A Novel Scenario-Based Comparative Framework for Short- and Medium-Term Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Deep Learning Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Study Motivation
1.2. Case Study Contribution
- This study establishes the first comprehensive deep learning forecasting benchmark for Southeastern Anatolia, a region characterized by high solar potential yet high meteorological volatility. Unlike studies relying on simulated data, this work utilizes high-resolution field data to validate model robustness against specific regional climatic stressors.
- Rather than a generic performance evaluation, the proposed framework designs six distinct forecasting scenarios (ranging from 1-h to 1-month horizons) to systematically stress-test the temporal generalization capabilities of Recurrent (LSTM, GRU) versus Convolutional (CNN) architectures under varying observational windows.
- The study provides empirical evidence demonstrating the superior adaptability of localized LSTM models over CNNs for medium-term horizons in this specific geographical context, offering a validated roadmap for grid operators in similar semi-arid climate zones.
2. Materials and Methods
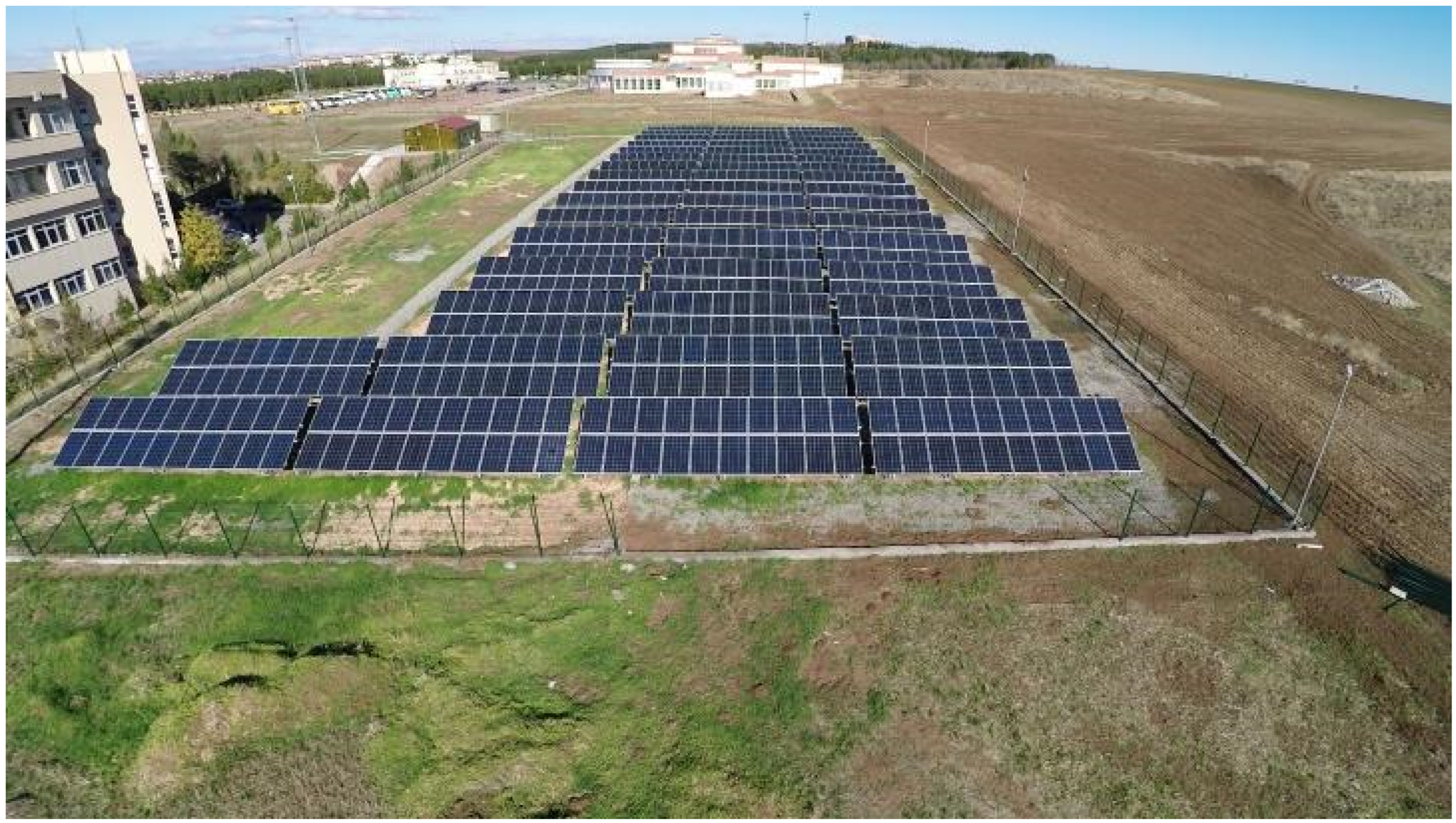
2.1. System Description
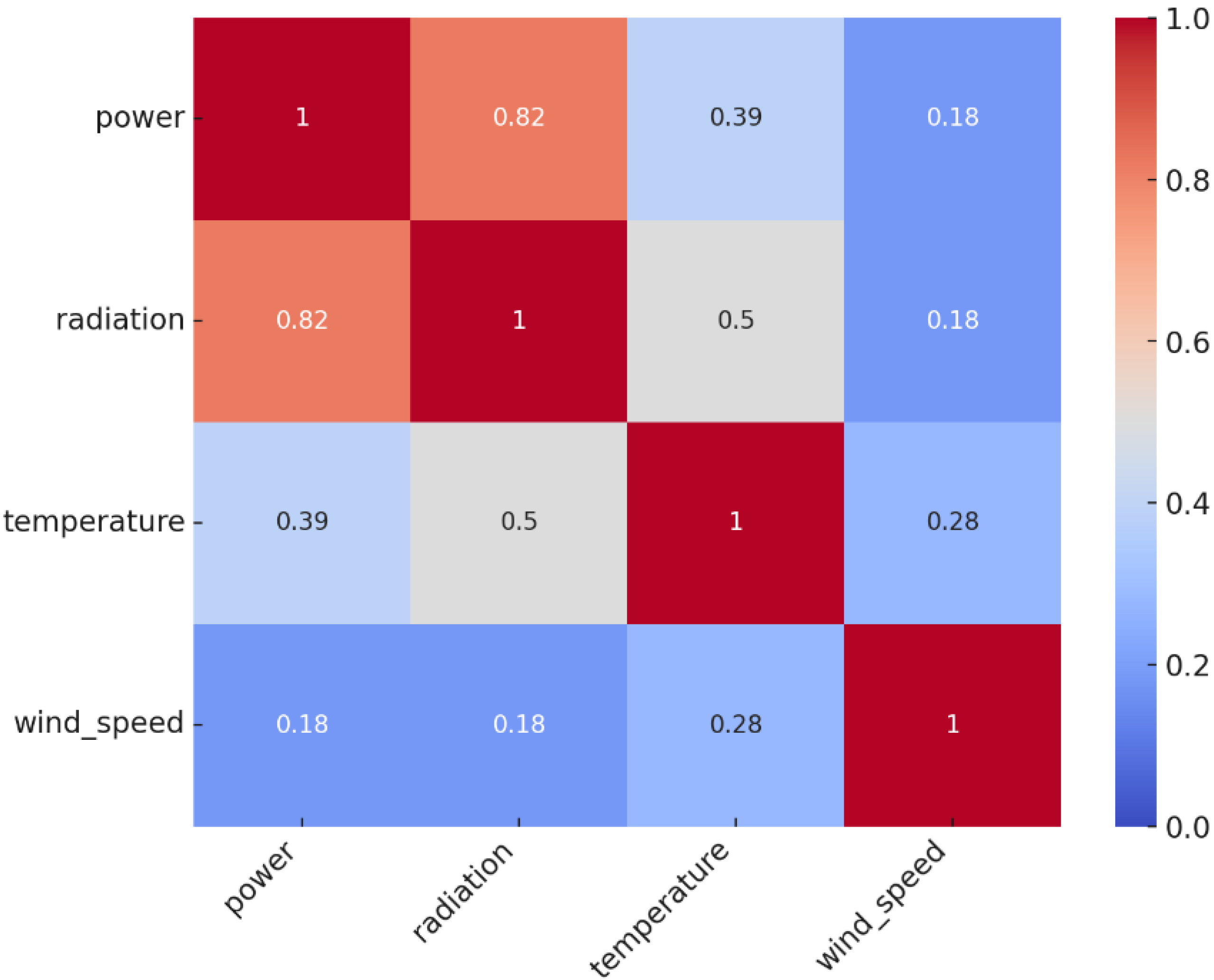
2.2. Data Statistical Analysis
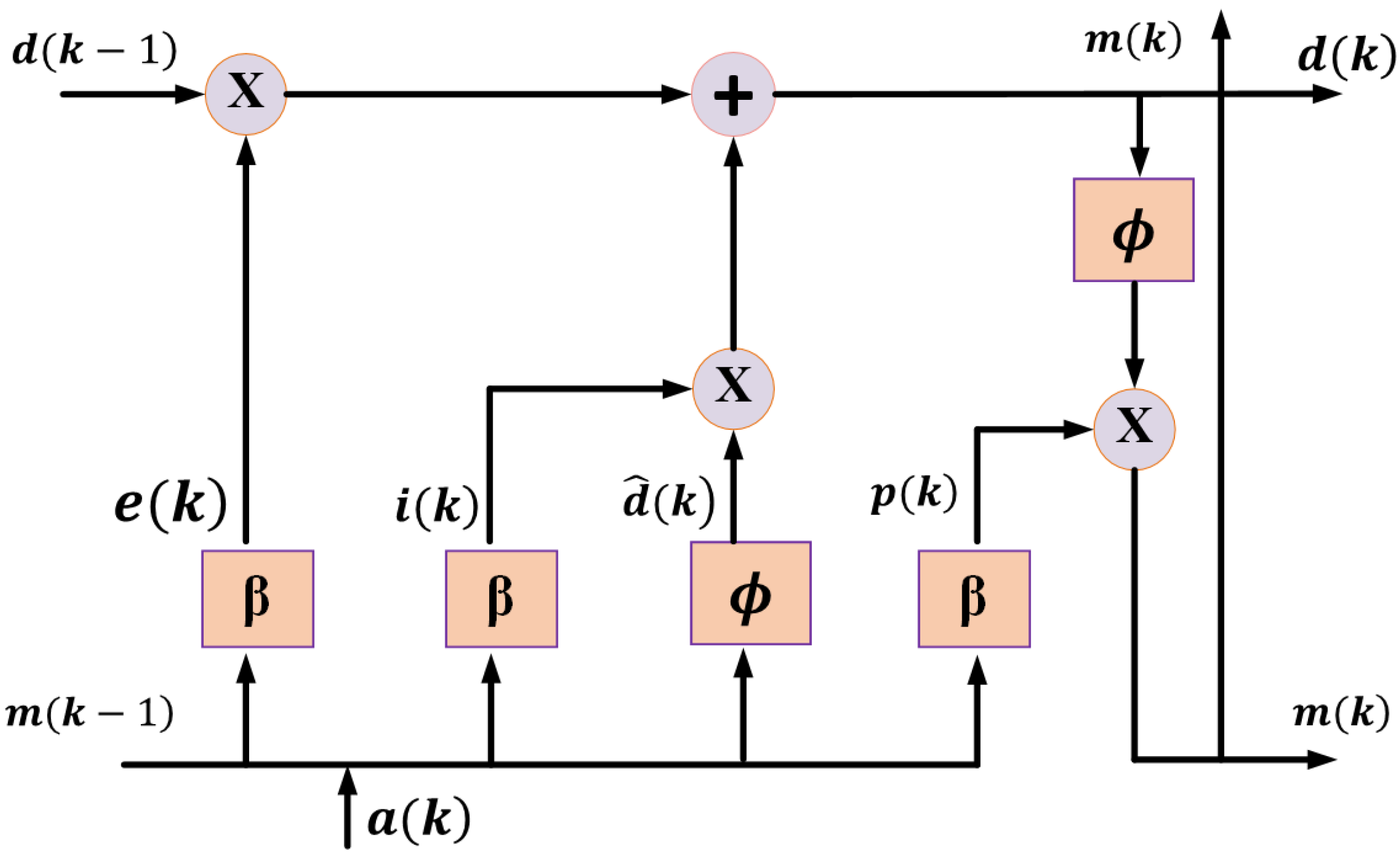
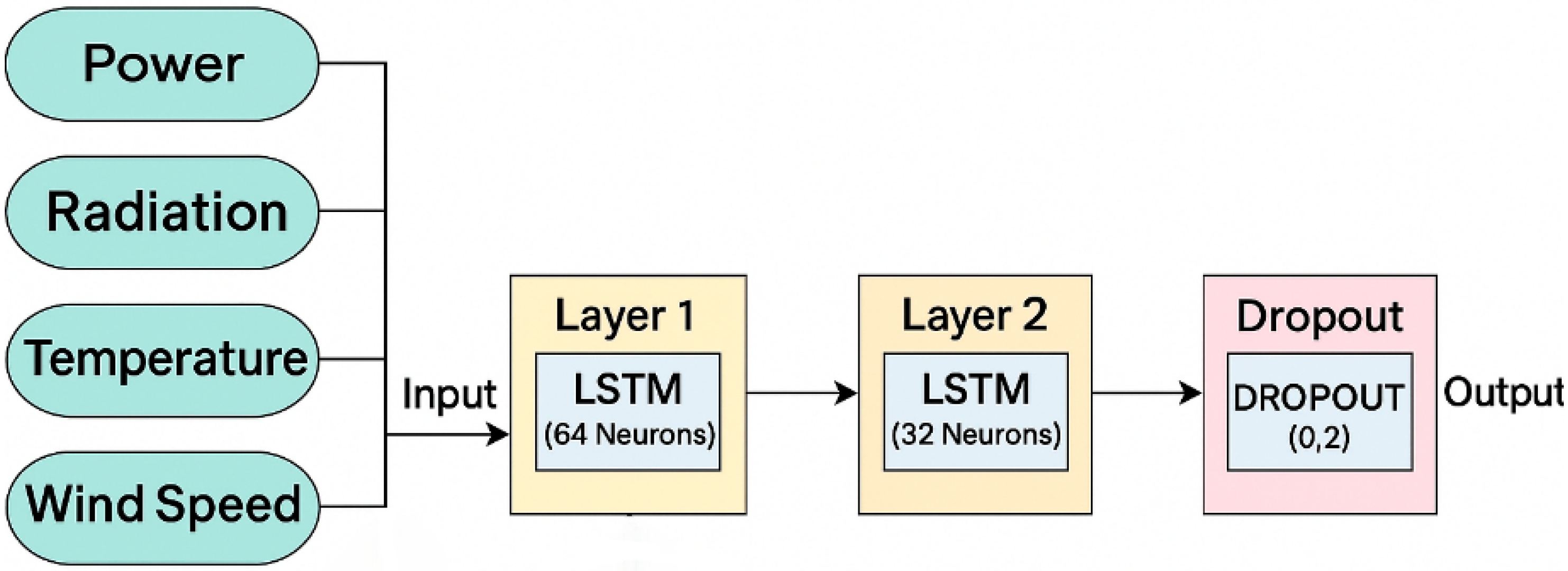
2.3. LSTM Model
2.4. CNN Model
2.5. GRU Model
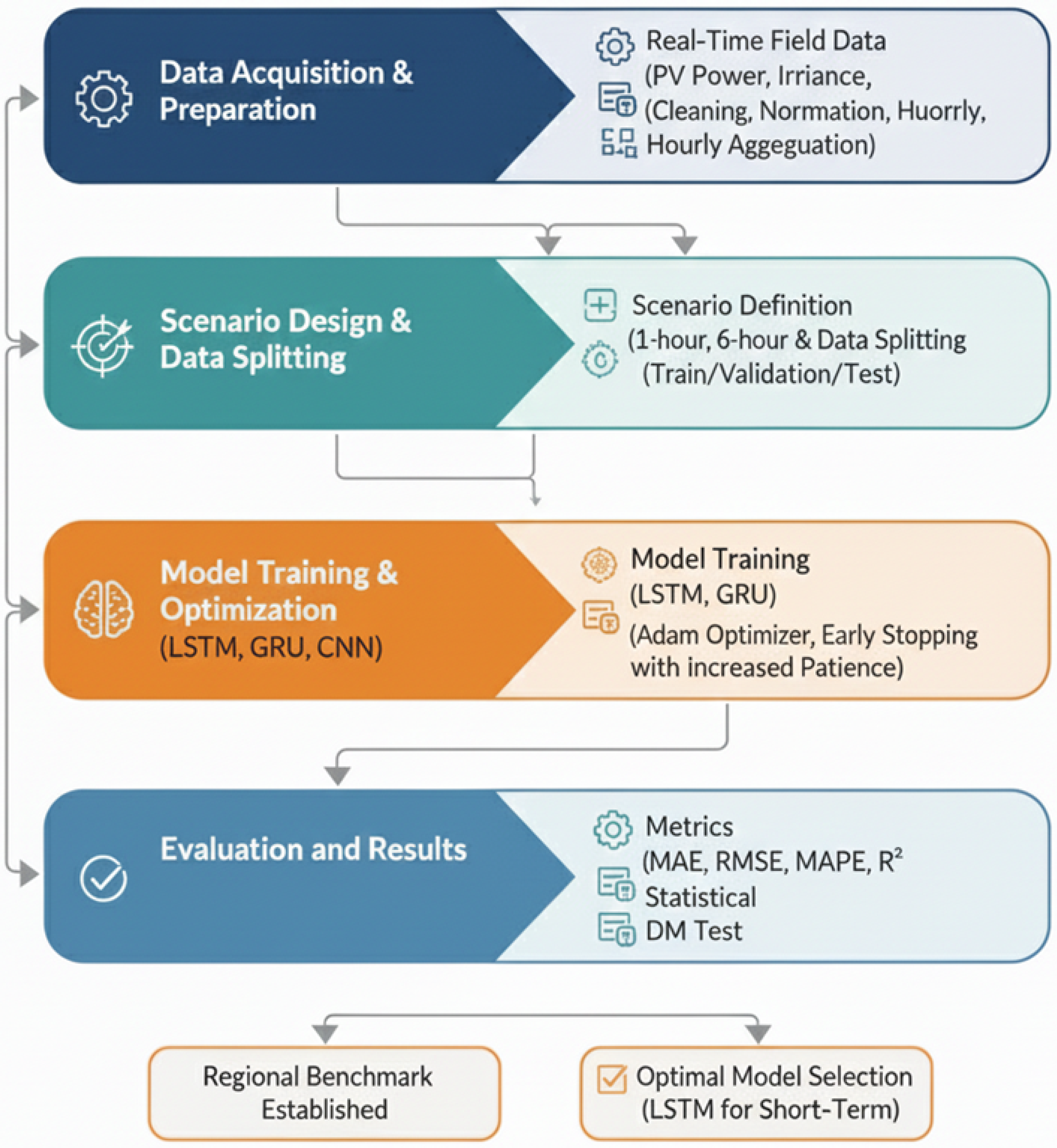
2.6. Experimental Setup and Data Partitioning
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Evaluation of Deep Learning Models
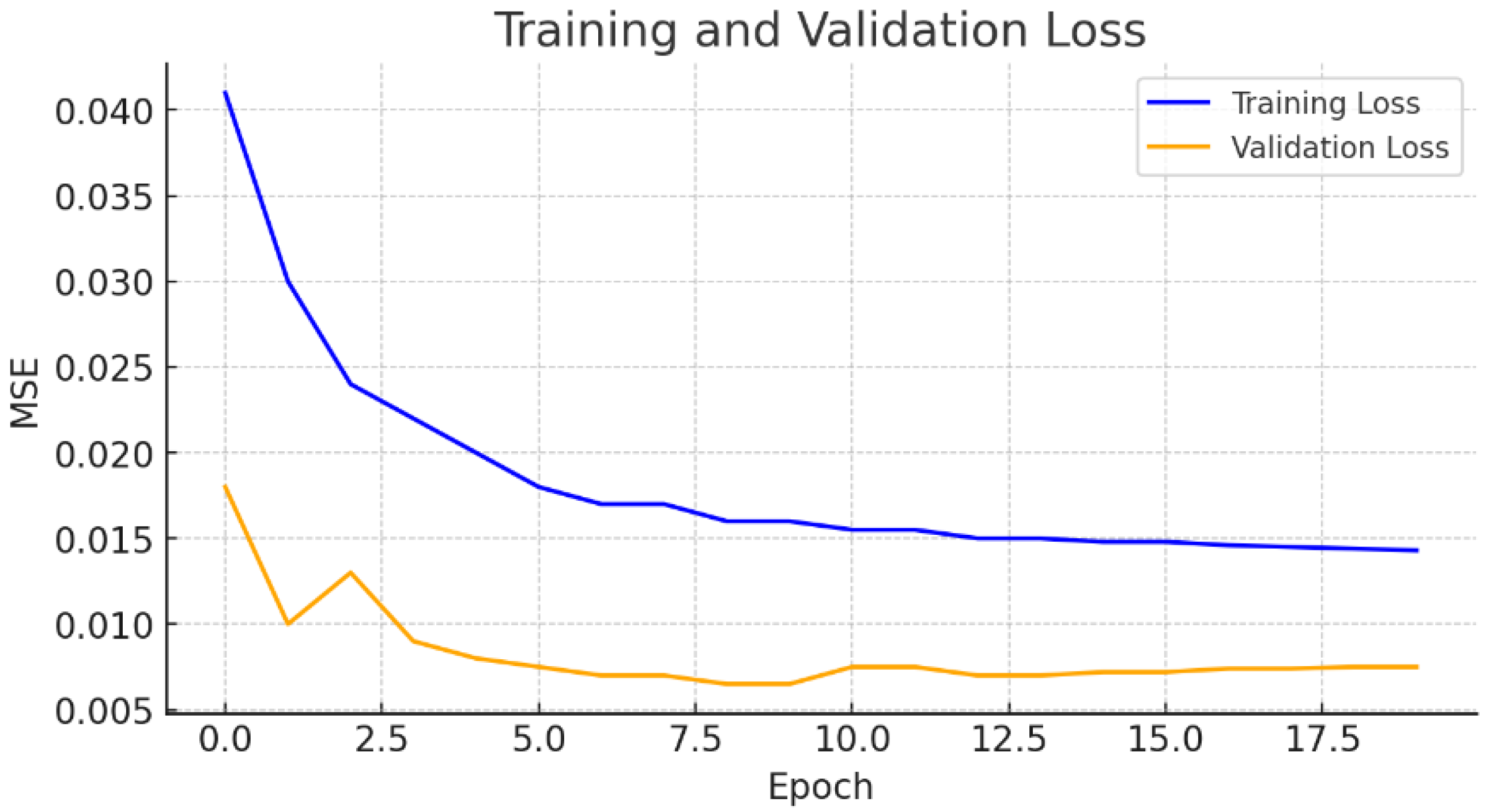
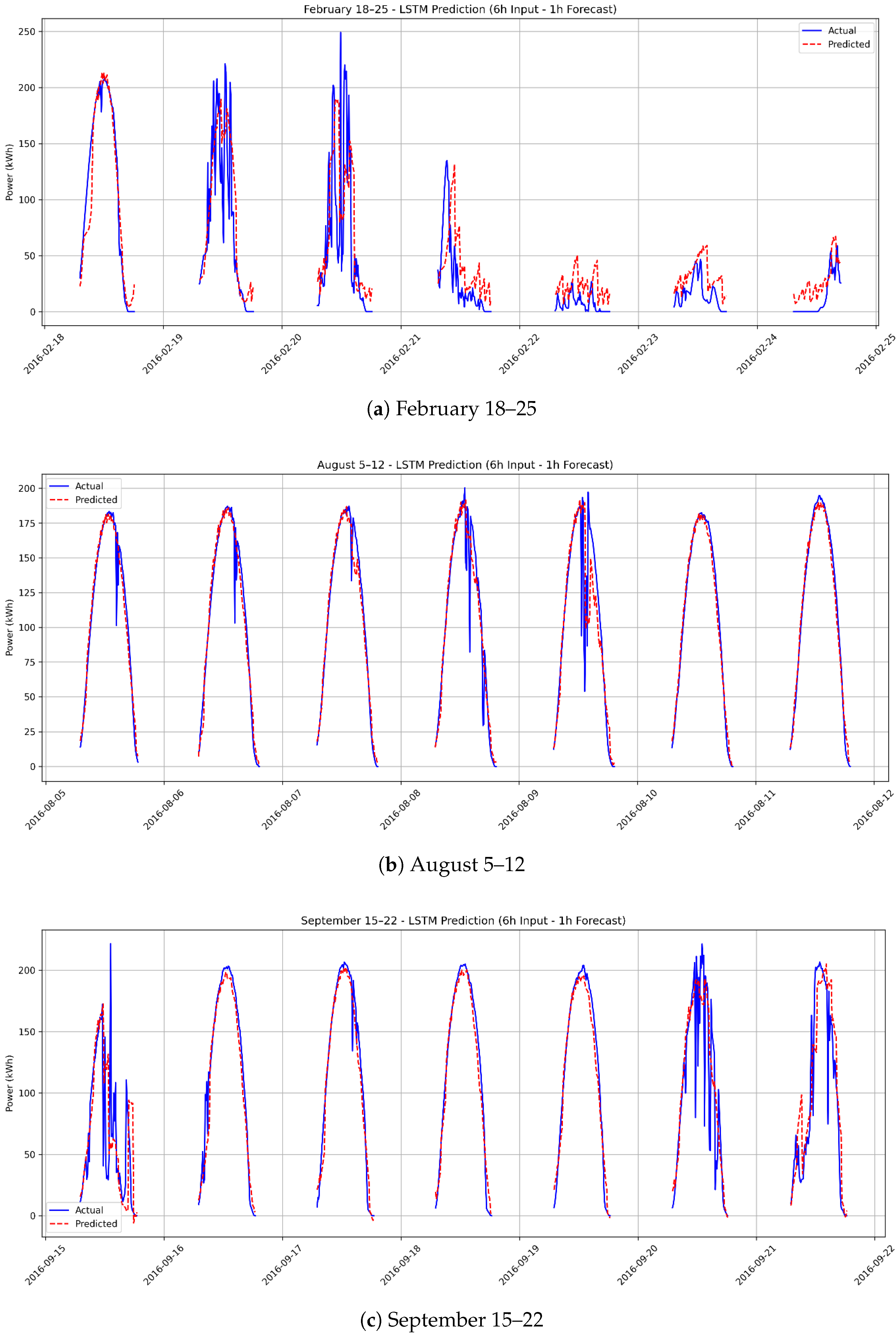
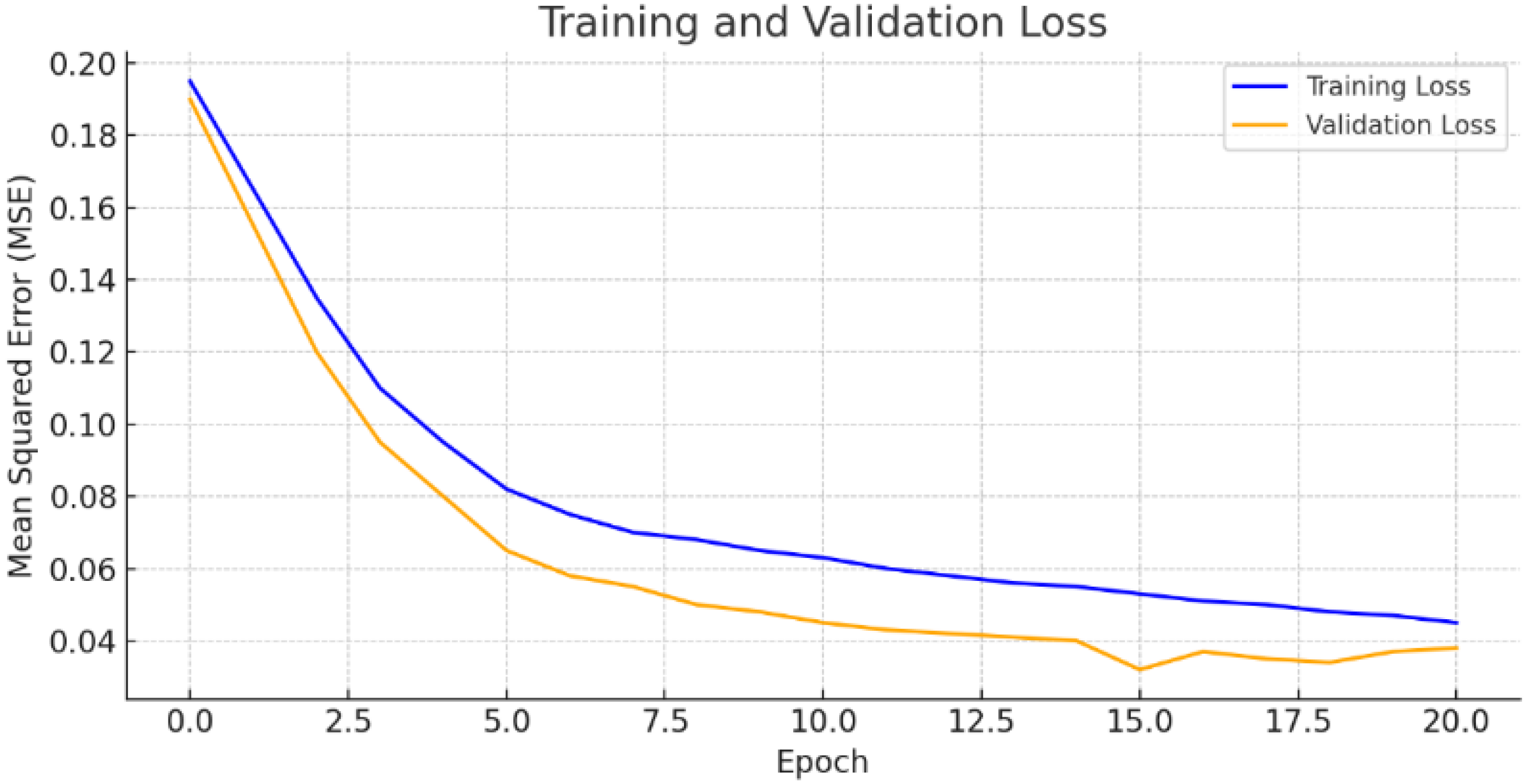
3.2. Scenario 1: One-Hour Forecasting Using 6 Hours of Real Data
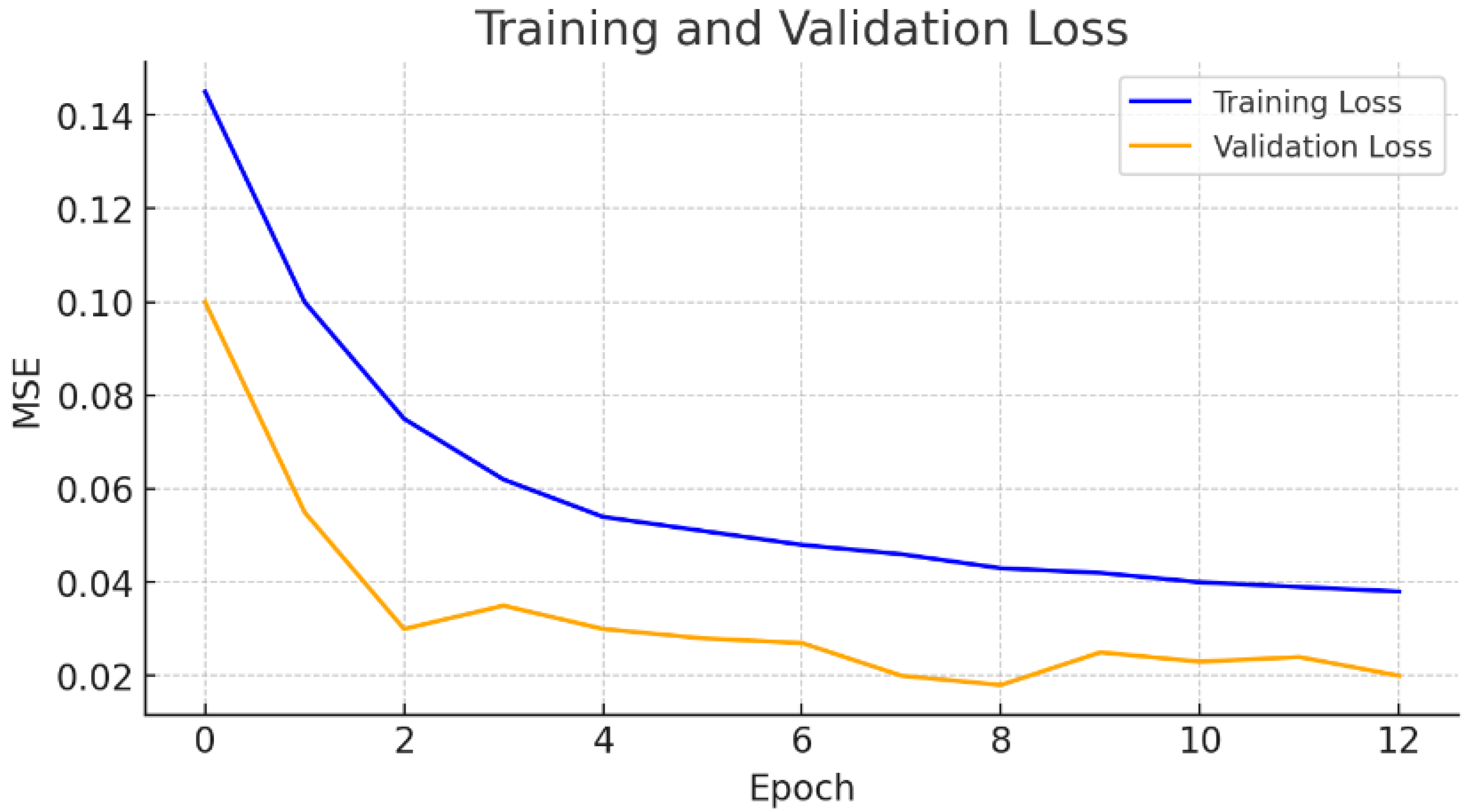
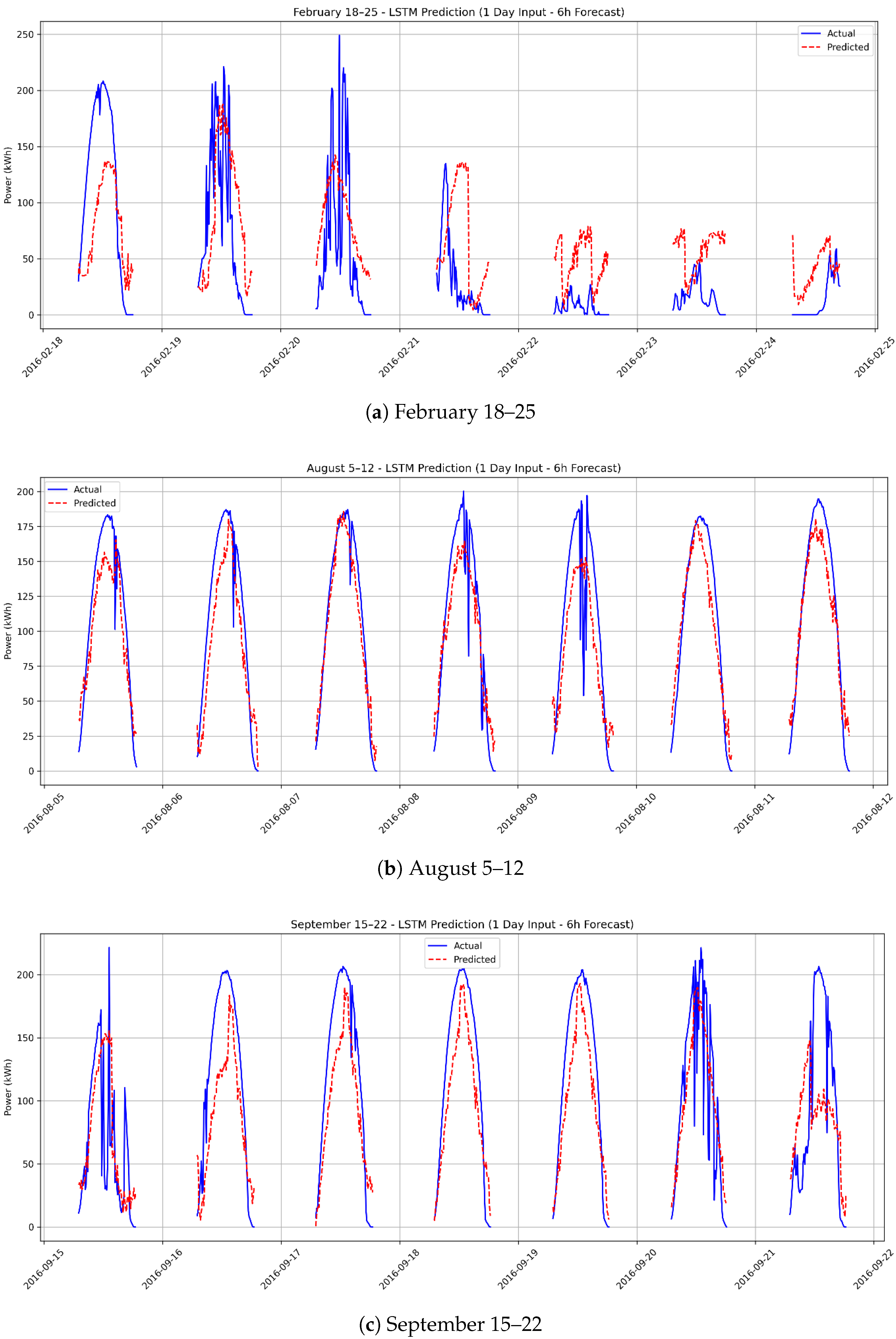
3.3. Scenario 2: Six-Hour Forecasting Using 1 Day of Actual Data
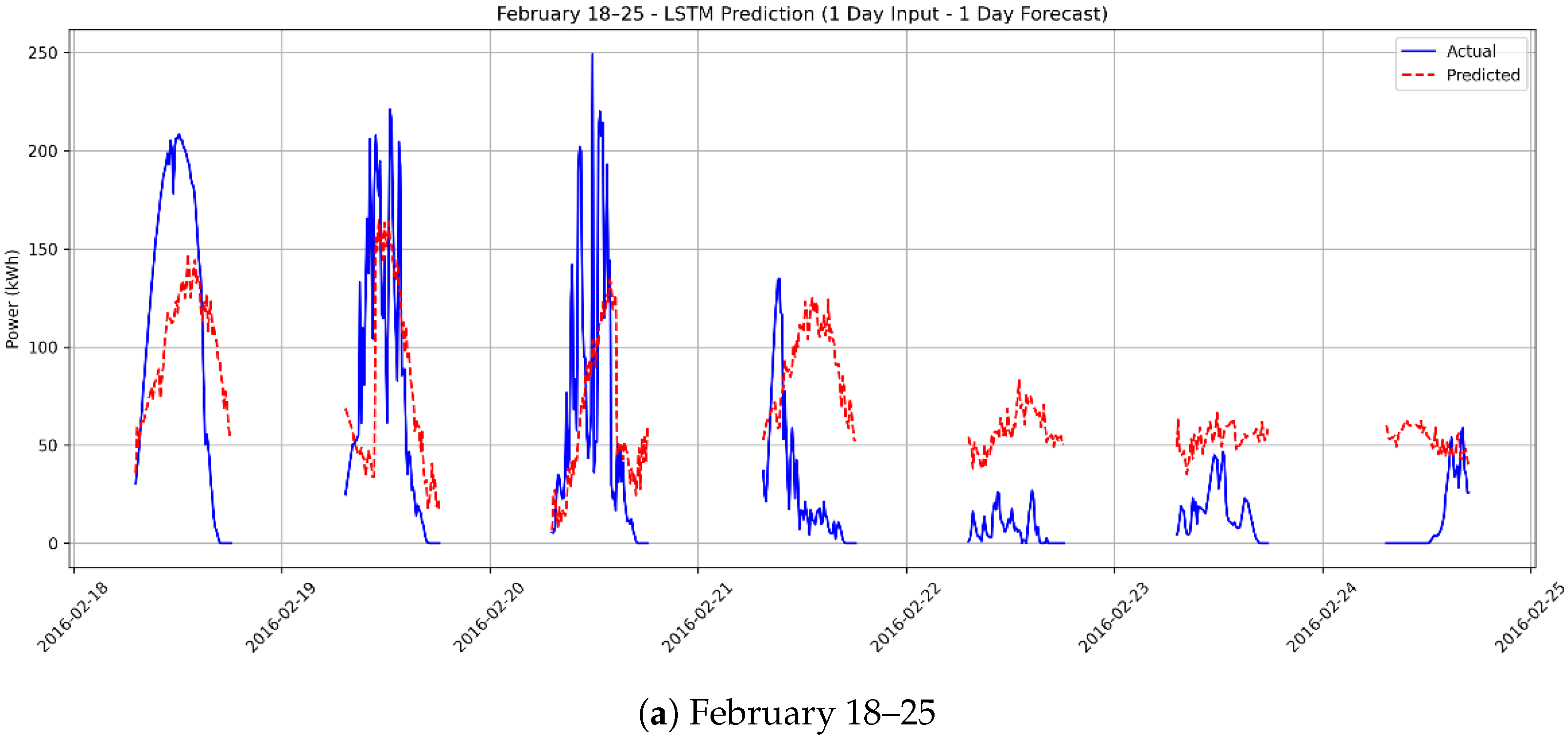
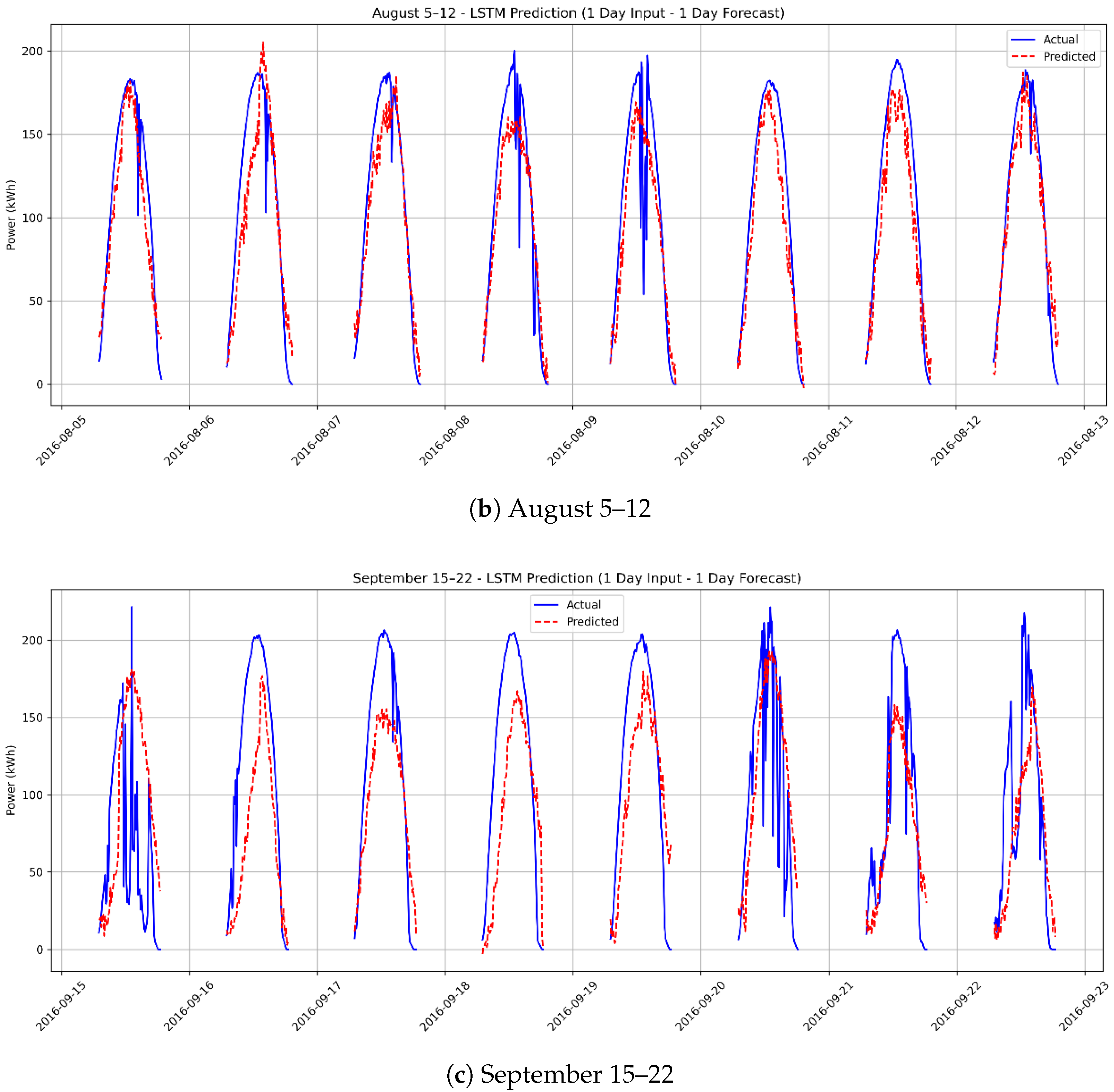
3.4. Scenario 3: One-Day Forecasting Using 1 Day of Actual Data
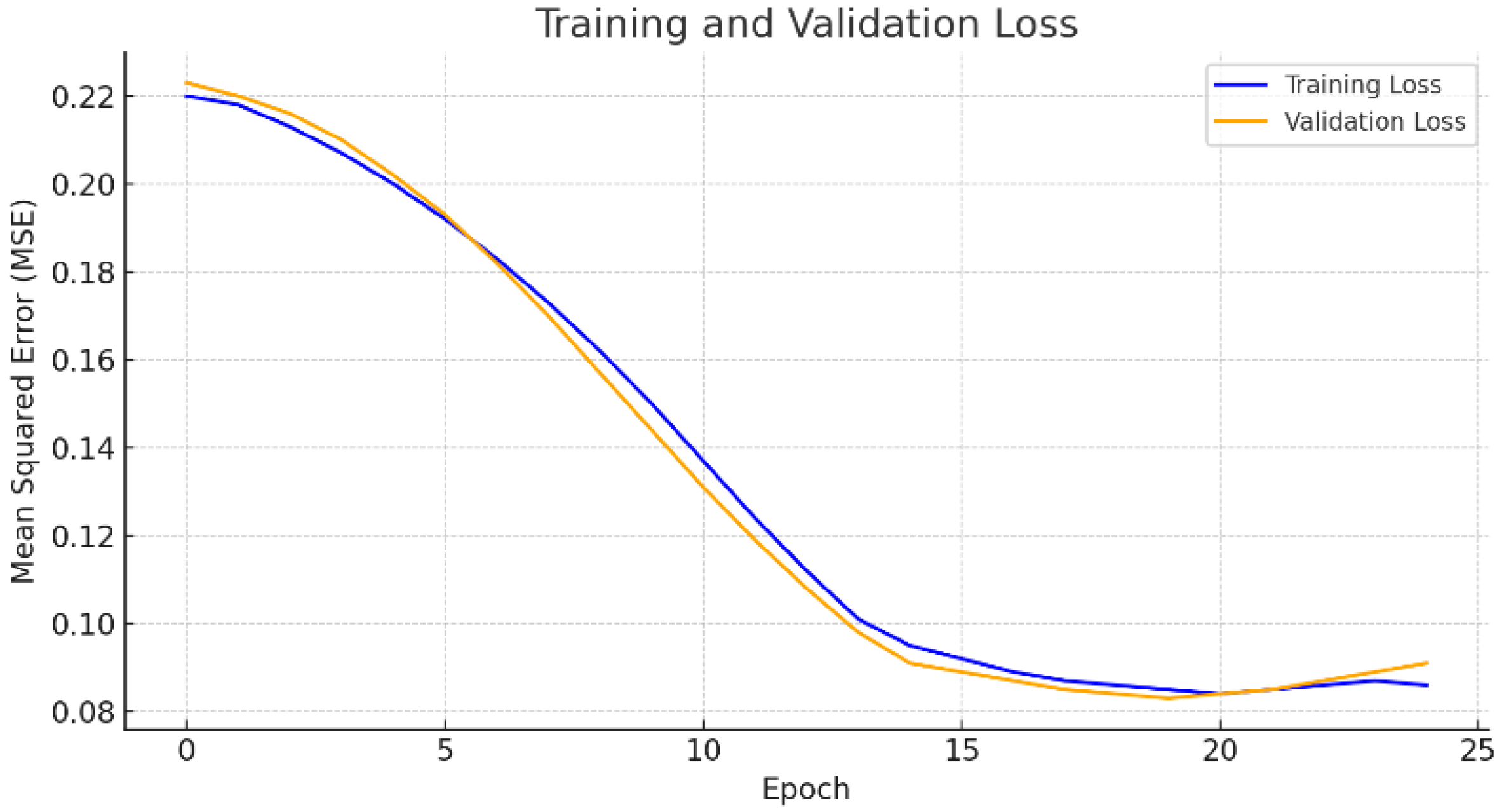
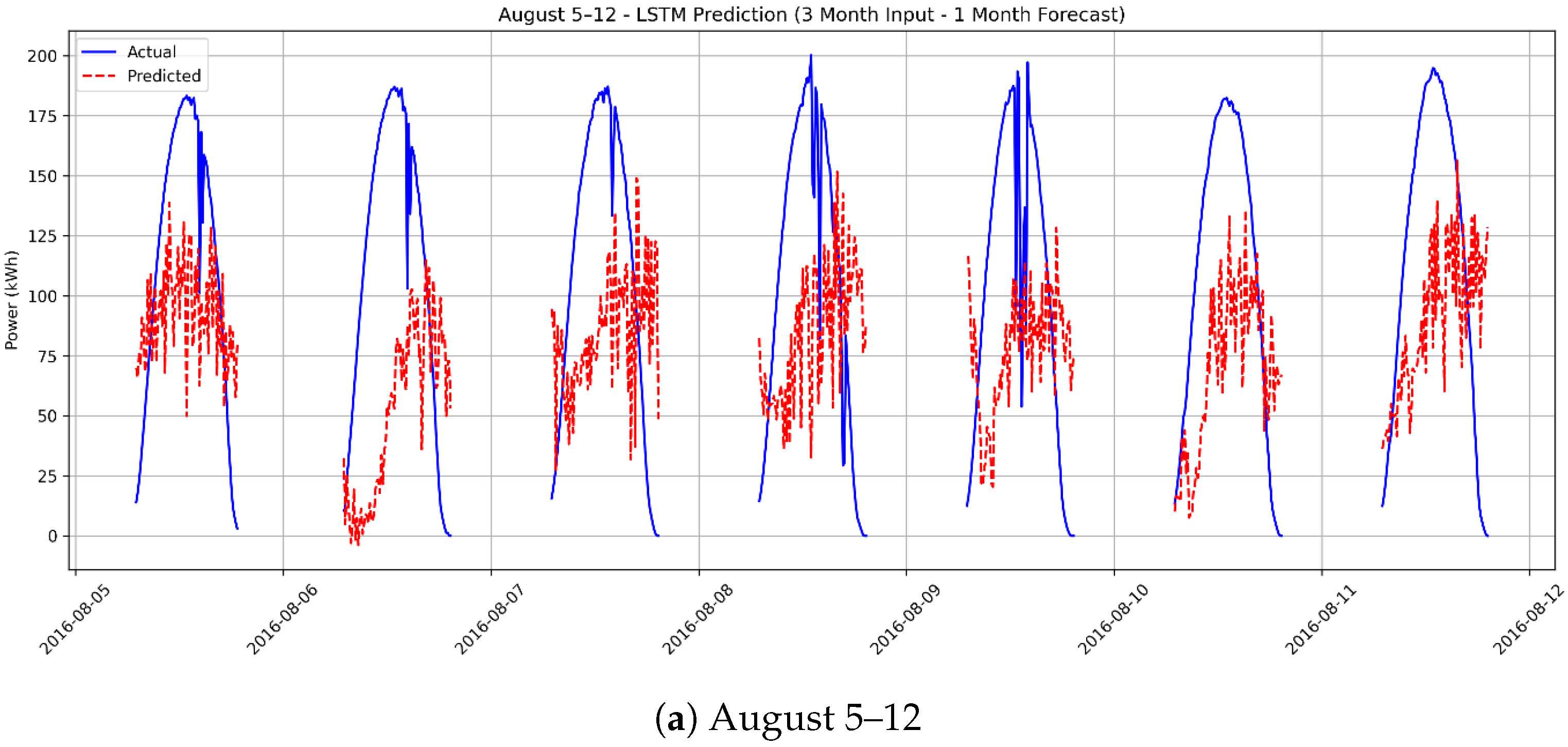
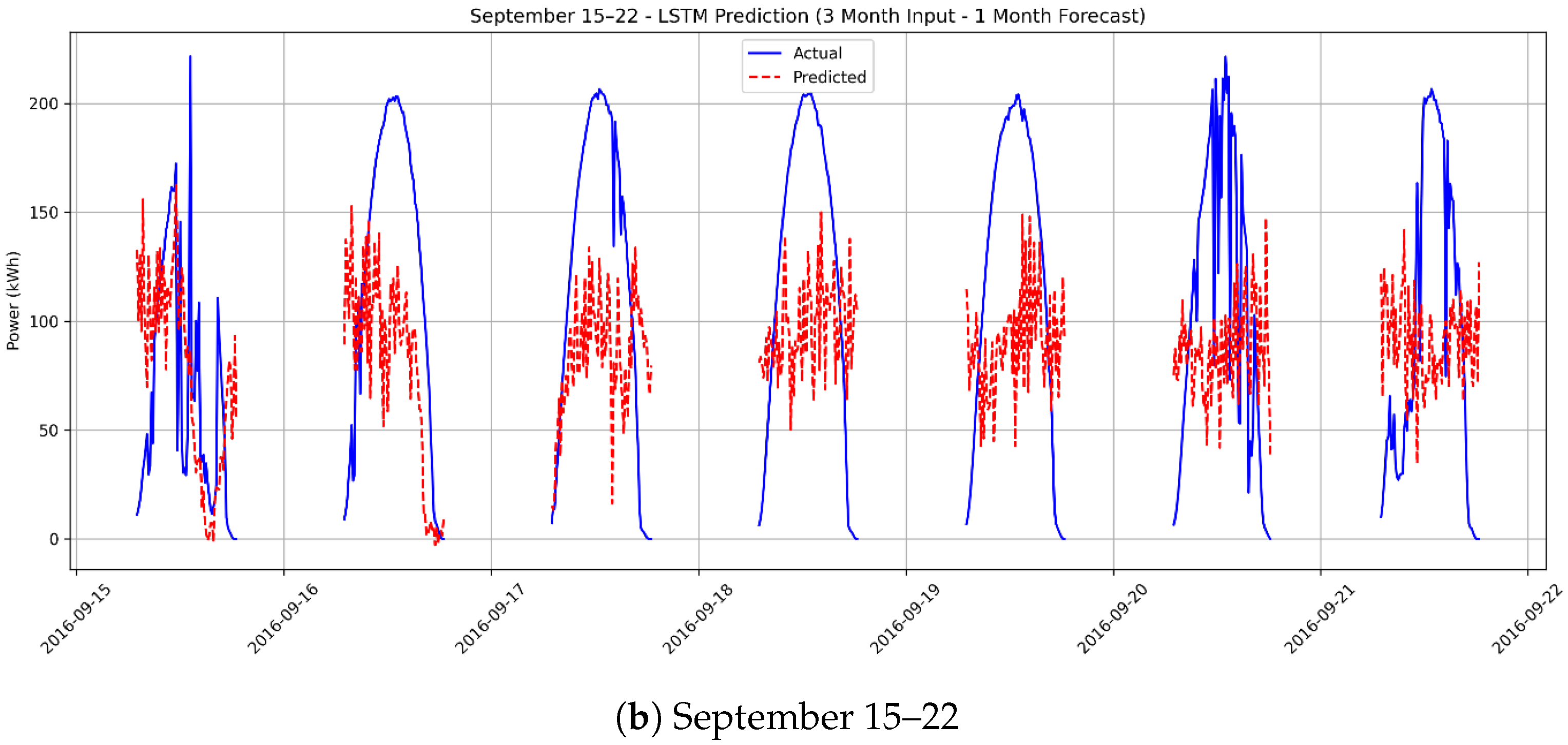
3.5. Scenario 4: One-Month Ahead Forecasting Using 3 Months of Actual Data
4. Conclusions
Limitations and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IEA | International Energy Agency |
| RES | Renewable Energy Sources |
| PV | Photovoltaic Power |
| EMRA | Energy Market Regulatory Authority |
| RMSE | Root Mean Square Error |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error |
| MAPE | Mean Absolute Percentage Error |
| LSTM | Long Short Term Memory |
| BiLSTM | Bi-Directional Long Short-Term Memory |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| DWT | Discrete Wavelet Transform |
| SARIMA | Seasonal Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| NWP | Numerical Weather Prediction |
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| GNN | Graph Neural Networks |
References
- International Energy Agency (IEA). World Energy Outlook 2024. 2024. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/world-energy-outlook-2024 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Demir, E.K.; Haydaroğlu, C.; Kılıç, H.; Çelikpençe, M.; Şahin, M.M. IoT-driven Monitoring and Optimization of Hybrid Energy Storage Systems with Supercapacitors in Distribution Networks. Turk. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2025, 5, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Türk, İ.; Kılıç, H.; Haydaroğlu, C.; Top, A. Robust Load Frequency Control in Hybrid Microgrids Using Type-3 Fuzzy Logic Under Stochastic Variations. Symmetry 2025, 17, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Electricity Market Report 2023. 2023. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/electricity-market-report-2023 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Hasnat, M.A.; Asadi, S.; Alemazkoor, N. A graph attention network framework for generalized-horizon multi-plant solar power generation forecasting using heterogeneous data. Renew. Energy 2025, 243, 122520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Geng, H.; Zhang, H. Multi-step power forecasting method for distributed photovoltaic (PV) stations based on multimodal model. Sol. Energy 2025, 298, 113572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Energy Agency (IEA). Renewables 2022: Analysis and Forecast to 2027. 2022. Available online: https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2022 (accessed on 12 November 2025).
- Ansong, M.; Huang, G.; Nyang’onda, T.N.; Musembi, R.J.; Richards, B.S. Very short-term solar irradiance forecasting based on open-source low-cost sky imager and hybrid deep-learning techniques. Sol. Energy 2025, 294, 113516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Chen, Z.; Liang, Y. Precise solar radiation forecasting for sustainable energy integration: A hybrid CEEMD-SCM-GA-LGBM model for day-ahead power and hydrogen production. Renew. Energy 2024, 237, 121732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.Y.; Wu, Y.K.; Phan, Q.T.; Tan, W.S. A Novel QR-based Probabilistic Forecasting Method for Solar power Generation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2025, 61, 5381–5393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, R.; Roy, S.K.; Giri, C. Solar power forecasting using domain knowledge. Energy 2024, 302, 131709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, B.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Fu, J.; Zhang, D. Deep probabilistic solar power forecasting with Transformer and Gaussian process approximation. Appl. Energy 2025, 382, 125294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.U.; Khan, A.D.; Khan, K.; Al Khatib, S.A.K.; Khan, S.; Khan, M.Q.; Ullah, A. A review of degradation and reliability analysis of a solar PV module. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 185036–185056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharazi, S.; Amjady, N.; Nejati, M.; Zareipour, H. A new closed-loop solar power forecasting method with sample selection. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2023, 15, 687–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.; Kumar, R.; Rao, Y.K.; Mondloe, D.S.; Dhapekar, N.K.; Sharma, A.; Yadav, A.S. Hybrid KNN-SVM machine learning approach for solar power forecasting. Environ. Challenges 2024, 14, 100838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piantadosi, G.; Dutto, S.; Galli, A.; De Vito, S.; Sansone, C.; Di Francia, G. Photovoltaic power forecasting: A Transformer based framework. Energy AI 2024, 18, 100444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodhi, E.; Dahmani, N.; Bukhari, S.M.S.; Gyawali, S.; Thapa, S.; Qiu, L.; Zafar, M.H.; Akhtar, N. Enhancing microgrid forecasting accuracy with SAQ-MTCLSTM: A self-adjusting quantized multi-task ConvLSTM for optimized solar power and load demand predictions. Energy Convers. Manag. X 2024, 24, 100767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswaran, D.; Cho, Y. Efficient solar power generation forecasting for greenhouses: A hybrid deep learning approach. Alex. Eng. J. 2024, 91, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erniyazov, S.; Lim, C.G. GNN-enhanced temporal patch segmentation and frequency fusion model for robust solar energy production forecasting. Energy Rep. 2025, 13, 4962–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salman, D.; Direkoglu, C.; Kusaf, M.; Fahrioglu, M. Hybrid deep learning models for time series forecasting of solar power. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 9095–9112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panamtash, H.; Mahdavi, S.; Sun, Q.Z.; Qi, G.J.; Liu, H.; Dimitrovski, A. Very short-term solar power forecasting using a frequency incorporated deep learning model. IEEE Open Access J. Power Energy 2023, 10, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ling, Q. Spatial–temporal multimodal fusion model for intra-hour solar power forecasting under variable weather conditions. Renew. Energy 2025, 248, 123043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Obregon, J.; Park, H.; Jung, J.Y. Multi-step photovoltaic power forecasting using transformer and recurrent neural networks. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 200, 114479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, N.; Yilmaz, A.; Bayrak, G.; Koç, M. Eliminating Meteorological Dependencies in Solar Power Forecasting: A Deep Learning Solution with NeuralProphet and Real-World Data. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 93287–93301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, L.; AlSkaif, T.; Hu, J.; Louwen, A.; van Sark, W. On the value of expert knowledge in estimation and forecasting of solar photovoltaic power generation. Sol. Energy 2023, 251, 86–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Venugopal, V.; Brandt, A.R. Short-term solar power forecast with deep learning: Exploring optimal input and output configuration. Sol. Energy 2019, 188, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, W.; Li, Y.; Niu, G. Short-Term Photovoltaic Power Forecasting Using a Bi-LSTM Neural Network Optimized by Hybrid Algorithms. Sustainability 2025, 17, 5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suanpang, P.; Jamjuntr, P. Machine learning models for solar power generation forecasting in microgrid application implications for smart cities. Sustainability 2024, 16, 6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, M.; De Hoog, J.; Bandara, K.; Senanayake, D.; Halgamuge, S. Day-ahead regional solar power forecasting with hierarchical temporal convolutional neural networks using historical power generation and weather data. Appl. Energy 2024, 361, 122971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Xiao, F.; Chen, Z.; Madsen, H. Probabilistic ultra-short-term solar photovoltaic power forecasting using natural gradient boosting with attention-enhanced neural networks. Energy AI 2025, 20, 100496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Shao, H.; Shao, C.; Tang, W. A satellite-based novel method to forecast short-term (10 min–4 h) solar radiation by combining satellite-based cloud transmittance forecast and physical clear-sky radiation model. Sol. Energy 2025, 290, 113376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauladdawilah, H.; Balfaqih, M.; Balfagih, Z.; Pegalajar, M.d.C.; Gago, E.J. Deep Feature Selection of Meteorological Variables for LSTM-Based PV Power Forecasting in High-Dimensional Time-Series Data. Algorithms 2025, 18, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Leo, P.; Ciocia, A.; Malgaroli, G.; Spertino, F. Advancements and Challenges in Photovoltaic Power Forecasting: A Comprehensive Review. Energies 2025, 18, 2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, S.F.; Gomna, A.; Kadri, S.M.; Bonkoungou, D.; Ouedraogo, A.L.; Soro, Y.M.; Sawadogo, M. Performance Study and Implementation of Accurate Solar PV Power Prediction Methods for the Nagréongo Power Plant in Burkina Faso. Energies 2025, 18, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cican, G.; Buturache, A.N.; Silivestru, V. Predicting Photovoltaic Energy Production Using Neural Networks: Renewable Integration in Romania. Processes 2025, 13, 2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Chang-Silva, R.; Lee, K.; Park, S. Dynamic Model Selection in a Hybrid Ensemble Framework for Robust Photovoltaic Power Forecasting. Sensors 2025, 25, 4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Kim, D.; Noh, Y.; Choi, J.; Lee, J. Performance Comparison of LSTM and ESN Models in Time-Series Prediction of Solar Power Generation. Sustainability 2025, 17, 8538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massidda, L.; Bettio, F.; Marrocu, M. Probabilistic day-ahead prediction of PV generation. A comparative analysis of forecasting methodologies and of the factors influencing accuracy. Sol. Energy 2024, 271, 112422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydaroğlu, C.; Kılıç, H.; Gümüş, B. Performance Analysis and Comparison of Performance Ratio of Solar Power Plant. Turk. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2024, 4, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, B.; Kilic, H. Time dependent prediction of monthly global solar radiation and sunshine duration using exponentially weighted moving average in southeastern of Turkey. Therm. Sci. 2018, 22, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Q.; Feng, B.; Li, X. Prediction algorithm for power outage areas of affected customers based on CNN-LSTM. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 15007–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdemir, Ş.; Demir, Y.; Yildirim, Ö. The effect of input length on prediction accuracy in short-term multi-step electricity load forecasting: A CNN-LSTM approach. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 28419–28432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, Ö. A novel wavelet sequence based on deep bidirectional LSTM network model for ECG signal classification. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 96, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, O.; Baloglu, U.B.; Tan, R.S.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Acharya, U.R. A new approach for arrhythmia classification using deep coded features and LSTM networks. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 176, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Xie, X.; Chang, C. Short-term PV power prediction based on optimized VMD and LSTM. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 165849–165862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Qi, X.; Ma, H.; He, X.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y. LLR: Learning learning rates by LSTM for training neural networks. Neurocomputing 2020, 394, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Zhang, H.; Wu, H. Short-term wind speed prediction based on principal component analysis and LSTM. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gers, F.A.; Schmidhuber, J.; Cummins, F. Learning to forget: Continual prediction with LSTM. Neural Comput. 2000, 12, 2451–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Author | Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| [20] | Hybrid CNN–LSTM–Transformer |
|
|
| [21] | Frequency-Incorporated LSTM |
|
|
| [22] | Spatial–Temporal Multimodal Fusion |
|
|
| [23] | Multi-step Transformer–RNN |
|
|
| [24] | NeuralProphet (Without Meteorological Data) |
|
|
| This Study | LSTM–CNN–GRU |
|
|
| Variable | Mean | Min | Max | Std. Dev. | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PV Power (W) | 81,130.223 | 0.0 | 250,194.0 | 74,044.424 | 0.374 | −1.377 |
| Solar Radiation (W/m2) | 430.610 | 0.003 | 1115.0 | 296.519 | 0.187 | −1.195 |
| Ambient Temperature (°C) | 19.950 | −16.14 | 43.08 | 11.898 | −0.112 | −0.941 |
| Wind Speed (m/s) | 1.840 | 0.0 | 9.34 | 1.582 | 1.033 | 0.588 |
| Parameter | LSTM | CNN | GRU |
|---|---|---|---|
| Learning Rate | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| Batch Size | 16 | 64 | 64 |
| Epochs | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Optimizer | Adam | Adam | Adam |
| Dropout | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Hidden Units | LSTM(64 → 32) | Conv1D(16 filters) + Dense(50) | GRU(8 units) |
| Model | Scenario (Forecast–Past) | MAE (Normalized) | RMSE (Normalized) | MAPE (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LSTM | 1H – 6H | 0.0646 | 0.1008 | 19.76 | 0.8981 |
| LSTM | 6H – 1D | 0.1610 | 0.2109 | 31.34 | 0.5537 |
| LSTM | 1D – 1D | 0.2720 | 0.3172 | 42.80 | 0.0107 |
| CNN | 1H – 6H | 0.0914 | 0.1254 | 25.30 | 0.8422 |
| CNN | 6H – 1D | 0.1839 | 0.2277 | 31.46 | 0.4795 |
| CNN | 1D – 1D | 0.2555 | 0.3006 | 39.84 | 0.1114 |
| GRU | 1H – 6H | 0.1188 | 0.1429 | 28.58 | 0.7951 |
| GRU | 6H – 1D | 0.2512 | 0.2849 | 41.05 | 0.1853 |
| GRU | 1D – 1D | 0.2773 | 0.3236 | 47.52 | 0.0300 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aydın, E.Y.; Önal, K.; Haydaroğlu, C.; Kılıç, H.; Yıldırım, Ö.; Katar, O.; Erdoğan, H. A Novel Scenario-Based Comparative Framework for Short- and Medium-Term Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Deep Learning Models. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152412965
Aydın EY, Önal K, Haydaroğlu C, Kılıç H, Yıldırım Ö, Katar O, Erdoğan H. A Novel Scenario-Based Comparative Framework for Short- and Medium-Term Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Deep Learning Models. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(24):12965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152412965
Chicago/Turabian StyleAydın, Elif Yönt, Kevser Önal, Cem Haydaroğlu, Heybet Kılıç, Özal Yıldırım, Oğuzhan Katar, and Hüseyin Erdoğan. 2025. "A Novel Scenario-Based Comparative Framework for Short- and Medium-Term Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Deep Learning Models" Applied Sciences 15, no. 24: 12965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152412965
APA StyleAydın, E. Y., Önal, K., Haydaroğlu, C., Kılıç, H., Yıldırım, Ö., Katar, O., & Erdoğan, H. (2025). A Novel Scenario-Based Comparative Framework for Short- and Medium-Term Solar PV Power Forecasting Using Deep Learning Models. Applied Sciences, 15(24), 12965. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152412965









