Evaluation of Railway Bridge Responses to Blast Vibrations and Earthquake Ground Motions Based on Numerical Simulation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Analysis Model
2.1. Determination of Analysis Model
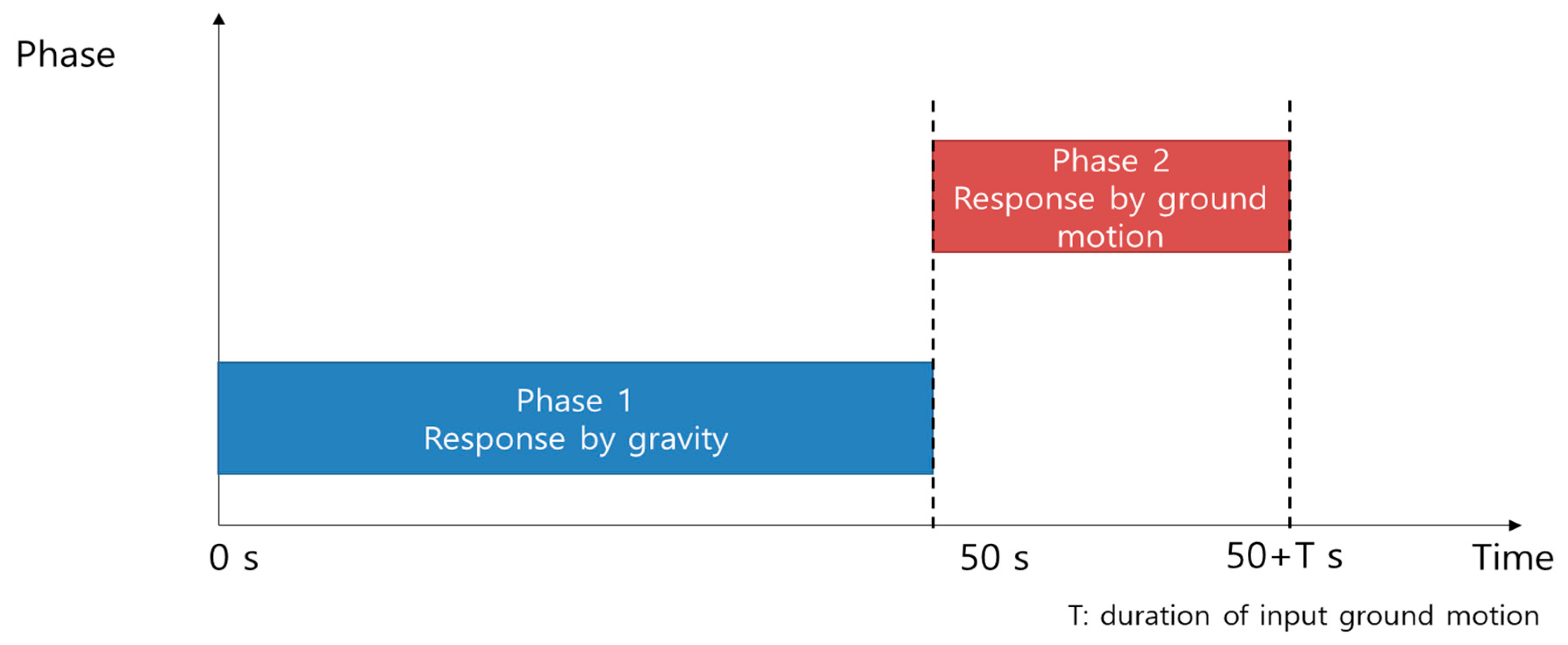
2.2. Numerical Analysis Condition
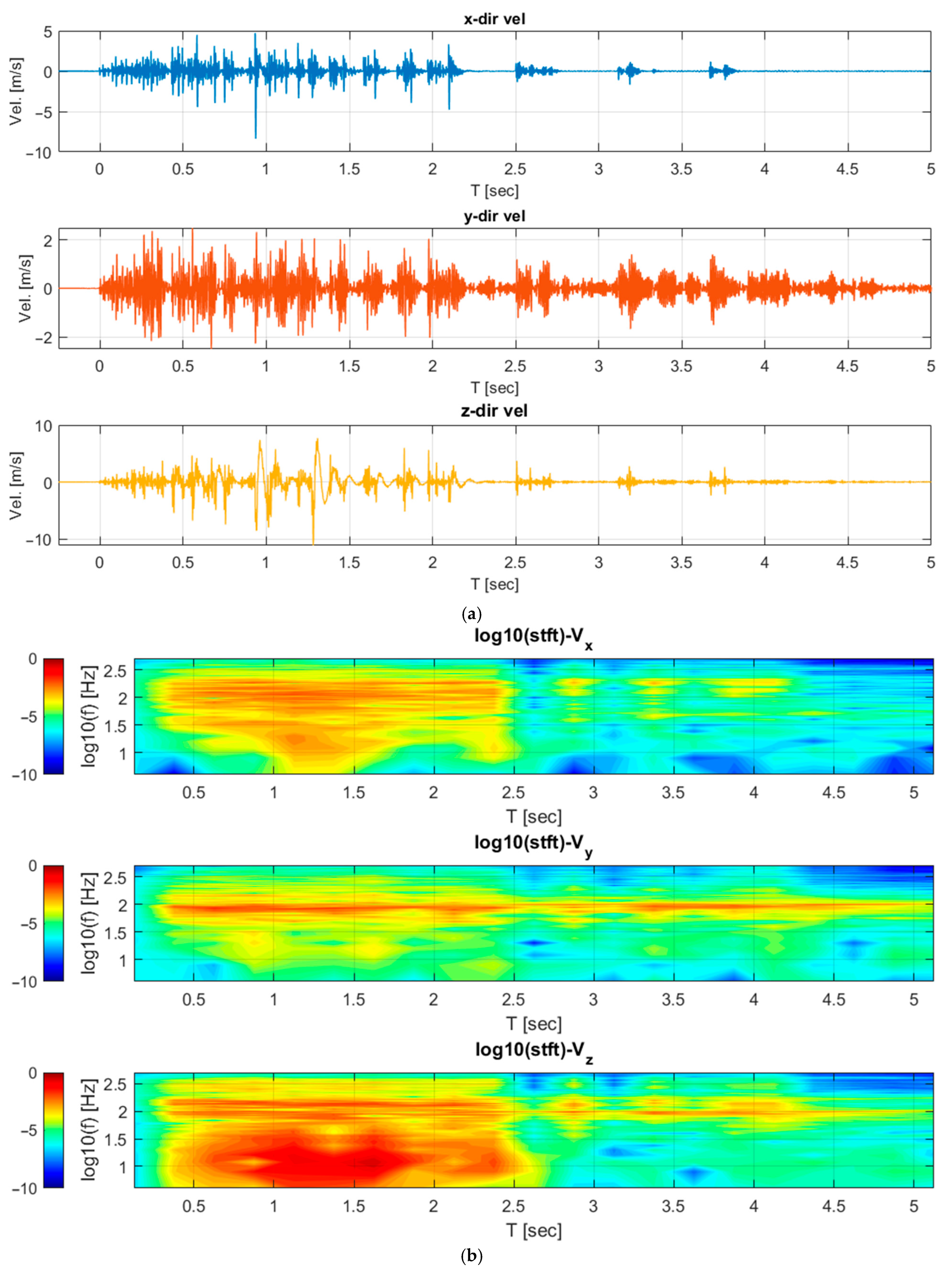
3. Numerical Analysis Results
4. Conclusions
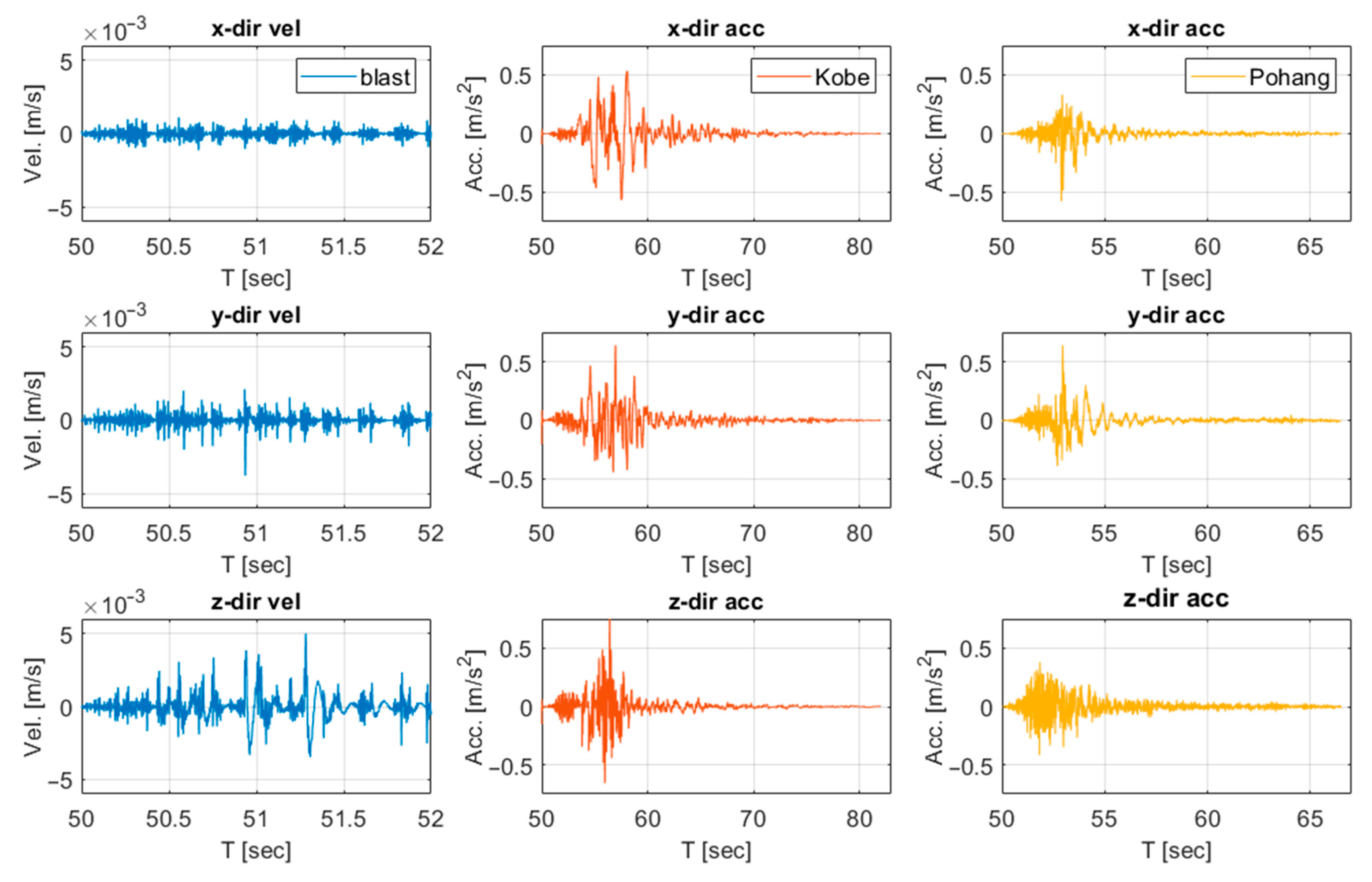
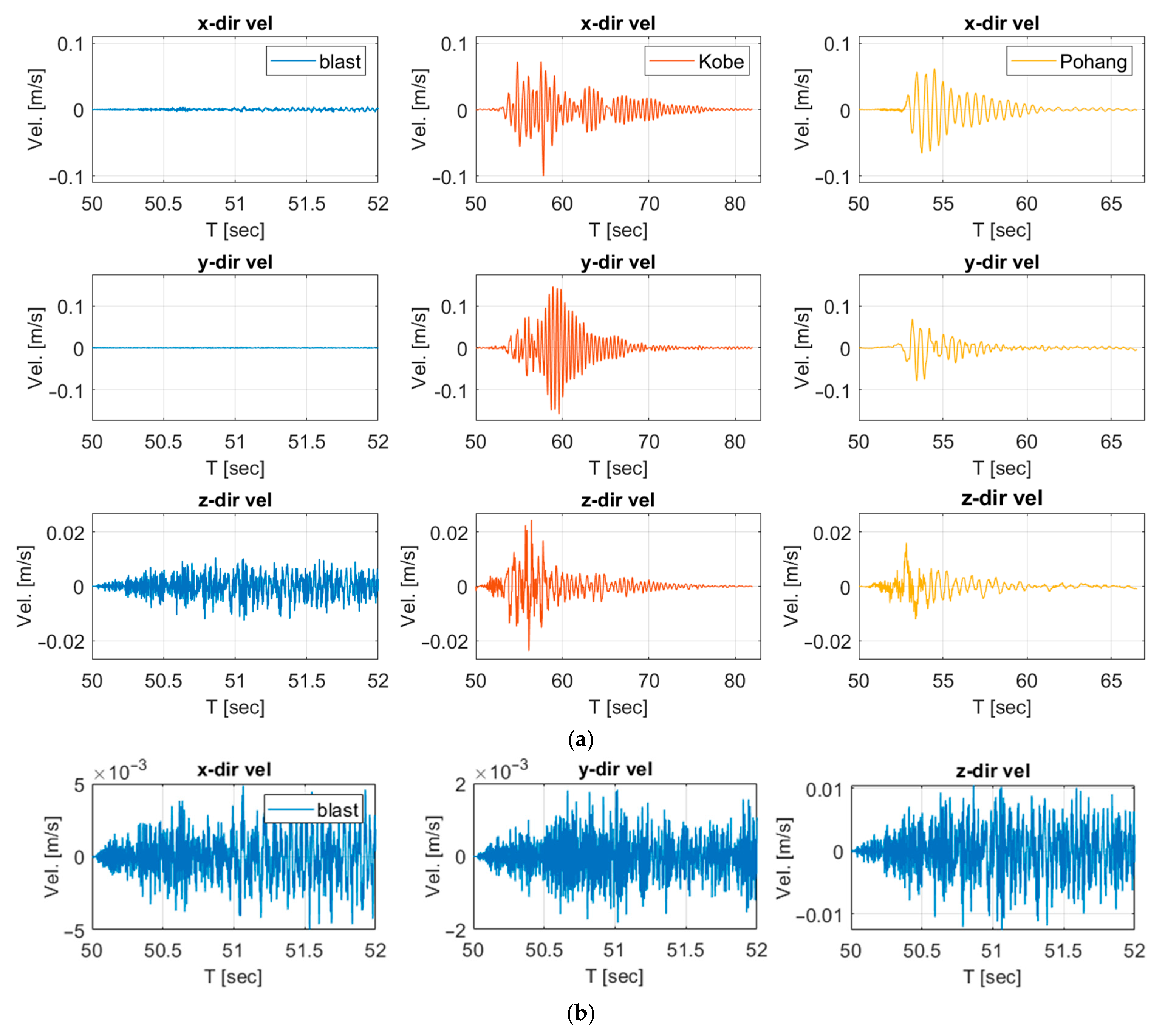
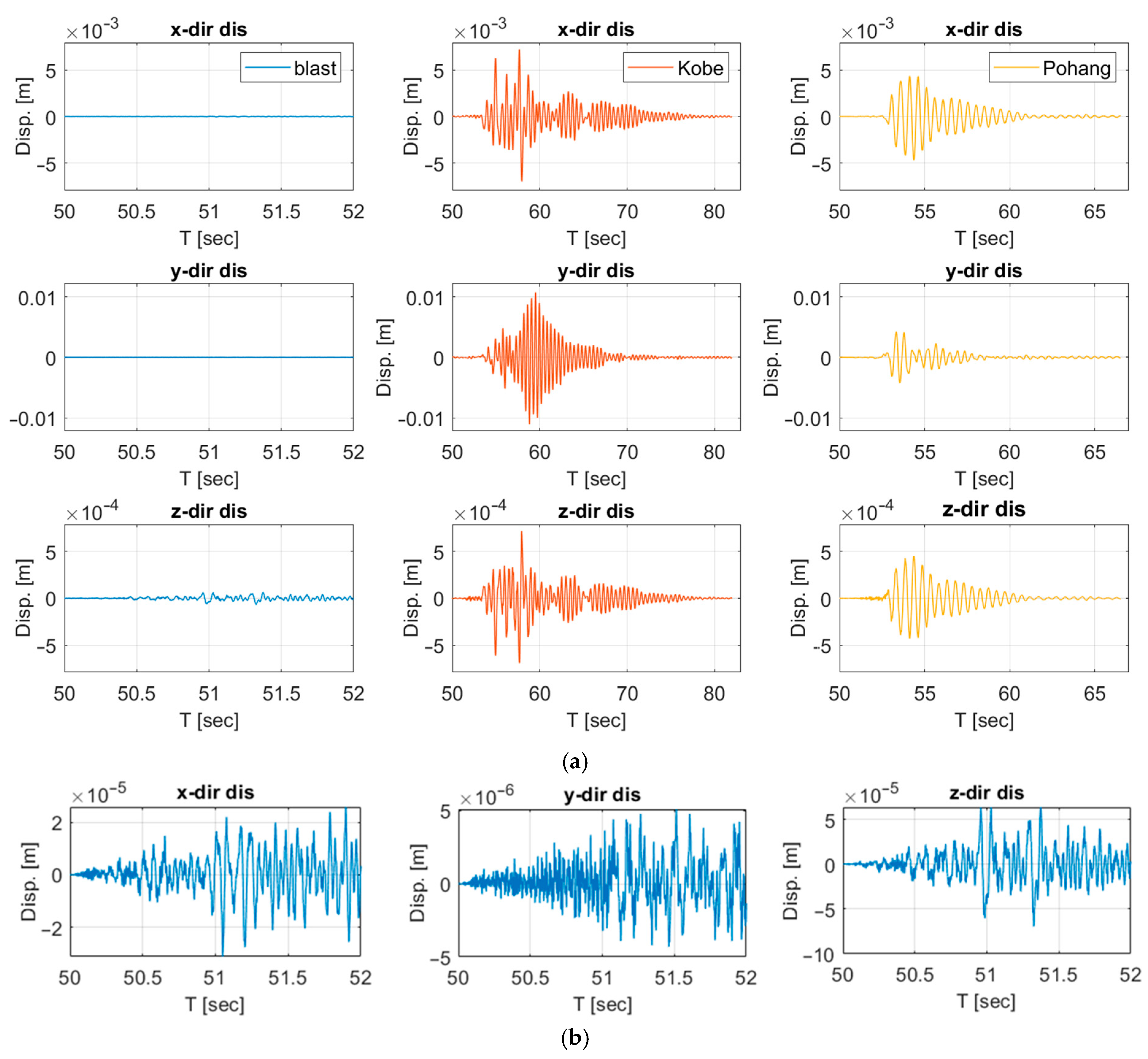
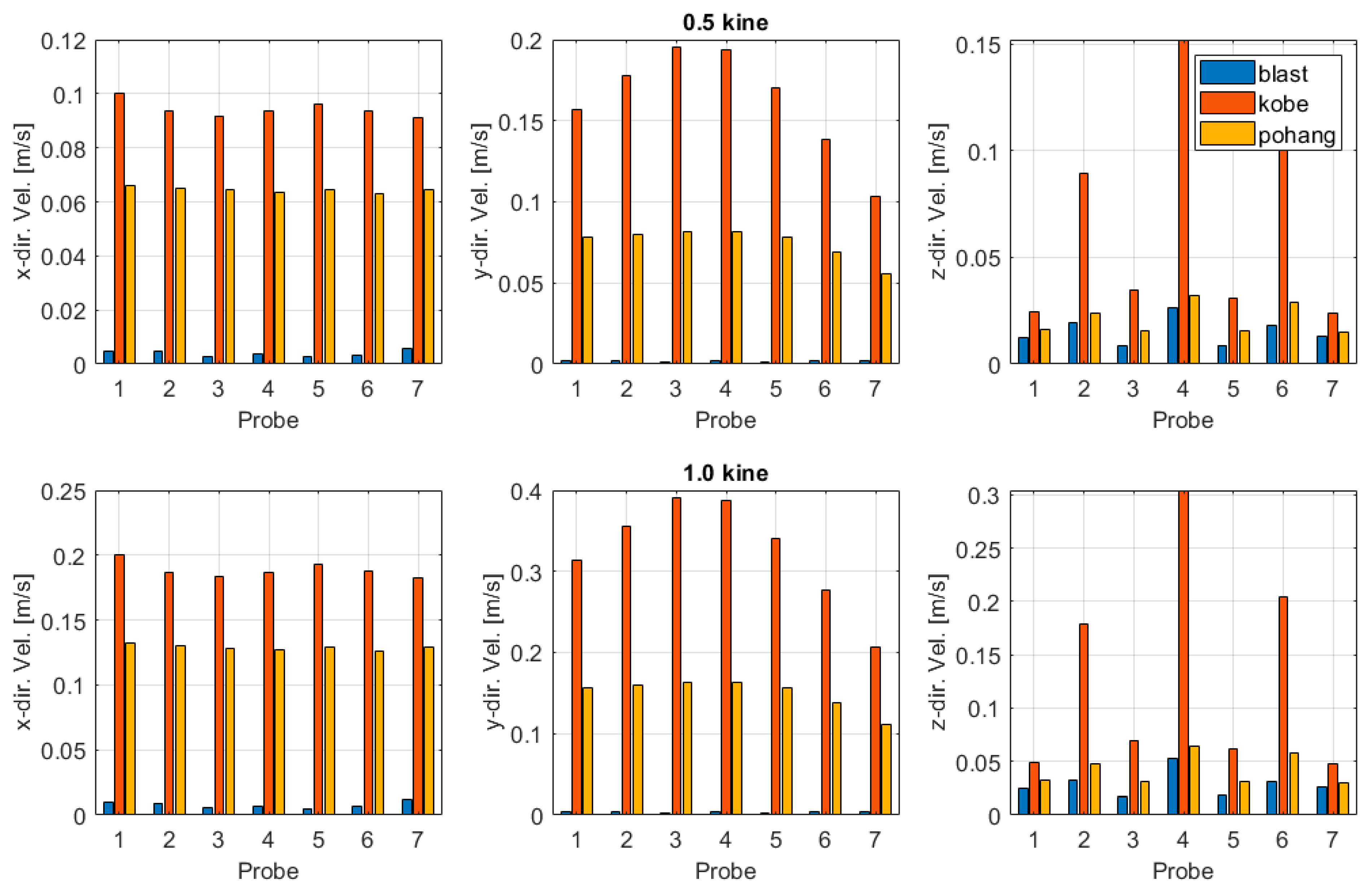
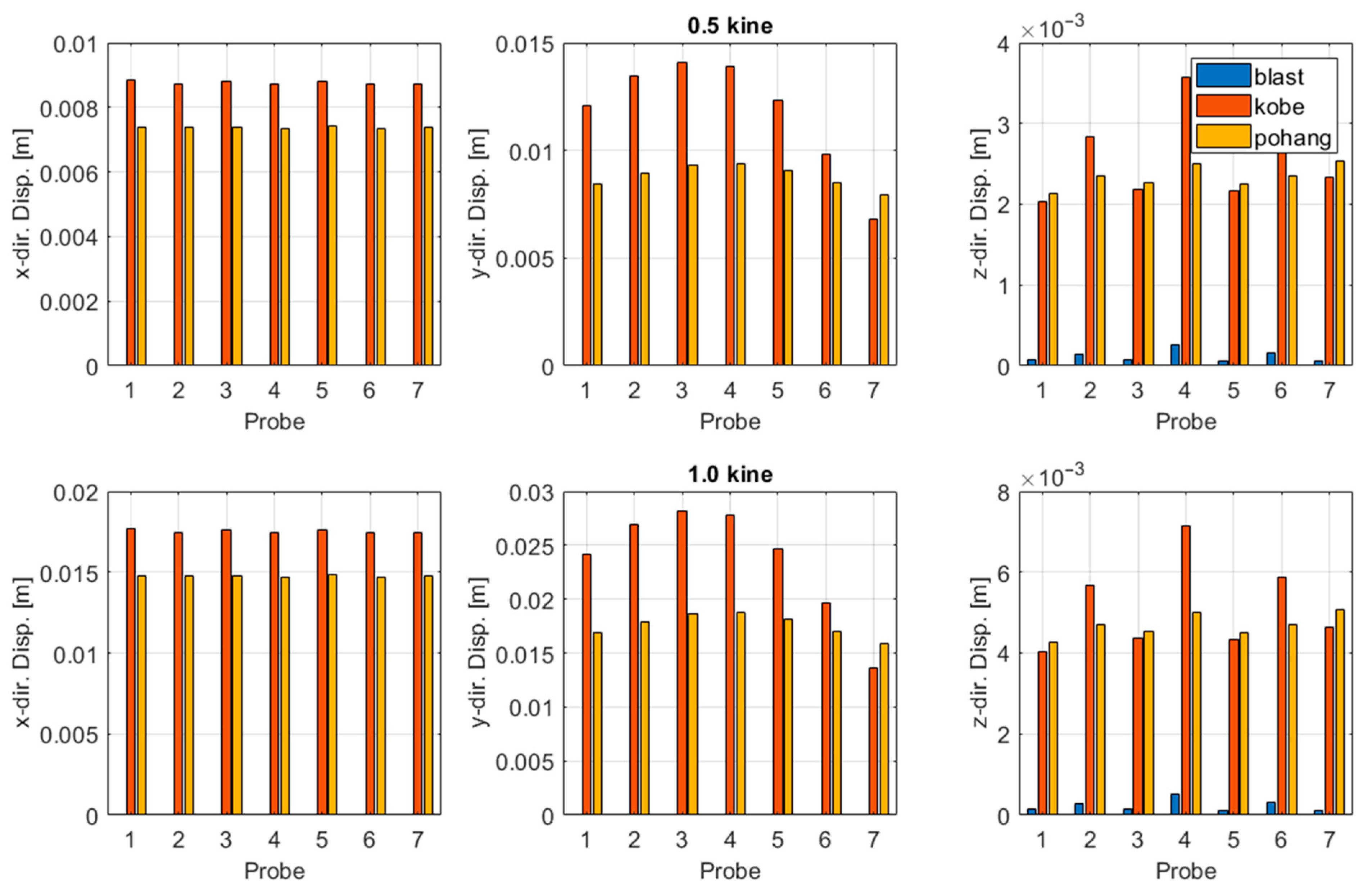
- Blast-induced ground motions produced extremely small structural responses. Maximum displacements remained below the millimeter scale and velocities below 0.03 m/s, indicating negligible influence on the railway bridge.
- Earthquake ground motions generated substantially larger displacements and velocities. The Kobe earthquake, with dominant long-period components, produced the highest responses, while the Pohang earthquake induced smaller but still significant demands.
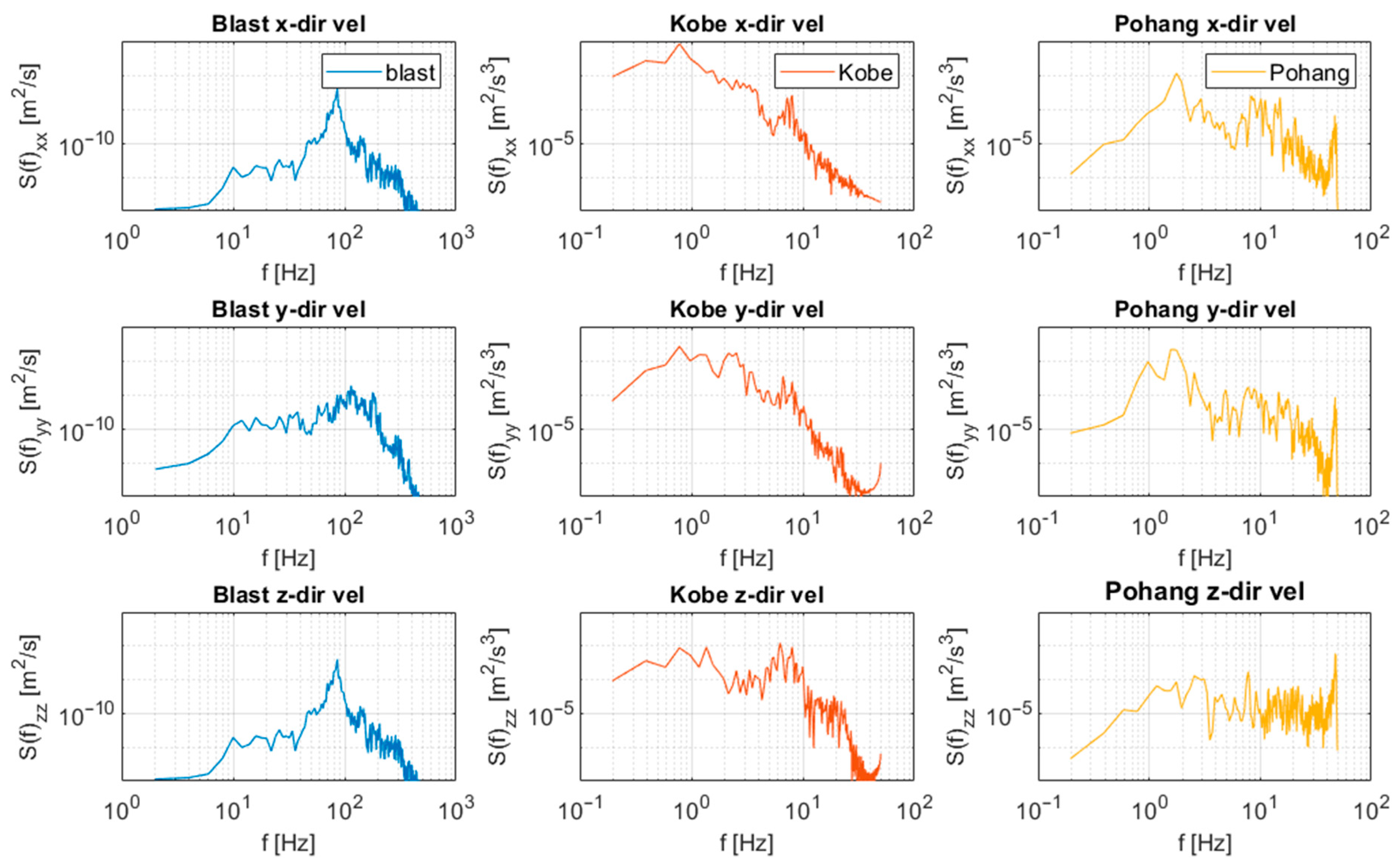
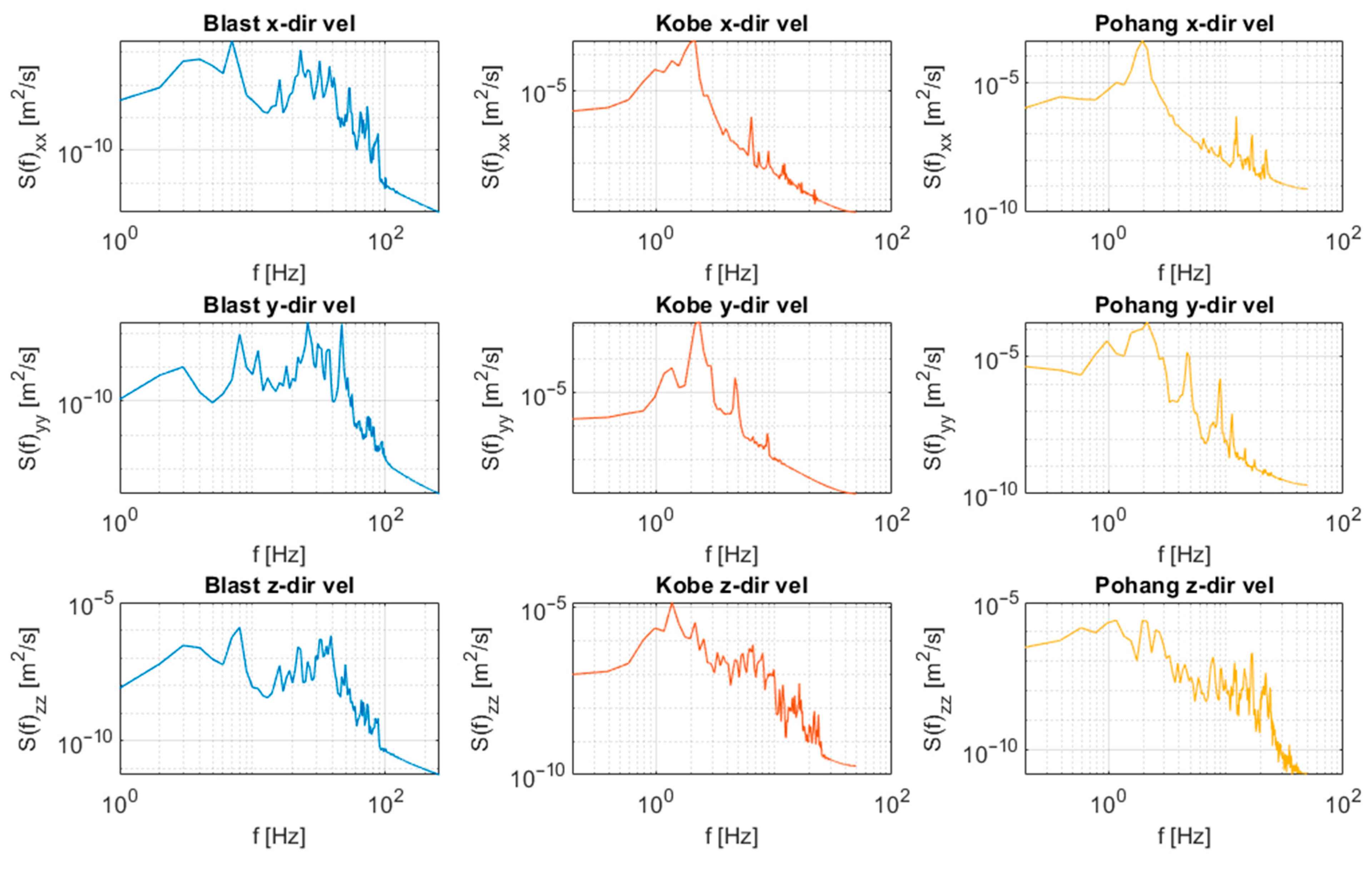
- The fundamental difference between blast and earthquake responses arises from their frequency content. High-frequency, short-duration blast pulses dissipate rapidly, whereas low-frequency earthquake energy excites the natural modes of the bridge, leading to amplified displacements.
- The comparison indicates that the blast vibration limits of 0.3–0.5 kine, provided in the Korean manual, are excessively conservative. Even at these threshold levels, blast-induced responses were negligible compared to earthquake-induced demands.
- The findings suggest the need for a rational reassessment of blast vibration standards for railway infrastructure. A revised framework that accounts for the actual dynamic response of bridges would ensure both structural safety and the efficient execution of underground construction projects.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nicholls, H.R.; Johnson, C.F.; Duvall, W.I. Blasting Vibrations and Their Effects on Structures (No. 656-660); US Department of the Interior, Bureau of Mines: Denver, CO, USA, 1971.
- Deutsches Institut für Normung. Vibrations in Buildings—Part 3: Effects on Structures (DIN 4150-3:2016-12); German Institute for Standardization: Berlin, Germany, 2016; p. 5940. [Google Scholar]
- The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Underground Safety Impact Assessment Standard Manual; The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2021; p. 171. (In Korean)
- Che, Y.; Chi, E. Study on the Vibration Effects of Cyclic Blasting on Bridge Structures under Construction. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Wang, M.; Yang, R.; Si, K. Blasting vibration hazard classification and prediction research. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2023, 15, 16878132231181068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Jiang, N.; Zhou, C.; Yao, Y.; Zhou, W.; Cai, Z. Safety assessment for a ballast railway induced by underground subway tunnel blasting: A case study. Int. J. Prot. Struct. 2024, 15, 166–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lai, S.K.; Ni, Y.Q.; Chen, L. Dynamic modelling and analysis of a physics-driven strategy for vibration control of railway vehicles. Veh. Syst. Dyn. 2024, 63, 1080–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Fei, H.; Yan, Y. Research and Advances in the Characteristics of Blast-Induced Vibration Frequencies. Buildings 2025, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyroudis, S.A.; Pitilakis, K.D. Seismic fragility curves of shallow tunnels in alluvial deposits. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2012, 35, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argyroudis, S.; Kaynia, A.M. Analytical seismic fragility functions for highway and railway embankments and cuts. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 2015, 44, 1863–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, S.; Chakraborty, S. Seismic fragility analysis in the probabilistic performance-based earthquake engineering framework: An overview. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Sci. Appl. Math. 2021, 13, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nettis, A.; Di Mucci, V.M.; Ruggieri, S.; Uva, G. Seismic fragility and risk assessment of isolated bridges subjected to pre-existing ground displacements. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 194, 109335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diao, Y.C.; Li, C.; Li, H.N. Seismic Fragility Analysis of Curved Bridges with Precast Segmental Pier Columns Considering Directionality of Multisupport Earthquake Motions. J. Struct. Eng. 2025, 151, 04025198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Lai, J.; Wu, S.; Feng, S.; Meng, X. Seismic fragility assessment of UHPC ribbed arch bridges. Soil Dyn. Earthq. Eng. 2025, 190, 109199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satyanarayana, A.; Dushyanth, V.B.R.; Riyan, K.A.; Geetha, L.; Kumar, R. Assessing the seismic sensitivity of bridge structures by developing fragility curves with ANN and LSTM integration. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 2024, 25, 5865–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Wang, X.; Pang, Y.; Ye, A. Machine learning-aided parameterized seismic fragility models of bridges for network-level functionality assessment. Eng. Struct. 2025, 340, 120771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Li, Z.X.; Ding, Y.; Su, J. Time-dependent seismic fragility and resilience assessment of a sea-crossing cable-stayed bridge under combined effects of corrosion and scour. Eng. Struct. 2025, 340, 120702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsar Dizaj, E.; Salami, M.R.; Kashani, M.M. Impact of asymmetrical corrosion of piers on seismic fragility of ageing irregular concrete bridges. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2025, 21, 1465–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport. Seismic Design Standards of Bridges (KDS 24 17 10); The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2018; p. 28. (In Korean)
- Al-Khafaji, M.S.; Mohammed, A.S.; Salman, M.A. ANSYS-based structural analysis study of elevated spherical tank exposed to earthquake. Eng. Technol. J. 2021, 39, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Bashir, M.; Li, C.; Wang, J. Dynamic analysis of 10 MW offshore wind turbines with different support structures subjected to earthquake loadings. Renew. Energy 2022, 193, 758–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, H.; Wu, K.; Ayasrah, M.M.; Huang, W. Study on Sunlight Temperature Field of Steel Box Arch Ribs in Irregular Arch Bridges. Symmetry 2024, 16, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, A.; Paul, G. A simulation based analysis for enhancement of performances of turbine blades in turbo jet engines with thermal barrier coatings (TBCs). Numer. Heat Transf. Part A Appl. 2024, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Wu, S.; Xue, M.; Leung, C.K.B.; Beetner, D.; Zhang, J. A practical simulation flow for singing capacitor based acoustic noise analysis. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility & Signal/Power Integrity (EMCSI), Spokane, WA, USA, 1–5 August 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 29–33. [Google Scholar]
- Sagar, S. Modelling and CFD Acoustic Analysis of Different Chevron Nozzles using Ansys for Jet Noise Reduction. Ph.D. Thesis, National Institute of Technology Patna, Bihar, India, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bagheri, M.; Arjomand, M.A.; Mostafaei, Y. Performance enhancement of Tuned Liquid Dampers in Fixed Offshore Platforms: A Coupled ANSYS Aqwa-Transient Structural Approach. Civ. Eng. Appl. Solut. 2025, 1, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Trad, A.; Amoura, N.; Abdellah Elhadj, A.; Kebir, H. Optimizing plastic shredder rotor design through structural finite element analysis: A comprehensive approach using experimental design and response surface methodology. Mech. Based Des. Struct. Mach. 2024, 52, 10682–10701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, N.; Anil, Ö. Prediction of load capacity of one way reinforced concrete slabs with openings using nonlinear finite element analysis. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 102945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.H.; Ree, J.H.; Kim, Y.; Kim, S.; Kang, S.Y.; Seo, W. Assessing whether the 2017 M w 5.4 Pohang earthquake in South Korea was an induced event. Science 2018, 360, 1007–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Rhie, J.; Kang, T.S.; Kim, K.H.; Kim, M.; Lee, S.J. The 12 September 2016 Gyeongju earthquakes: 1. Observation and remaining questions. Geosci. J. 2016, 20, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Society of Civil Engineering. Investigation and Analysis of Vibration Effects According to Ground Conditions; Korea Society of Civil Engineering: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2025; p. 33. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, A.; Khan, Z.; Attom, M.; Fattah, K.; Ali, T.; Mortula, M. Continuous Evaluation of Shear Wave Velocity from Bender Elements during Monotonic Triaxial Loading. Materials 2023, 16, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
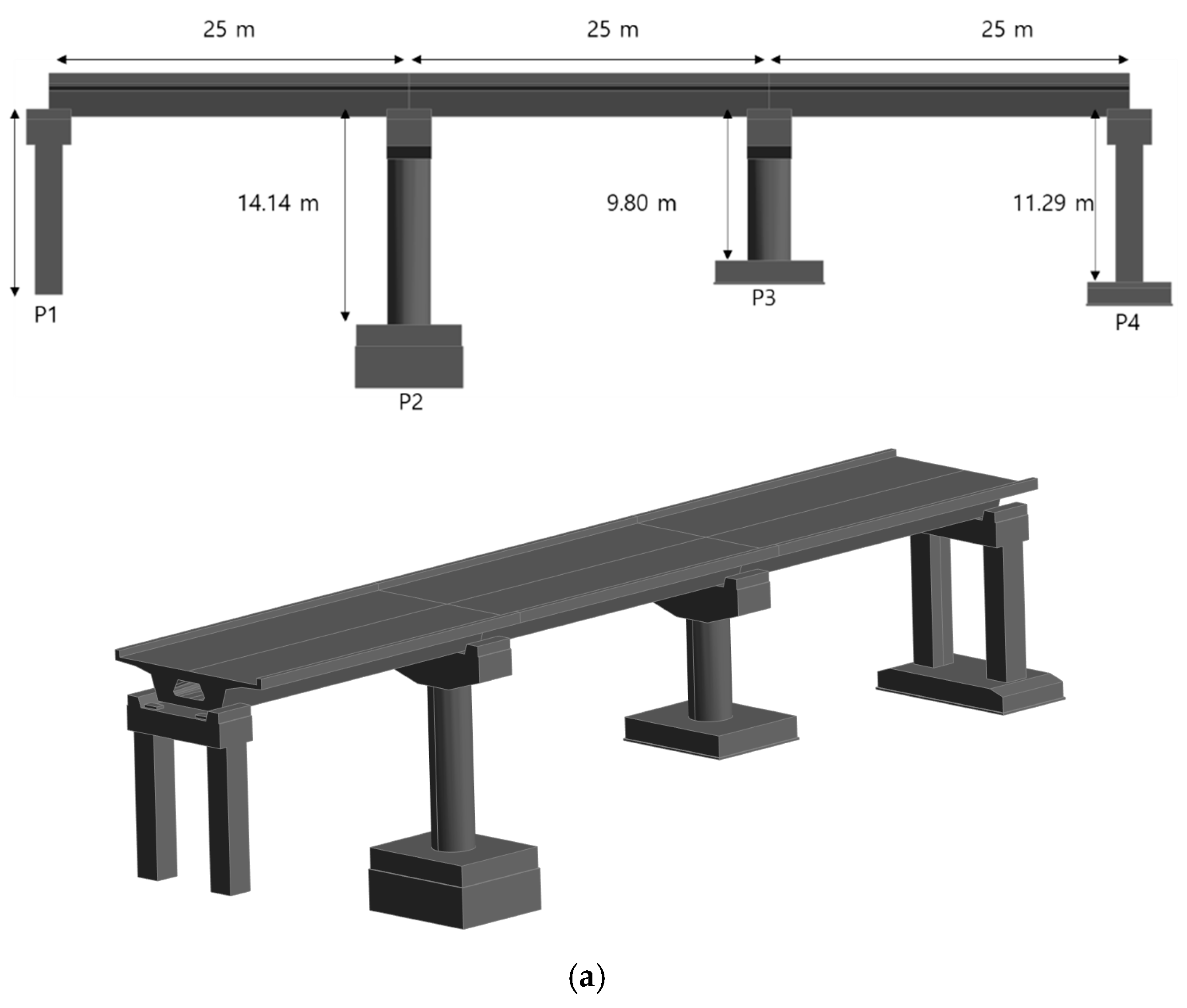
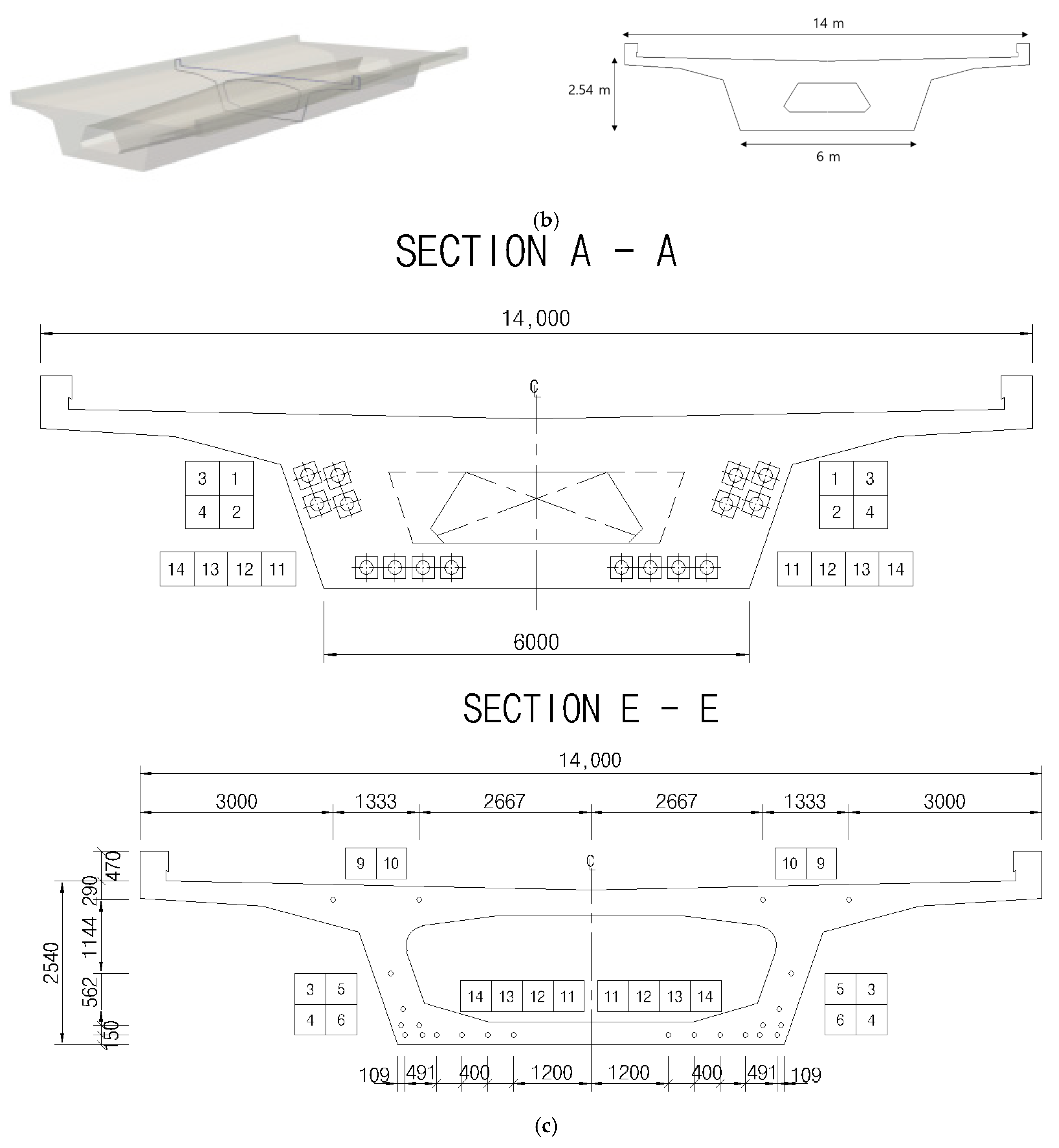
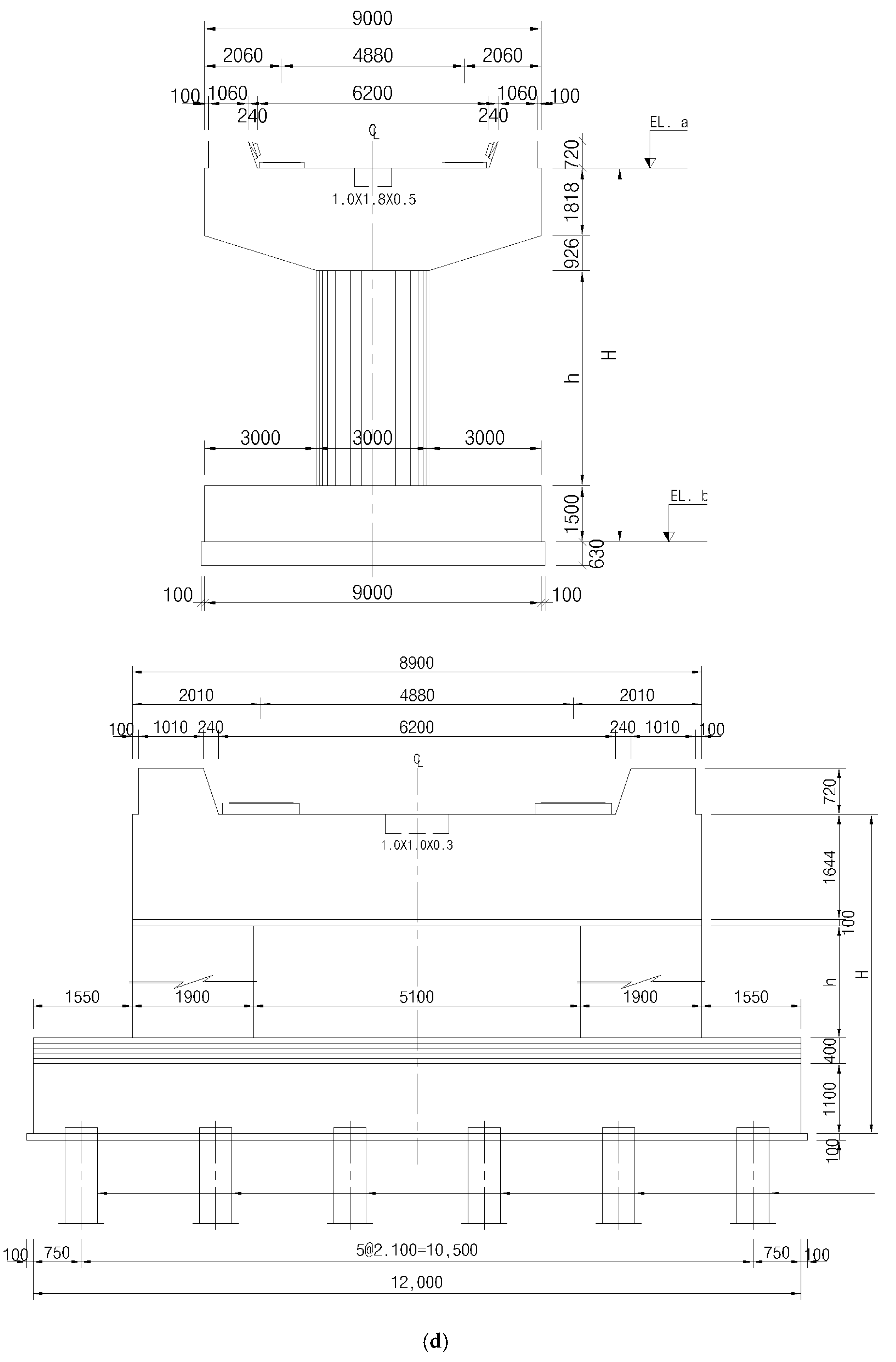
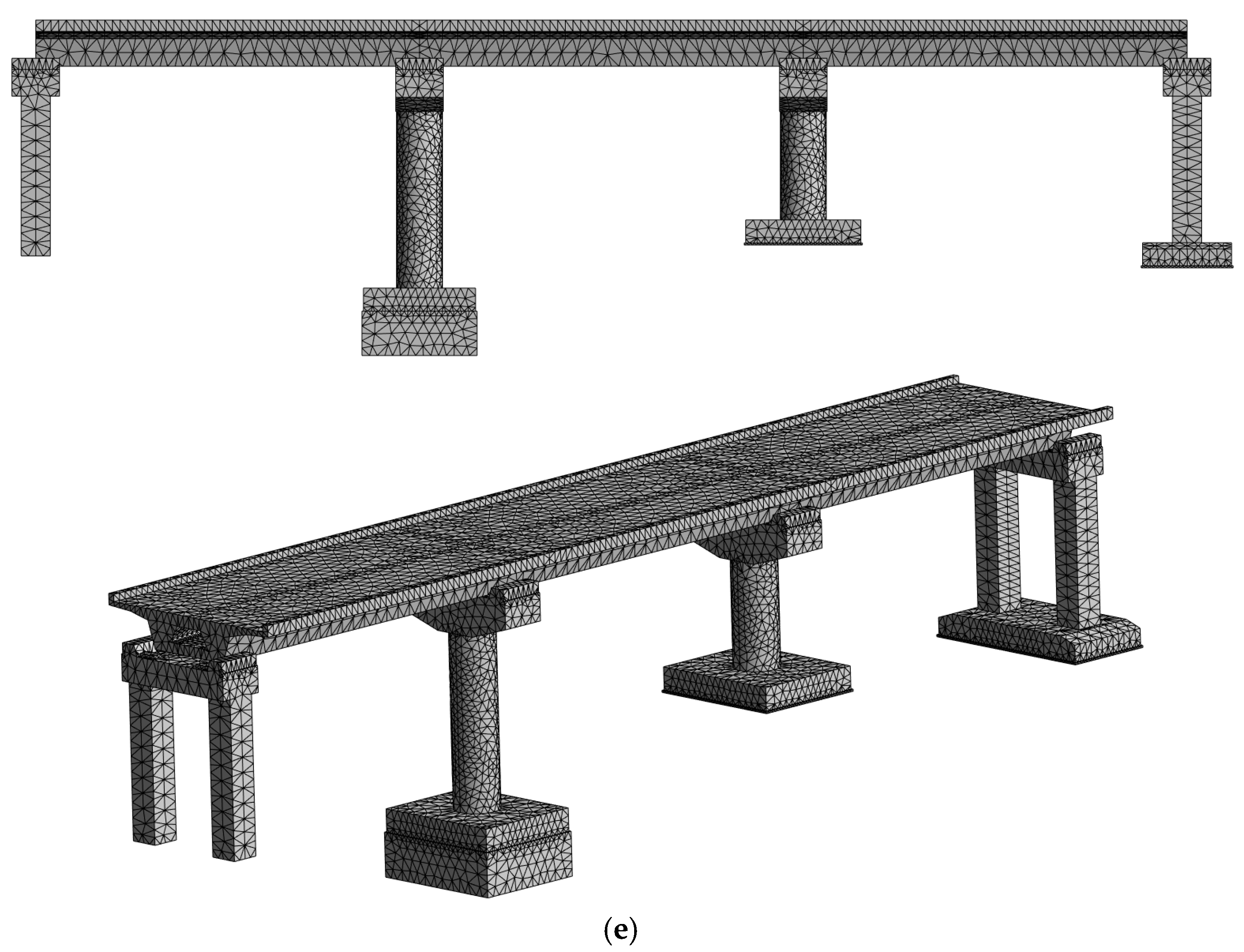
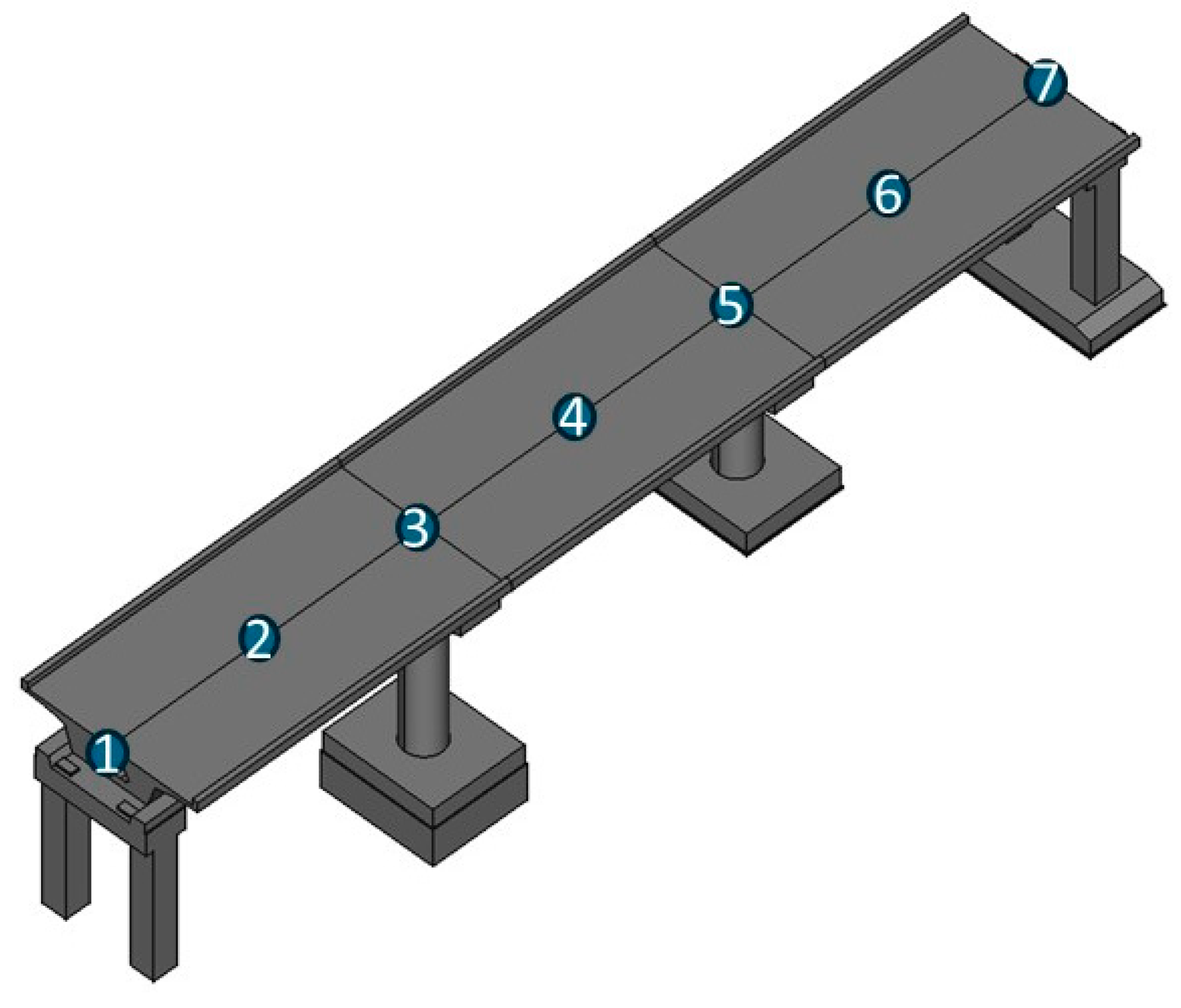

| Parameters | Density (kg/m3) | Modulus of Elasticity (MPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | Damping Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Properties | 2500 | 32,000 | 0.18 | 0.05 |
| Group | Case # | Input Ground Motion | Scale |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | Blast | Max. velocity of 0.5 kine |
| 2 | Kobe Earthquake | Max. acceleration of 0.064 g | |
| 3 | Pohang Earthquake | Max. acceleration of 0.064 g | |
| B | 4 | Blast | Max. velocity of 1.0 kine |
| 5 | Kobe Earthquake | Max. acceleration of 0.128 g | |
| 6 | Pohang Earthquake | Max. acceleration of 0.128 g |
| (unit: m/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | Motion | Probe 01 | Probe 02 | Probe 03 | Probe 04 | Probe 05 | Probe 06 | Probe 07 |
| x- direction | blast | 0.00498 | 0.00463 | 0.00301 | 0.00360 | 0.00261 | 0.00347 | 0.00595 |
| Kobe | 0.10016 | 0.09344 | 0.09185 | 0.09349 | 0.09634 | 0.09361 | 0.09104 | |
| Pohang | 0.06595 | 0.06514 | 0.06427 | 0.06343 | 0.06452 | 0.06325 | 0.06464 | |
| y- direction | blast | 0.00183 | 0.00193 | 0.00150 | 0.00222 | 0.00128 | 0.00180 | 0.00198 |
| Kobe | 0.15717 | 0.17779 | 0.19514 | 0.19336 | 0.17018 | 0.13850 | 0.10346 | |
| Pohang | 0.07855 | 0.08022 | 0.08200 | 0.08176 | 0.07811 | 0.06881 | 0.05574 | |
| z- direction | blast | 0.01257 | 0.01928 | 0.00885 | 0.02659 | 0.00891 | 0.01797 | 0.01319 |
| Kobe | 0.02440 | 0.08935 | 0.03487 | 0.15214 | 0.03101 | 0.10192 | 0.02379 | |
| Pohang | 0.01600 | 0.02379 | 0.01575 | 0.03206 | 0.01551 | 0.02869 | 0.01492 |
| (unit: m/s) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | Motion | Probe 01 | Probe 02 | Probe 03 | Probe 04 | Probe 05 | Probe 06 | Probe 07 |
| x- direction | blast | 0.00997 | 0.00926 | 0.00602 | 0.00719 | 0.00522 | 0.00693 | 0.01190 |
| Kobe | 0.20033 | 0.18692 | 0.18373 | 0.18700 | 0.19268 | 0.18724 | 0.18206 | |
| Pohang | 0.13189 | 0.13027 | 0.12853 | 0.12685 | 0.12904 | 0.12650 | 0.12927 | |
| y- direction | blast | 0.00366 | 0.00386 | 0.00300 | 0.00445 | 0.00257 | 0.00361 | 0.00397 |
| Kobe | 0.31428 | 0.35556 | 0.39032 | 0.38674 | 0.34029 | 0.27701 | 0.20692 | |
| Pohang | 0.15710 | 0.16045 | 0.16400 | 0.16351 | 0.15622 | 0.13762 | 0.11148 | |
| z- direction | blast | 0.02514 | 0.03253 | 0.01769 | 0.05319 | 0.01782 | 0.03171 | 0.02637 |
| Kobe | 0.04877 | 0.17869 | 0.06973 | 0.30421 | 0.06204 | 0.20380 | 0.04762 | |
| Pohang | 0.03201 | 0.04758 | 0.03151 | 0.06407 | 0.03102 | 0.05738 | 0.02984 |
| (unit: m) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | Motion | Probe 01 | Probe 02 | Probe 03 | Probe 04 | Probe 05 | Probe 06 | Probe 07 |
| x- direction | blast | 0.00003 | 0.00002 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00002 | 0.00002 | 0.00003 |
| Kobe | 0.00883 | 0.00874 | 0.00881 | 0.00874 | 0.00881 | 0.00872 | 0.00873 | |
| Pohang | 0.00738 | 0.00737 | 0.00739 | 0.00736 | 0.00741 | 0.00733 | 0.00738 | |
| y- direction | blast | 0.00001 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 |
| Kobe | 0.01206 | 0.01345 | 0.01407 | 0.01389 | 0.01236 | 0.00982 | 0.00681 | |
| Pohang | 0.00844 | 0.00896 | 0.00930 | 0.00936 | 0.00904 | 0.00848 | 0.00796 | |
| z- direction | blast | 0.00007 | 0.00015 | 0.00007 | 0.00026 | 0.00006 | 0.00015 | 0.00007 |
| Kobe | 0.00203 | 0.00284 | 0.00218 | 0.00357 | 0.00217 | 0.00293 | 0.00233 | |
| Pohang | 0.00213 | 0.00236 | 0.00227 | 0.00250 | 0.00226 | 0.00235 | 0.00253 |
| (unit: m) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direction | Motion | Probe 01 | Probe 02 | Probe 03 | Probe 04 | Probe 05 | Probe 06 | Probe 07 |
| x- direction | blast | 0.00006 | 0.00005 | 0.00003 | 0.00002 | 0.00003 | 0.00005 | 0.00006 |
| Kobe | 0.01767 | 0.01748 | 0.01763 | 0.01748 | 0.01763 | 0.01745 | 0.01747 | |
| Pohang | 0.01475 | 0.01473 | 0.01477 | 0.01472 | 0.01481 | 0.01466 | 0.01476 | |
| y- direction | blast | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 | 0.00001 |
| Kobe | 0.02411 | 0.02690 | 0.02814 | 0.02777 | 0.02472 | 0.01964 | 0.01362 | |
| Pohang | 0.01687 | 0.01791 | 0.01860 | 0.01873 | 0.01808 | 0.01696 | 0.01592 | |
| z- direction | blast | 0.00014 | 0.00029 | 0.00013 | 0.00053 | 0.00012 | 0.00031 | 0.00013 |
| Kobe | 0.00405 | 0.00569 | 0.00437 | 0.00715 | 0.00434 | 0.00586 | 0.00465 | |
| Pohang | 0.00426 | 0.00472 | 0.00454 | 0.00500 | 0.00451 | 0.00470 | 0.00507 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moon, J.S.; Yoo, M.; Haam, S.; Lee, Y.S. Evaluation of Railway Bridge Responses to Blast Vibrations and Earthquake Ground Motions Based on Numerical Simulation. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 11479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111479
Moon JS, Yoo M, Haam S, Lee YS. Evaluation of Railway Bridge Responses to Blast Vibrations and Earthquake Ground Motions Based on Numerical Simulation. Applied Sciences. 2025; 15(21):11479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111479
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoon, Jae Sang, Mintaek Yoo, Sunnie Haam, and Yu Seong Lee. 2025. "Evaluation of Railway Bridge Responses to Blast Vibrations and Earthquake Ground Motions Based on Numerical Simulation" Applied Sciences 15, no. 21: 11479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111479
APA StyleMoon, J. S., Yoo, M., Haam, S., & Lee, Y. S. (2025). Evaluation of Railway Bridge Responses to Blast Vibrations and Earthquake Ground Motions Based on Numerical Simulation. Applied Sciences, 15(21), 11479. https://doi.org/10.3390/app152111479






