areas for eventual vent opening, allowing us to improve the accuracy of future predictions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.M. and G.D.N.; methodology, F.M. and A.C.; software, A.C.; validation, F.M. and G.D.N.; formal analysis, F.M. and A.C.; investigation, F.M. and G.D.N.; resources, F.M.; writing—original draft preparation, F.M., A.C. and G.D.N.; writing—review and editing, F.M. and G.D.N.; visualization, F.M. and A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
European Union’s Copernicus Land Monitoring Service data, https://doi.org/10.2909/943e9cbb-f8ef-4378-966c-63eb761016a9 (accessed on 27 November 2024).
Acknowledgments
This publication was prepared using European Union’s Copernicus Land Monitoring Service information; DOI: https://doi.org/10.2909/943e9cbb-f8ef-4378-966c-63eb761016a9. We are grateful to reviewers and academic editors for their useful comments. Many thanks also to Germana Scepi and Raffaele Mattera for supporting us in statistical analysis.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Galetto, F.; Acocella, V.; Caricchi, L. Caldera resurgence driven by magma viscosity contrasts. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, B.D. On the mechanics of caldera resurgence. J. Geophys. Res. 1984, 89, 8245–8251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.; Wilcock, J.; Stix, J. Caldera resurgence during magma replenishment and rejuvenation at Valles and Lake City calderas. Bull. Volcanol. 2012, 74, 1833–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Silva, S.L.; Mucek, A.E.; Gregg, P.M.; Pratomo, I. Resurgent Toba—Field, chronologic, and model constraints on time scales and mechanisms of resurgence at large calderas. Front. Earth Sci. 2015, 3, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Pingue, F.; Allard, P.; Zollo, A. Geophysical and geochemical modelling of the 1982-1984 unrest phenomena at Campi Flegrei caldera (southern Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1991, 48, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurwitz, S.; Christiansen, L.B.; Hsieh, P.A. Hydrothermal fluid flow and deformation in large calderas: Inferences from numerical simulations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, B02206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, C.; De Natale, G.; Schiavone, R.; Somma, R.; Moretti, R. The Campi Flegrei caldera unrest: Discriminating magma intrusions from hydrothermal effects and implications for possible evolution. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2019, 188, 108–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acocella, V. Bridging the gap from caldera unrest to resurgence. Front. Earth Sci. 2019, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newhall, C.G.; Dzurisin, D. Historical Unrest at large Calderas of the World. US Geological Survey. Bulletin 1988, 1855, 1–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillipson, G.; Sobradelo, R.; Gottsmann, J. Global volcanic unrest in the 21st century: An analysis of the first decade. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2013, 264, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acocella, V.; Di Lorenzo, R.; Newhall, C.; Scandone, R. An overview of recent (1988 to 2014) caldera unrest: Knowledge and perspectives. Rev. Geophys. 2015, 53, 896–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlton, D.; Kilburn, C.; Edwards, S. Volcanic unrest scenarios and impact assessment at Campi Flegrei caldera, Southern Italy. J. Appl. Volcanol. 2020, 9, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberi, F.; Corrado, G.; Innocenti, F.; Luongo, G. Phlegraean fields 1982-1984: Brief chronicle of a volcano emergency in a densely populated area. Bull Volcanol. 1984, 47, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, D.; Scott, B.J.; Houghton, B.; Paton, D.; Dowrick, D.J.; Villamor, P.; Savage, J. Social and economic consequences of historic caldera unrest at the Taupo volcano, New Zealand and the management of future episodes of unrest. Bull. New Zealand Soc. Earthq. Eng. 2002, 35, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuester, I.; Forsyth, S. Rabaul eruption risk: Population awareness and preparedness survey. Disasters 1985, 9, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, C. Volcanoes and the economy. In Volcanoes and the Environment; Marti, J., Ernst, G.G.J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006; pp. 440–467. [Google Scholar]
- De Natale, G.; Troise, C.; Somma, R. Invited perspectives: The volcanoes of Naples: How can the highest volcanic risk in the world be effectively mitigated? Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 20, 2037–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INGV, 2024. Bollettino di Sorveglianza Campi Flegrei, mese di Giugno 2024. INGV, Sezione di Napoli–Osservatorio Vesuviano. p. 51. Available online: https://www.ov.ingv.it/index.php/monitoraggio-e-infrastrutture/bollettini-tutti/bollett-mensili-cf/anno-2024-3/1652-bollettino-mensile-campi-flegrei-2024-06/file (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Amoruso, A.; Crescentini, L. Clues of Ongoing Deep Magma Inflation at Campi Flegrei Caldera (Italy) from Empirical Orthogonal Function Analysis of SAR Data. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 5698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoruso, A.; Crescentini, L.; Sabbetta, I. Paired deformation sources of the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) required by recent (1980–2010) deformation history. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 858–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macedonio, G.; Giudicepietro, F.; D’Auria, L.; Martini, M. Sill intrusion as a source mechanism of unrest at volcanic calderas. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 3986–4000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, J.Y.L.; Kilburn, C.R.J. Intrusion and deformation at Campi Flegrei, southern Italy: Sills, dikes, and regional extension. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B12210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; Troise, C.; Sarno, F.; De Natale, G. Caldera unrest driven by CO2-induced drying of the deep hydrothermal system. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8309. [Google Scholar]
- Zollo, A., N. Maercklin, M. Vassallo, D. Dello Iacono, J. Virieux, and P. Gasparini. Seismic reflections reveal a massive melt layer feeding Campi Flegrei caldera. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudicepietro, F.; Casu, F.; Bonano, M.; De Luca, C.; De Martino, P.; Di Traglia, F.; Di Vito, M.A.; Macedonio, G.; Manunta, M.; Monterroso, F.; et al. First evidence of a geodetic anomaly in the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) ground deformation pattern revealed by DInSAR and GNSS measurements during the 2021–2023 escalating unrest phase. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2024, 132, 104060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotto di Uccio, F.; Lomax, A.; Natale, J.; Muzellec, T.; Festa, G.; Nazeri, S.; Convertito, V.; Bobbio, A.; Strumia, C.; Zollo, A. Delineation and fine-scale structure of fault zones activated during the 2014–2024 unrest at the Campi Flegrei caldera (Southern Italy) from high precision earthquake locations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2023GL107680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tramelli, A.; Convertito, V.; Godano, C. b value enlightens different rheological behaviour in Campi Flegrei caldera. Commun. Earth Env. 2024, 5, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pappalardo, L.; Civetta, L.; D’Antonio, M.; Deino, A.; Di Vito, M.; Orsi, G.; Carandente, A.; de Vita, S.; Isaia, R.; Piochi, M. Chemical and Sr-isotopical evolution of the Phlegraean magmatic system before the Campanian Ignimbrite and the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 141–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpati, C.; Sparice, D.; Perrotta, A. A crystal concentration method for calculating ignimbrite volume from distal ash fall deposits and a reappraisal of the magnitude of the Campanian Ignimbrite. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2014, 280, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, G.; De Vita, S.; Di Vito, M. The restless, resurgent Campi Flegrei nested caldera (Italy): Constraints on its evolution and configuration. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1996, 74, 179–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Vezzoli, L.; Aleotti, P.; De Censi, M. Interaction between caldera collapse and eruptive dynamics during the Campanian Ignimbrite eruption, Phlegraean Fields, Italy. Bull Volcanol. 1996, 57, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vivo, B.; Rolandi, G.; Gans, P.B.; Calvert, A.; Bohrson, W.A.; Spera, F.J.; Belkin, H.E. New constraints on the pyroclastic eruptive history of the Campanian volcanic plain (Italy). Mineral. Petrol. 2001, 73, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deino, A.L.; Orsi, G.; de Vita, S.; Piochi, M. The age of the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff caldera-forming eruption (Campi Flegrei caldera—Italy) assessed by 40Ar/39Ar dating method. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2004, 133, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, G.; D’Antonio, M.; de Vita, S.; Gallo, G. The Neapolitan Yellow Tuff, a large-magnitude trachytic phreato-plinian eruption: Eruptive dynamics, magma withdrawal and caldera collapse. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1992, 53, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohletz, K.; Orsi, G.; De Vita, S. Eruptive mechanisms of the Neapolitan Yellow Tuff interpreted from stratigraphic, chemical, and granulometric data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1995, 67, 263–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Troise, C.; Mark, D.; Mormone, A.; Piochi, M.; Di Vito, M.A.; Isaia, R.; Carlino, S.; Barra, D.; Somma, R. The Campi Flegrei Deep Drilling Project (CFDDP): New insight on caldera structure, evolution and hazard implications for the Naples area (Southern Italy). Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2016, 17, 4836–4847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Rolandi, G.; Kilburn, C.R.J.; Troise, C.; Somma, R.; Di Vincenzo, G.; Rolandi, R.; Woo, J.; Cole, P.D. The Campanian Ignimbrite of Southern Italy: A Fissure Eruption or Caldera-Forming Event? Earth Plan. Sci. Lett. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Rolandi, G.; De Natale, G.; Kilburn, C.R.J.; Troise, C.; Somma, R.; Di Lascio, M.; Fedele, A.; Rolandi, R. The 39 ka Campanian Ignimbrite eruption: New data on source area in the Campanian Plain. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; Vivo, B., Belkin, H.E., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Chapter 8; pp. 175–205. [Google Scholar]
- Rolandi, G.; Di Lascio, M.; Rolandi, R. The Neapolitan yellow tuff eruption as the source of 507 the Campi Flegrei caldera. In Vesuvius, Campi Flegrei, and Campanian Volcanism; De Vivo, B., Belkin, H.E., Rolandi, G., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 273–296. [Google Scholar]
- Orsi, G.; Civetta, L.; Del Gaudio, C.; de Vita, S.; Di Vito, M.A.; Isaia, R.; Petrazzuoli, S.M.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Ricco, C. Short-term deformations and seismicity in the resurgent Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy): An example of active block-resurgence in a densely populated area. J. Volcan. Geoth. Res. 1999, 91, 415–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Pepe, F.; Corradino, M.; Insinga, D.D.; Molisso, F.; Lubritto, C. The Neapolitan 1217 Yellow Tuff caldera offshore the Campi Flegrei: Stratal architecture and kinematic reconstruction 1218 during the last 15 ky. Mar. Geol. 2014, 354, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacchi, M.; Matano, F.; Molisso, F.; Passaro, S.; Caccavale, M.; Di Martino, G.; Guarino, A.; Innangi, S.; Tamburrino, S.; Tonielli, R.; et al. Geological framework of the Bagnoli–Coroglio coastal zone and continental shelf, Pozzuoli (Napoli) Bay. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 36, 529–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.A.; Isaia, R.; Orsi, G.; Southon, J.D.; De Vita, S.; D’Antonio, M.; Pappalardo, L.; Piochi, M. Volcanism and deformation since 12,000 years at the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 221–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Marianelli, P.; Sbrana, A. Caldera unrest prior to intense volcanism in Campi Flegrei (Italy) at 4.0 ka BP: Implications for caldera dynamics and future eruptive scenarios. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L21303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, V.; Arienzo, I.; Civetta, L.; D’Antonio, M.; Tonarini, S.; Di Vito, M.A.; Orsi, G. The magmatic feeding system of the Campi Flegrei caldera: Architecture and temporal evolution. Chem. Geol. 2011, 281, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.C.; Isaia, R.; Pearce, N.J.G. Tephrostratigraphy and glass compositions of post-15 kyr Campi Flegrei eruptions: Implications for eruption history and chronostratigraphic markers. Quat. Sci. Rev. 2011, 30, 3638–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lirer, L.; Luongo, G.; Scandone, R. On the volcanological evolution of Campi Flegrei. EOS 1987, 68, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vita, S.; Orsi, G.; Civetta, L.; Carandente, A.; D’Antonio, M.; Deino, A.; di Cesare, T.; Di Vito, M.A.; Fisher, R.V.; Isaia, R.; et al. The Agnano–Monte Spina eruption (4100 years BP) in the restless Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1999, 91, 269–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellino, P.; Dioguardi, F.; Isaia, R.; Sulpizio, R.; Mele, D. The impact of pyroclastic density currents duration on humans: The case of the AD 79 eruption of Vesuvius. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Vito, M.; Lirer, L.; Mastrolorenzo, G.; Rolandi, G. The 1538 Monte Nuovo eruption (Campi Flegrei, Italy). Bull. Volcanol. 1987, 49, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.; Acocella, V.; Aiello GBarra, D.; Battaglia, M.; Carandente, A.; Del Gaudio, C.; de Vita, S.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Ricco, C.; Scandone, R.; et al. Magma transfer at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) before the 1538 AD eruption. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piochi, M.; Mastrolorenzo, G.; Pappalardo, L. Magma ascent and eruptive processes from textural and compositional features of Monte Nuovo pyroclastic products, Campi Flegrei, Italy. Bull. Volcanol. 2005, 67, 663–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guidoboni, E.; Ciuccarelli, C. The Campi Flegrei caldera: Historical revision and new data on seismic crises, bradyseisms, the Monte Nuovo eruption and ensuing earthquakes (1582 AD). Bull. Volcanol. 2011, 73, 655–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandi, G.; Troise, C.; Sacchi, M.; di Lascio, M.; De Natale, G. The 1538 eruption at Campi Flegrei resurgent caldera: Implications for future unrest and eruptive scenarios. EGUsphere 2024, 2024, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Troise, C.; Pingue, F.; Mastrolorenzo, G.; Pappalardo, L.; Battaglia, M.; Boschi, E. The Campi Flegrei caldera: Unrest mechanisms and hazards. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2006, 269, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Isaia, R. Fractures and faults in volcanic rocks (Campi Flegrei, Southern Italy): Insight into volcano-tectonic processes. Int. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 103, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, J.; Camanni, G.; Ferranti, L.; Isaia, R.; Sacchi, M.; Spiess, V.; Steinmann, L.; Vitale, S. Fault systems in the ofshore sector of the Campi Flegrei caldera (southern Italy): Implications for nested caldera structure, resurgent dome, and volcano-tectonic evolution. J. Struct. Geol. 2022, 163, 104723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, L.; Spiess, V.; Sacchi, M. The Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy): Formation and evolution in interplay with sea-level variations since the Campanian Ignimbrite eruption at 39 ka. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2016, 327, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinmann, L.; Spiess, V.; Sacchi, M. Post-collapse evolution of a coastal caldera system: Insights from a 3D multichannel seismic survey from the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2018, 349, 83–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Vitale, S.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Iannuzzi, E.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Troiano, A. Stratigraphy, structure and volcano-tectonic evolution of Solfatara maar diatreme (Campi Flegrei, Italy). Geol. Soc. Am. Bull 2015, 127, 1485–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosi, M.; Sbrana, A. Phlegrean fields. Quaderni de la ricerca scientifica. Cons. Naz. Delle Ric. 1987, 114, 1–175. [Google Scholar]
- Campi Flegrei. Active Volcanoes of the World; Orsi, G., D’Antonio, M., Civetta, L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 201–217. [Google Scholar]
- Parascandola, A. I Fenomeni Bradisismici del Serapeo di Pozzuoli; Stabilmento tipografico G. Genovese: Napoli, Italy, 1947; pp. 1–117. [Google Scholar]
- Morhange, C.; Bourcier, M.; Laborel, J.; Giallanella, C.; Goiran, J.P.; Crimaco, L.; Vecchi, L. New data on historical relative sea level movements in Pozzuoli, Phlaegrean Fields, southern Italy. Phys. Chem. Earth Part A 1999, 24, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, F.; Woo, J.; Kilburn, C.R.J.; Rolandi, G. Mechanisms of activity and unrest at large calderas. Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 2006, 269, 141–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, M.; Troise, C.; Obrizzo, F.; Pingue, F.; De Natale, G. Evidence for fluid migration as the source of deformation at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L01307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Auria, L.; Pepe, S.; Castaldo, R.; Giudicepietro, F.; Macedonio, G.; Ricciolino, P.; Tizzani, P.; Casu, F.; Lanari, R.; Manzo, M.; et al. Magma injection beneath the urban area of Naples: A new mechanism for the 2012–2013 volcanic unrest at Campi Flegrei caldera. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.; De Vivo, B.; Spera, F.J.; Bodnar, R.J.; Milia, A.; Nunziata, C.; Belkin, H.E.; Cannatelli, C. Thermodynamic model for uplift and deflation episodes (Bradyseism) associated with magmatic hydrothermal activity at the Campi Flegrei active volcanic center (Italy). Earth Sci. Rev. 2009, 97, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todesco, M.; Neri, A.; Esposti Ongaro, T.; Papale, P.; Rosi, M. Pyroclastic flow dynamics and hazard in a caldera setting: Application to Phlegrean Fields (Italy). Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2006, 7, Q11003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannatelli, C.; Spera, F.J.; Bodnar, R.J.; Lima, A.; De Vivo, B. Ground movement (bradyseism) in the Campi Flegrei volcanic area: A review. De Vivo, B., Harvey, E., Belkin, Rolandi, G., Vesuvius, Flegrei, C., Volcanism, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 407–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Gaudio, C.; Aquino, I.; Ricciardi, G.P.; Ricco, C.; Scandone, R. Unrest episodes at Campi Flegrei: A reconstruction of vertical ground movements during 1905–2009. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 195, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barberi, F.; Cassano, E.; La Torre, P.; Sbrana, A. Structural evolution of Campi Flegrei caldera in light of volcanological and geophysical data. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1991, 48, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricco, C.; Petrosino, S.; Aquino, I.; Del Gaudio, C.; Falanga, M. Some Investigations on a Possible Relationship between Ground Deformation and Seismic Activity at Campi Flegrei and Ischia Volcanic Areas (Southern Italy). Geosciences 2019, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falanga, M.; Aquino, I.; De Lauro, E.; Petrosino, S.; Ricco, C. New insights on ground deformation at Campi Flegrei caldera inferred from kinematics and dynamics investigation of borehole tilt. Earth Space Sci. 2023, 10, e2022EA002702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilburn, C.R.J.; De Natale, G.; Carlino, S. Progressive approach to eruption at Campi Flegrei caldera in southern Italy. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Pingue, F. Ground Deformations in Collapsed Caldera Structures. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1993, 57, 19–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Petrazzuoli, S.M.; Pingue, F. The effect of collapse structures on ground deformations in calderas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, S.; Matano, F.; Caccavale, M.; Sacchi, M. Annual rates of ground deformation (1993-2010) at Campi Flegrei, Italy, revealed by Persistent Scatterer Pair (PSP)—SAR Interferometry. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 6160–6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciolino, P.; Lo Bascio, D.; Esposito, R. GOSSIP—Database sismologico Pubblico INGV-Osservatorio Vesuviano. Istituto Nazionale di Geofisica e Vulcanologia (INGV). 2024. Available online: https://terremoti.ov.ingv.it/gossip/ (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Ortolani, F.; Pagliuca, S. Principali effetti superficiali del bradisismo di Pozzuoli (Campania) e relazioni con le caratteristiche geologico-tecniche dei terreni. Mem. Soc. Geol. It. 1988, 41, 963–968. [Google Scholar]
- Pingue, F.; Petrazzuoli, S.M.; Obrizzo, F.; Tammaro, U.; De Martino, P.; Zuccaro, G. Monitoring system of buildings with high vulnerability in presence of slow ground deformations (The Campi Flegrei, Italy, case). Measurement 2011, 44, 1628–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somma, R.; Iuliano, S.; Matano, F.; Molisso, F.; Passaro, S.; Sacchi, M.; Troise, C.; De Natale, G. High-resolution morpho-bathymetry of Pozzuoli Bay, southern Italy. J. Maps 2016, 12, 222–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiglieri, M.; Falanga, M.; Tammaro, U.; De Martino, P.; Obrizzo, F.; Godano, C.; Pingue, F. Characterization of GPS time series at the Neapolitan volcanic area by statistical analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, B10416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, P.; Dolce, M.; Brandi, G.; Scarpato, G.; Tammaro, U. The Ground Deformation History of the Neapolitan Volcanic Area (Campi Flegrei Caldera, Somma-Vesuvius Volcano, and Ischia Island) from 20 years of continuous GPS observations (2000–2019). Rem. Sens. 2021, 13, 2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanseen, R.F. Radar Interferometry: Data Interpretation and Error Analysisf; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 978-0792369455. [Google Scholar]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L23611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardo, G.; Isaia, R.; Ventura, G.; De Martino, P.; Terranova, C. InSAR Permanent Scatterer analysis reveals fault re-activation during inflation and deflation episodes at Campi Flegrei caldera. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2373–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabriel, A.K.; Goldstein, R.M.; Zebker, H.A. Mapping small elevation changes over large areas: Differential radar interferometry. J. Geophys. Res. 1989, 94, 9183–9191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalavrezou, I.-E.; Castro-Melgar, I.; Nika, D.; Gatsios, T.; Lalechos, S.; Parcharidis, I. Application of Time Series IN-SAR (SBAS) Method Using Sentinel-1 for Monitoring Ground Deformation of the Aegina Island (Western Edge of Hel-lenic Volcanic Arc). Land 2024, 13, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poland, M.P.; Zebker, H.A. Volcano geodesy using InSAR in 2020; the past and next decades. Bull. Volcanol. 2022, 84, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccaro, L.; Tolomei, C.; Gianardi, R.; Sepe, V.; Bisson, M.; Colini, L.; De Ritis, R.; Spinetti, C. Multitemporal and multisensory InSAR analysis for ground displacement field assessment at Ischia volcanic island (Italy). Remote Sens. 2021, 13, 4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezquerro, P.; Bru, G.; Galindo, I.; Montserrat, O.; García-Davalillo, J.C.; Sánchez, N.; Montoya, I.; Palamá, R.; Mateos, R.M.; Pérez-López, R.; et al. Analysis of SAR-derived products to support emergency management during volcanic crisis: La Palma case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2023, 295, 113668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matano, F. Analysis and Classification of Natural and Human-Induced Ground Deformations at Regional Scale (Campania, Italy) Detected by Satellite Synthetic-Aperture Radar Interferometry Archive Datasets. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilardo, G.; Ventura, G.; Terranova, C.; Matano, F.; Nardò, S. Ground deformation due to tectonic, hydrothermal, gravity, hydrogeological and anthropic processes in the Campania Region (Southern Italy) from Permanent Scatterers Synthetic Aperture Radar Interferometry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosetto, M.; Solari, L.; Balasis-Levinsen, J.; Bateson, L.; Casagli, N.; Frei, M.; Oyen, A.; Moldestad, D.A.; Mróz, M. Deformation monitoring at European Scale: The Copernicus Ground Motion Service. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2021, 43, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbazi, S.; Crosetto, M.; Barra, A. Ground Deformation Analysis Using Basic Products of the Copernicus Ground Motion Service. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2022, 43, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Fumagalli, A.; Novali, F.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F.; Rucci, A. A new algorithm for processing interferometric data-stacks: SqueeSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 3460–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannaccone, G.; Guardato, S.; Donnarumma, G.P.; De Martino, P.; Dolce, M.; Macedonio, G.; Chierici, F.; Beranzoli, L. Measurement of seafloor deformation in the marine sector of the Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2018, 123, 66–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, S.; Natale, J. Combined volcano-tectonic processes for the drowning of the Roman western coastal settlements at Campi Flegrei (southern Italy). Earth Planets Space 2023, 75, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogi, K. Relations between the eruptions of various volcanoes and the deformations of the ground surfaces around them. Earthq. Res. Inst. 1958, 36, 99–134. [Google Scholar]
- Natale, J.; Vitale, S.; Repola, L.; Monti, L.; Isaia, R. Geomorphic analysis of digital elevation model generated from vintage aerial photographs: A glance at the pre-urbanization morphology of the active Campi Flegrei caldera. Geomorphology 2024, 460, 109267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natale, J. Geomorphic Analysis of Digital Elevation Model Generated from Vintage Aerial Photographs: A Glance at the Pre-Urbanization Morphology of the Active Campi Flegrei Caldera. OSF Data Repository. 2024. Available online: https://osf.io/tx9hv/ (accessed on 27 November 2024).
- Natale, J.; Ferranti, L.; Isaia, R.; Marino, C.; Sacchi, M.; Spiess, V.; Steinmann, L.; Vitale, S. Integrated on-land-offshore stratigraphy of the Campi Flegrei caldera: New insights into the volcano-tectonic evolution in the last 15 kyr. Basin Res. 2022, 34, 855–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, P.; Dolce, M.; Brandi, G.; Scarpato GTammaro, U. Campi Flegrei cGPS Daily Timeseries (2000–2019) [Data set]. Zenodo 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, P.; Dolce, M.; Brandi, G.; Scarpato, G. Campi Flegrei cGPS Weekly Positions Time Series [Data set]. Zenodo 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilacqua, A.; Neri, A.; De Martino, P.; Isaia, R.; Novellino, A.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S. Radial interpolation of GPS and leveling data of ground deforma-tion in a resurgent caldera: Application to Campi Flegrei (Italy). J. Geod. 2020, 94, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EGMS. Dataset Validated Ortho 2015–2021 (Vector). European Ground Motion Service. 2024. Available online: https://sdi.eea.europa.eu/catalogue/srv/api/records/943e9cbb-f8ef-4378-966c-63eb761016a9?language=all (accessed on 28 November 2024).
- Lundgren, P.; Usai, S.; Sansosti, E.; Lanari, R.; Tesauro, M.; Fornaro, G.; Berardino, P. Modeling surface deformation observed with synthetic aperture radar interferometry at Campi Flegrei caldera. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 19355–19366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaia, R.; Di Giuseppe, M.G.; Natale, J.; Troiano, A.; Tramparulo, F.D.A.; Vitale, S. Volcano-tectonic setting of the Pisciarelli Fumarole Field, Campi Flegrei caldera, southern Italy: Insights into fluid circulation patterns and hazard scenarios. Tectonics 2021, 40, e2020TC006227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrosino, S.; De Siena, L. Fluid migrations and volcanic earthquakes from depolarized ambient noise. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretti, R.; De Natale, G.; Troise, C. A geochemical and geophysical reappraisal to the significance of the recent unrest at Campi Flegrei caldera (Southern Italy). Geochem. Geophys. Geosystems 2017, 18, 1244–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Iannaccone, G.; Martini, M.; Zollo, A. Seismic sources and attenuation properties at Campi Flegrei volcanic area. Pure Appl. Geoph. 1987, 125, 883–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Novellis, V.; Carlino, S.; Castaldo, R.; Tramelli, A.; De Luca, C.; Pino, N.A.; Pepe, S.; Convertito, V.; Zinno, I. The 21st August 2017 Ischia (Italy) earthquake source model inferred from seismological, GPS and DInSAR measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 17296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Natale, G.; Zollo, A.; Ferraro, A.; Virieux, J. Accurate fault mechanism determinations for a 1984 earthquake swarm at Campi Flegrei caldera (Italy) during an unrest episode: Implications for volcanological research. J. Geophys. Res. 1995, 100, 24167–24185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troise, C.; De Natale, G.; Pingue, F.; Zollo, A. A model for earthquake generation during unrest episodes at Campi Flegrei and Rabaul calderas. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1997, 24, 1575–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mc Tigue, D.F. Elastic stress and deformation near a finite spherical magma body: Resolution of the point source paradox. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 12931–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).