Risk Assessment for Reducing Thermoset Waste: Predictive Modelling of Water Ageing in Epoxy Infrastructure
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Gravimetry
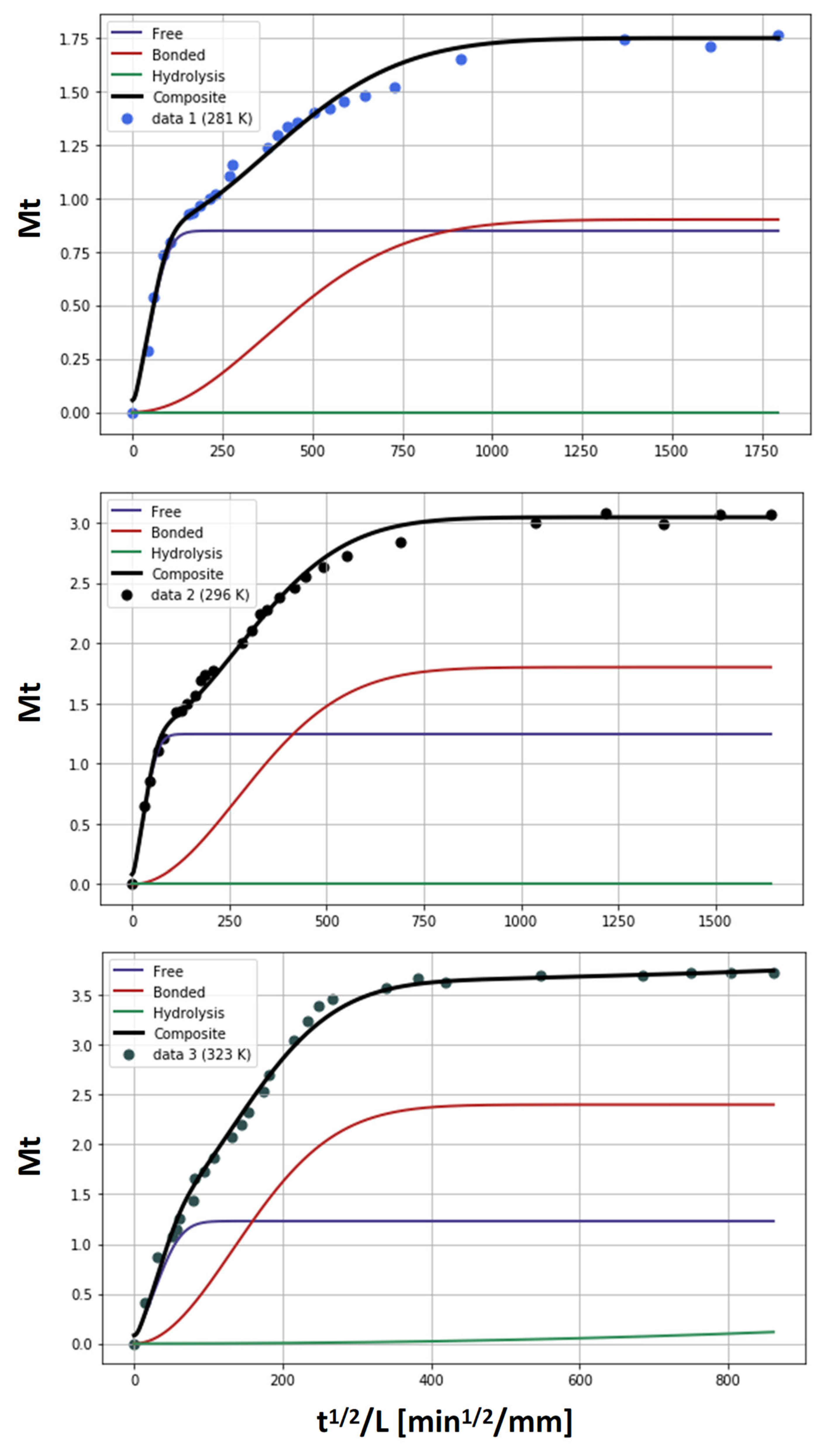
2.3. Water Absorption Model
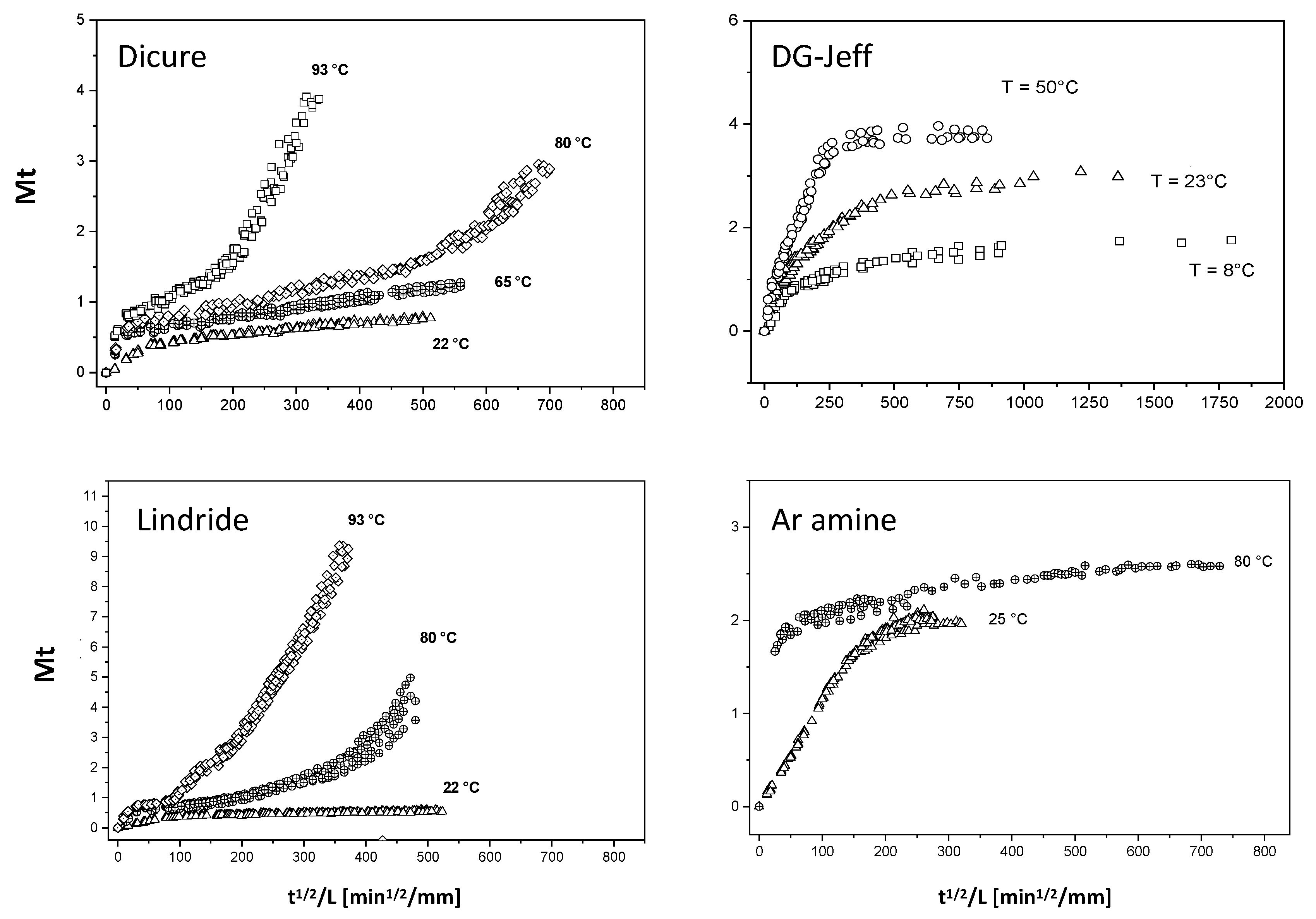
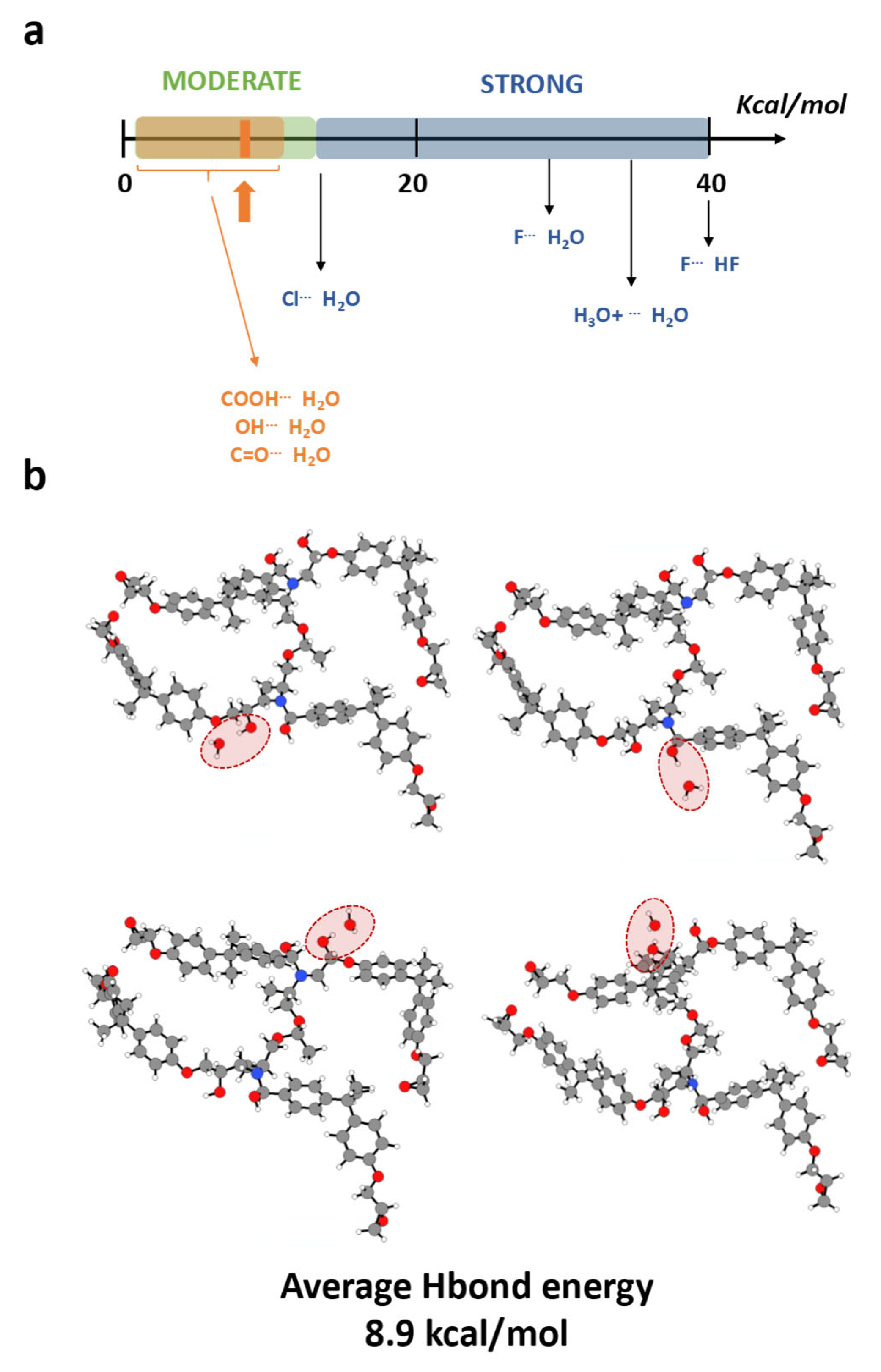
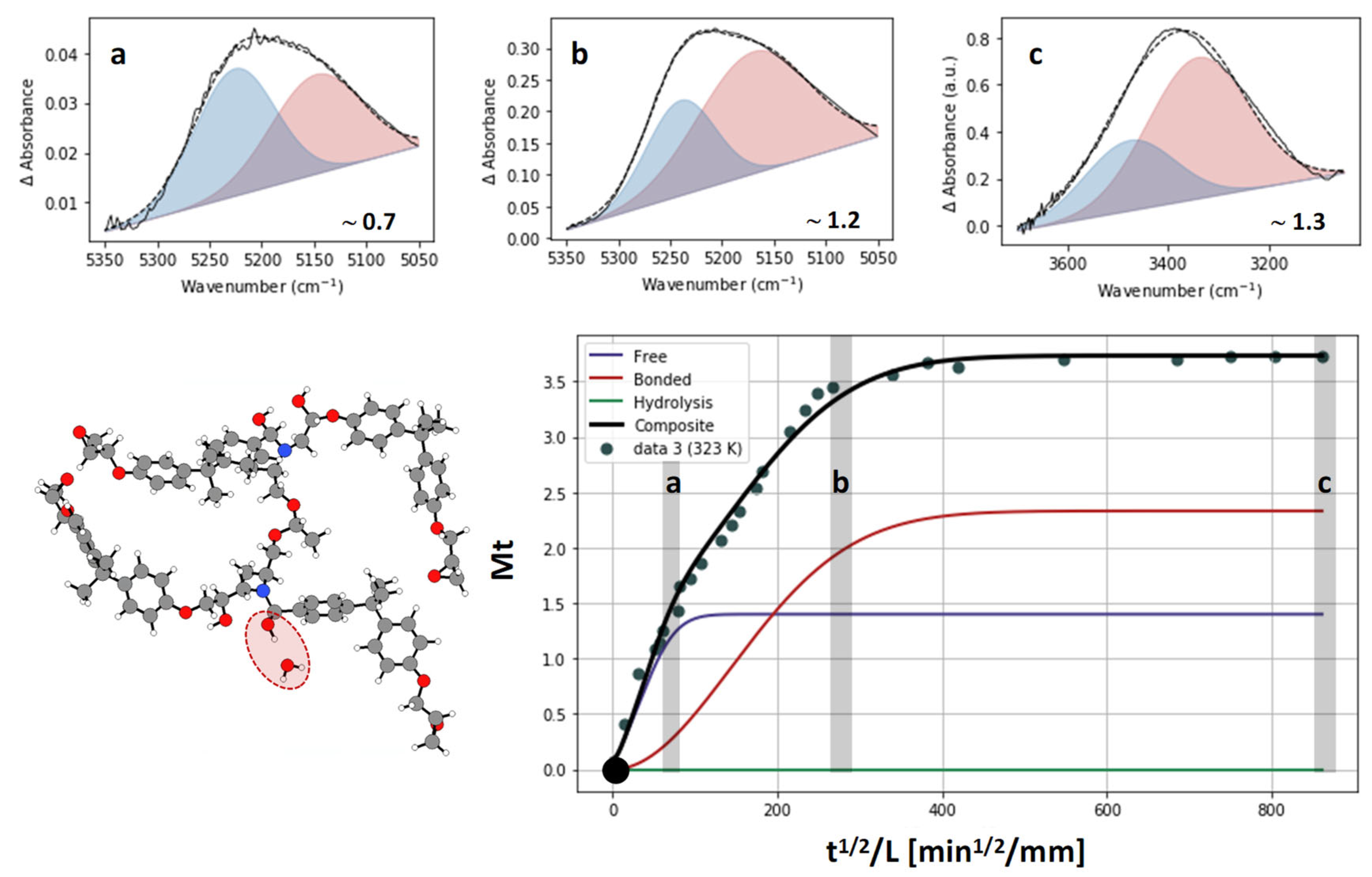
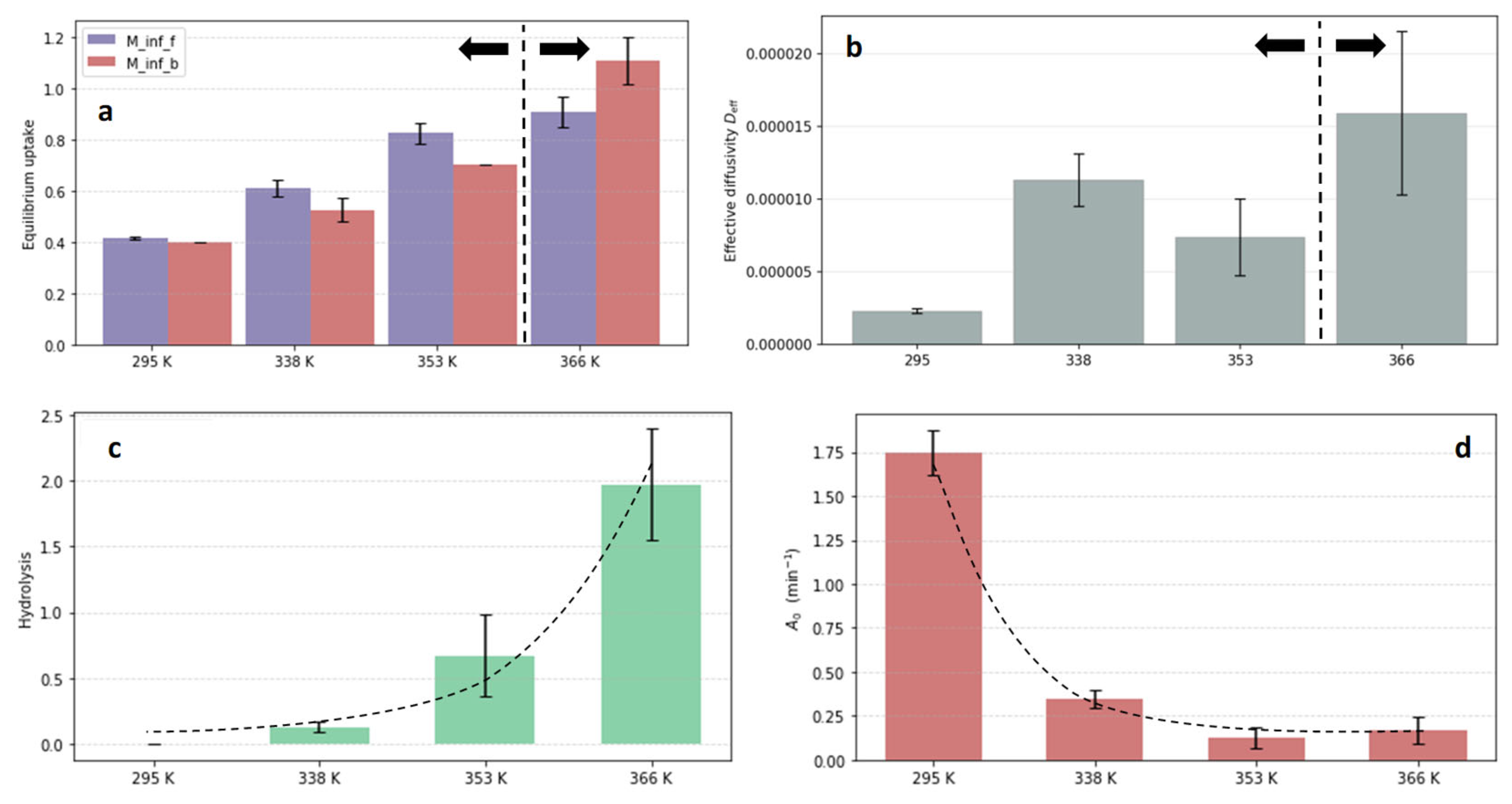
3. Results and Discussion
- Epoxy-amine networks: no hydrolysis (DGEBA-Jeffamine and DGEBA-Ancamine)
- Absorption with hydrolysis (DGEBA-Lindride and DGEBA-Dicure)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, D.; Gu, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, S.; Zhao, F.; Len, S.; Dou, J.; Qian, X.; Wang, J. Degradation Behavior and Ageing Mechanism of E-Glass Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Resin Composite Pipes under Accelerated Thermal Ageing Conditions. Compos. Part B Eng. 2024, 270, 111131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitriah, S.N.; Abdul Majid, M.S.; Ridzuan, M.J.M.; Daud, R.; Gibson, A.G.; Assaleh, T.A. Influence of Hydrothermal Ageing on the Compressive Behaviour of Glass Fibre/Epoxy Composite Pipes. Compos. Struct. 2017, 159, 350–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Ma, P.; Bi, J.; Ma, B.; Zhou, H.; Liu, K.; Geisbush, J.; Wu, H. Mitigating Aging Infrastructure Risks: An Optimized Epoxy Resin System for Water Supply Pipeline Rehabilitation. Polymer 2024, 315, 127791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargarnezhad, H.; Asselin, E.; Wong, D.; Lam, C.N.C. A Critical Review of the Time-Dependent Performance of Polymeric Pipeline Coatings: Focus on Hydration of Epoxy-Based Coatings. Polymers 2021, 13, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rocha, M.L.; Leite, M.C.d.O.; Ferreira, E.P.d.C.; Melo, J.D.D.; Barbosa, A.P.C. Accelerated Aging Effects in Composites Used as Repair for Pipes in Oil Industry. Polym. Compos. 2021, 42, 5918–5929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, W.; Jeffs, S.P.; Korkees, F.; Rawson, M. The Opportunities and Challenges of Hybrid Composite Driveshafts and Their Couplings in the Aerospace Industry: A Review. Compos. Struct. 2023, 320, 117203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crank, J. The Mathematics of Diffusion, 2nd ed.; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1975; ISBN 978-0-19-853344-3. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.H. Nonlinear Water Diffusion in Unsaturated Porous Solid Materials. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1992, 30, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggana, C.; Pissis, P. Water Sorption and Diffusion Studies in an Epoxy Resin System. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 1999, 37, 1165–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillet, C.; Tamssaouet, F.; Hassoune-Rhabbour, B.; Tchalla, T.; Nassiet, V. Parameters Influencing Moisture Diffusion in Epoxy-Based Materials during Hygrothermal Ageing—A Review by Statistical Analysis. Polymers 2022, 14, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, H.G.; Kibler, K.G. Langmuir-Type Model for Anomalous Moisture Diffusion In Composite Resins. J. Compos. Mater. 1978, 12, 118–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moy, P.; Karasz, F.E. Epoxy-water Interactions. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1980, 20, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soles, C.L.; Yee, A.F. A Discussion of the Molecular Mechanisms of Moisture Transport in Epoxy Resins. J. Polym. Sci. Part B 2000, 38, 792–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiel, G.; Miccio, L.A.; Montemartini, P.E.; Schwartz, G.A. Water Diffusion and Hydrolysis Effect on the Structure and Dynamics of Epoxy-Anhydride Networks. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2017, 143, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Yap, M.; Chern, W.K.; Oh, J.T.; Chen, Z. Degradation and Lifetime Prediction of Epoxy Composite Insulation Materials under High Relative Humidity. Polymers 2023, 15, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Yagoubi, J.; Lubineau, G.; Traidia, A.; Verdu, J. Monitoring and Simulations of Hydrolysis in Epoxy Matrix Composites during Hygrothermal Aging. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 68, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Sun, F.; Qie, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhao, G. The Change of Hydrogen Bonding Network during Adsorption of Multi-Water Molecules in Lignite: Quantitative Analysis Based on AIM and DFT. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2020, 247, 122863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, J.G.; Siddiqui, I.A. Activation Parameters and Mechanism of the Acid-Catalysed Hydrolysis of Epoxides. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2 1973, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrudková, H.; Švec, F.; Kálal, J. Reactive Polymers XIV. Hydrolysis of the Epoxide Groups of the Copolymer Glycidylmethacrylate—Ethylenedimethacrylate. Br. Polym. J. 1977, 9, 238–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.P. Effects of Hygrothermal Aging on Anisotropic Conductive Adhesive Joints: Experiments and Theoretical Analysis. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2006, 20, 1383–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parra, R.D.; Streu, K. Hydrogen Bond Cooperativity in Polyols: A DFT and AIM Study. Comput. Theor. Chem. 2011, 967, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filot, I.A.W.; Palmans, A.R.A.; Hilbers, P.A.J.; van Santen, R.A.; Pidko, E.A.; de Greef, T.F.A. Understanding Cooperativity in Hydrogen-Bond-Induced Supramolecular Polymerization: A Density Functional Theory Study. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 114, 13667–13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, G.; Gugliuzza, A.; Drioli, E. Competitive Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions in Modified Polymer Membranes: A Density Functional Theory Investigation. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 5473–5477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendler, K.; Thar, J.; Zahn, S.; Kirchner, B. Estimating the Hydrogen Bond Energy. J. Phys. Chem. A 2010, 114, 9529–9536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, F.C.; Kirwan, K.; Wilson, P.R.; Coles, S.R. Sustainable Alternative Composites Using Waste Vegetable Oil Based Resins. J. Polym. Environ. 2019, 27, 2464–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramón, E.; Sguazzo, C.; Moreira, P.M.G.P. A Review of Recent Research on Bio-Based Epoxy Systems for Engineering Applications and Potentialities in the Aviation Sector. Aerospace 2018, 5, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruzzi, E.; Stace, A.J. Experimental Measurements of Water Molecule Binding Energies for the Second and Third Solvation Shells of [Ca(H2O)n]2+ Complexes. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miccio, L.A.; Otegui, J.; Penoff, M.E.; Montemartini, P.E.; Schwartz, G.A. Fluorinated Networks Dynamics Studied by Means of Broadband Dielectric Spectroscopy. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 42690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miccio, L.A.; Kummali, M.M.; Montemartini, P.E.; Oyanguren, P.A.; Schwartz, G.A.; Alegra, N.; Colmenero, J. Determining Concentration Depth Profiles in Fluorinated Networks by Means of Electric Force Microscopy. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 135, 064704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.A.; Khan, M.M.R.; Mozumder, M.S.I. Adsorption Equilibrium and Adsorption Kinetics: A Unified Approach. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2004, 27, 1095–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.B.; Drzal, L.T.; Rich, M.J. The Physical Basis of Moisture Transport in a Cured Epoxy Resin System. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1985, 30, 4467–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.; Piggott, M.R. Water Absorption of Resins and Composites. I. Epoxy Homopolymers and Copolymers. J. Compos. Technol. Res. 1987, 9, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKague, E.L.; Reynolds, J.D.; Halkias, J.E. Swelling and Glass Transition Relations for Epoxy Matrix Material in Humid Environments. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1978, 22, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Pellechia, P.; Matthews, M.A. Kinetic Models of Concentrated NaBH4 Hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mac Leod, J.M.; Rosei, F. Hydrogen Bonding. In Comprehensive Nanoscience and Technology; Andrews, D.L., Scholes, G.D., Eds.; Elsevier Academic Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; ISBN 978-0-12-374390-9. [Google Scholar]
- Meyers, R.A. Hydrogen Bond. In Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 505–538. ISBN 978-0-12-227410-7. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Xian, G.; Karbhari, V.M. Hygrothermal Ageing of an Epoxy Adhesive Used in FRP Strengthening of Concrete. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamakita, E.; Nakashima, S. Water Retention of Calcium-Containing Pectin Studied by Quartz Crystal Microbalance and Infrared Spectroscopy with a Humidity Control System. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 9344–9352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, S.; Nakashima, S. Changes in IR Band Areas and Band Shifts during Water Adsorption to Lecithin and Ceramide. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 228, 117779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, P.; Ding, Y.; Li, S. Study on Diffusion Behavior of Water in Epoxy Resins Cured by Active Ester. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 1848–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.C.; Bendiksen, B.; Elabd, Y.A. Diffusion of Liquid Water in Free-Standing Polymer Films Using Pressure-Contact Time-Resolved Fourier Transform Infrared Attenuated Total Reflectance Spectroscopy. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 3464–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fame, C.M.; Ueda, T.; Ntjam Minkeng, M.A.; Wu, C. Durability of Epoxy and Vinyl Ester Polymers in Wet, Seawater, and Seawater Sea Sand Concrete Environments: Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 451, 138645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capiel, G.; Uicich, J.; Fasce, D.; Montemartini, P.E. Diffusion and Hydrolysis Effects during Water Aging on an Epoxy-Anhydride System. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2018, 153, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Equation | Description |
|---|---|
| Reversible diffusion of water molecules through free volume; controlled by the effective diffusivity [7]. | |
| Occupation of specific polar sites; reversible sorption [11,30,31]. | |
| Irreversible hydrolytic chain scission; temperature-dependent prefactor K(T) and power-law exponent α (α > 1 captures autocatalysis) [32,33,34]. | |
| Total mass gain (sum of contributions) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Penoff, M.E.; Capiel, G.; Montemartini, P.E.; Miccio, L.A. Risk Assessment for Reducing Thermoset Waste: Predictive Modelling of Water Ageing in Epoxy Infrastructure. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211857
Penoff ME, Capiel G, Montemartini PE, Miccio LA. Risk Assessment for Reducing Thermoset Waste: Predictive Modelling of Water Ageing in Epoxy Infrastructure. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(22):11857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211857
Chicago/Turabian StylePenoff, Marcela Elisabeth, Guillermina Capiel, Pablo E. Montemartini, and Luis A. Miccio. 2025. "Risk Assessment for Reducing Thermoset Waste: Predictive Modelling of Water Ageing in Epoxy Infrastructure" Applied Sciences 15, no. 22: 11857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211857
APA StylePenoff, M. E., Capiel, G., Montemartini, P. E., & Miccio, L. A. (2025). Risk Assessment for Reducing Thermoset Waste: Predictive Modelling of Water Ageing in Epoxy Infrastructure. Applied Sciences, 15(22), 11857. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152211857







