Challenges of Tunnel Support in Low Overburden Zones in Urban Areas—Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
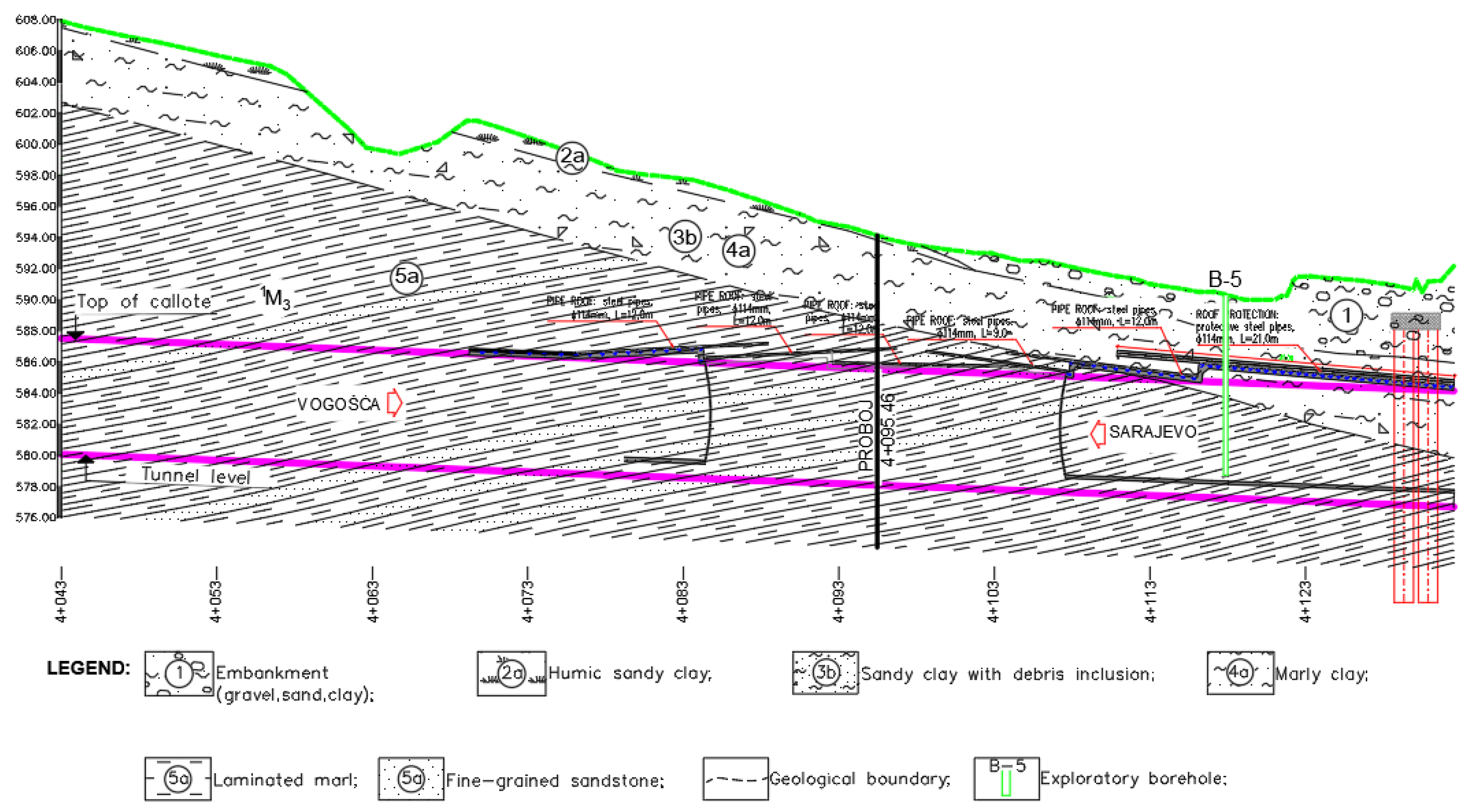
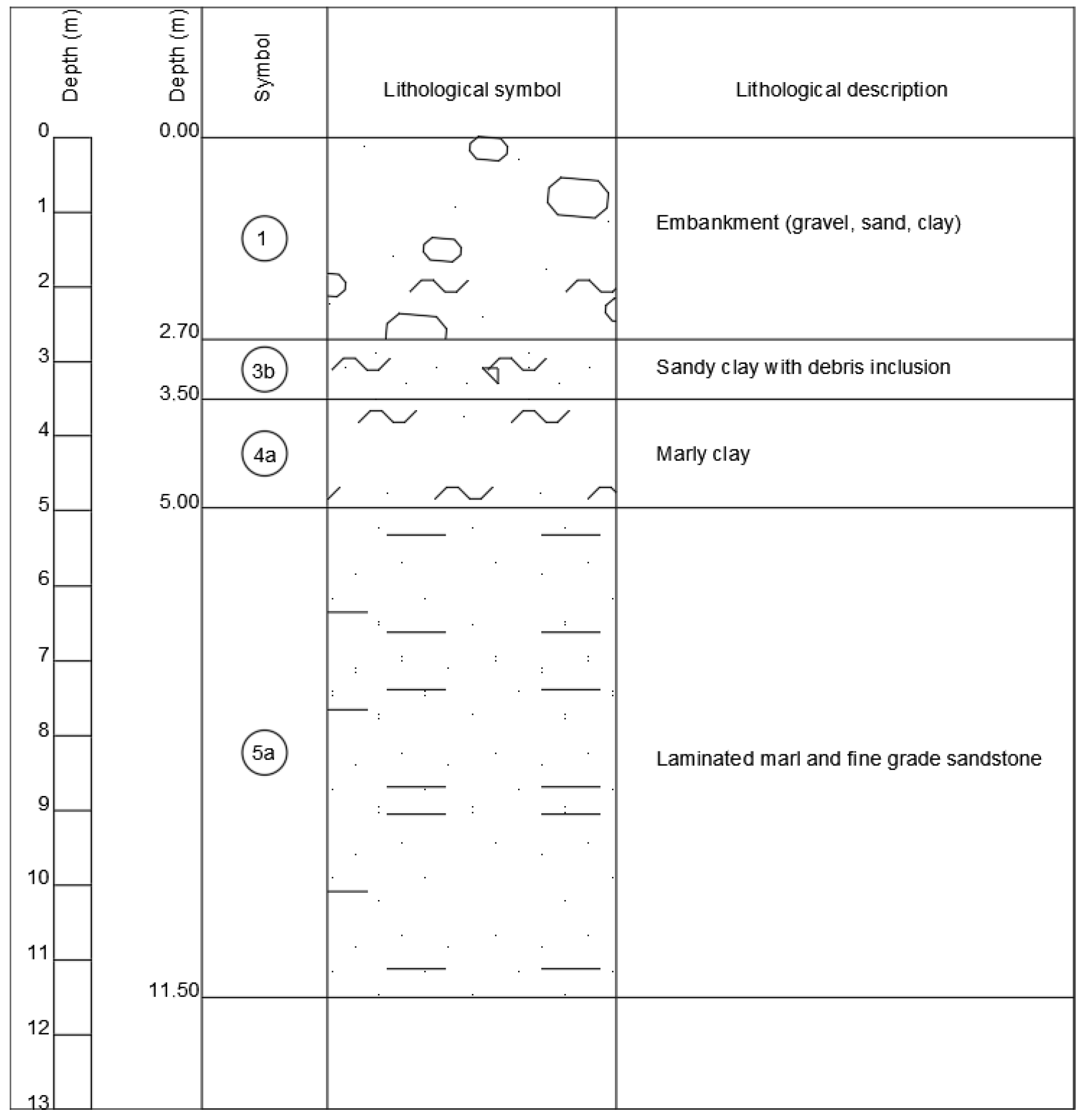
2. Engineering–Geological Characteristics
3. Case Study
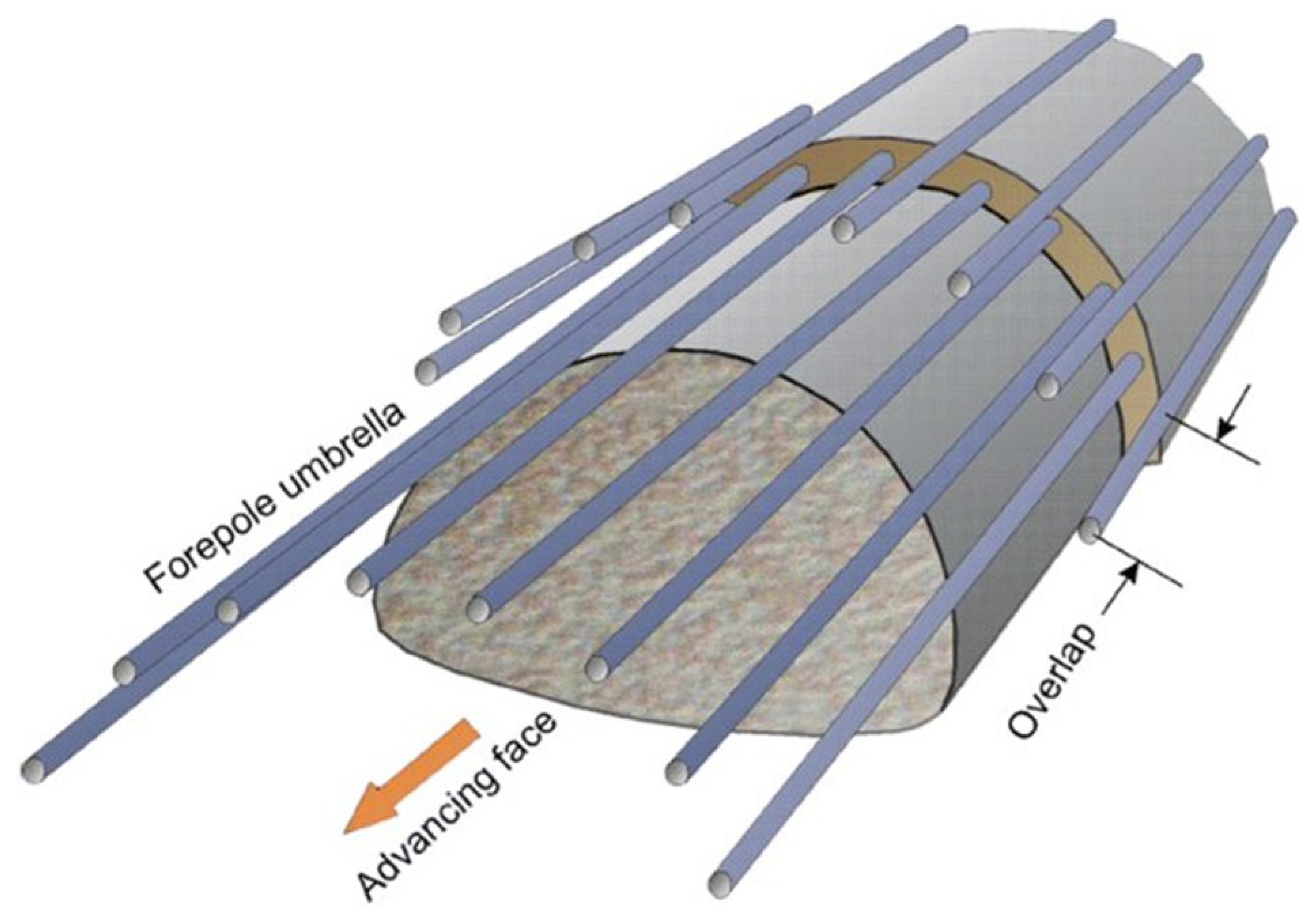
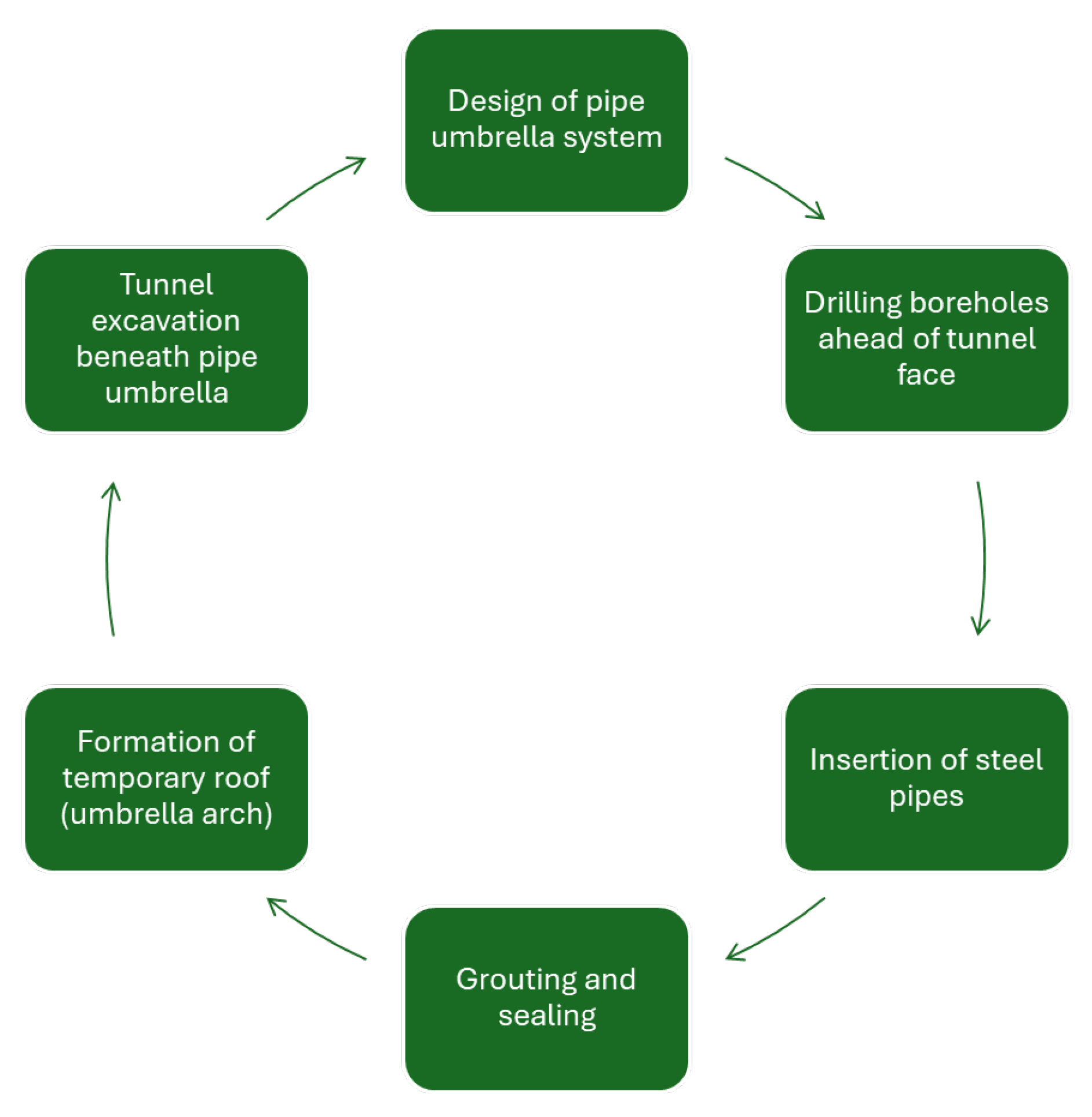
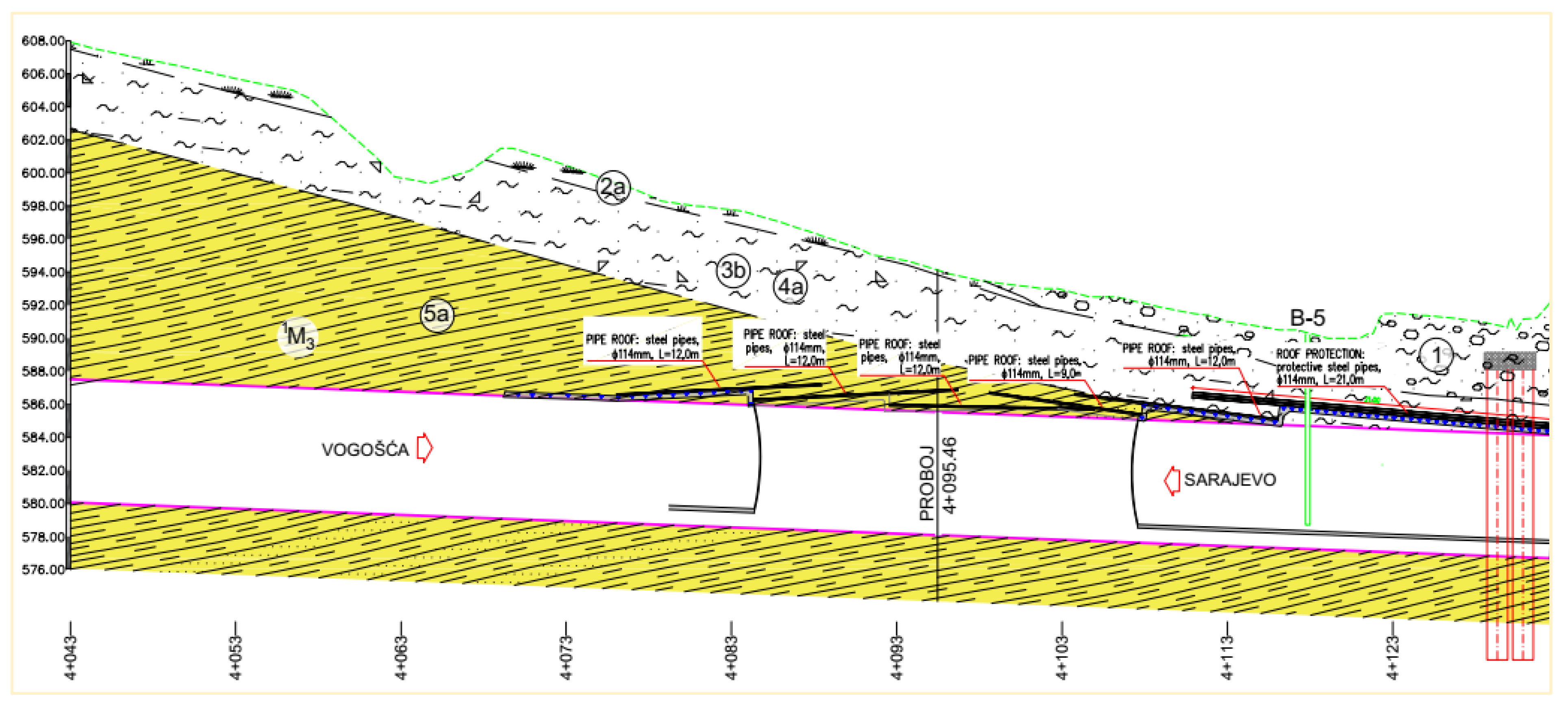
3.1. Pipe Umbrella as Method of Roof Support Prior to Excavation
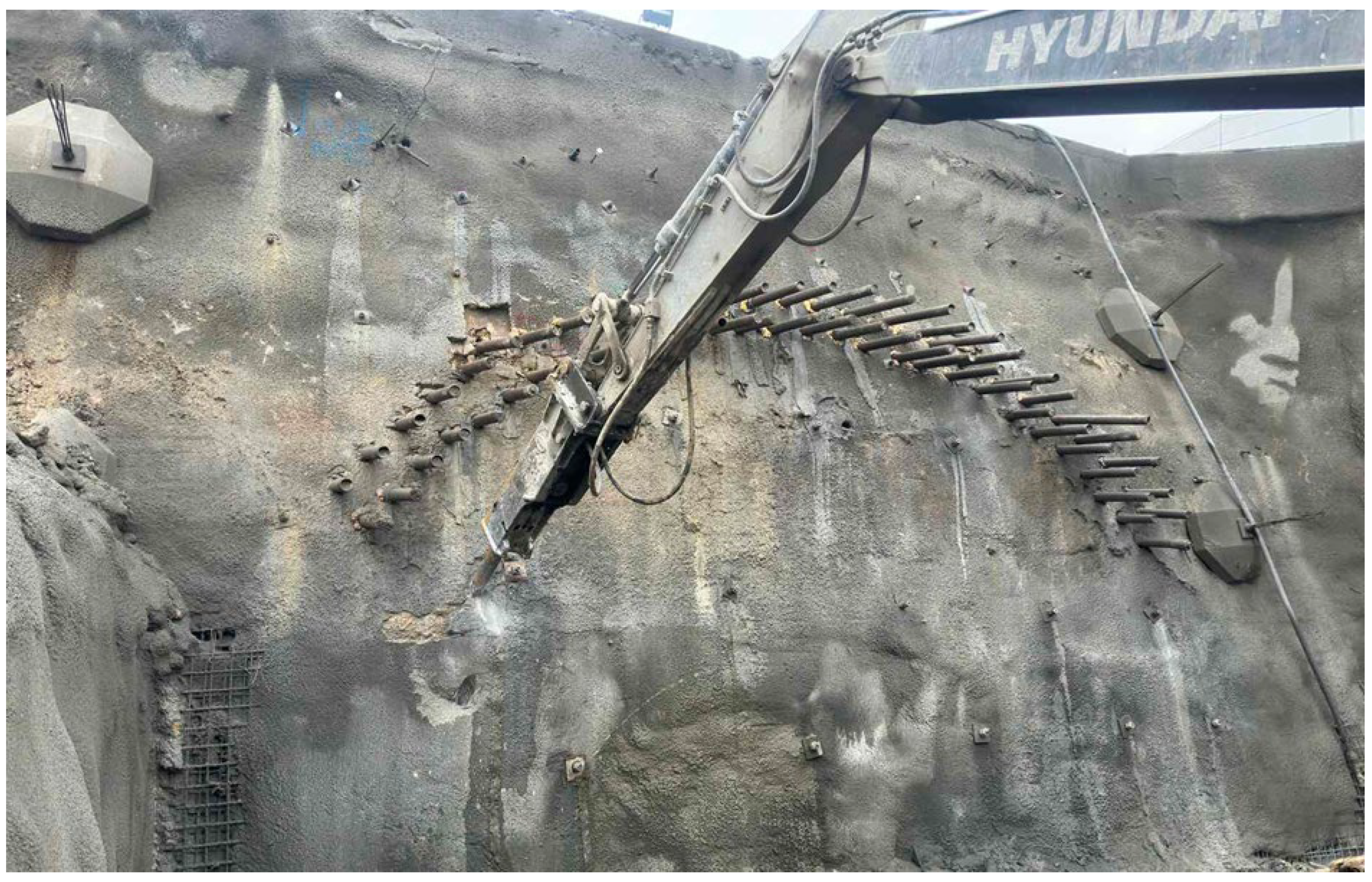
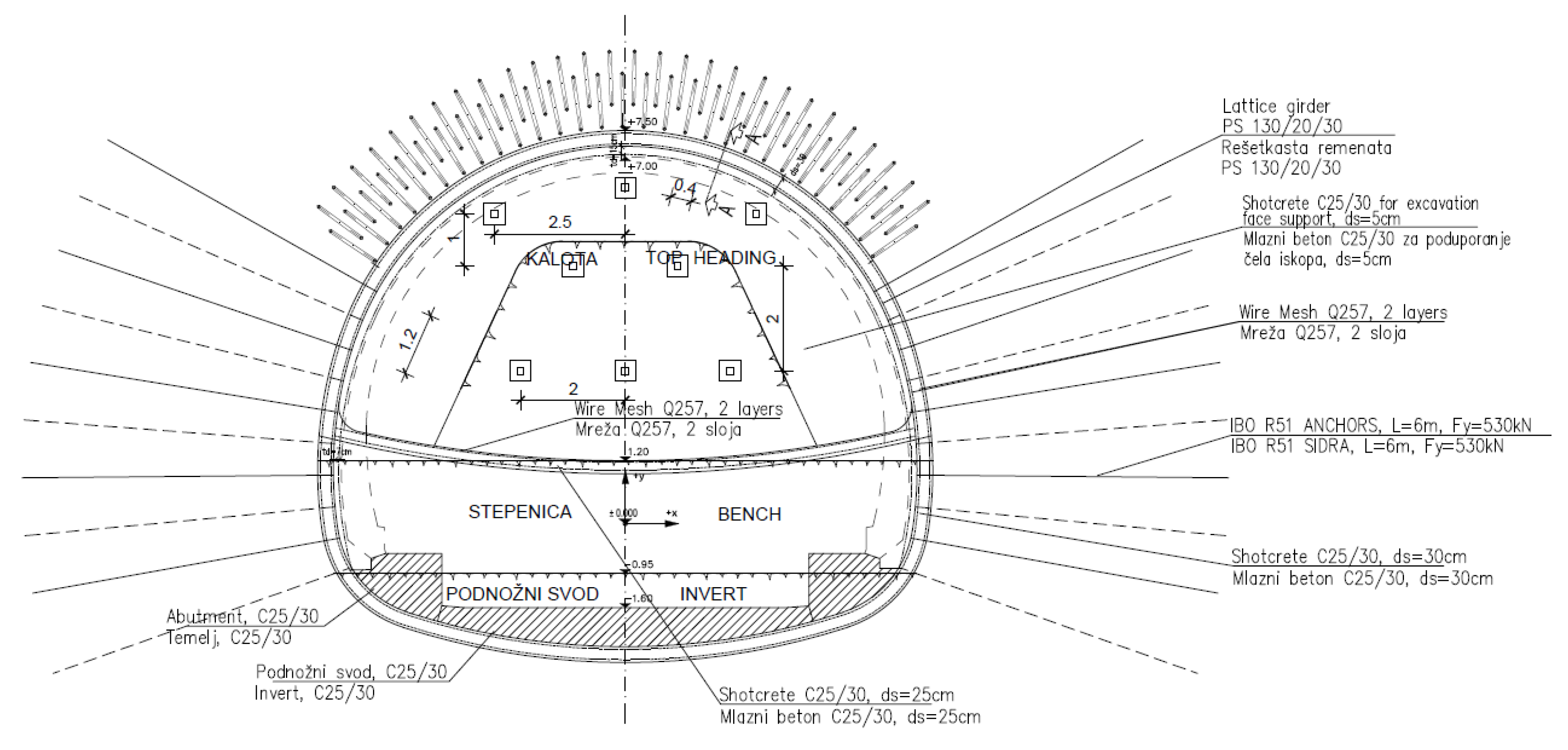
3.2. Support Measures During the Excavation of the Left Tunnel Tube from the Portal
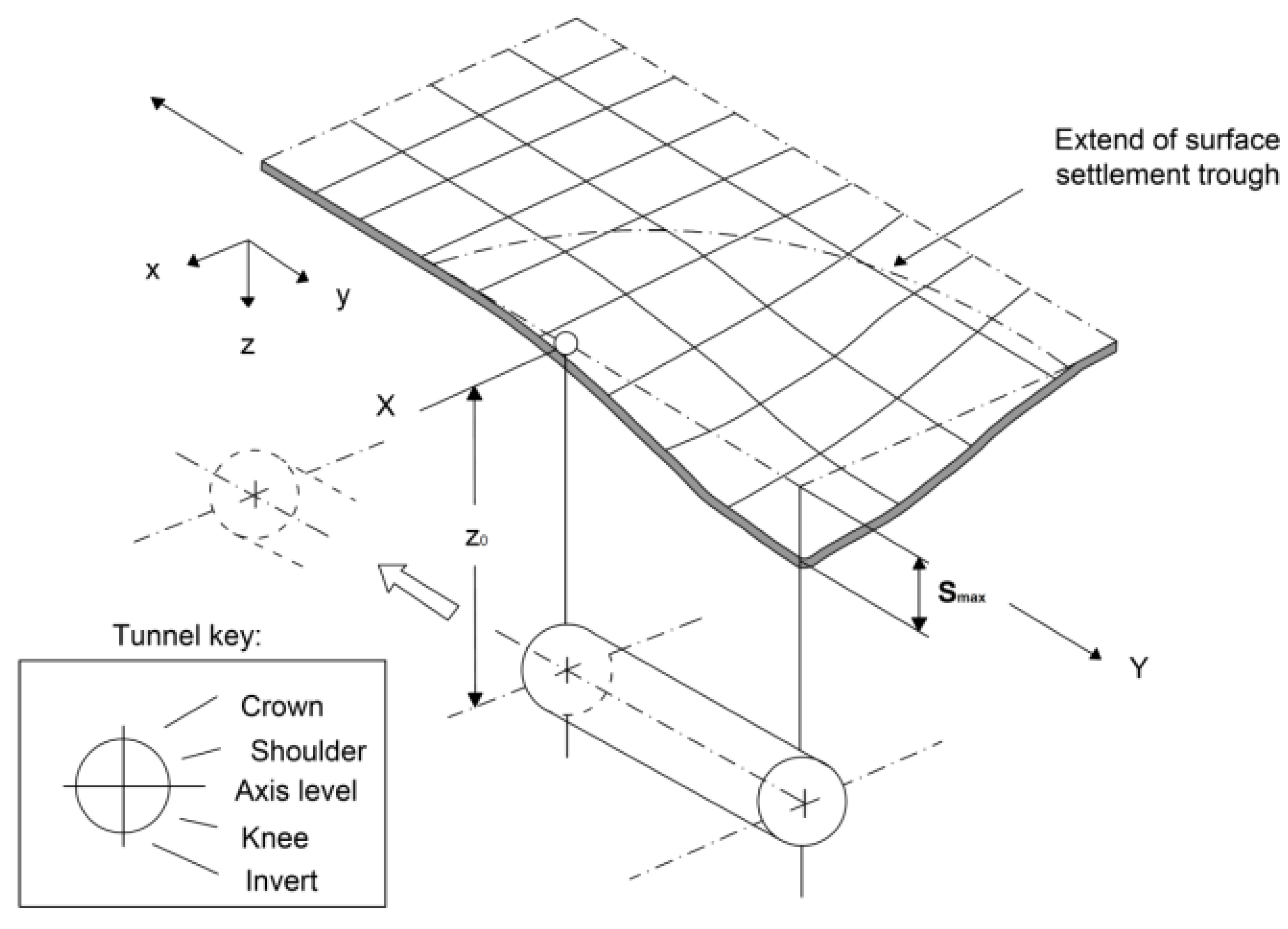
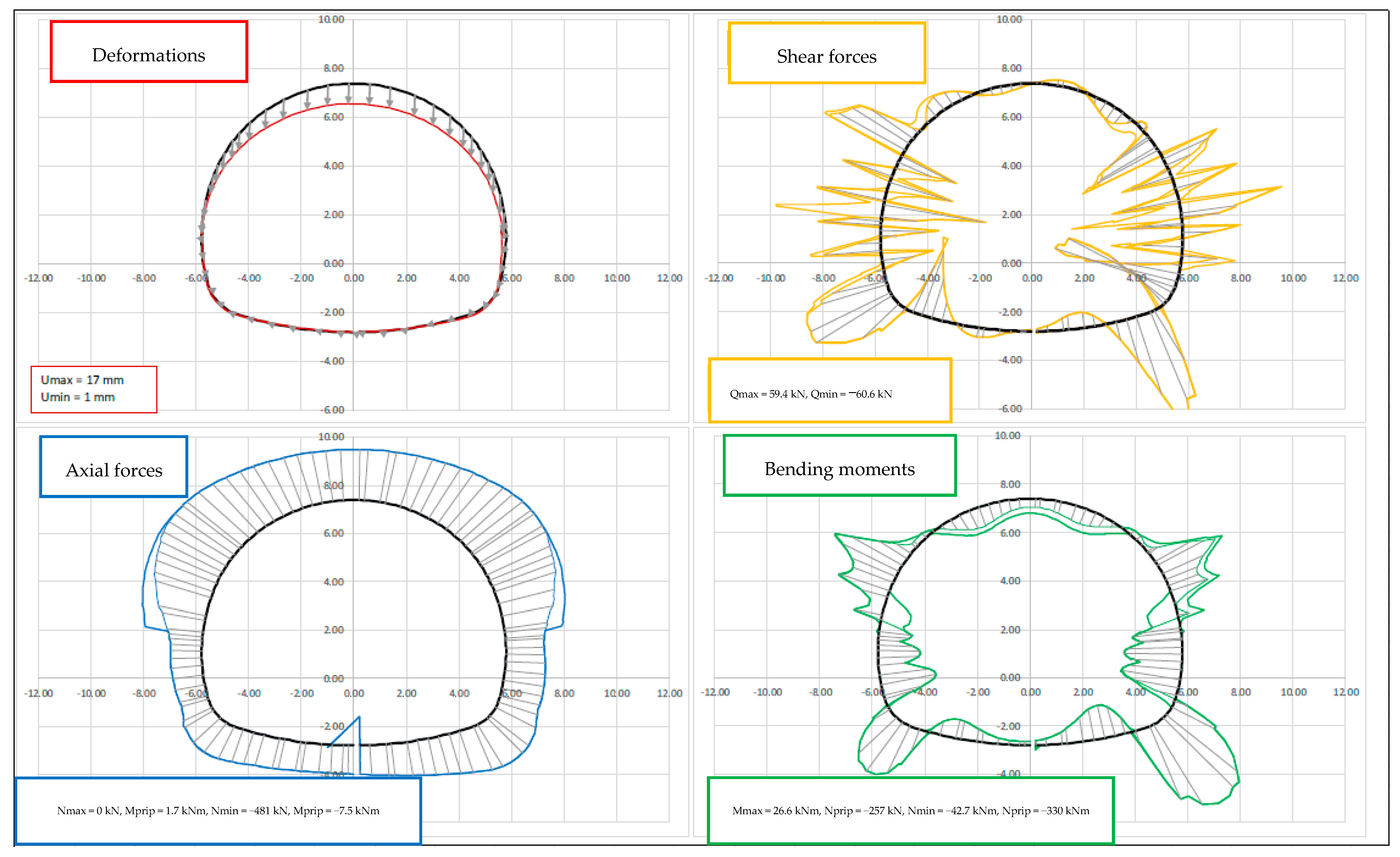
3.3. Methods of Predicting Surface Deformations
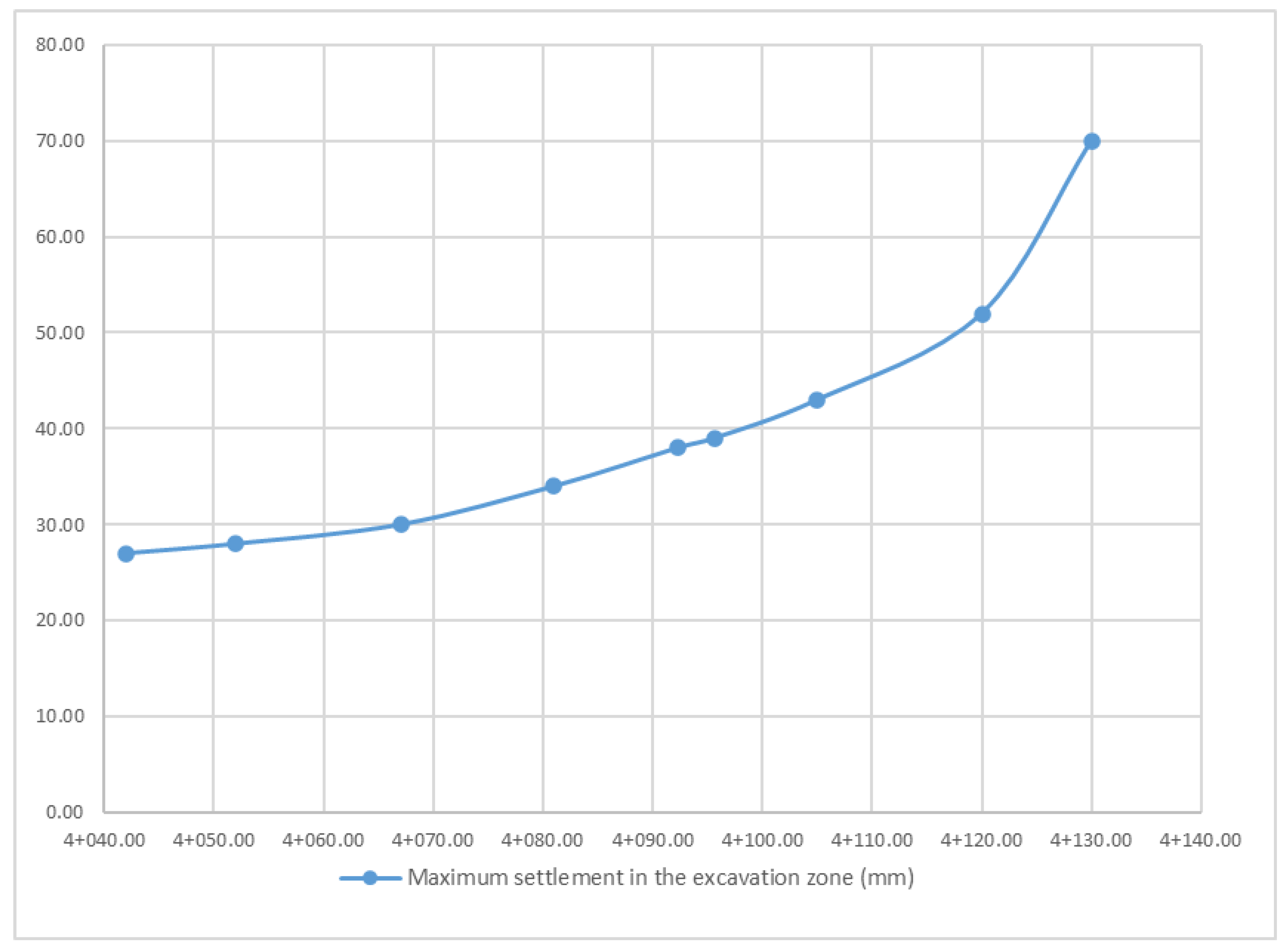
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bektašević, E.; Filipović, S.; Gutić, K.; Musa, N. Definiranje Optimalnog Razmaka Između Tehnoloških Sekvenci Pri Iskopu Tunela U Lošijoj Stjenskoj Masi. E-Zb. Elektron. Zb. Rad. Građevinskog Fak. 2024, 14, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektašević, E.; Mušija, A.; Gutić, K.; Beganović, S.; Čehajić, D. Analysis of the groundwater influence on the categorization of the rock mass and support type of the Zenica tunnel on the route of the VC corridor. J. Fac. Civ. Eng. 2023, 44, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektašević, E.; Gutić, K.; Kadrić, R.; Kadrić, S.; Sikira, D. Deformation analysis during tunnel excavation in poor rock mass. In Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Road and Rail Infrastructures–CETRA, Cavtat, Croatia, 15–17 May 2024; pp. 799–805. [Google Scholar]
- Bektašević, E.; Antičević, H.; Gutić, K.; Sikira, D. Application of seismic methods for determining the depth of the rock mass damage zone around the excavation profile by blasting. Glob. J. Eng. Technol. Adv. 2024, 18, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Highway Institute (US); Parsons Brinckerhoff, Quade & Douglas. Technical Manual for Design And Construction of Road Tunnels—Civil Elements; AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2010.
- Lee, K.; Kim, H. Analysis of ground surface settlement in a shallow tunnel using coupled Eulerian-Lagrangian technique. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2025, 84, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bektašević, E.; Filipović, S.; Gutić, K.; Hodžić, D.; Musa, N. Analysis of Surface Deformations During Excavation of A Small Overburden Tunnel in Weak Rock Masses. J. Fac. Civ. Eng. Archit. 2025, 40, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djenane, M.; Bezih, K. Shallow tunneling’s impact on surface settlements. J. Eng. Exact Sci. 2024, 10, 18591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahangir, E. Impacts of Shallow Tunneling in Urban Areas. Mines ParisTech—PSL Research University. 2015. Available online: https://alertgeomaterials.eu/wp-content/uploads/2015/03/Shallow-tunnels-Mines-ParisTech.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Haundi, T.; Nangulama, H.K.; Mbewe, V.R. Site characterisation, deep basement support, construction, and deformation control. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 1611–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.F.; Liao, S.M.; Liu, M.B.; Wu, D.P.; Pan, W.Q.; Li, H. A new construction method for metro stations in dense urban areas in Shanghai soft ground: Open-cut shafts combined with quasi-rectangular jacking boxes. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2022, 125, 104530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Long, L.; Bai, Y.; Huang, B. Advancing Shallow Tunnel Construction in Soft Ground: The Pipe-Umbrella Box Jacking Method. Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board 2024, 2678, 150–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Zhang, X.; Shi, B.; Jiang, J.; Lin, Z. Deformation in settlement and grouting remediation of thickened larger-diameter metro shield tunnel in soft soil: A case study. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e02736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; He, C.; Wang, Z. Analysis and prediction of dynamic stress concentration in jointed coal using boundary element method. Theor. Appl. Fract. Mech. 2025, 140, 105136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, H.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; Shi, C. Physical feature shared online transfer learning framework for cross-engineering rock mass quality perception during TBM excavation. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2025, 168, 107111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Yuan, D.; Zhou, S.; Zhao, D. Short-term and long-term displacement of surface and shield tunnel in soft soil: Field observations and numerical modeling. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipović, S.; Bektašević, E.; Gutić, K.; Musa, N.; Sakić, N. Research on the phenomenon of increasing borehole diameter at the installation of rod anchors in marl using wet technology compared to dry drilling procedure. Glob. J. Eng. Technol. Adv. 2025, 22, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Wang, H.; Kang, S.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X.; Wu, C.; Zhu, H.; Yang, C.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Factors influencing ground settlement during tunnel proximity construction. Sustainability 2023, 15, 13270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadrić, S.; Bektašević, E.; Gutić, K.; Sikira, D. Numeričke analize stabilnosti iskopa tunela ibarac i stabilizacija urušenog dijela, parking niše. Nauka Praksa 2023, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, G.; Li, T.; Tang, C.A.; Gong, B.; Wang, K. Influence of tunnel excavation on the deformation of a frame building. Buildings 2023, 13, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mair, R.J.; Taylor, R.N. Bored Tunnelling in the Urban Environments. In Fourteenth International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. Proceedings International Society for Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering. 1999, Volume 4. Available online: https://www.issmge.org/uploads/publications/1/31/1997_04_0049.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- IRGO Consulting d.o.o.; Lotus d.o.o. Glavni Projekt Izmjene Projekta Tunela Kobilja Glava“ na I Transverzali, od km 3 + 420.00 do km 4 + 180.00, Knjiga D, Mapa D.4 Tunelski Iskop; IRGO Consulting d.o.o.: Sarajevo, Ljubljana; Lotus d.o.o.: Sarajevo, Ljubljana, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rabcewicz, L. The New Austrian Tunnelling Method (NATM), Part I–III [PDF Lecture Notes]; University of British Columbia: Endowment Lands, Canada, 1964; Available online: https://www.eoas.ubc.ca/courses/eosc547/lecture-material/Rabcewicz-NATM.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- Jovanović, P. Izrada Podzemnih Prostorija Velikog Profila; Građevinska knjiga: Serbia, Beograd, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- De Farias, M.M.; Junior, A.H.M.; De Assis, A.P. Displacement control in tunnels excavated by the NATM: 3-D numerical simulations. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2004, 19, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavvadas, M.J. Monitoring ground deformation in tunnelling: Current practice in transportation tunnels. Eng. Geol. 2005, 79, 93–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabcewicz, L.V. The New Austrian Tunneling Method. Part One—Principles of the Method. Water Power 1965, 17, 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Kanojiya, S.; Mehta, G.K. Comprehensive deformation study in the new Austrian tunneling technique tunnel utilising artificial neural network model. AiBi Rev. Investig. Adm. E Ing. 2024, 12, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitschke, A.; Gall, V.; Ahuja, V. Modeling of pipe arch canopies in shallow soft ground tunnels constructed by sequential excavation methods. In Proceedings of the EURO: TUN 2009 2nd International Conference on Computational Methods in Tunnelling, Bochum, Germany, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bektašević, E.; Gutić, K.; Sikira, D. Tunneling—With Practical Examples; LAP LAMBERT Academic Publishing: Saarbrücken, Germany, 2024; ISBN 978-620-7-80623-2. [Google Scholar]
- Volkmann, G.; Button, E.; Schubert, W. A contribution to the design of tunnels supported by a pipe roof. In Proceedings of the ARMA US Rock Mechanics/Geomechanics Symposium, Golden, Colorado, 17–21 June 2006; ARMA. p. ARMA-06. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, H.; Li, G.; Shi, X. Load transferring mechanism of pipe umbrella support in shallow-buried tunnels. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2014, 43, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TerraRoc. Pipe Roofing Solutions. 2024. Available online: https://terrarocdrilling.com/drilling-equipment/drill-tools/casing-advancement-systems/pipe-roofing/ (accessed on 20 October 2025).
- IRGO Consulting d.o.o.; Lotus d.o.o. Geotehnička misija G32 br.32, Prijedlog br. 8.2; IRGO Consulting d.o.o.: Sarajevo, Ljubljana; Lotus d.o.o.: Sarajevo, Ljubljana, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Loganathan, N.; Poulos, H.G. Analytical prediction for tunneling-induced ground movements in clays. J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 1998, 124, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peck, R.B. Advantages and limitations of the observational method in applied soil mechanics. Geotechnique 1969, 19, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddasi, M.R.; Noorian-Bidgoli, M. ICA-ANN, ANN and multiple regression models for prediction of surface settlement caused by tunneling. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2018, 79, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos, F. Concerning an approximate equation of the subsidence trough and its time factors. In International strata control congress, Leipzig; Section fur Bergbau; Deutsche Akademie der Wissenschaften zu Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 1958; pp. 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.N. Modelling of Tunnel Behaviour. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng.Geotech. Eng. 1998, 131, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmanan, A.A.; Elarabi, H. Analysis of surface settlement due to tunneling in soft ground using empirical and numerical methods. In Proceedings of the The Fourth African Young Geotechnical Engineer’s Conference, Casablanca, Morocco, 12–13 November 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wu, H.N.; Chen, R.P.; Chan, T.H. Hybrid meta-heuristic and machine learning algorithms for tunneling-induced settlement prediction: A comparative study. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2020, 99, 103383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Cui, W.; Qin, Z.; Xu, R.; Wang, T.; Liu, Y. Analysis of Arch Forming Factors of Shallow Buried Hard Rock Tunnel under Overlying Load. Buildings 2023, 13, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsirawan, R.; Sheble, A.; Alnmr, A. Two-Dimensional Numerical Analysis for TBM Tunneling-Induced Structure Settlement: A Proposed Modeling Method and Parametric Study. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.G.; Pells, P.J.N. Impact of fire on tunnels in Hawkesbury sandstone. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2008, 23, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boscardin, M.D.; Cording, E.J. Building response to excavation-induced settlement. J. Geotech. Eng. 1989, 115, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burland, J.B. Assessment of risk of damage to buildings due to tunnelling and excavatioins. In Proceedings of the 1st Int. Conf. on Earthquake Geotech. Engrg., IS-Tokyo’95, Tokyo, Japan, 14–16 November 1995. [Google Scholar]


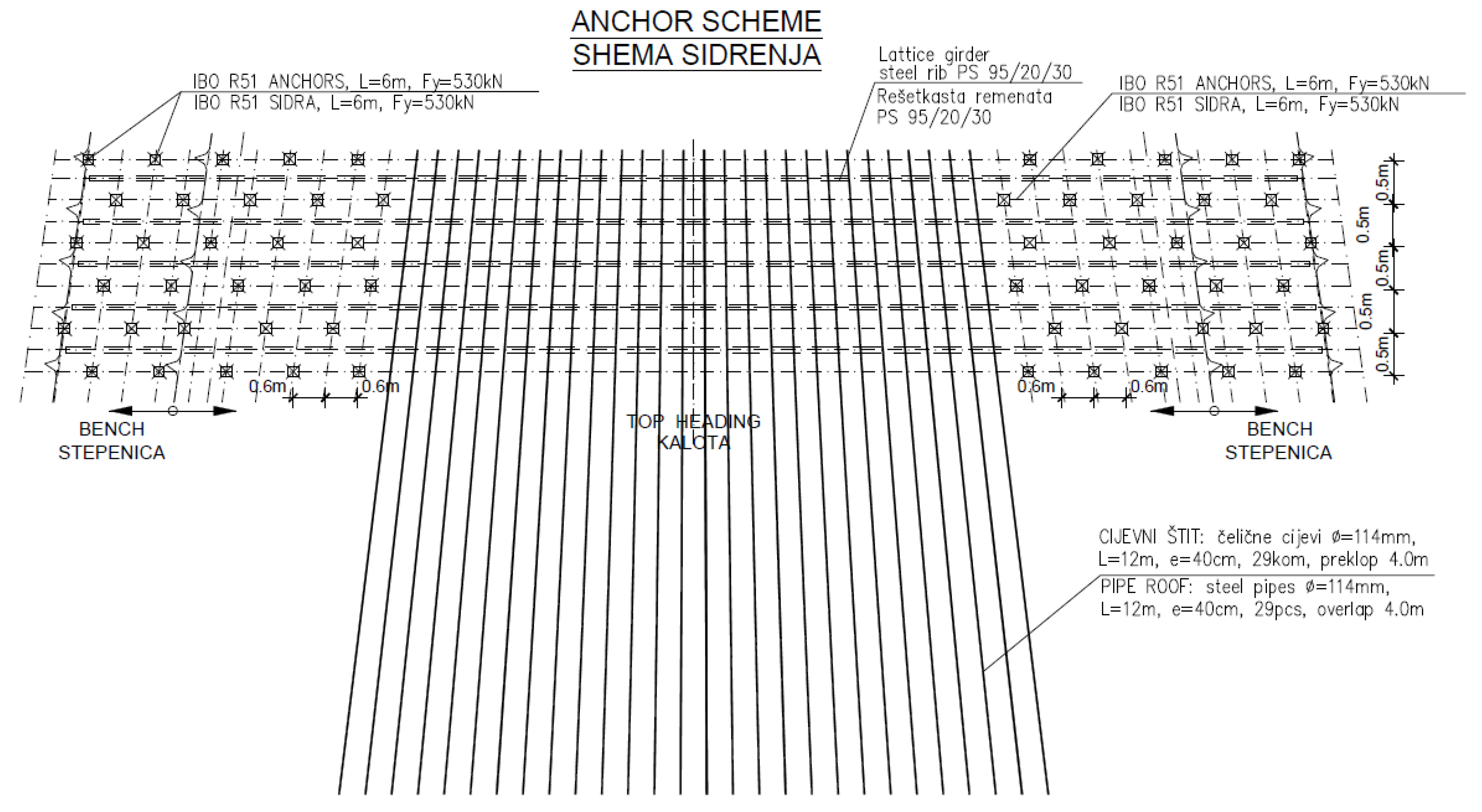

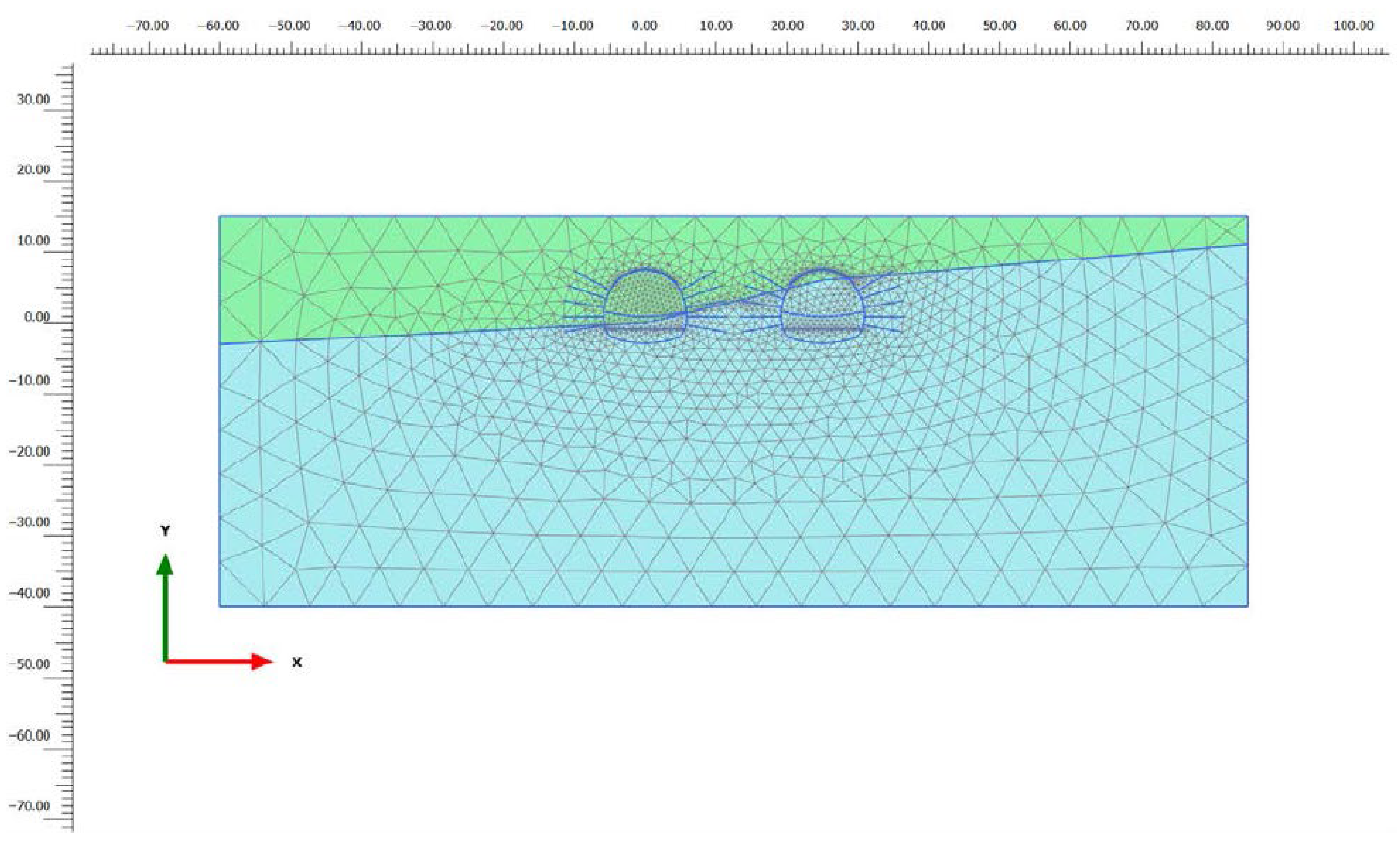
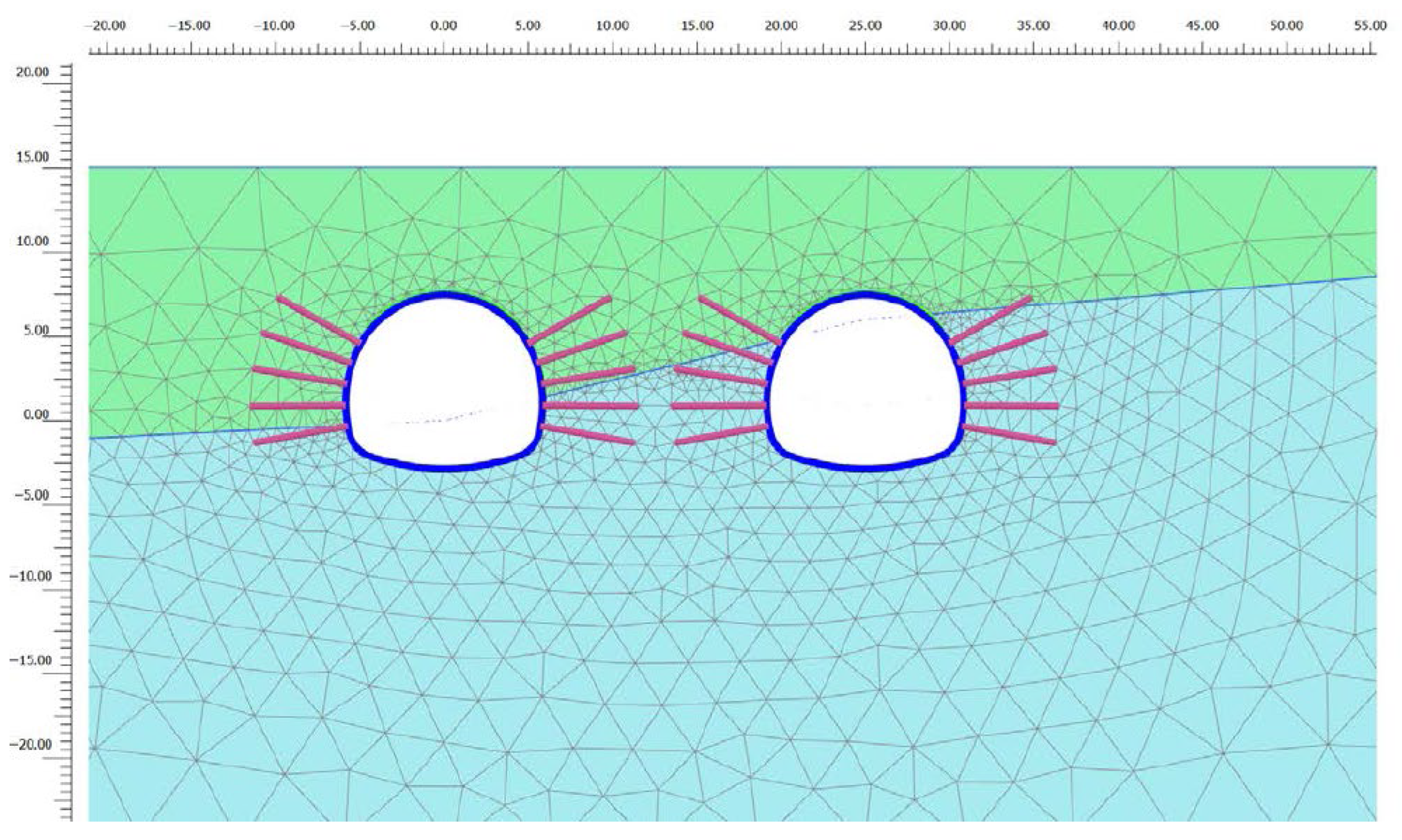


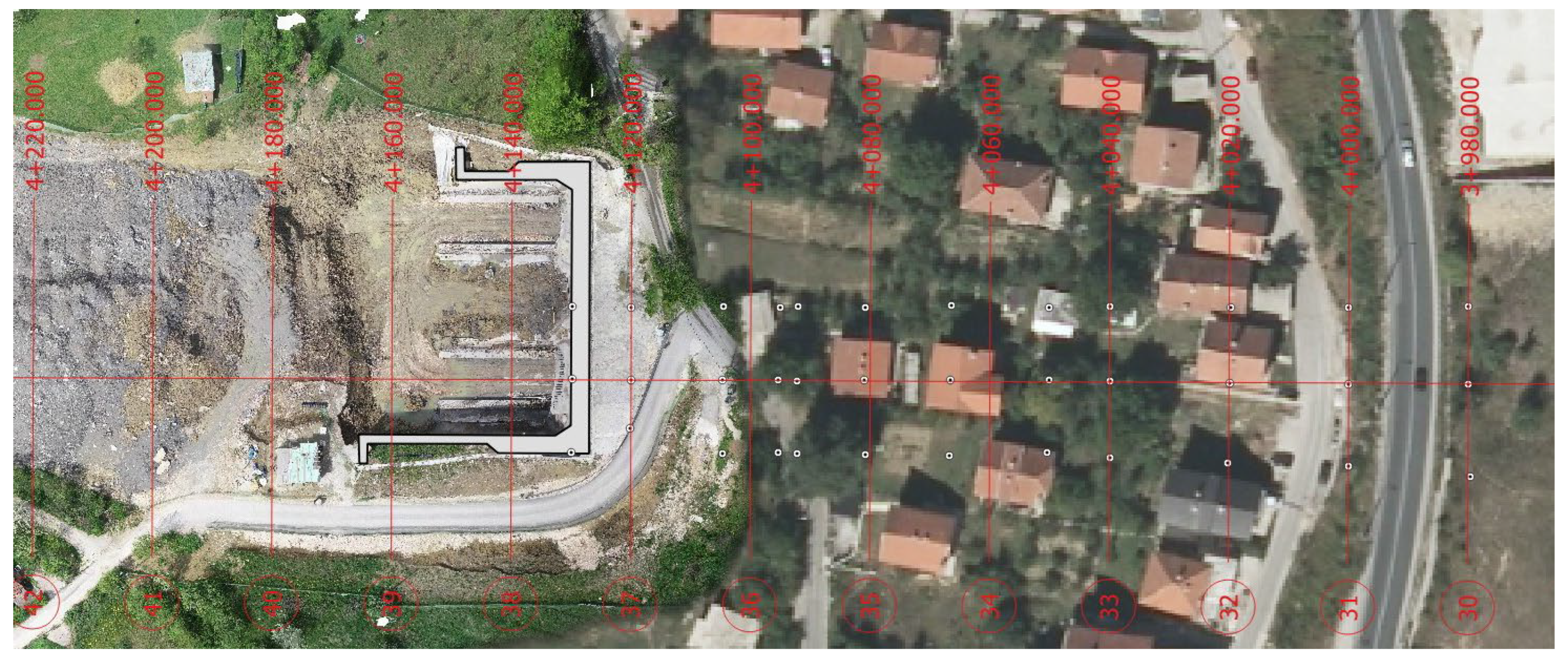
| ID | Material | Model | Drainage | Unit Weight γ (kN/m3) | Oedometer Modulus Eoed (kN/m3) | Unloading/Reloading Stiffness Eur (kN/m3) | Cohesion c (kN/m3) | Internal Friction Angel φ (°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | El-dl | Hardening soil | Drained | 19 | 30,000 | 120,000 | 9.50 | 23 |
| 2 | Marl | Hardening soil | Drained | 22 | 40,000 | 120,000 | 30 | 55 |
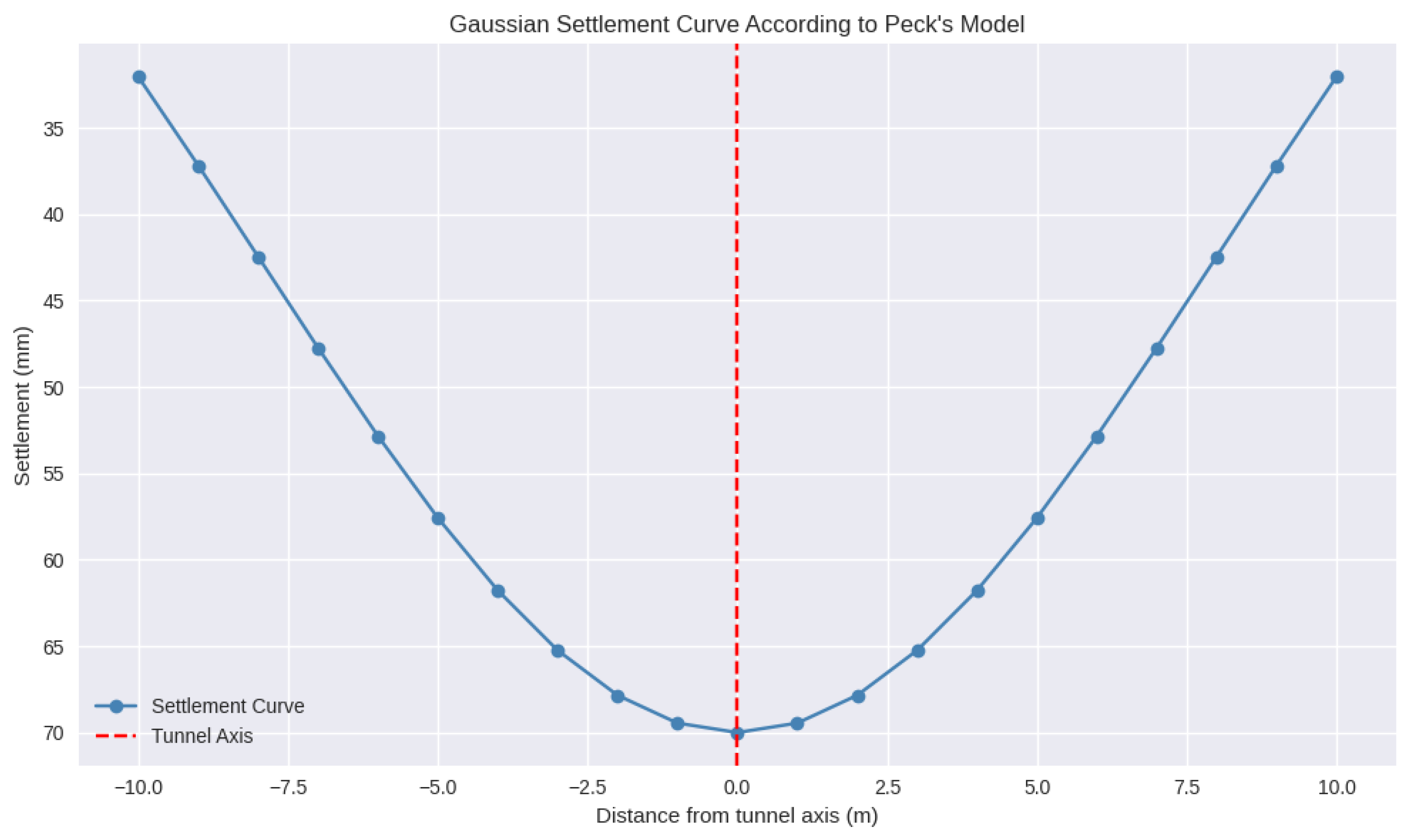
| Distance From the Tunnel Axis, x (m) | Calculated Settlement, S(x) (mm) |
|---|---|
| –10 | 43.94 |
| –9 | 48.94 |
| –8 | 53.59 |
| –7 | 57.73 |
| –6 | 61.30 |
| –5 | 64.26 |
| –4 | 66.56 |
| –3 | 68.17 |
| –2 | 69.06 |
| –1 | 69.41 |
| 0 | 70.00 |
| +1 | 69.41 |
| +2 | 69.06 |
| +3 | 68.17 |
| +4 | 66.56 |
| +5 | 64.26 |
| +6 | 61.30 |
| +7 | 57.73 |
| +8 | 53.59 |
| +9 | 48.94 |
| +10 | 43.94 |
| Damage Category | Range of θ | Damage Description |
|---|---|---|
| Negligible | ≤1/500 | No or very fine cracks, deformations almost imperceptible |
| Minor | 1/500–1/300 | Superficial cracks, not significant for structural stability |
| Moderate | 1/300–1/150 | Visible cracks in walls |
| Severe | 1/150–1/50 | Structural cracks, repair required |
| Very severe/Critical | >1/50 | Significant damage, risk to structural stability |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bektašević, E.; Filipović, S.; Crnogorac, L.; Gutić, K.; Požegić, Z.; Tokalić, R. Challenges of Tunnel Support in Low Overburden Zones in Urban Areas—Case Study. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 12094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212094
Bektašević E, Filipović S, Crnogorac L, Gutić K, Požegić Z, Tokalić R. Challenges of Tunnel Support in Low Overburden Zones in Urban Areas—Case Study. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):12094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212094
Chicago/Turabian StyleBektašević, Ekrem, Satko Filipović, Luka Crnogorac, Kemal Gutić, Zijad Požegić, and Rade Tokalić. 2025. "Challenges of Tunnel Support in Low Overburden Zones in Urban Areas—Case Study" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 12094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212094
APA StyleBektašević, E., Filipović, S., Crnogorac, L., Gutić, K., Požegić, Z., & Tokalić, R. (2025). Challenges of Tunnel Support in Low Overburden Zones in Urban Areas—Case Study. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 12094. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152212094