Investigation of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Systems Based on Recycled Tire Rubber–Sand Mixtures
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. The Concept of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation
1.2. Research on Geotechnical Seismic Isolation
2. Materials and Methods
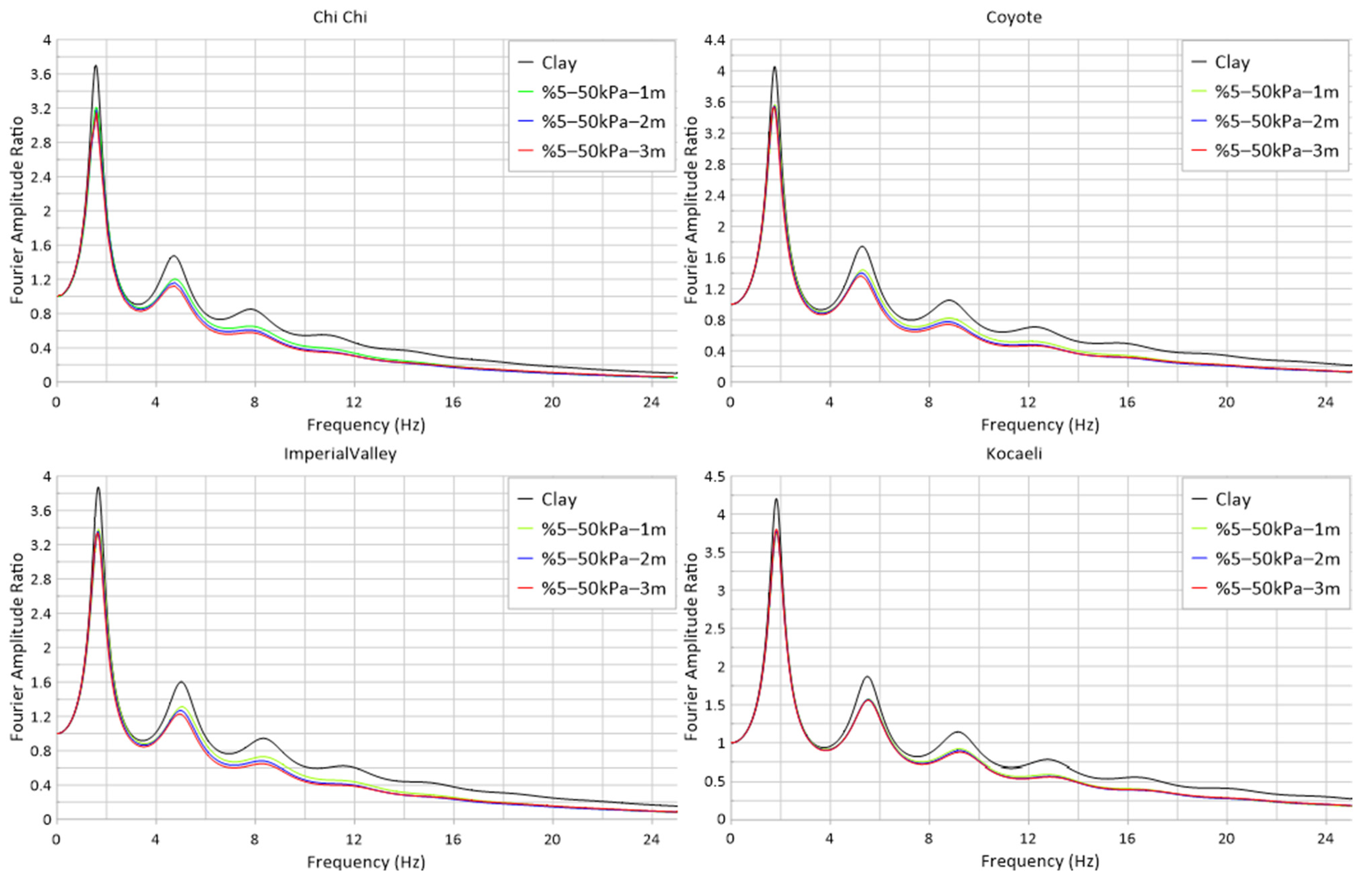
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Models’ Description
3.2. Ground Motions Selection
4. Conclusions and Recommendation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bozorgnia, Y.; Bertero, V. Damage spectra: Characteristics and applications to seismic risk reduction. ASCE J. Struct. Eng. 2003, 129, 1330–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, W.; Li, Y. Seismic isolation using granulated tire-soil mixtures for less developed regions: Experimental validation. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 42, 2187–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, A.W.; Igusa, T. Primer on Seismic Isolation; ASCE and Task Committee on Seismic Isolation: Reston, VA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Yegian, M.K.; Catan, M. Soil isolation for seismic protection using a smooth synthetic liner. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. ASCE 2004, 130, 1131–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edil, T.; Bosscher, P. Engineering properties of tire chips and soil mixtures. Geotech. Test. J. 1994, 17, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H. Seismic isolation by rubber-soil mixtures for developing countries. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2008, 37, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, H.H.; Lo, S.H.; Xu, X.; Sheikh, M.N. Seismic isolation for low-to-medium-rise buildings using granulated rubber-soil mixtures: Numerical study. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2012, 41, 2009–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Tian, W.; He, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, J. Seismic isolation effect of rubber-sand mixture cushion under different site classes based on a simplified analysis model. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2023, 166, 107738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Sun, H.; Jing, L.; Dong, R. Geotechnical seismic isolation system based on rubber-sand mixtures for rural residence buildings: Shaking table test. Materials 2022, 15, 7724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yıldız, Ö. Numerical analysis of geotechnical seismic isolation system for high-rise buildings. Naturengs MTU J. Eng. Nat. Sci. 2021, 34, 34–43. [Google Scholar]
- Pitilakis, K.; Karapetrou, S.; Tsagdi, K. Numerical investigation of the seismic response of RC buildings on soil replaced with rubber-sand mixtures. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2015, 79, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakhaei, A.; Marandin, K.; Kermani, B.; Bagheripour, M. Dynamic properties of granular soils mixed with granulated rubber. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2012, 43, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.Y.; Sutter, K.G. Dynamic properties of granulated rubber/sand mixtures. Geotech. Test. J. 2000, 23, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edincliler, A.; Yıldız, Ö. Effects of processing type on shear modulus and damping ratio of waste tire-sand mixtures. Geosynth. Int. 2022, 29, 389–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pistolas, S.; Anastasiadis, A.; Pitilakis, K. Dynamic behaviour of granular soil materials mixed with granulated rubber: Effect of rubber content and granularity on the small-strain shear modulus and damping ratio. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2018, 36, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Ntambakwa, E.; Mendes, B. Comparison of 1-D seismic site response analysis tools for layered liquefiable deposits at an offshore windfarm site. E3S Web Conf. 2020, 205, 12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashash, Y.M.A.; Musgrove, M.I.; Harmon, J.A.; Ilhan, O.; Xing, G.; Numanoglu, O.; Groholski, D.R.; Phillips, C.A.; Park, D. DEEPSOIL 7.0, User Manual; University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign: Urbana, IL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Elgamal, A.; Yang, Z.; Lu, J. Cyclic 1D Seismic Ground Response Version 1.4 User’s Manual; Department of Structural Engineering, University of California: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- PLAXIS. Ground Response Analysis in PLAXIS 2D; PLAXIS: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Niazi, S. Earthquake Response Analysis of Buildings. Master’s Thesis, Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, Norway, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bardet, J.P.; Ichii, K.; Lin, C.H. EERA—A Computer Program for Equivalent-Linear Earthquake Site Response Analyses of Layered Soil Deposits; Department of Civil Engineering, University of Southern California: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bildik, S.; Savaşeri, K.; Duale, A.Y.; Büyükgökçe, F.; Laman, M. The evaluation of the performance of improved soils experimetally and numerically. In Proceedings of the 8th International Geotechnical Symposium, Istanbul, Türkiye, 13–15 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Silahtar, A. Assessment of Isparta Basin by Using 1D Nonlinear Site Response Analysis Approach; 1914 Burdur (Ms: 7.0) Earthquake Scenario. J. Nat. Hazards Environ. 2021, 7, 226–239. [Google Scholar]
- Timur, S. The Effect of Local Site Characteristics on the Results of One-Dimensional Dynamic Site Response Analysis. Doctoral Dissertation, Dokuz Eylül University, Izmir, Türkiye, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, Y.; Kim, D.; Jeong, S.; Kim, H. Analysis of multilayered ground amplification characteristics by scaled-down model tests. Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 3432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.K.; Kim, H.C. Performance of a multi-story structure with a resilient-friction base isolation system. Comput. Struct. 2004, 82, 2271–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajan, S.; Saravanathiiban, S. Modeling of energy dissipation in structural devices and foundation soil during seismic loading. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2011, 31, 1106–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darendeli, M.B. Development of a New Family of Normalized Modulus Reduction and Material Damping Curves. Doctoral Dissertation, University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, B.O.; Drnevich, V.P. Shear modulus and damping in soils: Design equations and curves. J. Soil Mech. Found. Eng. Div. 1972, 98, 667–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, A.J.; Madabhushi, S.P.G. Amplification of seismic accelerations at slope crests. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göktepe, F.; Çelebi, E.; Omid, A.J. Numerical and experimental study on scaled soil-structure model for small shaking table tests. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2019, 119, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.M. Advanced Soil Mechanics; CRC Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, J.P. Dynamic Soil-Structure Interaction; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Naeim, F.; Kelly, J.M. Design of Seismic Isolated Structures; John Wiley Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]


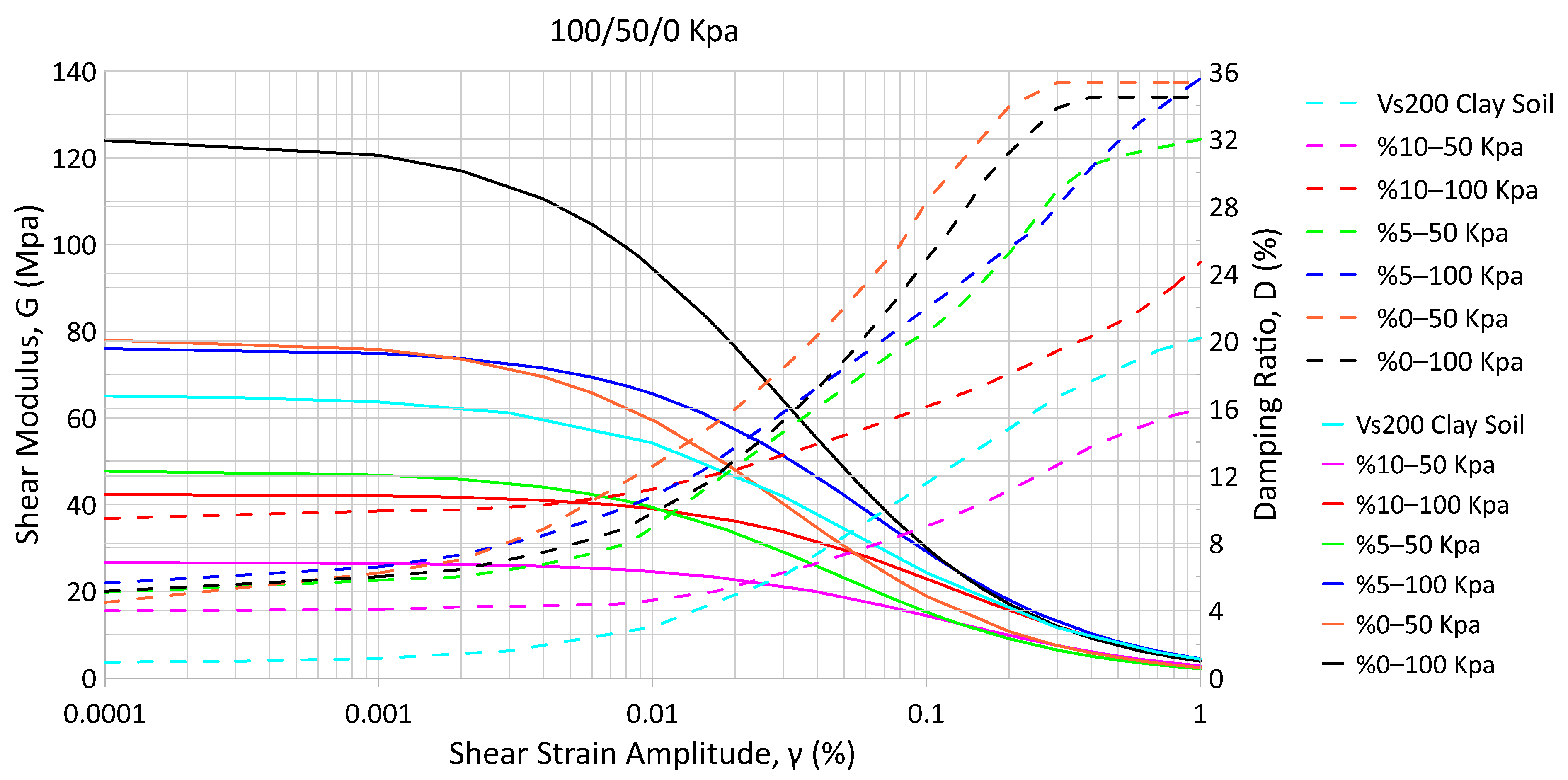
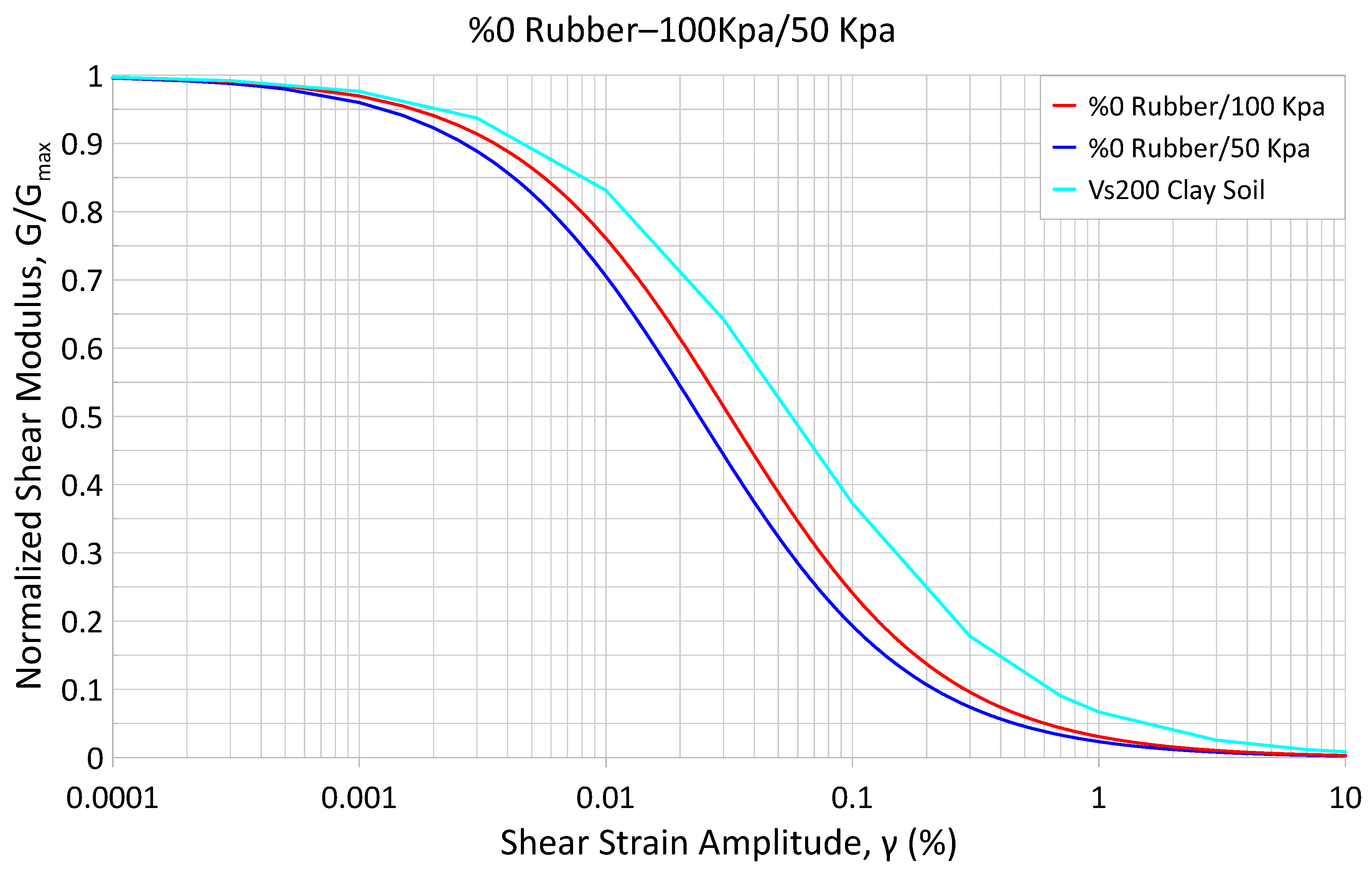


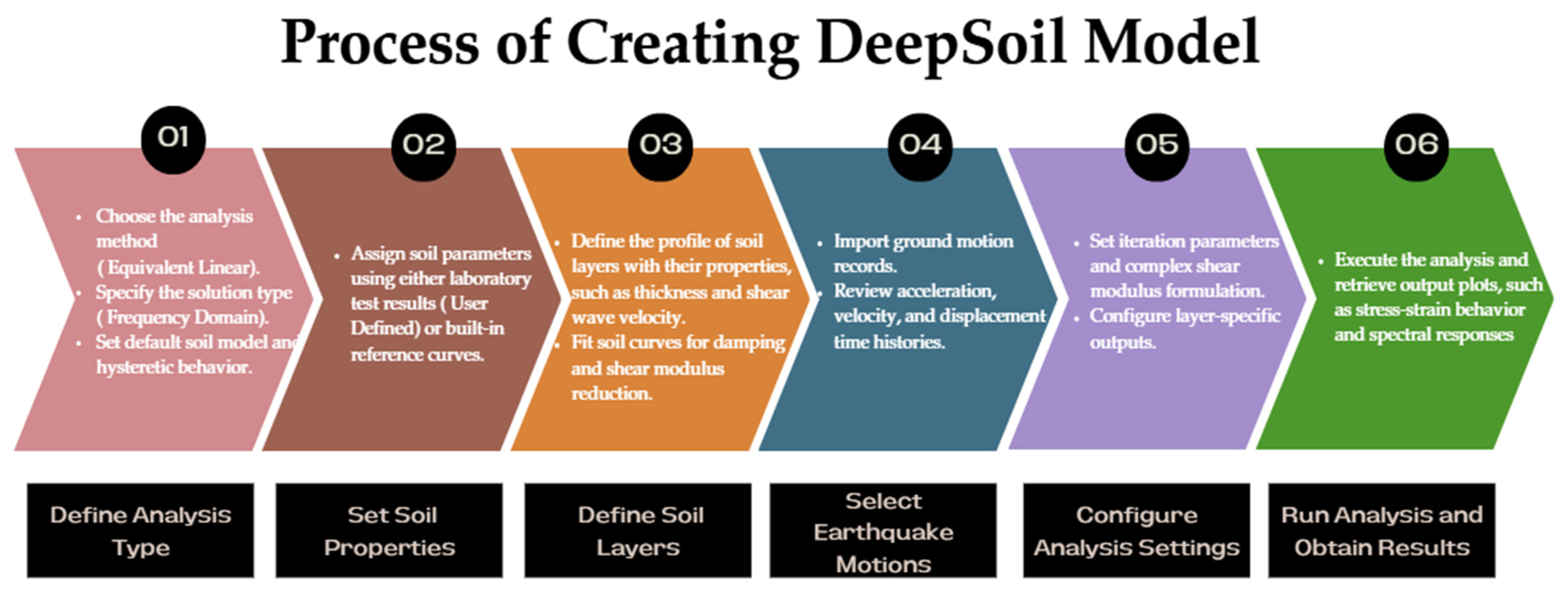








| Granular Rubber Content (%) | Moist Unit Weight (kN/m3) | Dry Unit Weight (kN/m3) | Void Ratio | Relative Density Dr (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.0 | 22.0 | 20.64 | 0.259 | 91.47 |
| 5.0 | 20.84 | 19.42 | 0.253 | 91.96 |
| 10.0 | 19.47 | 17.96 | 0.266 | 91.14 |
| Soil Type | z (m) | γ (kN/m3) | Vs (m/s) | σ3 (kPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Soft Clay | 20 | 16 | 200 | 160 |
| Sand with 10% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 17.96 | 152.14 | 100 |
| Sand with 5% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 19.415 | 196.09 | 100 |
| Sand with 0% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 20.64 | 243.15 | 100 |
| Sand with 10% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 17.96 | 120.61 | 50 |
| Sand with 5% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 19.415 | 155.45 | 50 |
| Sand with 0% Rubber Content | 1–3 | 20.64 | 192.77 | 50 |
| Earthquakes | Time (s) | Magnitude (MG) | Acceleration (g) | Arias Intensity (m/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ChiChi | 59.00 | 7.60 | 1.57 | 4.13 |
| Coyote | 26.83 | 5.74 | 0.92 | 0.57 |
| ImperialValley | 63.73 | 6.50 | 1.16 | 3.76 |
| Kocaeli | 30.00 | 7.50 | 1.18 | 0.68 |
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 152.14 | 152.14 | 152.14 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 9.91 | 9.91 | 9.91 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.461 | 2.424 | 2.387 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4063 | 0.4126 | 0.4189 | |||
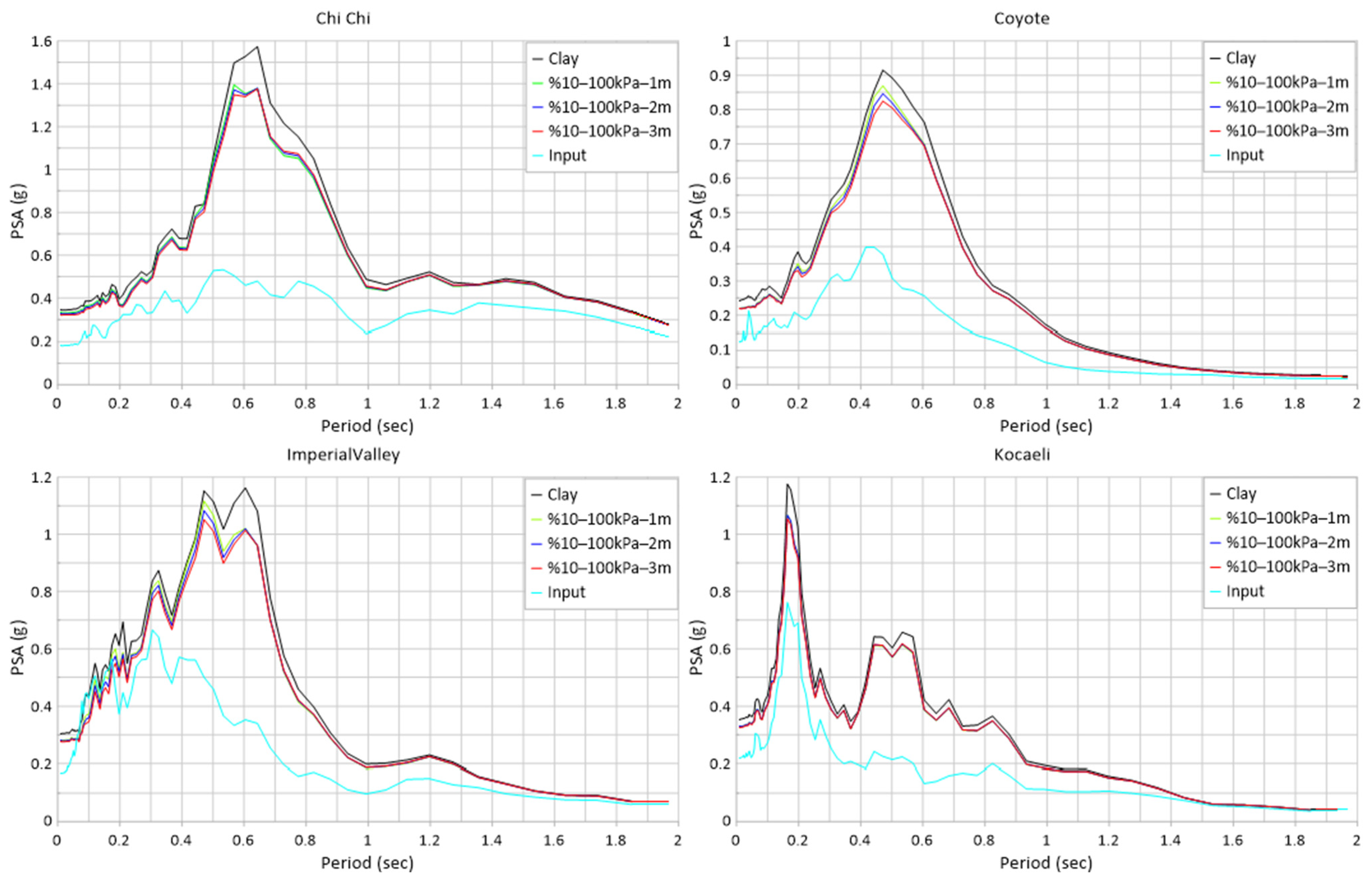
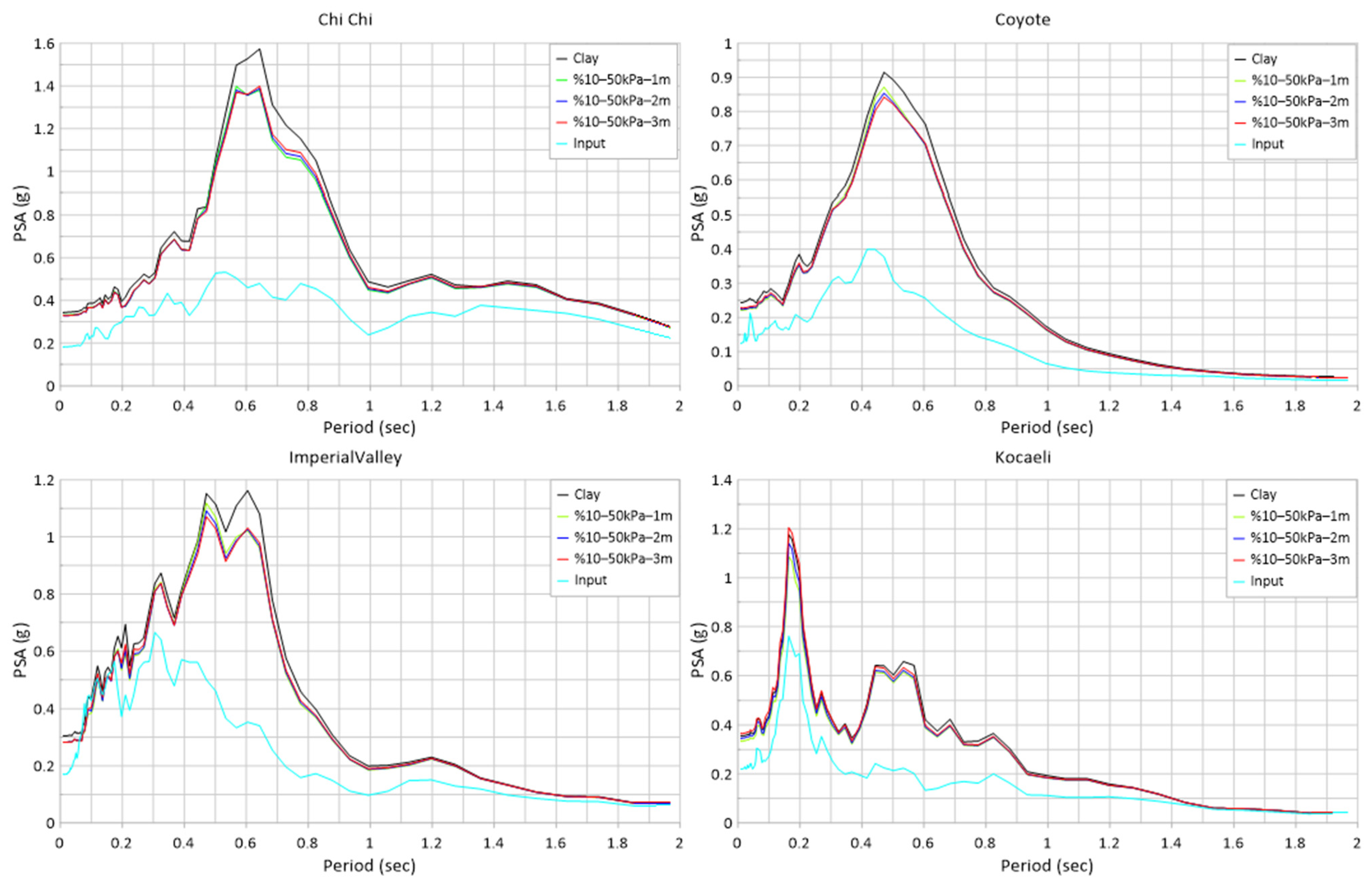
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %10–100 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–100 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–100 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.395 | −11.37% | 1.380 | −12.33% | 1.377 | −12.52% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.869 | −5.03% | 0.846 | −7.54% | 0.825 | −9.84% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.116 | −3.96% | 1.083 | −6.80% | 1.052 | −9.47% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.067 | −9.27% | 1.067 | −9.27% | 1.055 | −10.29% |
| Mean Value | −7.41% | −8.98% | −10.53% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 120.61 | 120.61 | 120.61 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 4.07 | 4.07 | 4.07 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.42 | 2.346 | 2.275 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4132 | 0.4263 | 0.4395 | |||
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %10–50 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–50 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–50 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.397 | −11.25% | 1.388 | −11.82% | 1.399 | −11.12% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.872 | −4.70% | 0.854 | −6.67% | 0.842 | −7.98% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.119 | −3.70% | 1.092 | −6.02% | 1.072 | −7.73% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.087 | −7.57% | 1.141 | −2.98% | 1.205 | 2.47% |
| Mean Value | −6.80% | −6.87% | −6.09% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 196.09 | 196.09 | 196.09 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 6.59 | 6.59 | 6.59 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.498 | 2.495 | 2.493 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4004 | 0.4008 | 0.4012 | |||
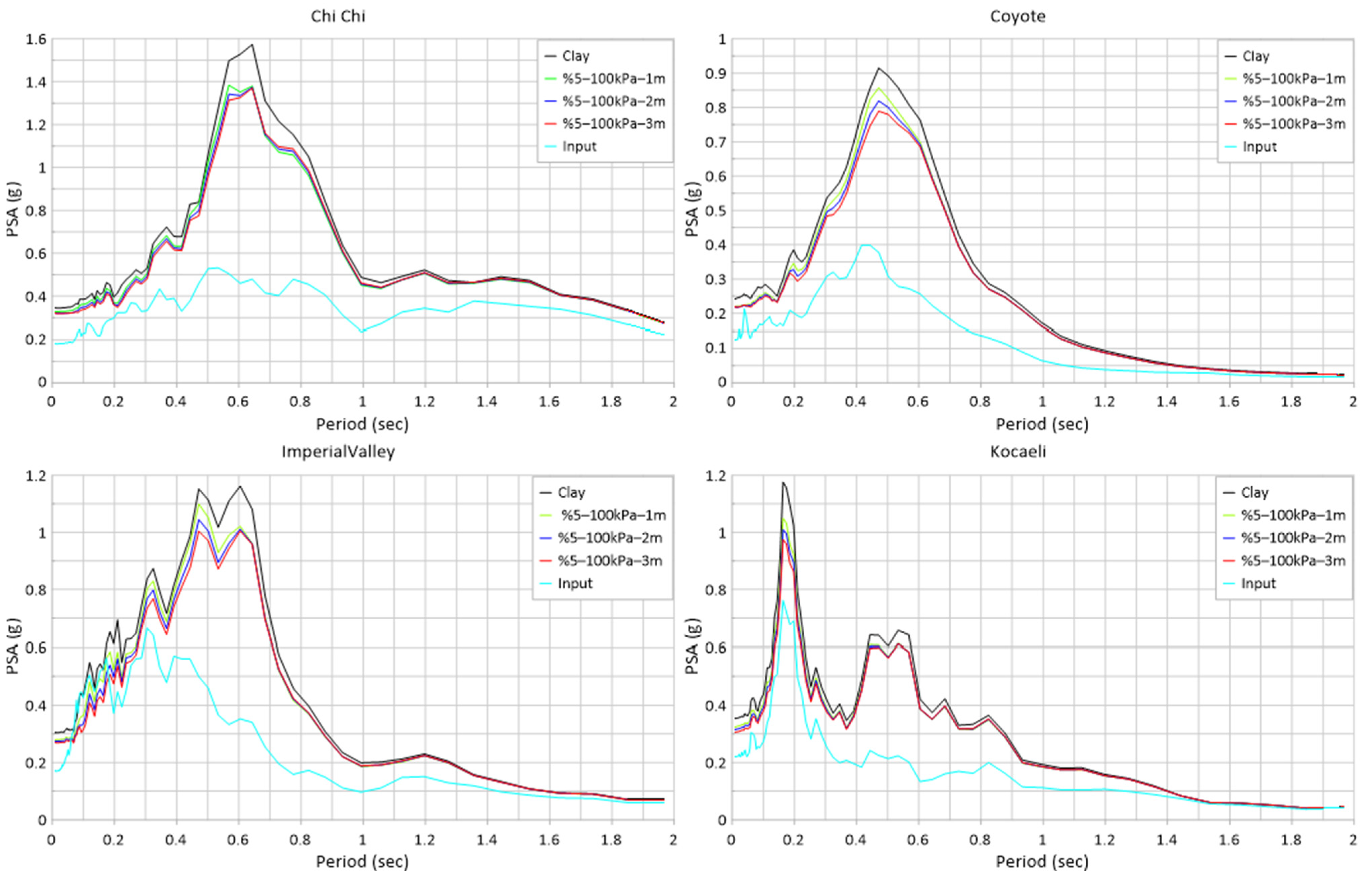
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %5–100 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–100 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–100 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.384 | −12.07% | 1.374 | −12.71% | 1.370 | −12.96% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.857 | −6.34% | 0.819 | −10.49% | 0.789 | −13.77% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.100 | −5.34% | 1.045 | −10.07% | 1.005 | −13.51% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.049 | −10.80% | 1.009 | −14.20% | 0.975 | −17.09% |
| Mean Value | −8.64% | −11.87% | −14.33% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 155.45 | 155.45 | 155.45 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 5.80 | 5.80 | 5.80 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.465 | 2.43 | 2.397 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4057 | 0.4115 | 0.4175 | |||
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %5–50 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–50 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–50 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.385 | −12.01% | 1.381 | −12.26% | 1.378 | −12.45% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.859 | −6.12% | 0.825 | −9.84% | 0.797 | −12.90% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.101 | −5.25% | 1.054 | −9.29% | 1.013 | −12.82% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.060 | −9.86% | 1.048 | −10.88% | 1.039 | −11.65% |
| Mean Value | −8.31% | −10.57% | −12.46% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 243.15 | 243.15 | 243.15 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 9.38 | 9.38 | 9.38 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.522 | 2.545 | 2.568 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.3965 | 0.3929 | 0.3894 | |||
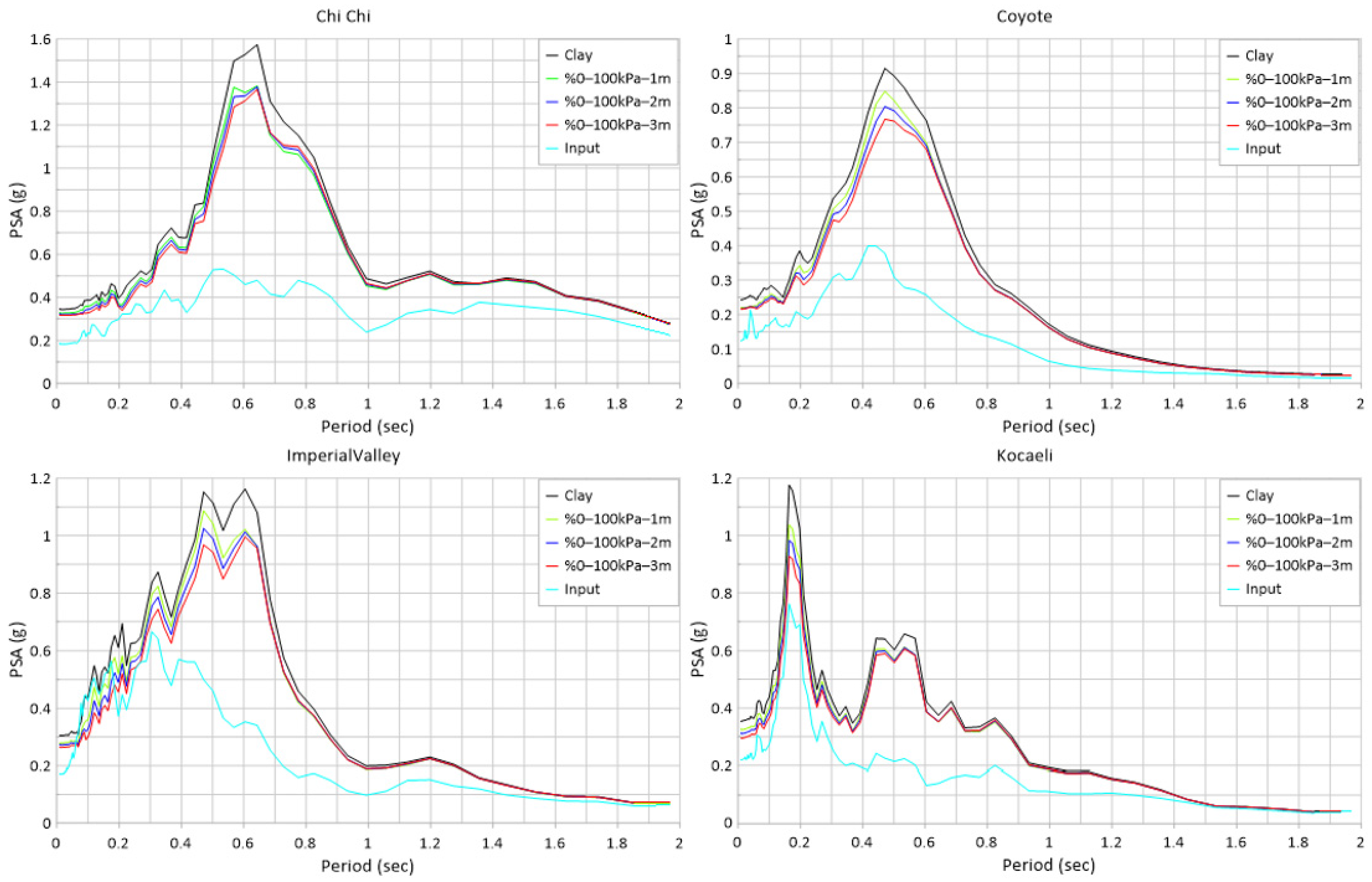
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %0–100 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–100 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–100 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.382 | −12.20% | 1.378 | −12.45% | 1.366 | −13.21% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.848 | −7.32% | 0.804 | −12.13% | 0.767 | −16.17% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.087 | −6.45% | 1.026 | −11.70% | 0.996 | −14.29% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.038 | −11.73% | 0.983 | −16.41% | 0.929 | −21.00% |
| Mean Value | −9.43% | −13.17% | −16.17% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 192.77 | 192.77 | 192.77 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 6.23 | 6.23 | 6.23 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.495 | 2.491 | 2.486 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4008 | 0.4015 | 0.4023 | |||
| Earthquake | EL PSA (g) | %0–50 kPa 1 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–50 kPa 2 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–50 kPa 3 m PSA (g) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 1.574 | 1.382 | −12.20% | 1.373 | −12.77% | 1.373 | −12.77% |
| Coyote | 0.915 | 0.849 | −7.21% | 0.793 | −13.33% | 0.773 | −15.52% |
| Imp. Valley | 1.162 | 1.088 | −6.37% | 1.007 | −13.34% | 1.001 | −13.86% |
| Kocaeli | 1.176 | 1.043 | −11.31% | 0.985 | −16.24% | 0.968 | −17.69% |
| Mean Value | −9.27% | −13.92% | −14.96% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 152.14 | 152.14 | 152.14 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 9.91 | 9.91 | 9.91 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.461 | 2.424 | 2.387 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4063 | 0.4126 | 0.4189 | |||
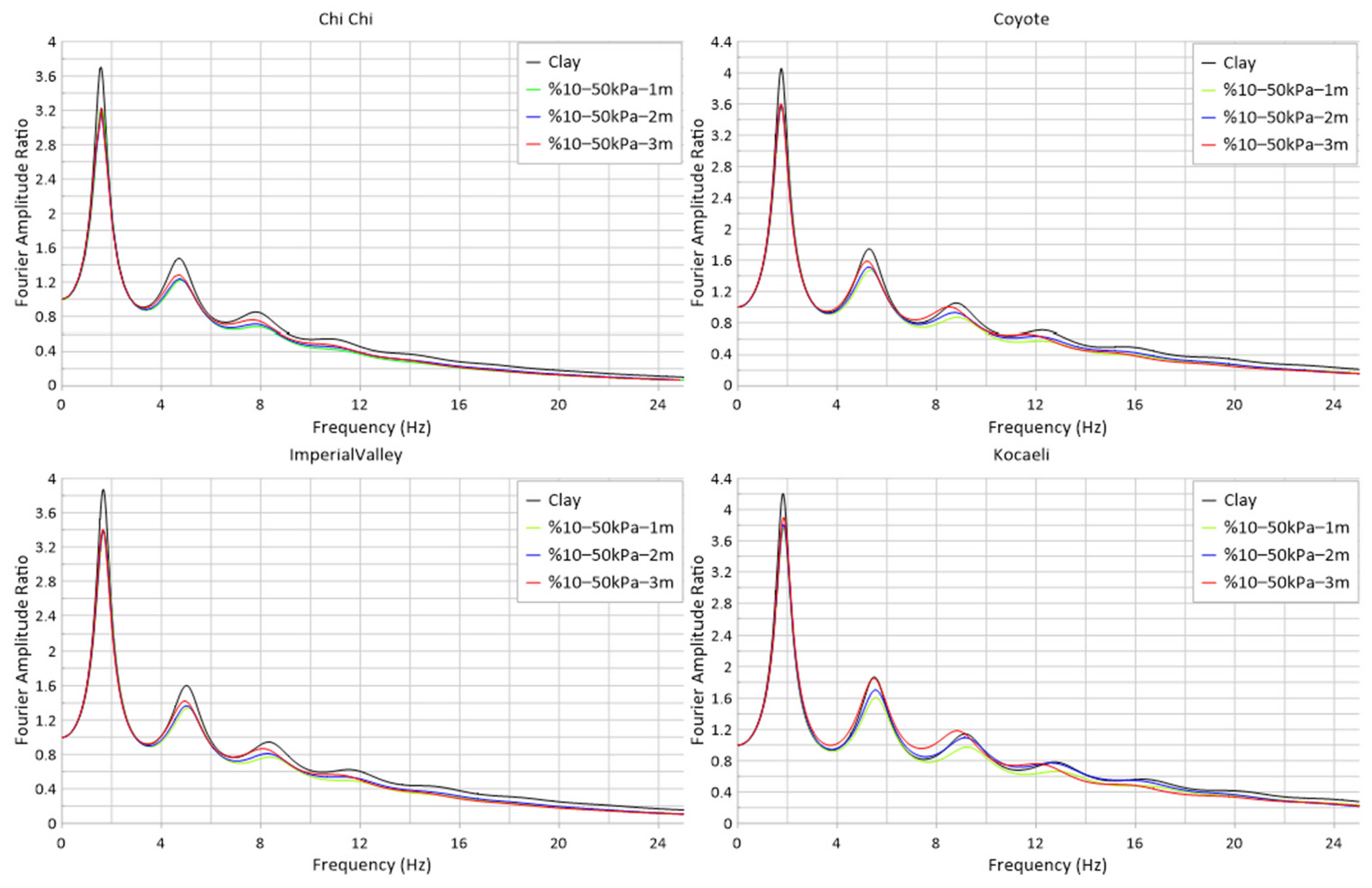
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %10–100 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–100 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–100 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.212 | −13.24% | 3.199 | −13.59% | 3.179 | −14.13% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.567 | −12.06% | 3.554 | −12.38% | 3.534 | −12.87% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.383 | −12.65% | 3.364 | −13.14% | 3.343 | −13.68% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.745 | −10.83% | 3.770 | −10.24% | 3.790 | −9.76% |
| Mean Value | −12.19% | −12.34% | −12.61% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 120.61 | 120.61 | 120.61 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 4.07 | 4.07 | 4.07 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.42 | 2.346 | 2.275 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4132 | 0.4263 | 0.4395 | |||
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %10–50 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–50 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %10–50 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.217 | −13.10% | 3.220 | −13.02% | 3.232 | −12.70% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.574 | −11.88% | 3.580 | −11.74% | 3.603 | −11.17% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.389 | −12.50% | 3.388 | −12.52% | 3.403 | −12.14% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.753 | −10.64% | 3.808 | −9.33% | 3.899 | −7.17% |
| Mean Value | −12.03% | −11.65% | −10.79% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 196.09 | 196.09 | 196.09 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 6.59 | 6.59 | 6.59 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.498 | 2.495 | 2.493 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4004 | 0.4008 | 0.4012 | |||
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %5–100 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–100 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–100 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.207 | −13.37% | 3.166 | −14.48% | 3.141 | −15.15% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.562 | −12.18% | 3.527 | −13.04% | 3.506 | −13.56% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.376 | −12.83% | 3.334 | −13.92% | 3.313 | −14.46% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.744 | −10.86% | 3.747 | −10.79% | 3.755 | −10.60% |
| Mean Value | −12.31% | −13.06% | −13.44% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 155.45 | 155.45 | 155.45 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 5.80 | 5.80 | 5.80 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.465 | 2.43 | 2.397 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4057 | 0.4115 | 0.4175 | |||
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %5–50 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–50 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %5–50 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.210 | −13.29% | 3.187 | −13.91% | 3.158 | −14.69% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.566 | −12.08% | 3.547 | −12.55% | 3.533 | −12.89% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.379 | −12.75% | 3.355 | −13.37% | 3.336 | −13.87% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.748 | −10.76% | 3.774 | −10.14% | 3.802 | −9.48% |
| Mean Value | −12.22% | −12.49% | −12.73% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 243.15 | 243.15 | 243.15 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 9.38 | 9.38 | 9.38 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.522 | 2.545 | 2.568 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.3965 | 0.3929 | 0.3894 | |||
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %0–100 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–100 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–100 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.206 | −13.40% | 3.169 | −14.40% | 3.106 | −16.10% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.561 | −12.20% | 3.530 | −12.97% | 3.490 | −13.95% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.373 | −12.91% | 3.339 | −13.79% | 3.297 | −14.87% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.745 | −10.83% | 3.752 | −10.67% | 3.738 | −11.00% |
| Mean Value | −12.34% | −12.96% | −13.98% | ||||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Clay Soil Layer (m/s) | 200 | ||||||
| Profile Depth (m) | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | |||
| Isolation (m) | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |||
| Shear Wave Velocity of Isolation Layer (m/s) | - | 192.77 | 192.77 | 192.77 | |||
| Initial Damping Ratio (%) | - | 6.23 | 6.23 | 6.23 | |||
| Natural Frequency (Hz) | 2.5 | 2.495 | 2.491 | 2.486 | |||
| Natural Period (s) | 0.4 | 0.4008 | 0.4015 | 0.4023 | |||
| Earthquake | EL (Hz) | %0–50 kPa 1 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–50 kPa 2 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) | %0–50 kPa 3 m Amp. Ratio (Hz) | Damping Ratio (%) |
| ChiChi | 3.702 | 3.208 | −13.34% | 3.164 | −14.53% | 3.165 | −14.51% |
| Coyote | 4.056 | 3.563 | −12.15% | 3.512 | −13.41% | 3.511 | −13.44% |
| Imp. Valley | 3.873 | 3.375 | −12.86% | 3.319 | −14.30% | 3.316 | −14.38% |
| Kocaeli | 4.200 | 3.748 | −10.76% | 3.738 | −11.00% | 3.772 | −10.19% |
| Mean Value | −12.28% | −13.31% | −13.13% | ||||
| Earthquakes | 1 m | 2 m | 3 m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% rubber at 50 kPa | %6.8 | %6.87 | %6.09 |
| 10% rubber at 100 kPa | %7.41 | %8.98 | %10.53 |
| 5% rubber at 50 kPa | %8.31 | %10.57 | %12.46 |
| 5% rubber at 100 kPa | %8.64 | %11.87 | %14.33 |
| 0% rubber at 50 kPa | %9.27 | %13.92 | %14.96 |
| 0% rubber at 100 kPa | %9.43 | %13.17 | %16.17 |
| Earthquakes | 1 m | 2 m | 3 m |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10% rubber at 50 kPa | 2.420 Hz | 2.346 Hz | 2.275 Hz |
| 10% rubber at 100 kPa | 2.461 Hz | 2.424 Hz | 2.387 Hz |
| 5% rubber at 50 kPa | 2.465 Hz | 2.430 Hz | 2.397 Hz |
| 5% rubber at 100 kPa | 2.498 Hz | 2.495 Hz | 2.493 Hz |
| 0% rubber at 50 kPa | 2.495 Hz | 2.491 Hz | 2.486 Hz |
| 0% rubber at 100 kPa | 2.522 Hz | 2.545 Hz | 2.568 Hz |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sağlam, D.; Tonaroğlu, M. Investigation of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Systems Based on Recycled Tire Rubber–Sand Mixtures. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042133
Sağlam D, Tonaroğlu M. Investigation of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Systems Based on Recycled Tire Rubber–Sand Mixtures. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(4):2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042133
Chicago/Turabian StyleSağlam, Doğan, and Murat Tonaroğlu. 2025. "Investigation of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Systems Based on Recycled Tire Rubber–Sand Mixtures" Applied Sciences 15, no. 4: 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042133
APA StyleSağlam, D., & Tonaroğlu, M. (2025). Investigation of Geotechnical Seismic Isolation Systems Based on Recycled Tire Rubber–Sand Mixtures. Applied Sciences, 15(4), 2133. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15042133





